WO2009151094A1 - ヒトアドレナリンβ3受容体リガンド、これを含む食品及び医薬品 - Google Patents
ヒトアドレナリンβ3受容体リガンド、これを含む食品及び医薬品 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2009151094A1 WO2009151094A1 PCT/JP2009/060682 JP2009060682W WO2009151094A1 WO 2009151094 A1 WO2009151094 A1 WO 2009151094A1 JP 2009060682 W JP2009060682 W JP 2009060682W WO 2009151094 A1 WO2009151094 A1 WO 2009151094A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- acid
- receptor ligand
- fatty acid
- human
- adrenergic
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K45/00—Medicinal preparations containing active ingredients not provided for in groups A61K31/00 - A61K41/00
- A61K45/06—Mixtures of active ingredients without chemical characterisation, e.g. antiphlogistics and cardiaca
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/185—Acids; Anhydrides, halides or salts thereof, e.g. sulfur acids, imidic, hydrazonic or hydroximic acids
- A61K31/19—Carboxylic acids, e.g. valproic acid
- A61K31/20—Carboxylic acids, e.g. valproic acid having a carboxyl group bound to a chain of seven or more carbon atoms, e.g. stearic, palmitic, arachidic acids
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/185—Acids; Anhydrides, halides or salts thereof, e.g. sulfur acids, imidic, hydrazonic or hydroximic acids
- A61K31/19—Carboxylic acids, e.g. valproic acid
- A61K31/20—Carboxylic acids, e.g. valproic acid having a carboxyl group bound to a chain of seven or more carbon atoms, e.g. stearic, palmitic, arachidic acids
- A61K31/201—Carboxylic acids, e.g. valproic acid having a carboxyl group bound to a chain of seven or more carbon atoms, e.g. stearic, palmitic, arachidic acids having one or two double bonds, e.g. oleic, linoleic acids
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/185—Acids; Anhydrides, halides or salts thereof, e.g. sulfur acids, imidic, hydrazonic or hydroximic acids
- A61K31/19—Carboxylic acids, e.g. valproic acid
- A61K31/20—Carboxylic acids, e.g. valproic acid having a carboxyl group bound to a chain of seven or more carbon atoms, e.g. stearic, palmitic, arachidic acids
- A61K31/202—Carboxylic acids, e.g. valproic acid having a carboxyl group bound to a chain of seven or more carbon atoms, e.g. stearic, palmitic, arachidic acids having three or more double bonds, e.g. linolenic
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P19/00—Drugs for skeletal disorders
- A61P19/06—Antigout agents, e.g. antihyperuricemic or uricosuric agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
- A61P3/04—Anorexiants; Antiobesity agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
- A61P3/06—Antihyperlipidemics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
- A61P3/08—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism for glucose homeostasis
- A61P3/10—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism for glucose homeostasis for hyperglycaemia, e.g. antidiabetics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P43/00—Drugs for specific purposes, not provided for in groups A61P1/00-A61P41/00
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
- A61P9/12—Antihypertensives
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a human adrenergic ⁇ 3 receptor ligand, foods and medicaments containing the same.
- Adrenergic receptors are receptors that bind to catecholamine agonists such as adrenaline and noradrenaline released from sympathetic nerves, and are classified into two types, ⁇ receptors and ⁇ receptors, depending on the sensitivity to catecholamine agonists.
- the adrenergic ⁇ receptor is sensitive in the order of noradrenaline ⁇ adrenaline> dopamine> isoproterenol, and the adrenergic ⁇ receptor is sensitive in the order of isoproterenol> adrenaline ⁇ noradrenaline> dopamine.
- Adrenergic ⁇ receptors include ⁇ 1 , ⁇ 2 , and ⁇ 3 receptors, and the presence of ⁇ 4 receptors has recently been suggested.
- Adrenergic ⁇ 1 receptor agonists are heart rate increasing, adrenaline ⁇ 1 receptor antagonists are antihypertensive, adrenergic ⁇ 2 receptor agonists are bronchial smooth muscle relaxing, adrenergic ⁇ 3 receptors
- Agonists are known to have an effect of activating heat production and promoting lipolysis.
- an adrenergic ⁇ 3 receptor agonist is effective in preventing and / or improving lifestyle-related diseases such as obesity.
- Non-patent Document 1 human adrenergic ⁇ 3 receptor agonists
- Patent Document 1 a human ⁇ 3 adrenergic receptor agonist agent containing yam extract as an active ingredient has also been reported.
- chitosan-containing polysaccharides produced from agaricus, shiitake mushrooms, enokitake mushrooms, shimeji mushrooms, maiko, namoko, etc. have a lowering effect on blood pressure, urine sugar level, blood glucose level, uric acid level, total cholesterol level, neutral fat level, etc. It has been reported that it has a great effect on improving test values of lifestyle-related diseases such as hypertension and diabetes and adult diseases (Patent Document 2).
- JP 2006-96666 WO2004 / 033502 Yasutaka Takakura, Toshihide Yoshida, Japanese Pharmacology Journal, 118, 315-320, 2001 C. Weyer, et al., Diabetes & Metabolism, 25, 11-21, 1999
- An object of the present invention is to provide a human adrenergic ⁇ 3 receptor ligand. Another object of the present invention is to provide foods and pharmaceuticals comprising the above human adrenergic ⁇ 3 receptor ligand. Still another object of the present invention is to provide an agent for preventing and / or improving lifestyle-related diseases such as obesity, obesity, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, gout and the like, which contains a human adrenergic ⁇ 3 receptor ligand. It is to be.
- the present invention provides a human adrenergic ⁇ 3 receptor ligand comprising a combination of the following specific unsaturated fatty acid and saturated fatty acid as an active ingredient, a food and a pharmaceutical containing the same.
- a human adrenergic ⁇ 3 receptor ligand comprising the following three components.
- the human adrenergic ⁇ 3 receptor ligand of the present invention has a high binding activity to human adrenergic ⁇ 3 receptor, such as blood pressure, urinary glucose level, blood glucose level, uric acid level, total cholesterol level, neutral fat level, visceral fat level, etc. It has a lowering effect and is effective for the prevention and / or treatment of lifestyle-related diseases such as hypertension, diabetes, obesity, hypercholesterolemia, and hyperlipidemia.
- the active ingredient of the present invention has low cytotoxicity and can be safely used as a food or a pharmaceutical product.
- the unsaturated fatty acid having 3 or more double bonds of the active ingredient (A) of the present invention preferably has 8 to 24 carbon atoms, more preferably 10 to 20 carbon atoms.
- Triunsaturated fatty acids include ⁇ -linolenic acid (18: 3, 9,12,15-triunsaturated fatty acid), ⁇ -eleostealic acid (18: 3, 9c, 11t, 13t), ⁇ -eleostealic acid (18: 3, 9t, 11t, 13t), punicic acid (18: 3, 9c, 11t, 13c), calendic acid (18: 3, 8t, 10t, 12c), jarcaric acid (18: 3, 8c, 10t, 12c), catalpic acid (18: 3, 9t, 11t, 13c), kamlolenic acid (kamlolenic acid) acid) (18OH, 9c, 11t, 13t), tetraunsaturated fatty acids such as stearidonic acid (6,9,12,15-tetraunsaturated
- the unsaturated fatty acid having one or two double bonds of the active ingredient (B) of the present invention preferably has 8 to 24 carbon atoms, more preferably 10 to 20 carbon atoms.
- monounsaturated fatty acids myristoleic acid (carbon number 14), palmitoleic acid (carbon number 16), oleic acid (carbon number 18), elaidic acid (elaidic acid) 18 carbon atoms, vaccenic acid (18 carbon atoms), gadoleic acid (20 carbon atoms), erucic acid (22 carbon atoms), nervonic acid (carbon number) 24) and the like are diunsaturated fatty acids such as linoleic acid (carbon number 18).
- the saturated fatty acid of the active ingredient (C) of the present invention preferably has 8 to 24 carbon atoms, more preferably 10 to 20 carbon atoms.
- Specific examples include octanoic acid, nonanoic acid, decanoic acid, dodecanoic acid, tetradecanoic acid, pentadecanoic acid, hexadecanoic acid, heptadecanoic acid, octadecanoic acid, nonadecanoic acid, icosanoic acid, docosanoic acid, tetradocosanoic acid, hexadocosanoic acid, octadocosanoic acid, And triacontanoic acid.
- the active ingredients (A), (B) and (C) may be in the form of a salt, ester, amide or the like.
- the salt is not particularly limited as long as it is foodically, nutritionally, or pharmacologically acceptable, and is a metal salt such as sodium salt or calcium salt, ammonium salt, methylamine, ethylamine, diethylamine, triethylamine.
- salts with organic bases such as pyrrolidine, piperidine, morpholine, hexamethyleneimine, aniline and pyridine, and salts with amino acids such as arginine, glutamic acid and ornithine.
- the ester derivative may be selected from any food-acceptable, nutritionally, or pharmacologically acceptable ester derivative, and ethyl ester, butyl ester, propyl ester, and glycerol ester are preferable, and more preferable.
- ethyl esters and glycerol esters are preferable.
- the glycerol ester derivative any form of monoglyceride, diglyceride and triglyceride may be used, but diglyceride and triglyceride are preferred, and triglyceride is most preferred.
- the amide derivative is not particularly limited as long as it is foodically, nutritionally, or pharmacologically acceptable, and examples thereof include acetamide, propionamide, butyramide, and barrel amide.
- the mass ratio of the component (A) to the component (B) is preferably 1:90 to 8: 2, more preferably 1:60 to 3: 7.
- the ratio of the total mass of component (A) and component (B) to the mass of component (C) is preferably 50: 1 to 1: 3, more preferably 40: 1 to 1: 1.
- the adrenergic ⁇ 3 receptor ligand of the present invention can be used only with an active ingredient, but can also be used in a form to which an excipient or the like is added.
- the active ingredient includes a preservative such as sodium benzoate, methyl p-oxybenzoate, sodium dehydroacetate, malic acid, ascorbic acid, citric acid, acetic acid.
- a solubilizing agent such as a coloring agent, a flavoring agent, a flavoring agent, a sweetening agent such as glucose and mannitol, and the like, and a diluent such as distilled water and physiological saline as necessary. Or prepare food.
- compositions containing the above ingredients as active ingredients are usually prepared in the form of solid preparations such as tablets, pills, powders, granules, capsules and suppositories. At that time, these pharmaceutical preparations are prepared using diluents or excipients such as fillers, extenders, binders, moisturizers, disintegrants, surfactants, lubricants and the like that are usually used. .
- conventionally known carriers can be widely used as carriers, such as lactose, mannitol, sucrose, sodium chloride, glucose, starch, calcium carbonate, kaolin, crystalline cellulose and other excipients, Distilled water, physiological saline, simple syrup, glucose solution, starch solution, gelatin solution, carboxymethylcellulose, potassium phosphate, polyvinylpyrrolidone and other binders, dried starch, sodium alginate, agar powder, sodium bicarbonate, calcium carbonate, lauryl Disintegrants such as sodium sulfate, stearic acid monoglyceride, starch, lactose, disintegration inhibitors such as sucrose, stearin, cocoa butter, hydrogenated oil, dissolution absorption accelerators such as acetic acid, ascorbic acid, malic acid, glycerin, starch, lactose , Kaolin, bentonite, colloid Adsorbent such as Jo silicate, purified talc, stealine, simple syrup
- conventionally known carriers can be widely used as carriers, such as glucose, lactose, mannitol, starch, cacao butter, hydrogenated vegetable oil, kaolin, talc and other excipients, gum arabic Powders, disintegrating agents such as gelatin are listed.
- a conventionally known carrier can be widely used as the carrier, and examples thereof include cocoa butter, higher alcohol esters, and gelatin.
- the content of the active ingredient is not particularly limited and is selected within a wide range, but the active ingredients (A), (B) and (C) as a whole are usually 0.001 to 30% by mass, preferably 0. The content is preferably 01 to 10% by mass.
- the dose is not particularly limited, and may be appropriately selected depending on the usage, patient age, sex, disease degree, and other conditions.
- the total amount of the active ingredients (A), (B) and (C) is 0.01 to 20 mg, preferably 0.02 to 10 mg per 1 kg body weight.
- the foodstuff containing the active ingredient (A) of this invention, (B) and (C) is not specifically limited, For example, soup, miso soup, drink, jelly, gummy, etc. are mentioned.
- the total content of the active ingredients (A), (B) and (C) in these foods is preferably 0.001 to 30% by mass, more preferably 0.01 to 10% by mass.
- HEK-293 cells expressing human recombinant adrenergic ⁇ 3 receptor are used for the adrenergic ⁇ 3 receptor binding activity
- Test example 1 Using rat primary preadipocytes (visceral fat, epididymal fat around the body, subcutaneous white fat and brown fat), preliminary studies were conducted in vitro on the effect of inhibiting fat accumulation and fat release by the composition of the present invention. I did it. Dimethyl Sulfoxide (hereinafter DMSO) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.) was used as a test material and test method negative control substance. Test substance A component containing the components shown in Table 1 below in the mass ratio shown in Table 1 was dissolved in DMSO to 1 w / v%, and the adipocyte differentiation medium (Primary Cell, Ltd., Lot. No. 080411) was dissolved. It was used by adding to a final concentration of 10 ⁇ g / mL. The adrenergic ⁇ 3 receptor binding activity test was performed as described above.
- DMSO Dimethyl Sulfoxide
- Test substance A component containing the components shown in Table 1 below in the mass ratio shown in Table 1 was dissolved in DMSO to
- adipocyte culture kit 3 types set H-3 primary, rat, primary cell: visceral adipose precursor cells (hereafter VAC) Lot.No.FIHA-FV / subcutaneous white precursor fat cells (hereafter SAC) FIHA -FS / epididymal preadipocytes (hereinafter EAC) FIHA-FE) and brown adipocyte culture kit F-8 (primary, rat, primary cell: Lot. No. HDOA-1) were used.
- Norepinephrine hereinafter NE
- SIGMA No. 103K0979
- Preparation of cell lysate TRI-Reagent (Molecular Research Center: Lot No.3681) was used.
- Test method Culture operation (1) Three types of preadipocytes (VAC, SAC, EAC) Three types of adipocyte progenitor cells (visceral fat, epididymis, subcutaneous white) 1.5 ⁇ 10 6 cells are seeded in 12 wells of a 24-well plate (cell count is 1.2 ⁇ 10 5 cells / mL / well), 4 Pre-culture was performed in a day adipocyte differentiation medium. After the preculture (4 days after seeding), the negative control substance and the test substance were prepared with a visceral adipose differentiation medium to a prescribed concentration, and the prepared medium was added to the cells.
- the medium was changed on the 0th, 2nd and 4th days after addition of the test substance (seeding days 4, 6 and 8), and a freshly prepared medium was added after the collection.
- the cell lysate is prepared as it is for the NE-untreated group, and for the NE-treated group, the test substance and negative control substance are set to the specified concentrations and NE is 1 x 10 -6 M 6 hours before cell lysate preparation.
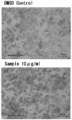
- Brown adipocytes (hereinafter BAT) Brown adipocytes seeded in a 24-well plate were cultured in a growth medium for 3 days and confirmed to be confluent. The medium was replaced with a differentiation-inducing medium, and cultured for 2 days. Negative control substances and test substances were adjusted to a specified concentration with a maintenance medium, and the prepared medium was added to the cells and cultured for 4 days. For NE treatment, the same treatment as VAC was performed with maintenance medium. Microscopic observation was performed before and after the addition of NE, and photographs of representative examples were taken with a Hoffman module lens. The composition of the test group is shown in Table 2 and Table 3 below.
- Test result Cell morphology observation micrograph Day 0 of test substance administration (day 4 of seeding) On day 4 after seeding the visceral fat cells, 1 mL of a normal medium and a culture solution prepared with the test substance were added, and microscopic observation and photography of representative examples were performed. When the whole of each well was observed, it was confirmed that fat droplets began to accumulate little by little in the fat cells. There was no difference between each group, confirming that the test system was conducted under the same conditions for each group.
- EAC Cell morphology observation micrograph
- Formulation Example 1 10 g of malic acid and 10 g of ascorbic acid were added to 10 g of the composition produced in Example 1, dissolved in 1000 ml of water, and lyophilized. This has the property of instantly dissolving in pure water.
- 20 g of this lyophilized product 20 g of mannitol, 50 g of lactose and 20 g of polydextrose were added and mixed well, and 2 g of sucrose fatty acid ester was added as a binder to form a tablet.
- Formulation Example 2 (granule) After 1 g of the composition produced in Example 2 was sufficiently dispersed in 100 g of dextrin, this was mixed with 900 g of dextrin, and granules were prepared by fluidized bed granulation.
- Formulation Example 3 (Jelly) 10 g of ascorbic acid is added to 1 g of the composition produced in Example 3 and dispersed and dissolved in 500 g of liquid sugar, 0.1 g of a gelling agent, 0.1 g of lemon flavoring and 500 ml of water are added and filled into a plastic container. Cool down and make jelly.
- VAC cell form observation micrograph
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Diabetes (AREA)
- Obesity (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Endocrinology (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Child & Adolescent Psychology (AREA)
- Emergency Medicine (AREA)
- Pain & Pain Management (AREA)
- Rheumatology (AREA)
- Physical Education & Sports Medicine (AREA)
- Acyclic And Carbocyclic Compounds In Medicinal Compositions (AREA)
- Coloring Foods And Improving Nutritive Qualities (AREA)
Priority Applications (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP09762524A EP2316445A4 (en) | 2008-06-11 | 2009-06-11 | HUMAN BETA3 ADRENERGER RECEPTOR LIGAND AND THEREOF FOOD OR PHARMACEUTICAL PREPARATION |
| US12/997,498 US20110098358A1 (en) | 2008-06-11 | 2009-06-11 | Human beta3 adrenergic receptor ligand, and food or pharmaceutical product containing the same |
| CN200980131312.3A CN102149375B (zh) | 2008-06-11 | 2009-06-11 | 人肾上腺素β3受体配体、含有其的食品及药品 |
| CA2727223A CA2727223C (en) | 2008-06-11 | 2009-06-11 | Human .beta.3 adrenergic receptor ligand, and food or pharmaceutical product containing the same |
| JP2010516877A JP5544660B2 (ja) | 2008-06-11 | 2009-06-11 | ヒトアドレナリンβ3受容体リガンド、これを含む食品及び医薬品 |
| KR1020117000640A KR101274543B1 (ko) | 2008-06-11 | 2009-06-11 | 인간 아드레날린 β3 수용체 리간드, 이를 포함하는 식품 및 의약품 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008153390 | 2008-06-11 | ||
| JP2008-153390 | 2008-06-11 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2009151094A1 true WO2009151094A1 (ja) | 2009-12-17 |
Family
ID=41416798
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2009/060682 Ceased WO2009151094A1 (ja) | 2008-06-11 | 2009-06-11 | ヒトアドレナリンβ3受容体リガンド、これを含む食品及び医薬品 |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20110098358A1 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP2316445A4 (enExample) |
| JP (2) | JP5544660B2 (enExample) |
| KR (1) | KR101274543B1 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN102149375B (enExample) |
| CA (1) | CA2727223C (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2009151094A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021020855A (ja) * | 2019-07-24 | 2021-02-18 | 国立大学法人 東京大学 | 血中尿酸値低下剤及び血中尿酸値低下用食品組成物 |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3215004B1 (en) * | 2014-11-03 | 2022-06-08 | Société des Produits Nestlé S.A. | Methods using facial temperature to evaluate post-ingestive impact of food ingredients on fat oxidation |
| US9561206B2 (en) * | 2015-01-07 | 2017-02-07 | The United States Of America, As Represented By The Secretary Of The Navy | Use of heptadecanoic acid (C17:0) to detect risk of and treat hyperferritinemia and metabolic syndrome |
| US10792266B2 (en) | 2017-10-23 | 2020-10-06 | Epitracker, Inc. | Fatty acid analogs and their use in the treatment of conditions related to metabolic syndrome |
| JP2021525249A (ja) | 2018-05-23 | 2021-09-24 | エピトラッカー インコーポレイテッドEpitracker, Inc. | 加齢及び長期性の質に関連する状態の診断及び治療のための組成物及び方法 |
| EP3908374A4 (en) | 2019-01-09 | 2022-12-28 | Epitracker, Inc. | COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR THE DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASES |
| JP7404382B2 (ja) | 2019-03-04 | 2023-12-25 | エピトラッカー インコーポレイテッド | 脂肪酸アナログ、ならびに認知機能障害、行動症状および慢性疼痛の処置におけるそれらの使用 |
| US12370166B2 (en) | 2021-11-03 | 2025-07-29 | Epitracker, Inc. | Pentadecanoylcarnitine for treatment of conditions related to the quality of aging and longevity |
Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1996031240A1 (en) * | 1995-04-07 | 1996-10-10 | Brandeis University | Increasing the hdl level and the hdl/ldl ratio in human serum by balancing saturated and polyunsaturated dietary fatty acids |
| JP2004075653A (ja) * | 2002-06-19 | 2004-03-11 | Nisshin Oillio Ltd | 体脂肪分解促進剤および飲食物 |
| WO2004022049A1 (ja) * | 2002-09-05 | 2004-03-18 | The Nisshin Oillio Group, Ltd. | 痩身剤およびその飲食物 |
| WO2004022050A1 (ja) * | 2002-09-05 | 2004-03-18 | The Nisshin Oillio Group, Ltd. | 脂質代謝調整剤および飲食物 |
| WO2004033502A1 (ja) | 2002-10-08 | 2004-04-22 | Ricom Corporation | キトサン含有多糖、その製造方法及び用途 |
| JP2004536619A (ja) * | 2001-08-08 | 2004-12-09 | ソシエテ デ プロデユイ ネツスル ソシエテ アノニム | 筋肉細胞内脂質水準を増大させるために設計されたオレイン脂肪酸及びオメガ−6脂肪酸を含有する脂質ブレンド及び食料品 |
| JP2005179264A (ja) * | 2003-12-19 | 2005-07-07 | Shokubutsu Kogaku Kenkyusho:Kk | 体重増加抑制剤 |
| JP2006096666A (ja) | 2002-10-31 | 2006-04-13 | Kaneka Corp | 選択的ヒトβ3アドレナリン受容体アゴニスト剤 |
| WO2006042733A2 (en) * | 2004-10-18 | 2006-04-27 | Oleoyl-Estrone Developments, S.L. | Methods of using fatty-acid esters of estrogens and thermogenic compounds for reducing the body weight of a mammal and compositions containing the same |
| WO2006073147A1 (ja) * | 2005-01-04 | 2006-07-13 | Mochida Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | 脂肪毒性の改善剤 |
| WO2008000440A1 (en) * | 2006-06-27 | 2008-01-03 | Lipid Nutrition B.V. | Use of a polyunsaturated fatty acid compound |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA2173545C (en) * | 1995-04-07 | 2004-06-29 | Kalyana Sundram | Increasing the hdl level and the hdl/ldl ratio in human serum by balancing saturated and polyunsaturated dietary fatty acids |
| DK1427436T3 (da) * | 2001-08-23 | 2008-10-13 | Westgate Biolog Ltd | Anvendelse af mælkeserumapoproteiner til profylakse eller behandling af mikrobiel eller viral infektion |
| AU2003241807A1 (en) * | 2002-05-27 | 2003-12-12 | Morinaga And Co., Ltd. | Composition against periodontal bacteria and foods, drinks and mouth washers against periodontal bacteria containing the composition |
| JP2005015358A (ja) * | 2003-06-25 | 2005-01-20 | Pharma Design Inc | 摂食障害の治療に供される医薬組成物 |
| AU2004285803A1 (en) * | 2003-11-04 | 2005-05-12 | Meiji Dairies Corporation | Plant-origin beta3-adrenoceptor agonist and use of the same |
| US20080200707A1 (en) * | 2005-01-04 | 2008-08-21 | Mochida-Pharmaceuticals Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Lipotoxicity Relieving Agent |
| GB0514463D0 (en) * | 2005-01-31 | 2005-08-17 | Loders Croklaan Bv | Use of pinolenic acid |
-
2009
- 2009-06-11 KR KR1020117000640A patent/KR101274543B1/ko not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2009-06-11 EP EP09762524A patent/EP2316445A4/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2009-06-11 WO PCT/JP2009/060682 patent/WO2009151094A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2009-06-11 CA CA2727223A patent/CA2727223C/en active Active
- 2009-06-11 US US12/997,498 patent/US20110098358A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2009-06-11 CN CN200980131312.3A patent/CN102149375B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2009-06-11 JP JP2010516877A patent/JP5544660B2/ja active Active
-
2014
- 2014-01-28 JP JP2014013224A patent/JP2014080432A/ja active Pending
Patent Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1996031240A1 (en) * | 1995-04-07 | 1996-10-10 | Brandeis University | Increasing the hdl level and the hdl/ldl ratio in human serum by balancing saturated and polyunsaturated dietary fatty acids |
| JP2004536619A (ja) * | 2001-08-08 | 2004-12-09 | ソシエテ デ プロデユイ ネツスル ソシエテ アノニム | 筋肉細胞内脂質水準を増大させるために設計されたオレイン脂肪酸及びオメガ−6脂肪酸を含有する脂質ブレンド及び食料品 |
| JP2004075653A (ja) * | 2002-06-19 | 2004-03-11 | Nisshin Oillio Ltd | 体脂肪分解促進剤および飲食物 |
| WO2004022049A1 (ja) * | 2002-09-05 | 2004-03-18 | The Nisshin Oillio Group, Ltd. | 痩身剤およびその飲食物 |
| WO2004022050A1 (ja) * | 2002-09-05 | 2004-03-18 | The Nisshin Oillio Group, Ltd. | 脂質代謝調整剤および飲食物 |
| WO2004033502A1 (ja) | 2002-10-08 | 2004-04-22 | Ricom Corporation | キトサン含有多糖、その製造方法及び用途 |
| JP2006096666A (ja) | 2002-10-31 | 2006-04-13 | Kaneka Corp | 選択的ヒトβ3アドレナリン受容体アゴニスト剤 |
| JP2005179264A (ja) * | 2003-12-19 | 2005-07-07 | Shokubutsu Kogaku Kenkyusho:Kk | 体重増加抑制剤 |
| WO2006042733A2 (en) * | 2004-10-18 | 2006-04-27 | Oleoyl-Estrone Developments, S.L. | Methods of using fatty-acid esters of estrogens and thermogenic compounds for reducing the body weight of a mammal and compositions containing the same |
| WO2006073147A1 (ja) * | 2005-01-04 | 2006-07-13 | Mochida Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | 脂肪毒性の改善剤 |
| WO2008000440A1 (en) * | 2006-06-27 | 2008-01-03 | Lipid Nutrition B.V. | Use of a polyunsaturated fatty acid compound |
Non-Patent Citations (5)
| Title |
|---|
| BARRE D. E.: "Potential of Evening Primrose, Borage, Black Currant, and Fungal Oils in Human Health", NUTRITION & METABOLISM, vol. 45, 2001, pages 47 - 57, XP001027476 * |
| C. WEYER ET AL., DIABETES & METABOLISM, vol. 25, 1999, pages 11 - 21 |
| FEVE ET AL.: "Cell Biology", PROC. NATL. ACAD. SCI. USA 91, vol. 91, 1994, pages 5677 - 5681 |
| See also references of EP2316445A4 |
| YASUTO TAKAKURA; TOSHIHIDE YOSHIDA, FOLIA PHARMACOL. JPN., vol. 118, 2001, pages 315 - 320 |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021020855A (ja) * | 2019-07-24 | 2021-02-18 | 国立大学法人 東京大学 | 血中尿酸値低下剤及び血中尿酸値低下用食品組成物 |
| JP7500037B2 (ja) | 2019-07-24 | 2024-06-17 | 国立大学法人 東京大学 | 血中尿酸値低下剤及び血中尿酸値低下用食品組成物 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20110098358A1 (en) | 2011-04-28 |
| KR101274543B1 (ko) | 2013-06-17 |
| CA2727223A1 (en) | 2009-12-17 |
| JP2014080432A (ja) | 2014-05-08 |
| EP2316445A4 (en) | 2011-12-21 |
| EP2316445A1 (en) | 2011-05-04 |
| JP5544660B2 (ja) | 2014-07-09 |
| JPWO2009151094A1 (ja) | 2011-11-17 |
| CA2727223C (en) | 2014-10-07 |
| KR20110017437A (ko) | 2011-02-21 |
| CN102149375A (zh) | 2011-08-10 |
| CN102149375B (zh) | 2015-09-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5544660B2 (ja) | ヒトアドレナリンβ3受容体リガンド、これを含む食品及び医薬品 | |
| EP2393483B1 (en) | Pharmaceutical compositions comprising brivaracetam | |
| EP3157936B1 (en) | Mineral amino-acid complexes of active agents | |
| JP2014507411A (ja) | 骨及び関節の成長、回復、及び維持の促進のための食事サプリメント | |
| EP3463310B1 (en) | Tablets with high active ingredient content of omega-3 fatty acid amino acid salts | |
| DE102017105036A1 (de) | Mittel zur Anwendung bei der Behandlung der Dyslipidämie | |
| JP5770449B2 (ja) | PPARα活性化剤 | |
| HK1157216A (en) | Human b3 adrenergic receptor ligand, and food or pharmaceutical product containing the same | |
| CA2966574C (en) | Agents for maintaining undifferentiated state and promoting proliferation of stem cells | |
| WO2018012773A1 (ko) | 울다비오시드 a 화합물을 함유하는 항염증 조성물 | |
| WO2007040006A1 (ja) | ペルオキシソーム増殖剤応答性受容体PPARγ活性化剤、および該活性化剤を含有する特定症状の予防または改善用組成物 | |
| US20100028465A1 (en) | Composition for ameliorating cerebral function | |
| JP2015193547A (ja) | 運動様作用を有するレスベラトロール加熱処理組成物 | |
| JP2019172614A (ja) | 遺伝子発現制御剤及び筋委縮の抑制剤、予防剤又は改善剤 | |
| KR20210016163A (ko) | 커큐민 및 다가 불포화 지방산을 유효성분으로 함유하는 관절염의 예방 및 치료용 조성물 | |
| CN103006749A (zh) | 丝瓜子的新用途 | |
| JP2007217311A (ja) | 神経細胞分化誘導剤 | |
| JP2010095456A (ja) | 脂質代謝改善剤 | |
| EP2805717A1 (en) | Appetite suppressant | |
| JP2015124151A (ja) | レスベラトロール加熱処理組成物 | |
| JP2010059106A (ja) | 糖尿病進行抑制作用を有する組成物 | |
| JP2007230912A (ja) | 神経再生促進剤、および該促進剤を含む機能性食品 | |
| JP2012131761A (ja) | 抗炎症剤 | |
| JP2009167154A (ja) | 血糖値上昇抑制剤 | |
| JP2012041283A (ja) | 血管新生抑制剤 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 200980131312.3 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 09762524 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2727223 Country of ref document: CA |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 12997498 Country of ref document: US Ref document number: 2010516877 Country of ref document: JP |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2009762524 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20117000640 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |