WO2013128784A1 - 板バネユニット及びそれを用いた鉄道車両用台車 - Google Patents
板バネユニット及びそれを用いた鉄道車両用台車 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2013128784A1 WO2013128784A1 PCT/JP2013/000092 JP2013000092W WO2013128784A1 WO 2013128784 A1 WO2013128784 A1 WO 2013128784A1 JP 2013000092 W JP2013000092 W JP 2013000092W WO 2013128784 A1 WO2013128784 A1 WO 2013128784A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- leaf spring
- leaf
- vehicle
- spring unit
- leaf springs
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B61—RAILWAYS
- B61F—RAIL VEHICLE SUSPENSIONS, e.g. UNDERFRAMES, BOGIES OR ARRANGEMENTS OF WHEEL AXLES; RAIL VEHICLES FOR USE ON TRACKS OF DIFFERENT WIDTH; PREVENTING DERAILING OF RAIL VEHICLES; WHEEL GUARDS, OBSTRUCTION REMOVERS OR THE LIKE FOR RAIL VEHICLES
- B61F5/00—Constructional details of bogies; Connections between bogies and vehicle underframes; Arrangements or devices for adjusting or allowing self-adjustment of wheel axles or bogies when rounding curves
- B61F5/26—Mounting or securing axle-boxes in vehicle or bogie underframes
- B61F5/30—Axle-boxes mounted for movement under spring control in vehicle or bogie underframes
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B61—RAILWAYS
- B61F—RAIL VEHICLE SUSPENSIONS, e.g. UNDERFRAMES, BOGIES OR ARRANGEMENTS OF WHEEL AXLES; RAIL VEHICLES FOR USE ON TRACKS OF DIFFERENT WIDTH; PREVENTING DERAILING OF RAIL VEHICLES; WHEEL GUARDS, OBSTRUCTION REMOVERS OR THE LIKE FOR RAIL VEHICLES
- B61F3/00—Types of bogies
- B61F3/02—Types of bogies with more than one axle
- B61F3/08—Types of bogies with more than one axle without driven axles or wheels
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B61—RAILWAYS
- B61F—RAIL VEHICLE SUSPENSIONS, e.g. UNDERFRAMES, BOGIES OR ARRANGEMENTS OF WHEEL AXLES; RAIL VEHICLES FOR USE ON TRACKS OF DIFFERENT WIDTH; PREVENTING DERAILING OF RAIL VEHICLES; WHEEL GUARDS, OBSTRUCTION REMOVERS OR THE LIKE FOR RAIL VEHICLES
- B61F5/00—Constructional details of bogies; Connections between bogies and vehicle underframes; Arrangements or devices for adjusting or allowing self-adjustment of wheel axles or bogies when rounding curves
- B61F5/26—Mounting or securing axle-boxes in vehicle or bogie underframes
- B61F5/30—Axle-boxes mounted for movement under spring control in vehicle or bogie underframes
- B61F5/301—Axle-boxes mounted for movement under spring control in vehicle or bogie underframes incorporating metal springs
- B61F5/302—Leaf springs
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B61—RAILWAYS
- B61F—RAIL VEHICLE SUSPENSIONS, e.g. UNDERFRAMES, BOGIES OR ARRANGEMENTS OF WHEEL AXLES; RAIL VEHICLES FOR USE ON TRACKS OF DIFFERENT WIDTH; PREVENTING DERAILING OF RAIL VEHICLES; WHEEL GUARDS, OBSTRUCTION REMOVERS OR THE LIKE FOR RAIL VEHICLES
- B61F5/00—Constructional details of bogies; Connections between bogies and vehicle underframes; Arrangements or devices for adjusting or allowing self-adjustment of wheel axles or bogies when rounding curves
- B61F5/50—Other details
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B61—RAILWAYS
- B61F—RAIL VEHICLE SUSPENSIONS, e.g. UNDERFRAMES, BOGIES OR ARRANGEMENTS OF WHEEL AXLES; RAIL VEHICLES FOR USE ON TRACKS OF DIFFERENT WIDTH; PREVENTING DERAILING OF RAIL VEHICLES; WHEEL GUARDS, OBSTRUCTION REMOVERS OR THE LIKE FOR RAIL VEHICLES
- B61F5/00—Constructional details of bogies; Connections between bogies and vehicle underframes; Arrangements or devices for adjusting or allowing self-adjustment of wheel axles or bogies when rounding curves
- B61F5/50—Other details
- B61F5/52—Bogie frames
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B61—RAILWAYS
- B61G—COUPLINGS; DRAUGHT AND BUFFING APPLIANCES
- B61G11/00—Buffers
- B61G11/02—Buffers with metal springs
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16F—SPRINGS; SHOCK-ABSORBERS; MEANS FOR DAMPING VIBRATION
- F16F1/00—Springs
- F16F1/02—Springs made of steel or other material having low internal friction; Wound, torsion, leaf, cup, ring or the like springs, the material of the spring not being relevant
- F16F1/18—Leaf springs
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a leaf spring unit and a railcar bogie using the leaf spring unit without a side beam.
- the bogie frame includes a lateral beam extending in the lateral direction and a pair of left and right side beams extending in the front-rear direction from both ends of the lateral beam.
- a shaft spring comprising a coil spring interposed between the upper side beams is provided.
- Patent Document 2 proposes a cart that omits the side beam portion of the cart frame.
- the primary suspension is a leaf spring
- the center portion in the front-rear direction of the leaf spring is fixed to both end portions in the vehicle width direction of the horizontal beam, and both end portions in the front-rear direction of the leaf spring are mounted on the axle box. It is set as the structure inserted in the spring receptacle provided in. According to this, since the side beam portion of the bogie frame is omitted, the bogie frame is reduced in weight and the assembly work is simplified.
- an object of the present invention is to ensure the function of the leaf spring even if the leaf spring should be damaged, while reducing the occupied space in the thickness direction of the leaf spring.
- a leaf spring unit includes a lateral beam for supporting a vehicle body of a railway vehicle, and a pair of front and rear axles arranged along the vehicle width direction at the front and rear in the longitudinal direction of the vehicle across the lateral beam.
- a leaf spring unit applicable to a railway vehicle carriage provided on both sides of the axle in the vehicle width direction and provided with a bearing rotatably supporting the axle and an axle box housing the bearing;
- a plurality of leaf springs extending in the longitudinal direction of the vehicle in a state in which both ends in the vehicle width direction of the lateral support are supported, the longitudinal both ends being supported by the axle box, and elastically deforming in the thickness direction which is the vertical direction.
- the plurality of leaf springs are arranged side by side in the width direction perpendicular to the longitudinal direction and the thickness direction thereof.
- the railcar bogie of the present invention is a pair of front and rear beams arranged along the vehicle width direction at the front and rear in the longitudinal direction of the vehicle across the horizontal beam for supporting the vehicle body of the railcar.
- a vehicle that is provided on both sides in the vehicle width direction of the axle, supports the axle rotatably, a shaft box that accommodates the bearing, and both ends of the side wall in the vehicle width direction.
- a leaf spring unit extending in the longitudinal direction and having both ends in the longitudinal direction supported by the axle box, and the leaf spring unit includes a plurality of leaf springs that are elastically deformed in a thickness direction that is the vertical direction. The plurality of leaf springs are arranged side by side in the width direction perpendicular to the longitudinal direction and the thickness direction thereof.
- the plurality of leaf springs constituting the leaf spring unit are arranged in the width direction, not in the thickness direction that is the up and down direction of the leaf spring unit. An increase in the occupied space can be suppressed. And since the leaf
- the function of the leaf spring can be ensured even if the leaf spring is damaged, while reducing the vertical space occupied by the leaf spring unit. .
- FIG. 1 is a perspective view showing a railway vehicle carriage according to a first embodiment. It is a top view of the trolley
- FIG. 8 is a sectional view taken along line VIII-VIII in FIG. 7.
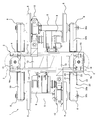
- FIG. 1 is a perspective view showing a railway vehicle carriage 1 according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 2 is a plan view of the carriage 1 shown in FIG.
- FIG. 3 is a side view of the carriage 1 shown in FIG.
- the railcar bogie 1 includes a bogie frame 3 for supporting a vehicle body 11 via an air spring 2 serving as a secondary suspension.
- the carriage frame 3 includes lateral beams 4 that extend in the vehicle width direction (also simply referred to as the width direction), which is the left-right direction.
- the vehicle frame 3 extends from both ends in the vehicle width direction of the lateral beams 4 (hereinafter also referred to as the front-rear direction).
- a pair of front and rear axles 5 are arranged along the vehicle width direction at the front and rear of the side beam 4, and wheels 6 are fixed to both sides of the axle 5 in the vehicle width direction.
- bearings 7 that rotatably support the axle 5 are provided outside the wheels 6 in the vehicle width direction, and the bearings 7 are accommodated in the axle box 8.
- An electric motor 9 is attached to the side beam 4, and a gear box 10 in which a reduction gear for transmitting power to the axle 5 is accommodated is connected to the output shaft of the electric motor 9.
- the side beam 4 includes a pair of square pipes 12 extending in the vehicle width direction and connection plates 13 and 14 for connecting the square pipes 12.
- the connection plates 13 and 14 are bolted to the square pipe 12 or the like. It is fixed by.
- a pair of cylindrical connecting plates 14 are provided at both ends 4a in the vehicle width direction of the side beam 4 with a space therebetween, and an air spring base 15 is installed on the upper surface thereof.
- Both end portions 4 a in the vehicle width direction of the lateral beam 4 are connected to the axle box 8 by a connecting mechanism 16.
- the coupling mechanism 16 includes a shaft beam 17 that extends integrally from the axle box 8 along the front-rear direction.
- the end portion of the shaft beam 17 is provided with a cylindrical portion 18 whose inner peripheral surface is cylindrical and whose both sides in the vehicle width direction are open.
- a mandrel 20 is inserted into the internal space of the cylindrical portion 18 via a rubber bush (not shown).
- a pair of receiving seats 21, 22 constituting the coupling mechanism 16 are provided in the vehicle width direction both ends 4 a of the lateral beam 4 so as to protrude in the front-rear direction.
- the receiving seats 21 and 22 are formed with insertion grooves 25 that open downward.
- the both ends of the mandrel 20 in the horizontal direction are fitted into the fitting groove 25 from below.
- the lid member 26 is fixed to the receiving seats 21 and 22 by bolts (not shown) so as to close the lower opening of the fitting groove 25, and the mandrel 20 is supported from below by the lid member 26. Yes.
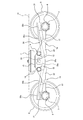
- a leaf spring unit 30 extending in the front-rear direction is bridged between the side beam 4 and the axle box 8, and the longitudinal center portion 30 a of the plate spring unit 30 is opposite to both ends 4 a in the vehicle width direction of the beam 4.
- the longitudinal end portions 30c of the leaf spring unit 30 are supported by the axle box 8. That is, the leaf spring unit 30 has both the function of the primary suspension and the function of the conventional side beam.
- the central part 30 a in the longitudinal direction of the leaf spring unit 30 is arranged so as to sink under the side beam 4.
- An abutting member 33 having an arcuate lower surface 33a is provided at the lower part of both end portions 4a in the vehicle width direction of the lateral beam 4, and the abutting member 33 is placed on the longitudinal center portion 30a of the leaf spring unit 30 from above. Being in free contact. That is, the contact member 33 is in contact with the upper surface of the leaf spring 30 by a downward load due to gravity from the lateral beam 4 without fixing the leaf spring unit 30 in the vertical direction.
- a support member 31 is attached to the upper end portion of the axle box 8, and both longitudinal end portions 30 c of the leaf spring unit 30 are supported by the support member 31 from below. Both end portions 30 c in the longitudinal direction of the leaf spring unit 30 are also placed on the support member 31 from above and are in free contact with the upper surface of the support member 31 by the downward load from the leaf spring 30.
- An extension 30b between the longitudinal center 30a and both longitudinal ends 30c of the leaf spring unit 30 is inclined downward toward the longitudinal center 30a in a side view.
- the longitudinal center portion 30 a is located below the longitudinal end portions 30 c of the leaf spring unit 30. That is, the leaf spring unit 30 is formed in a bow shape that protrudes downward as a whole in a side view.
- a part of the extending portion 30 b of the leaf spring 30 passes through the space 27 sandwiched between the pair of receiving seats 21 and 22, passes below the connecting plate 23, and reaches the lower position of the lateral beam 4. That is, a part of the extending portion 30b of the leaf spring unit 30 is disposed at a position overlapping the connecting mechanism 16 in a side view.
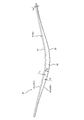
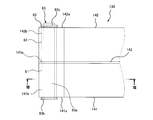
- FIG. 4 is a side view of the leaf spring unit 30 shown in FIG.
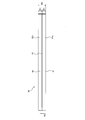
- FIG. 5 is a plan view of the leaf spring unit 30 shown in FIG.
- FIG. 6 is an exploded perspective view of the leaf spring unit 30 shown in FIG. 4 to 6, an outer skin 44 (see FIG. 1) described later is not shown.
- the leaf spring unit 30 includes a pair of leaf springs 41 and 42 that are elastically deformed in the thickness direction (vertical direction). And the width direction (left-right direction) orthogonal to the thickness direction.
- the pair of leaf springs 41 and 42 are the same as each other and have the same material, configuration, outer shape, and dimensions. In the present embodiment, the number of leaf springs is two, but is not limited to this.
- the spring constant of the leaf spring unit can be adjusted. For example, when the spring constant of one leaf spring is 50 kg / mm, the spring constant of a leaf spring unit using two leaf springs is 100 kg / mm, and the spring constant of a leaf spring unit using three leaf springs is 150 kg. / Mm.
- an intervening material 43 having a hardness lower than that of the leaf springs 41, 42 is interposed.
- the interposed material 43 is a rubber sheet, and the width W3 (sheet thickness) of the interposed material 43 in the vehicle width direction is considerably smaller than the width W1 of the leaf springs 41 and 42.
- the both sides of the interposition material 43 are sandwiched between the opposing side surfaces of the pair of leaf springs 41 and 42.
- the intervening material 43 is formed in a shape that follows the contours of the side surfaces (opposing surfaces) of the leaf springs 41 and 42.
- the shape of the intervention material 43 is substantially the same as the shape of the side surfaces (opposing surfaces) of the leaf springs 41 and 42.
- the interposition 43 should just be a material lower than the hardness of the leaf
- the leaf springs 41 and 42 and the interposing material 43 are collectively wrapped by an outer skin 44 (see FIG. 1) as a holding member. That is, the outer skin 44 entirely covers the surface of the assembly composed of the leaf springs 41 and 42 sandwiching the interposing material 43.
- the intervening material 43 wrapped together with the leaf springs 41 and 42 by the outer skin 44 is in contact with the leaf springs 41 and 42 without being bonded.
- the outer skin 44 only needs to be flexible and can hold the leaf springs 41 and 42 and the interposition material 43. For example, a nonflammable cloth or a heat-shrinkable tube may be used.
- the plate springs 41 and 42 are formed in a bow shape that protrudes downward as a whole in a side view. Therefore, the upper surfaces 41a and 42a and the lower surfaces 41b and 42b of the leaf springs 41 and 42 have different shapes.
- the leaf springs 41 and 42 have an upper layer 51, an intermediate layer 52, and a lower layer 53, and are formed by combining different types of fiber reinforced resins.
- the volume of the intermediate layer 52 is larger than the entire volume of the upper layer 51 and the lower layer 53.
- the upper layer 51 and the lower layer 53 are formed of CFRP, and the intermediate layer 52 is formed of GFRP. CFRP has higher strength against tension or compression than GFRP, and GFRP is less expensive than CFRP.
- the thickness T4 of the leaf springs 41 and 42 is formed such that the central portion in the longitudinal direction is the thickest and gradually decreases toward both ends in the longitudinal direction.
- the wall thickness T2 of the intermediate layer 52 is formed so as to gradually decrease from the longitudinal center to both longitudinal ends, and the wall thicknesses T1 and T3 of the upper layer 51 and the lower layer 53 are constant. It is.
- a compression load is applied to the upper layer 51 and a tensile load is applied to the lower layer 53.
- the thickness T3 of the lower layer 53 is made thinner than the thickness T1 of the upper layer 51 from the knowledge that the strength against tension is higher than the strength against compression.
- the width W1 of the leaf springs 41, 42 is larger than the value of the thickness T4 of the thinnest portion (both ends in the longitudinal direction) of the leaf springs 41, 42.
- the thickness T5 of the interposition material 43 is 2% or more and 20% or less of the width W1 of the leaf springs 41 and 42. This prevents the overall width W2 of the plate spring unit 30 from becoming excessive while preventing the thickness T4 of the entire plate spring unit 30 from becoming excessive.
- the surfaces of the leaf springs 41 and 42 are painted (not shown) to protect them from ultraviolet rays or the like.
- the leaf springs 41 and 42 divided along the longitudinal direction constituting the leaf spring unit 30 are arranged in the width direction rather than in the thickness direction of the leaf spring unit 30. Therefore, it is possible to suppress an increase in the occupied space in the thickness direction of the leaf spring unit 30 (that is, the height direction of the carriage 1). Therefore, it is possible to contribute to lowering the floor of the vehicle body 11 and the like. And since the leaf
- the leaf springs 41 and 42 cannot be stacked one above the other.
- the plate springs 41 and 42 are arranged in the width direction rather than in the vertical direction (thickness direction), the plate springs 41 and 42 can be made the same. Therefore, it is not necessary to design and produce a plurality of types of leaf springs that match each position and behavior, and the efficiency of design and production can be improved.
- the leaf springs 41 and 42 are prevented from rubbing against each other.
- the leaf springs 41 and 42 can be protected.
- the interposition material 43 is in a sheet shape and is disposed so that the thickness T5 direction thereof coincides with the width W1 direction of the leaf springs 41 and 42, the thickness T4 and the width W2 of the leaf spring unit 30 as a whole are excessive. Can be prevented.
- plate springs 41 and 42 and the interposition material 43 are hold
- the interposition material 43 is held in position without adhering to the leaf springs 41 and 42, so that the adhering work and the use of the adhesive can be reduced.
- the outer skin 44 may be eliminated, and the interposition material 43 may be bonded to the adjacent leaf springs 41 and 42 so that the position of the interposition material 43 with respect to the leaf springs 41 and 42 can be maintained.
- FIG. 7 is a plan view of a main part of a leaf spring unit 130 according to the second embodiment.
- 8 is a cross-sectional view taken along line VIII-VIII in FIG.
- the leaf springs 141 and 142 aligned in the width direction have through holes 141b and 142b that penetrate in the width direction at both longitudinal ends 141a and 142a. have.
- plate springs 141 and 142 are mutually connectedly hold
- the leaf springs 141 and 142 have an upper layer 151, an intermediate layer 152, and a lower layer 153, and further have edge portions 154 that connect the upper layer 151 and the lower layer 153 to each other at both longitudinal ends 141a and 142a. is doing.
- the end edge portion 154 has an arc shape that is curved so as to bulge outward in the longitudinal direction of the leaf springs 141 and 142.
- insertion holes 141 b and 142 b having a circular cross section are formed by the inner peripheral surface of the arc-shaped end edge 154 and the longitudinal edge of the intermediate layer 152.
- the upper layer 151, the lower layer 153, and the edge portion 154 are formed of CFRP, and the intermediate layer 152 is formed of GFRP.
- Metal cylindrical collars 61 and 62 are inserted through the insertion holes 141b and 142b, respectively.
- the collars 61 and 62 are integrated with the leaf springs 141 and 142 by insert molding.
- the collars 61 and 62 protrude from the insertion holes 141b and 142b of the leaf springs 141 and 142 on both sides in the width direction.
- the collar 61 of one leaf spring 141 and the collar 62 of the other leaf spring 142 abut against each other, so that a gap is formed between the leaf spring 141 and the leaf spring 142, and the gap is made of a rubber sheet or the like.
- a dressing 143 is disposed. Note that insertion holes 143a through which the collars 61 and 62 and the pins 63 are inserted are formed at both ends in the longitudinal direction of the interposing material 143.
- the pin 63 includes a shaft portion 63a that is passed through the insertion holes 141b and 142b through the collars 61 and 62, a head portion 63b that is provided at one end of the shaft portion 63a and has a larger diameter than the shaft portion 63a, and a shaft portion. And an annular groove 63c formed on the outer peripheral surface of the other end of 63a.
- a stopper member 65 (for example, a C ring) is fitted into the groove 63c, and the stopper 63 and the head 63b prevent the pin 63 from coming off.
- the leaf springs 141 and 142 and the interposing material 143 can be easily held, and the thickness of the leaf spring unit 130 can be reduced by the amount not using the outer skin.
- the leaf springs 141 and 142 can rotate relative to each other around the axis of the pin 63, mutual load transmission between the leaf springs 141 and 142 is reduced, and the independence of the leaf springs 141 and 142 is increased. be able to.
- the collars 61 and 62 that secure a predetermined gap between the adjacent leaf springs 141 and 142 are provided, it is possible to prevent a load in the width direction from being applied to the interposition material 143 more than a predetermined amount. it can. Since other configurations are the same as those of the first embodiment described above, description thereof is omitted.
- the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiments, and the configuration can be changed, added, or deleted without departing from the spirit of the present invention.
- the above embodiments may be arbitrarily combined with each other. For example, some configurations or methods in one embodiment may be applied to other embodiments.
- the interposition material may be adhered to one of the adjacent leaf springs.
- the holding member that holds the adjacent leaf springs so as not to be separated from each other by more than a predetermined value is not limited to the outer skin, the pin, the adhesive, or the like.
- a holding clamp member may be used. Moreover, you may adhere
- the leaf spring unit according to the present invention and the railcar bogie using the leaf spring reduce the occupied space in the thickness direction of the leaf spring, and even if the leaf spring is damaged, It is beneficial to apply it widely to a railway vehicle bogie that has the excellent effect of ensuring the function of the above and can demonstrate the significance of this effect.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Springs (AREA)
- Vibration Prevention Devices (AREA)
Abstract
Description
前記横ばりの車幅方向両端部を支持した状態で車両長手方向に延びて、その長手方向両端部が前記軸箱に支持され、上下方向となる厚さ方向に弾性変形する複数の板バネを備え、前記複数の板バネは、互いにその長手方向及び厚さ方向に直交する幅方向に並んで配置されている。
図1は、第1実施形態に係る鉄道車両用台車1を表した斜視図である。図2は、図1に示す台車1の平面図である。図3は、図1に示す台車1の側面図である。図1乃至3に示すように、鉄道車両用台車1は、二次サスペンションとなる空気バネ2を介して車体11を支持するための台車枠3を備えている。台車枠3は、左右方向である車幅方向(単に、幅方向ともいう)に延びる横ばり4を備えているが、横ばり4の車幅方向両端部から車両長手方向(以下、前後方向ともいう)に延びる側ばりを備えていない。横ばり4の前方及び後方には、車幅方向に沿って前後一対の車軸5が配置されており、車軸5の車幅方向両側には車輪6が固定されている。車軸5の車幅方向両端部には、車輪6よりも車幅方向外側にて車軸5を回転自在に支持する軸受7が設けられ、その軸受7は軸箱8に収容されている。横ばり4には、電動機9が取り付けられており、その電動機9の出力軸には、車軸5に動力を伝達する減速ギヤが収容されたギヤボックス10が接続されている。
図7は、第2実施形態に係る板バネユニット130の要部平面図である。図8は、図7のVIII-VIII線断面図である。図7及び8に示すように、本実施形態の板バネユニット130では、幅方向に並んだ板バネ141,142が、その長手方向両端部141a,142aにおいて幅方向に貫通する挿通穴141b,142bを有している。そして、それら挿通穴141b,142bに保持部材としてのピン63が挿通されることで、板バネ141,142が互いに連結保持されている。
4 横ばり
4a 車幅方向両端部
5 車軸
7 軸受
8 軸箱
11 車体
30,130 板バネ
30a 長手方向中央部
30c 長手方向両端部
41,42,141,142 板バネ
43,143 介装材
44 外皮(保持部材)
51,151 上層
52,152 中間層
53,153 下層
Claims (9)
- 鉄道車両の車体を支持するための横ばりと、前記横ばりを挟んで車両長手方向の前方及び後方において車幅方向に沿って配置された前後一対の車軸と、前記車軸の車幅方向両側に設けられて、前記車軸を回転自在に支持する軸受と、前記軸受を収容する軸箱とを備えた鉄道車両用台車に適用可能な板バネユニットであって、
前記横ばりの車幅方向両端部を支持した状態で車両長手方向に延びて、その長手方向両端部が前記軸箱に支持され、上下方向となる厚さ方向に弾性変形する複数の板バネを備え、
前記複数の板バネは、互いにその長手方向及び厚さ方向に直交する幅方向に並んで配置されている、板バネユニット。 - 前記板バネの上面と下面とは、互いに異なる形状であり、
前記複数の板バネは、互いの外形及び寸法が略同一である、請求項1に記載の板バネユニット。 - 前記複数の板バネの間に介装され、前記板バネよりも硬度の低い介装材をさらに備えている、請求項1又は2に記載の板バネユニット。
- 前記介装材は、シート状であり、その両面が前記複数の板バネの対向する側面により挟まれている、請求項3に記載の板バネユニット。
- 前記介装材はゴム製である、請求項3又は4に記載の板バネユニット。
- 前記複数の板バネをまとめて保持する保持部材をさらに備え、
前記保持部材によって前記板バネとともに保持された前記介装材は、前記板バネに対して接着されずに当接している、請求項3乃至5のいずれかに記載の板バネユニット。 - 前記介装材は、前記複数の板バネのうち前記介装材に隣接する少なくとも一方の板バネに接着されている、請求項3乃至5のいずれかに記載の板バネユニット。
- 前記板バネは、少なくとも上層、中間層及び下層を有し、
前記上層及び前記下層は第1のFRPによって形成され、前記中間層は第2のFRPによって形成され、前記第1のFRPは前記第2のFRPよりも前記長手方向の荷重に対する強度が高い、請求項1乃至7のいずれかに記載の板バネユニット。 - 鉄道車両の車体を支持するための横ばりと、
前記横ばりを挟んで車両長手方向の前方及び後方において車幅方向に沿って配置された前後一対の車軸と、
前記車軸の車幅方向両側に設けられて、前記車軸を回転自在に支持する軸受と、
前記軸受を収容する軸箱と、
前記横ばりの車幅方向両端部を支持した状態で車両長手方向に延びて、その長手方向両端部が前記軸箱に支持されている板バネユニットと、を備え、
前記板バネユニットは、上下方向となる厚さ方向に弾性変形する複数の板バネを有し、前記複数の板バネは、互いにその長手方向及び厚さ方向に直交する幅方向に並んで配置されている、鉄道車両用台車。
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201380002269.7A CN103687776B (zh) | 2012-02-29 | 2013-01-11 | 板簧单元及使用该板簧单元的铁道车辆用转向架 |
| US14/382,300 US9493174B2 (en) | 2012-02-29 | 2013-01-11 | Plate spring unit and railcar bogie using same |
| EP13754813.7A EP2824011B1 (en) | 2012-02-29 | 2013-01-11 | Plate spring unit and railcar bogie using same |
| KR1020137034311A KR101525725B1 (ko) | 2012-02-29 | 2013-01-11 | 판스프링 유닛 및 이를 이용한 철도 차량용 대차 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012-043135 | 2012-02-29 | ||
| JP2012043135A JP5878791B2 (ja) | 2012-02-29 | 2012-02-29 | 板バネユニット及びそれを用いた鉄道車両用台車 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2013128784A1 true WO2013128784A1 (ja) | 2013-09-06 |
Family
ID=49082003
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2013/000092 WO2013128784A1 (ja) | 2012-02-29 | 2013-01-11 | 板バネユニット及びそれを用いた鉄道車両用台車 |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9493174B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP2824011B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5878791B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR101525725B1 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN103687776B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2013128784A1 (ja) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2018155139A1 (ja) * | 2017-02-23 | 2018-08-30 | 川崎重工業株式会社 | 鉄道車両用台車枠及びそれを備えた台車 |
| US11104360B2 (en) * | 2016-05-16 | 2021-08-31 | Kawasaki Jukogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Method of assembling railcar bogie, measurement jig, and railcar bogie |
Families Citing this family (23)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104477197B (zh) * | 2012-04-06 | 2017-04-12 | 川崎重工业株式会社 | 铁道车辆用转向架 |
| US9352757B2 (en) * | 2012-04-06 | 2016-05-31 | Kawasaki Jukogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Railcar bogie |
| JP5765292B2 (ja) * | 2012-05-21 | 2015-08-19 | 新日鐵住金株式会社 | 鉄道車両の台車枠 |
| JP5772761B2 (ja) * | 2012-08-13 | 2015-09-02 | 新日鐵住金株式会社 | 鉄道車両の台車枠 |
| JP6110669B2 (ja) * | 2013-01-10 | 2017-04-05 | 川崎重工業株式会社 | 鉄道車両用台車及びそれを備えた鉄道車両 |
| JP6190148B2 (ja) * | 2013-04-24 | 2017-08-30 | 川崎重工業株式会社 | 鉄道車両用台車 |
| JP6383282B2 (ja) * | 2014-12-17 | 2018-08-29 | 川崎重工業株式会社 | 鉄道車両用台車 |
| JP6506630B2 (ja) * | 2015-06-03 | 2019-04-24 | 川崎重工業株式会社 | 板バネユニット及び鉄道車両用台車 |
| TWD174067S (zh) * | 2015-07-07 | 2016-03-01 | 溫芫鋐 | 來令片散熱結構之部分 |
| JP6510938B2 (ja) * | 2015-09-10 | 2019-05-08 | 川崎重工業株式会社 | 鉄道車両用台車の電極付き板バネの製造方法 |
| JP6557596B2 (ja) * | 2015-12-25 | 2019-08-07 | 川崎重工業株式会社 | 鉄道車両用台車、その輪重調整方法、及び輪重調整システム |
| CN105905126B (zh) * | 2016-06-03 | 2018-06-12 | 中车株洲电力机车有限公司 | 一种构架及其转向架 |
| JP6650352B2 (ja) * | 2016-06-21 | 2020-02-19 | 川崎重工業株式会社 | 鉄道車両台車の組立方法及びそれに用いる軸距固定治具 |
| RU172935U1 (ru) * | 2017-04-28 | 2017-08-01 | РЕЙЛ 1520 АйПи ЛТД | Боковая рама тележки грузового вагона |
| USD842981S1 (en) * | 2017-05-24 | 2019-03-12 | Hamworthy Combustion Engineering Limited | Atomizer |
| RU173544U1 (ru) * | 2017-05-31 | 2017-08-30 | РЕЙЛ 1520 АйПи ЛТД | Надбуксовая накладка для боковой рамы вагонной тележки |
| JP6530806B1 (ja) * | 2017-12-26 | 2019-06-12 | 川崎重工業株式会社 | 鉄道車両用台車 |
| JP6622842B2 (ja) * | 2018-04-16 | 2019-12-18 | 川崎重工業株式会社 | 鉄道車両用駆動台車 |
| CN112298244A (zh) * | 2019-08-02 | 2021-02-02 | 中车唐山机车车辆有限公司 | 一种轨道车辆及其转向架 |
| CN112298251B (zh) * | 2019-08-02 | 2022-07-26 | 中车唐山机车车辆有限公司 | 一种转向架 |
| JP1681707S (ja) * | 2019-10-22 | 2021-03-22 | ||
| DE102020133694B3 (de) * | 2020-12-16 | 2022-05-05 | CG Rail - Chinesisch-Deutsches Forschungs- und Entwicklungszentrum für Bahn- und Verkehrstechnik Dresden GmbH | Anordnung aus einem Kinematikpaket und einem Federhebel für ein Drehgestell |
| CN114670890B (zh) * | 2022-03-18 | 2022-10-11 | 常州市新创智能科技有限公司 | 一种转向架构架、制造模具及制造方法 |
Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5474057A (en) * | 1977-11-24 | 1979-06-13 | Toray Ind Inc | Fiber reinforced resin leaf spring |
| JPS5547950A (en) | 1978-09-27 | 1980-04-05 | Sumitomo Metal Ind | Truck for railway rolling stock that side beam is omitted |
| JPS5877941A (ja) * | 1981-10-31 | 1983-05-11 | Hino Motors Ltd | 繊維強化樹脂製板ばね |
| JPS58118342A (ja) * | 1981-12-28 | 1983-07-14 | Hino Motors Ltd | 繊維強化樹脂製板ばね |
| JPS596443A (ja) * | 1982-06-29 | 1984-01-13 | Hino Motors Ltd | 繊維強化樹脂製板ばね |
| JPH0367746A (ja) * | 1989-08-07 | 1991-03-22 | Nhk Spring Co Ltd | Frp部材 |
| JPH03125039A (ja) * | 1989-10-06 | 1991-05-28 | Horikiri Bane Seisakusho:Kk | 車両懸架用板ばね |
| JPH0454337A (ja) * | 1990-06-22 | 1992-02-21 | Nkk Corp | 減衰能を有するバネ体 |
| JPH04197873A (ja) * | 1990-11-29 | 1992-07-17 | Railway Technical Res Inst | 鉄道車両用台車枠 |
| JPH04119266U (ja) * | 1991-04-01 | 1992-10-26 | 日本車輌製造株式会社 | 鉄道車両用台車 |
| JP2799078B2 (ja) | 1991-01-24 | 1998-09-17 | 川崎重工業株式会社 | 軸箱支持装置 |
Family Cites Families (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2097418A (en) * | 1935-05-27 | 1937-10-26 | American Steel Foundries | Spring |
| US3948188A (en) * | 1970-06-05 | 1976-04-06 | Swiss Aluminium Ltd. | Resilient railway bogie |
| JPS5586935A (en) * | 1978-12-25 | 1980-07-01 | Nhk Spring Co Ltd | Frp leaf spring |
| JPS5834246A (ja) * | 1981-08-26 | 1983-02-28 | Nhk Spring Co Ltd | 重ね板ばね装置 |
| JPH0662051B2 (ja) * | 1984-04-28 | 1994-08-17 | 日本発条株式会社 | 車輌懸架用frp板ばね装置 |
| JPS60194636U (ja) * | 1984-06-06 | 1985-12-25 | いすゞ自動車株式会社 | Frp製スプリング |
| DE3612176A1 (de) * | 1986-04-11 | 1987-10-15 | Messerschmitt Boelkow Blohm | Biegetraeger |
| JPH052281U (ja) | 1991-06-17 | 1993-01-14 | 日本信号株式会社 | 自動販売機等の金額表示装置 |
| JPH0522881U (ja) * | 1991-09-09 | 1993-03-26 | 日産デイーゼル工業株式会社 | リーフスプリングのサイレンサ構造 |
| IT1253908B (it) * | 1991-12-10 | 1995-08-31 | Firema Ricerche Srl | Carrello ferroviario plurifunzionale |
| BE1010823A3 (nl) * | 1996-12-24 | 1999-02-02 | Dsm Nv | Constructieveer van met vezels versterkte kunststof. |
| DE19731867C1 (de) * | 1997-07-24 | 1998-10-29 | Abb Daimler Benz Transp | Laufwerk für ein Schienenfahrzeug |
| FR2782687B1 (fr) | 1998-09-02 | 2003-01-10 | Alstom Technology | Bogie a longerons composites |
| FR2862935B1 (fr) | 2003-12-02 | 2006-03-03 | Alstom | Dispositif de liaison souple entre un longeron et une boite d'essieu |
| CN201575098U (zh) * | 2009-12-15 | 2010-09-08 | 中通客车控股股份有限公司 | 新型等截面钢板弹簧结构 |
-
2012
- 2012-02-29 JP JP2012043135A patent/JP5878791B2/ja active Active
-
2013
- 2013-01-11 EP EP13754813.7A patent/EP2824011B1/en active Active
- 2013-01-11 US US14/382,300 patent/US9493174B2/en active Active
- 2013-01-11 WO PCT/JP2013/000092 patent/WO2013128784A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2013-01-11 KR KR1020137034311A patent/KR101525725B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2013-01-11 CN CN201380002269.7A patent/CN103687776B/zh active Active
Patent Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5474057A (en) * | 1977-11-24 | 1979-06-13 | Toray Ind Inc | Fiber reinforced resin leaf spring |
| JPS5547950A (en) | 1978-09-27 | 1980-04-05 | Sumitomo Metal Ind | Truck for railway rolling stock that side beam is omitted |
| JPS5877941A (ja) * | 1981-10-31 | 1983-05-11 | Hino Motors Ltd | 繊維強化樹脂製板ばね |
| JPS58118342A (ja) * | 1981-12-28 | 1983-07-14 | Hino Motors Ltd | 繊維強化樹脂製板ばね |
| JPS596443A (ja) * | 1982-06-29 | 1984-01-13 | Hino Motors Ltd | 繊維強化樹脂製板ばね |
| JPH0367746A (ja) * | 1989-08-07 | 1991-03-22 | Nhk Spring Co Ltd | Frp部材 |
| JPH03125039A (ja) * | 1989-10-06 | 1991-05-28 | Horikiri Bane Seisakusho:Kk | 車両懸架用板ばね |
| JPH0454337A (ja) * | 1990-06-22 | 1992-02-21 | Nkk Corp | 減衰能を有するバネ体 |
| JPH04197873A (ja) * | 1990-11-29 | 1992-07-17 | Railway Technical Res Inst | 鉄道車両用台車枠 |
| JP2799078B2 (ja) | 1991-01-24 | 1998-09-17 | 川崎重工業株式会社 | 軸箱支持装置 |
| JPH04119266U (ja) * | 1991-04-01 | 1992-10-26 | 日本車輌製造株式会社 | 鉄道車両用台車 |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11104360B2 (en) * | 2016-05-16 | 2021-08-31 | Kawasaki Jukogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Method of assembling railcar bogie, measurement jig, and railcar bogie |
| WO2018155139A1 (ja) * | 2017-02-23 | 2018-08-30 | 川崎重工業株式会社 | 鉄道車両用台車枠及びそれを備えた台車 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2824011B1 (en) | 2020-01-08 |
| EP2824011A4 (en) | 2015-11-25 |
| KR101525725B1 (ko) | 2015-06-03 |
| CN103687776A (zh) | 2014-03-26 |
| US20150158506A1 (en) | 2015-06-11 |
| KR20140027417A (ko) | 2014-03-06 |
| CN103687776B (zh) | 2016-08-17 |
| US9493174B2 (en) | 2016-11-15 |
| EP2824011A1 (en) | 2015-01-14 |
| JP2013177097A (ja) | 2013-09-09 |
| JP5878791B2 (ja) | 2016-03-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5878791B2 (ja) | 板バネユニット及びそれを用いた鉄道車両用台車 | |
| WO2013150720A1 (ja) | 鉄道車両用台車 | |
| JP6289549B2 (ja) | 鉄道車両用台車 | |
| US8656839B2 (en) | Railcar bogie | |
| WO2014109278A1 (ja) | 鉄道車両用台車及びそれを備えた鉄道車両 | |
| EP2944534B1 (en) | Railcar bogie | |
| JP6190148B2 (ja) | 鉄道車両用台車 | |
| KR101707342B1 (ko) | 철도 차량의 대차 프레임 | |
| WO2022032809A1 (zh) | 轨道车辆 | |
| US9352757B2 (en) | Railcar bogie | |
| WO2014174788A1 (ja) | 鉄道車両用台車 | |
| JP6620183B2 (ja) | 鉄道車両用台車枠 | |
| JP2019010947A (ja) | 車両のドディオン式懸架装置 | |
| KR101462239B1 (ko) | 강도 보강 연결부를 갖는 차량용 복합재 판 스프링 | |
| WO2019203018A1 (ja) | 鉄道車両用駆動台車 | |
| WO2022032808A1 (zh) | 转向架 | |
| JP2019182316A (ja) | 鉄道車両用台車枠 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 13754813 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20137034311 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 14382300 Country of ref document: US |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2013754813 Country of ref document: EP |