WO2010021111A1 - Inhbb epitope peptides and vaccines containing the same - Google Patents
Inhbb epitope peptides and vaccines containing the same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2010021111A1 WO2010021111A1 PCT/JP2009/003894 JP2009003894W WO2010021111A1 WO 2010021111 A1 WO2010021111 A1 WO 2010021111A1 JP 2009003894 W JP2009003894 W JP 2009003894W WO 2010021111 A1 WO2010021111 A1 WO 2010021111A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- peptide
- peptides
- antigen
- set forth
- present
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K4/00—Peptides having up to 20 amino acids in an undefined or only partially defined sequence; Derivatives thereof
- C07K4/12—Peptides having up to 20 amino acids in an undefined or only partially defined sequence; Derivatives thereof from animals; from humans
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/70—Carbohydrates; Sugars; Derivatives thereof
- A61K31/7088—Compounds having three or more nucleosides or nucleotides
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K39/0005—Vertebrate antigens
- A61K39/0011—Cancer antigens
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K39/0005—Vertebrate antigens
- A61K39/0011—Cancer antigens
- A61K39/001102—Receptors, cell surface antigens or cell surface determinants
- A61K39/001122—Ephrin Receptors [Eph]
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K40/00—Cellular immunotherapy
- A61K40/10—Cellular immunotherapy characterised by the cell type used
- A61K40/11—T-cells, e.g. tumour infiltrating lymphocytes [TIL] or regulatory T [Treg] cells; Lymphokine-activated killer [LAK] cells
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K40/00—Cellular immunotherapy
- A61K40/40—Cellular immunotherapy characterised by antigens that are targeted or presented by cells of the immune system
- A61K40/41—Vertebrate antigens
- A61K40/42—Cancer antigens
- A61K40/4202—Receptors, cell surface antigens or cell surface determinants
- A61K40/422—Ephrin Receptors [Eph]
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P35/00—Antineoplastic agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P37/00—Drugs for immunological or allergic disorders
- A61P37/02—Immunomodulators
- A61P37/04—Immunostimulants
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K14/00—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof
- C07K14/435—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof from animals; from humans
- C07K14/46—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof from animals; from humans from vertebrates
- C07K14/47—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof from animals; from humans from vertebrates from mammals
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K7/00—Peptides having 5 to 20 amino acids in a fully defined sequence; Derivatives thereof
- C07K7/04—Linear peptides containing only normal peptide links
- C07K7/06—Linear peptides containing only normal peptide links having 5 to 11 amino acids
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K2039/57—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies characterised by the type of response, e.g. Th1, Th2
- A61K2039/572—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies characterised by the type of response, e.g. Th1, Th2 cytotoxic response
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K38/00—Medicinal preparations containing peptides
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N2500/00—Screening for compounds of potential therapeutic value
Definitions
- the present invention relates to the field of biological science, more specifically to the field of cancer therapy.
- the present invention relates to novel peptides that are extremely effective as cancer vaccines, and drugs for treating and preventing tumors.
- CD8 positive CTLs recognize epitope peptides derived from the tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) found on major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecule, and then kill the tumor cells.
- TAAs tumor-associated antigens
- MHC major histocompatibility complex
- NPL 3 Harris CC, J Natl Cancer Inst 1996 Oct 16, 88(20): 1442-55; NPL 4 : Butterfield LH et al., Cancer Res 1999 Jul 1, 59(13): 3134-42; NPL 5: Vissers JL et al., Cancer Res 1999 Nov 1, 59(21): 5554-9; NPL 6: van der Burg SH et al., J Immunol 1996 May 1, 156(9): 3308-14; NPL 7: Tanaka F et al., Cancer Res 1997 Oct 15, 57(20): 4465-8; NPL 8: Fujie T et al., Int J Cancer 1999 Jan 18, 80(2): 169-72; NPL 9: Kikuchi M et al., Int J Cancer 1999 May 5, 81(3): 459-66; NPL 10: Oiso
- NPL 11 Belli F et al., J Clin Oncol 2002 Oct 15, 20(20): 4169-80
- NPL 12 Coulie PG et al., Immunol Rev 2002 Oct, 188: 33-42
- NPL 13 Rosenberg SA et al., Nat Med 2004 Sep, 10(9): 909-15).
- Inhibins are heterodimeric glycoproteins composed of an alpha subunit (INHA) and one of two beta subunits (beta-A or beta-B).
- Inhibin, beta B (INHBB) is a subunit of both inhibin and activin, two closely related glycoproteins with opposing biological effects.
- INHBB is an interesting target for cancer immunotherapy and CTL inducing epitope peptides derived therefrom are sought by those in the art.
- the present invention is based in part on the discovery of suitable targets of immunotherapy. Because TAAs often induce immune tolerance and therefore elicit poor immunogenicity, the discovery of appropriate targets is of extreme importance. Recognizing that INHBB has been identified as up-regulated in cancer tissues of cholangio cellular carcinoma, esophageal cancer, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), renal carcinoma, small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and soft tissue tumor, the present invention targets the Homo sapiens inhibin, beta B (INHBB) protein (SEQ ID NO: 16) encoded by the gene of GenBank Accession No. NM_002193 (SEQ ID NO: 15)) for further analysis.
- INHBB Homo sapiens inhibin, beta B (INHBB) protein
- INHBB gene products containing epitope peptides that elicit CTLs specific to the corresponding molecules were selected for study.
- Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) obtained from a healthy donor were stimulated using HLA-A*0201 binding candidate peptides derived from INHBB.
- CTLs that specifically recognize HLA-A02 positive target cells pulsed with the respective candidate peptides were established, and HLA-A02 restricted epitope peptides that can induce potent and specific immune responses against INHBB expressed on the surface of tumor cells were identified.
- the present invention provides peptides having CTL inducibility as well as an amino acid sequence selected from the group of SEQ ID NOs: 1 to 14, and which have CTL inducibility.
- the present invention contemplates modified peptides, wherein one, two or more amino acids are substituted or added, so long as the modified peptides retain the original CTL inducibility.
- the present peptides When administered to a subject, the present peptides are presented on the surface of antigen-expressing cells and then induce CTLs targeting the respective peptides. Therefore, it is an object of the present invention to provide antigen-presenting cells and exosomes that present any of the present peptides, as well as methods for inducing antigen-presenting cells.
- An anti-tumor immune response is induced by the administration of the present INHBB polypeptides or polynucleotide encoding the polypeptides, as well as exosomes and antigen-presenting cells which present the INHBB polypeptides. Therefore, it is yet another object of the present invention to provide pharmaceutical agents containing the polypeptides or polynucleotides encoding them, as well as the exosomes and antigen-presenting cells as their active ingredients.
- the pharmaceutical agents of the present invention find use as vaccines.
- the CTLs of the invention also find use as vaccines against cancer.
- the cancer include, but are not limited to, cholangio cellular carcinoma, esophageal cancer, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), renal carcinoma, small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and soft tissue tumor.
- Figure 1 includes a series of photographs, (a) - (n), depicting the results of IFN-gamma ELISPOT assay on CTLs that were induced with peptides derived from INHBB.
- the CTLs in well #4 stimulated with INHBB-A02-9-213 (SEQ ID NO: 1) (a), well #5 and #7 stimulated with INHBB-A02-9-174 (SEQ ID NO: 2) (b), well #8 stimulated with INHBB-A02-9-257 (SEQ ID NO: 3) (c), well #1 and #8 stimulated with INHBB-A02-9-313 (SEQ ID NO: 4) (d), well #1, #4 and #8 stimulated with INHBB-A02-9-139 (SEQ ID NO: 5) (e), well #4 stimulated with INHBB-A02-9-8 (SEQ ID NO: 6) (f), well #6 stimulated with INHBB-A02-9-250 (SEQ ID NO: 7) (g), well #5 stimulated with I
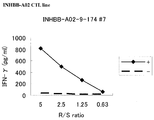
- Figure 2 depicts a line graph showing the results of establishment of CTL lines stimulated with INHBB-A02-9-174 (SEQ ID NO: 2) with IFN-gamma ELISA assay.
- the depicted results demonstrate that CTL line established by stimulation with the peptide showed potent IFN-gamma production as compared with the control.
- “+” indicates that the target cells were pulsed with the appropriate peptide and "-” indicates that the target cells had not been pulsed with any peptides.
- polypeptide peptide
- protein protein
- amino acid polymers in which one or more amino acid residue is a modified residue, or a non-naturally occurring residue, such as an artificial chemical mimetic of a corresponding naturally occurring amino acid, as well as to naturally occurring amino acid polymers.
- amino acid refers to naturally occurring and synthetic amino acids, as well as amino acid analogs and amino acid mimetics that similarly function to the naturally occurring amino acids.
- Naturally occurring amino acids are those encoded by the genetic code, as well as those modified after translation in cells (e.g., hydroxyproline, gamma-carboxyglutamate, and O-phosphoserine).
- amino acid analog refers to compounds that have the same basic chemical structure (an alpha carbon bound to a hydrogen, a carboxy group, an amino group, and an R group) as a naturally occurring amino acid but have a modified R group or modified backbones (e.g., homoserine, norleucine, methionine, sulfoxide, methionine methyl sulfonium).
- modified R group or modified backbones e.g., homoserine, norleucine, methionine, sulfoxide, methionine methyl sulfonium.
- amino acid mimetic refers to chemical compounds that have different structures but similar functions to general amino acids.
- Amino acids may be referred to herein by their commonly known three letter symbols or the one-letter symbols recommended by the IUPAC-IUB Biochemical Nomenclature Commission.
- cancer refers to cancers over-expressing the INHBB gene, examples of which include, but are not limited to, cholangio cellular carcinoma, esophageal cancer, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), renal carcinoma, small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and soft tissue tumor.
- NSCLC non-small cell lung cancer
- SCLC small cell lung cancer
- cytotoxic T lymphocyte refers to a sub-group of T lymphocytes that are capable of recognizing non-self cells (e.g., tumor cells, virus-infected cells) and inducing the death of such cells.
- non-self cells e.g., tumor cells, virus-infected cells
- peptides derived from INHBB function as an antigen recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs)
- CTLs cytotoxic T lymphocytes
- peptides derived from INHBB SEQ ID NO: 16 were analyzed to determine whether they were antigen epitopes restricted by HLA-A02 which are commonly encountered HLA alleles (Date Y et al., Tissue Antigens 47: 93-101, 1996; Kondo A et al., J Immunol 155: 4307-12, 1995; Kubo RT et al., J Immunol 152: 3913-24, 1994).
- Candidates of HLA-A02 binding peptides derived from INHBB were identified based on their binding affinities to HLA-A02.
- INHBB-A02-9-213 SEQ ID NO: 1
- INHBB-A02-9-174 SEQ ID NO: 2
- INHBB-A02-9-257 SEQ ID NO: 3
- INHBB-A02-9-313 SEQ ID NO: 4
- INHBB-A02-9-139 SEQ ID NO: 5
- INHBB-A02-9-8 SEQ ID NO: 6
- INHBB-A02-9-250 SEQ ID NO: 7
- INHBB-A02-10-179 SEQ ID NO: 8
- INHBB-A02-10-237 SEQ ID NO: 9
- INHBB-A02-10-313 SEQ ID NO: 10
- INHBB-A02-10-173 SEQ ID NO: 11
- INHBB-A02-10-256 INHBB-A02-10-256
- the INHBB gene is over expressed in most cancer tissues, such as cholangio cellular carcinoma, esophageal cancer, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), renal carcinoma, small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and soft tissue tumor, it is a good target for immunotherapy.
- NSCLC non-small cell lung cancer
- SCLC small cell lung cancer
- the present invention provides nonapeptides (peptides consisting of nine amino acid residues) and decapeptides (peptides consisting of ten amino acid residues) corresponding to CTL-recognized epitopes of INHBB.
- Particularly preferred examples of nonapeptides and decapeptides of the present invention include those peptides having an amino acid sequence selected from among SEQ ID NOs: 1 to 14.
- the nonapeptides and decapeptides of the present invention can be flanked with additional amino acid residues so long as the resulting peptides retain their CTL inducibility.
- Such peptides having CTL inducibility are typically less than about 40 amino acids, often less than about 20 amino acids, usually less than about 15 amino acids.
- the particular amino acid sequences flanking the nonapeptides and decapeptides of the present invention i.e., peptides consisting of the amino acid sequence selected from among SEQ ID NOs: 1 to 14
- the present invention also provides peptides having CTL inducibility and the amino acid sequence selected from among SEQ ID NOs: 1 to 14.
- modified peptides i.e., peptides composed of an amino acid sequence in which one, two or several amino acid residues have been modified (i.e., substituted, deleted, added or inserted) as compared to an original reference sequence
- modified peptides have been known to retain the biological activity of the original peptide (Mark et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1984, 81: 5662-6; Zoller and Smith, Nucleic Acids Res 1982, 10: 6487-500; Dalbadie-McFarland et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1982, 79: 6409-13).
- the peptides of the present invention may have both CTL inducibility and an amino acid sequence selected from among SEQ ID NO: 1 to 14 wherein one, two or even more amino acids are deleted, inserted,
- amino acid side chain characteristics that are desirable to conserve include, for example, hydrophobic amino acids (A, I, L, M, F, P, W, Y, V), hydrophilic amino acids (R, D, N, C, E, Q, G, H, K, S, T), and side chains having the following functional groups or characteristics in common: an aliphatic side-chain (G, A, V, L, I, P); a hydroxyl group containing side-chain (S, T, Y); a sulfur atom containing side-chain (C, M); a carboxylic acid and amide containing side-chain (D, N, E, Q); a base containing side-chain (R, K, H); and an aromatic containing side-chain (H, F, Y, W).
- A, I, L, M, F, P, W, Y, V hydrophilic amino acids
- R, D, N, C, E, Q amino acids
- G, A, V, L, I, P a hydroxyl group containing side
- the following eight groups each contain amino acids that are accepted in the art as conservative substitutions for one another: 1) Alanine (A), Glycine (G); 2) Aspartic acid (D), Glutamic acid (E); 3) Aspargine (N), Glutamine (Q); 4) Arginine (R), Lysine (K); 5) Isoleucine (I), Leucine (L), Methionine (M), Valine (V); 6) Phenylalanine (F), Tyrosine (Y), Tryptophan (W); 7) Serine (S), Threonine (T); and 8) Cysteine (C), Methionine (M) (see, e.g., Creighton, Proteins 1984).
- Such conservatively modified peptides are also considered to be peptides of the present invention.
- peptides of the present invention are not restricted thereto and can include non-conservative modifications, so long as the modified peptide retains the CTL inducibility of the original peptide.
- modified peptides should not exclude CTL inducible peptides of polymorphic variants, interspecies homologues, and alleles of INHBB.
- a small number for example, 1, 2 or several
- a small percentage of amino acids for example, 1, 2 or several
- the term "several" means 5 or fewer amino acids, for example, 3 or fewer.
- the percentage of amino acids to be modified is preferably 20% or less, more preferably 15% of less, even more preferably 10% or less or 1 to 5%.
- INHBB-A02-9-213 SEQ ID NO: 1
- INHBB-A02-9-174 SEQ ID NO: 2
- INHBB-A02-9-257 SEQ ID NO: 3
- INHBB-A02-9-313 SEQ ID NO: 4
- INHBB-A02-9-139 SEQ ID NO: 5
- INHBB-A02-9-8 SEQ ID NO: 6
- INHBB-A02-9-250 SEQ ID NO: 7
- INHBB-A02-10-179 SEQ ID NO: 8
- INHBB-A02-10-237 SEQ ID NO: 9
- INHBB-A02-10-313 SEQ ID NO: 10
- INHBB-A02-10-173 SEQ ID NO: 11
- INHBB-A02-10-256 SEQ ID NO: 12
- INHBB-A02-10-162 SEQ ID NO: 13
- INHBB-A02-10-85 SEQ ID NO: 14
- these peptides are expected to be highly useful for eliciting immunity in tumor patients against INHBB on cancer cells, such as cholangio cellular carcinoma, esophageal cancer, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), renal carcinoma, small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and soft tissue tumor.
- cancer cells such as cholangio cellular carcinoma, esophageal cancer, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), renal carcinoma, small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and soft tissue tumor.
- peptides of the present invention When used in the context of immunotherapy, peptides of the present invention should be presented on the surface of a cell or exosome, preferably as a complex with an HLA antigen. Therefore, it is preferable to select peptides that not only induce CTLs but also that possess high binding affinity to the HLA antigen. To that end, the peptides can be modified by substitution, insertion, deletion, and/or addition of the amino acid residues to yield a modified peptide having improved binding affinity.
- peptides having the amino acid sequences of SEQ ID NOs: 1 to 14 wherein the second amino acid from the N-terminus of the amino acid sequence of the SEQ ID NOs is substituted with leucine or methionine and/or wherein the C-terminus of the amino acid sequence of the SEQ ID NOs is substituted with valine or leucine are encompassed by the present invention. Substitutions can be introduced not only at the terminal amino acids but also at the position of potential TCR recognition of peptides.
- amino acid substitutions in a peptide can be equal to or better than the original, for example, CAP1, p53 (264-272), Her-2/neu (369-377) or gp100 (209-217) (Zaremba et al., Cancer Res. 57, 4570-4577, 1997, T. K. Hoffmann et al., J Immunol. (2002) Feb 1;168(3):1338-47., S. O. Dionne et al., Cancer Immunol immunother. (2003) 52: 199-206 and S. O. Dionne et al., Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2004) 53, 307-314).
- the present invention also contemplates the addition one to two amino acids to the N and/or C-terminus of the present peptides.
- modified peptides having high HLA antigen binding affinity and retained CTL inducibility are also included in the present invention.
- the peptide sequence is identical to a portion of the amino acid sequence of an endogenous or exogenous protein having a different function, side effects such as autoimmune disorders and/or allergic symptoms against specific substances may be induced. Therefore, it is preferable to first perform homology searches using available databases to avoid situations in which the sequence of the peptide matches the amino acid sequence of another protein.
- the objective peptide can be modified in order to increase its binding affinity with HLA antigens, and/or increase its CTL inducibility without any danger of such side effects.
- CTL inducibility indicates the ability of the peptide to induce cytotoxic lymphocytes (CTLs) when presented on antigen-presenting cells.
- CTL inducibility includes the ability of the peptide to induce CTL activation and/or CTL proliferation, promote CTL lysis of target cells, and to increase CTL IFN-gamma production.
- Confirmation of CTL inducibility is accomplished by inducing antigen-presenting cells carrying human MHC antigens (for example, B-lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells (DCs)), or more specifically DCs derived from human peripheral blood mononuclear leukocytes, and after stimulation with the peptides, mixing with CD8-positive cells, and then measuring the IFN-gamma produced and released by CTL against the target cells.
- human MHC antigens for example, B-lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells (DCs)
- DCs dendritic cells
- transgenic animals that have been produced to express a human HLA antigen (for example, those described in BenMohamed L, Krishnan R, Longmate J, Auge C, Low L, Primus J, Diamond DJ, Hum Immunol 2000 Aug, 61(8): 764-79, Related Articles, Books, Linkout Induction of CTL response by a minimal epitope vaccine in HLA A*0201/DR1 transgenic mice: dependence on HLA class II restricted T(H) response) can be used.
- the target cells can be radiolabeled with 51 Cr and such, and cytotoxic activity can be calculated from radioactivity released from the target cells.
- CTL inducibility can be assessed by measuring IFN-gamma produced and released by CTL in the presence of antigen-presenting cells (APCs) that carry immobilized peptides, and visualizing the inhibition zone on the media using anti-IFN-gamma monoclonal antibodies.
- APCs antigen-presenting cells
- the peptides of the present invention can also be linked to other substances, so long as the resulting linked peptide retains the requisite CTL inducibility of the original peptide.
- suitable substances include, but are not limited to: peptides, lipids, sugar and sugar chains, acetyl groups, natural and synthetic polymers, etc.
- the peptides can contain modifications such as glycosylation, side chain oxidation, or phosphorylation, etc., provided the modifications do not destroy the biological activity of the original peptide. These kinds of modifications can be performed to confer additional functions (e.g., targeting function, and delivery function) or to stabilize the polypeptide.
- polypeptides For example, to increase the in vivo stability of a polypeptide, it is known in the art to introduce D-amino acids, amino acid mimetics or unnatural amino acids; this concept can also be adapted to the present polypeptides.
- the stability of a polypeptide can be assayed in a number of ways. For instance, peptidases and various biological media, such as human plasma and serum, can be used to test stability (see, e.g., Verhoef et al., Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokin 1986, 11: 291-302).
- the peptides of the present invention may be linked to other peptides via spacers or linkers.
- other peptides include, but are not limited to, CTL inducible peptides derived from other TAAs.
- two or more peptides of the present invention may be linked via spacers or linkers.
- the peptides linked via spacers or linkers may be the same or different each other.
- Spacers or linkers are not specifically limited, but are preferably peptides, more preferably peptides having one or more cleavage sites which are capable of being cleaved by enzymes such as peptidases, proteases and proteasomes.
- linkers or spacers include, but are not limited to: AAY (P. M. Daftarian et al., J Trans Med 2007, 5:26), AAA, NKRK (R. P. M. Sutmuller et al., J Immunol. 2000, 165: 7308-7315) or, one to several lysine redsidues (S. Ota et al., Can Res. 62, 1471-1476, K. S. Kawamura et al., J Immunol. 2002, 168: 5709-5715).
- the peptide of the present invention encompass those peptides linked to other peptides via spacers or linkers.
- the peptides of the present invention may be existed on the surface of a cell carrying human MHC antigens (e.g. antigen presenting cell) or an exosome as complexes in combination with MHC molecules and then induce CTLs.
- the cells and the exosomes can be prepared by well-known methods in the art, for example, the cells may be prepared by contacting with the peptides of the present invention, and the exosomes may be prepared by collecting an exosome-containing fraction from the cells contacted with the peptides of the present invention (see, e.g., Japanese Patent Application Kohyo Publications Nos. Hei 11-510507 and WO99/03499).
- the peptides of the present invention encompass those peptides existed on the surface of a cell or an exosome as complexes in combination with MHC molecules.
- the peptides of the present invention can also be described as "INHBB peptide(s)" or "INHBB polypeptide(s)".
- the peptides of the present invention can be prepared using well known techniques. For example, the peptides can be prepared synthetically, using recombinant DNA technology or chemical synthesis. Peptides of the present invention can be synthesized individually or as longer polypeptides composed of two or more peptides. The peptides can then be isolated i.e., purified or isolated so as to be substantially free of other naturally occurring host cell proteins and fragments thereof, or any other chemical substances.
- a peptide of the present invention can be obtained through chemical synthesis based on the selected amino acid sequence.
- Examples of conventional peptide synthesis methods that can be adapted to the synthesis include, but are not limited to: (i) Peptide Synthesis, Interscience, New York, 1966; (ii) The Proteins, Vol. 2, Academic Press, New York, 1976; (iii) Peptide Synthesis (in Japanese), Maruzen Co., 1975; (iv) Basics and Experiment of Peptide Synthesis (in Japanese), Maruzen Co., 1985; (v) Development of Pharmaceuticals (second volume) (in Japanese), Vol. 14 (peptide synthesis), Hirokawa, 1991; (vi) WO99/67288; and (vii) Barany G. & Merrifield R.B., Peptides Vol. 2, "Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis", Academic Press, New York, 1980, 100-118.
- the present peptides can be obtained adapting any known genetic engineering methods for producing peptides (e.g., Morrison J, J Bacteriology 1977, 132: 349-51; Clark-Curtiss & Curtiss, Methods in Enzymology (eds. Wu et al.) 1983, 101: 347-62).
- a suitable vector harboring a polynucleotide encoding the objective peptide in an expressible form e.g., downstream of a regulatory sequence corresponding to a promoter sequence
- the host cell is then cultured to produce the peptide of interest.
- the peptide can also be produced in vitro adopting an in vitro translation system.
- polynucleotides which encodes any of the aforementioned peptides of the present invention. These include polynucleotides derived from the natural occurring INHBB gene (GenBank Accession No. NM_002193 (SEQ ID NO: 15)) as well as those having a conservatively modified nucleotide sequence thereof.
- conservatively modified nucleotide sequence refers to sequences which encode identical or essentially identical amino acid sequences. Due to the degeneracy of the genetic code, a large number of functionally identical nucleic acids encode any given protein.
- the codons GCA, GCC, GCG, and GCU all encode the amino acid alanine.
- the codon can be altered to any of the corresponding codons described without altering the encoded polypeptide.
- Such nucleic acid variations are "silent variations," which are one species of conservatively modified variations. Every nucleic acid sequence herein which encodes a peptide also describes every possible silent variation of the nucleic acid.
- each codon in a nucleic acid can be modified to yield a functionally identical molecule. Accordingly, each silent variation of a nucleic acid that encodes a peptide is implicitly described in each disclosed sequence.
- the polynucleotide of the present invention can be composed of DNA, RNA, and derivatives thereof.
- a DNA is suitably composed of bases such as A, T, C, and G, and T is replaced by U in an RNA.
- the polynucleotide of the present invention can encode multiple peptides of the present invention, with or without intervening amino acid sequences in between.
- the intervening amino acid sequence can provide a cleavage site (e.g., enzyme recognition sequence) of the polynucleotide or the translated peptides.
- the polynucleotide can include any additional sequences to the coding sequence encoding the peptide of the present invention.
- the polynucleotide can be a recombinant polynucleotide that includes regulatory sequences required for the expression of the peptide or can be an expression vector (plasmid) with marker genes and such.
- such recombinant polynucleotides can be prepared by the manipulation of polynucleotides through conventional recombinant techniques using, for example, polymerases and endonucleases.
- a polynucleotide can be produced by insertion into an appropriate vector, which can be expressed when transfected into a competent cell.
- a polynucleotide can be amplified using PCR techniques or expression in suitable hosts (see, e.g., Sambrook et al., Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, 1989).
- a polynucleotide can be synthesized using the solid phase techniques, as described in Beaucage SL & Iyer RP, Tetrahedron 1992, 48: 2223-311; Matthes et al., EMBO J 1984, 3: 801-5.
- Vectors containing the polynucleotide of the present invention and host cells harboring the vectors are also included in the present invention.
- Exosomes The present invention further provides intracellular vesicles called exosomes, which present complexes formed between the peptides of the present invention and HLA antigens on their surface.
- Exosomes can be prepared, for example, by using the methods detailed in Japanese Patent Application Kohyo Publications Nos. Hei 11-510507 and WO99/03499, and can be prepared using APCs obtained from patients who are subject to treatment and/or prevention.
- the exosomes of this invention can be inoculated as vaccines, in a fashion similar to the peptides of this invention.
- the type of HLA antigens included in the complexes must match that of the subject requiring treatment and/or prevention.
- HLA-A02 type is prevalent in the Japanese and Caucasian populations.
- the use of the A02 type is favorable for obtaining effective results in these populations, with subtypes such as A0201 also finding use.
- the type of HLA antigen of the patient requiring treatment is investigated in advance, which enables the appropriate selection of peptides having high levels of binding affinity to the particular antigen, or having CTL inducibility by antigen presentation.
- substitution, insertion and/or addition of 1, 2, or several amino acids can be performed based on the amino acid sequence of the naturally occurring INHBB partial peptide.
- the peptides having the sequence selected from among SEQ ID NO: 1 to 14 find use.
- the present invention also provides isolated APCs that present complexes formed between HLA antigens and the peptides of this invention on its surface.
- the APCs that are obtained by contacting the peptides of this invention, or introducing the nucleotides encoding the peptides of this invention in an expressible form can be derived from patients who are subject to treatment and/or prevention, and can be administered as vaccines by themselves or in combination with other drugs including the peptides of this invention, exosomes, or cytotoxic T cells.
- the APCs are not limited to a particular kind of cells and include dendritic cells (DCs), Langerhans cells, macrophages, B cells, and activated T cells, which are known to present proteinaceous antigens on their cell surface so as to be recognized by lymphocytes. Since DC is a representative APC having the strongest CTL inducing action among APCs, DCs find use as the APCs of the present invention.
- DCs dendritic cells
- Langerhans cells macrophages
- B cells and activated T cells, which are known to present proteinaceous antigens on their cell surface so as to be recognized by lymphocytes. Since DC is a representative APC having the strongest CTL inducing action among APCs, DCs find use as the APCs of the present invention.
- an APC can be obtained by inducing DCs from peripheral blood monocytes and then contacting (stimulating) them with the peptides of this invention in vitro, ex vivo or in vivo.
- APCs that present the peptides of this invention are induced in the body of the subject.
- the phrase "inducing APC” includes contacting (stimulating) a cell with the peptides of this invention, or nucleotides encoding the peptides of this invention to present complexes formed between HLA antigens and the peptides of this invention on cell's surface.
- the APCs can be administered to the subject as a vaccine.
- the ex vivo administration can include the steps of: a: collecting APCs from a first subject, b: contacting with the APCs of step a, with the peptide and c: administering the peptide-loaded APCs to a second subject.
- the first subject and the second subject can be the same individual, or may be different individuals.
- use of the peptides of the present invention for manufacturing a pharmaceutical composition inducing antigen-presenting cells is provided.
- the present invention provides a method or process for manufacturing a pharmaceutical composition inducing antigen-presenting cells, wherein the method includes the step of admixing or formulating the peptide of the present invention with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
- the present invention also provides the peptides of the present invention for inducing antigen-presenting cells.
- the APCs obtained by step b can be administered to the subject as a vaccine.
- the APCs of the present invention have a high level of CTL inducibility.
- the high level is relative to the level of that by APCs contacted with no peptide or peptides which can not induce the CTL.
- Such APCs having a high level of CTL inducibility can be prepared by a method which includes the step of transferring genes containing polynucleotides that encode the peptides of this invention to APCs in vitro.
- the introduced genes can be in the form of DNAs or RNAs. Examples of methods for introduction include, without particular limitations, various methods conventionally performed in this field, such as lipofection, electroporation, and calcium phosphate method can be used.
- Cytotoxic T cells A cytotoxic T cell induced against any of the peptides of the present invention strengthens the immune response targeting tumor-associated endothelia in vivo and thus can be used as vaccines, in a fashion similar to the peptides per se.
- the present invention also provides isolated cytotoxic T cells that are specifically induced or activated by any of the present peptides.
- Such cytotoxic T cells can be obtained by (1) administering the peptide of the present invention to a subject, and then collecting cytotoxic T cells from the subject, or (2) contacting (stimulating) subject-derived APCs, and CD8-positive cells, or peripheral blood mononuclear leukocytes in vitro with the peptides of the present invention and then isolating cytotoxic T cells.
- the cytotoxic T cells which have been induced by stimulation with APCs that present the peptides of this invention, can be derived from patients who are subject to treatment and/or prevention, and can be administered by themselves or in combination with other drugs including the peptides of this invention or exosomes for the purpose of regulating effects.
- the obtained cytotoxic T cells act specifically against target cells presenting the peptides of this invention, or for example, the same peptides used for induction.
- the cytotoxic T cells can recognize (i.e., binding to) a complex formed between a HLA antigen and the peptide of the present invention on a target cell surface with the T cell receptor and then attack the target cell to induce the death of the target cell.
- the target cells can be cells that endogenously express INHBB, or cells that are transfected with the INHBB gene; and cells that present a peptide of this invention on the cell surface due to stimulation by the peptide can also serve as targets of activated CTL attack.
- T cell receptor The present invention also provides a composition composed of a nucleic acid sequence encoding polypeptides that are capable of forming a subunit of a T cell receptor (TCR), and methods of using the same.
- the TCR subunits have the ability to form TCRs that confer specificity to T cells against tumor cells presenting INHBB.
- the nucleic acid sequence of alpha- and beta- chains of the TCR expressed in the CTL induced with one or more peptides of this invention can be identified (WO2007/032255 and Morgan et al., J Immunol, 171, 3288 (2003)).
- the derivative TCRs can bind to the INHBB peptide displaying on the target cells with high avidity, and optionally mediate efficient killing of target cells presenting the INHBB peptide in vivo and in vitro.
- the nucleic acids sequence encoding the TCR subunits can be incorporated into suitable vectors e.g. retroviral vectors. These vectors are well known in the art.
- the nucleic acids or the vectors containing them usefully can be transferred into a T cell, for example, a T cell from a patient.
- the invention provides an off-the-shelf composition allowing rapid modification of a patient's own T cells (or those of another mammal) to rapidly and easily produce modified T cells having excellent cancer cell killing properties.
- the present invention provides CTLs which are prepared by transduction with the nucleic acids encoding the TCR subunit polypeptides that bind to the INHBB peptide e.g. SEQ ID NOs: 1 to 14 in the context of HLA-A02.
- the transduced CTLs are capable of homing to cancer cells in vivo, and can be expanded by well known culturing methods in vitro (e.g., Kawakami et al., J Immunol., 142, 3452-3461 (1989)).
- the T cells of the invention can be used to form an immunogenic composition useful in treating or the prevention of cancer in a patient in need of therapy or protection (WO2006/031221).
- Prevention and prophylaxis include any activity which reduces the burden of mortality or morbidity from disease. Prevention and prophylaxis can occur "at primary, secondary and tertiary prevention levels.” While primary prevention and prophylaxis avoid the development of a disease, secondary and tertiary levels of prevention and prophylaxis encompass activities aimed at the prevention and prophylaxis of the progression of a disease and the emergence of symptoms as well as reducing the negative impact of an already established disease by restoring function and reducing disease-related complications. Alternatively, prevention and prophylaxis include a wide range of prophylactic therapies aimed at alleviating the severity of the particular disorder, e.g. reducing the proliferation and metastasis of tumors.
- Treating and/or for the prophylaxis of cancer or tumor and/or the prevention of postoperative recurrence thereof includes any of the following steps, such as surgical removal of cancer cells, inhibition of the growth of cancerous cells, involution or regression of a tumor, induction of remission and suppression of occurrence of cancer, tumor regression, and reduction or inhibition of metastasis.
- Effectively treating and/or the prophylaxis of cancer decreases mortality and improves the prognosis of individuals having cancer, decreases the levels of tumor markers in the blood, and alleviates detectable symptoms accompanying cancer.
- reduction or improvement of symptoms constitutes effectively treating and/or the prophylaxis include 10%, 20%, 30% or more reduction, or stable disease.
- the peptides of this invention or polynucleotides encoding such peptides can be used for the treatment and/or for the prophylaxis of cancer, and/or prevention of postoperative recurrence thereof.
- the present invention provides a pharmaceutical agent or composition for treating and/or preventing cancer, and/or preventing the postoperative recurrence thereof, which includes one or more of the peptides of this invention, or polynucleotides encoding the peptides as an active ingredient.
- the present peptides can be expressed on the surface of any of the foregoing exosomes or cells, such as APCs for the use as pharmaceutical agents or compositions.
- the aforementioned cytotoxic T cells which target any of the peptides of the present invention can also be used as the active ingredient of the present pharmaceutical agents or compositions.
- the phrase "targeting a peptide” refers to recognizing (i.e., binding to) a complex formed between a HLA antigen and a peptide on a target cell surface with the T cell receptor, and then attacking the target cell to induce the death of the target cell.
- the present invention also provides the use of an active ingredient selected from among: (a) a peptide of the present invention, (b) a nucleic acid encoding such a peptide as disclosed herein in an expressible form, (c) an APC of the present invention, and (d) a cytotoxic T cells of the present invention in manufacturing a pharmaceutical composition or agent for treating cancer.
- the present invention further provides an active ingredient selected from among: (a) a peptide of the present invention, (b) a nucleic acid encoding such a peptide as disclosed herein in an expressible form, (c) an APC of the present invention, and (d) a cytotoxic T cells of the present invention for use in treating cancer.
- the present invention further provides a method or process for manufacturing a pharmaceutical composition or agent for treating cancer, wherein the method or process includes the step of formulating a pharmaceutically or physiologically acceptable carrier with an active ingredient selected from among: (a) a peptide of the present invention, (b) a nucleic acid encoding such a peptide as disclosed herein in an expressible form, (c) an APC of the present invention, and (d) a cytotoxic T cells of the present invention as active ingredients.
- a pharmaceutically or physiologically acceptable carrier with an active ingredient selected from among: (a) a peptide of the present invention, (b) a nucleic acid encoding such a peptide as disclosed herein in an expressible form, (c) an APC of the present invention, and (d) a cytotoxic T cells of the present invention as active ingredients.
- the present invention also provides a method or process for manufacturing a pharmaceutical composition or agent for treating cancer, wherein the method or process includes the step of admixing an active ingredient with a pharmaceutically or physiologically acceptable carrier, wherein the active ingredient is selected from among: (a) a peptide of the present invention, (b) a nucleic acid encoding such a peptide as disclosed herein in an expressible form, (c) an APC of the present invention, and (d) a cytotoxic T cells of the present invention.
- composition or agent of the present invention may be used for either or both the prophylaxis of cancer and prevention of postoperative recurrence thereof.
- the present pharmaceutical agents or compositions find use as a vaccine.
- the phrase "vaccine” also referred to as an “immunogenic composition” refers to a substance that has the function to induce anti-tumor immunity upon inoculation into animals.
- the pharmaceutical agents or compositions of the present invention can be used to treat and/or prevent cancers, and/or prevention of postoperative recurrence thereof in subjects or patients including human and any other mammal including, but not limited to, mouse, rat, guinea-pig, rabbit, cat, dog, sheep, goat, pig, cattle, horse, monkey, baboon, and chimpanzee, particularly a commercially important animal or a domesticated animal.
- polypeptides having an amino acid sequence selected from among SEQ ID NOs: 1 to 14 or polypeptides having an amino acid sequence selected from among SEQ ID NOs: 1 to 14 have been found to be HLA-A02 restricted epitope peptides or candidates, respectively, that can induce potent and specific immune response. Therefore, the present pharmaceutical agents or compositions which include any of these polypeptides with the amino acid sequences selected from among SEQ ID NOs: 1 to 14 are particularly suited for the administration to subjects whose HLA antigen is HLA-A02. The same applies to pharmaceutical agents or compositions which include polynucleotides encoding any of these polypeptides.
- Cancers to be treated by the pharmaceutical agents or compositions of the present invention are not limited and include all kinds of cancers wherein INHBB is involved, including, for example, cholangio cellular carcinoma, esophageal cancer, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), renal carcinoma, small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and soft tissue tumor.
- NSCLC non-small cell lung cancer
- SCLC small cell lung cancer
- the present pharmaceutical agents or compositions can contain in addition to the aforementioned active ingredients, other peptides which have the ability to induce CTLs against cancerous cells, other polynucleotides encoding the other peptides, other cells that present the other peptides, or such.
- the other peptides that have the ability to induce CTLs against cancerous cells are exemplified by cancer specific antigens (e.g., identified TAAs), but are not limited thereto.
- the pharmaceutical agents or compositions of the present invention can optionally include other therapeutic substances as an active ingredient, so long as the substance does not inhibit the antitumoral effect of the active ingredient, e.g., any of the present peptides.
- formulations can include anti-inflammatory agents or compositions, pain killers, chemotherapeutics, and the like.
- the medicaments of the present invention can also be administered sequentially or concurrently with the one or more other pharmacologic agents or compositions.
- the amounts of medicament and pharmacologic agent or composition depend, for example, on what type of pharmacologic agent(s) or composition(s) is/are used, the disease being treated, and the scheduling and routes of administration.
- the pharmaceutical agents or compositions of this invention can include other agents or compositions conventional in the art having regard to the type of formulation in question.
- the present pharmaceutical agents or compositions can be included in articles of manufacture and kits containing materials useful for treating the pathological conditions of the disease to be treated, e.g., cancer.
- the article of manufacture can include a container of any of the present pharmaceutical agents or compositions with a label. Suitable containers include bottles, vials, and test tubes. The containers can be formed from a variety of materials, such as glass or plastic.
- the label on the container should indicate the agent or compositions is used for treating or prevention of one or more conditions of the disease.
- the label can also indicate directions for administration and so on.
- kits including a pharmaceutical agent or compositions of the present invention can optionally further include a second container housing a pharmaceutically-acceptable diluent. It can further include other materials desirable from a commercial and user standpoint, including other buffers, diluents, filters, needles, syringes, and package inserts with instructions for use.
- compositions can, if desired, be presented in a pack or dispenser device which can contain one or more unit dosage forms containing the active ingredient.
- the pack can, for example, include metal or plastic foil, such as a blister pack.
- the pack or dispenser device can be accompanied by instructions for administration.
- compositions containing the peptides as the active ingredient can be administered directly as a pharmaceutical agent or composition, or if necessary, that has been formulated by conventional formulation methods.
- carriers, excipients, and such that are ordinarily used for drugs can be included as appropriate without particular limitations. Examples of such carriers are sterilized water, physiological saline, phosphate buffer, culture fluid and such.
- the pharmaceutical agents or compositions can contain as necessary, stabilizers, suspensions, preservatives, surfactants and such.
- the pharmaceutical agents or compositions of this invention can be used for anticancer purposes.
- the peptides of this invention can be prepared as a combination composed of two or more of peptides of the invention, to induce CTL in vivo.
- the peptide combination can take the form of a cocktail or can be conjugated to each other using standard techniques.
- the peptides can be chemically linked or expressed as a single fusion polypeptide sequence.
- the peptides in the combination can be the same or different.
- APCs that present any of the peptides of this invention on their cell surface which may be obtained by stimulating APCs (e.g., DCs) derived from a subject with the peptides of this invention, may be administered to the subject, and as a result, CTLs are induced in the subject and aggressiveness towards the cancer cells, such as cholangio cellular carcinoma, esophageal cancer, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), renal carcinoma, small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and soft tissue tumor can be increased.
- APCs e.g., DCs
- the pharmaceutical agents or compositions for the treatment and/or prevention of cancer which include a peptide of this invention as the active ingredient, can also include an adjuvant known to effectively establish cellular immunity. Alternatively, they can be administered with other active ingredients, and they can be administered by formulation into granules.
- An adjuvant refers to a compound that enhances the immune response against the protein when administered together (or successively) with the protein having immunological activity. Adjuvants contemplated herein include those described in the literature (Clin Microbiol Rev 1994, 7: 277-89). Examples of suitable adjuvants include, but are not limited to, aluminum phosphate, aluminum hydroxide, alum, cholera toxin, salmonella toxin, and such, but are not limited thereto.
- liposome formulations may be conveniently used.
- granular formulations in which the peptide is bound to few-micrometers diameter beads, and formulations in which a lipid is bound to the peptide may be conveniently used.
- the pharmaceutical agents or compositions of the invention may further include a component which primes CTL.
- Lipids have been identified as agents or compositions capable of priming CTL in vivo against viral antigens.
- palmitic acid residues can be attached to the epsilon- and alpha-amino groups of a lysine residue and then linked to a peptide of the invention.
- the lipidated peptide can then be administered either directly in a micelle or particle, incorporated into a liposome, or emulsified in an adjuvant.
- lipid priming of CTL responses E.
- coli lipoproteins such as tripalmitoyl-S-glycerylcysteinlyseryl- serine (P3CSS) can be used to prime CTL when covalently attached to an appropriate peptide (see, e.g., Deres et al., Nature 1989, 342: 561-4).
- P3CSS tripalmitoyl-S-glycerylcysteinlyseryl- serine
- the method of administration can be oral, intradermal, subcutaneous, intravenous injection, or such, and systemic administration or local administration to the vicinity of the targeted sites.
- the administration can be performed by single administration or boosted by multiple administrations.
- the dose of the peptides of this invention can be adjusted appropriately according to the disease to be treated, age of the patient, weight, method of administration, and such, and is ordinarily 0.001 mg to 1000 mg, for example, 0.001 mg to 1000 mg, for example, 0.1 mg to 10 mg, and can be administered once in a few days to few months.
- One skilled in the art can appropriately select a suitable dose.
- compositions containing polynucleotides as the active ingredient can also contain nucleic acids encoding the peptides disclosed herein in an expressible form.
- the phrase "in an expressible form” means that the polynucleotide, when introduced into a cell, will be expressed in vivo as a polypeptide that induces anti-tumor immunity.
- the nucleic acid sequence of the polynucleotide of interest includes regulatory elements necessary for expression of the polynucleotide.
- the polynucleotide(s) can be equipped so to achieve stable insertion into the genome of the target cell (see, e.g., Thomas KR & Capecchi MR, Cell 1987, 51: 503-12 for a description of homologous recombination cassette vectors). See, e.g., Wolff et al., Science 1990, 247: 1465-8; U.S. Patent Nos. 5,580,859; 5,589,466; 5,804,566; 5,739,118; 5,736,524; 5,679,647; and WO 98/04720.
- DNA-based delivery technologies include "naked DNA”, facilitated (bupivacaine, polymers, peptide-mediated) delivery, cationic lipid complexes, and particle-mediated (“gene gun”) or pressure-mediated delivery (see, e.g., U.S. Patent No. 5,922,687).
- the peptides of the present invention can also be expressed by viral or bacterial vectors.
- expression vectors include attenuated viral hosts, such as vaccinia or fowlpox. This approach involves the use of vaccinia virus, e.g., as a vector to express nucleotide sequences that encode the peptide. Upon introduction into a host, the recombinant vaccinia virus expresses the immunogenic peptide, and thereby elicits an immune response.
- Vaccinia vectors and methods useful in immunization protocols are described in, e.g., U.S. Patent No. 4,722,848. Examples of another vector include BCG (Bacille Calmette Guerin).
- BCG vectors are described in Stover et al., Nature 1991, 351: 456-60.
- a wide variety of other vectors useful for therapeutic administration or immunization e.g., adeno and adeno-associated virus vectors, retroviral vectors, Salmonella typhi vectors, detoxified anthrax toxin vectors, and the like, will be apparent. See, e.g., Shata et al., Mol Med Today 2000, 6: 66-71; Shedlock et al., J Leukoc Biol 2000, 68: 793-806; Hipp et al., In Vivo 2000, 14: 571-85.
- Delivery of a polynucleotide into a subject can be either direct, in which case the subject is directly exposed to a polynucleotide-carrying vector, or indirect, in which case, cells are first transformed with the polynucleotide of interest in vitro, then the cells are transplanted into the subject.
- two approaches are known, respectively, as in vivo and ex vivo gene therapies.
- the method of administration can be oral, intradermal, subcutaneous, intravenous injection, or such, and systemic administration or local administration to the vicinity of the targeted sites finds use.
- the administration can be performed by single administration or boosted by multiple administrations.
- the dose of the polynucleotide in the suitable carrier or cells transformed with the polynucleotide encoding the peptides of this invention can be adjusted appropriately according to the disease to be treated, age of the patient, weight, method of administration, and such, and is ordinarily 0.001 mg to 1000 mg, for example, 0.001 mg to 1000 mg, for example, 0.1 mg to 10 mg, and can be administered once every a few days to once every few months.
- One skilled in the art can appropriately select the suitable dose.
- peptides, exosomes, APCs and CTLs Methods using the peptides, exosomes, APCs and CTLs
- the peptides of the present invention and polynucleotides encoding such peptides can be used for inducing APCs and CTLs.
- the exosomes and APCs of the present invention can be also used for inducing CTLs.
- the peptides, polynucleotides, exosomes and APCs can be used in combination with any other compounds so long as the compounds do not inhibit their CTL inducibility.
- any of the aforementioned pharmaceutical agents or compositions of the present invention can be used for inducing CTLs, and in addition thereto, those including the peptides and polynucleotides can be also be used for inducing APCs as discussed below.
- APCs antigen-presenting cells
- the present invention provides methods of inducing APCs using the peptides of this invention or polynucleotides encoding the peptides.
- the induction of APCs can be performed as described above in section "VI. Antigen-presenting cells”.
- This invention also provides a method for inducing APCs having a high level of CTL inducibility, the induction of which has been also mentioned under the item of "VI. Antigen-presenting cells", supra.
- the methods for inducing APCs include at least one step selected from among: a: contacting APCs with the peptides of the present invention, and b: introducing the polypeptides of the present invention in an expressible form into APCs.
- Such methods for inducing APCs are preferably performed in vitro or ex vivo.
- APCs to be induced may be obtained from a subject to be treated or others whose HLA antigens are the same as the subject.
- the present invention provides methods for inducing CTLs using the peptides of this invention, polynucleotides encoding the peptides, or exosomes or APCs presenting the peptides.
- the present invention also provides methods for inducing CTLs using a polynucleotide encoding a polypeptide that is capable of forming a T cell receptor (TCR) subunit recognizing (i.e., binding to) a complex of the peptides of the present invention and HLA antigens on a cell surface.
- TCR T cell receptor
- the methods for inducing CTLs include at least one step selected from among: a: contacting a CD8-positive T cell with an antigen-presenting cell and/or an exosome that presents on its surface a complex of an HLA antigen and a peptide of the present invention, and b: introducing a polynucleotide encoding a polypeptide that is capable of forming a TCR subunit recognizing a complex of a peptide of the present invention and an HLA antigen into a CD8 positive T cell.
- the peptides of this invention When the peptides of this invention are administered to a subject, CTL is induced in the body of the subject, and the strength of the immune response targeting the tumor-associated endothelia is enhanced.
- the peptides and polynucleotides encoding the peptides can be used for an ex vivo therapeutic method, in which subject-derived APCs, and CD8-positive cells, or peripheral blood mononuclear leukocytes are contacted (stimulated) with the peptides of this invention in vitro, and after inducing CTL, the activated CTL cells are returned to the subject.
- the method can include steps of: a: collecting APCs from subject, b: contacting with the APCs of step a, with the peptide, c: mixing the APCs of step b with CD 8+ T cells, and co-culturing for inducing CTLs, and d: collecting CD 8+ T cells from the co-culture of step c.
- the present invention provides a method or process for manufacturing a pharmaceutical agent or composition inducing CTLs, wherein the method includes the step of admixing or formulating the peptide of the present invention with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. Further, the present invention also provides the peptide of the present invention for inducing CTLs.
- the CD 8+ T cells having cytotoxic activity obtained by step d can be administered to the subject as a vaccine.
- the APCs to be mixed with the CD 8+ T cells in above step c can also be prepared by transferring genes coding for the present peptides into the APCs as detailed above in section "VI. Antigen-presenting cells"; but are not limited thereto and any APC or exosome which effectively presents the present peptides to the T cells can be used for the present method.
- Cell lines H2 HLA-A02
- human B-lymphoblastoid cell line H2
- COS7 COS7
- DCs In vitro CTL Induction Monocyte-derived dendritic cells (DCs) were used as antigen-presenting cells (APCs) to induce cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses against peptides presented on human leukocyte antigen (HLA). DCs were generated in vitro as described elsewhere (Nakahara S et al., Cancer Res 2003 Jul 15, 63(14): 4112-8). Specifically, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) isolated from a normal volunteer (HLA-A*0201 positive) by Ficoll-Plaque (Pharmacia) solution were separated by adherence to a plastic tissue culture dish (Becton Dickinson) so as to enrich them as the monocyte fraction.
- PBMCs peripheral blood mononuclear cells isolated from a normal volunteer (HLA-A*0201 positive) by Ficoll-Plaque (Pharmacia) solution were separated by adherence to a plastic tissue culture dish (Becton Dickinson) so as to enrich them as the mon
- the monocyte-enriched population was cultured in the presence of 1000 U/ml of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) (R&D System) and 1000 U/ml of interleukin (IL)-4 (R&D System) in AIM-V Medium (Invitrogen) containing 2% heat-inactivated autologous serum (AS). After 7 days of culture, the cytokine-induced DCs were pulsed with 20 mcg/ml of each of the synthesized peptides in the presence of 3 mcg/ml of beta2-microglobulin for 3 hr at 37 degrees C in AIM-V Medium.
- GM-CSF granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor
- IL interleukin-4
- AS heat-inactivated autologous serum
- the generated cells appeared to express DC-associated molecules, such as CD80, CD83, CD86 and HLA class II, on their cell surfaces (data not shown).
- DC-associated molecules such as CD80, CD83, CD86 and HLA class II
- MMC Mitomycin C
- CD8 Positive Isolation Kit CD8 Positive Isolation Kit
- These cultures were set up in 48-well plates (Corning); each well contained 1.5 x 10 4 peptide-pulsed DCs, 3 x 10 5 CD8+ T cells and 10 ng/ml of IL-7 (R&D System) in 0.5 ml of AIM-V/2% AS medium.
- CTL Expansion Procedure CTLs were expanded in culture using the method similar to the one described by Riddell et al. (Walter EA et al., N Engl J Med 1995 Oct 19, 333(16): 1038-44; Riddell SR et al., Nat Med 1996 Feb, 2(2): 216-23). A total of 5 x 10 4 CTLs were suspended in 25 ml of AIM-V/5% AS medium with 2 kinds of human B-lymphoblastoid cell lines, inactivated by MMC, in the presence of 40 ng/ml of anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody (Pharmingen). One day after initiating the cultures, 120 IU/ml of IL-2 were added to the cultures.
- interferon (IFN)-gamma enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) assay and IFN-gamma enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) were performed. Specifically, peptide-pulsed T2 (1 x 10 4 /well) was prepared as stimulator cells. Cultured cells in 48 wells were used as responder cells. IFN-gamma ELISPOT assay and IFN-gamma ELISA assay were performed under manufacture procedure.
- INHBB expression was validly elevated in the following cancers: 10 out of 21 in cholangiocellular carcinoma, 12 out of 12 in esophageal cancer, 10 out of 13 in NSCLC, 22 out of 24 in renal carcinoma, 8 out of 14 in SCLC cancer and 45 out of 49 in soft tissue tumor, in comparing with corresponding normal tissue.
- Stimulation of the T cells using the predicted peptides from INHBB restricted with HLA-A0201 and establishment for CTL lines stimulated with INHBB derived peptides CTLs for those peptides derived from INHBB were generated according to the protocols set forth in "Materials and Methods" section above.
- INHBB-A02-9-213 SEQ ID NO: 1
- INHBB-A02-9-174 SEQ ID NO: 2
- INHBB-A02-9-257 SEQ ID NO: 3
- INHBB-A02-9-313 SEQ ID NO: 4
- INHBB-A02-9-139 SEQ ID NO: 5
- INHBB-A02-9-8 SEQ ID NO: 6
- INHBB-A02-9-250 SEQ ID NO: 7
- INHBB-A02-10-179 SEQ ID NO: 8
- INHBB-A02-10-237 SEQ ID NO: 9
- INHBB-A02-10-313 SEQ ID NO: 10
- INHBB-A02-10-173 SEQ ID NO: 11
- INHBB-A02-10-256 SEQ ID NO: 12
- INHBB-A02-10-162 SEQ ID NO: 13
- the cells in the positive well number #7 stimulated with SEQ ID NO: 2 were expanded and CTL line was established.
- the CTL line having higher specific CTL activity against the peptide-pulsed target as compared to the activity against target without peptide pulse was determined by IFN-gamma ELISA ( Figure 2).
- the results herein demonstrate that the CTL line demonstrated potent IFN-gamma production against the target cells pulsed with corresponding peptide as compared to target cells without peptide pulse.
- the peptides which could establish CTL line were selected as potent CTL stimulation peptide.
- novel HLA-A02 epitope peptides derived from INHBB were identified and demonstrated to be applicable for cancer immunotherapy.
- the present invention describes new TAAs, particularly those derived from INHBB, that induce potent and specific anti-tumor immune responses and have applicability to a wide array of cancer types.
- TAAs warrant further development as peptide vaccines against diseases associated with INHBB, e.g., cancer, more particularly, cholangio cellular carcinoma, esophageal cancer, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), renal carcinoma, small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and soft tissue tumor.
- diseases associated with INHBB e.g., cancer, more particularly, cholangio cellular carcinoma, esophageal cancer, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), renal carcinoma, small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and soft tissue tumor.
- NSCLC non-small cell lung cancer
- SCLC small cell lung cancer
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Proteomics, Peptides & Aminoacids (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Toxicology (AREA)
- Oncology (AREA)
- Mycology (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Gastroenterology & Hepatology (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Cell Biology (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Peptides Or Proteins (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Antibodies Or Antigens For Use As Internal Diagnostic Agents (AREA)
- Medicines That Contain Protein Lipid Enzymes And Other Medicines (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Material From Animals Or Micro-Organisms (AREA)
- Micro-Organisms Or Cultivation Processes Thereof (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
Priority Applications (8)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2009801413475A CN102186977A (zh) | 2008-08-19 | 2009-08-14 | Inhbb表位肽及包含它的疫苗 |
| CA2734515A CA2734515A1 (en) | 2008-08-19 | 2009-08-14 | Inhbb epitope peptides and vaccines containing the same |
| US13/059,617 US20110280898A1 (en) | 2008-08-19 | 2009-08-14 | Inhbb epitope peptides and vaccines containing the same |
| AU2009283762A AU2009283762A1 (en) | 2008-08-19 | 2009-08-14 | INHBB epitope peptides and vaccines containing the same |
| EP09808047A EP2326718A4 (en) | 2008-08-19 | 2009-08-14 | INHBB EPITOP PEPTIDES AND VACCINES CONTAINING THEM |
| JP2011507725A JP2012500001A (ja) | 2008-08-19 | 2009-08-14 | Inhbbエピトープペプチドおよびそれを含むワクチン |
| MX2011001880A MX2011001880A (es) | 2008-08-19 | 2009-08-14 | Peptidos de epitope inhbb y vacunas que contienen los mismos. |
| IL211131A IL211131A0 (en) | 2008-08-19 | 2011-02-09 | Inhbb epitope and vaccines containing the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US8997308P | 2008-08-19 | 2008-08-19 | |
| US61/089,973 | 2008-08-19 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2010021111A1 true WO2010021111A1 (en) | 2010-02-25 |
Family
ID=41707002
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2009/003894 Ceased WO2010021111A1 (en) | 2008-08-19 | 2009-08-14 | Inhbb epitope peptides and vaccines containing the same |
Country Status (13)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (7) | US20110280898A1 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP2326718A4 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP2012500001A (enExample) |
| KR (1) | KR20110063456A (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN102186977A (enExample) |
| AU (1) | AU2009283762A1 (enExample) |
| CA (1) | CA2734515A1 (enExample) |
| IL (1) | IL211131A0 (enExample) |
| MX (1) | MX2011001880A (enExample) |
| RU (1) | RU2011110504A (enExample) |
| SG (1) | SG193214A1 (enExample) |
| TW (1) | TW201008574A (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2010021111A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2011122022A1 (en) * | 2010-04-02 | 2011-10-06 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Ect2 peptides and vaccines including the same |
| US9017669B2 (en) | 2009-12-28 | 2015-04-28 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Anti-CDH3 antibodies and uses thereof |
| US10576097B2 (en) | 2014-08-04 | 2020-03-03 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | URLC10-derived peptide and vaccine containing same |
Families Citing this family (38)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7847060B2 (en) * | 2005-02-25 | 2010-12-07 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Peptide vaccines for lung cancers expressing TTK, URLC10 or KOC1 polypeptides |
| US9732131B2 (en) | 2006-02-27 | 2017-08-15 | Calviri, Inc. | Identification and use of novopeptides for the treatment of cancer |
| CN101432303A (zh) * | 2006-02-28 | 2009-05-13 | 肿瘤疗法科学股份有限公司 | 利用抗cdh3抗体的效应物功能来损伤细胞的方法 |
| JP2009531273A (ja) * | 2006-02-28 | 2009-09-03 | オンコセラピー・サイエンス株式会社 | 抗EphA4抗体のエフェクター機能を用いて細胞を障害する方法 |
| EP2468887A1 (en) * | 2006-12-13 | 2012-06-27 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | TTK as tumor marker and therapeutic target for lung cancer |
| WO2009016691A1 (en) * | 2007-07-30 | 2009-02-05 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Cancer associated gene ly6k |
| CA2696591C (en) * | 2007-08-20 | 2016-10-11 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Cdh3 peptide and medicinal agent comprising the same |
| RU2011103199A (ru) | 2008-06-30 | 2012-08-10 | Онкотерапи Сайенс, Инк. (Jp) | Антитела против cdh3, меченные радиоизотопной меткой, и их применение |
| TWI580431B (zh) | 2008-08-19 | 2017-05-01 | 腫瘤療法 科學股份有限公司 | Hig2與urlc10抗原決定位胜肽以及含此胜肽之疫苗 |
| CN104086625B (zh) | 2008-10-22 | 2016-08-31 | 肿瘤疗法科学股份有限公司 | Rab6kifl/kif20a表位肽及包含它的疫苗 |
| TWI500932B (zh) | 2008-12-05 | 2015-09-21 | Oncotherapy Science Inc | Wdrpuh抗原決定位胜肽以及含此胜肽之疫苗 |
| TW201102081A (en) | 2009-05-11 | 2011-01-16 | Oncotherapy Science Inc | TTK peptides and vaccines including the same |
| GB201004575D0 (en) | 2010-03-19 | 2010-05-05 | Immatics Biotechnologies Gmbh | Composition of tumor associated peptides and related anti cancer vaccine for the treatment of gastric cancer and other cancers |
| JP2015509914A (ja) * | 2011-12-23 | 2015-04-02 | メディカル リサーチ カウンシル | 選択的gpcrリガンド |
| WO2013133405A1 (ja) * | 2012-03-09 | 2013-09-12 | オンコセラピー・サイエンス株式会社 | ペプチドを含む医薬組成物 |
| EP2872530A4 (en) | 2012-07-10 | 2016-04-06 | Oncotherapy Science Inc | KIF20A EPITOPE PEPTIDES FOR TH1 CELLS AND VACCINES CONTAINING SAME |
| EP2872531A4 (en) * | 2012-07-10 | 2016-04-06 | Oncotherapy Science Inc | LY6K EPITOPE PEPTIDES FOR TH1 CELLS AND VACCINES CONTAINING SAME |
| CN105121715B (zh) | 2012-12-11 | 2018-10-26 | 艾伯特叶史瓦大学爱因斯坦医学院 | 高通量受体:配体鉴定方法 |
| TWI658049B (zh) * | 2013-03-12 | 2019-05-01 | 腫瘤療法 科學股份有限公司 | Kntc2胜肽及含此胜肽之疫苗 |
| GB201315946D0 (en) * | 2013-09-06 | 2013-10-23 | Immune Targeting Systems Its Ltd | Oncology vaccine |
| US9884921B2 (en) | 2014-07-01 | 2018-02-06 | Pfizer Inc. | Bispecific heterodimeric diabodies and uses thereof |
| IL250848B (en) | 2014-09-08 | 2022-07-01 | Rin Inst Inc | Cancer-cell-specific antibody, anticancer agent, and cancer testing method |
| WO2016090177A1 (en) * | 2014-12-03 | 2016-06-09 | Verik Bio, Inc. | Identification, selection and use of high curative potential t cell epitopes |
| GB201604458D0 (en) * | 2016-03-16 | 2016-04-27 | Immatics Biotechnologies Gmbh | Peptides and combination of peptides for use in immunotherapy against cancers |
| CA3022331A1 (en) | 2016-05-18 | 2017-11-23 | Albert Einstein College Of Medicine, Inc. | Variant pd-l1 polypeptides, t-cell modulatory multimeric polypeptides, and methods of use thereof |
| CN109475628A (zh) | 2016-05-18 | 2019-03-15 | 库尔生物制药有限公司 | T细胞调节性多聚体多肽及其使用方法 |
| DE102016123893A1 (de) | 2016-12-08 | 2018-06-14 | Immatics Biotechnologies Gmbh | T-Zellrezeptoren mit verbesserter Bindung |
| AU2017379900B2 (en) | 2016-12-22 | 2024-12-05 | Cue Biopharma, Inc. | T-cell modulatory multimeric polypeptides and methods of use thereof |
| WO2018129474A1 (en) | 2017-01-09 | 2018-07-12 | Cue Biopharma, Inc. | T-cell modulatory multimeric polypeptides and methods of use thereof |
| IL268919B2 (en) * | 2017-03-03 | 2023-10-01 | Treos Bio Zrt | A personalized immunogenic peptide identification platform |
| EP3596118B1 (en) | 2017-03-15 | 2024-08-21 | Cue Biopharma, Inc. | Combination of multimeric fusion polypeptides and immune checkpoint inhibitor for treating hpv-associated cancer |
| US20200276285A1 (en) | 2017-06-02 | 2020-09-03 | Arizona Board Of Regents On Behalf Of Arizona State University | A method to create personalized cancer vaccines |
| US12025615B2 (en) | 2017-09-15 | 2024-07-02 | Arizona Board Of Regents On Behalf Of Arizona State University | Methods of classifying response to immunotherapy for cancer |
| WO2019139896A1 (en) | 2018-01-09 | 2019-07-18 | Cue Biopharma, Inc. | Multimeric t-cell modulatory polypeptides and methods of use thereof |
| JP7642530B2 (ja) | 2018-09-04 | 2025-03-10 | トレオス バイオ リミテッド | ペプチドワクチン |
| WO2021067550A1 (en) | 2019-10-02 | 2021-04-08 | Arizona Board Of Regents On Behalf Of Arizona State University | Methods and compositions for identifying neoantigens for use in treating and preventing cancer |
| EP4149534A4 (en) | 2020-05-12 | 2024-09-04 | Cue Biopharma, Inc. | MULTIMERIC POLYPEPTIDES MODULATING T CELLS AND METHODS OF USE THEREOF |
| WO2022056014A1 (en) | 2020-09-09 | 2022-03-17 | Cue Biopharma, Inc. | Mhc class ii t-cell modulatory multimeric polypeptides for treating type 1 diabetes mellitus (t1d) and methods of use thereof |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2008102557A1 (en) * | 2007-02-21 | 2008-08-28 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Peptide vaccines for cancers expressing tumor-associated antigens |
Family Cites Families (96)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3322314C2 (de) | 1983-06-21 | 1986-01-02 | Gebhard, Dietrich, 7502 Malsch | Schaltungsanordnung für ein Zugfahrzeug |
| US5089396A (en) | 1985-10-03 | 1992-02-18 | Genentech, Inc. | Nucleic acid encoding β chain prodomains of inhibin and method for synthesizing polypeptides using such nucleic acid |
| NZ217727A (en) | 1985-10-03 | 1990-05-28 | Genentech Inc | Nucleic acid encoding alpha or b chain of inhibin, its production and compositions containing it |
| CA2084180A1 (en) | 1991-12-11 | 1993-06-12 | Paul P. Hung | Expression of specific immunogens using viral antigens |
| CA2189028A1 (en) | 1994-04-15 | 1995-10-26 | Gary M. Fox | Hek5, hek7, hek8, hek11, new eph-like receptor protein tyrosine kinases |
| AU6795898A (en) | 1997-04-04 | 1998-10-30 | Board Of Regents, The University Of Texas System | Proteins and compositions for modulating mitosis |
| US6800744B1 (en) | 1997-07-02 | 2004-10-05 | Genome Therapeutics Corporation | Nucleic acid and amino acid sequences relating to Streptococcus pneumoniae for diagnostics and therapeutics |
| US5891432A (en) | 1997-07-29 | 1999-04-06 | The Immune Response Corporation | Membrane-bound cytokine compositions comprising GM=CSF and methods of modulating an immune response using same |
| EP1375515A3 (en) | 1997-10-07 | 2004-04-21 | Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Polypeptide, cDNA encoding the same, and use thereof |
| US6747137B1 (en) | 1998-02-13 | 2004-06-08 | Genome Therapeutics Corporation | Nucleic acid sequences relating to Candida albicans for diagnostics and therapeutics |
| US6551795B1 (en) | 1998-02-18 | 2003-04-22 | Genome Therapeutics Corporation | Nucleic acid and amino acid sequences relating to pseudomonas aeruginosa for diagnostics and therapeutics |
| US6783961B1 (en) * | 1999-02-26 | 2004-08-31 | Genset S.A. | Expressed sequence tags and encoded human proteins |
| US20070014787A1 (en) * | 1998-07-15 | 2007-01-18 | Human Genome Sciences, Inc. | 71 human secreted proteins |
| EP1103561B1 (en) | 1998-07-28 | 2006-04-19 | Green Peptide Co., Ltd. | Hla-a2 restraint tumor antigen peptide originating in sart-1 |
| WO2001011055A1 (en) | 1999-08-04 | 2001-02-15 | Adelbert Bacher | Isoprenoid biosynthesis |
| WO2001029221A2 (en) | 1999-10-20 | 2001-04-26 | Zymogenetics, Inc. | Proteins and polynucleotides encoding them |
| US6682902B2 (en) | 1999-12-16 | 2004-01-27 | Schering Aktiengesellschaft | DNA encoding a novel RG1 polypeptide |
| US20030013649A1 (en) | 2000-01-31 | 2003-01-16 | Rosen Craig A. | Nucleic acids, proteins, and antibodies |
| WO2001062776A1 (en) | 2000-02-23 | 2001-08-30 | Epimmune Inc. | Hla binding peptides and their uses |
| AU2001238347A1 (en) | 2000-02-28 | 2001-09-12 | Hyseq, Inc. | Novel nucleic acids and polypeptides |
| CN1469926A (zh) | 2000-03-29 | 2004-01-21 | 科里克萨有限公司 | 治疗和诊断肺癌的组合物和方法 |
| JP2004526401A (ja) | 2000-03-29 | 2004-09-02 | コリクサ コーポレイション | 肺癌の治療および診断のための組成物および方法 |
| WO2002008262A2 (en) | 2000-07-26 | 2002-01-31 | Stanford University | Bstp-5 proteins and related reagents and methods of use thereof |
| US6830885B1 (en) | 2000-08-18 | 2004-12-14 | Phenogene Therapeutiques Inc. | Nucleic acid molecule, method and kit for selecting a nucleic acid having a desired feature |
| US20090062512A1 (en) | 2000-10-10 | 2009-03-05 | Hildebrand William H | Comparative ligand mapping from MHC class I positive cells |
| US7033832B2 (en) | 2000-10-13 | 2006-04-25 | University Of Medicine And Dentistry Of New Jersey | Endothelial cell—cell cohesion |
| EP1474528A4 (en) | 2000-10-13 | 2006-06-14 | Protein Design Labs Inc | METHODS FOR DIAGNOSING PROSTATE CANCER, COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR SCREENING PROSTATE CANCER MODULATORS |
| US7919467B2 (en) | 2000-12-04 | 2011-04-05 | Immunotope, Inc. | Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-inducing immunogens for prevention, treatment, and diagnosis of cancer |
| US7214786B2 (en) | 2000-12-14 | 2007-05-08 | Kovalic David K | Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants and uses thereof for plant improvement |
| CN100400099C (zh) | 2001-01-04 | 2008-07-09 | 北京迪威华宇生物技术有限公司 | 预防和治疗人前列腺癌的重组蛋白疫苗 |
| US20040236091A1 (en) | 2001-03-28 | 2004-11-25 | Chicz Roman M. | Translational profiling |
| AU2002309583A1 (en) | 2001-04-18 | 2002-11-05 | Protein Desing Labs, Inc. | Methods of diagnosis of lung cancer, compositions and methods of screening for modulators of lung cancer |
| JP2005508144A (ja) | 2001-06-18 | 2005-03-31 | イオス バイオテクノロジー,インコーポレイティド | 卵巣癌の診断方法、卵巣癌のモジュレーターをスクリーニングする組成物及び方法 |
| US20030124579A1 (en) | 2001-09-05 | 2003-07-03 | Eos Biotechnology, Inc. | Methods of diagnosis of ovarian cancer, compositions and methods of screening for modulators of ovarian cancer |
| US20040142325A1 (en) | 2001-09-14 | 2004-07-22 | Liat Mintz | Methods and systems for annotating biomolecular sequences |
| US20030232350A1 (en) | 2001-11-13 | 2003-12-18 | Eos Biotechnology, Inc. | Methods of diagnosis of cancer, compositions and methods of screening for modulators of cancer |
| US7314974B2 (en) | 2002-02-21 | 2008-01-01 | Monsanto Technology, Llc | Expression of microbial proteins in plants for production of plants with improved properties |
| WO2003080640A1 (en) | 2002-03-07 | 2003-10-02 | Ludwig Institute For Cancer Research | Lymphatic and blood endothelial cell genes |
| US20030194704A1 (en) | 2002-04-03 | 2003-10-16 | Penn Sharron Gaynor | Human genome-derived single exon nucleic acid probes useful for gene expression analysis two |
| US20070015271A1 (en) * | 2002-04-04 | 2007-01-18 | Rosen Craig A | Human secreted proteins |
| WO2004001072A2 (en) | 2002-06-19 | 2003-12-31 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Method for diagnosis of colorectal tumors |
| WO2004007770A2 (en) | 2002-07-10 | 2004-01-22 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Method for diagnosis of intestinal-type gastric tumors |
| FI116178B (fi) | 2002-08-22 | 2005-09-30 | Abb Oy | Vaihtosuuntaajan lähtökuristinsovitelma |
| WO2004035732A2 (en) | 2002-08-29 | 2004-04-29 | Five Prime Therapeutics, Inc. | Human polypeptides encoded by polynucleotides and methods of their use |
| DE60321356D1 (de) | 2002-08-30 | 2008-07-10 | Oncotherapy Science Inc | Verfahren zur diagnostik von eierstock endometriose |
| US20050214836A1 (en) | 2002-08-30 | 2005-09-29 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Method of diagnosing ovarian endometriosis |
| US20050259483A1 (en) | 2002-09-30 | 2005-11-24 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Genes and polypeptides relating to prostate cancers |
| TW200413539A (en) | 2002-09-30 | 2004-08-01 | Oncotherapy Science Inc | Genes and polypeptides relating to prostate cancers |
| WO2004031411A2 (en) | 2002-09-30 | 2004-04-15 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Genes and polypeptides relating to human pancreatic cancers |
| US20060024692A1 (en) | 2002-09-30 | 2006-02-02 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Method for diagnosing non-small cell lung cancers |
| TW200413725A (en) | 2002-09-30 | 2004-08-01 | Oncotherapy Science Inc | Method for diagnosing non-small cell lung cancers |
| US20050260639A1 (en) | 2002-09-30 | 2005-11-24 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Method for diagnosing pancreatic cancer |
| JP2006500946A (ja) | 2002-09-30 | 2006-01-12 | オンコセラピー・サイエンス株式会社 | 精巣精上皮腫の診断方法 |
| AU2003295328A1 (en) | 2002-10-02 | 2004-04-23 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumor |
| AU2003300680A1 (en) | 2002-12-10 | 2004-07-09 | Centre National De La Recherche Scientifique Cnrs | Thap proteins as nuclear receptors for chemokines and roles in transcriptional regulation, cell proliferation and cell differentiation |
| AU2003297318A1 (en) | 2002-12-20 | 2004-07-22 | Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Methods and compositions for treating cancer using 15986, 2188, 20743, 9148, 9151, 9791, 44252, 14184, 42461, 8204, 7970, 25552, 21657, 26492, 2411, 15088, 1905, 28899, 63380, 33935, 10480, 12686, 25501, 17694, 15701, 53062, 49908, 21612, 38949, 6216, 46863, 9235, 2201, 6985, 9883, 12238, 18057, 21617, 39228, 49928, 54476. |
| TWI324608B (en) | 2003-02-28 | 2010-05-11 | Oncotherapy Science Inc | Genes and polypeptides relating to human colorectal cancers |
| US7337154B2 (en) | 2003-05-19 | 2008-02-26 | Raytheon Company | Method for solving the binary minimization problem and a variant thereof |
| US20050100933A1 (en) | 2003-06-18 | 2005-05-12 | Arcturus Bioscience, Inc. | Breast cancer survival and recurrence |
| WO2005019258A2 (en) | 2003-08-11 | 2005-03-03 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the treatment of immune related diseases |
| JP4614952B2 (ja) | 2003-08-20 | 2011-01-19 | オンコセラピー・サイエンス株式会社 | 腎細胞癌(rcc)の潜在的な新規治療標的としての低酸素誘導タンパク質2(hig2) |
| JP4579246B2 (ja) | 2003-09-24 | 2010-11-10 | オンコセラピー・サイエンス株式会社 | 乳癌を診断する方法 |
| EP1762094A4 (en) | 2003-12-08 | 2007-11-14 | Silicon Image Inc | INTEGRATED ADDRESSING SCHEME FOR USE IN A SYSTEM WITH A TREE STRUCTURE |
| WO2005083086A2 (en) | 2004-02-27 | 2005-09-09 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Epha4 as therapeutic target of prc and pdaca |
| WO2005090572A2 (en) | 2004-03-24 | 2005-09-29 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Compositions and methods for treating pancreatic cancer |
| US8193332B2 (en) | 2004-04-09 | 2012-06-05 | Genecare Research Institute Co., Ltd. | Cancer cell-specific apoptosis-inducing agents that target chromosome stabilization-associated genes |
| WO2005118626A2 (en) | 2004-06-01 | 2005-12-15 | Innogenetics N.V. | Peptides for inducing a ctl and/or htl response to hepatitis c virus |
| CA2576293C (en) * | 2004-07-12 | 2016-10-04 | Nicola J. Mabjeesh | Agents capable of downregulating an msf-a-dependent hif-1alpha and use thereof in cancer treatment |
| WO2006055371A2 (en) | 2004-11-16 | 2006-05-26 | Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Functional screening of antibody libraries |
| CN100381460C (zh) | 2004-11-30 | 2008-04-16 | 北京市肿瘤防治研究所 | Her-2模拟抗原表位及含有该表位的肽 |
| EP2295601A1 (en) | 2005-02-10 | 2011-03-16 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Method of diagnosing bladder cancer |
| KR20080003321A (ko) | 2005-02-24 | 2008-01-07 | 세미네스 인코퍼레이티드 | 생물학적 샘플을 분류하는 조성물 및 방법 |
| US8088976B2 (en) | 2005-02-24 | 2012-01-03 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Methods for genetic control of plant pest infestation and compositions thereof |
| US7847060B2 (en) | 2005-02-25 | 2010-12-07 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Peptide vaccines for lung cancers expressing TTK, URLC10 or KOC1 polypeptides |
| EP1854473A1 (en) | 2005-03-03 | 2007-11-14 | Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited | Preventive/therapeutic agent for cancer |
| CN100348614C (zh) | 2005-06-03 | 2007-11-14 | 北京大学 | 一种肝癌-睾丸特异性抗原蛋白质和抗原肽 |
| NZ591569A (en) | 2005-07-20 | 2012-10-26 | Agriculture Victoria Serv Pty | Modification of flavonoid biosynthesis in plants with transparent testa 2 |
| US8053183B2 (en) | 2005-07-27 | 2011-11-08 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Method of diagnosing esophageal cancer |
| WO2007013665A2 (en) | 2005-07-27 | 2007-02-01 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Method of diagnosing small cell lung cancer |
| WO2007013575A2 (en) | 2005-07-28 | 2007-02-01 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Method for diagnosing and treating renal cell carcinoma |
| JP5150855B2 (ja) | 2005-07-29 | 2013-02-27 | オンコセラピー・サイエンス株式会社 | Cdca1−kntc2複合体を標的とするスクリーニングおよびnsclcの治療方法 |
| WO2007018047A1 (ja) | 2005-08-09 | 2007-02-15 | Kurume University | Hla-a24分子結合性扁平上皮癌抗原由来ペプチド |
| PL1760088T3 (pl) | 2005-09-05 | 2008-10-31 | Immatics Biotechnologies Gmbh | Związane z nowotworem peptydy wiążące się w sposób niedyskryminujący z cząsteczkami antygenu ludzkiego leukocytu klasy II (HLA) |
| US20090263832A1 (en) | 2005-11-30 | 2009-10-22 | Roberto Polakiewicz | Reagents for the Detection of Protein Phosphorylation in Leukemia Signaling Pathways |
| JP2009531273A (ja) | 2006-02-28 | 2009-09-03 | オンコセラピー・サイエンス株式会社 | 抗EphA4抗体のエフェクター機能を用いて細胞を障害する方法 |
| CN101432303A (zh) | 2006-02-28 | 2009-05-13 | 肿瘤疗法科学股份有限公司 | 利用抗cdh3抗体的效应物功能来损伤细胞的方法 |
| US7695928B2 (en) | 2006-04-10 | 2010-04-13 | Genentech, Inc. | Disheveled PDZ modulators |
| EP2468887A1 (en) | 2006-12-13 | 2012-06-27 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | TTK as tumor marker and therapeutic target for lung cancer |
| WO2008102906A1 (en) | 2007-02-20 | 2008-08-28 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Hspc-hrpc transition genes |
| US20090081659A1 (en) | 2007-03-07 | 2009-03-26 | Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. | Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in carcinoma signaling pathways |
| EP1983003A3 (en) | 2007-04-19 | 2009-03-11 | Peter Hornbeck | Tyrosine phosphorylation sites and antibodies specific for them |
| WO2009016691A1 (en) | 2007-07-30 | 2009-02-05 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Cancer associated gene ly6k |
| CA2696591C (en) | 2007-08-20 | 2016-10-11 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Cdh3 peptide and medicinal agent comprising the same |
| EP2080812A1 (en) | 2008-01-18 | 2009-07-22 | Transmedi SA | Compositions and methods of detecting post-stop peptides |
| TWI580431B (zh) | 2008-08-19 | 2017-05-01 | 腫瘤療法 科學股份有限公司 | Hig2與urlc10抗原決定位胜肽以及含此胜肽之疫苗 |
| EP2483690A1 (de) | 2009-09-29 | 2012-08-08 | Protagen AG | Markersequenzen für pankreaskrebserkrankungen, pankreaskarzinom und deren verwendung |
-
2009
- 2009-08-13 TW TW098127225A patent/TW201008574A/zh unknown
- 2009-08-14 CN CN2009801413475A patent/CN102186977A/zh not_active Withdrawn
- 2009-08-14 SG SG2013062708A patent/SG193214A1/en unknown
- 2009-08-14 WO PCT/JP2009/003894 patent/WO2010021111A1/en not_active Ceased
- 2009-08-14 KR KR1020117005944A patent/KR20110063456A/ko not_active Withdrawn
- 2009-08-14 JP JP2011507725A patent/JP2012500001A/ja not_active Ceased
- 2009-08-14 EP EP09808047A patent/EP2326718A4/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2009-08-14 AU AU2009283762A patent/AU2009283762A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2009-08-14 US US13/059,617 patent/US20110280898A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2009-08-14 RU RU2011110504/10A patent/RU2011110504A/ru not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2009-08-14 CA CA2734515A patent/CA2734515A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2009-08-14 MX MX2011001880A patent/MX2011001880A/es not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2009-08-17 US US12/542,638 patent/US8383590B2/en active Active
-
2011
- 2011-02-09 IL IL211131A patent/IL211131A0/en unknown
-
2012
- 2012-05-04 US US13/464,831 patent/US8623829B2/en active Active
-
2013
- 2013-01-17 US US13/744,354 patent/US8759481B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2013-11-13 US US14/079,144 patent/US9067973B2/en active Active
-
2014
- 2014-05-09 US US14/274,373 patent/US9284349B2/en active Active
-
2016
- 2016-01-06 US US14/989,741 patent/US20160200764A1/en not_active Abandoned
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2008102557A1 (en) * | 2007-02-21 | 2008-08-28 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Peptide vaccines for cancers expressing tumor-associated antigens |
Non-Patent Citations (5)
| Title |
|---|
| KUZUSHIMA K ET AL., BLOOD, vol. 98, no. 6, 2001, pages 1872 - 81 |
| NAKAHARA S ET AL., CANCER RES, vol. 63, no. 14, 15 July 2003 (2003-07-15), pages 4112 - 8 |
| PARKER KC ET AL., J IMMUNOL, vol. 152, no. 1, 1994, pages 163 - 75 |
| See also references of EP2326718A4 |
| WORBS S. ET AL.: "Expression of the inhibin/activin subunits (-alpha, -betaA and -betaB) in normal and carcinogenic endometrial tissue: possible immunohistochemical differentiation markers.", ONCOL. REP., vol. 17, no. 1, 2007, pages 97 - 104, XP008144361 * |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9017669B2 (en) | 2009-12-28 | 2015-04-28 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Anti-CDH3 antibodies and uses thereof |
| WO2011122022A1 (en) * | 2010-04-02 | 2011-10-06 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | Ect2 peptides and vaccines including the same |
| US8951975B2 (en) | 2010-04-02 | 2015-02-10 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | ECT2 peptides and vaccines including the same |
| EA027940B1 (ru) * | 2010-04-02 | 2017-09-29 | Онкотерапи Сайенс, Инк. | Пептиды, обладающие способностью индуцировать цитотоксические т-лимфоциты, и их применение |
| US10576097B2 (en) | 2014-08-04 | 2020-03-03 | Oncotherapy Science, Inc. | URLC10-derived peptide and vaccine containing same |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| IL211131A0 (en) | 2011-04-28 |
| US20130189291A1 (en) | 2013-07-25 |
| US8623829B2 (en) | 2014-01-07 |
| US20110280898A1 (en) | 2011-11-17 |
| US20140141027A1 (en) | 2014-05-22 |
| US9067973B2 (en) | 2015-06-30 |
| US20120321649A1 (en) | 2012-12-20 |
| EP2326718A4 (en) | 2012-03-07 |
| CN102186977A (zh) | 2011-09-14 |
| US20100040641A1 (en) | 2010-02-18 |
| US8759481B2 (en) | 2014-06-24 |
| SG193214A1 (en) | 2013-09-30 |
| JP2012500001A (ja) | 2012-01-05 |
| TW201008574A (en) | 2010-03-01 |
| US20140248300A1 (en) | 2014-09-04 |
| RU2011110504A (ru) | 2012-09-27 |
| US8383590B2 (en) | 2013-02-26 |
| KR20110063456A (ko) | 2011-06-10 |
| US9284349B2 (en) | 2016-03-15 |
| MX2011001880A (es) | 2011-03-29 |
| EP2326718A1 (en) | 2011-06-01 |
| US20160200764A1 (en) | 2016-07-14 |
| AU2009283762A1 (en) | 2010-02-25 |
| CA2734515A1 (en) | 2010-02-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2010021111A1 (en) | Inhbb epitope peptides and vaccines containing the same | |
| US8367799B2 (en) | TEM8 peptides and vaccines comprising the same | |
| EP2303912B1 (en) | Cdca1 epitope peptides and vaccines containing the same | |
| EP2328600B1 (en) | Hig2 and urlc10 epitope peptide and vaccines containing the same | |
| US9675680B2 (en) | MELK epitope peptides and vaccines containing the same | |
| WO2009150835A1 (en) | Iqgap3 epitope peptides and vaccines containing the same | |
| WO2009150822A1 (en) | Mybl2 epitope peptides and vaccines containing the same | |
| HK1156341B (en) | Melk epitope peptides and vaccines containing the same | |
| HK1155757A (en) | Cdca1 epitope peptides and vaccines containing the same | |
| HK1155757B (en) | Cdca1 epitope peptides and vaccines containing the same | |
| HK1157204B (en) | Hig2 and urlc10 epitope peptide and vaccines containing the same | |
| HK1175197B (en) | Tem8 peptides and vaccines comprising the same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 200980141347.5 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 09808047 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2009283762 Country of ref document: AU |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 211131 Country of ref document: IL |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2734515 Country of ref document: CA |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2011507725 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: MX/A/2011/001880 Country of ref document: MX |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2009808047 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2009283762 Country of ref document: AU Date of ref document: 20090814 Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 1723/CHENP/2011 Country of ref document: IN |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20117005944 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2011110504 Country of ref document: RU |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 13059617 Country of ref document: US |