WO2012057336A1 - 育毛剤組成物 - Google Patents
育毛剤組成物 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2012057336A1 WO2012057336A1 PCT/JP2011/074983 JP2011074983W WO2012057336A1 WO 2012057336 A1 WO2012057336 A1 WO 2012057336A1 JP 2011074983 W JP2011074983 W JP 2011074983W WO 2012057336 A1 WO2012057336 A1 WO 2012057336A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- hair
- group
- paps
- effect
- test
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K8/00—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations
- A61K8/18—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition
- A61K8/30—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition containing organic compounds
- A61K8/60—Sugars; Derivatives thereof
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61Q—SPECIFIC USE OF COSMETICS OR SIMILAR TOILETRY PREPARATIONS
- A61Q7/00—Preparations for affecting hair growth
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/70—Carbohydrates; Sugars; Derivatives thereof
- A61K31/7042—Compounds having saccharide radicals and heterocyclic rings
- A61K31/7052—Compounds having saccharide radicals and heterocyclic rings having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. nucleosides, nucleotides
- A61K31/706—Compounds having saccharide radicals and heterocyclic rings having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. nucleosides, nucleotides containing six-membered rings with nitrogen as a ring hetero atom
- A61K31/7064—Compounds having saccharide radicals and heterocyclic rings having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. nucleosides, nucleotides containing six-membered rings with nitrogen as a ring hetero atom containing condensed or non-condensed pyrimidines
- A61K31/7076—Compounds having saccharide radicals and heterocyclic rings having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. nucleosides, nucleotides containing six-membered rings with nitrogen as a ring hetero atom containing condensed or non-condensed pyrimidines containing purines, e.g. adenosine, adenylic acid
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K8/00—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations
- A61K8/18—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition
- A61K8/30—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition containing organic compounds
- A61K8/49—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition containing organic compounds containing heterocyclic compounds
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K8/00—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations
- A61K8/18—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition
- A61K8/30—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition containing organic compounds
- A61K8/60—Sugars; Derivatives thereof
- A61K8/606—Nucleosides; Nucleotides; Nucleic acids
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P17/00—Drugs for dermatological disorders
- A61P17/14—Drugs for dermatological disorders for baldness or alopecia
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a hair restorer composition.
- Hair is produced in an organ called a hair follicle.
- the human hair follicle autonomously repeats the process of tissue regeneration and regression (growth-regression-rest period) called the hair cycle throughout life.
- tissue regeneration and regression growth-regression-rest period
- the ratio of the anagen hair is decreased, and the ratio of the anagen hair and the resting hair is increased, whereby thin hair and hair loss become prominent and alopecia is caused.
- the most common type of alopecia is male pattern hair loss. In this case, the hair growth becomes shorter and the hair becomes thinner and shorter.
- Alopecia is thought to result from a complex interplay of factors such as male hormones, genetic predisposition, stress, nutrition, and aging.
- Minoxidil has a peripheral vasodilatory effect and is used as an oral antihypertensive agent for the treatment of hypertension.
- attention has been paid to hairiness as a side effect, and application as a hair growth agent has been proposed (for example, Patent Documents 1 and 2). Thereafter, the hair growth effect of minoxidil was confirmed clinically, and is currently marketed as a hair growth agent.
- adenosine and adenosine-related compounds are also known to have effects such as preventing hair loss and promoting hair growth.
- Conventional hair restoration containing adenosine 5'-2-phosphate Patent Document 3
- hair restoration containing adenosine having adenosine receptor stimulating action and adenosine-related compounds as active ingredients Patent Document 4
- adenosine as active ingredients Hair conditioner Patent Document 5 and the like contained as is reported.
- minoxidil and adenosine-related compounds are known as hair growth agents.
- the effect is limited.
- minoxidil as specified in the instruction manual for Rogaine (Rogaine (registered trademark)
- Rogaine Rogaine
- the probability of hair regenerating to the extent that there is no problem in appearance is only about 10% for men (Non-patent Document 1). Therefore, the subject of this invention is providing the hair restorer composition with a higher hair-restoration effect.
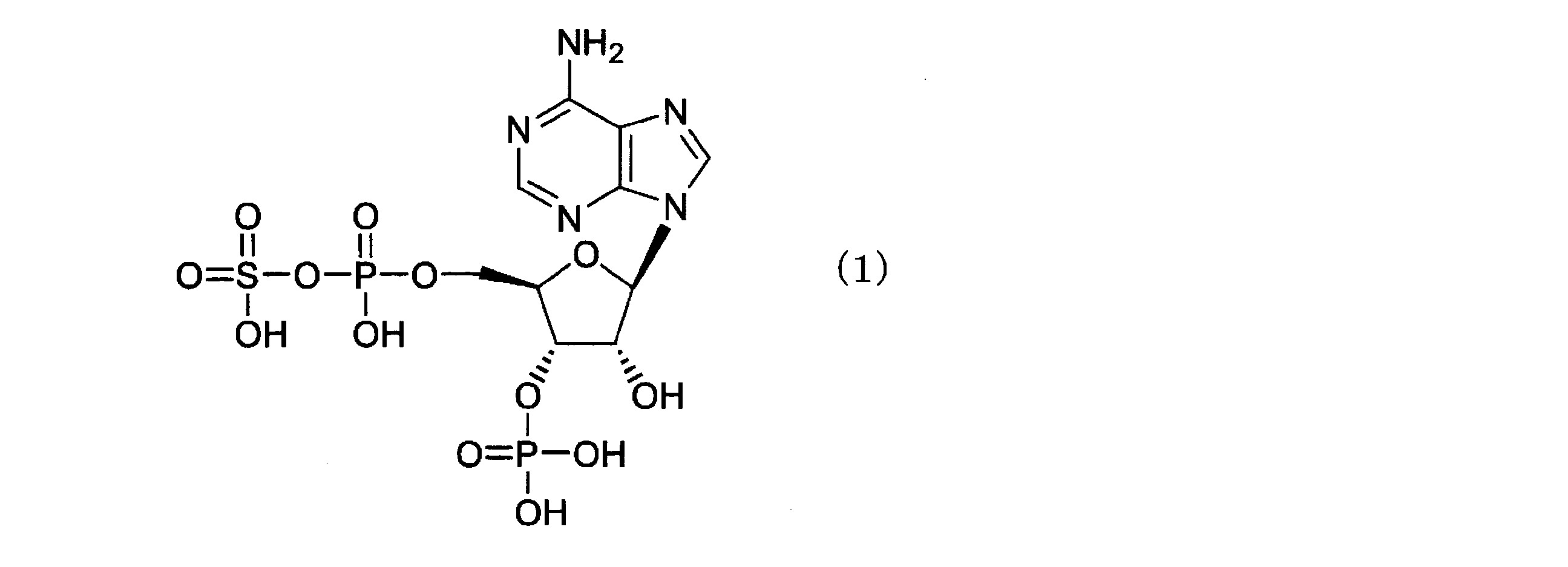
- PAPS 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate
- PAPS plays an important role as a sulfate group donor in sulfation reactions in vivo.
- PAPS is an indispensable substance for biosynthesis of glycosaminoglycans such as chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, heparan sulfate, and keratan sulfate, and various sulfated glycolipids and sulfated proteins.
- glycosaminoglycans such as chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, heparan sulfate, and keratan sulfate
- various sulfated glycolipids and sulfated proteins are highly water-soluble and has a high negative charge, it is unlikely that it will permeate the cell membrane.
- the present invention provides a hair restorer composition containing PAPS represented by the formula (1) or a salt thereof.
- the present invention also provides PAPS represented by the above formula (1) or a salt thereof for hair growth. Moreover, this invention provides use of PAPS represented by the said Formula (1) or its salt for hair restorer manufacture. Furthermore, the present invention provides a hair-growth method characterized by administering an effective amount of PAPS represented by the above formula (1) or a salt thereof.
- PAPS not only has an effect of promoting hair elongation, but also has an effect of maintaining and extending the growth period in the hair cycle, and has an extremely high effect of suppressing hair loss. Therefore, the hair-restoring agent composition of the present invention exhibits a powerful hair-restoring effect compared to conventional hair-restoring compositions. Moreover, since PAPS is an in vivo component, it is highly safe.
- FIG. 6 is a graph showing the ratio of the state of all hair follicle organs in each group 6 days after the start of tests (1) to (3). It is a figure which shows the ratio of the state of the hair follicle organ of each group 6 days after the test start of a test (4).
- the hair restorer composition of the present invention contains PAPS or a salt thereof as an active ingredient.
- “containing” means that the hair restorer composition of the present invention may be composed only of PAPS, and that the hair restorer composition may contain other components other than PAPS.
- the hair nourishing effect means an effect of maintaining / extending the growth period of human hair follicles or an effect of suppressing hair loss. Further, the hair growth effect means an effect of promoting the elongation of human hair.
- PAPS is a known in vivo component and may be produced by any method such as an enzymatic method or a chemical method.
- Patent No. 3098591, Patent No. 3078067, Patent No. 3029915, Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 27, 171-172 (1992), WO 2006-080313, etc. can be employed.
- PAPS salts include metal salts such as sodium salts, ammonium salts, various amine salts, amino acid salts, imidazole salts, and the like.
- PAPS salts may be a prodrug of PAPS or a salt thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of a prodrug.
- the content of PAPS in the hair restorer composition of the present invention is preferably 0.001 to 10% (w / v) from the viewpoint of effectiveness and safety, and 0.01 to 1% (w / V) is more preferable.
- optional components include purified water, ethanol, oily components, humectants, thickeners, preservatives, emulsifiers, medicinal components, powders, ultraviolet absorbers, dyes, fragrances, and emulsion stabilizers. Can do.
- the hair restorer composition of the present invention is preferably a skin external preparation in the form of liquid, emulsion, ointment, cream, gel, aerosol and the like.
- the hair-restoring agent composition of this invention can be used in various fields, such as a pharmaceutical, a quasi-drug, or cosmetics.
- the hair restorer composition of the present invention can be used for the treatment and prevention of hair loss.
- it can be widely used for the treatment and prevention of male pattern hair loss, the treatment and prevention of diffuse alopecia, which is common in women, and the treatment of alopecia areata.
- the alopecia name shown here is an illustration, The disease which can use the hair restorer of this invention for these alopecia is not limited.
- the hair-restoring agent composition of the present invention can be used not only for hair growth, but also for eyebrows and eyelashes.
- the hair growth composition of the present invention is characterized by not only having an effect of promoting hair elongation, but also having an effect of maintaining and extending the growth period in the hair cycle and suppressing hair loss.
- hair follicles are independent units for hair elongation control.
- This human hair follicle organ culture method is considered to be a highly reliable evaluation method because cell-cell interaction or cell-extracellular matrix interaction is maintained in vivo.
- the hair elongation promoting effect of the drug can be evaluated by comparing the amount of hair elongation before and after the test. That is, the hair growth effect can also be evaluated.
- the hair restorer composition of the present invention may be applied to the skin 1 to 3 times a day, and the application amount is preferably 0.1 to 10 mg per time as PAPS or a salt thereof.
- all% means weight% (w / v).
- Example 1 Evaluation of hair restoration effect of PAPS (1) Using hair follicles collected from three male pattern baldness men (37-year-old male, 63-year-old male, 62-year-old male), the following tests were carried out three times (each of test (1), test (2), Test (referred to as (3)). About 10 mm 2 of human scalp tissue (occipital region) was collected and immediately immersed in ice-cold phosphate buffered saline. Subsequently, after immersing and sterilizing with a disinfecting iodine solution for 10 seconds, immersing and cleaning was performed twice with 70% ethanol for 20 seconds, and further, immersing and cleaning was performed twice with phosphate buffered saline.
- DMEM medium Dulbecco's modified MEM medium
- hair follicle organs were separated one by one using a micro knife under a stereomicroscope.
- the hair follicle organs were grouped into 4 groups so that the hair follicle sizes and forms were evenly distributed (the number of hair follicle organs [n] in each group per test was 8 to 10).
- Add 0.5 mL of hair follicle culture medium (William's Medium E medium with 2 mM L-Glutamine, streptomycin (100 ⁇ g / mL) and penicillin (100 units / mL)) to each well of a 12-well plate in advance.
- the isolated hair follicles were allowed to stand in each well. After pre-culture for 24 hours in a carbon dioxide incubator (carbon dioxide concentration 5%) adjusted to 37 ° C, the following four types of test substances were added to each group, and the test was started. Thereafter, the medium exchange and the addition of the test substance were repeated every 48 hours. Distilled water was added to the first group as a control. To the second group, PAPS, 4Na was added to a final concentration of 0.25%. To the third group, PAPS, 4Na was added to a final concentration of 0.05%.
- Group 4 contains a medium supplement containing insulin as a positive control (10 ⁇ g / mL insulin, 10 ng / mL hydrocortisone, 10 ⁇ g / mL transferrin, 10 ng / mL sodium selenite at final concentrations) (hereinafter referred to as “insulins”). Added).
- insulins a medium supplement containing insulin as a positive control (10 ⁇ g / mL insulin, 10 ng / mL hydrocortisone, 10 ⁇ g / mL transferrin, 10 ng / mL sodium selenite at final concentrations).
- insulins 10 ⁇ g / mL insulin, 10 ng / mL hydrocortisone, 10 ⁇ g / mL transferrin, 10 ng / mL sodium selenite at final concentrations
- Insulins 10 ⁇ g / mL insulin, 10 ng / mL hydrocortisone, 10 ⁇ g /
- the rates were as high as 56% and 60%, respectively.
- Example 2 Evaluation of hair restoration effect of PAPS (2) Using the hair follicles newly collected from two other male pattern baldness men (56-year-old male and 63-year-old male), the following test was conducted (referred to as test (4)).
- a hair follicle organ was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1. The hair follicle organs were grouped into 3 groups taking care that the hair follicle size and morphology were evenly distributed.
- 0.5 mL of hair follicle culture medium (William's Medium E medium supplemented with 2 mM L-Glutamine and ampicillin (50 ⁇ g / mL)) was placed in advance and isolated hair follicles.
- the result of determining the hair follicle state 6 days after the start of the test is shown in FIG.
- the rate was significantly high at 45%.
- the ratio of hair follicles in the “hair regression” state was 55% in the distilled water group and 65% in the 0.05% minoxidil group, whereas it was high in the 0.05% PAPS group. The rate was significantly low at 20%.
- Example 3 Evaluation of hair-restoring effect of PAPS (3)
- the state of each hair follicle of Example 2 is determined every two days, and is classified into three groups of “hair elongation”, “hair regression”, and “no change” as in Example 1, and among these, “no change”. Were excluded from this evaluation.
- the ratio of the number of follicles of the remaining two groups of “hair elongation” and “hair regression” was determined at each evaluation point, and the change with time was followed.
- FIG. 9 shows the result of comparative analysis of the hair extension duration days of each hair follicle.
- the average value of the hair extension duration days of the first group (distilled water group) was 3.1 days, and the same value of the second group (0.05% minoxidil group) was 3.3 days.
- the equivalent value in the third group (0.05% PAPS group) was 6.0 days, which was about twice as high.
- the hair extension duration days of the third group are statistically significantly higher than the equivalent values of the first group and the second group (p value ⁇ 0.05 by Mann-Whitney U test). It was revealed that PAPS has a remarkable hair elongation maintaining effect (that is, an effect of maintaining / prolonging the growth phase in the hair cycle) exceeding that of minoxidil at the same concentration.
- the hair elongation amount of the first group (distilled water group) at the end of the culture period was 0.67 mm, while the equivalent value of the second group (0.05% minoxidil group) was 0.38 mm.
- the equivalent value of Group 3 (0.05% PAPS group) was 0.82 mm, and it was revealed that PAPS has an excellent hair elongation promoting effect.
- Example 4 Evaluation of hair growth effect of PAPS (4) The following test was carried out using a hair follicle collected from one male pattern baldness male (66-year-old male) (referred to as test (5)).
- a hair follicle tissue was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1.
- the following three types of test substances were added to each group, one by one. Distilled water was added to the first group as a control.
- adenosine was added as a positive control to a final concentration of 0.05%.
- the change with time of the hair follicle state ratio of each group is shown in FIG. 11, FIG. 12, and FIG. Comparing the hair follicle state 4 days after the start of the test, the ratio of the hair follicle in the “hair elongation” state was 67% in the distilled water group and 58% in the 0.05% adenosine group, whereas it was 0%. In the 0.05% PAPS group, it was 92%, which was higher than the other two groups. Furthermore, when comparing the hair follicle state 8 days after the start of the test, the ratio of the hair follicle in the “hair extension” state was 17% in the distilled water group and 0% in the 0.05% adenosine group, 4 days after the start of the test.
- the ratio decreased, while the 0.05% PAPS group maintained a high rate of 50%.
- the ratio of “unchanged” hair follicles was 25% in the distilled water group and 42% in the 0.05% adenosine group, but 8% in the 0.05% PAPS group. The rate was significantly lower. From these results, it can be seen that PAPS has the effect of increasing the ratio of hair follicles in the “hair elongation” state, which was not observed with the same concentration of adenosine, that is, the effect of maintaining and extending the growth period in the hair cycle. found.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Dermatology (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Birds (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Cosmetics (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
Description
従って、本発明の課題は、より育毛養毛効果の高い育毛剤組成物を提供することにある。
男性型脱毛症男性3名(37歳男性、63歳男性、62歳男性)各々より採取した毛包を用いて、以下の試験を3回実施した(それぞれ試験(1)、試験(2)、試験(3)と称する)。約10mm2のヒト頭皮組織(後頭部)を採取し、氷冷したリン酸緩衝生理的食塩水に速やかに浸漬した。続いて、消毒用ヨード液で10秒間浸漬消毒した後、70%エタノールで20秒間の浸漬洗浄を2度行い、さらに、リン酸緩衝生理的食塩水で2度浸漬洗浄した。この後、10%牛胎児血清を添加したダルベッコ変法MEM培地(DMEM培地)に組織を浸漬させ、実体顕微鏡下で、マイクロメスを用いて毛包器官を1ケずつ分離した。この毛包器官を、毛包のサイズや形態が均等に分布するよう留意して4群に群分けした(試験1回あたりの各群の毛包器官数〔n〕は8~10本)。あらかじめ12ウェルプレートの各ウェルに0.5mLの毛包培養培地(William’s Medium E培地に2mM L-Glutamine、ストレプトマイシン(100μg/mL)、ペニシリン(100units/mL)を添加したもの)を入れておき、単離した毛包を各ウェルに1本ずつ静置した。37℃に調温した炭酸ガスインキュベーター(炭酸ガス濃度5%)中で24時間の前培養を行った後、以下に示す4種類の被検物質を各群に1種類ずつ添加して試験を開始し、その後、48時間毎に培地交換および被検物質の添加を繰り返した。第1群には対照として蒸留水を添加した。第2群にはPAPS,4Naを終濃度0.25%となるよう添加した。第3群にはPAPS,4Naを終濃度0.05%となるよう添加した。第4群には陽性対照としてインスリンを含む培地添加物(いずれも終濃度で10μg/mLインスリン、10ng/mLハイドロコルチゾン、10μg/mLトランスフェリン、10ng/mL亜セレン酸ナトリウム)(以降、インスリン類と称する)を添加した。試験開始後、定期的に各毛包の状態を評価し、当該毛包の状態に応じて以下の3つのグループに分類した。評価時点において、毛伸長が継続している毛包を「毛伸長」、毛球部の退行変化を伴って毛伸長が停止した毛包を「毛退行」、試験期間を通じて変化が認められなかった毛包を「無変化」と分類した。
新たに別の男性型脱毛症男性2名(56歳男性、63歳男性)より採取した毛包を用いて、以下の試験を実施した(試験(4)と称する)。実施例1と同様の方法で毛包器官を得た。この毛包器官を、毛包のサイズや形態が均等に分布するよう留意して3群に群分けした。あらかじめ12ウェルプレートの各ウェルに0.5mLの毛包培養培地(William’s Medium E培地に2mM L-Glutamine、アンピシリン(50μg/mL)を添加したもの)を入れておき、単離した毛包を各ウェルに1本ずつ静置した。37℃に調温した炭酸ガスインキュベーター(炭酸ガス濃度5%)中で24時間の前培養を行った後、以下に示す3種類の被検物質を各群に1種類ずつ添加して試験を開始し、その後、48時間毎に培地交換および被検物質の添加を繰り返した。第1群には対照として蒸留水を添加した。第2群には陽性対照としてミノキシジルを終濃度0.05%となるよう添加した。第3群にはPAPS,4Naを終濃度0.05%となるよう添加した。試験開始後、各毛包の状態を実施例1と同様に定期的に判定し、「毛伸長」、「毛退行」、「無変化」の3グループに分類した。
実施例2の各毛包の状態を2日毎に判定し、実施例1と同様に「毛伸長」、「毛退行」、「無変化」の3グループに分類し、この内、「無変化」のグループを本評価から除外した。残る「毛伸長」と「毛退行」の2グループの毛包数の比率を各評価時点で求め、その経時的な変化を追った。
男性型脱毛症男性1名(66歳男性)より採取した毛包を用いて、以下の試験を実施した(試験(5)と称する)。実施例1と同様の方法で毛包組織を得た。この毛包組織を、毛包のサイズや形態が均等に分布するよう留意して3群に群分けした(それぞれn=12)。実施例2と同様の方法で、24時間の前培養を行った後、以下に示す3種類の被検物質を各群に1種類ずつ添加した。第1群には対照として蒸留水を添加した。第2群には陽性対照としてアデノシンを終濃度0.05%となるよう添加した。第3群にはPAPS,4Naを終濃度0.05%となるよう添加した。被検物質添加後、2日毎に培地交換および被検物質の添加を行い、炭酸ガスインキュベーター(炭酸ガス濃度5%)中で12日間培養し、2日毎に写真撮影した。PAPSが器官培養毛包の毛包状態変化に及ぼす影響を詳細に解析するために、実施例1と同様の方法で毛包の状態を経時的に評価した。
Claims (14)
- 3’-ホスホアデノシン5’-ホスホ硫酸又はその塩を0.001~10%(w/v)含有する請求項1記載の育毛剤組成物。
- 皮膚外用剤である請求項1又は2記載の育毛剤組成物。
- 皮膚外用剤の形態で使用するものである請求項4記載の化合物。
- 皮膚外用剤中に0.001~10%(w/v)含有される請求項5の化合物。
- 育毛剤組成物中に3’-ホスホアデノシン5’-ホスホ硫酸又はその塩を0.001~10%(w/v)含有する請求項7記載の使用。
- 育毛剤組成物が、皮膚外用剤である請求項7記載の使用。
- 育毛剤組成物が、3’-ホスホアデノシン5’-ホスホ硫酸又はその塩を0.001~10%(w/v)含有する皮膚外用剤である請求項7記載の使用。
- 3’-ホスホアデノシン5’-ホスホ硫酸又はその塩を0.001~10%(w/v)含有する組成物を投与する請求項11記載の方法。
- 投与手段が、皮膚外用である請求項11記載の方法。
- 3’-ホスホアデノシン5’-ホスホ硫酸又はその塩を0.001~10%(w/v)含有する組成物を、皮膚外用する請求項11記載の方法。
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020137007471A KR101880776B1 (ko) | 2010-10-29 | 2011-10-28 | 육모제 조성물 |
| JP2012540982A JP5730328B2 (ja) | 2010-10-29 | 2011-10-28 | 育毛剤組成物 |
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010-243143 | 2010-10-29 | ||
| JP2010243143 | 2010-10-29 | ||
| JP2011-038346 | 2011-02-24 | ||
| JP2011038346 | 2011-02-24 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2012057336A1 true WO2012057336A1 (ja) | 2012-05-03 |
Family
ID=45994038
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2011/074983 WO2012057336A1 (ja) | 2010-10-29 | 2011-10-28 | 育毛剤組成物 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5730328B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR101880776B1 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2012057336A1 (ja) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012201665A (ja) * | 2011-03-28 | 2012-10-22 | Yamasa Shoyu Co Ltd | 保湿作用を有する皮膚外用剤 |
| US9975964B2 (en) | 2013-12-02 | 2018-05-22 | Ostrich Pharma Kk | Antibody against alopecia-inducing substance as antigen, composition and production method |
| KR20230004466A (ko) | 2020-04-03 | 2023-01-06 | 렌슬러 폴리테크닉 인스티튜트 | 황산화된 다당류의 제조 방법 및 paps의 제조 방법 |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH02311411A (ja) * | 1989-05-29 | 1990-12-27 | Kobayashi Kose Co Ltd | 養毛料 |
| JP2000198718A (ja) * | 1998-10-26 | 2000-07-18 | Shiseido Co Ltd | 血行促進外用剤 |
| JP2000297015A (ja) * | 1999-02-10 | 2000-10-24 | Taisho Pharmaceut Co Ltd | 育毛剤及び育毛作用を有する物質のスクリーニング方法 |
| JP2006223198A (ja) * | 2005-02-17 | 2006-08-31 | National Institute Of Advanced Industrial & Technology | 転移酵素による化合物ライブラリーおよびその製造方法 |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4596812A (en) | 1976-05-24 | 1986-06-24 | The Upjohn Company | Methods and solutions for treating male pattern alopecia |
| US4139619A (en) | 1976-05-24 | 1979-02-13 | The Upjohn Company | 6-Amino-4-(substituted amino)-1,2-dihydro-1-hydroxy-2-iminopyrimidine, topical compositions and process for hair growth |
| EP0998907B1 (en) * | 1998-10-26 | 2004-01-14 | Shiseido Company, Ltd. | Hair tonic composition comprising adenosine |
| JP3957690B2 (ja) | 1998-10-26 | 2007-08-15 | 株式会社資生堂 | 養毛料 |
-
2011
- 2011-10-28 KR KR1020137007471A patent/KR101880776B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2011-10-28 WO PCT/JP2011/074983 patent/WO2012057336A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2011-10-28 JP JP2012540982A patent/JP5730328B2/ja active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH02311411A (ja) * | 1989-05-29 | 1990-12-27 | Kobayashi Kose Co Ltd | 養毛料 |
| JP2000198718A (ja) * | 1998-10-26 | 2000-07-18 | Shiseido Co Ltd | 血行促進外用剤 |
| JP2000297015A (ja) * | 1999-02-10 | 2000-10-24 | Taisho Pharmaceut Co Ltd | 育毛剤及び育毛作用を有する物質のスクリーニング方法 |
| JP2006223198A (ja) * | 2005-02-17 | 2006-08-31 | National Institute Of Advanced Industrial & Technology | 転移酵素による化合物ライブラリーおよびその製造方法 |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| KAZUYA ISHIGE: "Seitainai Ryusanki Kyoyotai 3'-phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate no Kikan Baiyo Hito Tohatsu Moho ni Taisuru Seichoki Encho Koka", SKIN SURGERY, vol. 20, no. 1, 31 January 2011 (2011-01-31), pages 103 * |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012201665A (ja) * | 2011-03-28 | 2012-10-22 | Yamasa Shoyu Co Ltd | 保湿作用を有する皮膚外用剤 |
| US9975964B2 (en) | 2013-12-02 | 2018-05-22 | Ostrich Pharma Kk | Antibody against alopecia-inducing substance as antigen, composition and production method |
| US10246520B2 (en) | 2013-12-02 | 2019-04-02 | Ostrich Pharma Kk | Antibody against alopecia-inducing substance as antigen, composition and production method |
| KR20230004466A (ko) | 2020-04-03 | 2023-01-06 | 렌슬러 폴리테크닉 인스티튜트 | 황산화된 다당류의 제조 방법 및 paps의 제조 방법 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20130136984A (ko) | 2013-12-13 |
| KR101880776B1 (ko) | 2018-07-20 |
| JP5730328B2 (ja) | 2015-06-10 |
| JPWO2012057336A1 (ja) | 2014-05-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1498101B1 (en) | Composition for cell proliferation | |
| JP7300988B2 (ja) | 外用組成物 | |
| US7557093B2 (en) | Composition for promoting collagen production | |
| JPWO2005044205A1 (ja) | 毛髪の太毛化の方法及び組成物 | |
| EP1844757A1 (fr) | Utilisation de dérivé c-glycosides comme agent protecteur et/ou activateur des lymphocytes gamma delta t | |
| JP5730328B2 (ja) | 育毛剤組成物 | |
| CN110548031A (zh) | 包含乌地那非作为活性成分的用于增强脂肪干细胞的生发诱导能力的组合物 | |
| US20090325890A1 (en) | Use of galactose c-glycoside derivatives as protective agent and/or gama delta t lymphocyte activator | |
| WO2007116017A1 (fr) | Utilisation de dérivé de d- et l-fucose comme agent protecteur et/ou activateur des lymphocytes gamma delta t | |
| JP7135106B2 (ja) | 頭皮頭髪用組成物 | |
| EP3991734A1 (en) | Agent for promoting hair growth | |
| US10543227B2 (en) | Hair growth composition | |
| JP2020186218A (ja) | 発毛因子産生促進剤及び/又は毛再生剤及び/又は脱毛抑制剤 | |
| WO2023191015A1 (ja) | コラーゲン産生促進剤、化粧料組成物又は皮膚外用剤、及び経口投与剤 | |
| JP7203519B2 (ja) | クローディン発現促進剤およびタイトジャンクション形成促進剤 | |
| CN112043627B (zh) | 一种毛发生长的氨基酸溶液组合物及其制备方法 | |
| RU2805147C2 (ru) | Биологическая добавка для введения в состав косметических и заживляющих средств, способ ее получения, косметические и заживляющие составы на ее основе | |
| KR102386651B1 (ko) | 티플락스티닌을 유효성분으로 함유하는 탈모 예방 또는 치료용 조성물 | |
| KR102540969B1 (ko) | 소듐 2-메르캅토에탄 설포네이트를 함유하는 피부 재생 촉진용 조성물 | |
| JP2021155406A (ja) | 育毛促進用組成物 | |
| US20100160251A1 (en) | Imidazo compounds |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 11836469 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2012540982 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20137007471 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 11836469 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |