WO2017056795A1 - クリーニングブレード - Google Patents
クリーニングブレード Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2017056795A1 WO2017056795A1 PCT/JP2016/074674 JP2016074674W WO2017056795A1 WO 2017056795 A1 WO2017056795 A1 WO 2017056795A1 JP 2016074674 W JP2016074674 W JP 2016074674W WO 2017056795 A1 WO2017056795 A1 WO 2017056795A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- cleaning blade
- blade
- plate
- conductive
- mass
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03G—ELECTROGRAPHY; ELECTROPHOTOGRAPHY; MAGNETOGRAPHY
- G03G21/00—Arrangements not provided for by groups G03G13/00 - G03G19/00, e.g. cleaning, elimination of residual charge
- G03G21/0005—Arrangements not provided for by groups G03G13/00 - G03G19/00, e.g. cleaning, elimination of residual charge for removing solid developer or debris from the electrographic recording medium
- G03G21/0011—Arrangements not provided for by groups G03G13/00 - G03G19/00, e.g. cleaning, elimination of residual charge for removing solid developer or debris from the electrographic recording medium using a blade; Details of cleaning blades, e.g. blade shape, layer forming
- G03G21/0017—Details relating to the internal structure or chemical composition of the blades
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a cleaning blade, and more particularly to a cleaning blade used in an electrophotographic image forming apparatus.
- a cleaning blade is used to clean the surface of an image carrier such as a photoreceptor or an intermediate transfer belt.
- the edge portion at the tip of the blade portion is pressed against the surface of the image carrier or the intermediate transfer belt, which is a counterpart member. Residual toner remaining on the surface of the mating member is scraped off and removed by the sliding contact between the mating member and the edge portion.
- a cleaning blade for example, a cleaning having a metal support having a plate-like portion and a blade portion made of plate-like polyurethane rubber bonded to the front end side of the plate-like portion via an adhesive layer. Blades are widely known.
- Prior Patent Document 1 describes a conductive composition containing a polyol, a urethane polymer, and a borate ester compound as a conductive elastic layer forming material in a cleaning blade.
- the residual toner is usually in a charged state. Therefore, an electrostatic repulsive force is generated between the toners collected in the toner collection box. Therefore, there is a case where the toner does not fit in the toner collection box and the toner overflows from the toner collection box.
- a method of scraping off the residual toner with a cleaning blade while discharging can be considered.
- a method for making the blade portion conductive a method of adding carbon black or an ionic conductive agent can be considered.
- the present invention has been made in view of the above background, and it is an object of the present invention to provide a cleaning blade that hardly pollutes the counterpart member, hardly hinders the reactivity of the urethane catalyst, and can scrape off the remaining toner while removing electricity. To do.
- One aspect of the present invention is a cleaning blade used for removing residual toner remaining on the surface of a counterpart member by sliding contact with the counterpart member in an image forming apparatus employing an electrophotographic method
- a conductive support having a plate-like part, a polyurethane rubber blade part formed on the plate-like part, and a conductive adhesive containing a conductive agent interposed between the plate-like part and the blade part. And has a layer, The said blade part exists in the cleaning blade containing 0.3 mass% or more and less than 10 mass% potassium salt.
- the cleaning blade contains a potassium salt in the specific range in the blade portion. Therefore, it can suppress that the potassium salt which is an ionic conductive agent bleeds and blooms on the surface of a blade part. Therefore, the cleaning blade hardly contaminates the mating member.
- potassium salts are unlikely to inhibit the reactivity of the urethane catalyst like ionic conductive agents such as LiTFSI and LiFSI. Therefore, the above-mentioned cleaning blade is hardened even under the conventional manufacturing conditions, the adhesion of the blade part to the plate-like part is secured, and the rubber elasticity of the blade part by polyurethane rubber can be sufficiently secured. it can.
- the cleaning blade Since the cleaning blade has high adhesion between the plate-like portion of the blade portion and the conductive adhesive layer, when the cleaning blade is used, it is difficult for floating due to peeling or the like to occur at the interface between the blade portion and the conductive adhesive layer. . Therefore, the cleaning blade can suppress an increase in contact electric resistance between the blade portion and the conductive adhesive layer. Therefore, according to the cleaning blade, the conductive path by the blade portion, the conductive adhesive layer, and the conductive support is reliably ensured. Therefore, the cleaning blade is incorporated in the image forming apparatus while being grounded, so that the toner can be scraped and removed by utilizing the rubber elasticity of the polyurethane rubber of the blade portion while discharging the residual toner.
- the present invention it is possible to provide a cleaning blade that hardly pollutes the counterpart member, hardly hinders the reactivity of the urethane catalyst, and can scrape off the remaining toner while removing electricity.
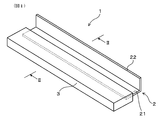
- FIG. 2 is a perspective view of a cleaning blade of Example 1.
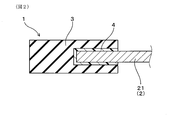
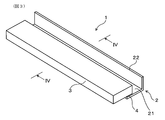
- FIG. It is the figure which showed typically the II-II line cross section in FIG. 10 is a perspective view of a cleaning blade of Example 2.
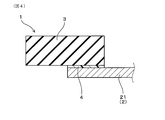
- FIG. 4 is a diagram schematically showing a cross section taken along line IV-IV in FIG. 3.
- the cleaning blade is used to remove residual toner remaining on the surface of the mating member by sliding contact with the mating member in the image forming apparatus employing an electrophotographic system.
- the image forming apparatus include image forming apparatuses such as a copying machine, a printer, a facsimile machine, a multifunction machine, and an on-demand printing machine that employ an electrophotographic system using a charged image.
- the counterpart member include an image carrier such as a photosensitive drum, an intermediate transfer belt, and the like.
- the intermediate transfer belt is used to primarily transfer the toner image carried on the image carrier to the belt, and then secondarily transfer the toner image from the belt to a transfer material such as paper.
- the cleaning blade is a sliding contact portion for sliding the edge portion of the tip of the blade portion into contact with the mating member, and is brought into contact with the surface of the mating member in operation, It can be used to scrape off and remove residual toner on the surface of the mating member that has been carried to the sliding contact portion.
- the cleaning blade has a conductive support having a plate-like portion.
- the conductive support can be composed of a conductive material such as a metal material.
- the plate-like portion can have a shape such as a rectangular shape having a predetermined thickness.
- the length of the plate-like portion in the longitudinal direction can be preferably 230 to 360 mm.
- the thickness of the plate-like portion can be preferably 1.2 to 2 mm.
- the conductive support is connected to a plate-like portion, and can be configured to have an attachment portion for attachment to a member of the image forming apparatus.
- the conductive support may have a shape such as a cross-sectional “L” shape as a whole.
- the cleaning blade has a polyurethane rubber blade portion formed in a plate-like portion.
- the blade portion can be formed on the tip end side in the short direction of the plate-like portion.
- the tip of the plate-like part may be embedded in the blade part.
- the blade portion may be bonded to any one plate surface side of the plate-like portion. In this case, a part of the blade part may be bonded to the tip surface of the plate-like part.
- the blade part contains a potassium salt. That is, in the cleaning blade, the blade portion is made conductive by the potassium salt. Potassium salt functions as an ionic conductive agent. For this reason, the cleaning blade can easily stabilize the volume electrical resistance of the blade portion as compared with the case where carbon black or the like as an electronic conductive agent is added to the blade portion. In addition, the cleaning blade is unlikely to deteriorate in compression set and elongation at the blade portion, and is difficult to increase in hardness.
- the content of the potassium salt in the blade portion is set to 0.3% by mass or more.
- content of potassium salt is a ratio (%) of the mass of the potassium salt contained in a blade part with respect to the whole mass of a blade part.
- the content of the potassium salt in the blade portion is preferably 0.5% by mass or more, more preferably 0.7% by mass or more, and further preferably 1% by mass or more from the viewpoint of ensuring the effect of addition. be able to.
- the content of the potassium salt in the blade portion is less than 10% by mass.
- the content of the potassium salt in the blade portion is preferably 9% by mass or less, more preferably 8% by mass or less, and still more preferably 7% from the viewpoint of the effect of addition, the balance of potassium salt bleed, bloom, production cost, and the like. It can be set to not more than mass%, more preferably not more than 6 mass%, most preferably not more than 5 mass%.
- the anion in the potassium salt is, for example, CF 3 SO 2 C 4 F 9 SO 2 N ⁇ ⁇ nonafluoro-N-[(trifluoromethane) sulfonyl] butanesulfonylamide anion>, (CF 3 SO 2 ) 2 N ⁇ ⁇ bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide anion>, (FSO 2 ) 2 N ⁇ ⁇ bis (fluorosulfonyl) imidoimide anion>, C 28 H 20 BO 6 ⁇ , AlCl 4 ⁇ , Al 2 Cl 7 ⁇ , NO 3 ⁇ , BF 4 ⁇ , PF 6 ⁇ , CH 3 COO ⁇ , CF 3 COO ⁇ , CF 3 SO 3 ⁇ , (CF 3 SO 2 ) 3 C ⁇ , AsF 6 ⁇ , SbF 6 ⁇ , F (HF) N -, CF 3 CF 2 CF 2 CF 2 CF
- the blade portion may contain one or more potassium salts.
- the anion in the potassium salt is preferably (CF 3 SO 2 ) 2 N ⁇ , CF 3 SO 2 C 4 F 9 SO 2 N ⁇ , C 28 H 20 from the viewpoint of ensuring the above effect.
- BO 6 - may be.
- the cleaning blade is interposed between the plate-like portion and the blade portion, and has a conductive adhesive layer containing a conductive agent.
- the conductive adhesive layer not only bonds the conductive blade portion and the conductive support, but also has a role of electrically connecting the two.
- the conductive adhesive layer is formed on one plate surface of the plate-like portion, the other plate surface, and the blade portion facing each plate surface. It can be interposed between the parts.
- the conductive adhesive layer can be further interposed between the tip surface of the plate-like portion and the portion of the blade portion facing the tip surface.
- the conductive adhesive layer has either one plate surface of the plate-like portion and the blade portion facing the plate surface. It can be interposed between the parts. In this case, the conductive adhesive layer can be further interposed between the tip surface of the plate-like portion and a part of the surface of the blade portion.
- the conductive agent contained in the conductive adhesive layer may be either an electronic conductive agent or an ionic conductive agent. More specifically, examples of the electronic conductive agent include carbon black, carbon nanotube, graphene, metal fine particles, metal oxide fine particles, and the like. These can be used alone or in combination of two or more. Examples of the ionic conductive agent include quaternary ammonium salts, alkali metal salts, alkaline earth metal salts, and the like. These can be used alone or in combination of two or more. As the conductive agent, an electronic conductive agent can be preferably used from the viewpoint of dispersibility in the conductive adhesive layer and the like. Specifically, carbon black can be suitably used as the electronic conductive agent from the viewpoints of dispersibility in the conductive adhesive layer and ease of dispersion control.
- the conductive adhesive layer is preferably 0.1% by mass or more, more preferably 0.5% by mass or more, and even more preferably 1% by mass or more from the viewpoint of imparting conductivity. Can be contained.
- the conductive adhesive layer specifically contains, for example, a conductive agent from the viewpoint of adhesion and the like, preferably 10% by mass or less, more preferably 8% by mass or less, and further preferably 5% by mass or less. be able to.
- the conductive adhesive layer can be composed of a resin adhesive containing a conductive agent.
- the resin adhesive any thermosetting resin adhesive or thermoplastic resin adhesive can be used as long as the blade portion made of polyurethane rubber and the conductive support can be bonded to each other.
- a thermosetting resin adhesive is preferable from the viewpoint of adhesiveness.
- Specific examples of the thermosetting resin adhesive include an epoxy resin adhesive and an acrylic resin adhesive.
- the thickness of the conductive adhesive layer is preferably 0.1 ⁇ m or more, more preferably 0.3 ⁇ m or more, and even more preferably 0.5 ⁇ m or more from the viewpoint of ensuring adhesion.
- the thickness of the conductive adhesive layer is preferably 20 ⁇ m or less, more preferably 15 ⁇ m or less, and even more preferably 10 ⁇ m or less, from the viewpoint of processing stability.
- the volume electrical resistance of the conductive adhesive layer may be equal to or less than the volume electrical resistance of the blade portion. In this case, even if the conductive adhesive layer thinner than the blade portion has a thickness variation, it can be a variation in the volume electrical resistance of the entire cleaning blade. Therefore, it becomes easy to reduce the difference in volume electric resistance between the cleaning blades.
- the volume electrical resistance of the conductive adhesive layer can be preferably smaller than the volume electrical resistance of the blade portion.
- the above-mentioned cleaning blade has a volume electric resistance of preferably less than 1 ⁇ 10 10 ⁇ , more preferably 9 ⁇ 10 9 ⁇ or less, and further preferably from the viewpoint of being advantageous for scraping off residual toner while removing electricity. It can be 8 ⁇ 10 9 ⁇ or less.
- Example 1 The cleaning blade of Example 1 will be described with reference to FIGS. As shown in FIG. 1 and FIG. 2, the cleaning blade 1 of this example has a residual toner (if only toner is left) remaining on the surface of the mating member by sliding contact with the mating member in the image forming apparatus employing the electrophotographic system. In addition, toner external additives are also included).
- the counterpart member is specifically a photosensitive drum in an electrophotographic image forming apparatus.
- the cleaning blade 1 is interposed between the conductive support 2 having the plate-like portion 21, the polyurethane rubber blade portion 3 formed on the plate-like portion 21, and the plate-like portion 21 and the blade portion 3. And a conductive adhesive layer 4 containing a conductive agent (not shown).
- the blade part 3 contains a potassium salt (not shown) of 0.3 mass% or more and less than 10 mass%.
- the conductive support 2 has an attachment portion 22 that is integrally connected to the plate-like portion 21.
- the attachment part 22 is a part for attaching to a member of the image forming apparatus.
- the conductive support 2 is formed in a cross-sectional “L” shape as a whole.
- the blade part 3 is formed on the front end side in the short direction of the plate-like part 21.
- the front end portion of the plate-like portion 21 is embedded in the blade portion 3.
- the conductive adhesive layer 4 is interposed between one plate surface of the plate-like portion 21, the other plate surface, the portion of the blade portion 3 facing each plate surface, and the tip surface of the plate-like portion 21; It is also interposed between the blade portion 3 and the tip surface.
- Example 2 The cleaning blade of Example 2 will be described with reference to FIGS. As shown in FIGS. 3 and 4, in the cleaning blade 1 of this example, the blade portion 3 is bonded to one plate surface side of the plate-like portion 21. The conductive adhesive layer 4 is interposed between one plate surface of the plate-like portion 21 and the portion of the blade portion 3 facing the plate surface. Other configurations are the same as those of the first embodiment.
- polybutylene adipate (Tosoh Corp., “Nipporan 4010”): 87 parts by mass, 1,4-butanediol (Mitsubishi Chemical Corp.) and trimethylolpropane (Guangei Perstorp)
- Low molecular weight polyol mixed at 6 4: 13 parts by mass and triethylenediamine as a catalyst (manufactured by Tosoh Corporation): 0.01 part by mass in a nitrogen atmosphere at 80 ° C. for 1 hour.
- a curing agent solution having a hydroxyl value (OHV) of 210 KOHmg / g
- the above-prepared main agent solution, curing agent solution and ionic conductive agent are blended so that the curing agent solution is 94 parts by mass with respect to 100 parts by mass of the main agent solution, and the ionic conductive agent has a content shown in Table 1.
- the mixture was mixed at 60 ° C. for 3 minutes in a vacuum atmosphere and sufficiently degassed. This prepared each urethane rubber composition used for formation of a blade part in each cleaning blade.
- urethane rubber composition ⁇ Curability of urethane rubber composition> Each urethane rubber composition was applied to a sheet having a thickness of 2 mm and heated at 130 ° C. When the urethane rubber composition is cured in 1 minute, the reactivity of the urethane catalyst by the ionic conductive agent is not hindered, and the curability of the urethane rubber composition is good under the conventional production conditions. did. Further, when the urethane rubber composition does not cure even after 5 minutes, the reactivity of the urethane catalyst by the ionic conductive agent is hindered, and the urethane rubber composition has poor curability under the conventional production conditions. C ”.
- An epoxy resin adhesive (“Aronmite AS-60” manufactured by Toagosei Co., Ltd.) is an electronic conductive agent so that the content of the conductive agent in the formed adhesive layer is the value shown in Table 1. Carbon black (“# 3030B” manufactured by Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation) was added and mixed well for 30 minutes. Thereby, each adhesive used for forming an adhesive layer in each cleaning blade was prepared. For some adhesives, no conductive agent was added for comparison.
- a mold composed of an upper mold and a lower mold was prepared.
- the upper mold and the lower mold are brought close to each other and clamped to form a cavity having a size corresponding to two substantially long plate-like blade portions.
- the cavity is provided with two opposing storage portions.
- Each of these accommodating portions is configured such that a plate-like portion of a conductive support made of a long metal plate (plate thickness: 2 mm) bent into an L-shaped cross section can be arranged.
- a predetermined adhesive was applied to the front and back plate-like surfaces and the tip surface of the tip portion of the plate-like portion of the conductive support so as to have the thickness of the adhesive layer shown in Table 1 described later.
- coating width was made into the range to 2 mm from the front end surface of a plate-shaped part to a base end side.
- a conductive support coated with an adhesive is set in each housing portion of the mold, and after clamping, a predetermined urethane rubber composition is injected into the cavity and heated at 130 ° C. for 5 minutes. Thus, the urethane rubber composition was cured. Thereafter, the molded body was taken out from the mold and cut into two pieces to have a predetermined size. This produced a cleaning blade sample in which the blade portion (thickness 2 mm) made of polyurethane rubber and the conductive support were integrated via the adhesive layer.
- the curability of the urethane rubber composition was “C” evaluation, a cleaning blade sample was prepared by heating for more than 5 minutes until it was cured at 130 ° C.
- Table 1 summarizes the detailed configuration and evaluation results of each cleaning blade.
- sample 2C the content of potassium salt in the blade part exceeds the specified range. Therefore, the sample 2C cannot suppress the bleed and bloom of the ion conductive agent.
- Samples 3C to 6C use ionic conductive agents other than potassium salts. Therefore, in these samples, the reactivity of the urethane catalyst is inhibited, and the curability of the urethane rubber composition is poor under the conventional production conditions.
- Sample 7C has no conductivity because the adhesive layer does not contain a conductive agent. Therefore, it is difficult for sample 7C to scrape off the residual toner while removing the charge.
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Cleaning In Electrography (AREA)
Abstract
相手部材を汚染し難く、ウレタン触媒の反応性を阻害し難く、残留トナーを除電しながら掻き取ることが可能なクリーニングブレード(1)を提供する。クリーニングブレード(1)は、電子写真方式を採用する画像形成装置内の相手部材との摺接によって相手部材の表面に残留する残留トナーを除去するために用いられる。クリーニングブレード(1)は、板状部(21)を有する導電性支持体(2)と、板状部(21)に形成されたポリウレタンゴム製のブレード部(3)と、板状部(21)とブレード部(3)との間に介在し、導電剤を含有する導電性接着層(4)とを有している。ブレード部(3)は、0.3質量%以上10質量%未満のカリウム塩を含有している。
Description
本発明は、クリーニングブレードに関し、さらに詳しくは、電子写真方式の画像形成装置に用いられるクリーニングブレードに関する。
電子写真方式の画像形成装置では、例えば、感光体等の像担持体や中間転写ベルトの表面をクリーニングするためにクリーニングブレードが用いられている。クリーニングブレードは、ブレード部における先端のエッジ部が、相手部材である像担持体や中間転写ベルトの表面に押し付けられている。相手部材とエッジ部との摺接により、相手部材表面に残留する残留トナーが掻き取られて除去される。
従来のクリーニングブレードとしては、例えば、板状部を有する金属製の支持体と、板状部における先端側に、接着層を介して接着された板状のポリウレタンゴムからなるブレード部とを有するクリーニングブレードが広く知られている。
なお、先行する特許文献1には、クリーニングブレードにおける導電性弾性層形成材料として、ポリオール、ウレタンポリマー、ホウ酸エステル化合物を含有する導電性組成物が記載されている。
近年、画像形成装置では、高画質化の要請から、球形かつ小径のトナーが使用されるようになっている。そのため、相手部材表面とブレード部のエッジ部との間に生じた僅かな隙間を通じてトナーがすり抜けやすい。それ故、ブレード部のゴム弾性を利用し、残留トナーをトナー回収ボックス内に効率よく掻き落とすことが難しくなってきている。
画像形成装置において、残留トナーは、通常、荷電された状態にある。そのため、トナー回収ボックス内に回収されたトナー同士の間には、静電気的な反発力が生じる。それ故、トナー回収ボックス内にトナーが収まらず、トナー回収ボックスからトナーが溢れ出す場合がある。
上記問題に対処するため、クリーニングブレードにて残留トナーを除電しながら掻き取る方法が考えられる。そのためには、ブレード部を導電化する必要がある。ブレード部を導電化する方法としては、カーボンブラックやイオン導電剤を添加する方法が考えられる。
しかしながら、カーボンブラックは、分散状態の制御が難しく、ブレード部の体積電気抵抗を安定化することが難しい。また、ブレード部にカーボンブラックを添加すると、ブレード部の圧縮永久ひずみや永久伸びが悪化し、硬度上昇によってポリウレタンゴムのゴム弾性が損なわれ、トナーの掻き取りに支障が出る。
一方、ブレード部に、イオン液体を添加すると、ブリードが生じやすく、ブリードしたイオン液体により相手部材を汚染するという問題が生じる。また、リチウムビス(トリフルオロメタンスルホニル)イミド(LiTFSI)や、リチウムビス(フルオロスルホニル)イミド(LiFSI)などの一般的なイオン導電剤は、ブレード部を形成する際にウレタン触媒の反応性を悪化させる。そのため、従来の製造条件では、ブレード部の硬化性が低下してブレード部の板状部への接着性が悪くなり、その結果、残留トナーを除電しながら掻き取ることが可能なクリーニングブレードを得ることができない。
本発明は、上記背景に鑑みてなされたものであり、相手部材を汚染し難く、ウレタン触媒の反応性を阻害し難く、残留トナーを除電しながら掻き取ることが可能なクリーニングブレードを提供しようとするものである。
本発明の一態様は、電子写真方式を採用する画像形成装置内の相手部材との摺接によって上記相手部材の表面に残留する残留トナーを除去するために用いられるクリーニングブレードであって、
板状部を有する導電性支持体と、上記板状部に形成されたポリウレタンゴム製のブレード部と、上記板状部と上記ブレード部との間に介在し、導電剤を含有する導電性接着層とを有しており、
上記ブレード部は、0.3質量%以上10質量%未満のカリウム塩を含有する、クリーニングブレードにある。
板状部を有する導電性支持体と、上記板状部に形成されたポリウレタンゴム製のブレード部と、上記板状部と上記ブレード部との間に介在し、導電剤を含有する導電性接着層とを有しており、
上記ブレード部は、0.3質量%以上10質量%未満のカリウム塩を含有する、クリーニングブレードにある。
上記クリーニングブレードは、ブレード部に上記特定範囲でカリウム塩を含有している。そのため、イオン導電剤であるカリウム塩がブレード部の表面にブリード、ブルームするのを抑制することができる。したがって、上記クリーニングブレードは、相手部材を汚染し難い。また、カリウム塩は、LiTFSIやLiFSIなどのイオン導電剤のように、ウレタン触媒の反応性を阻害し難い。そのため、上記クリーニングブレードは、従来の製造条件であってもブレード部が硬化し、ブレード部の板状部への接着性が確保され、ブレード部のポリウレタンゴムによるゴム弾性を十分に確保することができる。そして、上記クリーニングブレードは、ブレード部の板状部と導電性接着層との密着性が高いため、クリーニングブレードの使用時に、ブレード部と導電性接着層との界面に剥離による浮き等が生じ難い。そのため、上記クリーニングブレードは、ブレード部と導電性接着層との間における接触電気抵抗の増大を抑制することが可能となる。したがって、上記クリーニングブレードによれば、ブレード部、導電性接着層、および、導電性支持体による導電経路が確実に確保される。それ故、上記クリーニングブレードは、画像形成装置に接地した状態で組み込まれることにより、残留トナーを除電しながら、ブレード部のポリウレタンゴムによるゴム弾性を利用してトナーを掻き取り除去することができる。
よって、本発明によれば、相手部材を汚染し難く、ウレタン触媒の反応性を阻害し難く、残留トナーを除電しながら掻き取ることが可能なクリーニングブレードを提供することができる。
上記クリーニングブレードは、電子写真方式を採用する画像形成装置内の相手部材との摺接によって相手部材の表面に残留する残留トナーを除去するために用いられる。画像形成装置としては、具体的には、帯電像を用いる電子写真方式を採用する複写機、プリンター、ファクシミリ、複合機、オンデマンド印刷機等の画像形成装置を例示することができる。また、相手部材としては、感光ドラム等の像担持体や中間転写ベルトなどを例示することができる。なお、中間転写ベルトは、像担持体に担持されたトナー像を当該ベルトに一次転写した後、このトナー像を当該ベルトから用紙等の転写材へ二次転写するためのものである。上記クリーニングブレードは、より具体的には、ブレード部の先端のエッジ部が相手部材と摺接させるための摺接部とされ、動作する相手部材の表面に摺り合った状態で接触させることにより、摺接部まで運ばれてきた相手部材表面の残留トナーを掻き取って除去するように使用することができる。
上記クリーニングブレードは、板状部を有する導電性支持体を有している。導電性支持体は、金属材料等の導電性材料から構成することができる。板状部は、具体的には、例えば、所定の厚みを有する長方形状等の形状を有することができる。この場合、板状部は、長手方向の長さを、好ましくは230~360mmとすることができる。また、板状部の厚みは、好ましくは1.2~2mmとすることができる。導電性支持体は、より具体的には、例えば、板状部と繋がっており、画像形成装置の部材に取り付けるための取付部を有する構成とすることができる。この場合、導電性支持体は、全体として断面「L」字状等の形状を有することができる。
上記クリーニングブレードは、板状部に形成されたポリウレタンゴム製のブレード部を有している。ブレード部は、具体的には、板状部の短手方向の先端部側に形成することができる。板状部の先端部は、ブレード部に埋設されていてもよい。また、板状部のいずれか一方の板面側にブレード部が接着されていてもよい。この場合、ブレード部の一部が板状部の先端面に接着されていてもよい。
ブレード部は、カリウム塩を含有している。つまり、上記クリーニングブレードにおいて、ブレード部が、カリウム塩によって導電化されている。カリウム塩はイオン導電剤として機能する。そのため、上記クリーニングブレードは、ブレード部に電子導電剤であるカーボンブラック等が添加されている場合に比べ、ブレード部の体積電気抵抗を安定化させやすい。また、上記クリーニングブレードは、ブレード部の圧縮永久ひずみや永久伸びが悪化し難く、硬度上昇も生じ難い。
但し、ブレード部におけるカリウム塩の含有量が0.3質量%未満になると、添加による導電性付与効果が得られなくなる。よって、ブレード部におけるカリウム塩の含有量を0.3質量%以上とする。なお、カリウム塩の含有量は、ブレード部の全体質量に対するブレード部に含まれるカリウム塩の質量の割合(%)である。ブレード部におけるカリウム塩の含有量は、添加による効果を確実なものとする観点から、好ましくは0.5質量%以上、より好ましくは0.7質量%以上、さらに好ましくは1質量%以上とすることができる。一方、ブレード部におけるカリウム塩の含有量が10質量%以上になると、カリウム塩がブリード、ブルームする傾向が見られ、カリウム塩の使用量増大によって製造コストも上昇する。よって、ブレード部におけるカリウム塩の含有量を10質量%未満とする。ブレード部におけるカリウム塩の含有量は、添加による効果、カリウム塩のブリード、ブルーム、製造コスト等のバランスなどの観点から、好ましくは9質量%以下、より好ましくは8質量%以下、さらに好ましくは7質量%以下、さらにより好ましくは6質量%以下、もっとも好ましくは5質量%以下とすることができる。
上記カリウム塩におけるアニオンは、具体的には、例えば、CF3SO2C4F9SO2N-<ノナフルオロ-N-[(トリフルオロメタン)スルホニル]ブタンスルホニルアミドアニオン>、(CF3SO2)2N-<ビス(トリフルオロメタンスルホニル)イミドアニオン>、(FSO2)2N-<ビス(フルオロスルホニル)イミドイミドアニオン>、C28H20BO6
-、AlCl4
-、Al2Cl7
-、NO3
-、BF4
-、PF6
-、CH3COO-、CF3COO-、CF3SO3
-、(CF3SO2)3C-、AsF6
-、SbF6
-、F(HF)N-、CF3CF2CF2CF2SO3
-、(CF3CF2SO2)2N-、CF3CF2CF2COO-、(C4F9SO2)2N-、CF2(CF2SO2)2N-、CF3SO2NH2
-などを例示することができる。これらは1種または2種以上併用することができる。また、ブレード部には、1種または2種以上のカリウム塩が含まれていてもよい。上記カリウム塩におけるアニオンは、上記効果を確実なものとするなどの観点から、好ましくは、(CF3SO2)2N-、CF3SO2C4F9SO2N-、C28H20BO6
-であるとよい。
上記クリーニングブレードは、板状部とブレード部との間に介在し、導電剤を含有する導電性接着層を有している。導電性接着層は、導電化されたブレード部と導電性支持体とを接着するだけでなく、両者を電気的に接続する役割を有している。導電性接着層は、具体的には、板状部の先端部がブレード部に埋設されている場合、板状部における一方の板面、他方の板面、各板面に対向するブレード部の部分との間に介在することができる。この場合、導電性接着層は、さらに、板状部の先端面と、当該先端面に対向するブレード部の部分との間に介在することもできる。また、導電性接着層は、板状部のいずれか一方の板面側にブレード部が接着されている場合、板状部のいずれか一方の板面と、当該板面に対向するブレード部の部分との間に介在することができる。この場合、導電性接着層は、さらに、板状部の先端面と、ブレード部の表面の一部との間に介在することもできる。
導電性接着層に含まれる導電剤は、具体的には、電子導電剤、イオン導電剤のいずれであってよい。電子導電剤としては、より具体的には、例えば、カーボンブラック、カーボンナノチューブ、グラフェン、金属微粒子、金属酸化物微粒子等を例示することができる。これらは1種または2種以上併用することができる。イオン導電剤としては、4級アンモニウム塩、アルカリ金属塩、アルカリ土類金属塩等を例示することができる。これらは1種または2種以上併用することができる。導電剤としては、導電性接着層への分散性等の観点から、好ましくは、電子導電剤を好適に用いることができる。電子導電剤としては、導電性接着層への分散性、分散制御のしやすさ等の観点から、具体的には、カーボンブラックを好適に用いることができる。
導電性接着層は、具体的には、例えば、導電性付与の観点から、導電剤を、好ましくは0.1質量%以上、より好ましくは0.5質量%以上、さらに好ましくは1質量%以上含有することができる。一方、導電性接着層は、具体的には、例えば、接着性などの観点から、導電剤を、好ましくは10質量%以下、より好ましくは8質量%以下、さらに好ましくは5質量%以下含有することができる。
導電性接着層は、具体的には、導電剤を含有する樹脂接着剤より構成することができる。樹脂接着剤は、ポリウレタンゴム製のブレード部と導電性支持体とを接着させることができれば、いずれの熱硬化性樹脂接着剤、熱可塑性樹脂接着剤でも用いることができる。樹脂接着剤としては、接着性などの観点から、熱硬化性樹脂接着剤が好適である。熱硬化性樹脂接着剤としては、具体的には、例えば、エポキシ樹脂系接着剤、アクリル樹脂系接着剤などを例示することができる。
導電性接着層の厚みは、接着性確保などの観点から、好ましくは0.1μm以上、より好ましくは0.3μm以上、さらに好ましくは0.5μm以上とすることができる。また、導電性接着層の厚みは、加工安定性などの観点から、好ましくは20μm以下、より好ましくは15μm以下、さらに好ましくは10μm以下とすることができる。
上記クリーニングブレードにおいて、導電性接着層の体積電気抵抗は、ブレード部の体積電気抵抗以下であるとよい。この場合には、ブレード部よりも薄い導電性接着層に厚みばらつきがある場合でも、クリーニングブレード全体の体積電気抵抗のばらつきとすることができる。そのため、クリーニングブレード毎の体積電気抵抗の差を小さくしやすくなる。導電性接着層の体積電気抵抗は、好ましくは、ブレード部の体積電気抵抗よりも小さくすることができる。
上記クリーニングブレードは、残留トナーを除電しながら掻き取るのに有利であるなどの観点から、体積電気抵抗を、好ましくは1×1010Ω未満、より好ましくは9×109Ω以下、さらに好ましくは8×109Ω以下とすることができる。
なお、上述した各構成は、上述した各作用効果等を得るなどのために必要に応じて任意に組み合わせることができる。
以下、実施例のクリーニングブレードについて、図面を用いて説明する。なお、同一部材については同一の符号を用いて説明する。
(実施例1)
実施例1のクリーニングブレードについて、図1、図2を用いて説明する。図1、図2に示されるように、本例のクリーニングブレード1は、電子写真方式を採用する画像形成装置内の相手部材との摺接によって相手部材の表面に残留する残留トナー(トナーのみならず、トナー外添剤も含む)を除去するために用いられるものである。本例では、相手部材は、具体的には、電子写真方式の画像形成装置内における感光ドラムである。
実施例1のクリーニングブレードについて、図1、図2を用いて説明する。図1、図2に示されるように、本例のクリーニングブレード1は、電子写真方式を採用する画像形成装置内の相手部材との摺接によって相手部材の表面に残留する残留トナー(トナーのみならず、トナー外添剤も含む)を除去するために用いられるものである。本例では、相手部材は、具体的には、電子写真方式の画像形成装置内における感光ドラムである。
クリーニングブレード1は、板状部21を有する導電性支持体2と、板状部21に形成されたポリウレタンゴム製のブレード部3と、板状部21とブレード部3との間に介在し、導電剤(不図示)を含有する導電性接着層4とを有している。ブレード部3は、0.3質量%以上10質量%未満のカリウム塩(不図示)を含有している。
本例では、導電性支持体2は、板状部21と一体的に繋がる取付部22を有している。取付部22は、画像形成装置の部材に取り付けるための部位である。導電性支持体2は、全体として断面「L」字状に形成されている。ブレード部3は、板状部21の短手方向の先端部側に形成されている。板状部21の先端部は、ブレード部3に埋設されている。導電性接着層4は、板状部21における一方の板面、他方の板面、各板面に対向するブレード部3の部分との間に介在するとともに、板状部21の先端面と、当該先端面に対向するブレード部3の部分との間にも介在している。
(実施例2)
実施例2のクリーニングブレードについて、図3、図4を用いて説明する。図3、図4に示されるように、本例のクリーニングブレード1は、板状部21の一方の板面側にブレード部3が接着されている。導電性接着層4は、板状部21の一方の板面と、当該板面に対向するブレード部3の部分との間に介在している。その他の構成は、実施例1と同様である。
実施例2のクリーニングブレードについて、図3、図4を用いて説明する。図3、図4に示されるように、本例のクリーニングブレード1は、板状部21の一方の板面側にブレード部3が接着されている。導電性接着層4は、板状部21の一方の板面と、当該板面に対向するブレード部3の部分との間に介在している。その他の構成は、実施例1と同様である。
以下、実験例を用いてより具体的に説明する。
<ウレタンゴム組成物の調製>
80℃にて1時間、真空脱泡したポリブチレンアジペート(PBA)(東ソー社製、「ニッポラン4010」):44質量部と、4,4′-ジフェニルメタンジイソシアネート(MDI)(東ソー社製、「ミリオネートMT」):56質量部とを混合し、窒素雰囲気下、80℃で3時間反応させることにより、ウレタンプレポリマーを含む主剤液を調製した。なお、主剤液中のNCO%(質量%)は、17.0%である。
80℃にて1時間、真空脱泡したポリブチレンアジペート(PBA)(東ソー社製、「ニッポラン4010」):44質量部と、4,4′-ジフェニルメタンジイソシアネート(MDI)(東ソー社製、「ミリオネートMT」):56質量部とを混合し、窒素雰囲気下、80℃で3時間反応させることにより、ウレタンプレポリマーを含む主剤液を調製した。なお、主剤液中のNCO%(質量%)は、17.0%である。
また、ポリブチレンアジペート(PBA)(東ソー社製、「ニッポラン4010」):87質量部と、1,4-ブタンジオール(三菱化学社製)とトリメチロールプロパン(広栄パーストープ社製)とが重量比6:4にて混合されてなる低分子量ポリオール:13質量部と、触媒としてのトリエチレンジアミン(東ソー社製):0.01質量部とを、窒素雰囲気下、80℃にて1時間混合することにより、水酸基価(OHV)が210(KOHmg/g)の硬化剤液を調製した。
次いで、上記調製した主剤液と硬化剤液とイオン導電剤とを、主剤液100質量部に対して硬化剤液94質量部、イオン導電剤が表1に示される含有量となるように配合し、真空雰囲気下、60℃で3分間混合し、十分に脱泡した。これにより、各クリーニングブレードにおけるブレード部の形成に用いる各ウレタンゴム組成物を調製した。
なお、イオン導電剤には下記のものを用いた。
・カチオン種:K+、アニオン種:CF3SO2C4F9SO2N-(三菱マテリアル電子化成社製、「EF-N142」)
・カチオン種:K+、アニオン種:(CF3SO2)2N-(三菱マテリアル電子化成社製、「EF-N112」)
・カチオン種:K+、アニオン種:C28H20BO6 -(日本カーリット社製、「LR-147」)
・カチオン種:Li+、アニオン種:CF3SO2C4F9SO2N-(三菱マテリアル電子化成社製、「EF-N145」)
・カチオン種:Li+、アニオン種:(CF3SO2)2N-(三菱マテリアル電子化成社製、「EF-N115」)
・カチオン種:Na+、アニオン種:(CF3SO2)2N-(三菱マテリアル電子化成社製、「EF-N113」)
・カチオン種:(C4H9)4P+、アニオン種:Br-(広栄化学社製、「IL-AP1B」)
・カチオン種:K+、アニオン種:CF3SO2C4F9SO2N-(三菱マテリアル電子化成社製、「EF-N142」)
・カチオン種:K+、アニオン種:(CF3SO2)2N-(三菱マテリアル電子化成社製、「EF-N112」)
・カチオン種:K+、アニオン種:C28H20BO6 -(日本カーリット社製、「LR-147」)
・カチオン種:Li+、アニオン種:CF3SO2C4F9SO2N-(三菱マテリアル電子化成社製、「EF-N145」)
・カチオン種:Li+、アニオン種:(CF3SO2)2N-(三菱マテリアル電子化成社製、「EF-N115」)
・カチオン種:Na+、アニオン種:(CF3SO2)2N-(三菱マテリアル電子化成社製、「EF-N113」)
・カチオン種:(C4H9)4P+、アニオン種:Br-(広栄化学社製、「IL-AP1B」)
<ウレタンゴム組成物の硬化性>
各ウレタンゴム組成物を、厚み2mmのシート状に塗工し、130℃で加熱した。ウレタンゴム組成物が1分で硬化した場合に、イオン導電剤によるウレタン触媒の反応性が阻害されておらず、従来の製造条件でウレタンゴム組成物の硬化性が良好であるとして「A」とした。また、ウレタンゴム組成物が5分経っても硬化しなかった場合に、イオン導電剤によるウレタン触媒の反応性が阻害されており、従来の製造条件ではウレタンゴム組成物の硬化性が悪いとして「C」とした。
各ウレタンゴム組成物を、厚み2mmのシート状に塗工し、130℃で加熱した。ウレタンゴム組成物が1分で硬化した場合に、イオン導電剤によるウレタン触媒の反応性が阻害されておらず、従来の製造条件でウレタンゴム組成物の硬化性が良好であるとして「A」とした。また、ウレタンゴム組成物が5分経っても硬化しなかった場合に、イオン導電剤によるウレタン触媒の反応性が阻害されており、従来の製造条件ではウレタンゴム組成物の硬化性が悪いとして「C」とした。
<接着剤の調製>
形成される接着層における導電剤の含有量が、表1に示される値となるように、エポキシ樹脂系接着剤(東亞合成社製、「アロンマイテイAS-60」)に、電子導電剤であるカーボンブラック(三菱化学社製、「#3030B」)を添加し、30分間十分に混合した。これにより、各クリーニングブレードにおける接着層の形成に用いる各接着剤を調製した。なお、一部の接着剤については、比較のため、導電剤を添加しなかった。
形成される接着層における導電剤の含有量が、表1に示される値となるように、エポキシ樹脂系接着剤(東亞合成社製、「アロンマイテイAS-60」)に、電子導電剤であるカーボンブラック(三菱化学社製、「#3030B」)を添加し、30分間十分に混合した。これにより、各クリーニングブレードにおける接着層の形成に用いる各接着剤を調製した。なお、一部の接着剤については、比較のため、導電剤を添加しなかった。
<クリーニングブレード試料の作製>
上型と下型とから構成される金型を準備した。金型は、上型と下型とを接近させて型締めすることにより、略長尺板状のブレード部二つ分の大きさを有するキャビティが内部に形成される。このキャビティには、対向する二つの収容部が設けられている。これら各収容部には、断面L字状に折り曲げ形成された金属製の長尺板材(板厚2mm)からなる導電性支持体の板状部がそれぞれ配置できるように構成されている。
上型と下型とから構成される金型を準備した。金型は、上型と下型とを接近させて型締めすることにより、略長尺板状のブレード部二つ分の大きさを有するキャビティが内部に形成される。このキャビティには、対向する二つの収容部が設けられている。これら各収容部には、断面L字状に折り曲げ形成された金属製の長尺板材(板厚2mm)からなる導電性支持体の板状部がそれぞれ配置できるように構成されている。
次いで、導電性支持体における板状部の先端部における表裏の板状面および先端面に、所定の接着剤を、後述する表1に示される接着層の厚みとなるように塗布した。なお、上記塗布幅は、板状部の先端面から基端側へ2mmまでの範囲とした。
次いで、上記金型の各収容部に接着剤が塗布された導電性支持体をそれぞれセットし、型締めした後、キャビティ内に所定のウレタンゴム組成物を注入し、130℃で5分間加熱することによりウレタンゴム組成物を硬化させた。その後、成形体を金型から取り出し、所定の大きさとなるように二つに切断した。これによりポリウレタンゴム製のブレード部(厚み2mm)と導電性支持体とが接着層を介して一体化されたクリーニングブレード試料を作製した。なお、ウレタンゴム組成物の硬化性が「C」評価であった場合には、130℃で硬化するまで5分を超えて加熱することにより、クリーニングブレード試料を作製した。
<耐ブリード・ブルーム性>
各クリーニングブレードを、40℃×95%RHの湿熱環境に2週間放置した。その後、ブレード部表面におけるイオン導電剤のブリード、ブルームを目視にて確認した。ブレード部表面にイオン導電剤のブリード、ブルームが何ら認められなかった場合を、耐ブリード、ブルーム性に優れ、相手部材を汚染し難いとして「A」とした。ブレード部表面にイオン導電剤のブリード、ブルームが認められた場合を、相手部材を汚染するとして「C」とした。
各クリーニングブレードを、40℃×95%RHの湿熱環境に2週間放置した。その後、ブレード部表面におけるイオン導電剤のブリード、ブルームを目視にて確認した。ブレード部表面にイオン導電剤のブリード、ブルームが何ら認められなかった場合を、耐ブリード、ブルーム性に優れ、相手部材を汚染し難いとして「A」とした。ブレード部表面にイオン導電剤のブリード、ブルームが認められた場合を、相手部材を汚染するとして「C」とした。
<除電性および掻き取り性>
100Vの直流電圧を印加可能な金属ローラに、クリーニングブレードにおけるブレード部の先端部のエッジ部を接触させた。また、クリーニングブレードにおける導電性支持体に電圧計を接続するとともに接地した。そして、クリーニングブレードのブレード部が接触した状態で、金属ローラに100V印加した時のクリーニングブレード全体の体積電気抵抗を測定した。体積電気抵抗が1×1010Ω未満であった場合を、残留トナーを除電しながら掻き取り可能として「A」とした。体積電気抵抗が1×1010Ω以上であった場合を、残留トナーを除電しながら掻き取りできないとして「C」とした。
100Vの直流電圧を印加可能な金属ローラに、クリーニングブレードにおけるブレード部の先端部のエッジ部を接触させた。また、クリーニングブレードにおける導電性支持体に電圧計を接続するとともに接地した。そして、クリーニングブレードのブレード部が接触した状態で、金属ローラに100V印加した時のクリーニングブレード全体の体積電気抵抗を測定した。体積電気抵抗が1×1010Ω未満であった場合を、残留トナーを除電しながら掻き取り可能として「A」とした。体積電気抵抗が1×1010Ω以上であった場合を、残留トナーを除電しながら掻き取りできないとして「C」とした。
表1に、各クリーニングブレードの詳細構成、評価結果をまとめて示す。
表1によれば、以下のことがわかる。試料1Cは、ブレード部におけるカリウム塩の含有量が規定範囲を下回っている。そのため、試料1Cは、残留トナーを除電しながら掻き取ることができない。
試料2Cは、ブレード部におけるカリウム塩の含有量が規定範囲を上回っている。そのため、試料2Cは、イオン導電剤のブリード、ブルームを抑制することができない。
試料3C~6Cは、カリウム塩以外のイオン導電剤を用いている。そのため、これら試料では、ウレタン触媒の反応性が阻害され、従来の製造条件ではウレタンゴム組成物の硬化性が悪い。
試料7Cは、接着層が導電剤を含有していないため導電性がない。そのため、試料7Cは、残留トナーを除電しながら掻き取ることが困難である。
これらに対し、試料1~5によれば、相手部材を汚染し難く、ウレタン触媒の反応性を阻害し難く、残留トナーを除電しながら掻き取ることが可能なクリーニングブレードを提供することができるといえる。
以上、本発明の実施例について詳細に説明したが、本発明は上記実施例に限定されるものではなく、本発明の趣旨を損なわない範囲内で種々の変更が可能である。
Claims (7)
- 電子写真方式を採用する画像形成装置内の相手部材との摺接によって上記相手部材の表面に残留する残留トナーを除去するために用いられるクリーニングブレードであって、
板状部を有する導電性支持体と、上記板状部に形成されたポリウレタンゴム製のブレード部と、上記板状部と上記ブレード部との間に介在し、導電剤を含有する導電性接着層とを有しており、
上記ブレード部は、0.3質量%以上10質量%未満のカリウム塩を含有する、クリーニングブレード。 - 上記カリウム塩におけるアニオンは、CF3SO2C4F9SO2N-、(CF3SO2)2N-、(FSO2)2N-、C28H20BO6 -、AlCl4 -、Al2Cl7 -、NO3 -、BF4 -、PF6 -、CH3COO-、CF3COO-、CF3SO3 -、(CF3SO2)3C-、AsF6 -、SbF6 -、F(HF)N-、CF3CF2CF2CF2SO3 -、(CF3CF2SO2)2N-、CF3CF2CF2COO-、(C4F9SO2)2N-、CF2(CF2SO2)2N-、CF3SO2NH2 -からなる群より選択される少なくとも1種である、請求項1に記載のクリーニングブレード。
- 上記導電剤は、電子導電剤である、請求項1または2に記載のクリーニングブレード。
- 上記電子導電剤は、カーボンブラックである、請求項3に記載のクリーニングブレード。
- 体積電気抵抗が1×1010Ω未満である、請求項1~4のいずれか1項に記載のクリーニングブレード。
- 上記導電性接着層の厚みは、0.1~20μmの範囲内にある、請求項1~5のいずれか1項に記載のクリーニングブレード。
- 上記導電性接着層は、上記導電剤を0.1~10質量%含有する、請求項1~6のいずれか1項に記載のクリーニングブレード。
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201680034190.6A CN107710078A (zh) | 2015-09-30 | 2016-08-24 | 清洁刮板 |
| US15/865,497 US20180150018A1 (en) | 2015-09-30 | 2018-01-09 | Cleaning blade |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015-192404 | 2015-09-30 | ||
| JP2015192404A JP6537949B2 (ja) | 2015-09-30 | 2015-09-30 | クリーニングブレード |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/865,497 Continuation US20180150018A1 (en) | 2015-09-30 | 2018-01-09 | Cleaning blade |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2017056795A1 true WO2017056795A1 (ja) | 2017-04-06 |
Family
ID=58423234
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2016/074674 WO2017056795A1 (ja) | 2015-09-30 | 2016-08-24 | クリーニングブレード |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20180150018A1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6537949B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN107710078A (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2017056795A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6831736B2 (ja) | 2017-03-30 | 2021-02-17 | 株式会社アルファ | ステアリングロック装置 |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07113040A (ja) * | 1993-10-15 | 1995-05-02 | Fukoku Co Ltd | イオン伝導性を有する複写機用ブレード |
| JP2001074034A (ja) * | 1999-09-02 | 2001-03-23 | Tokai Rubber Ind Ltd | 導電性ロール |
| JP2003140427A (ja) * | 2001-08-23 | 2003-05-14 | Tokai Rubber Ind Ltd | 導電性発泡部材 |
| JP2007226185A (ja) * | 2006-01-27 | 2007-09-06 | Kyocera Corp | 画像形成装置 |
| JP2008008957A (ja) * | 2006-06-27 | 2008-01-17 | Bando Chem Ind Ltd | 電子写真装置用弾性部材及びその製造方法 |
| JP2011102859A (ja) * | 2009-11-10 | 2011-05-26 | Ricoh Co Ltd | クリーニング装置、画像形成方法及び画像形成装置 |
| JP2012032808A (ja) * | 2010-07-05 | 2012-02-16 | Canon Inc | 画像形成方法 |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4330599B2 (ja) * | 2006-05-25 | 2009-09-16 | バンドー化学株式会社 | 電子写真装置用クリーニングブレード |
| JP5037292B2 (ja) * | 2007-10-09 | 2012-09-26 | 株式会社リコー | クリーニング装置、像担持体ユニット及び画像形成装置 |
| JP5611004B2 (ja) * | 2010-03-30 | 2014-10-22 | キヤノン株式会社 | 電子写真装置用ブレード |
| JP5449447B2 (ja) * | 2012-04-27 | 2014-03-19 | 住友ゴム工業株式会社 | 導電性ローラ |
-
2015
- 2015-09-30 JP JP2015192404A patent/JP6537949B2/ja active Active
-
2016
- 2016-08-24 CN CN201680034190.6A patent/CN107710078A/zh not_active Withdrawn
- 2016-08-24 WO PCT/JP2016/074674 patent/WO2017056795A1/ja active Application Filing
-
2018
- 2018-01-09 US US15/865,497 patent/US20180150018A1/en not_active Abandoned
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07113040A (ja) * | 1993-10-15 | 1995-05-02 | Fukoku Co Ltd | イオン伝導性を有する複写機用ブレード |
| JP2001074034A (ja) * | 1999-09-02 | 2001-03-23 | Tokai Rubber Ind Ltd | 導電性ロール |
| JP2003140427A (ja) * | 2001-08-23 | 2003-05-14 | Tokai Rubber Ind Ltd | 導電性発泡部材 |
| JP2007226185A (ja) * | 2006-01-27 | 2007-09-06 | Kyocera Corp | 画像形成装置 |
| JP2008008957A (ja) * | 2006-06-27 | 2008-01-17 | Bando Chem Ind Ltd | 電子写真装置用弾性部材及びその製造方法 |
| JP2011102859A (ja) * | 2009-11-10 | 2011-05-26 | Ricoh Co Ltd | クリーニング装置、画像形成方法及び画像形成装置 |
| JP2012032808A (ja) * | 2010-07-05 | 2012-02-16 | Canon Inc | 画像形成方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2017067971A (ja) | 2017-04-06 |
| CN107710078A (zh) | 2018-02-16 |
| US20180150018A1 (en) | 2018-05-31 |
| JP6537949B2 (ja) | 2019-07-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6463255B2 (ja) | 電子写真用部材および画像形成装置 | |
| JP4257771B2 (ja) | 導電性ブレード | |
| CN105652620B (zh) | 电子照相用构件、处理盒和图像形成设备 | |
| KR101630100B1 (ko) | 현상 부재와 그 제조 방법 및 전자 사진 화상 형성 장치 | |
| KR101454139B1 (ko) | 대전 부재, 프로세스 카트리지 및 전자 사진 장치 | |
| CN104635450B (zh) | 充电部件、充电装置、处理盒以及成像设备 | |
| CN1321427C (zh) | 半导电性橡胶部件 | |
| JP2016139145A (ja) | 導電性部材、プロセスカートリッジ及び電子写真装置 | |
| WO2017056795A1 (ja) | クリーニングブレード | |
| CN102372917A (zh) | 电子照相设备用导电性橡胶组合物及使用其的带电辊 | |
| JP6502964B2 (ja) | クリーニングブレード | |
| JP4509274B2 (ja) | 導電部材 | |
| CN102419532B (zh) | 充电元件,处理盒,以及成像装置 | |
| JP5317178B2 (ja) | 導電性ゴム部材 | |
| JP6106553B2 (ja) | 紙送り用ローラ | |
| JP5724087B2 (ja) | 導電性ゴム部材及び帯電ロール | |
| JP2004151534A (ja) | 導電性ローラ | |
| CN109074022B (zh) | 清洁刮板 | |
| JP4000220B2 (ja) | 導電部材 | |
| JP2003103686A (ja) | 弾性部材及び電子写真装置用ブレード | |
| JP2002040896A (ja) | 導電性ブレード | |
| JP2009180950A (ja) | 電子写真機器用現像ロール | |
| JP2008248149A (ja) | 導電性ゴム組成物及びそれを用いてなる導電性ロール | |
| JPH07113040A (ja) | イオン伝導性を有する複写機用ブレード | |
| JP5176264B2 (ja) | 電子写真用帯電部材及びそれを用いた電子写真画像形成装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 16850971 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| DPE1 | Request for preliminary examination filed after expiration of 19th month from priority date (pct application filed from 20040101) | ||
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 16850971 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |