WO2017090704A1 - 新規乳酸菌 - Google Patents
新規乳酸菌 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2017090704A1 WO2017090704A1 PCT/JP2016/084894 JP2016084894W WO2017090704A1 WO 2017090704 A1 WO2017090704 A1 WO 2017090704A1 JP 2016084894 W JP2016084894 W JP 2016084894W WO 2017090704 A1 WO2017090704 A1 WO 2017090704A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- cells
- lactic acid
- strain
- present
- lactococcus lactis
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A23—FOODS OR FOODSTUFFS; TREATMENT THEREOF, NOT COVERED BY OTHER CLASSES
- A23C—DAIRY PRODUCTS, e.g. MILK, BUTTER OR CHEESE; MILK OR CHEESE SUBSTITUTES; MAKING OR TREATMENT THEREOF
- A23C9/00—Milk preparations; Milk powder or milk powder preparations
- A23C9/12—Fermented milk preparations; Treatment using microorganisms or enzymes
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A23—FOODS OR FOODSTUFFS; TREATMENT THEREOF, NOT COVERED BY OTHER CLASSES
- A23L—FOODS, FOODSTUFFS OR NON-ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; PREPARATION OR TREATMENT THEREOF
- A23L31/00—Edible extracts or preparations of fungi; Preparation or treatment thereof
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A23—FOODS OR FOODSTUFFS; TREATMENT THEREOF, NOT COVERED BY OTHER CLASSES
- A23L—FOODS, FOODSTUFFS OR NON-ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; PREPARATION OR TREATMENT THEREOF
- A23L33/00—Modifying nutritive qualities of foods; Dietetic products; Preparation or treatment thereof
- A23L33/10—Modifying nutritive qualities of foods; Dietetic products; Preparation or treatment thereof using additives
- A23L33/135—Bacteria or derivatives thereof, e.g. probiotics
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N1/00—Microorganisms, e.g. protozoa; Compositions thereof; Processes of propagating, maintaining or preserving microorganisms or compositions thereof; Processes of preparing or isolating a composition containing a microorganism; Culture media therefor
- C12N1/20—Bacteria; Culture media therefor
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a strain of lactic acid bacteria derived from cranberries having a high immunomodulatory action, and beverages and foods containing the cells.
- it relates to Lactococcus lactis.
- Lactic acid bacteria have been used in various processed foods and drinks such as fermented milk products such as yogurt and various pickles for various purposes such as imparting taste and flavor, enhancing nutrition, and improving food storage stability.
- fermented milk products such as yogurt and various pickles for various purposes such as imparting taste and flavor, enhancing nutrition, and improving food storage stability.
- attention has been focused on effective physiological activities such as allergy suppression of lactic acid bacteria, and research is being conducted energetically.
- Th cells that play an important role in the immune system are classified into Th1 cells and Th2 cells according to the cytokines produced.
- Th1 cells produce cytokines mainly related to cellular immunity such as interferon ⁇ (hereinafter referred to as “IFN- ⁇ ”), and Th2 cells mainly produce cytokines related to humoral immunity such as interleukin 4 (hereinafter referred to as “IL-4”).
- IFN- ⁇ interferon ⁇
- IL-4 interleukin 4
- Th1 cells and Th2 cells antagonize each other and maintain balance to maintain homeostasis of the immune system, but when Th1 cells predominate, autoimmune disease, and when Th2 cells predominate, IgE production increases Allergy develops (Non-patent Document 1).
- An object of the present invention is to provide a cranberry-derived lactic acid bacterium having a high immunomodulatory action and a food or drink containing the lactic acid bacterium.
- the first invention of the present application is a Lactococcus genus having an immunomodulatory action derived from cranberries, and more specifically, Lactococcus lactis T21 strain (NITE BP-02164).
- the applicant of the present application also intends foods and drinks containing the lactic acid bacteria. That is, the second invention of the present application is a food or drink containing Lactococcus lactis T21 strain (NITE BP-02164).
- the lactic acid bacterium of the present invention has a high immunoregulatory effect. When ingested, allergy can be suppressed by activating immune function.
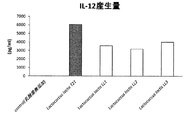
- FIG. 1 is a diagram comparing IL-12 production (pg / ml) between the strain of the present invention and a comparative strain.
- FIG. 2 is a diagram comparing the skim milk medium growth of the strain of the present invention and the comparative strain.
- Lactococcus lactis T21 strain (NITE BP-02164)
- the lactic acid bacterium of the present invention is lactococcus lactis.
- Lactococcus lactis strain T21 Among the lactic acid bacteria belonging to Lactococcus lactis, Lactococcus lactis strain T21.
- the symbol T21 referred to in the present invention is a number uniquely assigned to the strain by Nissin Foods Holdings. This Lactococcus lactis strain T21 was first isolated from cranberries by one of the inventors.
- the Lactococcus lactis T21 strain of the present invention is deposited under the following conditions. (1) Depositary Institution: National Institute of Technology and Technology Patent Microorganisms Deposit Center (2) Contact: 2-9-8 Kazusa Kamashi, Kisarazu City, Chiba Prefecture 292-0818 Japan (3) Accession Number: NITE BP -02164 (4) Display for identification: T21 (5) Date of original deposit: November 20, 2015 (6) Date of transfer to deposit under the Budapest Treaty: October 12, 2016
- the bacteriological properties of the Lactococcus lactis strain T21 of the present invention are as follows: As shown in Tables 1 and 2. This bacteriological property is based on the method described in Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology Vol. 2 (1986).
- the Lactococcus lactis T21 strain of the present invention has a high immunomodulating action, that is, a high production induction ability of IL-12, as shown in the experimental examples described later. Confirmation of IL-12 production-inducing ability was performed by the following test method.
- ⁇ Preparation of bacterial cells The cells were cultured in MRS medium (Difco Lactobacilli MRS Broth) shown in Table 3 at 30 ° C. for 48 hours. Next, the grown cells were collected by centrifugation, and the separated cells were washed three times with sterilized water and frozen. Then, it lyophilized
- MRS medium Difco Lactobacilli MRS Broth
- J774.1 cells a mouse-derived macrophage-like cell line, were used as cells.
- J774.1 cells were cultured under conditions of 37 ° C. and CO 2 5%.
- 2 ml each of 2.5 ⁇ 10 5 cells / ml J774.1 cells was added to each well of the 24-well culture plate, and the dried cell powder obtained above was added to the 0.1 mg / ml J774.1 cell culture medium.
- the suspension was suspended to a concentration of ml, 100 ⁇ l was added, and the cells were cultured at 37 ° C. under 5% CO 2 for 24 hours. After the culture, the medium was collected and centrifuged at 3500 rpm for 2 minutes to obtain a culture supernatant. IL-12 in the culture supernatant was measured using Mouse Total IL-12 ELISA kit (Thermo scientific).
- the lactic acid bacteria of the present invention can be used by containing them in food / beverage products. Although the lactic acid bacteria of this invention can be used especially suitably for a drink, fermented milk and a lactic acid bacteria drink are considered, for example.
- the component standard should be fermented milk (non-fat milk solid content of 8.0% or more) or dairy lactic acid bacteria beverage (non-fat milk solid content of 3.0% or more) 1.0 ⁇ 10 7 production induction capacity / ml or more, 1.0 ⁇ 10 6 cfn / ml or more is required for lactic acid bacteria beverages (non-fat milk solid content less than 3.0%), but in fermented liquid such as milk
- the above-mentioned number of bacteria can be realized by growing or growing in the form of a final product.
- the food of the present invention may be in the form of a formulation (for example, powder, granule, capsule, tablet, etc.) by adding an appropriate carrier and additives as necessary together with the lactic acid bacteria. .
- the lactic acid bacteria of the present invention are also useful for inclusion in foods for specified health use, dietary supplements and the like in addition to general beverages and foods.
- the lactic acid bacteria of the present invention can also be used in cosmetics such as lotion, pharmaceuticals such as intestinal preparations, daily necessities such as toothpaste, silage, animal feed, and animal feed and plant fertilizers such as plant liquid fertilizer. Applicable.
- the cranberry-derived lactic acid bacteria (Lactococcus lactis T21 strain) of the present invention have a high immunoregulatory effect. When ingested, allergy can be suppressed by activating immune function.
- IL-12 production induction evaluation was carried out for Lactococcus lactis T21 strain of the present invention and three Lactococcus lactis comparative strains (LL1, LL2, LL3) owned by the company. .
- IL-12 production induction evaluation was performed according to the following procedure.
- the cells were cultured in MRS medium (Difco Lactobacilli MRS Broth) shown in Table 3 at 30 ° C for 48 hours, and the proliferated cells were collected by centrifugation and the separated cells were collected. Washed 3 times with sterilized water and frozen. Then, it lyophilized
- MRS medium Difco Lactobacilli MRS Broth
- J774.1 cells were cultured under conditions of 37 ° C. and CO 2 5%. Then, 2 ml each of 2.5 ⁇ 10 5 cells / ml J774.1 cells was added to each well of the 24-well culture plate, and the dried cell powder obtained above was added to the 0.1 mg / ml J774.1 cell culture medium. Each suspension was suspended to a concentration of ml, 100 ⁇ l was added, and the cells were cultured at 37 ° C.
- IL-12 in the culture supernatant was measured using Mouse Total IL-12 ELISA kit (Thermo scientific).
- the amount of IL-12 produced by the lactic acid bacterium of the present invention is 6056 pg / ml, compared with other in-house owned Lactococcus lactis. It was confirmed to have a high ability to induce IL-12 production.
- skim Milk Medium Proliferation Test A skim milk medium proliferation test was performed on the Lactococcus lactis T21 strain of the present invention and three Lactococcus lactis comparative strains (LL1, LL2, LL3) owned by the company.
- SM skimmed milk
- 10% SM (skimmed milk) medium was inoculated and cultured at 30 ° C. for 48 hours, and the growth on the skimmed milk medium was evaluated by the number of lactic acid bacteria and pH.
- the number of strains of the strain of the present invention (Lactococcus lactis T21 strain) was 7.6 ⁇ 10 8 cfu / ml, which was a level with no problem in producing fermented milk and lactic acid bacteria beverages.
Landscapes
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Food Science & Technology (AREA)
- Mycology (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- Nutrition Science (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Tropical Medicine & Parasitology (AREA)
- Virology (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Micro-Organisms Or Cultivation Processes Thereof (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Material From Animals Or Micro-Organisms (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Plant Substances (AREA)
- Coloring Foods And Improving Nutritive Qualities (AREA)
- Cosmetics (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015230538A JP6345642B2 (ja) | 2015-11-26 | 2015-11-26 | 新規乳酸菌 |
| JP2015-230538 | 2015-11-26 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2017090704A1 true WO2017090704A1 (ja) | 2017-06-01 |
Family
ID=58763519
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2016/084894 Ceased WO2017090704A1 (ja) | 2015-11-26 | 2016-11-25 | 新規乳酸菌 |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6345642B2 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2017090704A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20220411836A1 (en) * | 2021-06-22 | 2022-12-29 | SAIB & CO Inc. | Methods for extracting anthocyanins to improve urinary health by using cranberries and plant-based lactobacillus which enhance female reproductive health and extracts of thereby |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH10139674A (ja) * | 1996-11-11 | 1998-05-26 | Yakult Honsha Co Ltd | インターロイキン12産生促進剤 |
| JP2009256312A (ja) * | 2008-03-26 | 2009-11-05 | Fujicco Co Ltd | 免疫調節用組成物およびそれを用いた飲食品または飲食品素材 |
-
2015
- 2015-11-26 JP JP2015230538A patent/JP6345642B2/ja active Active
-
2016
- 2016-11-25 WO PCT/JP2016/084894 patent/WO2017090704A1/ja not_active Ceased
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH10139674A (ja) * | 1996-11-11 | 1998-05-26 | Yakult Honsha Co Ltd | インターロイキン12産生促進剤 |
| JP2009256312A (ja) * | 2008-03-26 | 2009-11-05 | Fujicco Co Ltd | 免疫調節用組成物およびそれを用いた飲食品または飲食品素材 |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| KIMOTO, H. ET AL.: "New Lactococcus Strain with Immunomodulatory Activity: Enhancement of Th1- Type Immune Response", MICROBIOL. IMMUNOL., vol. 48, no. 2, 2004, pages 75 - 82, XP002555796, ISSN: 1348-0421 * |
| YOSUKE SUNADA ET AL.: "Lactococcus lactis T21 Kabu no Kafunsho ni Taisuru Koka", PROCEEDINGS OF THE 2016 ANNUAL MEETING OF JAPAN SOCIETY FOR BIOSCIENCE, BIOTECHNOLOGY, AND AGROCHEMISTRY, 5 March 2016 (2016-03-05), ISSN: 2186-7976 * |
| YOSUKE SUNADA ET AL.: "Men'eki Chosetsu Sayo o Yusuru Nyusankin no Screening", ASSOCIATE JOURNAL OF JAPANESE SOCIETY FOR MEDICAL USE OF FUNCTIONAL FOODS, vol. 9, no. 4, 1 December 2015 (2015-12-01), pages 262, ISSN: 1348-2564 * |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20220411836A1 (en) * | 2021-06-22 | 2022-12-29 | SAIB & CO Inc. | Methods for extracting anthocyanins to improve urinary health by using cranberries and plant-based lactobacillus which enhance female reproductive health and extracts of thereby |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP6345642B2 (ja) | 2018-06-20 |
| JP2017093380A (ja) | 2017-06-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CA2793729C (en) | Novel lactobacillus classified as lactobacillus plantarum, and use thereof | |
| KR102028744B1 (ko) | 면역증강 활성, 항산화 활성 및 소화액 내성을 갖는 락토바실러스 플란타룸 hy7717 균주 및 그의 용도 | |
| US20210324326A1 (en) | Novel lactobacillus plantarum strain atg-k2, atg-k6 or atg-k8, and composition for preventing or treating vaginitis comprising same | |
| KR101239806B1 (ko) | 면역증강 활성을 가지는 신규한 락토바실러스 플란타룸 에이취와이 7712 | |
| KR101511976B1 (ko) | 면역증강 활성을 가지는 신규한 락토바실러스 퍼멘텀 hy7301 및 이를 유효성분으로 함유하는 제품 | |
| CN103857297A (zh) | 水果饮料中的益生菌 | |
| Vitheejongjaroen et al. | Antioxidant activity of Bifidobacterium animalis MSMC83 and its application in set-style probiotic yoghurt | |
| JP6495869B2 (ja) | ヒアルロン酸産生促進能を有する乳酸菌 | |
| JP4891255B2 (ja) | ワイン発酵もろみ由来の免疫調節作用を有する乳酸菌 | |
| JP5425337B1 (ja) | 新規乳酸菌 | |
| KR20200145941A (ko) | 락토바실러스 카제이 hy2782를 유효성분으로 함유하는 미세먼지에 의한 밀착연접단백질 관련 질환의 예방 또는 개선용 식품조성물 | |
| JP6345642B2 (ja) | 新規乳酸菌 | |
| KR101969906B1 (ko) | 락토바실러스 카제이 hy2782를 유효성분으로 함유하는 미세먼지로 인한 면역 불균형을 해소하여 면역 항상성을 유지하기 위한 조성물 | |
| KR102587892B1 (ko) | 홍삼을 영양원으로 이용하여 균주의 특성이 강화되고 면역 기능이 증진된 락토바실러스 파라카제이 hy7017 균주 및 이의 용도 | |
| Ricci et al. | Cocoa powder as delivery medium for probiotic Lactobacillus strains | |
| JP7663322B2 (ja) | ビフィズス菌増殖促進剤 | |
| JP7013419B2 (ja) | 炎症性サイトカインの産生誘導活性は低いが抗炎症性サイトカインの産生誘導活性が高いビフィズス菌 | |
| JP5980785B2 (ja) | 新規ビフィズス菌及びその利用 | |
| JP2018113892A (ja) | 抗炎症性サイトカイン産生誘導能力を有するビフィズス菌 | |
| JP6836298B1 (ja) | 乳酸菌及び納豆菌を含む組成物 | |
| JP2009254236A (ja) | 新規乳酸菌並びに新規乳酸菌を利用した飲食品及び免疫賦活剤 | |
| JP2022117889A (ja) | 酸化ストレス抵抗性付与能(il-8抑制能)及び小腸幹細胞遺伝子調節機能を有する乳酸菌 | |
| HK40060714A (en) | Bifidobacteria having low activity of inducing inflammatory cytokine production but high activity of inducing anti-inflammatory cytokine production | |
| HK1181420B (en) | Lactobacillus classified as lactobacillus plantarum and use thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| DPE2 | Request for preliminary examination filed before expiration of 19th month from priority date (pct application filed from 20040101) | ||
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 16868647 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 16868647 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |