WO2014054248A1 - 地図情報処理装置、及び記憶媒体 - Google Patents
地図情報処理装置、及び記憶媒体 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2014054248A1 WO2014054248A1 PCT/JP2013/005698 JP2013005698W WO2014054248A1 WO 2014054248 A1 WO2014054248 A1 WO 2014054248A1 JP 2013005698 W JP2013005698 W JP 2013005698W WO 2014054248 A1 WO2014054248 A1 WO 2014054248A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- road
- data
- unit
- vehicle
- travel locus
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01C—MEASURING DISTANCES, LEVELS OR BEARINGS; SURVEYING; NAVIGATION; GYROSCOPIC INSTRUMENTS; PHOTOGRAMMETRY OR VIDEOGRAMMETRY
- G01C21/00—Navigation; Navigational instruments not provided for in groups G01C1/00 - G01C19/00
- G01C21/26—Navigation; Navigational instruments not provided for in groups G01C1/00 - G01C19/00 specially adapted for navigation in a road network
- G01C21/34—Route searching; Route guidance
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01C—MEASURING DISTANCES, LEVELS OR BEARINGS; SURVEYING; NAVIGATION; GYROSCOPIC INSTRUMENTS; PHOTOGRAMMETRY OR VIDEOGRAMMETRY
- G01C21/00—Navigation; Navigational instruments not provided for in groups G01C1/00 - G01C19/00
- G01C21/38—Electronic maps specially adapted for navigation; Updating thereof
- G01C21/3804—Creation or updating of map data
- G01C21/3807—Creation or updating of map data characterised by the type of data
- G01C21/3815—Road data
- G01C21/3822—Road feature data, e.g. slope data
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01C—MEASURING DISTANCES, LEVELS OR BEARINGS; SURVEYING; NAVIGATION; GYROSCOPIC INSTRUMENTS; PHOTOGRAMMETRY OR VIDEOGRAMMETRY
- G01C21/00—Navigation; Navigational instruments not provided for in groups G01C1/00 - G01C19/00
- G01C21/38—Electronic maps specially adapted for navigation; Updating thereof
- G01C21/3804—Creation or updating of map data
- G01C21/3833—Creation or updating of map data characterised by the source of data
- G01C21/3837—Data obtained from a single source
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01C—MEASURING DISTANCES, LEVELS OR BEARINGS; SURVEYING; NAVIGATION; GYROSCOPIC INSTRUMENTS; PHOTOGRAMMETRY OR VIDEOGRAMMETRY
- G01C21/00—Navigation; Navigational instruments not provided for in groups G01C1/00 - G01C19/00
- G01C21/38—Electronic maps specially adapted for navigation; Updating thereof
- G01C21/3804—Creation or updating of map data
- G01C21/3833—Creation or updating of map data characterised by the source of data
- G01C21/3844—Data obtained from position sensors only, e.g. from inertial navigation
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S19/00—Satellite radio beacon positioning systems; Determining position, velocity or attitude using signals transmitted by such systems
- G01S19/38—Determining a navigation solution using signals transmitted by a satellite radio beacon positioning system
- G01S19/39—Determining a navigation solution using signals transmitted by a satellite radio beacon positioning system the satellite radio beacon positioning system transmitting time-stamped messages, e.g. GPS [Global Positioning System], GLONASS [Global Orbiting Navigation Satellite System] or GALILEO
- G01S19/42—Determining position
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G09—EDUCATION; CRYPTOGRAPHY; DISPLAY; ADVERTISING; SEALS
- G09B—EDUCATIONAL OR DEMONSTRATION APPLIANCES; APPLIANCES FOR TEACHING, OR COMMUNICATING WITH, THE BLIND, DEAF OR MUTE; MODELS; PLANETARIA; GLOBES; MAPS; DIAGRAMS
- G09B29/00—Maps; Plans; Charts; Diagrams, e.g. route diagram
- G09B29/10—Map spot or coordinate position indicators; Map reading aids
- G09B29/106—Map spot or coordinate position indicators; Map reading aids using electronic means
Definitions
- the present disclosure relates to a map information processing apparatus that reflects road information of a new road in map data when a new road is passed, and a storage medium that includes a command for reflecting the road information of the new road in map data.
- the car navigation device holds map data including road data and background data, and uses this map data to display the position of the vehicle, search for routes to the destination, and provide guidance.
- the road data of the newly established road may not be included in the map data.
- a new road is detected by comparing the map data with the travel locus data, and the road data of the detected new road is added to the map data.
- road attributes such as a parking lot, a tunnel, an underpass, and a bridge are set in the detected road data of the new road, and the road data of the new road is added to the map data.
- Patent Document 1 when a GPS signal is not received, a tunnel attribute is set for new road data.
- the tunnel attribute when the tunnel attribute is set in this way, there is a possibility that the tunnel attribute may be erroneously set when traveling on a new road that runs parallel to the elevated road in a high-rise building area where it is difficult to receive GPS signals.
- Patent Literature 1 when a GPS signal is not received and the travel locus data and the background data indicating the railway read from the map data overlap, an underpass attribute is set for the new road data. ing. However, when driving on a new road that overlaps with a subway in a high-rise building area, there is a possibility that an underpass attribute may be erroneously set.
- a parking lot attribute is set for new road data when the average speed between the start and end points of the travel locus data is equal to or less than a predetermined threshold.
- the vehicle may travel at the same speed as a normal road. In such a case, the parking lot attribute may not be set.
- An object of the present invention is to provide a storage medium including instructions that can be set.
- a map information processing apparatus includes a storage unit, a global positioning network (GPS) receiver, a self-contained navigation sensor, a position calculation unit, a comparison unit, a generation unit, a high-rise building area determination unit, and an attribute setting unit.
- storage part memorize
- the GPS receiver receives a plurality of GPS signals from GPS satellites and detects the absolute position of the vehicle.
- the position calculation unit calculates a current position of the vehicle based on the absolute position detected by the GPS receiver and the relative position detected by the self-contained navigation sensor.
- the comparison unit compares the road data with the current position calculated by the position calculation unit, and whether or not the current position deviates more than a predetermined distance from the target road included in the road data. Determine whether.
- the generation unit receives the GPS signal by the GPS receiver based on the current position. Traveling locus data indicating the traveling locus of the vehicle is generated so as to include reception state data indicating presence / absence.
- the high-rise building area determination unit stores the traveling locus data and the storage unit when the traveling locus data includes the reception state data indicating that the GPS signal is not received. Based on the map data, it is determined whether or not the travel locus passes through a high-rise building area.
- the attribute setting unit sets the attribute of the travel locus data as a tunnel when the high-rise building area determination unit determines that the travel locus does not pass through the high-rise building area.
- a computer-readable persistent and tangible storage medium includes the position calculation unit, the comparison unit, the generation unit, the high-rise building area determination unit of the map information processing apparatus according to the first aspect, and Instructions executed by a computer for realizing the function of the attribute setting unit are included.
- the map information processing apparatus is provided by a mobile terminal device, and the instructions are installed in the mobile terminal device.
- the storage medium it is possible to set a correct road attribute for the travel locus data indicating the travel locus of the vehicle.
- the map information processing apparatus includes a storage unit, a GPS receiver, a self-contained navigation sensor, a position calculation unit, a comparison unit, a generation unit, an overlap determination unit, and an attribute setting unit.
- storage part memorize
- the GPS receiver receives a plurality of GPS signals from GPS satellites and detects the absolute position of the vehicle.
- the self-contained navigation sensor detects a relative position of the vehicle.
- the position calculation unit calculates a current position of the vehicle based on the current position detected by the GPS receiver and the relative position detected by the self-contained navigation sensor.
- the comparison unit compares the road data with the current position calculated by the position calculation unit, and whether or not the current position deviates more than a predetermined distance from the target road included in the road data. Determine whether.
- the generation unit receives the GPS signal by the GPS receiver based on the current position. Traveling locus data indicating the traveling locus of the vehicle is generated so as to include reception state data indicating presence / absence.
- the overlap determining unit includes the traveling locus data and the map data stored in the storage unit. Based on the above, it is determined whether or not the travel locus and the underground track overlap.
- the underground track is one of the plurality of tracks and is located underground.
- the attribute setting unit sets the attribute of the traveling locus data as an underpass when the overlap determining unit determines that the traveling locus and the underground track do not overlap.
- the computer-readable persistent and tangible storage medium includes the position calculation unit, the comparison unit, the generation unit, the overlap determination unit, and the attribute of the map information processing apparatus according to the third aspect. Instructions executed by a computer for realizing the function of the setting unit are included.
- the map information processing apparatus is provided by a mobile terminal device, and the instructions are installed in the mobile terminal device.
- the storage medium it is possible to set a correct road attribute for the travel locus data indicating the travel locus of the vehicle.
- the map information processing apparatus includes a storage unit, a GPS receiver, a self-contained navigation sensor, a position calculation unit, a gradient calculation unit, a comparison unit, a generation unit, an underpass determination unit, and an attribute setting unit.
- storage part memorize
- the GPS receiver receives a plurality of GPS signals from GPS satellites and detects the absolute position of the vehicle.
- the position calculation unit calculates a current position of the vehicle based on the absolute position detected by the GPS receiver and the relative position detected by the self-contained navigation sensor.
- the gradient calculation unit calculates a gradient of a traveling road corresponding to the traveling locus of the vehicle.
- the comparison unit compares the road data with the current position calculated by the position calculation unit, and whether or not the current position deviates more than a predetermined distance from the target road included in the road data. Determine whether.
- the generation unit calculates the traveling road calculated by the gradient calculation unit based on the current position Traveling locus data indicating the traveling locus is generated so as to include gradient data indicating the gradient of the vehicle and reception state data indicating whether or not the GPS signal is received by the GPS receiver.
- the underpass determination unit when the traveling locus data includes the reception state data indicating that the GPS signal is not received, the traveling extracted from the road data stored in the storage unit Based on the altitude at the start point and the end point of the trajectory and the gradient data indicating the gradient of the travel road included in the travel trajectory data, it is determined whether or not the travel trajectory is an underpass.
- the attribute setting unit sets the attribute of the travel locus data as an underpass when the underpass determination unit determines that the travel locus is an underpass.
- a computer-readable persistent and tangible storage medium includes the position calculation unit, the gradient calculation unit, the comparison unit, the generation unit, and the underpass of the map information processing apparatus according to the fifth aspect. It includes instructions executed by a computer for realizing the functions of the determination unit and the attribute setting unit.
- the map information processing apparatus is provided by a mobile terminal device, and the instructions are installed in the mobile terminal device.
- the storage medium it is possible to set a correct road attribute for the travel locus data indicating the travel locus of the vehicle.
- the map information processing apparatus includes a storage unit, a position calculation unit, a comparison unit, a generation unit, a vehicle determination unit, and an attribute setting unit.
- storage part memorize
- the position calculation unit calculates a current position of the vehicle.
- the comparison unit compares the road data with the current position calculated by the position calculation unit, and whether or not the current position deviates more than a predetermined distance from the target road included in the road data. Determine whether.
- the generation unit generates travel locus data indicating a travel locus of the vehicle based on the current position when the comparison unit determines that the current position deviates more than the predetermined distance from the target road.
- the vehicle determination unit is configured to start the vehicle between a start point and an end point of the travel locus. It is determined whether or not the shift position of the transmission of the vehicle is reversed.
- the attribute setting unit sets the attribute of the travel locus data as a parking lot when the vehicle determination unit determines that the start switch is switched and the shift position of the transmission is reversed.
- the computer-readable persistent and tangible storage medium includes the position calculation unit, the comparison unit, the generation unit, the vehicle determination unit, and the attribute of the map information processing device according to the seventh aspect. Instructions executed by a computer for realizing the function of the setting unit are included.
- the map information processing apparatus is provided by a mobile terminal device, and the instructions are installed in the mobile terminal device.
- the storage medium it is possible to set a correct road attribute for the travel locus data indicating the travel locus of the vehicle.
- FIG. 1 is a configuration diagram of an in-vehicle navigation device according to an embodiment of the present disclosure.
- FIG. 2 is a flowchart illustrating a processing procedure for adding a new road according to the first embodiment of the present disclosure.
- FIG. 3 is a subroutine showing a processing procedure for creating travel locus data.
- FIG. 4 is a subroutine showing a processing procedure for determining whether or not it is a tunnel,
- FIG. 5 is a flowchart illustrating a processing procedure for adding a new road according to the second embodiment of the present disclosure.
- FIG. 6 is a subroutine showing a processing procedure for determining whether or not the underpass.
- FIG. 7 is a flowchart illustrating a processing procedure for adding a new road according to the third embodiment of the present disclosure.
- FIG. 8 is a subroutine showing a processing procedure for determining whether an underpass or not.
- FIG. 9 is a flowchart illustrating a processing procedure for adding a new road according to the fourth embodiment of the present disclosure.
- FIG. 10 is a subroutine showing a processing procedure for creating travel locus data.
- FIG. 11 is a subroutine showing a processing procedure for determining whether or not the parking lot.
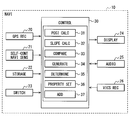
- FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating a configuration of a navigation apparatus 10 when the map information processing apparatus according to the first embodiment of the present disclosure is applied to a navigation apparatus (NAVI) 10.
- the navigation device 10 determines whether the new road is a tunnel and adds the new road data to the map data.
- the navigation device 10 includes a global positioning network (GPS) receiver (GPS REC) 20, a self-contained navigation sensor (SELF-CON NAVI SENS) 21, a storage device (STORAGE) 22, an operation switch group (SWITCH) 23, a display device ( DISPLAY 24, voice input / output device (AUDIO) 25, VICS (registered trademark) receiver (VICS REC) 26, and control device (CONTROL) 30.
- GPS global positioning network
- SELF-CON NAVI SENS self-contained navigation sensor
- SWITCH storage device
- SWITCH display device
- DISPLAY voice input / output device
- AUDIO voice input / output device
- VICS registered trademark
- VICS REC
- the GPS receiver 20 receives a GPS signal transmitted from a GPS satellite and detects the absolute position and the absolute direction of the vehicle.
- the current position of the vehicle detected by the GPS receiver 20 and the received intensity of the GPS signal by the GPS receiver 20 are sent to the control device 30.
- the self-contained navigation sensor 21 includes a gyroscope, a vehicle speed sensor, and an acceleration sensor.
- the gyroscope is a vibrating gyroscope mainly composed of a vibrator, and detects an angular velocity when the vehicle turns when a Coriolis force generated according to an angular velocity of a rotational motion applied to the vehicle acts on the vibrator.
- the vehicle speed sensor detects the moving speed of the vehicle based on a vehicle speed pulse sent from the vehicle every time the vehicle travels a predetermined distance.
- the acceleration sensor detects acceleration applied in the traveling direction of the vehicle.
- the self-contained navigation sensor 21 detects the position of the vehicle with respect to a predetermined initialization position as a relative position based on the above-described angular velocity, moving speed, and acceleration of the vehicle, and transmits the detected relative position of the vehicle to the control device 30. .
- the storage device 22 is composed of a DVD device or a hard disk device, and stores map data.
- the map data includes a header, road data, background data, and character data.
- the road data includes node data having longitude / latitude information and representing a node such as an intersection, and link data representing a road between nodes by combining the node data.
- the link data is associated with road attributes representing road attributes, altitudes, and the like.
- the background data is composed of data for defining the background of the map.
- the background data is associated with the type of background data, shape coordinates, altitude, and the like. As types of background data, railways, green spaces, rivers, seas, parking lots, apartments, facilities, and the like are defined.
- the character data is composed of data representing characters displayed on the map.
- the header includes information such as the storage position and size of road data, background data, and character data in addition to the map data version.
- the operation switch group 23 includes a mechanical key switch provided on the instrument panel of the vehicle and a touch switch integrated with the display device 24.
- the operation switch group 23 may be provided in a remote control terminal (not shown).
- the operation switch group 23 is used by the user to input a departure point, a destination, and the like, and outputs a command signal corresponding to the switch operation by the user to the control device 30.
- the display device 24 is configured using a liquid crystal display, an organic EL (Electro Luminescence), a plasma display, or the like.
- the display device 24 is installed at a position visible to the user in the vehicle interior, and provides the user with the current location of the vehicle on the map, route guidance from the current location to the destination, and the like.
- the voice input / output device 25 outputs facility guidance on the map data and voice for various notifications from the speaker.
- the voice input / output device 25 converts voice input from the microphone by the user into an electrical signal and outputs the electrical signal to the control device 30. Thereby, the user can operate the navigation apparatus 10 by operating the operation switch group 23 by inputting sound from the microphone.
- the VICS receiver 26 acquires road traffic information such as traffic jam information and traffic regulation information in real time from the VICS information center via FM multiplex broadcasting, optical beacons installed on the roadside, and radio wave beacons.
- the control device 30 is a general microcomputer including a CPU, a ROM and a RAM, and an input / output device.
- the ROM includes a position calculation unit (POSI CALC) 31, a gradient calculation unit (SLOPE CALC) 32, a comparison unit (COMPARE) 33, a generation unit (GENERATE) 34, a determination unit (DETERMINE) 35, and an attribute setting unit (PROPERTY SET).
- POSI CALC position calculation unit
- SLOPE CALC gradient calculation unit
- COMPARE comparison unit
- GENE generation unit
- DETERMINE determination unit
- PROPERTY SET attribute setting unit
- control device 30 receives the departure point and the destination from the operation switch group 23 or the voice input / output device 25, the control device 30 calculates a route from the departure point to the destination based on the map data read from the storage device 22, The calculated route is sent to the display device 24.
- the position calculation unit 31 sets the absolute position and the absolute direction of the vehicle detected by the GPS receiver 20 and the relative position of the vehicle detected by the self-contained navigation sensor 21 based on the angular velocity and the moving speed of the vehicle. Based on this, the coordinates of the current position of the vehicle are calculated.
- the coordinates of the current position are also referred to as the current position of the vehicle.
- the gradient calculation unit 32 calculates the gradient of the road on which the vehicle is traveling.
- the gyroscope method the gyroscope is mounted not only with sensitivity in the vehicle roll direction but also with sensitivity in the vehicle pitch direction, or in both roll and pitch sensitivity. Equipped with a 3D gyroscope with Then, the gradient of the road on which the vehicle is traveling is detected by detecting the amount of turning in the pitch direction.
- the vehicle speed sensor method detects the road gradient as follows. What is obtained by differentiating the vehicle speed detected by the vehicle speed sensor and adding the traveling direction component of gravity acceleration applied to the vertical direction of the vehicle (the sine of gravity acceleration) is the vehicle traveling direction detected by the acceleration sensor. Acceleration. Therefore, if the vehicle speed detected by the vehicle speed sensor is subtracted from the acceleration detected by the acceleration sensor, the sine of gravitational acceleration can be obtained. Since the gravitational acceleration is known, the road gradient is obtained from the sine of the gravitational acceleration.
- the gradient calculation unit 32 calculates the gradient of the road on which the vehicle is traveling by performing a weighted average of the gradient of the road acquired by the gyroscope method and the gradient of the road acquired by the vehicle speed sensor method.
- the comparison unit 33 compares the road data read from the storage device 22 with the current position calculated by the position calculation unit 31, and determines whether or not the current position deviates more than a predetermined distance from the road indicated by the road data. To do.
- the comparison unit 33 increases the predetermined distance as the GPS signal reception intensity by the GPS receiver 20 is smaller, and maximizes the predetermined distance when there is no GPS signal reception by the GPS receiver 20.
- the vehicle position calculated based on the angular velocity and the moving speed of the vehicle detected by the self-contained navigation sensor 21 deviates more than a predetermined distance from the road indicated by the road data. It is determined whether or not.
- the generation unit 34 generates travel locus data based on the current position when the current position deviates more than a predetermined distance from the road indicated by the road data.
- the travel locus data is data indicating the travel locus of the vehicle, and includes data indicating the gradient of the travel locus calculated by the gradient calculating unit 32 and data indicating whether or not the GPS signal is received by the GPS receiver 20.
- the data indicating whether or not a GPS signal is received is also referred to as reception state data.
- the determination unit 35 reads the background data stored in the storage device 22 when the travel locus data generated by the generation unit 34 includes data indicating that the GPS signal is not received, and It is determined whether or not the traveling locus passes through the high-rise building area.
- the determination unit 35 functions as a high-rise building area determination unit.
- the attribute setting unit 36 sets a tunnel attribute in the travel locus data on the condition that the determination unit 35 determines that the travel locus of the vehicle does not pass through the high-rise building area.
- the addition unit 37 adds the travel locus data as new road data to the map data stored in the storage device 22.
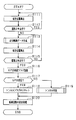
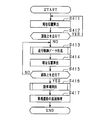
- FIG. 2 is a flowchart illustrating a procedure of a new road addition process performed by the navigation device 10.
- the position calculation unit 31 calculates the current position of the vehicle. Subsequently, in S ⁇ b> 112, the comparison unit 33 determines whether the vehicle is traveling on the road indicated by the road data stored in the storage device 22. Specifically, it is determined whether or not the current position deviates more than a predetermined distance from the road indicated by the road data stored in the storage device 22. If it is determined that the current position does not deviate more than the predetermined distance, that is, the vehicle is traveling on the road (YES), the process returns to S111, and the processes of S111 to S112 are repeated.
- the current position of the vehicle is calculated as in S111.
- S115 as in S112, it is determined whether or not the vehicle is traveling on the road indicated by the road data. If it is determined in S115 that the vehicle is not traveling on the road, that is, the vehicle has not returned to the existing road existing in the map data (NO), the process returns to S113, and the processes of S113 to S115 are repeated.
- the map data of the new road data is recognized by recognizing that the new road has returned to the existing road existing in the map data. Add processing to start.
- a GPS reception flag that is, data indicating whether or not the GPS signal is received by the GPS receiver 20 is acquired from the travel locus data generated by the generation unit 34.
- the tunnel flag is a flag that is set when it is determined that the new road is a tunnel, and is added to the travel locus data.
- the travel locus data is added as new road data to the map data stored in the storage device 22.
- road data indicating a new road is added to the map data.
- FIG. 3 is a subroutine showing a processing procedure for creating travel locus data.
- S1131 the coordinates of the current position of the vehicle calculated by the position calculation unit 31 are added.
- S1132 the gradient of the new road at the current position calculated by the gradient calculation unit 32 is added.
- S1133 it is determined whether or not a GPS signal is received by the GPS receiver 20. If a GPS signal is received (YES), a GPS reception flag is set in S1134. On the other hand, if no GPS signal is received (NO), the GPS reception flag is reset in S1135.
- the traveling locus data including the traveling locus of the vehicle, the data indicating the gradient of the traveling locus, and the data indicating whether or not the GPS signal is received is generated. Thereafter, the process proceeds to S114.
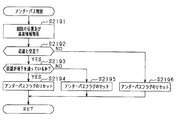
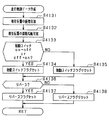
- FIG. 4 is a subroutine showing a processing procedure for determining whether or not the new road is a tunnel.
- the GPS signal may not be received not only when passing through a tunnel but also when passing through a road in an area where high-rise buildings are lined up. Therefore, in this subroutine, it is determined whether or not the travel trajectory indicated by the travel trajectory data passes through the high-rise building area, and the tunnel flag is not set erroneously when traveling on a new road in the high-rise building area. To.
- the height information of the buildings existing around the section of the travel locus where the GPS signal could not be received is acquired from the background data stored in the storage device 22. Subsequently, in S1192, based on the building height information acquired in S1191, whether or not the periphery of the section of the travel locus where the GPS signal could not be received is a high-rise building area, that is, the GPS signal cannot be received. It is determined whether or not the travel locus section passes through the high-rise building area. Specifically, it is determined that the building is a high-rise building area when a building higher than a predetermined height exists around the travel locus at a density higher than the predetermined density.
- the tunnel flag is reset in S1193. Note that the tunnel flag is not set when passing through a tunnel in a high-rise building area. However, it is rare that a tunnel exists in the high-rise building area, so this is not a problem. On the other hand, if it is determined in S1192 that the travel locus does not pass through the high-rise building area (NO), a tunnel flag is set in S1194 corresponding to a section in which the GPS reception flag is not set. Thereafter, the process proceeds to S120.
- the tunnel attribute is set in the travel locus data indicating the new road. That is, when a GPS signal cannot be received by traveling on a new road in a high-rise building area, it is possible to suppress setting an incorrect tunnel attribute in the travel locus data indicating the new road. Therefore, when passing through a new road, the road data of the new road having the correct road attribute can be added to the map data.
- the current position calculated based on the absolute position detected by the GPS receiver 20 may be more deviated from the actual position as the GPS signal reception intensity decreases. Therefore, the smaller the GPS signal reception intensity, the greater the determination value (predetermined distance) for determining whether or not the current position deviates from the road indicated by the road data. Although it is doing, it can suppress that it determines with driving
- the map information processing apparatus includes a storage unit 22, a GPS receiver 20, a self-contained navigation sensor 21, a position calculation unit 31, a comparison unit 33, a generation unit 34, a high-rise building area determination unit 35, and attribute settings.
- Part 36 is provided.
- storage part 22 memorize
- the GPS receiver 20 receives a plurality of GPS signals from GPS satellites and detects the absolute position of the vehicle.
- the position calculation unit 31 calculates the current position of the vehicle based on the absolute position detected by the GPS receiver 20 and the relative position detected by the self-contained navigation sensor.
- the comparison unit 33 compares the road data with the current position calculated by the position calculation unit 31, and determines whether or not the current position deviates more than a predetermined distance from the target road included in the road data. .
- the generation unit 34 receives a GPS signal received by the GPS receiver 20 based on the current position.
- the travel locus data indicating the travel locus of the vehicle is generated so as to include the data.
- the high-rise building area determination unit 35 is based on the travel trajectory data and the map data stored in the storage unit 22 when the travel trajectory data includes reception state data indicating that no GPS signal is received. Then, it is determined whether or not the traveling locus passes through the high-rise building area.
- the attribute setting unit 36 sets the attribute of the traveling locus data as a tunnel.
- a computer for realizing the functions of the position calculation unit 31, the comparison unit 33, the generation unit 34, the high-rise building area determination unit 35, and the attribute setting unit 36 of the map information processing apparatus according to the present embodiment; It may be a computer-readable persistent and tangible storage medium.
- the map information processing apparatus is provided by the mobile terminal device, and the instruction is installed in the mobile terminal device.
- the road data included in the map data is compared with the current position.
- the driving locus data including the driving locus of the vehicle and the presence / absence of reception of the GPS signal is generated. .
- GPS signals may not be received not only in tunnels but also in high-rise buildings areas. Therefore, when the generated traveling locus data includes data indicating that no GPS signal is received, the traveling locus of the vehicle passes through the high-rise building area based on the traveling locus data and the map data. It is determined whether or not. A tunnel attribute is set in the travel locus data on the condition that it is determined that the travel locus of the vehicle does not pass through the high-rise building area.
- the tunnel attribute is set in the travel locus data indicating the new road only when the GPS signal cannot be received by traveling on the new road outside the high-rise building area. That is, when a GPS signal cannot be received by traveling on a new road in a high-rise building area, it is possible to suppress setting an incorrect tunnel attribute in the travel locus data indicating the new road. Therefore, when passing through a new road, the road data of the new road having the correct road attribute can be added to the map data.
- the navigation apparatus 10 according to the second embodiment determines whether the new road is an underpass and adds the new road data to the map data.
- the determination unit 35 of the navigation device 10 stores the data in the storage device 22 when the travel locus data generated by the generation unit 34 includes data indicating that no GPS signal is received.
- the read background data is read out, and it is determined whether or not the traveling locus of the vehicle overlaps the track on the ground. Therefore, the determination unit 35 functions as an overlap determination unit.
- the attribute setting unit 36 sets an underpass attribute in the travel track data on condition that the determination unit 35 determines that the vehicle travel track and the underground track do not overlap.
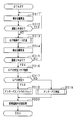
- FIG. 5 is a flowchart illustrating a procedure of a new road addition process performed by the navigation device 10.
- S211 to S217 the same processing as S111 to S117 is performed. If it is determined in S217 that the GPS signal has been received (YES), it is recognized that the new road is not an underpass, and the underpass flag is reset in S218.
- the underpass flag is a flag that is set when it is determined that the new road is underpass, and is added to the travel locus data.
- the travel locus data is added to the map data stored in the storage device 22 as new road data.
- FIG. 6 is a subroutine showing a processing procedure for determining whether or not the new road is an underpass.
- this subroutine it is determined whether or not the traveling locus indicated by the traveling locus data overlaps the underground track, and when the underground track overlaps the underground track, the underpass flag is not set erroneously.
- S2192 it is determined whether or not the section of the traveling locus where the GPS signal could not be received overlaps the railway track. If it is determined in S2192 that the section of the travel locus where the GPS signal could not be received and the railway track do not overlap (NO), it is recognized that the GPS signal could not be received due to disturbance such as multipath, and S2196. To reset the underpass flag.
- the railway traveling on the track that overlaps the travel locus Determine if you are passing through the basement.
- the traveling locus is the ground track.
- the underpass flag is set corresponding to the section in which the GPS reception flag is not set.
- the underpass attribute is set in the travel locus data indicating the new road only when the GPS signal cannot be received by traveling on the new road overlapping the ground track.
- the road data of the new road having the correct road attribute can be added to the map data.
- the map information processing apparatus includes a storage unit 22, a GPS receiver 20, a self-contained navigation sensor 21, a position calculation unit 31, a comparison unit 33, a generation unit 34, an overlap determination unit 35, and an attribute setting unit 36.
- storage part 22 memorize
- the GPS receiver 20 receives a plurality of GPS signals from GPS satellites and detects the absolute position of the vehicle.
- the self-contained navigation sensor 21 detects the relative position of the vehicle.
- the position calculation unit 31 calculates the current position of the vehicle based on the current position detected by the GPS receiver 20 and the relative position detected by the self-contained navigation sensor.
- the comparison unit 33 compares the road data with the current position calculated by the position calculation unit 31, and determines whether or not the current position deviates more than a predetermined distance from the target road included in the road data. .
- the generation unit 34 receives a GPS signal received by the GPS receiver 20 based on the current position.
- the travel locus data indicating the travel locus of the vehicle is generated so as to include the data.
- the overlap determination unit 35 travels based on the traveling locus data and the map data stored in the storage unit 22. It is determined whether or not the track and the underground track overlap.
- the underground track is one of a plurality of tracks and is located underground.
- the attribute setting unit 36 sets the attribute of the traveling locus data as an underpass when the overlap determining unit 35 determines that the traveling locus and the underground track do not overlap.
- Computer-readable including instructions executed by a computer for realizing the functions of the position calculation unit 31, the comparison unit 33, the generation unit 34, the overlap determination unit 35, and the attribute setting unit 36 of the map information processing apparatus according to the present embodiment. It may be a persistent and tangible storage medium.
- the map information processing apparatus is provided by the mobile terminal device, and the instruction is installed in the mobile terminal device.
- the vehicle travel locus when it is determined that the current position deviates more than a predetermined distance from the road indicated by the road data, the vehicle travel locus is included and data indicating whether or not a GPS signal is received is included. Traveling track data is generated. If the generated travel locus data includes data indicating that no GPS signal is received, the vehicle travels based on the travel locus data and background data including the position and altitude of the track. It is determined whether the trajectory and the underground track overlap. An underpass attribute is set in the travel track data on the condition that it is determined that the travel track of the vehicle and the underground track do not overlap.
- the underpass attribute is set in the travel locus data indicating the new road only when the GPS signal cannot be received by traveling on the new road overlapping the ground track.
- the road data of the new road having the correct road attribute can be added to the map data.
- the navigation device 10 according to the third embodiment determines whether or not the new road is an underpass, and adds the new road data to the map data.
- the determination unit 35 of the navigation device 10 is configured such that when the travel locus data generated by the generation unit 34 includes data indicating that no GPS signal is received, the travel locus of the vehicle is It is determined whether it is an underpass. Specifically, based on the altitudes at the start and end points of the travel track extracted from the road data stored in the storage device 22 and the gradient of the travel track included in the travel track data, whether the travel track is an underpass or not. To determine. Therefore, the determination unit 35 functions as an underpass determination unit.
- the attribute setting unit 36 sets an underpass attribute in the travel track data on condition that the determination unit 35 determines that the travel track of the vehicle is an underpass.
- FIG. 7 is a flowchart illustrating a processing procedure for adding a new road performed by the navigation device 10.
- S311 to S317 processing similar to S111 to S117 is performed. If it is determined in S317 that a GPS signal has been received (YES), it is recognized that the new road is not an underpass, and the underpass flag is reset in S318.
- the underpass flag is a flag that is set when it is determined that the new road is underpass, and is added to the travel locus data.
- the travel locus data is added as new road data to the map data stored in the storage device 22.
- FIG. 8 is a subroutine showing a processing procedure for determining whether or not the new road is an underpass.
- the gradient shape of the traveling locus indicated by the traveling locus data is calculated, and it is determined whether or not the section of the traveling locus where the GPS signal cannot be received is an underpass.
- the gradient information of the traveling locus calculated by the gradient calculating unit 32 is acquired from the traveling locus data.
- a GPS signal can be received based on the altitudes at the start and end points of the travel locus acquired from the storage device 22 in S3191 and the gradient of the travel locus calculated by the gradient calculation unit 32 acquired in S3192. It is determined whether or not the section of the travel locus that has not existed is an underpass. Specifically, when the starting point and the ending point of the traveling locus are lower than a predetermined altitude and the vehicle travels on the uphill after the downgrading in the section from the starting point to the ending point of the traveling locus, it is determined that it is an underpass.
- the underpass is determined based on the altitude and gradient of the travel locus, so it is possible to accurately determine the underpass even on a short underpass road. Therefore, when passing through a new road, the road data of the new road having the correct road attribute can be added to the map data.
- the map information processing apparatus includes a storage unit 22, a GPS receiver 20, a self-contained navigation sensor 21, a position calculation unit 31, a gradient calculation unit 32, a comparison unit 33, a generation unit 34, and an underpass determination unit. 35 and an attribute setting unit 36.
- storage part 22 memorize
- the GPS receiver 20 receives a plurality of GPS signals from GPS satellites and detects the absolute position of the vehicle.
- the self-contained navigation sensor 21 detects the relative position of the vehicle.
- the position calculation unit 31 calculates the current position of the vehicle based on the absolute position detected by the GPS receiver 20 and the relative position detected by the self-contained navigation sensor.
- the gradient calculation unit 32 calculates the gradient of the traveling road corresponding to the traveling locus of the vehicle.
- the comparison unit 33 compares the road data with the current position calculated by the position calculation unit 31, and determines whether or not the current position deviates more than a predetermined distance from the target road included in the road data. . When the comparison unit 33 determines that the current position deviates more than a predetermined distance from the target road, the generation unit 34 indicates the gradient of the traveling road calculated by the gradient calculation unit 32 based on the current position.
- the traveling locus data indicating the traveling locus is generated so as to include the data and reception state data indicating whether or not the GPS signal is received by the GPS receiver 20.
- the underpass determination unit 35 determines the altitude of the starting point of the traveling path extracted from the road data stored in the storage unit 22. Based on the altitude of the end point and the gradient data indicating the gradient of the traveling road included in the traveling locus data, it is determined whether or not the traveling locus is an underpass.
- the attribute setting unit 36 sets the attribute of the travel locus data as an underpass when the underpass determination unit 35 determines that the travel locus is an underpass.
- the map information processing apparatus is implemented by a computer for realizing the functions of the position calculation unit 31, the gradient calculation unit 32, the comparison unit 33, the generation unit 34, the underpass determination unit 35, and the attribute setting unit 36. It may be a computer-readable persistent and tangible storage medium containing instructions. In this case, the map information processing apparatus is provided by the mobile terminal device, and the instruction is installed in the mobile terminal device.
- the vehicle traveling locus when it is determined that the current position deviates more than a predetermined distance from the road indicated by the road data, the vehicle traveling locus is indicated, and the gradient of the vehicle traveling locus and the reception of the GPS signal are displayed.
- Traveling track data including data indicating the presence or absence of is generated. If the generated travel locus data includes data indicating that the GPS signal is not received, based on the altitudes at the start and end points of the vehicle travel locus and the gradient of the vehicle travel locus. Then, it is determined whether or not the traveling locus of the vehicle is an underpass. Then, under the condition that the traveling locus of the vehicle is determined to be an underpass, an underpass attribute is set in the traveling locus data.
- an underpass is determined based on the altitude and gradient of the travel locus, so that it is possible to accurately determine an underpass even on a short underpass road. Therefore, when passing through a new road, the road data of the new road having the correct road attribute can be added to the map data.
- the navigation apparatus 10 according to the fourth embodiment determines whether or not the new road is a parking lot, and adds the new road data to the map data.
- the generation unit 34 of the navigation device 10 generates travel locus data based on the current position when the current position deviates more than a predetermined distance from the road indicated by the road data.
- the travel locus data is data indicating the travel locus of the vehicle, the data indicating the gradient of the travel locus calculated by the gradient calculating unit 32, the data indicating whether the start switch of the vehicle is switched, and the transmission of the vehicle. Data indicating whether the shift position is reverse is included.
- the start switch starts various devices of the vehicle, the engine, and the like, and includes a so-called ignition switch, a push start button, a power switch, and the like.
- the determination unit 35 determines whether the start switch of the vehicle is switched from on to off or from off to on between the start point and the end point of the travel locus, and whether the shift position of the vehicle transmission is reversed. Determine whether or not. Therefore, the determination unit 35 functions as a vehicle determination unit.
- the attribute setting unit 36 sets the parking lot attribute in the travel locus data on the condition that the determination unit 35 determines that the start switch of the vehicle has been switched and the shift position of the vehicle transmission has been reversed. Set.
- FIG. 9 is a flowchart illustrating a processing procedure for adding a new road performed by the navigation device 10.
- the travel locus data is added to the map data stored in the storage device 22 as new road data.
- FIG. 10 is a subroutine showing a processing procedure for creating travel locus data.
- S4131 the coordinates of the current position of the vehicle calculated by the position calculation unit 31 are added.
- S4132 the gradient of the new road at the current position calculated by the gradient calculation unit 32 is added.
- S4133 it is determined whether or not the vehicle start switch has been switched from on to off or from off to on while traveling on a new road. If the start switch has been switched (YES), the start switch flag is set in S4134. On the other hand, if the start switch has not been switched (NO), the start switch flag is reset in S4135.
- S4136 it is determined whether or not the shift position of the vehicle transmission has been switched to reverse while traveling on a new road. If the shift position of the transmission is switched to reverse (YES), a reverse flag is set in S4137. On the other hand, if the shift position of the transmission is not switched to reverse (NO), the reverse flag is reset in S4138.
- the traveling locus data including the traveling locus of the vehicle and the data indicating the gradient of the traveling locus, the data indicating whether or not the start switch is switched, and the data indicating whether or not the shift position of the transmission is reverse is generated. Is done. Thereafter, the process proceeds to S414.
- FIG. 11 is a subroutine showing a processing procedure for determining whether or not the new road is a parking lot. Normally, if you enter the parking space backward and park, you will move forward from the parking space. Conversely, if you enter the parking space and park, you exit the parking space backward.
- the parking lot flag is a flag that is set when it is determined that the new road is a parking lot, and is added to the travel locus data.
- a start switch flag and a reverse flag are acquired from the travel locus data generated by the generation unit 34.
- S4162 based on the start switch flag acquired in S4161, it is determined whether or not the start switch has been switched between the departure from the road indicated by the road data and the return. If it is determined in S4162 that the start switch has been switched (YES), based on the reverse flag acquired in S4161, in S4163, the transmission is deviated until it returns from the road indicated by the road data. It is determined whether or not the shift position is reversed. If it is determined in S4163 that the transmission position of the transmission has been reversed (YES), the new road is recognized as a parking lot, and a parking lot flag is set.
- the map information processing apparatus includes a storage unit 22, a position calculation unit 31, a comparison unit 33, a generation unit 34, a vehicle determination unit 35, and an attribute setting unit 36.
- storage part 22 memorize
- the position calculation unit 31 calculates the current position of the vehicle.
- the comparison unit 33 compares the road data with the current position calculated by the position calculation unit 31, and determines whether or not the current position deviates more than a predetermined distance from the target road included in the road data. .
- the generation unit 34 If the comparison unit 33 determines that the current position deviates more than a predetermined distance from the target road, the generation unit 34 generates travel locus data indicating the travel locus of the vehicle based on the current position.
- the vehicle determination unit 35 determines whether the vehicle start switch has been switched between the start point and the end point of the travel locus. It is determined whether or not the shift position of the transmission of the vehicle is reversed.
- the attribute setting unit 36 sets the attribute of the travel locus data as a parking lot when the vehicle determination unit 35 determines that the start switch is switched and the shift position of the transmission is reversed.
- Computer-readable including instructions executed by a computer for realizing the functions of the position calculation unit 31, the comparison unit 33, the generation unit 34, the vehicle determination unit 35, and the attribute setting unit 36 of the map information processing apparatus according to the present embodiment. It may be a persistent and tangible storage medium.
- the map information processing apparatus is provided by the mobile terminal device, and the instruction is installed in the mobile terminal device.
- the traveling locus data indicating the traveling locus of the vehicle is generated and the traveling locus of the vehicle is generated. It is determined whether or not the start switch has been switched between the start point and the end point and whether or not the shift position of the transmission has been reversed.
- the parking lot attribute is set in the travel locus data on the condition that it is determined that the start switch has been switched and the shift position of the transmission of the vehicle has been reversed.
- the background data stored in the storage device 22 may include information indicating that it is a high-rise building area, and based on the information, it can be determined whether or not the traveling locus passes through the high-rise building area.
- Map information processing device GPS receiver, autonomous navigation sensor, storage device storing map data, operation switch group, display device, voice input / output device, VICS receiver, smartphone equipped with control device, tablet terminal device, etc. You may comprise by the portable terminal device.
- a portable terminal device can be configured as a map information processing device by installing a computer program that realizes the functions of the position calculation unit, the gradient calculation unit, the comparison unit, the generation unit, the determination unit, and the attribute setting unit in the portable terminal device. .
- Mobile information processing device such as GPS receiver, storage device storing map data, operation switch group, display device, voice input / output device, VICS receiver, mobile terminal device such as tablet terminal device equipped with control device And a self-contained navigation sensor.
- a map information processing device a GPS receiver, a self-contained navigation sensor, an operation switch group, a display device, a voice input / output device, a VICS receiver, a portable terminal device such as a tablet terminal device equipped with a control device, and map data
- a server that calculates a route to the destination based on the current position calculated by the mobile terminal device.
- the travel locus data generated by the mobile terminal device is transmitted to the server, and the travel locus data is added to the map data in the server as a new road.
- Map information processing device GPS receiver, autonomous navigation sensor, storage device storing map data, operation switch group, display device, voice input / output device, VICS receiver, smartphone equipped with control device, tablet terminal device, etc.
- You may comprise from a portable terminal device, a display apparatus, a voice input / output device, and the vehicle-mounted apparatus provided with the switch operation group.
- the operation content of the switch operation group of the in-vehicle device and the input content of the voice input / output device of the in-vehicle device are transmitted to the mobile terminal device. Further, the content displayed on the display device of the mobile terminal device is transmitted to the in-vehicle device and displayed on the display device of the in-vehicle device.
- the facility data is read from the background data, and it is determined whether or not the traveling locus indicated by the traveling locus data passes through the site such as the shopping center.
- a parking lot flag may be set. If it does in this way, even when entering the parking space forward and exiting forward, it can be determined that it is a parking lot.
- the gradient calculating unit may not be provided.
- the travel locus data may not include data indicating the gradient of the travel locus.
- Both the first embodiment and the second embodiment may be implemented.
- an incorrect tunnel attribute and an incorrect underpass attribute are set in the travel locus data indicating the new road. Can be suppressed.
- the underpass determination in S219 and the tunnel determination in S119 may be performed in order. That is, the tunnel attribute may be set in the travel track data on the condition that it is determined that the travel track is not an underpass and that the travel track does not pass through the high-rise building area.
- Both the first embodiment and the third embodiment may be implemented.
- an incorrect tunnel attribute and an incorrect underpass attribute are set in the travel locus data indicating the new road. Can be suppressed.
- the underpass determination in S319 and the tunnel determination in S119 may be performed in order. That is, the tunnel attribute may be set in the travel track data on the condition that it is determined that the travel track is not an underpass and that the travel track does not pass through the high-rise building area.
- the first embodiment, the second embodiment, and the third embodiment may all be implemented.
- An accurate underpass attribute can be set.
- the underpass determination in S219 and 319 and the tunnel determination in S119 may be performed in order. . That is, the tunnel attribute may be set in the travel locus data on the condition that it is determined in S219 and 319 that the travel locus is not an underpass and that the travel locus does not pass through the high-rise building area.
- the first embodiment, the second embodiment, the third embodiment, and the fourth embodiment may all be implemented. It is possible to suppress an incorrect tunnel attribute from being set in the travel locus data indicating the new road, to set an accurate underpass attribute, and to accurately set a parking lot attribute to the travel locus data.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Radar, Positioning & Navigation (AREA)
- Remote Sensing (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Educational Administration (AREA)
- Educational Technology (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Navigation (AREA)
- Instructional Devices (AREA)
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE112013004874.4T DE112013004874T5 (de) | 2012-10-05 | 2013-09-26 | Karteninformation-Verarbeitungseinrichtung und Speichermedium |
| CN201380052095.5A CN104736967A (zh) | 2012-10-05 | 2013-09-26 | 地图信息处理装置及存储介质 |
| US14/431,514 US20150247733A1 (en) | 2012-10-05 | 2013-09-26 | Map information processing device and storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012-223433 | 2012-10-05 | ||
| JP2012223433A JP2014074699A (ja) | 2012-10-05 | 2012-10-05 | 地図情報処理装置、コンピュータプログラム |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2014054248A1 true WO2014054248A1 (ja) | 2014-04-10 |
Family
ID=50434594
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2013/005698 Ceased WO2014054248A1 (ja) | 2012-10-05 | 2013-09-26 | 地図情報処理装置、及び記憶媒体 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20150247733A1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP2014074699A (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN104736967A (enExample) |
| DE (1) | DE112013004874T5 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2014054248A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104596500A (zh) * | 2014-08-28 | 2015-05-06 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | 一种导航方法、装置及终端 |
| CN108267759A (zh) * | 2016-12-30 | 2018-07-10 | 沈阳美行科技有限公司 | 车辆定位、导航方法和装置及相关系统、应用 |
| CN108267761A (zh) * | 2016-12-30 | 2018-07-10 | 沈阳美行科技有限公司 | 定位、导航方法和装置及相关系统、应用 |
| US20230332918A1 (en) * | 2020-11-17 | 2023-10-19 | Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. | Data generation apparatus, data generation method, and computer program |
Families Citing this family (23)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9616773B2 (en) | 2015-05-11 | 2017-04-11 | Uber Technologies, Inc. | Detecting objects within a vehicle in connection with a service |
| JP6207553B2 (ja) | 2015-07-16 | 2017-10-04 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 運転支援装置、運転支援方法 |
| CN105216830A (zh) * | 2015-09-21 | 2016-01-06 | 深圳市航盛电子股份有限公司 | 一种列车进入隧道预警方法 |
| US10712160B2 (en) | 2015-12-10 | 2020-07-14 | Uatc, Llc | Vehicle traction map for autonomous vehicles |
| US10119827B2 (en) | 2015-12-10 | 2018-11-06 | Uber Technologies, Inc. | Planning trips on a road network using traction information for the road network |
| US10018472B2 (en) | 2015-12-10 | 2018-07-10 | Uber Technologies, Inc. | System and method to determine traction of discrete locations of a road segment |
| US9840256B1 (en) * | 2015-12-16 | 2017-12-12 | Uber Technologies, Inc. | Predictive sensor array configuration system for an autonomous vehicle |
| US9841763B1 (en) | 2015-12-16 | 2017-12-12 | Uber Technologies, Inc. | Predictive sensor array configuration system for an autonomous vehicle |
| US9990548B2 (en) | 2016-03-09 | 2018-06-05 | Uber Technologies, Inc. | Traffic signal analysis system |
| US10459087B2 (en) | 2016-04-26 | 2019-10-29 | Uber Technologies, Inc. | Road registration differential GPS |
| US9672446B1 (en) | 2016-05-06 | 2017-06-06 | Uber Technologies, Inc. | Object detection for an autonomous vehicle |
| US10852744B2 (en) | 2016-07-01 | 2020-12-01 | Uatc, Llc | Detecting deviations in driving behavior for autonomous vehicles |
| US10255525B1 (en) | 2017-04-25 | 2019-04-09 | Uber Technologies, Inc. | FPGA device for image classification |
| EP3711647A4 (en) * | 2017-11-16 | 2021-04-28 | Chiba Institute of Technology | SELF-PROPELLED VACUUM CLEANER |
| US11260875B2 (en) | 2017-12-07 | 2022-03-01 | Uatc, Llc | Systems and methods for road surface dependent motion planning |
| CN110182176A (zh) * | 2018-02-23 | 2019-08-30 | 上海博泰悦臻电子设备制造有限公司 | 车窗清扫装置的控制方法、系统、终端、及存储介质 |
| US11334753B2 (en) | 2018-04-30 | 2022-05-17 | Uatc, Llc | Traffic signal state classification for autonomous vehicles |
| US11334960B2 (en) | 2018-06-08 | 2022-05-17 | Uatc, Llc | Systems and methods for pipelined processing of sensor data using hardware |
| CN109736228B (zh) * | 2019-02-01 | 2020-10-16 | 荆门思安机械设备有限公司 | 旋转开关的转动式车辆阻拦系统 |
| CN109629482B (zh) * | 2019-02-14 | 2020-10-16 | 荆门思安机械设备有限公司 | 旋转开关的转动式多车道后轮拦截的车辆阻拦系统 |
| JP7172740B2 (ja) * | 2019-03-01 | 2022-11-16 | 株式会社デンソー | 駐車支援装置 |
| JP7136073B2 (ja) * | 2019-12-20 | 2022-09-13 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 車両用制御データの生成方法、車両用制御装置、車両用制御システム、および車両用学習装置 |
| JP7524809B2 (ja) * | 2021-03-26 | 2024-07-30 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 走行道路特定装置、走行道路特定方法及び走行道路特定用コンピュータプログラム |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001305953A (ja) * | 2000-02-14 | 2001-11-02 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 地図情報作成装置、および、これを用いた地図情報表示装置 |
| JP2004150827A (ja) * | 2002-10-28 | 2004-05-27 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 移動端末装置及び地図データ管理方法 |
| JP2004251790A (ja) * | 2003-02-20 | 2004-09-09 | Denso Corp | 車両のナビゲーション装置 |
| JP2004301804A (ja) * | 2003-04-01 | 2004-10-28 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | ナビゲーション・システム |
| JP2005172578A (ja) * | 2003-12-10 | 2005-06-30 | Toyota Motor Corp | ナビゲーション装置 |
| JP2005328140A (ja) * | 2004-05-12 | 2005-11-24 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | 車両用通信システム及び車両用通信方法 |
| JP2007292912A (ja) * | 2006-04-24 | 2007-11-08 | Pioneer Electronic Corp | 情報生成装置、情報生成処理プログラム及び情報生成方法 |
| JP2008196996A (ja) * | 2007-02-14 | 2008-08-28 | Denso Corp | カーナビゲーション装置 |
| JP2011154404A (ja) * | 2011-05-02 | 2011-08-11 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 地図情報処理装置 |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6313786B1 (en) * | 1998-07-02 | 2001-11-06 | Snaptrack, Inc. | Method and apparatus for measurement processing of satellite positioning system (SPS) signals |
| JP2004170880A (ja) * | 2002-11-22 | 2004-06-17 | Denso Corp | 地図データ生成装置 |
| JP2004272123A (ja) * | 2003-03-11 | 2004-09-30 | Ricoh Co Ltd | 情報更新システム |
| US7755472B2 (en) * | 2007-12-10 | 2010-07-13 | Grossman Victor A | System and method for setting functions according to location |
| US8620339B2 (en) * | 2008-03-31 | 2013-12-31 | Verizon Patent And Licensing Inc. | System and method for providing quality of service mapping |
| WO2011016819A1 (en) * | 2009-08-03 | 2011-02-10 | Tele Atlas North America | Method of verifying attribute information of a digital transport network database using interpolation and probe traces |
| US20120271864A1 (en) * | 2009-10-29 | 2012-10-25 | Clayton Richard Morlock | Method for assisted road extrapolation from imagery |
| US8510077B1 (en) * | 2009-11-23 | 2013-08-13 | Marvell International Ltd. | Methods and apparatus for self-assisting positioning system |
| CN102288190B (zh) * | 2010-05-13 | 2013-11-06 | 株式会社电装 | 路径引导装置 |
| US8473196B2 (en) * | 2011-02-11 | 2013-06-25 | GM Global Technology Operations LLC | Use of self and neighboring vehicle GPS/GNSS data to estimate current and approaching sky visibility changes |
| US9366764B2 (en) * | 2013-11-18 | 2016-06-14 | General Motors Llc | Vehicular GPS/DR navigation with environmental-adaptive kalman filter gain |
-
2012
- 2012-10-05 JP JP2012223433A patent/JP2014074699A/ja not_active Withdrawn
-
2013
- 2013-09-26 CN CN201380052095.5A patent/CN104736967A/zh active Pending
- 2013-09-26 DE DE112013004874.4T patent/DE112013004874T5/de not_active Withdrawn
- 2013-09-26 WO PCT/JP2013/005698 patent/WO2014054248A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2013-09-26 US US14/431,514 patent/US20150247733A1/en not_active Abandoned
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001305953A (ja) * | 2000-02-14 | 2001-11-02 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 地図情報作成装置、および、これを用いた地図情報表示装置 |
| JP2004150827A (ja) * | 2002-10-28 | 2004-05-27 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 移動端末装置及び地図データ管理方法 |
| JP2004251790A (ja) * | 2003-02-20 | 2004-09-09 | Denso Corp | 車両のナビゲーション装置 |
| JP2004301804A (ja) * | 2003-04-01 | 2004-10-28 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | ナビゲーション・システム |
| JP2005172578A (ja) * | 2003-12-10 | 2005-06-30 | Toyota Motor Corp | ナビゲーション装置 |
| JP2005328140A (ja) * | 2004-05-12 | 2005-11-24 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | 車両用通信システム及び車両用通信方法 |
| JP2007292912A (ja) * | 2006-04-24 | 2007-11-08 | Pioneer Electronic Corp | 情報生成装置、情報生成処理プログラム及び情報生成方法 |
| JP2008196996A (ja) * | 2007-02-14 | 2008-08-28 | Denso Corp | カーナビゲーション装置 |
| JP2011154404A (ja) * | 2011-05-02 | 2011-08-11 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 地図情報処理装置 |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104596500A (zh) * | 2014-08-28 | 2015-05-06 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | 一种导航方法、装置及终端 |
| CN108267759A (zh) * | 2016-12-30 | 2018-07-10 | 沈阳美行科技有限公司 | 车辆定位、导航方法和装置及相关系统、应用 |
| CN108267761A (zh) * | 2016-12-30 | 2018-07-10 | 沈阳美行科技有限公司 | 定位、导航方法和装置及相关系统、应用 |
| US20230332918A1 (en) * | 2020-11-17 | 2023-10-19 | Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. | Data generation apparatus, data generation method, and computer program |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN104736967A (zh) | 2015-06-24 |
| DE112013004874T5 (de) | 2015-07-02 |
| US20150247733A1 (en) | 2015-09-03 |
| JP2014074699A (ja) | 2014-04-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2014054248A1 (ja) | 地図情報処理装置、及び記憶媒体 | |
| JP5022259B2 (ja) | 車載用ナビゲーション装置及び駐車場案内方法 | |
| JP4598120B2 (ja) | 位置登録装置、経路探索装置、位置登録方法、位置登録プログラムおよび記録媒体 | |
| JP4568782B2 (ja) | 位置登録装置、ナビゲーション装置、経路探索装置、位置登録方法、位置登録プログラムおよび記録媒体 | |
| US20120316775A1 (en) | Navigation Device, Route Guidance Method, and Program | |
| US20160054137A1 (en) | Navigation device with enhanced widgets and applications | |
| JP2015034767A (ja) | ナビゲーション装置、経由地受付システム、経由地受付方法およびプログラム | |
| JP4598121B2 (ja) | 位置登録装置、経路探索装置、位置登録方法、位置登録プログラムおよび記録媒体 | |
| US20070021907A1 (en) | Navigation system | |
| JP2009103524A (ja) | ナビゲーション装置、ナビゲーション方法、ナビゲーションプログラムおよびコンピュータに読み取り可能な記録媒体 | |
| JP6117671B2 (ja) | 車両支援装置 | |
| JP2011232271A (ja) | ナビゲーション装置、車載センサの精度推定方法、および、プログラム | |
| JP2006266759A (ja) | 車載ナビゲーション装置 | |
| JP2012149957A (ja) | 車載地図表示装置 | |
| JP5445287B2 (ja) | 車載ナビゲーション装置 | |
| JP2007256118A (ja) | 経路探索装置、経路探索方法、経路探索プログラム、および記録媒体 | |
| JP2005265464A (ja) | 経路算出装置及び地図データ記憶媒体 | |
| JP2005326210A (ja) | 地図情報表示制御装置、地図情報表示装置、それらのシステム、それらの方法、そのプログラム、および、そのプログラムを記録した記録媒体 | |
| JP5607353B2 (ja) | ナビゲーション装置、経路誘導方法、および、プログラム | |
| JP2007256207A (ja) | 位置登録装置、経路探索装置、位置登録方法、位置登録プログラムおよび記録媒体 | |
| WO2007108354A1 (ja) | ナビゲーション装置、経路設定方法、走行経路設定方法、これらの方法を実行するプログラムおよび記録媒体 | |
| JP2006292691A (ja) | 車載ナビゲーション装置 | |
| JP2015125026A (ja) | 徒歩利用施設表示装置、徒歩利用施設表示方法およびプログラム | |
| JP2013210198A (ja) | ナビゲーション装置 | |
| JP2011033403A (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、情報処理プログラムおよび記録媒体 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 13843130 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 14431514 Country of ref document: US |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 112013004874 Country of ref document: DE Ref document number: 1120130048744 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 13843130 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |