WO2020121809A1 - 流体機械 - Google Patents
流体機械 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2020121809A1 WO2020121809A1 PCT/JP2019/046317 JP2019046317W WO2020121809A1 WO 2020121809 A1 WO2020121809 A1 WO 2020121809A1 JP 2019046317 W JP2019046317 W JP 2019046317W WO 2020121809 A1 WO2020121809 A1 WO 2020121809A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- fixed
- fluid machine
- sliding
- machine according
- fluid
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04C—ROTARY-PISTON, OR OSCILLATING-PISTON, POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; ROTARY-PISTON, OR OSCILLATING-PISTON, POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
- F04C18/00—Rotary-piston pumps specially adapted for elastic fluids
- F04C18/02—Rotary-piston pumps specially adapted for elastic fluids of arcuate-engagement type, i.e. with circular translatory movement of co-operating members, each member having the same number of teeth or tooth-equivalents
Definitions
- the disclosure in this specification relates to fluid machinery.
- the scroll-type fluid machine disclosed in Patent Document 1 includes a rotation preventing mechanism that includes an annular hole provided in a movable scroll and a pin that is pivoted inside the annular hole while being restricted by an inner peripheral wall forming the annular hole. Have a section.
- the orbiting scroll orbits around the revolution center with respect to the fixed scroll, while the rotation preventing mechanism portion prevents the movable scroll from rotating.
- the force to rotate the orbiting scroll acts. Since the rotation preventing mechanism receives the reaction force of this force, the pin and the inner peripheral wall forming the annular hole collide with each other, which causes noise.
- the purpose of disclosing in this specification is to provide a fluid machine for improving noise caused by the rotation prevention mechanism section.
- One of the disclosed fluid machines includes a fixed scroll having a spiral fixed side wrap and a spiral orbiting side wrap forming a fluid chamber for sucking, compressing and discharging a fluid between the fixed scroll and the fixed side wrap.
- a plurality of orbiting scrolls each having a orbiting scroll, and a restricting portion having a circular inner peripheral wall for preventing rotation of the orbiting scroll and a projecting portion which is restricted by the inner peripheral wall of the restricting portion and revolves inside the restricting portion.
- a rotation prevention mechanism section is provided.
- the protruding portion is provided on one end side and slides on the inner peripheral wall of the regulation portion
- the fixed portion is provided on the other end side and is fixed to the fixed side member
- the fixed portion is fixed.
- an unsupported portion that is not supported between the sliding portion and the sliding portion.
- the unsupported portion is provided in the protruding portion that swivels with respect to the regulating portion, when the load is applied to the protruding portion, the protruding portion is not formed between the fixed portion and the sliding portion. It is possible to bend it.
- the bendable portion on the protrusion in this manner, the rigidity of the protrusion on the fixed portion side relative to the sliding portion can be reduced when a load is applied during the turning motion.
- the impact force at the sliding portion and the regulation portion can be suppressed, which contributes to reducing noise. Therefore, the fluid machine can improve the noise caused by the rotation prevention mechanism section.
- One of the disclosed fluid machines is a swirl having a fixed scroll having a spiral fixed side wrap and a swirl side wrap forming a fluid chamber for sucking, compressing and discharging fluid between the fixed scroll and the fixed side wrap.
- a plurality of rotation preventive members each having a restricting portion having a circular inner peripheral wall and a protruding portion that is restricted by the inner peripheral wall of the restricting portion and revolves inside the restricting portion. And a mechanical section.
- the protruding portion has a sliding portion that is provided on one end side and slides with respect to the inner peripheral wall of the restriction portion, and a fixed portion that is provided and fixed on the other end side. Between the sliding portion and the fixed portion, the fixed portion is supported by an elastic deformation member formed of a material having a larger deformation amount with respect to the load than the fixed member.
- the elastically deformable member which is a material whose deformation amount with respect to the load is larger than that of the fixed side member, is provided in the protruding portion that swivels with respect to the restricting portion, when the protruding portion is loaded Therefore, the elastically deformable member can be easily deformed. Accordingly, it is possible to bend the intermediate portion of the protruding portion while the both ends of the fixed portion and the sliding portion are supported.
- the protruding portion has the bendable portion, the rigidity of the protruding portion closer to the fixed portion than the sliding portion can be reduced when a load is applied during the turning motion. Therefore, since the fluid machine can suppress the impact force in the sliding portion and the restriction portion, it contributes to the reduction of noise, and the noise caused by the rotation prevention mechanism portion can be improved.
- FIG. 3 is a partial cross-sectional view showing a cross section taken along the line III-III of FIG. 1 for the second housing and the non-supporting portion of the protrusion. It is the fragmentary sectional view showing the 2nd housing and the non-supporting part of the projection part in a 2nd embodiment. It is a fragmentary sectional view shown about a projection part and a 2nd housing in a 3rd embodiment. It is a fragmentary sectional view showing the projection part and the 2nd housing in a 4th embodiment.
- Fluid machines capable of achieving the objects disclosed herein include machines that compress fluids or devices that expand fluids.
- the fluid machine 1 disclosed in the first embodiment is capable of compressing or expanding a liquid, a gas, a gas-liquid mixed fluid, or the like adopted as a working fluid, and causing the liquid to flow to the outside.
- the working fluid is air, water, various refrigerants, or the like.
- the fluid machine 1 is a scroll type fluid machine including a fixed scroll 33 and an orbiting scroll 20.
- the fluid machine 1 at least the orbiting scroll 20 is made of resin, and can be used without oil. Therefore, the fluid machine 1 does not require an auxiliary device such as an oil separator.
- the fluid machine 1 can be applied as an air pressure source that supplies clean air, such as medical air or factory air.
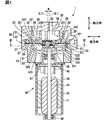
- the fluid machine 1 includes a housing 30, a fixed scroll 33, an orbiting scroll 20, a motor unit 40, and the like.
- the housing 30 includes a first housing 31 and a second housing 32.
- the first housing 31 and the second housing 32 are stationary side members that are stationary with respect to the orbiting scroll 20 that is movable.
- Both the first housing 31 and the second housing 32 are formed of a metal having high thermal conductivity such as aluminum.
- the first housing 31 and the second housing 32 are fixed by bolting or welding.
- the first housing 31 and the second housing 32 are installed such that their outer walls are exposed to the atmosphere. At least a part of the first housing 31 and the second housing 32 may be made of metal. It is sufficient that the first housing 31 and the second housing 32 are configured so that at least a part thereof is exposed to the atmosphere.
- the fixed scroll 33 and the orbiting scroll 20 are provided inside the housing 30.
- the fixed scroll 33 is configured as a part of the first housing 31. That is, the fixed scroll 33 and the first housing 31 form one member.
- the fixed scroll 33 and the orbiting scroll 20 may be collectively referred to as both scroll members. Both scroll members constitute a compression mechanism portion for sucking in, compressing, and discharging air, which is an example of a working fluid.
- the fixed scroll 33 includes a disk-shaped base portion 330 and a fixed-side tooth portion 331 protruding from the base portion 330.
- the fixed side tooth portion 331 is a fixed side wrap provided on the fixed scroll 33, and is formed in a spiral shape when the fixed scroll 33 is viewed in the axial direction.
- a cylindrical wall portion 332 that is coupled to the second housing 32 in the first housing 31 is provided on an outer peripheral edge portion of the base portion 330. As shown in FIG. 1, the tubular wall portion 332 projects in the axial direction of the fluid machine 1 so as to surround the base portion 330 from the outer peripheral edge portion of the base portion 330.
- the base portion 330 of the first housing 31 is provided with an intake port 34 that supplies air to a compression chamber 38 formed between both scroll members, and a discharge port 35 that discharges air from the compression chamber 38.
- the orbiting scroll 20 has a disk-shaped base portion 21 and a turning-side tooth portion 22 provided on the base portion 21.
- the orbiting side tooth portion 22 is a orbiting side wrap provided on the orbiting scroll 20, and is formed in a spiral shape when the orbiting scroll 20 is viewed in the axial direction.
- the compression chamber 38 is a fluid chamber that sucks, compresses, and discharges fluid between the fixed-side wrap and the swirling-side wrap.
- the compression chamber 38 is formed in a crescent shape when viewed in the axial direction.
- a cylindrical boss portion 24 is provided on the side of the base portion 21 opposite to the compression chamber 38.
- the fixed-side tooth portion 331 and the swivel-side tooth portion 22 are in a relationship of forming an asymmetric spiral structure having different winding angle ranges.
- the difference between the winding angle range of the fixed side tooth portion 331 and the winding angle range of the turning side tooth portion 22 is preferably 30 degrees or more.
- the fixed-side tooth portion 331 has a spiral portion located radially outside of the radially outer portion of the swivel-side tooth portion 22.
- the spiral portion of the fixed side tooth portion 331 is provided on the cylindrical wall portion 332.
- the winding angle range of the fixed-side tooth portion 331 is larger than the winding angle range of the turning-side tooth portion 22 by the angle included in the range of 170 to 190 degrees. Is preferred. This is because, in the case of having such an asymmetrical spiral structure, the inside and outside of the scroll can be effectively used and the physique can be made smaller than the suction volume.
- intensive studies have shown that in the case of a fluid machine in which the fixed side wrap and the orbiting side wrap have an asymmetric spiral shape or a fluid machine in which air is the working fluid, the rotation torque is easy to reverse. ing.
- the fluid chamber has a configuration that moves from the central portion of the fixed scroll 33 toward the outer end portion.
- the suction port 34 functions as a discharge port and the discharge port 35 functions as a suction port, so that the volume of the fluid chamber changes so as to increase, and the fluid is taken into the fluid chamber from the center side. The fluid will expand.
- the orbiting scroll 20 is preferably made of resin. This is because this configuration can reduce the vibration of the orbiting scroll 20 due to the centrifugal force and is advantageous in terms of vibration and noise. However, since the resin-made orbiting scroll 20 is lighter in weight than metal, the self-excited vibration of the rotation preventing mechanism section 50 is likely to occur.
- a swivel-side sliding surface 23 that slides on the housing-side sliding surface 36 of the first housing 31 is provided at a portion of the base portion 21 that is radially outward of the swivel-side tooth portion 22.
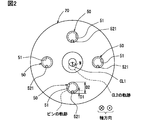
- the fluid machine 1 is provided with a rotation prevention mechanism section 50 for preventing rotation of the orbiting scroll 20.
- the rotation preventing mechanism portion 50 includes a regulation portion 51 and a protruding portion 52 which is regulated by the inner peripheral wall of the regulation portion 51 and swivels inside the regulation portion 51.
- the fluid machine 1 includes four rotation preventing mechanism parts 50.
- the four rotation preventing mechanism parts 50 are located around the central axis of the orbiting scroll 20 at substantially equal intervals.
- substantially evenly spaced is meant to include a configuration that is evenly spaced and a configuration that is deviated with respect to the equally spaced within a predetermined dimensional tolerance.
- the predetermined dimensional tolerance is about ⁇ 5 degrees.
- the rotation preventing mechanism portion 50 included in the fluid machine 1 may be five or more.
- the restriction portion 51 is a hole formed by a circular inner peripheral wall or a recess having a bottom surface.
- the restricting portion 51 is, for example, a recess having a predetermined depth provided on the base portion 21 of the orbiting scroll 20 on the side opposite to the fixed scroll 33.
- the restriction portion 51 faces the end surface of the second housing 32 that is orthogonal to the rotation axis CL1.
- the restriction portion 51 is configured to have an inner peripheral wall having a circular opening end and a bottom portion closing the inner peripheral wall on the fixed scroll 33 side.
- the inner peripheral wall and the bottom are a part of the base 21 made of resin.
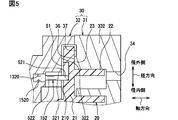
- the protruding portion 52 is a rod-shaped body having a fixed portion 520 fixed to the second housing 32 and a sliding portion 521 as a tip side portion protruding toward the bottom surface of the regulating portion 51.
- the protrusion 52 is formed of iron or an alloy containing iron.
- the protrusion 52 is also called a pin.
- the fixed portion 520 of the protruding portion 52 is fixed in a state of being press-fitted into a cylindrical recess 320 formed in the second housing 32.
- the protruding portion 52 is fixed to the second housing 32 in a state where the tip of the sliding portion 521 and the bottom surface of the restricting portion 51 are separated from each other.
- the sliding portion 521 slides along the inner peripheral wall of the restricting portion 51 while being displaced in a circular shape.
- the protruding portion 52 is supported by the second housing 32, which is a fixed member, and the orbiting scroll 20, which is a movable member, in the fixed portion 520 and the sliding portion 521 located at both ends.
- the protruding portion 52 has an unsupported portion 522 that is not supported between the fixed portion 520 and the sliding portion 521.
- the non-supporting portion 522 is a portion that is set to the entire axial length between the fixed portion 520 and the sliding portion 521, or is partially set with respect to the axial length.
- the surface of the base portion 21 opposite to the fixed scroll 33 and the surface of the second housing 32 facing this surface are slightly separated from each other.
- the non-supporting portion 522 is located closer to the fixed portion 520 than the surface of the second housing 32 facing the restricting portion 51.
- the second housing 32 which is a fixed member, includes a separating wall 321 that is separated from the non-supporting portion 522 in the radial direction.
- the spacing wall 321 forms a space between itself and the non-supporting portion 522. This space is a region where the working fluid flowing from the compression chamber 38 into the back pressure chamber 39 through the back pressure introduction passage 25 exists, but is not occupied by the solid object. That is, between the separation wall 321 and the non-supporting portion 522, there is no solid object that contacts both of them.
- the non-supporting portion 522 is a portion that is not held from the outside, it has a lower strength and rigidity with respect to the load than the other portions in the entire axial direction of the protruding portion 52, and has a function of making the protruding portion 52 largely bendable. ..
- the separation wall 321 is a wall portion that surrounds the outer peripheral side of the fixed-side member and the circumferential side of the fixed-side member in the periphery of the unsupported portion 522.
- the separation wall 321 is not provided radially inside the non-support portion 522.
- the spacing wall 321 surrounds the unsupported portion 522 in a U-shape when viewed in the axial direction. With this configuration, the space portion between the separation wall 321 and the non-supporting portion 522 in each rotation prevention mechanism portion 50 communicates with the back pressure chamber 39 on the radially inner side.
- the length of the separating wall 321 along the axial direction of the protruding portion 52 be longer than the length of the sliding portion 521 in the axial direction. Accordingly, the axial length of the space provided around the non-supporting portion 522 is longer than the axial length of the sliding portion 521. Further, the axial length of the non-supporting portion 522 is longer than the axial length of the sliding portion 521.
- the length of the separating wall 321 along the axial direction of the protruding portion 52 is longer than the outer diameter dimension of the sliding portion 521.
- the length of the space provided around the non-supporting portion 522 in the axial direction is longer than the outer diameter dimension of the sliding portion 521.
- the axial length of the non-supporting portion 522 is longer than the outer diameter dimension of the sliding portion 521.
- the unsupported portion 522 having each of the above configurations is a part of the protruding portion 52 that is not supported by the solid object between the fixed portion 520 and the sliding portion 521.
- the protruding portion 52 is fixed to the solid-side member at the fixed portion 520 on the one end side, and is slidably supported by the regulating portion 51 at the sliding portion 521 on the other end side which is the tip. For this reason, the protruding portion 52 has a rigidity characteristic that it is easily bent in the non-supporting portion 522 when a load is applied to the sliding portion 521 and the like.
- the protrusion 52 has low rigidity up to the vicinity of the sliding portion as compared with a conventional pin that is a fixed portion, and has a large amount of bending with respect to a load. Therefore, the projecting portion 52 can reduce the reaction force acting on the regulation portion 51 against the load, has a high ability to absorb the load, and has an effect of suppressing the impact force in the rotation prevention mechanism portion 50.
- the second housing 32 is integrally provided with a motor unit 40 on the side opposite to the first housing 31.
- the motor unit 40 has a stator 42, a rotor 43, a shaft 44, and the like inside a motor case 41.
- As the motor unit 40 various motors such as a brush motor or a brushless motor can be adopted.
- the shaft 44 is rotatably provided by a bearing 45 and a bearing 46 provided inside the motor case 41.
- the shaft 44 is rotationally driven by the motor unit 40.
- the end of the shaft 44 is inserted inside the second housing 32.
- An eccentric portion 47 is fixed to the end of the shaft 44.
- the central axis CL2 of the eccentric portion 47 is installed at a position eccentric to the rotation axis CL1 of the shaft 44.
- the eccentric portion 47 is provided inside the boss portion 24 provided on the base portion 21 of the orbiting scroll 20 via a bearing 48.
- the shaft 44 rotates about the rotation axis CL1.
- the torque output by the motor unit 40 is transmitted to the boss portion 24 of the orbiting scroll 20 via the eccentric portion 47.
- the orbiting scroll 20 revolves around the rotation axis CL1 of the shaft 44 while being prevented from rotating by the rotation preventing mechanism section 50.
- the revolution radius is equal to the distance W between the central axis CL2 and the rotation axis CL1.
- centrifugal force acts on the orbiting scroll 20 and the rotation preventing mechanism 50.
- a dashed circle passing through the central axis CL2 shown in FIG. 2 is an orbit of the central axis CL2.
- the sliding portion 521 of the protruding portion 52 also draws a revolution locus indicated by a broken line circle along the inner peripheral wall of the regulation portion 51.
- W is a relationship of W ⁇ (D2-D1)/2 between the distance W, the outer diameter D1 of the sliding portion 521, and the inner diameter D2 of the inner peripheral wall of the regulating portion 51.
- the compression chamber 38 formed between both scroll members orbits from the radially outer side to the radially inner side.
- the compression chamber 38 located on the suction port 34 side gradually changes its volume while approaching the rotation axis CL1 or the discharge port 35 while the rotation angle of the shaft 44 changes from 0 degree to 360 degrees. ..
- the air supplied from the outside of the fluid machine 1 to the compression chamber 38 through the suction port 34 is compressed, and this air is discharged from the discharge port 35 to the outside of the fluid machine 1.
- a back pressure chamber 39 is provided between the surface of the base portion 21 opposite to the fixed scroll 33 and the separation wall 321 which is the inner wall of the second housing 32 on the rotation axis CL1 side.
- a part of the air compressed in the compression chamber 38 is supplied to the back pressure chamber 39 via the back pressure introduction passage 25 penetrating the base portion 21.
- the back pressure introducing passage 25 is a passage that connects the compression chamber 38 and the back pressure chamber 39.
- a housing-side sliding surface 36 that slides on the turning-side sliding surface 23 is provided at a portion of the first housing 31 that faces the turning-side sliding surface 23.
- the orbiting scroll 20 revolves, the orbiting scroll 20 is biased toward the fixed scroll 33 by the pressure of air in the back pressure chamber 39. Therefore, the turning side sliding surface 23 and the housing side sliding surface 36 always slide in a state of being in contact with each other.
- the housing side sliding surface 36 functions as a thrust bearing portion for receiving the axial load of the orbiting scroll 20.
- the orbiting scroll 20 revolves while being supported by the housing side sliding surface 36 as a thrust bearing portion.
- the high pressure air supplied from the compression chamber 38 to the back pressure chamber 39 passes through the gap and the low pressure inside the fixed scroll 33. It is possible that it leaks into the space.
- the orbiting scroll 20 is urged toward the fixed scroll 33 by the pressure of the air in the back pressure chamber 39, so that the orbiting side sliding surface 23 and the housing side sliding surface 36 are reliably in contact with each other. Slide. Therefore, there is an effect of preventing high-pressure air in the back pressure chamber 39 from leaking into the low-pressure space inside the fixed scroll 33. According to this fluid machine 1, it is possible to prevent a decrease in the compression efficiency of air.
- the housing side sliding surface 36 is preferably provided with a coating containing self-lubricating fluorine or molybdenum disulfide. As a result, the coefficient of friction of the housing side sliding surface 36 can be lowered.
- a coating containing self-lubricating fluorine or molybdenum disulfide As a result, the coefficient of friction of the housing side sliding surface 36 can be lowered.
- the fluorine coating coating with polytetrafluoroethylene is preferable. Further, since this coating is a thin film, it has an effect that heat transfer from the orbiting scroll 20 to the housing 30 is not easily obstructed. Therefore, even when the turning side sliding surface 23 and the housing side sliding surface 36 slide under a higher load, it is possible to suppress the temperature rise of the sliding portion.
- the first housing 31 is provided with a recessed portion 37 that is recessed so as to be separated from the orbiting scroll 20 radially outside the housing-side sliding surface 36.
- the recess 37 is a portion that does not come into contact with the orbiting-side sliding surface 23 of the orbiting scroll 20.
- a gap is provided between the tip of the fixed tooth portion 331 and the base portion 21 of the orbiting scroll 20.
- a gap is provided between the tip end of the orbiting side tooth portion 22 and the base portion 330 of the fixed scroll 33. Accordingly, the tip of the fixed-side tooth portion 331 is located closer to the base portion 330 side than the swivel-side sliding surface 23 and the housing-side sliding surface 36, so that the swivel-side sliding surface 23 and the housing-side sliding surface 36 are Slides while making sure contact. This has the effect of preventing high-pressure air in the back pressure chamber 39 from leaking into the low-pressure space inside the fixed scroll 33.
- the fluid machine 1 includes a fixed scroll 33 having a spiral fixed side wrap and an orbiting scroll 20 having a orbiting side wrap forming a fluid chamber for sucking, compressing and discharging fluid between the fixed side wrap.
- the fluid machine 1 includes a restricting portion 51 having a circular inner peripheral wall, and a protruding portion 52 that is restricted by the inner peripheral wall of the restricting portion 51 and revolves inside the restricting portion 51.
- a plurality of rotation preventing mechanism parts 50 each having The protruding portion 52 includes a sliding portion 521 that is provided on one end side and slides on the inner peripheral wall of the restriction portion 51, and a fixed portion 520 that is provided on the other end side and is fixed to a fixed side member. , And a non-supporting portion 522 that is not supported between the fixed portion 520 and the sliding portion 521.
- the unsupported portion 522 is provided on the protruding portion 52 that swivels with respect to the regulation portion 51.
- the protruding portion 52 when a load is applied to the protruding portion 52, it is possible to bend the protruding portion 52 between the fixed portion 520 and the sliding portion 521. Since the non-supporting portion 522 is a bendable portion of the protruding portion 52, when a load is applied to the sliding portion 521 or the like in the turning motion, the unsupported portion 522 of the protruding portion 52 closer to the fixed portion 520 than the sliding portion 521 is. The rigidity can be reduced.
- the fluid machine 1 can improve the noise caused by the rotation prevention mechanism section 50.
- the fixed side wrap and the orbiting side wrap form an asymmetrical spiral shape and the rotation torque is easy to reverse forward and backward, or when the resin orbiting scroll is lightweight and self-excited vibration occurs.
- it is easy it is possible to provide a useful fluid machine 1 that is particularly effective.
- the non-supporting portion 522 is a portion located closer to the fixed portion 520 than the surface of the fixed member facing the regulating portion 51.
- the stationary member includes a separating wall 321 that is spaced apart from the non-supporting portion 522 in the radial direction and forms a space between the non-supporting portion 522 and the non-supporting portion 522.
- the axial length of the non-supporting portion 522 can be set by adjusting the axial dimension of the spacing wall 321, so that the impact of the protruding portion 52 can be changed by changing the shape of the fixed-side member.
- the absorption capacity can be easily set.
- the length of the separating wall 321 along the axial direction of the protruding portion 52 is longer than the axial length of the sliding portion 521. According to this configuration, since the axial dimension of the separating wall 321 is larger than the axial dimension of the sliding portion 521, the unsupported portion 522 can be made longer than the portion of the protruding portion 52 supported on the tip side. As a result, the non-supporting portion 522 largely bends in the same direction as the direction of the external force applied to the tip side, so that the projecting portion 52 can absorb the external force and greatly reduce the impact.
- the length of the separating wall 321 along the axial direction of the protruding portion 52 is longer than the outer diameter dimension of the sliding portion 521.
- the axial dimension of the separating wall 321 is larger than the outer diameter dimension of the sliding portion 521, so that the length of the non-supporting portion 522 can be sufficiently secured in the protruding portion 52.
- the length of the separating wall 321 along the axial direction of the protruding portion 52 is longer than the radial distance between the separating wall 321 and the outer peripheral surface of the non-supporting portion 522.
- the fixed-side member can be formed such that the radial position of the separation wall 321 in the fixed-side member is closer to the outer peripheral surface of the non-supported portion 522 than the axial length of the non-supported portion 522. it can.
- the second embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
- the second embodiment differs from the first embodiment in the shape of the spacing wall 1321 that is radially spaced from the non-supporting portion 522 of the protrusion 52.
- the configurations, operations, and effects that are not particularly described in the second embodiment are similar to those in the first embodiment, and only different points will be described below.
- the separating wall 1321 is a part of the second housing 132 and constitutes an inner peripheral wall surrounding the periphery of the non-supporting portion 522.
- the separating wall 1321 forms a cylindrical recess having a bottom portion at which the fixed portion 520 is fixed.
- the unsupported portion 522 is provided coaxially with the spacing wall 1321.
- a gap is formed between the inner peripheral surface of the separating wall 1321 and the outer peripheral surface of the non-supporting portion 522, which is a uniform distance over the entire circumference.
- a tubular space portion is formed between the separation wall 1321 and the non-supporting portion 522. This space is a region in which the working fluid exists but is not occupied by a solid object. Between the separating wall 1321 and the non-supporting portion 522, there is no solid object that comes into contact with both of them.
- the protruding portion 52 of the second embodiment has the non-supporting portion 522 that is not held by the second housing 132 between the fixed portion 520 and the sliding portion 521.
- the space between the separating wall 1321 and the non-supporting portion 522 and the back pressure chamber 39 are partitioned by the second housing 132.
- a third embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
- the third embodiment is different from the first embodiment in the shape of the protruding portion 152.
- the configurations, operations, and effects that are not particularly described in the third embodiment are the same as those in the first embodiment, and only differences from the first embodiment will be described below.
- the surface 210 of the base portion 21 opposite to the fixed scroll 33 and the surface 322 of the second housing 32 facing the surface 210 are slightly separated from each other.
- the non-supporting portion 522 is located closer to the fixed portion 1520 than the surface 322 of the second housing 32 that faces the regulating portion 51.
- the protruding portion 152 includes a fixed portion 1520 having an outer diameter larger than that of the non-supporting portion 522 and the sliding portion 521.
- the fixed portion 1520 is fixed in a state of being press-fitted into a cylindrical recess 1320 formed in the second housing 32.
- the fixed portion 1520 has a larger outer diameter than the non-supporting portion 522 and the sliding portion 521, the contact area between the cylindrical recess 1320 and the fixed portion 1520 can be increased. Thereby, even when the non-supporting portion 522 is largely bent, the fixing force for the protruding portion 152 can be secured, and the rotation preventing mechanism portion 50 that can exhibit a desired function can be provided.
- the unsupported portion 522 is a portion thinner than the fixed portion 1520. According to this structure, since the rigidity of the non-supporting portion 522 is smaller than that of the fixed portion 1520, it is possible to provide the projecting portion 152 in which the non-supporting portion 522 is largely flexible. Thereby, the ability of the protruding portion 152 to absorb the external force can be secured, and the rotation preventing mechanism portion 50 can secure the ability to absorb the impact.
- a fourth embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
- the fourth embodiment is different from the third embodiment in the positional relationship between the cylindrical recess 1320 and the fixed portion 2520.
- the configurations, operations, and effects that are not particularly described in the fourth embodiment are the same as those in the first and third embodiments, and only points different from the first embodiment will be described below.
- the protruding portion 252 includes a fixed portion 2520 having an outer diameter dimension larger than that of the non-supporting portion 522 and the sliding portion 521.
- the fixed portion 2520 has an axial length shorter than that of the cylindrical recess 1320. With this configuration, a part of the non-supporting portion 522 is located even inside the cylindrical recess 1320.
- the protrusion 252 since the protrusion 252 has a longer axial length of the non-supporting portion 522 than the protrusion 152, the protrusion 252 can be largely flexed, and an effect that a shock absorbing effect is large is achieved.
- the fifth embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
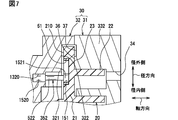
- the fifth embodiment differs from the third embodiment in the sliding portion 1521 and the regulating portion 151.
- the configurations, operations, and effects that are not particularly described in the fifth embodiment are similar to those in the first embodiment, and only differences from the above-described embodiment will be described below.
- the protruding portion 352 includes a sliding portion 1521 having an outer diameter dimension larger than that of the non-supporting portion 522. According to this configuration, the contact surface pressure between the restricting portion 151 and the sliding portion 1521 can be reduced. As a result, it is possible to provide the fluid machine 1 that suppresses wear of the sliding portion 1521 and the restriction portion 151 and that does not easily cause a seizure state.
- a tubular sleeve member is housed in the recess forming the above-mentioned restriction portion 51.
- the sleeve member may be fixed to the recess or may be rotatable. Further, the sliding portion 1521 orbits the inside of the sleeve member while being regulated by the inner peripheral wall of the sleeve member that is the regulating portion 151 as the orbiting scroll 20 revolves.
- the sleeve member is made of a material whose surface is harder than that of the orbiting scroll 20.
- the sleeve member is made of metal, for example.
- FIG. 6 A sixth embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
- the sixth embodiment differs from the first embodiment in that it has a ring-shaped member 53 that slides with respect to the restriction portion 51 and a displacement restriction structure of the ring-shaped member 53.
- the configurations, operations, and effects that are not particularly described in the sixth embodiment are similar to those in the first embodiment, and only differences from the above-described embodiment will be described below.
- a ring-shaped member 53 is attached to the protruding portion 52 at the tip side portion that slides with the regulating portion 51.
- the ring-shaped member 53 is rotatably installed outside the tip end side portion of the protrusion 52. Therefore, the sliding portion 521 of the sixth embodiment includes the ring-shaped member 53 rotatable with respect to the pin.
- the ring-shaped member 53 is made of a material whose surface is harder than that of the orbiting scroll 20.
- the ring-shaped member 53 is made of metal, for example. As the orbiting scroll 20 revolves, the ring-shaped member 53 rotates while being regulated by the inner peripheral wall of the regulation portion 51 while rotating inside the regulation portion 51 with respect to the pin.
- the contact surface pressure between the restriction portion 51 and the ring-shaped member 53 can be reduced. Further, it is possible to provide the fluid machine 1 in which abrasion of the sliding portion 521 is suppressed and the seizure is unlikely to occur.
- the plate-shaped member 54 is installed between the surface 210 of the base 21 and the surface 322 of the second housing 32 so as to face both the surface 210 and the surface 322.
- the plate-shaped member 54 functions as a displacement restriction structure that prevents the ring-shaped member 53 from axially displacing and falling off from the restriction portion 51, and is made of, for example, metal.
- the seventh embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
- the seventh embodiment differs from the first embodiment in the structure for fixing the fixed portion 520 to the fixed member.
- the configurations, operations, and effects that are not particularly described in the seventh embodiment are the same as those in the first embodiment, and only differences from the above-described embodiment will be described below.
- the second housing 32 which is the fixed member, has a swaged portion 323 that is swaged around the fixed portion 520 of the protrusion 52 or around the pressure inlet.
- the caulking portion 323 is a portion that is plastically deformed in the second housing 32 so as to apply an external force that pushes the outer peripheral surface of the fixed portion 520 press-fitted into the cylindrical recess 320 of the second housing 32 to the axial center side. ..
- the caulking portion 323 applies an external force in the axial direction to the caulking jig 60 in a state where the caulking jig 60 shown in FIG. It can be formed by plastically deforming the periphery of the fixed portion 520.
- the reaction force F2 in the opposite direction is present in the vicinity of the caulking portion 323 of the fixed portion 520.
- This reaction force F2 tends to increase as the axial length of the non-supporting portion 522 increases.
- the caulking portion 323 increases the contact surface pressure between the fixed-side member and the press-fitted fixed portion 520, and prevents the fixed portion 520 from falling off the fixed-side member due to the reaction force F2. Is playing.
- the eighth embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
- the eighth embodiment differs from the first and second embodiments in the structure for bending the intermediate portion of the protrusion 52 between the sliding portion 521 and the fixed portion 520.
- the configurations, operations, and effects that are not particularly described in the eighth embodiment are the same as those in the above-described embodiments, and only different points will be described below.
- the elastic member 55 is a cylindrical elastic deformation member formed of a material that easily elastically deforms with respect to a load.
- the elastic member 55 is in contact with the projecting portion 52 on the inner peripheral surface and is in contact with the spacing wall 1321 forming a cylindrical recess on the outer peripheral surface.
- the elastic member 55 has an axial length that supports the protrusion 52 over the entire axial length of the cylindrical recess.
- the elastic member 55 can be formed of a material that easily expands and contracts, such as elastomer, synthetic rubber, natural rubber, urethane, and fluorine-based rubber.
- the protruding portion 52 is supported between the fixed portion 520 and the sliding portion 521 by an elastic deformation member formed of a material having a larger deformation amount with respect to the load than the fixed member. Has been.
- the elastically deformable member is elastically deformed between the fixed portion 520 and the sliding portion 521 when a load is applied to the protruding portion 52, it is possible to bend the protruding portion 52. is there. Accordingly, when a load is applied to the sliding portion 521 or the like in the turning motion, the rigidity of the protruding portion 52 on the fixed portion 520 side of the sliding portion 521 can be reduced. In this way, the portion supported by the elastically deforming member is softer and elastically deformed more easily than the fixed-side member that fixes the fixed portion 520, so that the impact absorbing force of the protrusion 52 is improved.
- the fluid machine 1 has an effect of suppressing the impact force on the sliding portion 521 and the regulating portion 51, and contributes to reducing noise.
- the ninth embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
- the ninth embodiment differs from the eighth embodiment in the axial length of the elastic member 155 that is an elastically deformable member.
- the configurations, operations, and effects not particularly described in the ninth embodiment are the same as those in the eighth embodiment, and only different points will be described below.
- the elastic member 155 is in contact with the protrusion 52 in the middle of the cylindrical recess on the inner peripheral surface and in contact with the separation wall 1321 in the middle of the cylindrical recess on the outer peripheral surface.
- the protruding portion 52 of the ninth embodiment includes the unsupported portions 522 on both sides of the portion supported by the elastic member 155.
- the elastic member 55 has an axial length that supports the protrusion 52 over a part of the axial length of the cylindrical recess.
- the elastic member 155 can be formed of a material that easily expands and contracts, such as elastomer, synthetic rubber, natural rubber, urethane, and fluorine rubber.
- the protruding portion 52 is formed between the fixed portion 520 and the sliding portion 521 by an elastic deformation member formed of a material having a larger deformation amount with respect to the load than the fixed member. Supported.
- the elastic member 155 is elastically deformed between the fixed portion 520 and the sliding portion 521 when a load is applied to the protruding portion 52, it is possible to bend the protruding portion 52. is there.
- the portion supported by the elastic member 155 is softer and elastically deformed more easily than the fixed-side member that fixes the fixed portion 520, and thus the impact absorbing force of the protrusion 52 is improved.
- the disclosure of this specification is not limited to the illustrated embodiments.
- the disclosure encompasses the illustrated embodiments and variations on them based on them.
- the disclosure is not limited to the combination of parts and elements shown in the embodiments, and various modifications can be implemented.
- the disclosure can be implemented in various combinations.
- the disclosure may have additional parts that may be added to the embodiments.
- the disclosure includes parts and elements of the embodiments that are omitted.
- the disclosure includes replacements or combinations of parts, elements between one embodiment and another.
- the disclosed technical scope is not limited to the description of the embodiments.
- the disclosed technical scope is shown by the description of the claims, and should be understood to include meaning equivalent to the description of the claims and all modifications within the scope.
- the protrusion is a rod-shaped body such as a pin, but the protrusion that can achieve the object disclosed in the specification may be a rod-shaped body or a cylindrical body having a hollow inside.
- the fixed scroll 33 is a part of the first housing 31 in the above-described embodiment, but may be configured by a member separate from the first housing 31.
- the fixed scroll 33 which is a separate member, is integrated with the first housing 31 by being fixed to the first housing 31.
- the fixed scroll 33 is described as being formed of a metal such as aluminum in the above-described embodiment, it may be formed of a resin material. In this case, the fixed scroll 33 may be a part of the first housing 31 or a separate member fixed to the first housing 31.
- the fixed side wrap and the swiveling side wrap have been described as having the relationship of forming an asymmetric spiral structure having different winding angle ranges in the above-described embodiment, these wraps have a symmetrical spiral structure having the same winding angle range. It may be a relationship.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Rotary Pumps (AREA)
- Applications Or Details Of Rotary Compressors (AREA)
Abstract
流体機械は、固定スクロール(33)と、旋回スクロール(20)と、自転防止機構部(50)と、を備える。自転防止機構部(50)は、旋回スクロールの自転運動を阻止するために、円形状の内周壁を有する規制部(51;151)と、規制部の内周壁に規制されつつ規制部の内側において旋回する突出部(52;152;252;352)と、を有する。突出部は、一方端側に設けられて規制部の内周壁に対して摺動する摺動部(521;1521)と、他方端側に設けられて固定側部材(32)に固定されている被固定部(520;1520;2520)と、被固定部と摺動部との間において支えられていない非支持部(522)と、を有する。
Description
本出願は、2018年12月13日に出願された日本特許出願2018-233631号に基づくもので、ここにその記載内容を援用する。
この明細書における開示は、流体機械に関する。
特許文献1に開示されたスクロール型流体機械は、可動スクロールに設けられた円環孔と、円環孔を形成する内周壁に規制されつつ円環孔の内側に旋回するピンとを含む自転防止機構部を有している。流体機械は、自転防止機構部が可動スクロールの自転を阻止しながら、旋回スクロールが固定スクロールに対して公転中心周りに旋回運動する。
可動スクロールの旋回運動においては、旋回スクロールを自転させようとする力が作用する。自転防止機構部は、この力の反力を受けるため、ピンと円環孔を形成する内周壁とが衝突して、騒音の一因となっていた。
この明細書に開示する目的は、自転防止機構部を起因とする騒音の改善を図る流体機械を提供することである。
この明細書に開示された複数の態様は、それぞれの目的を達成するために、互いに異なる技術的手段を採用する。また、特許請求の範囲に記載した括弧内の符号は、一つの態様として後述する実施形態に記載の具体的手段との対応関係を示す一例であって、技術的範囲を限定するものではない。
開示された流体機械の一つは、渦巻き状の固定側ラップを有した固定スクロールと、固定側ラップとの間に流体を吸入、圧縮および吐出する流体室を形成する渦巻き状の旋回側ラップを有した旋回スクロールと、旋回スクロールの自転運動を阻止するために、円形状の内周壁を有する規制部と規制部の内周壁に規制されつつ規制部の内側において旋回する突出部とをそれぞれ有する複数の自転防止機構部と、を備える。
突出部は、一方端側に設けられて規制部の内周壁に対して摺動する摺動部と、他方端側に設けられて固定側部材に固定されている被固定部と、被固定部と摺動部との間において支えられていない非支持部と、を有する。
この流体機械によれば、規制部に対して旋回する突出部に非支持部が設けられているため、突出部に荷重がかかった場合に被固定部と摺動部との間で突出部を撓ませることが可能である。このように突出部に撓み可能部が設けられていることにより、旋回運動において荷重がかかった場合に、摺動部よりも被固定部側における突出部の剛性を低下させることができる。これにより、摺動部と規制部における衝撃力を抑制できるので、騒音を低下させることに寄与する。したがって、流体機械は、自転防止機構部を起因とする騒音の改善を図ることができる。
開示された流体機械の一つは、渦巻き状の固定側ラップを有した固定スクロールと、固定側ラップとの間に流体を吸入、圧縮および吐出する流体室を形成する旋回側ラップを有した旋回スクロールと、旋回スクロールの自転運動を阻止するために、円形状の内周壁を有する規制部と規制部の内周壁に規制されつつ規制部の内側において旋回する突出部とをそれぞれ有する複数の自転防止機構部と、を備える。
突出部は、一方端側に設けられて規制部の内周壁に対して摺動する摺動部と、他方端側に設けられて固定されている被固定部とを有し、被固定部と摺動部との間において、被固定部が固定されている固定側部材よりも荷重に対する変形量が大きい材質で形成されている弾性変形部材によって支えられている。
この流体機械によれば、規制部に対して旋回する突出部に、荷重に対する変形量が固定側部材よりも大きい材質である弾性変形部材が設けられているため、突出部に荷重がかかった場合に弾性変形部材を容易に変形させることができる。これにより、被固定部および摺動部の両端部が支持された状態で突出部の中間部分を撓ませることが可能である。この流体機械においても突出部に撓み可能部を有することにより、旋回運動において荷重がかかった場合に、摺動部よりも被固定部側における突出部の剛性を低下させることができる。したがって、流体機械は、摺動部と規制部における衝撃力を抑制できるので、騒音を低下させることに寄与し、自転防止機構部を起因とする騒音の改善を図ることができる。
以下に、図面を参照しながら本開示を実施するための複数の形態を説明する。各形態において先行する形態で説明した事項に対応する部分には同一の参照符号を付して重複する説明を省略する場合がある。各形態において構成の一部のみを説明している場合は、構成の他の部分については先行して説明した他の形態を適用することができる。各実施形態で具体的に組み合わせが可能であることを明示している部分同士の組み合わせばかりではなく、特に組み合わせに支障が生じなければ、明示していなくても実施形態同士を部分的に組み合せることも可能である。
(第1実施形態)
流体機械の一例を開示する第1実施形態について図1~図3を参照しながら説明する。明細書に開示の目的を達成可能な流体機械は、流体を圧縮する機械または流体を膨張する装置を含んでいる。第1実施形態に開示する流体機械1は、作動流体として採用される液体、気体、気液混合流体等を圧縮または膨張して外部へ流出させることができる。例えば作動流体は、空気、水、各種の冷媒等である。
流体機械の一例を開示する第1実施形態について図1~図3を参照しながら説明する。明細書に開示の目的を達成可能な流体機械は、流体を圧縮する機械または流体を膨張する装置を含んでいる。第1実施形態に開示する流体機械1は、作動流体として採用される液体、気体、気液混合流体等を圧縮または膨張して外部へ流出させることができる。例えば作動流体は、空気、水、各種の冷媒等である。
流体機械1は、固定スクロール33と旋回スクロール20とを備えるスクロール型流体機械である。流体機械1は、少なくとも旋回スクロール20が樹脂製であり、さらにオイルレスで使用することができる。このため、流体機械1は、オイルセパレータなどの付属装置が不要である。流体機械1は、例えば医療用エアや工場用エアなど、クリーンな空気を供給する空気圧源として適用することができる。
図1を参照して流体機械1の構成について説明する。図1に示すように、流体機械1は、ハウジング30、固定スクロール33、旋回スクロール20およびモータ部40等を備えている。ハウジング30は、第1ハウジング31と第2ハウジング32を含んで構成されている。第1ハウジング31と第2ハウジング32は、流体機械1において、可動する旋回スクロール20に対して、静止している固定側部材である。第1ハウジング31と第2ハウジング32はいずれも、例えばアルミニウムなど、熱伝導性の高い金属により形成されている。第1ハウジング31と第2ハウジング32は、ボルト締めまたは溶接等により固定されている。第1ハウジング31と第2ハウジング32はそれぞれの外壁が大気に露出するように設置されている。第1ハウジング31と第2ハウジング32は、少なくとも一部が金属により形成されていればよい。第1ハウジング31と第2ハウジング32は、少なくとも一部が大気に露出するように構成されていればよい。
ハウジング30の内側には、固定スクロール33と旋回スクロール20が設けられている。固定スクロール33は、第1ハウジング31の一部として構成されている。つまり、固定スクロール33と第1ハウジング31は一つの部材をなしている。以下、固定スクロール33と旋回スクロール20とを合わせて、両スクロール部材ということがある。両スクロール部材は、作動流体の一例である空気を吸入し圧縮し、吐き出すための圧縮機構部を構成している。固定スクロール33は、円盤状の基盤部330と、基盤部330から突出している固定側歯部331とを備えている。固定側歯部331は、固定スクロール33に設けられた固定側ラップであり、固定スクロール33を軸方向に視て渦巻状に形成されている。基盤部330の外周縁部には、第1ハウジング31において第2ハウジング32に結合される筒状壁部332が設けられている。図1に示すように、筒状壁部332は、基盤部330の外周縁部から基盤部330を取り囲むように流体機械1の軸方向に突出している。
第1ハウジング31の基盤部330には、両スクロール部材の間に形成される圧縮室38に空気を供給する吸入口34と、圧縮室38から空気を吐き出す吐出口35とが設けられている。旋回スクロール20は、円盤状の基盤部21と、基盤部21に設けられる旋回側歯部22とを有している。旋回側歯部22は、旋回スクロール20に設けられた旋回側ラップであり、旋回スクロール20を軸方向に視て渦巻状に形成されている。圧縮室38は、固定側ラップと旋回側ラップとの間に流体を吸入、圧縮および吐出する流体室である。圧縮室38は、軸方向に視て三日月状に形成されている。基盤部21のうち圧縮室38とは反対側には、円筒状のボス部24が設けられている。
固定側歯部331と旋回側歯部22は、巻き角度範囲が異なる非対称の渦巻き構造をなす関係にある。固定側歯部331の巻き角度範囲と旋回側歯部22の巻き角度範囲との差は、30度以上であることが好ましい。固定側歯部331は、旋回側歯部22における径方向外側部位よりもさらに径外側に位置する渦巻き状部を有している。固定側歯部331における、この渦巻き状部は、筒状壁部332に設けられている。筒状壁部332に設けられた渦巻き状部により、さらに固定側歯部331の巻き角度範囲は、旋回側歯部22の巻き角度範囲よりも170度~190度の範囲に含まれる角度分大きくなっていることが好ましい。このような非対称の渦巻き構造を有する場合、スクロールの内外を有効に使え、吸い込み容積に対し体格を小さくできるからである。しかしながら、鋭意研究によれば固定側ラップと旋回側ラップとが非対称の渦巻き状をなす流体機械や、空気を作動流体とする流体機械の場合には、自転トルクが正逆反転しやすいことがわかっている。
流体機械1が流体を膨張する膨張機である場合は、流体室が固定スクロール33の中心部から外端部へ向かって移動する構成を有する。この場合、吸入口34が吐出口として機能し、吐出口35が吸入口として機能することにより、流体室の容積が増大していくように変化し、中心部側から流体室に取込まれた流体が膨張するようになる。
旋回スクロール20は、樹脂製であることが好ましい。この構成は、旋回スクロール20の遠心力による振動を減らすことができ振動面および騒音面で有利となるからである。しかしながら、樹脂製の旋回スクロール20は、金属製に比べて軽量であるため、自転防止機構部50の自励振動を起こしやすい。基盤部21のうち、旋回側歯部22よりも径方向外側の部位には、第1ハウジング31のハウジング側摺動面36と摺動する旋回側摺動面23が設けられている。
図1および図2に示すように、流体機械1は、旋回スクロール20の自転を防止するための自転防止機構部50を備えている。自転防止機構部50は、規制部51と、規制部51の内周壁に規制されつつ規制部51の内側において旋回する突出部52とを備える。図2に示すように、流体機械1は、4個の自転防止機構部50を備えている。4個の自転防止機構部50は、旋回スクロール20の中心軸に周りに略等間隔に位置している。略等間隔とは、等間隔である構成と、所定の寸法公差の範囲で等間隔に対してずれている構成とを含む意味である。例えば、所定の寸法公差は±5度程度である。また、流体機械1が備える自転防止機構部50は、5個以上であってもよい。
規制部51は、円形状の内周壁によって形成された穴部、または底面を有する凹部である。規制部51は、例えば旋回スクロール20の基盤部21において、固定スクロール33とは反対側に設けられた所定の深さをもつ凹部である。規制部51は、第2ハウジング32において回転軸CL1に直交する端面に対向している。規制部51は、円形の開口端を有する内周壁と内周壁の固定スクロール33側を閉じている底部とを有した構成である。内周壁と底部とは、樹脂製である基盤部21の一部である。
突出部52は、第2ハウジング32に固定された被固定部520と、規制部51の底面に向けて突出する先端側部分としての摺動部521とを有した棒状体である。突出部52は鉄または鉄を含む合金によって形成されている。突出部52はピンとも呼ばれる。突出部52の被固定部520は、第2ハウジング32に形成された円柱状凹部320に圧入された状態で固定されている。突出部52は、摺動部521の先端と規制部51の底面とが離間した状態で第2ハウジング32に固定されている。摺動部521は、旋回スクロール20が公転する際に、規制部51の内周壁を沿うように滑りながら円形状を描いて変位する。突出部52は、両端に位置する、被固定部520と摺動部521とにおいて、固定側部材である第2ハウジング32と可動側部材である旋回スクロール20とによって支持されている。
突出部52は、被固定部520と摺動部521との間において支えられていない非支持部522を有する。非支持部522は、被固定部520と摺動部521との間における軸方向長さ全体に、または軸方向長さに対して部分的に設定された部分である。基盤部21における固定スクロール33とは反対側の面と、この面に対向する第2ハウジング32の面とは、わずかに離間している。非支持部522は、第2ハウジング32において規制部51に対向する面よりも、被固定部520寄りに位置している。
図1および図3に示すように、固定側部材である第2ハウジング32は、非支持部522に対して径方向に離間する離間壁321を備えている。離間壁321は、非支持部522との間に空間部を形成している。この空間部は、背圧導入通路25を通じて圧縮室38から背圧室39に流入した作動流体が存在しているが、固形物体によって占有されていない領域である。つまり、離間壁321と非支持部522との間には、この両者に接触する固形物体が存在していない。非支持部522は、外部から保持されていない部分であるため、突出部52の軸方向全体において他の部位よりも、荷重に対する強度、剛性が小さく、突出部52を大きく撓みやすくする機能をもつ。
離間壁321は、非支持部522の周囲のうち、固定側部材の外周側と、固定側部材の周方向の側とを囲む壁部である。非支持部522の周囲のうち径内側には、離間壁321は設けられていない。図3に示すように、離間壁321は、軸方向に視て非支持部522の周りをU字状に囲んでいる。この構成により、各自転防止機構部50について離間壁321と非支持部522との間の空間部は、径内側において背圧室39に連通している。
離間壁321は、突出部52の軸方向に沿う長さが摺動部521の軸方向長さよりも長くなることが好ましい。これにより、非支持部522の周りに設けられた空間部は、軸方向長さが摺動部521の軸方向長さよりも長くなっている。また非支持部522の軸方向長さは摺動部521の軸方向長さよりも長くなっている。
離間壁321は、突出部52の軸方向に沿う長さが摺動部521の外径寸法よりも長くなっていることが好ましい。これにより、非支持部522の周りに設けられた空間部は、軸方向長さが摺動部521の外径寸法よりも長くなっている。また非支持部522の軸方向長さは摺動部521の外径寸法よりも長くなっている。
以上の各構成を有する非支持部522は、被固定部520と摺動部521との間において固体物体によって支えられていない突出部52の一部である。突出部52は、一方端側の被固定部520において固体側部材に固定され、先端である他方端側の摺動部521において規制部51によって摺動しながら支持されている。このため、突出部52は、摺動部521等に荷重がかかった場合に非支持部522において撓みやすい剛性特性を有している。突出部52は、摺動部近傍まで被固定部である従来のピンに対して剛性が低く、荷重に対する撓み量が大きい。このため、突出部52は、荷重に対する規制部51へ作用する反力を低減でき、荷重を吸収する能力が高く、自転防止機構部50における衝撃力を抑える効果を奏する。
第2ハウジング32には、第1ハウジング31とは反対側においてモータ部40が一体に設けられている。モータ部40は、モータケース41の内側にステータ42、ロータ43およびシャフト44等を有している。モータ部40として、ブラシ付モータまたはブラシレスモータなど、種々のモータを採用することが可能である。シャフト44は、モータケース41の内側に設けられた軸受45、軸受46により回転可能に設けられている。
シャフト44は、モータ部40によって回転駆動される。シャフト44の端部は、第2ハウジング32の内側に挿入されている。シャフト44の端部には、偏心部47が固定されている。偏心部47の中心軸CL2は、シャフト44の回転軸CL1に対して偏心した位置に設置されている。偏心部47は、旋回スクロール20の基盤部21に設けられたボス部24の内側に軸受48を介して設けられている。
モータ部40に通電すると、シャフト44が回転軸CL1周りに自転する。その際、モータ部40が出力するトルクは、偏心部47を介して旋回スクロール20のボス部24に伝達される。図2に示すように、旋回スクロール20は、自転防止機構部50によって自転を規制されつつ、シャフト44の回転軸CL1の周りを公転する。公転半径は、中心軸CL2と回転軸CL1の距離Wと同等である。このとき、旋回スクロール20や自転防止機構部50には、遠心力が作用する。図2に示す、中心軸CL2を通る破線の円は、中心軸CL2の公転軌跡である。このとき、突出部52の摺動部521も規制部51の内周壁に沿うように、破線の円で示した公転軌跡を描く。距離Wと、摺動部521の外径D1と、規制部51の内周壁の内径D2との間には、W≒(D2-D1)/2が成立する関係がある。
旋回スクロール20が公転すると、両スクロール部材の間に形成される圧縮室38は、径方向外側から径方向内側に向かって旋回移動する。吸入口34側に位置する圧縮室38は、シャフト44の回転角度が0度から360度に変化する間に、回転軸CL1または吐出口35に近づきながら、その容積が次第に縮小するように変化する。これにより、流体機械1の外部から吸入口34を通じて圧縮室38に供給された空気は圧縮され、この空気は吐出口35から流体機械1の外部に吐き出される。
基盤部21における固定スクロール33とは反対側の面と、第2ハウジング32における回転軸CL1側の内壁である離間壁321との間には、背圧室39が設けられている。背圧室39には、圧縮室38で圧縮された空気の一部が、基盤部21を貫通する背圧導入通路25を経由して供給される。背圧導入通路25は、圧縮室38と背圧室39とを連通する通路である。これにより、旋回スクロール20は、背圧室39に供給された空気の圧力によって固定スクロール33側に付勢されている。
第1ハウジング31のうち旋回側摺動面23に対向する部位には、旋回側摺動面23と摺動するハウジング側摺動面36が設けられている。旋回スクロール20が公転する際、背圧室39の空気の圧力により旋回スクロール20は固定スクロール33側に付勢される。このため、旋回側摺動面23とハウジング側摺動面36とは、常に接した状態で摺動する。ハウジング側摺動面36は、旋回スクロール20の軸方向の荷重を受けるためのスラスト軸受部として機能する。旋回スクロール20は、スラスト軸受部としてのハウジング側摺動面36に支持されつつ公転する。
旋回側摺動面23とハウジング側摺動面36との間に隙間が生じた場合、圧縮室38から背圧室39に供給された高圧の空気がその隙間を通り固定スクロール33の内側の低圧空間に漏れることが考えられる。この実施形態では、旋回スクロール20は背圧室39の空気の圧力により固定スクロール33側に付勢されるので、旋回側摺動面23とハウジング側摺動面36とが確実に接した状態で摺動する。このため、背圧室39の高圧の空気が固定スクロール33の内側の低圧空間に漏れることを防ぐ効果がある。この流体機械1によれば、空気の圧縮効率の低下を防ぐことができる。
ハウジング側摺動面36には、自己潤滑性を有するフッ素または二硫化モリブデンを含有するコーティングが設けられていることが好ましい。これにより、ハウジング側摺動面36の摩擦係数を低くすることが可能である。フッ素コーティングとしては、ポリテトラフルオロエチレンによるコーティングが好ましい。また、このコーティングは薄膜であるので、旋回スクロール20からハウジング30への伝熱を阻害にくい効果を奏する。このため、旋回側摺動面23とハウジング側摺動面36とがより高荷重の下で摺動する場合でも摺動部の温度上昇を抑制することができる。
第1ハウジング31には、ハウジング側摺動面36よりも径方向外側に、旋回スクロール20と離間するように凹む凹部37が設けられている。凹部37は、旋回スクロール20の旋回側摺動面23と接触しない部位である。
固定側歯部331の先端と旋回スクロール20の基盤部21との間には、隙間が設けられている。旋回側歯部22の先端と、固定スクロール33の基盤部330との間には、隙間が設けられている。これにより、固定側歯部331の先端は、旋回側摺動面23およびハウジング側摺動面36よりも基盤部330側に位置するので、旋回側摺動面23とハウジング側摺動面36とが確実に接した状態で摺動する。背圧室39の高圧の空気が固定スクロール33の内側の低圧空間に漏れることを防ぐ効果を奏する。
モータ部40が出力するトルクにより旋回スクロール20が公転すると、旋回側摺動面23とハウジング側摺動面36とが摺動する。この摺動により生じた熱は、その場所にこもることなく、第1ハウジング31および第2ハウジング32を通じて熱拡散し、その外壁から大気に放熱される。これにより、旋回側摺動面23とハウジング側摺動面36の摺動による温度上昇が抑制されるので、旋回側摺動面23の耐摩耗性が向上するとともに、樹脂摺動面の溶融凝着を防ぐ効果を奏する。
第1実施形態の流体機械1がもたらす作用効果について説明する。流体機械1は、渦巻き状の固定側ラップを有した固定スクロール33と、固定側ラップとの間に流体を吸入、圧縮および吐出する流体室を形成する旋回側ラップを有した旋回スクロール20とを備える。流体機械1は、旋回スクロール20の自転運動を阻止するために、円形状の内周壁を有する規制部51と規制部51の内周壁に規制されつつ規制部51の内側において旋回する突出部52とをそれぞれ有する複数の自転防止機構部50を備える。突出部52は、一方端側に設けられて規制部51の内周壁に対して摺動する摺動部521と、他方端側に設けられて固定側部材に固定されている被固定部520と、被固定部520と摺動部521との間において支えられていない非支持部522とを有する。
この流体機械1によれば、規制部51に対して旋回する突出部52に非支持部522が設けられている。この構成により、突出部52に荷重がかかった場合に被固定部520と摺動部521との間で突出部52を撓ませることが可能である。非支持部522は、突出部52における撓み可能部であることにより、旋回運動において摺動部521などに荷重がかかった場合に、摺動部521よりも被固定部520側における突出部52の剛性を低下することができる。突出部52の剛性低下により、突出部52の衝撃吸収力が向上するため、摺動部521と規制部51における衝撃力を抑制する効果が得られ、騒音を低下させることに寄与する。したがって、流体機械1は、自転防止機構部50を起因とする騒音の改善を図ることができる。このような構成によれば、固定側ラップと旋回側ラップとが非対称の渦巻き状をなして自転トルクが正逆反転しやすい場合や、樹脂製の旋回スクロールのように軽量で自励振動を起こしやすい場合に、特に効果を奏する有用な流体機械1を提供できる。
非支持部522は、固定側部材において規制部51に対向する面よりも、被固定部520寄りに位置する部分である。固定側部材は、非支持部522に対して径方向に離間して非支持部522との間に空間部を形成する離間壁321を備えている。この構成によれば、離間壁321の軸方向寸法を調整することにより、非支持部522の軸方向長さを設定できるため、固定側部材の形状を変更することによって、突出部52のもつ衝撃吸収能力を容易に設定できる。
離間壁321は、突出部52の軸方向に沿う長さが摺動部521の軸方向長さよりも長い。この構成によれば、離間壁321の軸方向寸法が摺動部521の軸方向寸法よりも大きくなるため、突出部52において先端側の支持されている部分よりも非支持部522を長くできる。これにより、先端側に作用した外力の向きと同じ向きに非支持部522が大きく撓むことによって、突出部52は外力を吸収して衝撃を大きく緩和することができる。
離間壁321は、突出部52の軸方向に沿う長さが摺動部521の外径寸法よりも長い。この構成によれば、離間壁321の軸方向寸法が摺動部521の外径寸法よりも大きくなるため、突出部52において非支持部522の長さを十分に確保できる。これにより、外力に対して非支持部522を十分に撓ませることによって、突出部52が外力を吸収する能力を確保でき、自転防止機構部50は衝撃を緩和する能力を確保できる。
離間壁321は、突出部52の軸方向に沿う長さが、離間壁321と非支持部522の外周面との径方向距離よりも長い。この構成によれば、固定側部材における離間壁321の径方向位置を、非支持部522の軸方向長さよりも非支持部522の外周面に近づけるようにして、固定側部材を形成することができる。これにより、固定側部材の剛性低下を抑えつつ、突出部の剛性を低下させた流体機械1を提供できる。
(第2実施形態)
第2実施形態について図4を参照して説明する。第2実施形態は、第1実施形態に対して、突出部52の非支持部522に対して径方向に離間する離間壁1321の形状が相違する。第2実施形態で特に説明しない構成、作用、効果については、第1実施形態と同様であり、以下、異なる点についてのみ説明する。
第2実施形態について図4を参照して説明する。第2実施形態は、第1実施形態に対して、突出部52の非支持部522に対して径方向に離間する離間壁1321の形状が相違する。第2実施形態で特に説明しない構成、作用、効果については、第1実施形態と同様であり、以下、異なる点についてのみ説明する。
図4に示すように、離間壁1321は、第2ハウジング132の一部であって、非支持部522の周囲を取り囲む内周壁を構成する。離間壁1321は、被固定部520が固定されている部分を底部とする円柱状の凹部を形成している。非支持部522は離間壁1321に対して同軸状に設けられている。離間壁1321の内周面と非支持部522の外周面とは、全周において均等な距離である間隙が形成されている。離間壁1321と非支持部522との間には、筒状の空間部が形成されている。この空間部は作動流体が存在しているが、固形物体によって占有されていない領域である。離間壁1321と非支持部522との間には、この両者に接触する固形物体が存在していない。
この構成により、第2実施形態の突出部52は、被固定部520と摺動部521との間において第2ハウジング132によって保持されていない非支持部522を有する。離間壁1321と非支持部522との間の空間部と背圧室39とは、第2ハウジング132によって区画されている。
(第3実施形態)
第3実施形態について図5を参照して説明する。第3実施形態は、第1実施形態に対して、突出部152の形状が相違する。第3実施形態で特に説明しない構成、作用、効果については、第1実施形態と同様であり、以下、第1実施形態と異なる点についてのみ説明する。
第3実施形態について図5を参照して説明する。第3実施形態は、第1実施形態に対して、突出部152の形状が相違する。第3実施形態で特に説明しない構成、作用、効果については、第1実施形態と同様であり、以下、第1実施形態と異なる点についてのみ説明する。
図5に示すように、基盤部21における固定スクロール33とは反対側の面210と、第2ハウジング32における面210に対向する面322とは、わずかに離間している。非支持部522は、第2ハウジング32において規制部51に対向する面322よりも、被固定部1520寄りに位置している。突出部152は、非支持部522や摺動部521よりも外径寸法が大きい被固定部1520を備えている。被固定部1520は、第2ハウジング32に形成された円柱状凹部1320に圧入された状態で固定されている。被固定部1520は非支持部522や摺動部521よりも外径が大きいため、円柱状凹部1320と被固定部1520との接触面積を大きくできる。これにより、非支持部522が大きく撓んだ場合でも、突出部152に対する固定力を確保でき、所望の機能を発揮できる自転防止機構部50を提供できる。
第3実施形態によれば、非支持部522は被固定部1520よりも細い部分である。この構成によれば、非支持部522の剛性が被固定部1520よりも小さくなるため、非支持部522が大きく撓みやすい突出部152を提供できる。これにより、突出部152が外力を吸収する能力を確保でき、自転防止機構部50は衝撃を緩和する能力を確保できる。
(第4実施形態)
第4実施形態について図6を参照して説明する。第4実施形態は、第3実施形態に対して、円柱状凹部1320と被固定部2520との位置関係が相違する。第4実施形態で特に説明しない構成、作用、効果については、第1実施形態および第3実施形態と同様であり、以下、第1実施形態と異なる点についてのみ説明する。
第4実施形態について図6を参照して説明する。第4実施形態は、第3実施形態に対して、円柱状凹部1320と被固定部2520との位置関係が相違する。第4実施形態で特に説明しない構成、作用、効果については、第1実施形態および第3実施形態と同様であり、以下、第1実施形態と異なる点についてのみ説明する。
図6に示すように、突出部252は、非支持部522や摺動部521よりも外径寸法が大きい被固定部2520を備えている。被固定部2520は、軸方向長さが円柱状凹部1320よりも短くなっている。この構成により、非支持部522の一部は、円柱状凹部1320の内部にまで位置している。これにより、突出部252は、突出部152よりも、非支持部522の軸方向長さが長いため、大きく撓むことができ、衝撃吸収効果が大きいという効果を奏する。
(第5実施形態)
第5実施形態について図7を参照して説明する。第5実施形態は、第3実施形態に対して、摺動部1521と規制部151が相違する。第5実施形態で特に説明しない構成、作用、効果については、第1実施形態と同様であり、以下、前述の実施形態と異なる点についてのみ説明する。
第5実施形態について図7を参照して説明する。第5実施形態は、第3実施形態に対して、摺動部1521と規制部151が相違する。第5実施形態で特に説明しない構成、作用、効果については、第1実施形態と同様であり、以下、前述の実施形態と異なる点についてのみ説明する。
図7に示すように、突出部352は、非支持部522よりも外径寸法が大きい摺動部1521を備えている。この構成によれば、規制部151と摺動部1521との接触面圧を低減することができる。これにより、摺動部1521や規制部151の摩耗を抑制し、また焼き付き状態に至りにくい流体機械1を提供できる。
前述の規制部51を構成する凹部には、筒状のスリーブ部材が収容されている。スリーブ部材は、凹部に対して固定されている構成でもよいし回転可能な構成でもよい。さらに摺動部1521は、旋回スクロール20の公転に伴い、規制部151であるスリーブ部材の内周壁に規制されつつスリーブ部材の内側を旋回する。スリーブ部材は、表面が旋回スクロール20よりも硬い素材によって形成されている。スリーブ部材は、例えば金属によって形成されている。これらの構成により、規制部151と摺動部1521との接触面圧を低減できることに加え、耐摩耗性を有する規制部151によって摩耗速度を遅らせる流体機械を提供できる。
(第6実施形態)
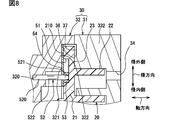
第6実施形態について図8を参照して説明する。第6実施形態は、第1実施形態に対して、規制部51に対して摺動するリング状部材53とリング状部材53の変位規制構造とを有する点が相違する。第6実施形態で特に説明しない構成、作用、効果については、第1実施形態と同様であり、以下、前述の実施形態と異なる点についてのみ説明する。
第6実施形態について図8を参照して説明する。第6実施形態は、第1実施形態に対して、規制部51に対して摺動するリング状部材53とリング状部材53の変位規制構造とを有する点が相違する。第6実施形態で特に説明しない構成、作用、効果については、第1実施形態と同様であり、以下、前述の実施形態と異なる点についてのみ説明する。
図8に示すように、突出部52には、規制部51と摺動する先端側部分にリング状部材53が装着されている。リング状部材53は、突出部52の先端側部分の外側において回転可能に設置されている。したがって、第6実施形態の摺動部521は、ピンに対して回転可能であるリング状部材53を含んでいる。リング状部材53は、表面が旋回スクロール20よりも硬い素材によって形成されている。リング状部材53は、例えば金属によって形成されている。リング状部材53は、旋回スクロール20の公転に伴い、規制部51の内周壁に規制されつつ規制部51の内側をピンに対して回転しながら旋回する。第6実施形態によれば、規制部51とリング状部材53との接触面圧を低減することができる。さらに摺動部521の摩耗を抑制し、また焼き付き状態に至りにくい流体機械1を提供できる。
プレート状部材54は、基盤部21における面210と第2ハウジング32における面322との間において、面210と面322の両方に対面するように設置されている。プレート状部材54は、リング状部材53が軸方向に変位して規制部51から脱落することを防止する変位規制構造として機能し、例えば金属で形成されている。
(第7実施形態)
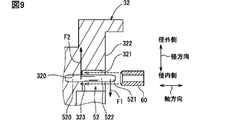
第7実施形態について図9を参照して説明する。第7実施形態は、第1実施形態に対して、被固定部520を固定側部材に固定する構造が相違する。第7実施形態で特に説明しない構成、作用、効果については、第1実施形態と同様であり、以下、前述の実施形態と異なる点についてのみ説明する。
第7実施形態について図9を参照して説明する。第7実施形態は、第1実施形態に対して、被固定部520を固定側部材に固定する構造が相違する。第7実施形態で特に説明しない構成、作用、効果については、第1実施形態と同様であり、以下、前述の実施形態と異なる点についてのみ説明する。
図9に示すように、固定側部材である第2ハウジング32は、突出部52の被固定部520の周り、または圧入口周囲において加締められた加締め部323を有している。加締め部323は、第2ハウジング32の円柱状凹部320に圧入された被固定部520の外周面に対して軸心側に押す外力を与えるように第2ハウジング32において塑性変形した部分である。加締め部323は、図9に示す加締め用治具60を突出部52の外側に嵌めた状態で、加締め用治具60に対して軸方向の外力を加えて第2ハウジング32における被固定部520の周囲を塑性変形させることにより、形成することができる。
第7実施形態によれば、摺動部521の旋回時に規制部51から摺動部521が受ける荷重F1に対して、被固定部520の加締め部323近傍には反対向きの反力F2が作用する。この反力F2は、非支持部522の軸方向長さが大きいほど大きくなる傾向がある。この懸念に対して、加締め部323は固定側部材と圧入された被固定部520との接触面圧を高め、反力F2によって被固定部520が固定側部材から脱落することを防止する効果を奏している。
(第8実施形態)
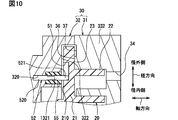
第8実施形態について図10を参照して説明する。第8実施形態は、第1実施形態および第2実施形態に対して、摺動部521と被固定部520との間における突出部52の中間部分を撓ませるための構造が相違する。第8実施形態で特に説明しない構成、作用、効果については、前述の実施形態と同様であり、以下、異なる点についてのみ説明する。
第8実施形態について図10を参照して説明する。第8実施形態は、第1実施形態および第2実施形態に対して、摺動部521と被固定部520との間における突出部52の中間部分を撓ませるための構造が相違する。第8実施形態で特に説明しない構成、作用、効果については、前述の実施形態と同様であり、以下、異なる点についてのみ説明する。
図10に示すように、突出部52は、被固定部520と摺動部521との間において、弾性部材55によって支えられている。弾性部材55は荷重に対して容易に弾性変形する材質によって形成されている筒状の弾性変形部材である。弾性部材55は、内周面において突出部52に接触し、外周面において円柱状凹部を形成する離間壁1321に接触している。弾性部材55は、円柱状凹部の軸方向長さ全体にわたって突出部52を支える軸方向長さを有している。弾性部材55は、伸縮容易な材質、例えばエラストマ、合成ゴム、天然ゴム、ウレタン、フッ素系ゴム等によって形成することができる。
第8実施形態の流体機械1において、突出部52は被固定部520と摺動部521との間において、固定側部材よりも荷重に対する変形量が大きい材質で形成されている弾性変形部材によって支えられている。
この流体機械1によれば、突出部52に荷重がかかった場合に被固定部520と摺動部521との間で弾性変形部材が弾性変形するため、突出部52を撓ませることが可能である。これにより、旋回運動において摺動部521などに荷重がかかった場合に、摺動部521よりも被固定部520側における突出部52の剛性を低下することができる。このように弾性変形部材によって支えられている部分は被固定部520を固定している固定側部材よりも柔らかく容易に弾性変形するため、突出部52の衝撃吸収力が向上する。この流体機械1は、摺動部521と規制部51における衝撃力を抑制する効果が得られ、騒音を低下させることに寄与する。
(第9実施形態)
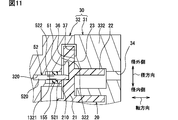
第9実施形態について図11を参照して説明する。第9実施形態は、第8実施形態に対して、弾性変形部材である弾性部材155の軸方向長さが相違する。第9実施形態で特に説明しない構成、作用、効果については、第8実施形態と同様であり、以下、異なる点についてのみ説明する。
第9実施形態について図11を参照して説明する。第9実施形態は、第8実施形態に対して、弾性変形部材である弾性部材155の軸方向長さが相違する。第9実施形態で特に説明しない構成、作用、効果については、第8実施形態と同様であり、以下、異なる点についてのみ説明する。
図11に示すように、弾性部材155は、内周面において円柱状凹部の中ほどで突出部52に接触し、外周面において円柱状凹部の中ほどで離間壁1321に接触している。この構成により、第9実施形態の突出部52は、弾性部材155に支えられている部分の両側に非支持部522を備えている。弾性部材55は、円柱状凹部の軸方向長さの一部にわたって突出部52を支える軸方向長さを有している。弾性部材155は、伸縮容易な材質、例えばエラストマ、合成ゴム、天然ゴム、ウレタン、フッ素系ゴム等によって形成することができる。
第9実施形態の流体機械1において、突出部52は被固定部520と摺動部521との間において、固定側部材よりも荷重に対する変形量が大きい材質で形成されている弾性変形部材によって部分的に支えられている。
この流体機械1によれば、突出部52に荷重がかかった場合に被固定部520と摺動部521との間で弾性部材155が弾性変形するため、突出部52を撓ませることが可能である。このように弾性部材155によって支えられている部分は被固定部520を固定している固定側部材よりも柔らかく容易に弾性変形するため、突出部52の衝撃吸収力が向上する。
(他の実施形態)
この明細書の開示は、例示された実施形態に制限されない。開示は、例示された実施形態と、それらに基づく当業者による変形態様を包含する。例えば、開示は、実施形態において示された部品、要素の組み合わせに限定されず、種々変形して実施することが可能である。開示は、多様な組み合わせによって実施可能である。開示は、実施形態に追加可能な追加的な部分をもつことができる。開示は、実施形態の部品、要素が省略されたものを包含する。開示は、一つの実施形態と他の実施形態との間における部品、要素の置き換え、または組み合わせを包含する。開示される技術的範囲は、実施形態の記載に限定されない。開示される技術的範囲は、特許請求の範囲の記載によって示され、さらに特許請求の範囲の記載と均等の意味および範囲内での全ての変更を含むものと解されるべきである。
この明細書の開示は、例示された実施形態に制限されない。開示は、例示された実施形態と、それらに基づく当業者による変形態様を包含する。例えば、開示は、実施形態において示された部品、要素の組み合わせに限定されず、種々変形して実施することが可能である。開示は、多様な組み合わせによって実施可能である。開示は、実施形態に追加可能な追加的な部分をもつことができる。開示は、実施形態の部品、要素が省略されたものを包含する。開示は、一つの実施形態と他の実施形態との間における部品、要素の置き換え、または組み合わせを包含する。開示される技術的範囲は、実施形態の記載に限定されない。開示される技術的範囲は、特許請求の範囲の記載によって示され、さらに特許請求の範囲の記載と均等の意味および範囲内での全ての変更を含むものと解されるべきである。
前述の実施形態において突出部はピンなどの棒状体であるが、明細書の開示する目的を達成可能な突出部は、内部に空洞があるような棒状体または筒状体であってもよい。
前述の実施形態において固定スクロール33は、第1ハウジング31の一部であるが、第1ハウジング31とは別個の部材によって構成してもよい。別個の部材である固定スクロール33は第1ハウジング31に固定されることによって、第1ハウジング31と一体になる。また、固定スクロール33は、前述の実施形態においてアルミニウム等の金属によって形成されていると記載したが、樹脂材料によって形成されている構成でもよい。この場合、固定スクロール33は、第1ハウジング31の一部であってもよいし、第1ハウジング31に固定された別個の部材であってもよい。
前述の実施形態において固定側ラップと旋回側ラップは、巻き角度範囲が異なる非対称の渦巻き構造をなす関係であると説明したが、これらのラップは巻き角度範囲が同等である対称の渦巻き構造をなす関係であってもよい。
Claims (14)
- 渦巻き状の固定側ラップ(331)を有した固定スクロール(33)と、
前記固定側ラップとの間に流体を吸入、圧縮および吐出する流体室(38)を形成する渦巻き状の旋回側ラップ(22)を有した旋回スクロール(20)と、
前記旋回スクロールの自転運動を阻止するために、円形状の内周壁を有する規制部(51;151)と前記規制部の前記内周壁に規制されつつ前記規制部の内側において旋回する突出部(52;152;252;352)とをそれぞれ有する複数の自転防止機構部(50)と、を備え、
前記突出部は、一方端側に設けられて前記規制部の前記内周壁に対して摺動する摺動部(521;1521)と、他方端側に設けられて固定側部材(32)に固定されている被固定部(520;1520;2520)と、前記被固定部と前記摺動部との間において支えられていない非支持部(522)と、を有する流体機械。 - 前記非支持部は、前記固定側部材(32)において前記規制部に対向する面(322)よりも、前記被固定部寄りに位置する部分であり、
前記固定側部材は、前記非支持部に対して径方向に離間して前記非支持部との間に空間部を形成する離間壁(321)を備えている請求項1に記載の流体機械。 - 前記離間壁は、前記突出部の軸方向に沿う長さが前記摺動部の軸方向長さよりも長い請求項2に記載の流体機械。
- 前記離間壁は、前記突出部の軸方向に沿う長さが前記摺動部の外径寸法よりも長い請求項2または請求項3に記載の流体機械。
- 前記離間壁は、前記突出部の軸方向に沿う長さが、前記離間壁と前記非支持部の外周面との径方向距離よりも長い請求項2から請求項4のいずれか一項に記載の流体機械。
- 前記非支持部は、前記被固定部よりも細い部分である請求項1から請求項5のいずれか一項に記載の流体機械。
- 前記摺動部は、前記非支持部よりも外径寸法が大きい請求項1から請求項6のいずれか一項に記載の流体機械。
- 前記規制部は、前記旋回スクロールに設けられた凹部に収容された筒状のスリーブ部材である請求項1から請求項7のいずれか一項に記載の流体機械。
- 前記摺動部は、前記突出部の先端側部分に対して回転可能に装着されたリング状部材(53)を含んでいる請求項1から請求項7のいずれか一項に記載の流体機械。
- 渦巻き状の固定側ラップ(331)を有した固定スクロール(33)と、
前記固定側ラップとの間に流体を吸入、圧縮および吐出する流体室(38)を形成する旋回側ラップ(22)を有した旋回スクロール(20)と、
前記旋回スクロールの自転運動を阻止するために、円形状の内周壁を有する規制部(51)と前記規制部の前記内周壁に規制されつつ前記規制部の内側において旋回する突出部(52)とをそれぞれ有する複数の自転防止機構部(50)と、を備え、
前記突出部は、一方端側に設けられて前記規制部の前記内周壁に対して摺動する摺動部(521)と、他方端側に設けられて固定されている被固定部(520)とを有し、前記被固定部と前記摺動部との間において、前記被固定部が固定されている固定側部材(32)よりも荷重に対する変形量が大きい材質で形成されている弾性変形部材(55;155)によって支えられている流体機械。 - 前記弾性変形部材は、前記被固定部と前記摺動部との間において前記突出部を部分的に支えている請求項10に記載の流体機械。
- 前記固定側部材は、前記被固定部の周りにおいて加締められた加締め部(323)を有する請求項1から請求項11のいずれか一項に記載の流体機械。
- 前記固定側ラップと前記旋回側ラップは巻き角度範囲が異なる非対称の渦巻き状をなす請求項1から請求項12のいずれか一項に記載の流体機械。
- 前記旋回スクロールの材質は樹脂である請求項1から請求項13のいずれか一項に記載の流体機械。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018233631A JP6973364B2 (ja) | 2018-12-13 | 2018-12-13 | 流体機械 |
| JP2018-233631 | 2018-12-13 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2020121809A1 true WO2020121809A1 (ja) | 2020-06-18 |
Family
ID=71075959
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2019/046317 WO2020121809A1 (ja) | 2018-12-13 | 2019-11-27 | 流体機械 |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6973364B2 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2020121809A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7540376B2 (ja) * | 2021-03-22 | 2024-08-27 | 株式会社豊田自動織機 | スクロール型圧縮機 |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07293466A (ja) * | 1994-04-27 | 1995-11-07 | Nippondenso Co Ltd | 圧縮機 |
| JP2006138243A (ja) * | 2004-11-11 | 2006-06-01 | Sanden Corp | スクロール型圧縮機 |
| JP2008267149A (ja) * | 2007-04-16 | 2008-11-06 | Sanden Corp | 流体機械 |
| JP2014098316A (ja) * | 2012-11-13 | 2014-05-29 | Toyota Industries Corp | スクロール型圧縮機 |
| WO2015016028A1 (ja) * | 2013-07-30 | 2015-02-05 | サンデン株式会社 | スクロール型流体機械 |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005188442A (ja) * | 2003-12-26 | 2005-07-14 | Sanden Corp | スクロール型圧縮機 |
| JP2006183527A (ja) * | 2004-12-27 | 2006-07-13 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | 流体機械 |
-
2018
- 2018-12-13 JP JP2018233631A patent/JP6973364B2/ja active Active
-
2019
- 2019-11-27 WO PCT/JP2019/046317 patent/WO2020121809A1/ja active Application Filing
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07293466A (ja) * | 1994-04-27 | 1995-11-07 | Nippondenso Co Ltd | 圧縮機 |
| JP2006138243A (ja) * | 2004-11-11 | 2006-06-01 | Sanden Corp | スクロール型圧縮機 |
| JP2008267149A (ja) * | 2007-04-16 | 2008-11-06 | Sanden Corp | 流体機械 |
| JP2014098316A (ja) * | 2012-11-13 | 2014-05-29 | Toyota Industries Corp | スクロール型圧縮機 |
| WO2015016028A1 (ja) * | 2013-07-30 | 2015-02-05 | サンデン株式会社 | スクロール型流体機械 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2020094555A (ja) | 2020-06-18 |
| JP6973364B2 (ja) | 2021-11-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| AU2005320203B2 (en) | Scroll fluid machine | |
| US20130089451A1 (en) | Scroll compressor with supporting member in axial direction | |
| JPH07253084A (ja) | スクロール型機械 | |
| JPH0545800B2 (ja) | ||
| WO2015190195A1 (ja) | スクロール圧縮機 | |
| JP2008240597A (ja) | 可変クランク機構及び可変クランク機構を備えたスクロール流体機械 | |
| EP3343065A1 (en) | Inertia adjuster and rotary compressor | |
| JP2003206873A (ja) | スクロール圧縮機 | |
| WO2020121809A1 (ja) | 流体機械 | |
| JP7010202B2 (ja) | 流体機械 | |
| JP2008057465A (ja) | スクロール式流体機械 | |
| KR20200057544A (ko) | 압축기 | |
| JP4013992B2 (ja) | スクロール型流体機械 | |
| KR102510338B1 (ko) | 스크롤 압축기 | |
| JP7263553B2 (ja) | スクロール圧縮機 | |
| JP2020094556A (ja) | 流体機械 | |
| CN110206728B (zh) | 一种涡旋压缩机和空调器 | |
| JP3874018B2 (ja) | スクロール型流体機械 | |
| JP3976070B2 (ja) | スクロール型流体機械 | |
| JPH0343476B2 (ja) | ||
| JP2021046806A (ja) | スクロール型流体機械 | |
| JP2005201148A (ja) | スクロール流体機械 | |
| JP2009275582A (ja) | スクロール圧縮機 | |
| JP6675480B2 (ja) | スクロール圧縮機 | |
| WO2020008798A1 (ja) | 流体機械 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 19897453 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 19897453 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |