WO2020105400A1 - 接続モジュール - Google Patents
接続モジュールInfo
- Publication number
- WO2020105400A1 WO2020105400A1 PCT/JP2019/043017 JP2019043017W WO2020105400A1 WO 2020105400 A1 WO2020105400 A1 WO 2020105400A1 JP 2019043017 W JP2019043017 W JP 2019043017W WO 2020105400 A1 WO2020105400 A1 WO 2020105400A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- holding
- fpc
- movable
- substrate
- connection module
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 68
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 23
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 46
- 210000000078 claw Anatomy 0.000 claims description 14
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 abstract description 21
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 abstract description 21
- 230000001012 protector Effects 0.000 abstract description 20
- 230000014759 maintenance of location Effects 0.000 abstract 6
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 31
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 8
- 230000005611 electricity Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005476 soldering Methods 0.000 description 2
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011889 copper foil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002452 interceptive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920003002 synthetic resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000000057 synthetic resin Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M50/00—Constructional details or processes of manufacture of the non-active parts of electrochemical cells other than fuel cells, e.g. hybrid cells
- H01M50/50—Current conducting connections for cells or batteries
- H01M50/502—Interconnectors for connecting terminals of adjacent batteries; Interconnectors for connecting cells outside a battery casing
- H01M50/519—Interconnectors for connecting terminals of adjacent batteries; Interconnectors for connecting cells outside a battery casing comprising printed circuit boards [PCB]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M10/00—Secondary cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M10/42—Methods or arrangements for servicing or maintenance of secondary cells or secondary half-cells
- H01M10/425—Structural combination with electronic components, e.g. electronic circuits integrated to the outside of the casing
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M50/00—Constructional details or processes of manufacture of the non-active parts of electrochemical cells other than fuel cells, e.g. hybrid cells
- H01M50/20—Mountings; Secondary casings or frames; Racks, modules or packs; Suspension devices; Shock absorbers; Transport or carrying devices; Holders
- H01M50/204—Racks, modules or packs for multiple batteries or multiple cells
- H01M50/207—Racks, modules or packs for multiple batteries or multiple cells characterised by their shape
- H01M50/209—Racks, modules or packs for multiple batteries or multiple cells characterised by their shape adapted for prismatic or rectangular cells
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M50/00—Constructional details or processes of manufacture of the non-active parts of electrochemical cells other than fuel cells, e.g. hybrid cells
- H01M50/20—Mountings; Secondary casings or frames; Racks, modules or packs; Suspension devices; Shock absorbers; Transport or carrying devices; Holders
- H01M50/249—Mountings; Secondary casings or frames; Racks, modules or packs; Suspension devices; Shock absorbers; Transport or carrying devices; Holders specially adapted for aircraft or vehicles, e.g. cars or trains
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M50/00—Constructional details or processes of manufacture of the non-active parts of electrochemical cells other than fuel cells, e.g. hybrid cells
- H01M50/20—Mountings; Secondary casings or frames; Racks, modules or packs; Suspension devices; Shock absorbers; Transport or carrying devices; Holders
- H01M50/284—Mountings; Secondary casings or frames; Racks, modules or packs; Suspension devices; Shock absorbers; Transport or carrying devices; Holders with incorporated circuit boards, e.g. printed circuit boards [PCB]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M50/00—Constructional details or processes of manufacture of the non-active parts of electrochemical cells other than fuel cells, e.g. hybrid cells
- H01M50/50—Current conducting connections for cells or batteries
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M50/00—Constructional details or processes of manufacture of the non-active parts of electrochemical cells other than fuel cells, e.g. hybrid cells
- H01M50/50—Current conducting connections for cells or batteries
- H01M50/502—Interconnectors for connecting terminals of adjacent batteries; Interconnectors for connecting cells outside a battery casing
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M50/00—Constructional details or processes of manufacture of the non-active parts of electrochemical cells other than fuel cells, e.g. hybrid cells
- H01M50/50—Current conducting connections for cells or batteries
- H01M50/502—Interconnectors for connecting terminals of adjacent batteries; Interconnectors for connecting cells outside a battery casing
- H01M50/503—Interconnectors for connecting terminals of adjacent batteries; Interconnectors for connecting cells outside a battery casing characterised by the shape of the interconnectors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M50/00—Constructional details or processes of manufacture of the non-active parts of electrochemical cells other than fuel cells, e.g. hybrid cells
- H01M50/50—Current conducting connections for cells or batteries
- H01M50/502—Interconnectors for connecting terminals of adjacent batteries; Interconnectors for connecting cells outside a battery casing
- H01M50/507—Interconnectors for connecting terminals of adjacent batteries; Interconnectors for connecting cells outside a battery casing comprising an arrangement of two or more busbars within a container structure, e.g. busbar modules
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M50/00—Constructional details or processes of manufacture of the non-active parts of electrochemical cells other than fuel cells, e.g. hybrid cells
- H01M50/50—Current conducting connections for cells or batteries
- H01M50/572—Means for preventing undesired use or discharge
- H01M50/574—Devices or arrangements for the interruption of current
- H01M50/578—Devices or arrangements for the interruption of current in response to pressure
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M2220/00—Batteries for particular applications
- H01M2220/20—Batteries in motive systems, e.g. vehicle, ship, plane
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/10—Energy storage using batteries
Definitions
- connection module The technology disclosed in this specification relates to a connection module.
- a battery module for an electric vehicle or a hybrid vehicle includes a battery block composed of a plurality of battery cells, and a connection module attached to the battery block and connecting a plurality of single batteries.
- a connection module there is known a flexible printed wiring board with a bus bar, which includes a flexible printed circuit board (FPC) and a plurality of bus bars connected to the flexible printed circuit board and connecting electrode terminals of adjacent power storage elements (Patent). Reference 1).
- -A dimensional tolerance occurs in a battery block composed of a large number of battery cells due to manufacturing dimensional errors in each battery cell, assembly errors in multiple battery cells, etc. Due to this dimensional tolerance, the bus bar and the electrode of each battery cell may be misaligned, which may make it difficult to assemble the connection module to the battery block. Further, since the flexible printed wiring board has flexibility, it has a problem that it is difficult to handle when it is assembled to the battery block and the assembling workability is poor.
- a connection module disclosed by the present specification is a connection module which is attached to a power storage element group configured by a plurality of power storage elements including electrode terminals to connect the plurality of power storage elements, and includes a flexible printed circuit board,
- the flexible printed circuit board includes a plurality of connecting members connected to the flexible printed circuit board and connecting the electrode terminals of the adjacent power storage elements to each other, and a holding member holding the plurality of connecting members and the flexible printed circuit board.
- the substrate includes a substrate body and a first movable portion that connects the substrate body and the connection member, and the holding member fixes the substrate holding portion to which the substrate body is fixed, and the connection member is fixed. And a second movable part connecting the substrate holding part and the connection member holding part, wherein the first movable part and the second movable part are the connection member.
- the connection member holding portion is connected to the substrate body and the substrate holding portion while allowing displacement.
- connection member and the connection member holding portion are allowed to be displaced with respect to the substrate body and the substrate holding portion in a state where the connection member and the connection member holding portion are assembled to each other. It is possible to avoid the difficulty of assembling the connection module to the electricity storage element group due to the positional displacement of the terminals, and improve the assembling workability. Further, by holding the flexible printed circuit board and the plurality of connecting members by the holding member, the shape of the flexible printed circuit board having flexibility is held constant, and together with the plurality of connecting members, the predetermined number of storage element groups is collectively determined. Since it can be set at the position, the workability of assembling can be improved.
- the first movable portion may include a linear spring-shaped first spring portion that extends from the substrate body and has at least one curved portion.
- connection member With such a configuration, it is possible to connect the connection member to the substrate body while allowing the displacement with a simple configuration.
- first spring portion is configured by the wire spring
- the connecting member is free to some extent in any of the direction in which it approaches and separates from the substrate body, the thickness direction of the substrate body, and the direction along the substrate body. Since the flexible printed circuit board can be displaced, the connecting work can be easily performed after the connecting member is connected to the flexible printed circuit board.
- the plurality of second movable portions are arranged side by side along one edge of the substrate holding portion, and each of the plurality of second movable portions expands and contracts in a direction along the one edge. It may have a possible second spring portion.
- the second spring portion allows the connection member holding portion to be displaced in a direction along one edge of the substrate holding portion. Therefore, by assembling the connection module to the storage element group so that one edge of the substrate holding section extends along the direction in which the plurality of storage elements are arranged, the connection member holding section and the connection held by the connection member holding section. Displacement of the member in the direction along the arrangement direction of the storage element groups is allowed. As a result, it is possible to avoid difficulty in assembling the connection module to the power storage element group due to the displacement of the electrode terminals due to the dimensional tolerance of the power storage element group, and improve the workability of assembly.
- the holding member may include a connecting portion that connects the adjacent connecting member holding portions while allowing the connecting member holding portions to be displaced in the direction along the one edge.
- the adjacent connecting member holding portions are connected to each other so as to stably hold the plurality of connecting members without interfering with the displacement of the connecting member holding portion in the direction along which the storage element groups are arranged. be able to.
- the substrate holding section is arranged along the substrate body with a holding body, and is arranged with a gap from the holding body, and holds the substrate body between the holding body. It may be provided with a pressing piece.
- the substrate holding section can hold the substrate body with a simple configuration.
- the substrate body has a positioning hole, and the substrate holding portion is inserted along the holding body disposed along the substrate body and protruding from the holding body into the positioning hole. Therefore, a positioning protrusion for positioning the substrate body with respect to the holding body may be provided.
- the substrate body can be positioned in the substrate holding portion with a simple configuration.
- connection member holding portion includes a base portion arranged along the connection member, and a locking portion continuous from the base portion, the locking portion is provided protruding from the base portion, A flexible portion that can bend and a locking claw that protrudes from the flexible portion and that holds the connection member by sandwiching the connection member between the base portion and the base portion may be provided.
- connection member holding portion Only by pushing the connection member toward the base portion, so that the workability of assembling the connection module is improved.
- connection module According to the connection module disclosed in this specification, the workability of assembling can be improved.
- FIG. 1 Perspective view of the electricity storage module of the embodiment Top view of the electricity storage module of the embodiment
- the perspective view of the connection module of the embodiment Top view of the connection module of the embodiment A partially enlarged view of the frame R1 in FIG. Sectional view taken along the line AA of FIG. Sectional view taken along the line BB of FIG. Sectional view taken along the line CC of FIG.
- the perspective view of the bus bar of the embodiment Top view of the bus bar of the embodiment
- the top view of the flexible printed circuit board of embodiment The perspective view of the resin protector of the embodiment Top view of the resin protector of the embodiment Front view of the resin protector of the embodiment Rear view of the resin protector of the embodiment A partially enlarged view of the frame R2 in FIG.
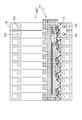
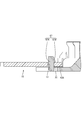
- connection module 1 of the present embodiment constitutes an electricity storage module M used as a drive source for vehicles such as electric vehicles and hybrid vehicles. As shown in FIG. 1, the connection module 1 is attached to a storage element group 90G in which a plurality of storage elements 90 are arranged in a line, and connects the plurality of storage elements 90 in series.
- the power storage element 90 is, for example, a secondary battery. As shown in FIG. 1, each power storage element 90 has a flat rectangular parallelepiped shape, and has an electrode placement surface 90F (upper surface in FIG. 1) perpendicular to a surface facing the adjacent power storage element 90. ing. Electrode terminals 91A and 91B are arranged on the electrode arrangement surface 90F. One of the electrode terminals 91A and 91B is the positive electrode terminal 91A, and the other is the negative electrode terminal 91B. Each of the electrode terminals 91A and 91B has a columnar shape, and although not shown in detail, the outer peripheral surface is threaded.
- a plurality of power storage elements 90 are arranged in a line to form a power storage element group 90G.
- the electrode terminals 91A and 91B of different polarities are adjacent to each other in the two power storage elements 90 adjacent to each other (that is, the positive electrode terminal 91A of one power storage element 90 and another adjacent to this).
- the negative electrode terminal 91B of the power storage element 90 is arranged adjacent to each other.
- the arrangement direction of the plurality of power storage elements 90 (lower left-upper right direction in FIG. 1) is the X-axis direction, and the direction along the surface of the power storage element 90 facing the adjacent power storage element 90 (in FIG. 1).
- the lower right-upper left direction will be described as the Y-axis direction, and the direction perpendicular to the electrode placement surface 90F (the vertical direction in FIG. 1) will be the Z-axis direction.
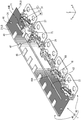
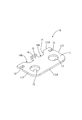
- connection module 1 is a member that is assembled to the surface (upper surface in FIG. 1) formed by the electrode placement surface 90F of each power storage element 90 in the power storage element group 90G. As shown in FIG. 3, the connection module 1 is connected to the flexible printed circuit board 20 (hereinafter referred to as “FPC 20”) and the FPC 20 to connect the positive electrode terminal 91 ⁇ / b> A and the negative electrode terminal 91 ⁇ / b> B of the adjacent power storage elements 90.
- FPC 20 flexible printed circuit board 20
- FIG. 1 A plurality of bus bars 10 (corresponding to a connecting member) and a resin protector 40 (corresponding to a holding member) that holds the bus bar 10 and the FPC 20 are provided.
- connection module 1 connected to one of the two columns of the electrode terminals 91A and 91B (lower right column) is illustrated, but the connection module 1 is similarly connected to the other column. 1 is connected.
- connection module 1 in the connection module 1, one bus bar 10 that connects the positive electrode terminal 91A at the right end and the negative electrode terminal 91B adjacent thereto is illustrated, and the other bus bars 10 are omitted. The same applies to FIG.
- Bus bar 10 Each of the plurality of bus bars 10 is made of metal, and as shown in FIGS. 9 and 10, an electrode connecting portion 11 that connects the positive electrode terminal 91A and the negative electrode terminal 91B of the adjacent power storage elements 90, and this electrode connection.
- An FPC connection piece 15 that is continuous from the portion 11 and is connected to the FPC 20 and a locking wall 16 that is continuous from the FPC connection piece 15 are provided.
- the electrode connection portion 11 is a rectangular plate-shaped portion as a whole, and has two electrode insertion holes 12 through which the electrode terminals 91A and 91B can be inserted, and two engagement recesses for engagement with the resin protector 40. 13 and 13.
- One electrode insertion hole 12 is arranged at a position close to one short side 11S of the electrode connecting portion 11, and one is arranged at a position close to the other short side 11S.
- One of the two engaging recesses 13 is a recess recessed from one short side 11S of the electrode connecting part 11, and the other is a recess recessed from the other short side 11S.
- the electrode connecting portion 11 has a connection recess 14 that is recessed from one long side 11LA of the pair of long sides 11LA and 11LB.
- the connection recess 14 is a recess defined by a first inner edge 14A parallel to the long side 11LA and a pair of first side edges 14B connecting both ends of the first inner edge 14A and the long side 11LA. ..
- the FPC connection piece 15 is a rectangular plate piece-shaped portion extending from the first inner edge 14A in the same plane as the electrode connection portion 11.
- the locking wall 16 is a short plate wall-shaped portion that extends vertically from the tip of the FPC connection piece 15.
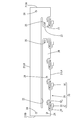
- the FPC 20 is a member for electrically connecting the plurality of bus bars 10 and the ECU (electronic control unit: not shown). Although not shown in detail, the FPC 20 has a plurality of conductive paths formed of copper foil. , And an insulating resin film that covers both surfaces of the conductive path. As shown in FIG. 11, the FPC 20 includes an FPC main body 21 (corresponding to a substrate main body) having a rectangular strip shape as a whole, a plurality of first movable portions 31 connected from the FPC main body 21, and a plurality of first movable portions 31. And a joining piece 35 joined to each of the plurality of bus bars 10.
- the FPC main body 21 has a first slit 22, a cutout portion 23, a plurality of positioning holes 24, and two engagement holes 25.
- the first slit 22 is provided at a substantially central position between the pair of long sides 21LA, 21LB of the FPC main body 21, parallel to the long sides 21LA, 21LB, and at both ends of the FPC main body 21 (a pair of short sides 21SA, 21SA). It is a slit that extends over almost the entire length except for a near portion.
- the notch 23 is a relatively wide gap that extends from the long side 21LA on one side (the lower side in FIG. 11) of the FPC main body 21 to the first slit 22, and is on one side of the FPC main body 21 (on the right side in FIG. 11). ) Is arranged near the short side 21SA.
- a part of the FPC body 21 sandwiched between the first slit 22 and the long side 21LA (a part below the first slit 22 in FIG. 11) is arranged on the short side 21SB side by the notch 23.
- the long first dividing portion 26 and the short second dividing portion 27 arranged on the short side 21SA side are divided.
- a plurality of positioning holes 24 are arranged at a position close to one short side 21SA, two at a position close to the other short side 21SB, and one at a substantially central position of the first dividing section 26.
- One of the two engaging holes 25 is arranged at a position close to the cutout portion 23 in the first dividing portion 26, and the other is arranged at a position close to the cutout portion 23 in the second dividing portion 27.
- the first movable portion 31 is composed of a linear spring-like portion (corresponding to a first spring portion) that is continuous from the FPC main body 21, extends from the long side 21LA of the FPC main body 21, and is curved in a U shape.
- the portion 32 (corresponding to the bending portion), the straight portion 33 continuous from the extending end of the first bending portion 32 and extending along the long side 21LA, and the straight portion 33 extending from the extending end of the straight portion 33 to the first bending portion 32.
- Has a second bending portion 34 (corresponding to a bending portion) that bends in a U shape in the opposite direction, and has a substantially S shape as a whole.
- the plurality of first movable portions 31 are arranged in a line along the long side 21LA, one of them is connected from the second dividing portion 27, and the rest are from the first dividing portion 26. It is in a row.
- the joining piece 35 is a rectangular plate piece-like portion that is continuous from the extended end of the second bending portion 34. A part of the conductive path is exposed as a bonding land (not shown) on one surface of the joining piece 35, and the FPC connecting piece 15 is connected thereto by soldering.
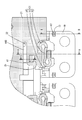
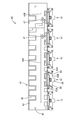
- the resin protector 40 is made of synthetic resin, and includes an FPC holding unit 41 (corresponding to a substrate holding unit) that holds the FPC main body 21, and a plurality of bus bar holding units 61 and 71 that hold the bus bar 10.
- the FPC holding portion 41 includes a holding plate portion 42 (corresponding to a holding body), side ribs 43 and center ribs 44A and 44B extending from the holding plate portion 42, a plurality of pressing pieces 45, and a plurality of holding pieces 45.
- the positioning protrusion 46 and the two FPC locking pieces 47 are provided.
- the holding plate portion 42 is in the form of a rectangular plate having substantially the same size as the FPC main body 21 as a whole.
- One surface (upper surface in FIG. 12) of the holding plate portion 42 is a mounting surface 42F on which the FPC main body 21 is mounted.
- the mounting surface 42F has side ribs 43, center ribs 44A and 44B, and pressing pieces. 45, a positioning protrusion 46, and an FPC locking piece 47 are arranged.
- the side rib 43 is a streak-like portion protruding from one long side 42LA (upper side in FIG. 12) of the pair of long sides 42LA, 42LB of the holding plate portion 42, and is arranged over substantially the entire length of the long side 42LA.
- the center ribs 44A and 44B are streak-shaped portions that extend parallel to the long sides 42LA and 42LB at a substantially central position between the pair of long sides 42LA and 42LB, and the pair of short sides 42SA and 42SB of the holding plate portion 42.
- One of the long sides is arranged near one of the short sides 42SA (on the left side of FIG. 12), and the other short side is arranged near the other short side 42SB.
- Each of the plurality of pressing pieces 45 is a plate piece-shaped portion extending from the side rib 43 in parallel with the holding plate portion 42, and the FPC main body 21 can be held between the holding plate portion 42 and the holding plate portion 42. ..
- Each of the plurality of positioning protrusions 46 is a circular protrusion extending from the holding plate portion 42, and is arranged at a position corresponding to each of the plurality of positioning holes 24 of the FPC main body 21.
- each of the two FPC locking pieces 47 includes a locking piece body 47A extending from the holding plate portion 42, and a locking protrusion 47B protruding from the tip of the locking piece body 47A.
- FPC main body 21 is arranged at a position corresponding to each of the two engagement holes 25.
- the holding plate portion 42 has a plurality of spring recesses 48 recessed inward from the other long side 42LB (corresponding to one edge). As shown in FIG. 16, the spring recess 48 includes a second inner edge 48A parallel to the long side 42LB and a pair of second side edges 48B connecting both ends of the second inner edge 48A and the long side 42LB. It is a defined recess.
- one that is closest to one short side 42SA of the holding plate portion 42 is the fixed bus bar holding portion 71, and the other is the second movable portion.
- a movable busbar holding portion 61 (corresponding to a connecting member holding portion) connected to the holding plate portion 42 via 51.
- the second movable portion 51 has a plate shape that is bent in a bellows shape as a whole, and is expandable / contractible in the direction along the long side 42LB of the holding plate portion 42. .. More specifically, the second movable portion 51 includes a plate-like spring connecting piece 52 (corresponding to a spring connecting portion) extending from the second inner edge 48A on the same plane as the holding plate portion 42, and the spring connecting portion. A pair of spring plate portions 53 (corresponding to a second spring portion) extending from the piece 52 along the second inner edge 48A while bending in opposite directions are provided.
- Each of the pair of spring plate portions 53 extends vertically from the extending end of the spring connecting piece 52 so as to be separated from the holding plate portion 42, is then folded back to extend toward the holding plate portion 42, and is further folded back. And has a S-shaped leaf spring shape extending away from the holding plate portion 42.
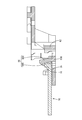
- the movable bus bar holding portion 61 includes a back plate portion 62 connected to the second movable portion 51, a bottom plate portion 63 (corresponding to a base portion) connected to the back plate portion 62, and an extension piece extending from the bottom plate portion 63. 65, a first bus bar locking piece 66 (corresponding to a locking portion), two second bus bar locking pieces 67 (corresponding to a locking portion), and a pair of abutting plates 68.
- the back plate portion 62 is a plate-shaped portion arranged in a posture perpendicular to the holding plate portion 42, and is connected to the respective tip portions of the pair of spring plate portions 53. There is.
- the bottom plate portion 63 is a plate-shaped portion that extends vertically from the back plate portion 62 in the direction opposite to the holding plate portion 42, and has two second slits 64. As shown in FIG. 13 and FIG. 16, each of the two second slits 64 extends from the extending end of the bottom plate portion 63 toward the back plate portion 62. 63 is divided into end plate portions 63A at both ends and a middle plate portion 63B at the center.
- the extension piece 65 is a plate piece-shaped portion that extends from the extension end of the bottom plate portion 63 on the same plane as the bottom plate portion 63.
- the first bus bar locking piece 66 extends from the middle plate portion 63B and is spaced from the back plate portion 62 by a first bending piece 66A (corresponding to a bending portion). ) And a first locking claw 66B (corresponding to a locking claw) projecting from the extension end of the first bending piece 66A in the direction opposite to the back plate portion 62.
- 66 A of 1st bending pieces incline slightly so that it separates from the back plate part 62, so that it separates from the intermediate plate part 63B.
- each of the two second bus bar locking pieces 67 includes a second bending piece 67A (corresponding to a bending portion) that extends vertically from the extending end of the two end plate portions 63A, and a second bending piece.
- a second locking claw 67B (corresponding to a locking claw) protruding from the tip of the piece 67A toward the back plate portion 62 is provided.
- each of the two abutting plates 68 is a plate-shaped portion that projects from the middle plate portion 63B along each slit edge of the two second slits 64, and is a back plate portion. It is arranged adjacent to 62.
- each movable busbar holding portion 61 with respect to the holding plate portion 42 is allowed to some extent by the second movable portion 51.
- the two spring plate portions 53 of the second movable portion 51 can be expanded and contracted to move in the direction along the long side 42LB of the holding plate portion 42 (X axis direction).
- the fixed bus bar holding portion 71 does not have the second movable portion 51, and the back bus portion 72 extends from the long side 42LB of the holding plate portion 42, except that the movable bus bar holding portion 71 extends. It has the same configuration as the holding portion 61.
- the same parts as those of the movable bus bar holding part 61 are designated by the same reference numerals, and the description thereof will be omitted.
- the fixed busbar holding portion 71, the movable busbar holding portion 61 adjacent to the fixed busbar holding portion 71, and the movable busbar holding portions 61 adjacent to each other are connected by a U-shaped leaf spring-like connecting portion 81 as shown in FIGS. 12 and 16. It is connected.
- the fixed busbar holding portion 71, the movable busbar holding portions 61 adjacent to the fixed busbar holding portion 71, and the movable busbar holding portions 61 adjacent to each other are arranged along the long side 42LB of the holding plate portion 42 (X-axis direction). It is possible to stably hold the plurality of busbars 10 that are assembled to the fixed busbar holding portion 71 and the movable busbar holding portion 61 by connecting without disturbing the displacement in the direction.
- connection module 1 An example of a procedure for assembling the connection module 1 having the above configuration will be described below.
- each bus bar 10 is in a state of being connected to the FPC body 21 via the first movable portion 31, and the first movable portion 31 is By being deformed, each bus bar 10 has a direction along the long side 21LA of the FPC main body 21 (X-axis direction), a direction approaching / separating from the FPC main body 21 (Y-axis direction), and a thickness of the FPC main body 21. It can be displaced to some extent in any direction (Z-axis direction).
- the joined body of the FPC 20 and the plurality of bus bars 10 is attached to the resin protector 40.
- the FPC main body 21 is attached to the FPC holding portion 41.
- the FPC main body 21 is placed on the holding plate portion 42 so as to be inserted into the gap between the holding plate portion 42 and the pressing piece 45, and the long side 21LB is set along the side rib 43.
- the FPC main body 21 is positioned on the holding plate portion 42 by inserting the positioning protrusions 46 into the positioning holes 24 and inserting the two center ribs 44A and 44B into the first slit 22. It Further, the FPC body 21 is pressed by the pressing piece 45 so as not to come off from the holding plate portion 42. As shown in FIG. 3 and FIG.
- each FPC engaging piece 47 is inserted into each engaging hole 25, and the engaging protrusion 47B engages with the FPC body 21, so that each dividing portion.
- the ends of 26 and 27 are pressed so that they do not turn up from the holding plate portion 42.
- each bus bar 10 is assembled to each bus bar holding portion 61, 71.
- Each of the second bus bar locking pieces 67 is inserted into each of the engaging recesses 13, the first bus bar locking piece 66 is bent by the locking wall 16, and the electrode connecting portion 11 is pushed toward the bottom plate portion 63.
- the first bus bar locking piece 66 elastically returns so that the locking wall 16 becomes the middle plate portion 63B and the first locking claw 66B. Sandwiched between.
- FIGS. 5 and 7 a portion of the electrode connecting portion 11 adjacent to the engaging recess 13 enters between the bottom plate portion 63 and the second locking claw 67B.
- each bus bar 10 is fixed to each bus bar holding portion 61, 71.
- the bus bar 10 can be easily assembled to the bus bar holding portions 61 and 71. It can be carried out. Further, since the busbar 10 can be easily assembled to the busbar holding portions 61 and 71 only by pushing the busbar 10 toward the bottom plate portion 63, the workability of assembling the connection module 1 is improved.
- the first bending portion 32 is arranged in the same plane as the FPC main body 21, and the linear portion 33 is the first portion, as shown in FIG. It is inclined so as to move away from the FPC main body 21 as it goes away from the bending portion 32.
- the second curved portion 34, the joint piece 35, and the bus bar 10 are arranged parallel to the FPC main body 21 and apart from the FPC main body 21.
- the linear portion 33 is passed through the gap between the first bus bar locking piece 66 and the back plate portion 62.
- the FPC main body 21 is held in a positioned state with respect to the FPC holding portion 41.
- each bus bar 10 is held in a positioned state by each movable bus bar holding portion 61.
- the bus bar 10 is displaceably connected to the FPC main body 21 by the first movable portion 31, and the movable bus bar holding portion 61 is displaceably connected to the FPC holding portion 41 by the second movable portion 51.
- the movable busbar holding portion 61 and the busbar 10 are assembled with each other, with respect to the FPC holding portion 41 and the FPC body 21, the long side 42LB of the holding plate portion 42 and the long side 21LA of the FPC body 21. Displacement in the direction along the axis (X-axis direction) is allowed.
- connection module 1 Assembly of Connection Module 1 to Storage Element Group 90G
- An example of a procedure for assembling the connection module 1 having the above configuration to the storage element group 90G will be described below.
- connection module 1 is arranged at a predetermined position on the storage element group 90G, and the electrode terminals 91A and 91B are inserted into the electrode insertion holes 12 of each bus bar 10. Then, the electrode terminals 91A and 91B are connected to the bus bar 10 by screwing nuts (not shown) to the electrode terminals 91A and 91B.
- the storage element group 90G configured by arranging a large number of storage elements 90 has a dimensional tolerance due to a dimensional error in manufacturing each storage element 90, an assembly error in a plurality of storage elements 90, and the like.
- the electrode terminals 91A and 91B may be displaced in a direction along the arrangement direction of the power storage elements 90 (X-axis direction).
- the electrodes caused by the dimensional tolerance of the storage element group 90G can be displaced according to the positional displacement of the terminals 91A and 91B and assembled to the electrode terminals 91A and 91B.
- each movable busbar holding portion 61 is referenced to the fixed busbar holding portion 71.
- it is displaced in the direction in which the fixed bus bar holding portion 71 is approached (the direction along the long side 42LB of the holding plate portion 42: the direction from the upper right to the lower left in FIG. 1).
- the fixed bus bar holding portion 71 located at one end of the resin protector 50 as a reference, the movable bus bar holding portion 61 located next to the fixed bus bar holding portion 71 and the interval between the adjacent movable bus bar holding portions 61 are narrow.
- the movable bus bar holding portion 61 is displaced so that Accordingly, with respect to one bus bar 10 held by the fixed bus bar holding portion 71, the other bus bar 10 is displaced so that the distance between the adjacent bus bars 10 becomes small, and the displacement of the electrode terminals 91A and 91B is dealt with. can do.
- each movable busbar holding portion 61 is referenced to the fixed busbar holding portion 71.
- it is displaced in the direction away from the fixed bus bar holding portion 71 (the direction along the long side 42LB of the holding plate portion 42: the direction from the lower left to the upper right in FIG. 1).
- the fixed busbar holding portion 71 located at one end of the resin protector 50 as a reference, the movable busbar holding portion 61 located next to the fixed busbar holding portion 71 and the interval between the adjacent movable busbar holding portions 61 are wide.
- the movable bus bar holding portion 61 is displaced so that As a result, one bus bar 10 held by the fixed bus bar holding portion 71 is used as a reference to displace another bus bar 10 so that the distance between the adjacent bus bars 10 becomes large, and the displacement of the electrode terminals 91A and 91B is dealt with. can do.
- connection module 1 it is possible to avoid difficulty in assembling the connection module 1 to the electricity storage element group 90G due to the dimensional tolerance of the electricity storage element group 90G, and improve the assembling workability.
- the shape of the flexible FPC 20 is kept constant, and the FPC 20 and the plurality of bus bars 10 are collectively placed at a predetermined position on the storage element group 90G. Since it can be set, assembly workability can be improved.
- the connection module 1 is a module that is attached to the storage element group 90G configured by the plurality of storage elements 90 including the electrode terminals 91A and 91B to connect the plurality of storage elements 90.
- the FPC 20 is provided with a plurality of bus bars 10 connected to the FPC 20 and connecting the electrode terminals 91A and 91B of the adjacent power storage elements 90 to each other, and the resin protector 40 holding the bus bar 10 and the FPC 20.
- the FPC 20 includes an FPC main body 21, and a first movable portion 31 that connects the FPC main body 21 and the bus bar 10, and the resin protector 40 includes an FPC holding portion 41 to which the FPC main body 21 is fixed and the bus bar 10.
- a movable busbar holding portion 61 that is fixed, and a plurality of second movable portions 51 that connect the FPC holding portion 41 and the movable busbar holding portion 61.
- the first movable portion 31 and the second movable portion 51 connect the busbar 10 and the movable busbar holding portion 61 to the FPC main body 21 and the FPC holding portion 41 while allowing displacement.
- the displacement of the bus bar 10 and the movable bus bar holding portion 61 relative to the FPC main body 21 and the FPC holding portion 41 is allowed in the assembled state. It is possible to avoid the difficulty of assembling the connection module 1 to the power storage element group 90G due to the positional displacement of the electrode terminals 91A and 91B caused by, and to improve the assembling workability. Further, by holding the FPC 20 and the plurality of bus bars 10 on the resin protector 40, the shape of the flexible FPC 20 is held constant, and the FPC 20 and the plurality of bus bars 10 are collectively placed at a predetermined position of the storage element group 90G. Since it can be set, assembly workability can be improved.
- the first movable portion 31 is constituted by a wire spring extending from the FPC main body 21 and having a first bending portion 32 and a second bending portion 34.
- the bus bar 10 can be connected to the FPC main body 21 while allowing the displacement with a simple configuration.
- the bus bar 10 can be arranged in any of a direction in which it approaches and separates from the FPC body 21, a thickness direction of the FPC body 21, and a direction along the FPC body 21.
- it can be freely displaced to some extent, it is possible to easily perform the assembling work when assembling the resin protector 40 after the bus bar 10 is connected to the FPC 20.
- the plurality of second movable portions 51 are arranged side by side along the long side 42LB of the FPC holding portion 41, and each of the plurality of second movable portions 51 is expandable / contractible in the direction along the long side 42LB.
- the spring plate portion 53 is provided.
- the second movable portion 51 allows the movable busbar holding portion 61 to be displaced in the direction along the long side 42LB of the FPC holding portion 41. Therefore, by attaching the connection module 1 to the storage element group 90G so that the long side 42LB of the FPC holding portion 41 extends along the arrangement direction of the plurality of storage elements 90, the movable busbar holding portion 61 and this movable busbar holding portion are held. Displacement of the bus bar 10 held by the portion 61 in the direction along the arrangement direction of the power storage element group 90G is allowed.
- connection module 1 it is possible to avoid the difficulty of assembling the connection module 1 to the power storage element group 90G due to the positional deviation of the electrode terminals 91A and 91B due to the dimensional tolerance of the power storage element group 90G, and to improve the workability of assembly. it can.
- the resin protector 50 may include a connecting portion 81 that connects the adjacent movable busbar holding portions 61 while allowing the displacement of the holding plate portion 42 of the FPC holding portion 41 in the direction along the long side 42LB. Absent.
- the movable busbar holding portions 61 are connected to each other without hindering the displacement of the movable busbar holding portions 61 in the direction along the arrangement direction of the storage element groups 90G, and the plurality of busbars 10 are stabilized. Can be held.
- the FPC holding portion 41 is arranged with a holding plate portion 42 arranged along the FPC main body 21 and a gap with respect to the holding plate portion 42, and holds the FPC main body 21 between the holding plate portion 42 and the holding plate portion 42.
- a pressing piece 45 for controlling.
- the FPC main body 21 has a positioning hole 24, and the FPC holding portion 41 is inserted through the holding plate portion 42 arranged along the FPC main body 21 and the holding plate portion 42 into the positioning hole 24.
- the positioning protrusion 46 is provided for positioning the FPC main body 21 with respect to the holding plate portion 42.
- the FPC main body 21 can be positioned in the FPC holding unit 41 with a simple configuration.
- the movable busbar holding portion 61 includes a bottom plate portion 63 arranged along the busbar 10, and a first busbar locking piece 66 and a second busbar locking piece 67 connected from the bottom plate portion 63.
- the first bus bar locking piece 66 is projectingly provided from the bottom plate portion 63, and holds the bus bar 10 by sandwiching the bus bar 10 between the bendable first bending piece 66A and the first bending piece 66A protruding from the bottom plate portion 63.
- the first locking claw 66B is provided.
- the second busbar locking piece 67 is provided so as to project from the bottom plate portion 63, and the busbar 10 is sandwiched between the second bending piece 67A that is bendable and the bottom plate portion 63 that projects from the second bending piece 67A. And a second locking claw 67B that holds the same.
- the busbar 10 can be easily assembled to the movable busbar holding portion 61 simply by pushing the busbar 10 toward the bottom plate portion 63, so that the workability of assembling the connection module 1 is improved.
- the first movable portion 31 includes the first bending portion 32 and the second bending portion 34, but the number of bending portions may be one or three or more.
- the second movable portion 51 includes the pair of spring plate portions 53 that are bent in a bellows shape.
- the shape of the second spring portion is not limited to that in the above-described embodiment, and one of the substrate holding portions is used. It suffices to have a spring shape that can expand and contract in the direction along the edge.
- the two spring plate portions 53 of the second movable portion 51 have a symmetrical shape with the spring connection piece 52 interposed therebetween, but the pair of second spring portions have an asymmetrical shape. May have.
- Connection module 10 ... Bus bar (connection member) 20 ... Flexible printed circuit board 21 ... FPC body (board body) 24 ... Positioning hole 31 ... 1st movable part (1st spring part) 32 ... 1st bending part (bending part) 34 ... 2nd bending part (bending part) 40 ... Resin protector (holding member) 41 ... FPC holding unit (board holding unit) 42 ... Holding plate part (holding body) 45 ... Pressing piece 46 ... Positioning projection 51 ... Second movable part 53 ... Spring plate part (second spring part) 61 ... Movable busbar holder (connecting member holder) 63 ... Bottom plate (base) 66 ... First bus bar locking piece (locking portion) 66A ...
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Electrochemistry (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Aviation & Aerospace Engineering (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Connection Of Batteries Or Terminals (AREA)
- Coupling Device And Connection With Printed Circuit (AREA)
Abstract
接続モジュール1は、FPC20と、FPC20に接続されて隣り合う蓄電素子90の電極端子91A、91B同士を接続する複数のバスバー10と、バスバー10とFPC20とを保持する樹脂プロテクタ40とを備える。FPC20は、FPC本体21と、FPC本体21とバスバー10とを連結する第1可動部31とを備えており、樹脂プロテクタ40が、FPC本体21が固定される複数のFPC保持部41と、バスバー10が固定される可動バスバー保持部61と、FPC保持部41と可動バスバー保持部61とを連結する複数の第2可動部51とを備えている。第1可動部31と第2可動部51とが、バスバー10と可動バスバー保持部61とを、FPC本体21とFPC保持部41とに対して変位を許容しつつ連結している。
Description
本明細書によって開示される技術は、接続モジュールに関する。
電気自動車やハイブリット車用の電池モジュールは、複数の電池セルにより構成される電池ブロックと、この電池ブロックに取り付けられて複数の単電池を接続する接続モジュールとを備えている。接続モジュールとして、フレキシブルプリント基板(FPC)と、このフレキシブルプリント基板に接続され、隣り合う蓄電素子の電極端子同士を接続する複数のバスバーとを備えるバスバー付きフレキシブルプリント配線板が知られている(特許文献1参照)。
多数の電池セルにより構成されている電池ブロックには、各電池セルの製造上の寸法誤差や、複数の電池セルの組み付け誤差等に起因して寸法公差が生じる。この寸法公差に起因して、バスバーと各電池セルの電極との間に位置ずれが生じ、接続モジュールの電池ブロックへの組み付けが困難となってしまうおそれがある。また、フレキシブルプリント配線板は柔軟性を有しているので、電池ブロックに組み付ける際に取り扱いづらく、組み付け作業性が悪いという問題がある。
本明細書によって開示される接続モジュールは、電極端子を備える複数の蓄電素子により構成される蓄電素子群に取り付けられて前記複数の蓄電素子を接続する接続モジュールであって、フレキシブルプリント基板と、前記フレキシブルプリント基板に接続されて、隣り合う前記蓄電素子の前記電極端子同士を接続する複数の接続部材と、複数の前記接続部材と前記フレキシブルプリント基板とを保持する保持部材とを備え、前記フレキシブルプリント基板が、基板本体と、前記基板本体と前記接続部材とを連結する第1可動部とを備えており、前記保持部材が、前記基板本体が固定される基板保持部と、前記接続部材が固定される接続部材保持部と、前記基板保持部と前記接続部材保持部とを連結する第2可動部とを備えており、前記第1可動部と前記第2可動部とが、前記接続部材と前記接続部材保持部とを、前記基板本体と前記基板保持部とに対して変位を許容しつつ連結している。
上記の構成によれば、接続部材と接続部材保持部とが、互いに組み付けられた状態で、基板本体と基板保持部とに対する変位が許容されているから、蓄電素子群の寸法公差に起因する電極端子の位置ずれによって、接続モジュールの蓄電素子群に対する組み付けが困難となることを回避し、組み付け作業性を向上させることができる。また、フレキシブルプリント基板と複数の接続部材とを保持部材に保持させることで、柔軟性を有するフレキシブルプリント基板の形状を一定に保持し、かつ、複数の接続部材とともに一括して蓄電素子群の所定位置にセットすることができるので、組み付け作業性を向上できる。
上記の構成において、前記第1可動部が、前記基板本体から延び、少なくとも1つの湾曲部を有する線ばね状の第1ばね部を備えていても構わない。
このような構成によれば、簡易な構成で、接続部材を、基板本体に対して変位を許容しつつ接続することができる。また、第1ばね部を線ばねによって構成することにより、接続部材は、基板本体に対して近接-離間する方向、基板本体の厚さ方向、および基板本体に沿う方向のいずれにも、ある程度自由に変位することができるので、フレキシブルプリント基板に接続部材を接続した後、保持部材に組み付ける際の組み付け作業を容易に行うことができる。
上記の構成において、複数の前記第2可動部が、前記基板保持部の一縁に沿って並んで配置されており、複数の前記第2可動部のそれぞれが、前記一縁に沿う方向に伸縮可能な第2ばね部を備えていても構わない。
このような構成によれば、第2ばね部によって、接続部材保持部の、基板保持部の一縁に沿う方向への変位が許容されている。したがって、基板保持部の一縁が複数の蓄電素子の並び方向に沿って延びるように、接続モジュールを蓄電素子群に組み付けることで、接続部材保持部、およびこの接続部材保持部に保持される接続部材の、蓄電素子群の並び方向に沿う方向の変位が許容される。これにより、蓄電素子群の寸法公差に起因する電極端子の位置ずれによって、接続モジュールの蓄電素子群に対する組み付けが困難となることを回避し、組み付け作業性を向上させることができる。
また、前記保持部材が、隣り合う前記接続部材保持部を、前記一縁に沿う方向への変位を許容しつつ連結する連結部を備えていても構わない。
このような構成によれば、接続部材保持部の、蓄電素子群の並び方向に沿う方向の変位を妨げることなく、隣り合う接続部材保持部を連結し、複数の接続部材を安定して保持させることができる。
上記の構成において、前記基板保持部が、前記基板本体に沿って配置される保持本体と、前記保持本体に対して隙間を空けて配置され、前記保持本体との間で前記基板本体を保持する押さえ片とを備えていても構わない。
このような構成によれば、簡易な構成で基板保持部に基板本体を保持させることができる。
上記の構成において、前記基板本体が位置決め孔を有しており、前記基板保持部が、前記基板本体に沿って配置される保持本体と、前記保持本体から突出して前記位置決め孔に挿通されることにより前記保持本体に対する前記基板本体の位置決めを行う位置決め突起を備えていても構わない。
このような構成によれば、簡易な構成で基板保持部に基板本体を位置決めすることができる。
上記の構成において、前記接続部材保持部が、前記接続部材に沿って配置される基部と、前記基部から連なる係止部とを備えており、前記係止部が、前記基部から突設され、撓み可能な撓み部と、前記撓み部から突出して前記基部との間で前記接続部材を挟み付けて保持する係止爪とを備えていても構わない。
このような構成によれば、接続部材を基部に向かって押し込むだけで、容易に接続部材保持部に組み付けることができるので、接続モジュールの組み立て作業性が向上する。
本明細書によって開示される接続モジュールによれば、組み付け作業性を向上できる。
実施形態を、図1~図16を参照しつつ説明する。本実施形態の接続モジュール1は、電気自動車やハイブリット自動車等の車両の駆動源として使用される蓄電モジュールMを構成する。接続モジュール1は、図1に示すように、複数の蓄電素子90が一列に並べられた蓄電素子群90Gに取り付けられて、複数の蓄電素子90を直列に接続する。
[蓄電素子90および蓄電素子群90G]
蓄電素子90は、例えば、二次電池である。各蓄電素子90は、図1に示すように、外形が扁平な直方体状であって、隣接する蓄電素子90と対向する面に対して垂直な電極配置面90F(図1の上面)を有している。電極配置面90Fには、電極端子91A、91Bが配置されている。電極端子91A、91Bのうち一方は正極端子91Aであり、他方は負極端子91Bである。各電極端子91A、91Bは円柱状であって、外周面には、詳細には図示しないが、ねじ山が切られている。
蓄電素子90は、例えば、二次電池である。各蓄電素子90は、図1に示すように、外形が扁平な直方体状であって、隣接する蓄電素子90と対向する面に対して垂直な電極配置面90F(図1の上面)を有している。電極配置面90Fには、電極端子91A、91Bが配置されている。電極端子91A、91Bのうち一方は正極端子91Aであり、他方は負極端子91Bである。各電極端子91A、91Bは円柱状であって、外周面には、詳細には図示しないが、ねじ山が切られている。
図1に示すように、複数の蓄電素子90が一列に並べられて蓄電素子群90Gを構成している。複数の蓄電素子90は、隣り合う2つの蓄電素子90において、異なる極性の電極端子91A、91Bが互いに隣り合うように(つまり、一の蓄電素子90の正極端子91Aと、これと隣接する他の蓄電素子90の負極端子91Bとが互いに隣り合うように)並べられている。
なお、以下の説明においては、複数の蓄電素子90の並び方向(図1の左下-右上方向)をX軸方向、蓄電素子90において隣接する蓄電素子90と対向する面に沿う方向(図1の右下-左上方向)をY軸方向、電極配置面90Fに垂直な方向(図1の上下方向)をZ軸方向として説明する。
[接続モジュール1]
接続モジュール1は、蓄電素子群90Gにおいて、各蓄電素子90の電極配置面90Fによって構成される面(図1の上面)に組み付けられる部材である。接続モジュール1は、図3に示すように、フレキシブルプリント基板20(以下、「FPC20」と記載する)と、FPC20に接続されて、隣り合う蓄電素子90の正極端子91Aと負極端子91Bとを接続する複数のバスバー10(接続部材に該当)と、バスバー10とFPC20とを保持する樹脂プロテクタ40(保持部材に該当)とを備えている。なお、図1では、電極端子91A、91Bの2つの列のうち一方の列(右下の列)に接続される接続モジュール1のみを図示しているが、他方の列にも同様に接続モジュール1が接続される。また、図1では、接続モジュール1において、右端の正極端子91Aと、これに隣接する負極端子91Bとを接続する1つのバスバー10を図示し、他のバスバー10については省略して示している。図2についても同様である。
接続モジュール1は、蓄電素子群90Gにおいて、各蓄電素子90の電極配置面90Fによって構成される面(図1の上面)に組み付けられる部材である。接続モジュール1は、図3に示すように、フレキシブルプリント基板20(以下、「FPC20」と記載する)と、FPC20に接続されて、隣り合う蓄電素子90の正極端子91Aと負極端子91Bとを接続する複数のバスバー10(接続部材に該当)と、バスバー10とFPC20とを保持する樹脂プロテクタ40(保持部材に該当)とを備えている。なお、図1では、電極端子91A、91Bの2つの列のうち一方の列(右下の列)に接続される接続モジュール1のみを図示しているが、他方の列にも同様に接続モジュール1が接続される。また、図1では、接続モジュール1において、右端の正極端子91Aと、これに隣接する負極端子91Bとを接続する1つのバスバー10を図示し、他のバスバー10については省略して示している。図2についても同様である。
(バスバー10)
複数のバスバー10のそれぞれは、金属製であって、図9および図10に示すように、隣り合う蓄電素子90の正極端子91Aと負極端子91Bとを接続する電極接続部11と、この電極接続部11から連なり、FPC20に接続されるFPC接続片15と、FPC接続片15から連なる係止壁16とを備えている。
複数のバスバー10のそれぞれは、金属製であって、図9および図10に示すように、隣り合う蓄電素子90の正極端子91Aと負極端子91Bとを接続する電極接続部11と、この電極接続部11から連なり、FPC20に接続されるFPC接続片15と、FPC接続片15から連なる係止壁16とを備えている。
電極接続部11は、全体として長方形の板状の部分であって、電極端子91A、91Bを挿通可能な2つの電極挿通孔12と、樹脂プロテクタ40との係合のための2つの係合凹部13とを有している。電極挿通孔12は、電極接続部11の一方の短辺11Sに近接した位置に1つ、他方の短辺11Sに近接した位置に1つが配置されている。2つの係合凹部13のうち一方は、電極接続部11の一方の短辺11Sから凹む凹部であり、他方は、他方の短辺11Sから凹む凹部である。
電極接続部11は、一対の長辺11LA、11LBのうち一方の長辺11LAから凹む接続用凹部14を有している。この接続用凹部14は、長辺11LAと平行な第1奥縁14Aと、この第1奥縁14Aの両端と長辺11LAとを繋ぐ一対の第1側縁14Bとで定義される凹部である。FPC接続片15は、第1奥縁14Aから電極接続部11と同一平面内に延びる矩形の板片状の部分である。係止壁16は、FPC接続片15の先端から垂直に延びる短い板壁状の部分である。
(FPC20)
FPC20は、複数のバスバー10とECU(電子制御ユニット:図示せず)とを電気的に接続するための部材であって、詳細には図示しないが、銅箔によって形成された複数の導電路と、導電路の両面を被覆する絶縁樹脂フィルムとを備えている。このFPC20は、図11に示すように、全体として長方形の帯状をなすFPC本体21(基板本体に該当)と、FPC本体21から連なる複数の第1可動部31と、複数の第1可動部31のそれぞれから連なり、複数のバスバー10のそれぞれに接合される接合片35とを備えている。
FPC20は、複数のバスバー10とECU(電子制御ユニット:図示せず)とを電気的に接続するための部材であって、詳細には図示しないが、銅箔によって形成された複数の導電路と、導電路の両面を被覆する絶縁樹脂フィルムとを備えている。このFPC20は、図11に示すように、全体として長方形の帯状をなすFPC本体21(基板本体に該当)と、FPC本体21から連なる複数の第1可動部31と、複数の第1可動部31のそれぞれから連なり、複数のバスバー10のそれぞれに接合される接合片35とを備えている。
FPC本体21は、第1スリット22と、切欠き部23と、複数の位置決め孔24と、2つの係合孔25とを有している。
第1スリット22は、FPC本体21の一対の長辺21LA、21LB間の概ね中央位置に、長辺21LA、21LBと平行に、FPC本体21の両端(一対の短辺21SA、21SA)のそれぞれに近い一部分を除くほぼ全長にわたって延びるスリットである。切欠き部23は、FPC本体21の一方(図11における下側)の長辺21LAから第1スリット22まで延びる、比較的幅の広い隙間であって、FPC本体21の一方(図11の右側)の短辺21SAに近接して配置されている。FPC本体21のうち、第1スリット22と長辺21LAに挟まれた部分(図11において、第1スリット22よりも下側の部分)は、切欠き部23によって、短辺21SB側に配置された長尺の第1分断部26と、短辺21SA側に配置された短尺の第2分断部27とに分断されている。
複数の位置決め孔24は、一方の短辺21SAに近接する位置に1つ、他方の短辺21SBに近接する位置に2つ、第1分断部26の概ね中央位置に1つが配置されている。2つの係合孔25のうち一方は、第1分断部26において切欠き部23に近接した位置に、他方は、第2分断部27において切欠き部23に近接した位置に配置されている。
第1可動部31は、FPC本体21から連なる線ばね状の部分(第1ばね部に該当)により構成されており、FPC本体21の長辺21LAから延び、U字状に湾曲する第1湾曲部32(湾曲部に該当)と、第1湾曲部32の延出端から連なり、長辺21LAに沿って延びる直線部33と、直線部33の延出端から連なり、第1湾曲部32とは反対向きに、U字状に湾曲する第2湾曲部34(湾曲部に該当)とを備えて、全体として略S字状をなしている。複数の第1可動部31は、長辺21LAに沿って一列に並んで配置されており、それらのうち1つは、第2分断部27から連なっており、残りは、第1分断部26から連なっている。
接合片35は、第2湾曲部34の延出端から連なる、矩形の板片状の部分である。接合片35の一面には、導電路の一部が接合用ランド(図示せず)として露出されており、ここに、FPC接続片15が半田付けにより接続される。
(樹脂プロテクタ40)
樹脂プロテクタ40は、合成樹脂製であって、FPC本体21を保持するFPC保持部41(基板保持部に該当)と、バスバー10を保持する複数のバスバー保持部61、71とを備えている。
樹脂プロテクタ40は、合成樹脂製であって、FPC本体21を保持するFPC保持部41(基板保持部に該当)と、バスバー10を保持する複数のバスバー保持部61、71とを備えている。
FPC保持部41は、図12に示すように、保持板部42(保持本体に該当)と、保持板部42から延びるサイドリブ43およびセンターリブ44A、44Bと、複数の押さえ片45と、複数の位置決め突起46および2つのFPC係止片47とを備えている。
保持板部42は、全体として、FPC本体21とほぼ同等の大きさの長方形の板状をなしている。保持板部42の一面(図12の上面)は、FPC本体21が載置される載置面42Fとなっており、この載置面42Fに、サイドリブ43、センターリブ44A、44Bと、押さえ片45、位置決め突起46およびFPC係止片47が配置されている。
サイドリブ43は、保持板部42の一対の長辺42LA、42LBのうち一方(図12の上方)の長辺42LAから突出するすじ状の部分であって、長辺42LAのほぼ全長にわたって配置されている。センターリブ44A、44Bは、一対の長辺42LA、42LB間の概ね中央位置に、長辺42LA、42LBと平行に延びるすじ状の部分であって、保持板部42の一対の短辺42SA、42SBのうち一方(図12の左側)の短辺42SAに近接して長尺の1本が、他方の短辺42SBに近接して短尺のもう1本が配置されている。
複数の押さえ片45のそれぞれは、サイドリブ43から保持板部42と平行に延びる板片状の部分であって、保持板部42との間でFPC本体21を挟んで保持できるようになっている。複数の位置決め突起46のそれぞれは、保持板部42から延びる円形の突部であって、FPC本体21の複数の位置決め孔24のそれぞれに対応する位置に配置されている。2つのFPC係止片47のそれぞれは、図8に示すように、保持板部42から延びる係止片本体47Aと、係止片本体47Aの先端から突出する係止突起47Bとを備えており、FPC本体21の2つの係合孔25のそれぞれに対応する位置に配置されている。
保持板部42は、他方の長辺42LB(一縁に該当)から内側に凹む複数のばね用凹部48を有している。ばね用凹部48は、図16に示すように、長辺42LBに平行な第2奥縁48Aと、この第2奥縁48Aの両端と長辺42LBとを繋ぐ一対の第2側縁48Bとで定義される凹部である。
図12に示すように、複数のバスバー保持部61、71のうち、保持板部42の一方の短辺42SAに最も近い1つは、固定バスバー保持部71であり、その他は、第2可動部51を介して保持板部42に連結された可動バスバー保持部61(接続部材保持部に該当)である。
第2可動部51は、図15および図16に示すように、全体として蛇腹状に屈曲された板状をなしており、保持板部42の長辺42LBに沿う方向に伸縮可能となっている。より具体的には、この第2可動部51は、第2奥縁48Aから保持板部42と同一平面上に延びる板片状のばね接続片52(ばね接続部に該当)と、このばね接続片52からそれぞれ第2奥縁48Aに沿って、互いに反対方向に屈曲しながら延びる一対のばね板部53(第2ばね部に該当)とを備えている。一対のばね板部53のそれぞれは、ばね接続片52の延出端から、保持板部42から離れるように垂直に延びた後、折り返されて保持板部42に近づくように延び、さらに折り返されて保持板部42から離れるように延びるS字の板ばね状をなしている。
可動バスバー保持部61は、図16に示すように、第2可動部51から連なる背板部62と、背板部62から連なる底板部63(基部に該当)と、底板部63から延びる延長片65、第1バスバー係止片66(係止部に該当)、2つの第2バスバー係止片67(係止部に該当)、および一対の突当板68を備えている。
背板部62は、図16に示すように、保持板部42に対して垂直な姿勢で配される板状の部分であって、一対のばね板部53のそれぞれの先端部に接続されている。
底板部63は、図16に示すように、背板部62から、保持板部42と反対方向に垂直に延びる板状の部分であって、2本の第2スリット64を有している。2本の第2スリット64のそれぞれは、図13および図16に示すように、底板部63の延出端から背板部62に向かって延びており、これらの第2スリット64によって、底板部63は、両端の端板部63Aと、中央の中板部63Bとに分割されている。延長片65は、底板部63の延出端から、底板部63と同一面上に延びる板片状の部分である。
第1バスバー係止片66は、図6および図16に示すように、中板部63Bから延び、背板部62に対して隙間を空けて配置される第1撓み片66A(撓み部に該当)と、第1撓み片66Aの延出端から背板部62と反対方向に突出する第1係止爪66B(係止爪に該当)とを備えている。第1撓み片66Aは、中板部63Bから離れるほど背板部62から離れるように僅かに傾斜している。
2つの第2バスバー係止片67のそれぞれは、図7に示すように、2つの端板部63Aの延出端から垂直に延びる第2撓み片67A(撓み部に該当)と、第2撓み片67Aの先端から背板部62に向かって突出する第2係止爪67B(係止爪に該当)とを備えている。
2つの突当板68のそれぞれは、図16に示すように、中板部63Bから、2つの第2スリット64のそれぞれのスリット縁に沿って突出する板状の部分であって、背板部62に隣接して配置されている。
各可動バスバー保持部61は、第2可動部51によって、保持板部42に対する変位がある程度許容されている。具体的には、第2可動部51の2つのばね板部53の伸縮によって、保持板部42の長辺42LBに沿う方向(X軸方向)に動くことができる。
固定バスバー保持部71は、図12に示すように、第2可動部51を有しておらず、背板部72が保持板部42の長辺42LBから延びている点を除いて、可動バスバー保持部61と同様の構成を有している。固定バスバー保持部71において、可動バスバー保持部61の各部位と同様の部位には、同一の符号を付して説明を省略する。
固定バスバー保持部71と、これと隣り合う可動バスバー保持部61、および、隣り合う可動バスバー保持部61同士は、図12および図16に示すように、U字の板ばね状の連結部81により連結されている。これにより、固定バスバー保持部71と、これと隣り合う可動バスバー保持部61、および、隣り合う可動バスバー保持部61同士を、保持板部42の長辺42LBに沿う方向(X軸方向)に沿う方向の変位を妨げることなく連結し、固定バスバー保持部71および可動バスバー保持部61に組み付けられる複数のバスバー10を安定して保持させることができる。
[接続モジュール1の組み立て]
上記の構成の接続モジュール1を組み立てる手順の一例を、以下に説明する。
上記の構成の接続モジュール1を組み立てる手順の一例を、以下に説明する。
まず、複数のバスバー10をFPC20に接続する。各バスバー10のFPC接続片15をFPC20の各接合片35に重ね、リフロー半田付けによって接合する。FPC20に接続された状態では、図3および図5に示すように、各バスバー10は、第1可動部31を介してFPC本体21と連結された状態となっており、第1可動部31が変形することによって、各バスバー10は、FPC本体21の長辺21LAに沿う方向(X軸方向)、FPC本体21に対して近接-離間する方向(Y軸方向)、およびFPC本体21の厚さ方向(Z軸方向)のいずれにも、ある程度自由に変位することができる。
次に、FPC20と複数のバスバー10との接合体を、樹脂プロテクタ40に組み付ける。
まず、FPC本体21をFPC保持部41に組み付ける。図3に示すように、FPC本体21を、保持板部42と押さえ片45との隙間に差し入れるようにして保持板部42上に重ね、長辺21LBがサイドリブ43に沿うようにセットする。複数の位置決め孔24のそれぞれに複数の位置決め突起46のそれぞれが挿通され、第1スリット22に2つのセンターリブ44A、44Bが挿通されることで、FPC本体21が保持板部42上に位置決めされる。また、押さえ片45によってFPC本体21が保持板部42から外れないように押さえられる。図3および図8に示すように、各FPC係止片47の係止片本体47Aが各係合孔25に挿通され、係止突起47BがFPC本体21に係合することにより、各分断部26、27の端部が保持板部42からめくれ上がらないように押さえられている。
次に、各バスバー10を各バスバー保持部61、71に組み付ける。各第2バスバー係止片67を各係合凹部13に挿通させ、第1バスバー係止片66を係止壁16によって撓ませつつ、電極接続部11を底板部63に向かって押し込む。電極接続部11が底板部63に当接すると、図6に示すように、第1バスバー係止片66が弾性復帰して、係止壁16が中板部63Bと第1係止爪66Bとの間で挟まれる。また、図5および図7に示すように、電極接続部11において係合凹部13に隣接する部分が底板部63と第2係止爪67Bとの間に入り込む。これらにより、各バスバー10が各バスバー保持部61、71に固定される。このとき、バスバー10は、第1可動部31が変形することによって、FPC本体21に対してある程度自由な変位が許容されているので、バスバー10のバスバー保持部61、71に対する組み付け作業を容易に行うことができる。また、バスバー10を底板部63に向かって押し込むだけで、容易にバスバー保持部61、71に組み付けることができるので、接続モジュール1の組み立て作業性が向上する。
バスバー10が各バスバー保持部61、71に組み付けられた状態では、図3に示すように、第1湾曲部32はFPC本体21と同一平面内に配置されており、直線部33は、第1湾曲部32から離れるほどFPC本体21から離れるように傾斜している。第2湾曲部34、接合片35およびバスバー10は、FPC本体21に対して平行に、FPC本体21とはずれて配置されている。直線部33は、第1バスバー係止片66と背板部62との隙間に通されている。
完成した接続モジュール1においては、FPC保持部41に対してFPC本体21が位置決め状態に保持されている。また、各可動バスバー保持部61に各バスバー10が位置決め状態に保持されている。そして、バスバー10が第1可動部31によってFPC本体21に対して変位可能に連結され、可動バスバー保持部61が第2可動部51によってFPC保持部41に対して変位可能に連結されている。これにより、可動バスバー保持部61とバスバー10とは、互いに組み付けられた状態で、FPC保持部41とFPC本体21とに対して、保持板部42の長辺42LBおよびFPC本体21の長辺21LAに沿う方向(X軸方向)への変位が許容されている。
[接続モジュール1の蓄電素子群90Gへの組み付け]
上記の構成の接続モジュール1を蓄電素子群90Gに組み付ける手順の一例を、以下に説明する。
上記の構成の接続モジュール1を蓄電素子群90Gに組み付ける手順の一例を、以下に説明する。
図1および図2に示すように、蓄電素子群90G上の所定位置に接続モジュール1を配置し、各バスバー10の電極挿通孔12に電極端子91A、91Bを挿通させる。その後、各電極端子91A、91Bに図示しないナットをねじ付けることにより、電極端子91A、91Bとバスバー10とを接続する。
ここで、多数の蓄電素子90を並べて構成されている蓄電素子群90Gには、各蓄電素子90の製造上の寸法誤差や、複数の蓄電素子90の組み付け誤差等に起因して、寸法公差が生じ、電極端子91A、91Bに、蓄電素子90の並び方向に沿う方向(X軸方向)の位置ずれが生じる場合がある。本実施形態では、上記したように、可動バスバー保持部61とバスバー10との、FPC保持部41とFPC本体21とに対する変位が許容されているから、蓄電素子群90Gの寸法公差に起因する電極端子91A、91Bの位置ずれに対応して、各バスバー10を変位させ、電極端子91A、91Bに組み付けることができる。
例えば、電極端子91A、91B間の距離が設計寸法よりも小さい場合には、第2可動部51と連結部81とを変形させて、各可動バスバー保持部61を、固定バスバー保持部71を基準として、固定バスバー保持部71に近接する方向(保持板部42の長辺42LBに沿う方向:図1の右上から左下に向かう方向)に変位させる。言い換えると、樹脂プロテクタ50の一端に位置する固定バスバー保持部71を基準として、固定バスバー保持部71の隣に位置する可動バスバー保持部61、および、隣り合う可動バスバー保持部61同士の間隔が狭くなるように、可動バスバー保持部61を変位させる。これにより、固定バスバー保持部71に保持された1つのバスバー10を基準として、隣り合うバスバー10間の距離が小さくなるように他のバスバー10を変位させ、電極端子91A、91Bの位置ずれに対応することができる。
また、電極端子91A、91B間の距離が設計寸法よりも大きい場合には、第2可動部51と連結部81とを変形させて、各可動バスバー保持部61を、固定バスバー保持部71を基準として、固定バスバー保持部71から離間する方向(保持板部42の長辺42LBに沿う方向:図1の左下から右上に向かう方向)に変位させる。言い換えると、樹脂プロテクタ50の一端に位置する固定バスバー保持部71を基準として、固定バスバー保持部71の隣に位置する可動バスバー保持部61、および、隣り合う可動バスバー保持部61同士の間隔が広くなるように、可動バスバー保持部61を変位させる。これにより、固定バスバー保持部71に保持された1つのバスバー10を基準として、隣り合うバスバー10間の距離が大きくなるように他のバスバー10を変位させ、電極端子91A、91Bの位置ずれに対応することができる。
このようにして、蓄電素子群90Gの寸法公差に起因して、接続モジュール1の蓄電素子群90Gに対する組み付けが困難となることを回避し、組み付け作業性を向上させることができる。
また、FPC20と複数のバスバー10とを樹脂プロテクタ40に組み付けることで、柔軟性を有するFPC20の形状を一定に保持し、かつ、複数のバスバー10とともに一括して蓄電素子群90G上の所定位置にセットすることができるので、組み付け作業性を向上できる。
[まとめ]
以上のように本実施形態によれば、接続モジュール1は、電極端子91A、91Bを備える複数の蓄電素子90により構成される蓄電素子群90Gに取り付けられて複数の蓄電素子90を接続するモジュールであって、FPC20と、FPC20に接続されて隣り合う蓄電素子90の電極端子91A、91B同士を接続する複数のバスバー10と、バスバー10とFPC20とを保持する樹脂プロテクタ40とを備える。FPC20は、FPC本体21と、FPC本体21とバスバー10とを連結する第1可動部31とを備えており、樹脂プロテクタ40が、FPC本体21が固定されるFPC保持部41と、バスバー10が固定される可動バスバー保持部61と、FPC保持部41と可動バスバー保持部61とを連結する複数の第2可動部51とを備えている。第1可動部31と第2可動部51とが、バスバー10と可動バスバー保持部61とを、FPC本体21とFPC保持部41とに対して変位を許容しつつ連結している。
以上のように本実施形態によれば、接続モジュール1は、電極端子91A、91Bを備える複数の蓄電素子90により構成される蓄電素子群90Gに取り付けられて複数の蓄電素子90を接続するモジュールであって、FPC20と、FPC20に接続されて隣り合う蓄電素子90の電極端子91A、91B同士を接続する複数のバスバー10と、バスバー10とFPC20とを保持する樹脂プロテクタ40とを備える。FPC20は、FPC本体21と、FPC本体21とバスバー10とを連結する第1可動部31とを備えており、樹脂プロテクタ40が、FPC本体21が固定されるFPC保持部41と、バスバー10が固定される可動バスバー保持部61と、FPC保持部41と可動バスバー保持部61とを連結する複数の第2可動部51とを備えている。第1可動部31と第2可動部51とが、バスバー10と可動バスバー保持部61とを、FPC本体21とFPC保持部41とに対して変位を許容しつつ連結している。
上記の構成によれば、バスバー10と可動バスバー保持部61とが、互いに組み付けられた状態で、FPC本体21とFPC保持部41とに対する変位が許容されているから、蓄電素子群90Gの寸法公差に起因する電極端子91A、91Bの位置ずれによって、接続モジュール1の蓄電素子群90Gに対する組み付けが困難となることを回避し、組み付け作業性を向上させることができる。また、FPC20と複数のバスバー10とを樹脂プロテクタ40に保持させることで、柔軟性を有するFPC20の形状を一定に保持し、かつ、複数のバスバー10とともに一括して蓄電素子群90Gの所定位置にセットすることができるので、組み付け作業性を向上できる。
また、第1可動部31が、FPC本体21から延び、第1湾曲部32および第2湾曲部34を有する線ばねによって構成されている。
このような構成によれば、簡易な構成で、バスバー10を、FPC本体21に対して変位を許容しつつ接続することができる。また、第1可動部31を線ばねによって構成することにより、バスバー10は、FPC本体21に対して近接-離間する方向、FPC本体21の厚さ方向、およびFPC本体21に沿う方向のいずれにも、ある程度自由に変位することができるので、FPC20にバスバー10を接続した後、樹脂プロテクタ40に組み付ける際の組み付け作業を容易に行うことができる。
また、複数の第2可動部51が、FPC保持部41の長辺42LBに沿って並んで配置されており、複数の第2可動部51のそれぞれが、長辺42LBに沿う方向に伸縮可能なばね板部53を備えている。
このような構成によれば、第2可動部51によって、可動バスバー保持部61の、FPC保持部41の長辺42LBに沿う方向への変位が許容されている。したがって、FPC保持部41の長辺42LBが複数の蓄電素子90の並び方向に沿って延びるように、接続モジュール1を蓄電素子群90Gに組み付けることで、可動バスバー保持部61、およびこの可動バスバー保持部61に保持されるバスバー10の、蓄電素子群90Gの並び方向に沿う方向の変位が許容される。これにより、蓄電素子群90Gの寸法公差に起因する電極端子91A、91Bの位置ずれによって、接続モジュール1の蓄電素子群90Gに対する組み付けが困難となることを回避し、組み付け作業性を向上させることができる。
また、樹脂プロテクタ50が、隣り合う可動バスバー保持部61を、FPC保持部41における保持板部42の長辺42LBに沿う方向への変位を許容しつつ連結する連結部81を備えていても構わない。
このような構成によれば、可動バスバー保持部61の、蓄電素子群90Gの並び方向に沿う方向の変位を妨げることなく、隣り合う可動バスバー保持部61を連結し、複数のバスバー10を安定して保持させることができる。
また、FPC保持部41が、FPC本体21に沿って配置される保持板部42と、保持板部42に対して隙間を空けて配置され、保持板部42との間でFPC本体21を保持する押さえ片45とを備えている。
このような構成によれば、簡易な構成でFPC保持部41にFPC本体21を保持させることができる。
また、FPC本体21が位置決め孔24を有しており、FPC保持部41が、FPC本体21に沿って配置される保持板部42と、保持板部42から突出して前記位置決め孔24に挿通されることにより保持板部42に対するFPC本体21の位置決めを行う位置決め突起46を備えている。
このような構成によれば、簡易な構成でFPC保持部41にFPC本体21を位置決めすることができる。
また、可動バスバー保持部61が、バスバー10に沿って配置される底板部63と、底板部63から連なる第1バスバー係止片66および第2バスバー係止片67とを備える。第1バスバー係止片66は、底板部63から突設され、撓み可能な第1撓み片66Aと、第1撓み片66Aから突出して底板部63との間でバスバー10を挟み付けて保持する第1係止爪66Bとを備える。第2バスバー係止片67は、同様に、底板部63から突設され、撓み可能な第2撓み片67Aと、第2撓み片67Aから突出して底板部63との間でバスバー10を挟み付けて保持する第2係止爪67Bとを備える。
このような構成によれば、バスバー10を底板部63に向かって押し込むだけで、容易に可動バスバー保持部61に組み付けることができるので、接続モジュール1の組み立て作業性が向上する。
<他の実施形態>
本明細書によって開示される技術は上記記述及び図面によって説明した実施形態に限定されるものではなく、例えば次のような種々の態様も含まれる。
本明細書によって開示される技術は上記記述及び図面によって説明した実施形態に限定されるものではなく、例えば次のような種々の態様も含まれる。
(1)上記実施形態では、第1可動部31が第1湾曲部32および第2湾曲部34を備えていたが、湾曲部は1つでも、3つ以上であっても構わない。
(2)上記実施形態では、第2可動部51が蛇腹状に屈曲する一対のばね板部53を備えていたが、第2ばね部の形状は上記実施形態に限らず、基板保持部の一縁に沿う方向に伸縮可能なばね形状を備えていればよい。
(3)上記実施形態では、第2可動部51の2つのばね板部53は、ばね接続片52を挟んで対称な形状を有していたが、一対の第2ばね部は互いに非対称な形状を有していても構わない。
1…接続モジュール
10…バスバー(接続部材)
20…フレキシブルプリント基板
21…FPC本体(基板本体)
24…位置決め孔
31…第1可動部(第1ばね部)
32…第1湾曲部(湾曲部)
34…第2湾曲部(湾曲部)
40…樹脂プロテクタ(保持部材)
41…FPC保持部(基板保持部)
42…保持板部(保持本体)
45…押さえ片
46…位置決め突起
51…第2可動部
53…ばね板部(第2ばね部)
61…可動バスバー保持部(接続部材保持部)
63…底板部(基部)
66…第1バスバー係止片(係止部)
66A…第1撓み片(撓み部)
66B…第1係止爪(係止爪)
67…第2バスバー係止片(係止部)
67A…第2撓み片(撓み部)
67B…第2係止爪(係止爪)
81…連結部
90…蓄電素子
90G…蓄電素子群
91A、91B…電極端子
10…バスバー(接続部材)
20…フレキシブルプリント基板
21…FPC本体(基板本体)
24…位置決め孔
31…第1可動部(第1ばね部)
32…第1湾曲部(湾曲部)
34…第2湾曲部(湾曲部)
40…樹脂プロテクタ(保持部材)
41…FPC保持部(基板保持部)
42…保持板部(保持本体)
45…押さえ片
46…位置決め突起
51…第2可動部
53…ばね板部(第2ばね部)
61…可動バスバー保持部(接続部材保持部)
63…底板部(基部)
66…第1バスバー係止片(係止部)
66A…第1撓み片(撓み部)
66B…第1係止爪(係止爪)
67…第2バスバー係止片(係止部)
67A…第2撓み片(撓み部)
67B…第2係止爪(係止爪)
81…連結部
90…蓄電素子
90G…蓄電素子群
91A、91B…電極端子
Claims (7)
- 電極端子を備える複数の蓄電素子により構成される蓄電素子群に取り付けられて前記複数の蓄電素子を接続する接続モジュールであって、
フレキシブルプリント基板と、
前記フレキシブルプリント基板に接続されて、隣り合う前記蓄電素子の前記電極端子同士を接続する複数の接続部材と、
複数の前記接続部材と前記フレキシブルプリント基板とを保持する保持部材とを備え、
前記フレキシブルプリント基板が、基板本体と、前記基板本体と前記接続部材とを連結する第1可動部とを備えており、
前記保持部材が、前記基板本体が固定される基板保持部と、前記接続部材が固定される接続部材保持部と、前記基板保持部と前記接続部材保持部とを連結する第2可動部とを備えており、
前記第1可動部と前記第2可動部とが、前記接続部材と前記接続部材保持部とを、前記基板本体と前記基板保持部とに対して変位を許容しつつ連結している、接続モジュール。 - 前記第1可動部が、前記基板本体から延び、少なくとも1つの湾曲部を有する線ばね状の第1ばね部を備える、請求項1に記載の接続モジュール。
- 複数の前記第2可動部が、前記基板保持部の一縁に沿って並んで配置されており、
複数の前記第2可動部のそれぞれが、前記一縁に沿う方向に伸縮可能な第2ばね部を備える、請求項1または請求項2に記載の接続モジュール。 - 前記保持部材が、隣り合う前記接続部材保持部を、前記一縁に沿う方向への変位を許容しつつ連結する連結部を備えている、請求項3に記載の接続モジュール。
- 前記基板保持部が、前記基板本体に沿って配置される保持本体と、前記保持本体に対して隙間を空けて配置され、前記保持本体との間で前記基板本体を保持する押さえ片とを備えている、請求項1~請求項4のいずれか1項に記載の接続モジュール。
- 前記基板本体が位置決め孔を有しており、
前記基板保持部が、前記基板本体に沿って配置される保持本体と、前記保持本体から突出して前記位置決め孔に挿通されることにより前記保持本体に対する前記基板本体の位置決めを行う位置決め突起を備えている、請求項1~請求項5のいずれか1項に記載の接続モジュール。 - 前記接続部材保持部が、
前記接続部材に沿って配置される基部と、前記基部から連なる係止部とを備えており、
前記係止部が、前記基部から突設され、撓み可能な撓み部と、前記撓み部から突出して前記基部との間で前記接続部材を挟み付けて保持する係止爪とを備える、請求項1~6のいずれか1項に記載の接続モジュール。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201980073359.2A CN112997354B (zh) | 2018-11-22 | 2019-11-01 | 连接模块 |
| US17/296,089 US20220013868A1 (en) | 2018-11-22 | 2019-11-01 | Connection module |
| CN202410187852.XA CN117996364A (zh) | 2018-11-22 | 2019-11-01 | 柔性印刷基板以及连接模块 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018219298A JP7212504B2 (ja) | 2018-11-22 | 2018-11-22 | 接続モジュール |
| JP2018-219298 | 2018-11-22 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2020105400A1 true WO2020105400A1 (ja) | 2020-05-28 |
Family
ID=70773176
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2019/043017 WO2020105400A1 (ja) | 2018-11-22 | 2019-11-01 | 接続モジュール |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20220013868A1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP7212504B2 (ja) |
| CN (2) | CN117996364A (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2020105400A1 (ja) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2022163420A1 (ja) * | 2021-02-01 | 2022-08-04 | 株式会社オートネットワーク技術研究所 | 配線モジュール |
| EP4071904A1 (en) * | 2021-03-18 | 2022-10-12 | Samsung SDI Co., Ltd. | Hybrid circuit board and battery pack having same |
| CN115332732A (zh) * | 2021-05-10 | 2022-11-11 | 矢崎总业株式会社 | 汇流条模块 |
Families Citing this family (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7403240B2 (ja) | 2019-06-07 | 2023-12-22 | 日本メクトロン株式会社 | 配線材及びバッテリモジュール |
| JP2020205176A (ja) * | 2019-06-17 | 2020-12-24 | 矢崎総業株式会社 | 回路体、基板と回路体との接続構造、及び、バスバモジュール |
| CN210467965U (zh) * | 2019-09-23 | 2020-05-05 | 宁德时代新能源科技股份有限公司 | 电池模组、电池包以及车辆 |
| JP6810946B1 (ja) | 2020-02-12 | 2021-01-13 | 国立研究開発法人農業・食品産業技術総合研究機構 | トバモウイルス抵抗性トマト植物、トバモウイルス抵抗性トマト植物の生産方法、トマト植物におけるトバモウイルス抵抗性の付与方法、トバモウイルス抵抗性トマト植物のスクリーニング方法およびトマト植物におけるトバモウイルス抵抗性の検出方法 |
| CN115769433A (zh) * | 2020-07-14 | 2023-03-07 | 株式会社自动网络技术研究所 | 配线模块 |
| JP7567448B2 (ja) | 2020-07-14 | 2024-10-16 | 株式会社オートネットワーク技術研究所 | 配線モジュール |
| JP7186760B2 (ja) * | 2020-12-21 | 2022-12-09 | プライムプラネットエナジー&ソリューションズ株式会社 | 蓄電モジュール |
| JP7253525B2 (ja) * | 2020-12-21 | 2023-04-06 | プライムプラネットエナジー&ソリューションズ株式会社 | 蓄電モジュール |
| CN113316314B (zh) * | 2021-07-28 | 2021-11-19 | 中航锂电科技有限公司 | 柔性电路器件及其制备方法、电池装置 |
| MX2024008374A (es) * | 2022-01-03 | 2024-07-29 | Cps Tech Holdings Llc | Bateria inteligente y metodo de ensamblaje. |
| JP2023135942A (ja) * | 2022-03-16 | 2023-09-29 | 株式会社オートネットワーク技術研究所 | 配線モジュール |
| CN114725630A (zh) * | 2022-03-30 | 2022-07-08 | 中创新航科技股份有限公司 | 电池装置 |
| WO2023201083A2 (en) * | 2022-04-14 | 2023-10-19 | Cps Technology Holdings Llc | Intelligent battery systems, components for intelligent battery systems, methods of manufacturing and operating intelligent battery systems and components of the same |
| WO2024145246A2 (en) * | 2022-12-28 | 2024-07-04 | Cps Technology Holdings Llc | Lead assembly for battery cell monitoring |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013143281A (ja) * | 2012-01-11 | 2013-07-22 | Auto Network Gijutsu Kenkyusho:Kk | 電池用配線モジュール |
| JP2015022965A (ja) * | 2013-07-22 | 2015-02-02 | 株式会社デンソー | 組電池 |
| JP2015049931A (ja) * | 2013-08-29 | 2015-03-16 | 古河電気工業株式会社 | 電池パックの電池内配線モジュール |
| JP2015185226A (ja) * | 2014-03-20 | 2015-10-22 | 愛三工業株式会社 | バスバーモジュール |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3625577B2 (ja) * | 1996-06-20 | 2005-03-02 | 三洋電機株式会社 | プリント基板を内蔵するパック電池 |
| KR20120003432A (ko) * | 2009-03-31 | 2012-01-10 | 산요덴키가부시키가이샤 | 전지 모듈, 배터리 시스템 및 전동 차량 |
| JP2013080620A (ja) * | 2011-10-04 | 2013-05-02 | Auto Network Gijutsu Kenkyusho:Kk | 電池用配線モジュール |
| JP6533500B2 (ja) * | 2016-08-12 | 2019-06-19 | 矢崎総業株式会社 | バスバモジュール及び電池パック |
| CN207779574U (zh) * | 2018-01-31 | 2018-08-28 | 长城汽车股份有限公司 | 用于电池的温感器安装组件及电池 |
| CN110707272B (zh) * | 2018-07-10 | 2022-05-17 | 矢崎总业株式会社 | 装配有连接器的电路体以及汇流条模块 |
-
2018
- 2018-11-22 JP JP2018219298A patent/JP7212504B2/ja active Active
-
2019
- 2019-11-01 WO PCT/JP2019/043017 patent/WO2020105400A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2019-11-01 US US17/296,089 patent/US20220013868A1/en active Pending
- 2019-11-01 CN CN202410187852.XA patent/CN117996364A/zh active Pending
- 2019-11-01 CN CN201980073359.2A patent/CN112997354B/zh active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013143281A (ja) * | 2012-01-11 | 2013-07-22 | Auto Network Gijutsu Kenkyusho:Kk | 電池用配線モジュール |
| JP2015022965A (ja) * | 2013-07-22 | 2015-02-02 | 株式会社デンソー | 組電池 |
| JP2015049931A (ja) * | 2013-08-29 | 2015-03-16 | 古河電気工業株式会社 | 電池パックの電池内配線モジュール |
| JP2015185226A (ja) * | 2014-03-20 | 2015-10-22 | 愛三工業株式会社 | バスバーモジュール |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2022163420A1 (ja) * | 2021-02-01 | 2022-08-04 | 株式会社オートネットワーク技術研究所 | 配線モジュール |
| EP4071904A1 (en) * | 2021-03-18 | 2022-10-12 | Samsung SDI Co., Ltd. | Hybrid circuit board and battery pack having same |
| CN115332732A (zh) * | 2021-05-10 | 2022-11-11 | 矢崎总业株式会社 | 汇流条模块 |
| EP4089787A1 (en) * | 2021-05-10 | 2022-11-16 | Yazaki Corporation | Busbar module |
| CN115332732B (zh) * | 2021-05-10 | 2024-05-24 | 矢崎总业株式会社 | 汇流条模块 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20220013868A1 (en) | 2022-01-13 |
| JP2020087665A (ja) | 2020-06-04 |
| CN117996364A (zh) | 2024-05-07 |
| JP7212504B2 (ja) | 2023-01-25 |
| CN112997354A (zh) | 2021-06-18 |
| CN112997354B (zh) | 2024-02-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2020105400A1 (ja) | 接続モジュール | |
| JP6691178B2 (ja) | プロテクタ、及び、バスバモジュール | |
| US11063322B2 (en) | Circuit body and battery module | |
| JP7041098B2 (ja) | バスバモジュール | |
| JP6533500B2 (ja) | バスバモジュール及び電池パック | |
| WO2020105401A1 (ja) | 接続モジュール | |
| CN114335910B (zh) | 连接模块 | |
| JP2013105571A (ja) | 電池配線モジュール | |
| JP6145314B2 (ja) | バスバモジュール及び電源装置 | |
| JP2020013829A (ja) | 回路体及び電池モジュール | |
| WO2014033950A1 (ja) | 電池配線モジュール | |
| JP2011124176A (ja) | 電池接続アセンブリ | |
| WO2020105399A1 (ja) | 接続モジュール | |
| CN110277518B (zh) | 汇流条模块和电池组 | |
| WO2020071069A1 (ja) | フレキシブルプリント基板、及び配線モジュール | |
| JP2017059481A (ja) | バスバモジュール及び電池パック | |
| JP7308328B2 (ja) | 接続モジュール | |
| CN112997352B (zh) | 连接模块 | |
| WO2024122238A1 (ja) | 積層回路体、及び、バスバモジュール | |
| KR20220049625A (ko) | 용량 가변 적응형 배터리 모듈의 결합 구조 | |
| CN116097381A (zh) | 车载用配线模块及柔性基板 | |
| JP2022147174A (ja) | 絶縁リング、組電池及び組電池の製造方法 | |
| JP2011250613A (ja) | 回路構成体 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 19887153 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 19887153 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |