WO2015079833A1 - 走行台車及び軌道式車両 - Google Patents
走行台車及び軌道式車両 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015079833A1 WO2015079833A1 PCT/JP2014/078088 JP2014078088W WO2015079833A1 WO 2015079833 A1 WO2015079833 A1 WO 2015079833A1 JP 2014078088 W JP2014078088 W JP 2014078088W WO 2015079833 A1 WO2015079833 A1 WO 2015079833A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- steering
- traveling
- guide device
- actuator
- vehicle
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B61—RAILWAYS
- B61F—RAIL VEHICLE SUSPENSIONS, e.g. UNDERFRAMES, BOGIES OR ARRANGEMENTS OF WHEEL AXLES; RAIL VEHICLES FOR USE ON TRACKS OF DIFFERENT WIDTH; PREVENTING DERAILING OF RAIL VEHICLES; WHEEL GUARDS, OBSTRUCTION REMOVERS OR THE LIKE FOR RAIL VEHICLES
- B61F5/00—Constructional details of bogies; Connections between bogies and vehicle underframes; Arrangements or devices for adjusting or allowing self-adjustment of wheel axles or bogies when rounding curves
- B61F5/38—Arrangements or devices for adjusting or allowing self- adjustment of wheel axles or bogies when rounding curves, e.g. sliding axles, swinging axles
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B61—RAILWAYS
- B61B—RAILWAY SYSTEMS; EQUIPMENT THEREFOR NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B61B13/00—Other railway systems
- B61B13/04—Monorail systems
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B61—RAILWAYS
- B61F—RAIL VEHICLE SUSPENSIONS, e.g. UNDERFRAMES, BOGIES OR ARRANGEMENTS OF WHEEL AXLES; RAIL VEHICLES FOR USE ON TRACKS OF DIFFERENT WIDTH; PREVENTING DERAILING OF RAIL VEHICLES; WHEEL GUARDS, OBSTRUCTION REMOVERS OR THE LIKE FOR RAIL VEHICLES
- B61F3/00—Types of bogies
- B61F3/16—Types of bogies with a separate axle for each wheel
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B61—RAILWAYS
- B61F—RAIL VEHICLE SUSPENSIONS, e.g. UNDERFRAMES, BOGIES OR ARRANGEMENTS OF WHEEL AXLES; RAIL VEHICLES FOR USE ON TRACKS OF DIFFERENT WIDTH; PREVENTING DERAILING OF RAIL VEHICLES; WHEEL GUARDS, OBSTRUCTION REMOVERS OR THE LIKE FOR RAIL VEHICLES
- B61F5/00—Constructional details of bogies; Connections between bogies and vehicle underframes; Arrangements or devices for adjusting or allowing self-adjustment of wheel axles or bogies when rounding curves
- B61F5/02—Arrangements permitting limited transverse relative movements between vehicle underframe or bolster and bogie; Connections between underframes and bogies
- B61F5/14—Side bearings
- B61F5/148—Side bearings between bolsterless bogies and underframes
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B61—RAILWAYS
- B61F—RAIL VEHICLE SUSPENSIONS, e.g. UNDERFRAMES, BOGIES OR ARRANGEMENTS OF WHEEL AXLES; RAIL VEHICLES FOR USE ON TRACKS OF DIFFERENT WIDTH; PREVENTING DERAILING OF RAIL VEHICLES; WHEEL GUARDS, OBSTRUCTION REMOVERS OR THE LIKE FOR RAIL VEHICLES
- B61F5/00—Constructional details of bogies; Connections between bogies and vehicle underframes; Arrangements or devices for adjusting or allowing self-adjustment of wheel axles or bogies when rounding curves
- B61F5/38—Arrangements or devices for adjusting or allowing self- adjustment of wheel axles or bogies when rounding curves, e.g. sliding axles, swinging axles
- B61F5/386—Arrangements or devices for adjusting or allowing self- adjustment of wheel axles or bogies when rounding curves, e.g. sliding axles, swinging axles fluid actuated
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B61—RAILWAYS
- B61F—RAIL VEHICLE SUSPENSIONS, e.g. UNDERFRAMES, BOGIES OR ARRANGEMENTS OF WHEEL AXLES; RAIL VEHICLES FOR USE ON TRACKS OF DIFFERENT WIDTH; PREVENTING DERAILING OF RAIL VEHICLES; WHEEL GUARDS, OBSTRUCTION REMOVERS OR THE LIKE FOR RAIL VEHICLES
- B61F9/00—Rail vehicles characterised by means for preventing derailing, e.g. by use of guide wheels
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a traveling carriage and a track type vehicle.
- This application claims priority based on Japanese Patent Application No. 2013-245814 filed in Japan on November 28, 2013, the contents of which are incorporated herein by reference.
- an orbital transportation system that travels on a track by running wheels made of rubber tires is known.
- This type of orbital traffic system is generally called “new traffic system”, “APM (Automated People Move)”, or the like.
- APM Automatic People Move
- guide wheels arranged on both sides of the vehicle are guided by guide rails provided along the track.
- the traveling wheel and the guide wheel are provided on a traveling carriage arranged at the lower part of the vehicle.
- the traveling carriage includes a mechanism that steers the traveling wheels (steering wheels) using a force (reaction force) that the guide wheels are pressed against the guide rails when the vehicle passes through the curved portion (for example, Patent Documents). 1).
- Patent Document 1 includes a guide device that has guide wheels and is mounted so as to be turnable with respect to the vehicle, and a steering mechanism (tie rod, tie rod arm) that steers the steered wheels according to the turning of the guide device.
- a traveling cart is disclosed.
- the present invention provides a traveling vehicle and a track-type vehicle that can steer a wide steering wheel while suppressing a reaction force received by a guide device to be small.
- the traveling carriage is a traveling carriage that is guided by a guide rail provided along a track, and is a steering wheel, and a carriage main body that supports the steering wheel;
- a guide device that is rotatably supported by the cart body and that turns by receiving a reaction force from the guide rail, and a steering device that applies a steering force to the steered wheels using the reaction force received by the guide device.
- a mechanism, and an assist mechanism that applies an auxiliary steering force to assist the steering force by the steering mechanism to the steered wheels.
- the guide device When the traveling carriage configured as described above travels on a curved portion of the track, the guide device is pressed against the guide rail, so that the guide device receives a reaction force from the guide rail and turns. Further, the steering force using the reaction force described above is applied to the steered wheels by the steering mechanism, so that the steered wheels can be steered, and the steered wheels can be directed in the traveling direction of the traveling carriage along the curved portion of the track.
- the assist steering force by the assist mechanism is also applied to the steering wheel. It becomes possible to steer the wheel.
- the assist mechanism in the traveling carriage, includes an actuator that generates the auxiliary steering force, a detection unit that detects a state of the guide device, and a detection result of the detection unit. And a controller for controlling the operation of the actuator according to the above.
- the state of the guide device detected by the detection unit is, for example, a turning angle of the guide device with respect to the main body of the vehicle or a reaction force that the guide device receives from the guide rail.
- the control unit controls the operation of the actuator based on the state of the guide device detected by the detection unit, it is possible to apply the auxiliary steering force to the steered wheels with high accuracy. . Therefore, it is possible to prevent the steering angle of the steered wheels steered by the steering mechanism from changing due to the application of the auxiliary steering force.
- the actuator in the traveling carriage, the actuator may be attached to the carriage body.
- the traveling vehicle having the above configuration, when the auxiliary steering force generated by the actuator is transmitted to the steering wheel, the reaction force of the auxiliary steering force can be received by the main body of the vehicle, so that the auxiliary steering force is efficiently applied to the steering wheel. can do.
- a pair of the steering wheels are provided at an interval in the vehicle width direction, and the actuators are provided individually for the pair of steering wheels. Also good.
- the magnitude of the auxiliary steering force generated in each actuator can be reduced as compared with the case where the auxiliary operating force of a single actuator is applied to a pair of steering wheels. That is, an actuator with a small output can be provided. Therefore, the assist mechanism can be configured by an inexpensive actuator, and the manufacturing cost of the traveling carriage can be reduced.
- a track-type vehicle includes the traveling carriage and a vehicle body supported by the traveling carriage.
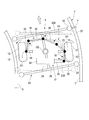
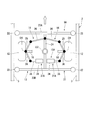
- a track type vehicle 1 (hereinafter simply referred to as a vehicle 1) in the present embodiment is provided by so-called side guide type guide rails 3 provided on both sides in the width direction of the track 2. It is guided and travels on the travel path 4 of the track 2.
- the vehicle 1 includes a vehicle body 5 and a traveling carriage 6.
- the vehicle body 5 has a hollow, substantially rectangular parallelepiped shape that is long in the traveling direction. A space that can accommodate passengers is formed inside the vehicle body 5.
- the traveling carriage 6 supports the vehicle body 5 from below and travels on the track 2.
- the traveling carriage 6 is disposed below the front part and the rear part of the vehicle body 5. Since each traveling cart 6 is only different in whether it is disposed at the front portion or the rear portion of the vehicle body 5, in the following description, only the traveling cart 6 disposed at the front portion will be described.
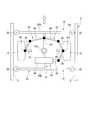
- the traveling carriage 6 includes a carriage body 11, a steering wheel 12, a guide device 13, and a steering mechanism 14.
- the cart body 11 supports the vehicle body 5 from below.
- the cart body 11 includes a cart frame 16, a shock absorber 17, and an axle 18.
- the shock absorber 17 is provided between the vehicle body 5 and the carriage frame 16.
- the shock absorber 17 prevents vibration due to unevenness on the road surface of the traveling road 4 from being transmitted to the vehicle body 5.
- the shock absorber 17 includes a spring member 19, for example.
- two spring members 19 are arranged at intervals in the vehicle width direction of the vehicle body 5.
- the spring member 19 may be an air spring, for example.
- the axle 18 is supported by the bogie frame 16.
- the axle 18 extends on both sides in the vehicle width direction from a gear box 20 disposed in the center in the vehicle width direction.
- the gear box 20 accommodates a mechanism such as a differential gear that transmits rotational power from a power source (not shown) such as a motor to the axle 18.
- a power source not shown
- the gear box 20 is fixed to the lower side of the carriage frame 16 so that the axle 18 is supported by the carriage frame 16 via the gear box 20, but the present invention is not limited thereto.
- the steering wheel 12 is a so-called wheel with a tire on which a rubber tire is mounted.
- the steering wheel 12 is connected to both ends of each axle 18 extending on both sides in the vehicle width direction, and is configured to be rotatable around the axle 18 together with the axle 18. Thereby, the vehicle 1 can travel on the travel path 4 of the track 2. Further, the steering wheel 12 is configured to be rotatable around a steering shaft O1 (for example, a king pin) disposed at both ends of the axle 18 in the vehicle width direction with respect to the carriage main body 11.
- the direction of the traveling direction of the vehicle 1 can be changed by turning the steering wheel 12 around the steering axis O1.
- the guide device 13 is arranged below the carriage main body 11 and is supported so as to be able to turn around a turning axis O2 extending in the vertical direction with respect to the carriage main body 11.
- the guide device 13 turns by receiving a reaction force from the guide rail 3.
- the guide device 13 includes a guide frame 21 and guide wheels 22.
- the guide frame 21 includes horizontal beams 23A and 23B and a vertical beam 24.
- the lateral beams 23A and 23B are formed so as to extend to both outer sides in the vehicle width direction from the steering wheel 12. Further, the cross beams 23A and 23B are respectively disposed in front and rear in the traveling direction of the steering wheel 12.
- the vertical beam 24 extends in the traveling direction of the steered wheel 12 and connects the pair of front and rear horizontal beams 23A and 23B at an intermediate portion in the vehicle width direction.
- the vertical beam 24 is attached to the carriage main body 11 so as to be capable of turning about the turning axis O2 at an intermediate portion in the extending direction.
- the guide wheels 22 are guided by guide rails 3 arranged on both sides of the track 2 in the vehicle width direction.
- the guide wheel 22 is attached to both ends of each of the horizontal beams 23A and 23B, and is configured to be rotatable about an axis O3 extending in the vertical direction.
- the guide wheel 22 rolls along the guide rail 3 by contacting the guide rail 3 when the vehicle 1 travels on the track 2.
- the width dimension of the guide device 13 along the extending direction of the cross beams 23 ⁇ / b> A and 23 ⁇ / b> B is set smaller than the dimension between the guide rails 3. Further, in the guide device 13, a part of the guide wheels 22 is pressed against the guide rail 3, thereby turning by receiving a reaction force from the guide rail 3 (see FIG. 5).
- the steering mechanism 14 applies a steering force to the steered wheels 12 using the reaction force received by the guide device 13 described above.
- the steering mechanism 14 connects the guide device 13 and the steering shaft O1 of the steering wheel 12 to each other, and when the guide device 13 turns, the steering wheel 12 moves around the steering axis O1 in the same direction as the turning direction of the guide device 13.
- a steering mechanism 14 is provided for each steering wheel 12.
- Each steering mechanism 14 includes a first connection arm 25 and a second connection arm 26. A first end in the longitudinal direction of the first connecting arm 25 is attached to the steering wheel 12 so as to be rotatable around the steering axis O1 (the steering direction of the steering wheel 12).
- the second connecting arm 26 connects the first connecting arm 25 and the vertical beam 24 of the guide frame 21.
- a first end in the longitudinal direction of the second connecting arm 26 is rotatably connected to a second end of the first connecting arm 25.
- a second end of the second connecting arm 26 is rotatably connected to the vertical beam 24 of the guide frame 21.
- a connection portion of the vertical beam 24 with the second connection arm 26 is located between the turning axis O2 and an end portion of the vertical beam 24 (connection portion between the horizontal beams 23A and 23B).
- the connecting portion of the first and second connecting arms 25 and 26 is located on the front side in the traveling direction of the vehicle 1 (traveling carriage 6) with respect to the steering shaft O1, and the second connecting arm in the vertical beam 24.
- connection part with 26 is located in the front side of the running direction of vehicle 1 (running carriage 6) rather than turning axis O2, it is not restricted to this.
- the connecting portion of the first and second connecting arms 25 and 26 is located on the rear side in the traveling direction of the vehicle 1 (traveling carriage 6) with respect to the steering shaft O1, and the second connecting arm 26 in the vertical beam 24 and May be located behind the turning axis O2 in the traveling direction of the vehicle 1 (traveling carriage 6).
- the steering mechanism 14 configured as described above, when the guide device 13 receives the reaction force from the guide rail 3 and turns around the turning axis O2, the second connecting arm 26 is displaced, and further, the first connecting arm 25 is moved to the steering shaft.
- the steered wheel 12 is steered in the same direction as the turning direction of the guide device 13 (see FIG. 5). That is, the steering mechanism 14 steers the steering wheel 12 in the same direction as the turning direction of the guide device 13 by applying a steering force to the steering wheel 12 using the reaction force received by the guide device 13.
- the traveling carriage 6 includes an assist mechanism 15 that applies an auxiliary steering force that assists the steering force by the steering mechanism 14 to the steering wheel 12.
- the assist mechanism 15 includes an actuator 31, a detection unit 32, and a control unit 33.
- the actuator 31 generates an auxiliary steering force.
- the actuator 31 of this embodiment is, for example, an air cylinder, a hydraulic cylinder, or an electric cylinder, and includes a cylinder body 34 and a piston rod 35.
- the cylinder body 34 is attached to the carriage body 11.
- the piston rod 35 is attached to the cylinder body 34 so as to extend and contract.
- the expansion / contraction direction of the piston rod 35 is set in the vehicle width direction.
- a first end of the assist arm 36 is rotatably connected to the tip of the piston rod 35 of the actuator 31.
- a second end of the assist arm 36 is attached to the steering wheel 12 so as to be rotatable around the steering axis O1.
- the piston rod 35 extends and contracts with respect to the cylinder body 34.
- the force for expanding and contracting the piston rod 35 is transmitted to the steering wheel 12 via the assist arm 36 and is applied to the steering wheel 12 as an auxiliary steering force.
- the force for expanding and contracting the piston rod 35 (auxiliary steering force) and the displacement of the piston rod 35 are controlled based on a control signal from the control unit 33 described later.
- the actuator 31 of this embodiment is connected to only one of the steering wheels 12 via the assist arm 36.
- the auxiliary steering force of the actuator 31 is transmitted to the other steering wheel 14 via the steering mechanism 14 coupled to one steering wheel 12, the guide frame 21 (vertical beam 24), and the steering mechanism 14 coupled to the other steering wheel 12. It is also given to the steering wheel 12.
- the detection unit 32 detects the state of the guide device 13.
- the detection unit 32 of the present embodiment detects the turning angle of the guide device 13 as the state of the guide device 13.
- the turning direction of the guide device 13 corresponds to the steering direction of the steered wheels 12 connected to the guide device 13 by the steering mechanism 14. Therefore, the detection unit 32 can detect the steering angle of the steered wheels 12 by detecting the turning angle of the guide device 13.
- the turning angle of the guide device 13 and the steering angle of the steered wheel 12 detected by the detection unit 32 are angles based on the direction of the steered wheel 12 in the straight traveling state (and the corresponding turning position of the guide device 13). It is.
- the detection unit 32 of this embodiment includes a detection link 37 and a detection sensor 38.
- the detection link 37 is rotatably attached to the cart body 11.
- the first end of the detection link 37 is connected to the cross beam 23 ⁇ / b> A of the guide device 13. Thereby, the detection link 37 rotates corresponding to the turning of the guide device 13.
- the second end of the detection link 37 is arranged so as to approach or separate from the detection sensor 38 fixed to the carriage body 11 according to the rotation of the detection link 37.
- the detection sensors 38 are arranged on both sides in the moving direction of the second end of the detection link 37, but may be arranged on only one side, for example.
- the detection sensor 38 detects the movement of the detection link 37, and an arbitrary type such as a load detection type, a contact type, a displacement detection type, or a laser detection type can be used.
- the detection result of the detection sensor 38 is output to the control unit 33 as a detection signal.
- the control unit 33 controls the operation of the actuator 31 based on the detection result of the detection unit 32 (detection sensor 38).
- the control unit 33 of the present embodiment will be described in detail.
- the control unit 33 Based on the turning angle of the guide device 13 (steering angle of the steering wheel 12) detected by the detection unit 32, the control unit 33 attempts to return the self-aligning torque (steering wheel 12 to the straight traveling state) of the steering wheel 12. (Rotational force) to be calculated as a reaction force received by the guide device 13.
- the width dimension and material of the steered wheels 12, the travel speed, the vehicle load applied to the steered wheels 12, and the like can be taken into consideration.
- the control unit 33 sets an auxiliary steering force to be applied to the steered wheels 12 based on the calculated reaction force.
- the auxiliary steering force is smaller than the reaction force received by the guide device 13, and is set to 50% of the reaction force, for example.
- the control unit 33 outputs a control signal including the set auxiliary steering force to the actuator 31.
- the actuator 31 generates an auxiliary steering force.
- control unit 33 prevents the steering wheel 12 from being excessively steered by the displacement of the piston rod 35 relative to the cylinder body 34 (displacement of the actuator 31) based on the turning angle of the guide device 13 detected by the detection unit 32. Then, the displacement of the actuator 31 is calculated. For example, the displacement of the actuator 31 is calculated so that the assist arm 36 rotates in accordance with the steering angle of the steered wheel 12 and the rotation of the assist arm 36 is not hindered by the piston rod 35. Thereafter, the control unit 33 outputs a control signal including the calculated displacement of the actuator 31 to the actuator 31.
- control unit 33 outputs a control signal including an auxiliary steering force to the actuator 31 when the calculated reaction force is equal to or less than a predetermined value and the turning angle of the guide device 13 or the steering angle of the steering wheel 12 is equal to or less than the predetermined angle. Is not output. That is, when the steering angle of the steered wheel 12 is equal to or smaller than the predetermined angle, the actuator 31 does not generate an auxiliary steering force.
- a steering force using the reaction force F described above is applied to the steering wheel 12 by the steering mechanism 14, and the steering wheel 12 has the same turning direction as the guide device 13 around the steering axis O ⁇ b> 1.
- the steered wheels 12 can be directed in the traveling direction of the vehicle 1 along the curved portion of the track 2.
- the vehicle 1 travels along the curved portion of the track 2.
- the assist steering force by the assist mechanism 15 is also applied to the steered wheel 12. This will be specifically described below.
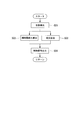
- the detection sensor 38 of the detection unit 32 detects the movement of the detection link 37 connected to the guide device 13.
- the control unit 33 receives a signal from the detection sensor 38 and detects the turning angle of the guide device 13 (the state of the guide device 13) (step S01).
- the control unit 33 calculates a reaction force F received by the guide device 13 based on the turning angle of the guide device 13, and further adds an auxiliary steering force to be applied to the steered wheels 12 based on the calculated reaction force F.
- Set step S02
- the control unit 33 calculates the displacement of the actuator 31 based on the turning angle of the guide device 13 (step S03).
- the displacement of the actuator 31 is calculated so that the steering wheel 12 is not excessively steered by the displacement.
- the control unit 33 outputs a control signal including the auxiliary steering force and the displacement of the actuator 31 set in Step S02 and Step S03 to the actuator 31 (Step S04).
- the processes in steps S01 to S04 are repeatedly performed while the vehicle is traveling on the traveling path 4 of the track 2.
- the actuator 31 generates an auxiliary steering force based on the control signal output from the control unit 33.
- This auxiliary steering force is applied to the steering wheel 12 via the assist arm 36.
- the displacement of the piston rod 35 with respect to the cylinder body 34 is set by the control signal output from the control unit 33, so that the steering wheel 12 can be prevented from being steered by the operation of the actuator 31.
- the traveling carriage 6 of the present embodiment and the vehicle 1 including the same when the steering wheel 12 is steered by the steering mechanism 14, the auxiliary steering force by the assist mechanism 15 is also applied to the steering wheel 12. The For this reason, even if the steered wheel 12 is wide, the steered wheel 12 can be steered while suppressing the reaction force that the guide device 13 receives from the guide rail 3. Therefore, it is possible to provide the vehicle 1 that can cope with an increase in load resistance and a high-speed track system.
- the control unit 33 controls the operation of the actuator 31 based on the turning angle of the guide device 13 (the state of the guide device 13) detected by the detection unit 32. Therefore, the auxiliary steering force can be applied to the steered wheels 12 with high accuracy. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the steering angle of the steered wheels 12 steered by the steering mechanism 14 from changing due to the application of the auxiliary steering force.
- the cylinder body 34 of the actuator 31 is attached to the carriage body 11, when the auxiliary steering force generated by the actuator 31 is transmitted to the steering wheel 12, the reaction force of the auxiliary steering force can be received by the carriage body 11. it can. For this reason, the auxiliary steering force can be efficiently applied to the steered wheels 12. Further, according to the present embodiment, even when the guide device 13 receives a minute reaction force from the guide rail 3 when the vehicle 1 travels on the straight portion of the track 2, the steering angle of the steered wheels 12 associated therewith is predetermined. If the angle is equal to or smaller than the angle, the auxiliary steering force is not applied to the steered wheels 12.
- the steering wheel 12 is quickly brought straight ahead by the self-aligning torque. It becomes possible to return. Therefore, the vehicle 1 can travel on the straight portion of the track 2 in a stable state.
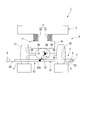
- the assist mechanism 15A included in the traveling vehicle 6A of the track type vehicle (vehicle) of the present embodiment includes the same actuator 31A as in the first embodiment.
- an actuator 31A is provided for each steered wheel 12.
- Each actuator 31A includes the same cylinder body 34 and piston rod 35 as in the first embodiment.
- the piston rod 35 of each actuator 31A is connected to each steered wheel 12 via each assist arm 36 as in the case of the first embodiment.
- the operation of each actuator 31A is controlled based on a control signal from the control unit 33 (see FIG. 3) similar to the first embodiment.
- the traveling cart 6A and the track type vehicle of the present embodiment have the same effects as the first embodiment. Further, according to the traveling carriage 6A and the track-type vehicle of the present embodiment, in each actuator 31A, compared to the configuration of the first embodiment in which the auxiliary steering force of the single actuator 31 is applied to the pair of steering wheels 12. The magnitude of the auxiliary steering force to be generated can be reduced. That is, the actuator 31A having a smaller output can be provided as compared with the case of the first embodiment. Therefore, the assist mechanism 15A can be configured by the inexpensive actuator 31A, and the manufacturing cost of the traveling carriage 6A can be reduced.
- the detection unit 32 of the assist mechanisms 15 and 15 ⁇ / b> A detects the turning angle of the guide device 13 as the state of the guide device 13.
- the reaction force received by the guide device 13 may be detected.
- the force by which the second end of the detection link 37 that rotates with the turning of the guide device 13 is pressed against the detection sensor 38 may be detected as a reaction force.
- the control unit 33 may set the auxiliary steering force based on the reaction force that is the detection result.
- the control part 33 should just calculate the displacement of the actuator 31 based on the reaction force which is a detection result.
- the present invention is not limited to the traveling carriage 6 that travels while being guided by the side guide type guide rails 3 provided at both ends in the width direction of the track 2 as in the above embodiment, for example, the center portion in the width direction of the track.
- the present invention is also applicable to a traveling carriage that is guided by a center guide type guide rail provided in the vehicle.
- this traveling carriage it is possible to steer a wide steered wheel while suppressing the reaction force received by the guide device from the guide rail.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Transportation (AREA)
- Platform Screen Doors And Railroad Systems (AREA)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/032,302 US10144438B2 (en) | 2013-11-28 | 2014-10-22 | Traveling bogie and track-type vehicle |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013245814A JP6222828B2 (ja) | 2013-11-28 | 2013-11-28 | 走行台車及び軌道式車両 |
| JP2013-245814 | 2013-11-28 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015079833A1 true WO2015079833A1 (ja) | 2015-06-04 |
Family
ID=53198783
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2014/078088 Ceased WO2015079833A1 (ja) | 2013-11-28 | 2014-10-22 | 走行台車及び軌道式車両 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10144438B2 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6222828B2 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2015079833A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108482182A (zh) * | 2018-04-17 | 2018-09-04 | 盐城华智超轨道科技有限公司 | 新型悬挂式永磁轨道磁浮交通系统 |
Families Citing this family (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6050156B2 (ja) * | 2013-03-11 | 2016-12-21 | 川崎重工業株式会社 | 案内軌条式車両用案内装置、及び案内軌条式車両 |
| JP5669914B1 (ja) * | 2013-10-18 | 2015-02-18 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 走行台車、及び軌道系交通システムの車両 |
| JP6077135B2 (ja) * | 2013-11-22 | 2017-02-08 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 走行台車、及び車両 |
| JP6213825B2 (ja) * | 2013-11-28 | 2017-10-18 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 走行台車及び軌道式車両 |
| JP5868930B2 (ja) * | 2013-11-28 | 2016-02-24 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 車両用サスペンション装置、走行台車、及び車両 |
| JP5730381B1 (ja) * | 2013-12-12 | 2015-06-10 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 案内輪、走行台車、及び車両 |
| CN110116585B (zh) | 2018-02-06 | 2022-03-15 | 比亚迪股份有限公司 | 轨道车辆的非驱动桥、轨道车辆和轨道交通系统 |
| CN110116584B (zh) * | 2018-02-06 | 2022-03-18 | 比亚迪股份有限公司 | 轨道车辆的驱动桥、轨道车辆和轨道交通系统 |
| JP6899345B2 (ja) * | 2018-02-23 | 2021-07-07 | 三菱重工エンジニアリング株式会社 | 台車、及び車両 |
| CN111517050B (zh) * | 2019-02-03 | 2023-05-02 | 北京京东乾石科技有限公司 | 运输车及其传动装置 |
| JP7130573B2 (ja) * | 2019-02-20 | 2022-09-05 | 三菱重工エンジニアリング株式会社 | 移動体制御装置、移動体、移動体制御方法及びプログラム |
| JP7190946B2 (ja) * | 2019-03-20 | 2022-12-16 | 三菱重工エンジニアリング株式会社 | 電源装置、自動操舵車両、及び電力供給方法 |
| CN113335327B (zh) * | 2020-03-03 | 2023-06-13 | 比亚迪股份有限公司 | 转向架以及具有其的轨道车辆、轨道交通系统 |
| CN114454910B (zh) * | 2021-12-03 | 2023-07-25 | 山东东铁动力科技有限公司 | 轨道车辆测试用牵引救援车底盘及其牵引救援车 |
| GB202301071D0 (en) | 2023-01-25 | 2023-03-08 | Heavy Lift Projects Ltd | Ring crane with hydraulic slewing drive |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS4942610U (enExample) * | 1972-07-18 | 1974-04-15 | ||
| JPS5214885B2 (enExample) * | 1971-11-29 | 1977-04-25 | ||
| JPS53140715A (en) * | 1977-05-11 | 1978-12-08 | Daimler Benz Ag | Traffic system for vehicles having wheels capable of being steered and guided on rail |
| JPS5724600Y2 (enExample) * | 1979-06-13 | 1982-05-28 | ||
| JPH0141547B2 (enExample) * | 1978-04-28 | 1989-09-06 | Daimler Benz Ag | |
| US6477963B1 (en) * | 1999-03-12 | 2002-11-12 | Bombardier Transportaion Gmbh | Apparatus and method for steering a guideway vehicle |
| WO2013094336A1 (ja) * | 2011-12-19 | 2013-06-27 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 交通システム |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4808507B2 (ja) | 2006-02-16 | 2011-11-02 | 公益財団法人鉄道総合技術研究所 | 鉄道車両用軸箱アシスト操舵台車 |
| JP5249509B2 (ja) * | 2006-11-10 | 2013-07-31 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 軌道系交通システムの分岐装置 |
| JP5107280B2 (ja) | 2009-02-26 | 2012-12-26 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 軌道系車両用台車 |
| JP5291503B2 (ja) | 2009-03-17 | 2013-09-18 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 軌道系車両用台車 |
-
2013
- 2013-11-28 JP JP2013245814A patent/JP6222828B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2014
- 2014-10-22 US US15/032,302 patent/US10144438B2/en active Active
- 2014-10-22 WO PCT/JP2014/078088 patent/WO2015079833A1/ja not_active Ceased
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5214885B2 (enExample) * | 1971-11-29 | 1977-04-25 | ||
| JPS4942610U (enExample) * | 1972-07-18 | 1974-04-15 | ||
| JPS53140715A (en) * | 1977-05-11 | 1978-12-08 | Daimler Benz Ag | Traffic system for vehicles having wheels capable of being steered and guided on rail |
| JPH0141547B2 (enExample) * | 1978-04-28 | 1989-09-06 | Daimler Benz Ag | |
| JPS5724600Y2 (enExample) * | 1979-06-13 | 1982-05-28 | ||
| US6477963B1 (en) * | 1999-03-12 | 2002-11-12 | Bombardier Transportaion Gmbh | Apparatus and method for steering a guideway vehicle |
| WO2013094336A1 (ja) * | 2011-12-19 | 2013-06-27 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 交通システム |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108482182A (zh) * | 2018-04-17 | 2018-09-04 | 盐城华智超轨道科技有限公司 | 新型悬挂式永磁轨道磁浮交通系统 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP6222828B2 (ja) | 2017-11-01 |
| US20160264156A1 (en) | 2016-09-15 |
| JP2015101312A (ja) | 2015-06-04 |
| US10144438B2 (en) | 2018-12-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6222828B2 (ja) | 走行台車及び軌道式車両 | |
| US8353248B2 (en) | Track-guided vehicle wheel track | |
| US8381660B2 (en) | Track-guided vehicle wheel truck | |
| CN102361788B (zh) | 轨道引导车辆用台车 | |
| KR101205164B1 (ko) | 철도 차량용 조타 대차, 철도 차량 및 연접 차량 | |
| JP6274115B2 (ja) | 車両、及び、軌道系交通システム | |
| WO2013094336A1 (ja) | 交通システム | |
| JP6213825B2 (ja) | 走行台車及び軌道式車両 | |
| WO2014171389A1 (ja) | ステアリング装置、そのステアリング装置を用いた車両、及び、4輪転舵機構を備えた車両 | |
| JP4930171B2 (ja) | 案内軌条式車両操舵系の振動制御方法及び装置 | |
| JP4808507B2 (ja) | 鉄道車両用軸箱アシスト操舵台車 | |
| JP4505508B2 (ja) | 後輪トー角可変車両 | |
| JP2000264198A (ja) | モノレール車両用台車及びモノレール車両 | |
| WO2016098316A1 (ja) | 鉄道車両用の操舵台車 | |
| JP4567068B2 (ja) | 後輪トー角可変車両 | |
| JP2007168510A (ja) | 鉄道車両用アシストボギー角操舵台車 | |
| JP4877036B2 (ja) | 案内軌条式車両の操舵装置 | |
| JP2016132430A (ja) | ステアリング装置 | |
| KR20140001470A (ko) | 후륜 조향 현가장치 | |
| JP2009234328A (ja) | 鉄道車両用操舵台車 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 14865590 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15032302 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 14865590 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |