JP5744575B2 - 複相組織ステンレス鋼鋼板および鋼帯、製造方法 - Google Patents
複相組織ステンレス鋼鋼板および鋼帯、製造方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5744575B2 JP5744575B2 JP2011050003A JP2011050003A JP5744575B2 JP 5744575 B2 JP5744575 B2 JP 5744575B2 JP 2011050003 A JP2011050003 A JP 2011050003A JP 2011050003 A JP2011050003 A JP 2011050003A JP 5744575 B2 JP5744575 B2 JP 5744575B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- phase
- stainless steel
- ferrite
- martensite
- less
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C21—METALLURGY OF IRON
- C21D—MODIFYING THE PHYSICAL STRUCTURE OF FERROUS METALS; GENERAL DEVICES FOR HEAT TREATMENT OF FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS METALS OR ALLOYS; MAKING METAL MALLEABLE, e.g. BY DECARBURISATION OR TEMPERING
- C21D6/00—Heat treatment of ferrous alloys
- C21D6/004—Heat treatment of ferrous alloys containing Cr and Ni
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C21—METALLURGY OF IRON
- C21D—MODIFYING THE PHYSICAL STRUCTURE OF FERROUS METALS; GENERAL DEVICES FOR HEAT TREATMENT OF FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS METALS OR ALLOYS; MAKING METAL MALLEABLE, e.g. BY DECARBURISATION OR TEMPERING
- C21D6/00—Heat treatment of ferrous alloys
- C21D6/005—Heat treatment of ferrous alloys containing Mn
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C21—METALLURGY OF IRON
- C21D—MODIFYING THE PHYSICAL STRUCTURE OF FERROUS METALS; GENERAL DEVICES FOR HEAT TREATMENT OF FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS METALS OR ALLOYS; MAKING METAL MALLEABLE, e.g. BY DECARBURISATION OR TEMPERING
- C21D8/00—Modifying the physical properties by deformation combined with, or followed by, heat treatment
- C21D8/02—Modifying the physical properties by deformation combined with, or followed by, heat treatment during manufacturing of plates or strips
- C21D8/0221—Modifying the physical properties by deformation combined with, or followed by, heat treatment during manufacturing of plates or strips characterised by the working steps
- C21D8/0226—Hot rolling
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C21—METALLURGY OF IRON
- C21D—MODIFYING THE PHYSICAL STRUCTURE OF FERROUS METALS; GENERAL DEVICES FOR HEAT TREATMENT OF FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS METALS OR ALLOYS; MAKING METAL MALLEABLE, e.g. BY DECARBURISATION OR TEMPERING
- C21D8/00—Modifying the physical properties by deformation combined with, or followed by, heat treatment
- C21D8/02—Modifying the physical properties by deformation combined with, or followed by, heat treatment during manufacturing of plates or strips
- C21D8/0221—Modifying the physical properties by deformation combined with, or followed by, heat treatment during manufacturing of plates or strips characterised by the working steps
- C21D8/0236—Cold rolling
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C21—METALLURGY OF IRON
- C21D—MODIFYING THE PHYSICAL STRUCTURE OF FERROUS METALS; GENERAL DEVICES FOR HEAT TREATMENT OF FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS METALS OR ALLOYS; MAKING METAL MALLEABLE, e.g. BY DECARBURISATION OR TEMPERING
- C21D8/00—Modifying the physical properties by deformation combined with, or followed by, heat treatment
- C21D8/02—Modifying the physical properties by deformation combined with, or followed by, heat treatment during manufacturing of plates or strips
- C21D8/0221—Modifying the physical properties by deformation combined with, or followed by, heat treatment during manufacturing of plates or strips characterised by the working steps
- C21D8/0242—Flattening; Dressing; Flexing
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C21—METALLURGY OF IRON
- C21D—MODIFYING THE PHYSICAL STRUCTURE OF FERROUS METALS; GENERAL DEVICES FOR HEAT TREATMENT OF FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS METALS OR ALLOYS; MAKING METAL MALLEABLE, e.g. BY DECARBURISATION OR TEMPERING
- C21D8/00—Modifying the physical properties by deformation combined with, or followed by, heat treatment
- C21D8/02—Modifying the physical properties by deformation combined with, or followed by, heat treatment during manufacturing of plates or strips
- C21D8/0247—Modifying the physical properties by deformation combined with, or followed by, heat treatment during manufacturing of plates or strips characterised by the heat treatment
- C21D8/0273—Final recrystallisation annealing
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C21—METALLURGY OF IRON
- C21D—MODIFYING THE PHYSICAL STRUCTURE OF FERROUS METALS; GENERAL DEVICES FOR HEAT TREATMENT OF FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS METALS OR ALLOYS; MAKING METAL MALLEABLE, e.g. BY DECARBURISATION OR TEMPERING
- C21D9/00—Heat treatment, e.g. annealing, hardening, quenching or tempering, adapted for particular articles; Furnaces therefor
- C21D9/46—Heat treatment, e.g. annealing, hardening, quenching or tempering, adapted for particular articles; Furnaces therefor for sheet metals
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
- C22C38/001—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing N
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
- C22C38/008—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing tin
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
- C22C38/02—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing silicon
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
- C22C38/04—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing manganese
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
- C22C38/18—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing chromium
- C22C38/40—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing chromium with nickel
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
- C22C38/18—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing chromium
- C22C38/40—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing chromium with nickel
- C22C38/42—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing chromium with nickel with copper
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
- C22C38/18—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing chromium
- C22C38/40—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing chromium with nickel
- C22C38/44—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing chromium with nickel with molybdenum or tungsten
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
- C22C38/18—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing chromium
- C22C38/40—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing chromium with nickel
- C22C38/54—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing chromium with nickel with boron
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
- C22C38/18—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing chromium
- C22C38/40—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing chromium with nickel
- C22C38/58—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing chromium with nickel with more than 1.5% by weight of manganese
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C21—METALLURGY OF IRON
- C21D—MODIFYING THE PHYSICAL STRUCTURE OF FERROUS METALS; GENERAL DEVICES FOR HEAT TREATMENT OF FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS METALS OR ALLOYS; MAKING METAL MALLEABLE, e.g. BY DECARBURISATION OR TEMPERING
- C21D2211/00—Microstructure comprising significant phases
- C21D2211/005—Ferrite
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C21—METALLURGY OF IRON
- C21D—MODIFYING THE PHYSICAL STRUCTURE OF FERROUS METALS; GENERAL DEVICES FOR HEAT TREATMENT OF FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS METALS OR ALLOYS; MAKING METAL MALLEABLE, e.g. BY DECARBURISATION OR TEMPERING
- C21D2211/00—Microstructure comprising significant phases
- C21D2211/008—Martensite
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C21—METALLURGY OF IRON
- C21D—MODIFYING THE PHYSICAL STRUCTURE OF FERROUS METALS; GENERAL DEVICES FOR HEAT TREATMENT OF FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS METALS OR ALLOYS; MAKING METAL MALLEABLE, e.g. BY DECARBURISATION OR TEMPERING
- C21D6/00—Heat treatment of ferrous alloys
- C21D6/02—Hardening by precipitation
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02P—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE PRODUCTION OR PROCESSING OF GOODS
- Y02P10/00—Technologies related to metal processing
- Y02P10/20—Recycling
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Metallurgy (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Heat Treatment Of Sheet Steel (AREA)
- Metal Rolling (AREA)
Description
γp =420C+470N+23Ni+7Mn+9Cu−11.5Cr−11.5Si−12Mo−7Sn−49Ti−47Nb−52Al+189・・・式(a)
この高強度複相組織ステンレス鋼は、更にB:0.0003〜0.0050%,Cu:0.30〜2.0%,Mo:0.30〜2.0%,Al:0.01〜0.1%の1種または2種以上を含むことができる。
Cはオーステナイト安定化元素であり、固溶強化により特にマルテンサイトの強化に有効である。溶体化時に未固溶の炭化物は、マルテンサイトの強化と共に耐摩耗性を向上させる効果も有する。これらの効果は0.02質量%以上の含有量で顕著になる。しかし、C含有量の増加に伴って、複相化焼鈍後の冷却過程で、Cr炭化物が析出し、Cr欠乏相を形成することで耐食性を低下させる現象、所謂鋭敏化現象が起こりやすくなるため、C含有量の上限を0.20質量%とした。好ましくは0.10〜0.15%である。
Siはフェライト安定化元素であり固溶強化能も大きく、フェライト、マルテンサイト相を硬化させる。また、製鋼工程においては、脱酸元素としても作用する。この作用はSi含有量が0.10質量%以上で顕著に表れる。しかし、1.0質量%を超えて含有させると、複相組織ステンレス鋼に好適な相バランスが保てなくなる。好ましくは、0.20〜0.70%である。
Mnはオーステナイト安定化元素であり、複相化焼鈍時によりオーステナイトおよびフェライトの適切な相バランスを得るために必要な合金元素であるため、0.20%以上含有させることが好ましい。オーステナイト安定化能は、Niの約半分であるが、Niに比べて安価な元素である。反面、Ms点を下げる効果がNiに比べると大きく、残留γの生成による硬度の低下が問題になる。また、耐酸化性を阻害する元素であり、焼鈍時の酸化による表面品質低下が問題になることがあるため、各品質への阻害影響が少ない範囲として2.0質量%以下とした。好ましくは0.50〜1.0%である。
Pは固溶強化能の大きな元素であるが、フェライト安定化元素であり、しかも耐食性や靭性に対して有害な元素である。ステンレス鋼の原料であるフェロクロムに不純物として含まれるが、ステンレス鋼の溶鋼から脱Pする技術が無いため、使用するフェロクロム原料の純度と量でPの量は決まる。しかし、低Pのフェロクロムは高価であるため、材質や耐食性を大きく劣化させない範囲である0.040質量%以下とした。好ましくは0.030%以下である。
Sは、硫化物系介在物を形成し、鋼材の一般的な耐食性(全面腐食や孔食)を劣化させるため、その含有量の上限は0.010質量%にする必要がある。Sの含有量は少ないほど耐食性は良好となるが、低S化には脱硫負荷が増大するので、下限を0.003質量%とするのが好ましい。好ましくは0.003〜0.008%である。
Crは、母材の一般的な耐食性(全面腐食、孔食)の改善に有効な元素であるが、15質量%未満では十分な耐食性の確保が難しい。しかし、Crはフェライト相(α相)安定化元素であり、18質量%超の添加はオーステナイト相(γ相)の安定性が低下し、複相組織化による高強度化が困難になる。好ましくは15.5〜17.5%である。
Niは、オーステナイト相の安定化元素であり、複相化焼鈍時のオーステナイト相分率に大きく影響する。適切な相分率を得るためには、Cr量に相応する量のNi添加が必要なため、その含有量は少なくとも0.5%質量%以上必要である。但し、Niは高価な元素であり、過剰な添加は、合金コストの増加になるため、SUS301系の材料と明確な価格差が出る量として、上限を2.5質量%以下とした。好ましくは1.0〜2.0%である。
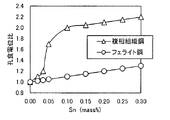
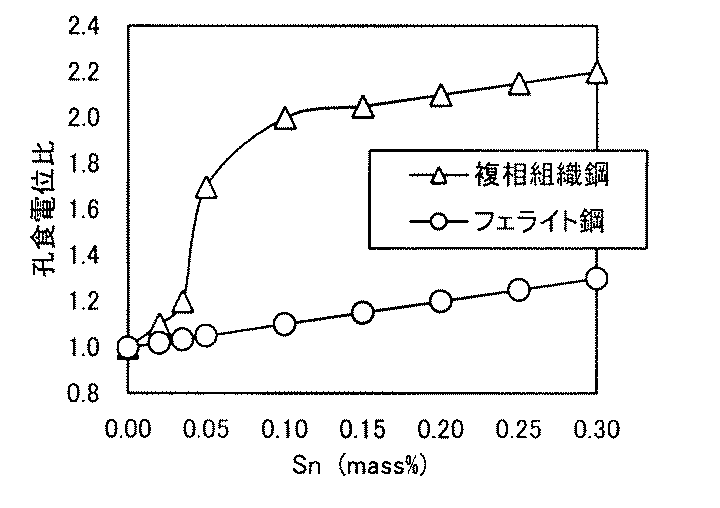
Snはフェライト相安定化元素であり、マルテンサイト相の耐食性向上に有効な元素である。複相化焼鈍時には、Crと同様にフェライト相に濃化するが、フェライトとマルテンサイトの複相組織において、Cr量の差を補う様に、マルテンサイト相の耐食性を向上させるため、フェライト相とマルテンサイト相の耐食性を同等とし、材料の耐食性を高めることができる。マルテンサイト相とフェライト相の耐食性をバランスするためには、最低でも0.05質量%以上必要である。Snを0.30質量%以上添加しても、Snによるマルテンサイト相の耐食性改善効果は飽和しており、合金コストを無駄に増加させることになるため、その上限を0.30質量%以下とした。好ましくは0.1〜0.25%である。
NはCと同様に、オーステナイト安定化元素であり、マルテンサイトの強化にも有効な元素であるため、0.010%以上含有させることが好ましい。また、固溶Nは不動態皮膜を強化や、鋭敏化の抑制により、耐食性を向上させる働きを持つ。しかしながら、過剰な添加は気泡系欠陥の原因になるため、その上限を0.10質量%以下とした。好ましくは0.02〜0.06%である。
B:0.0003〜0.0050質量%
Bは熱間圧延温度域においてフェライト相とオーステナイト相との変形抵抗差に起因したエッジクラックの発生を防止する効果があるため、0.0003%以上が望ましい。しかし、0.0050質量%を超えて添加すると、硼化物の析出による耐食性の低下や、熱間加工性の低下が生じるため、上限を0.0050質量%以下とする。好ましくは0.0005〜0.0030%である。
Cuは必要に応じて添加される元素である。オーステナイト安定化元素であり、複相化焼鈍時のオーステナイトおよびフェライトの相バランスを得るために有効な合金元素であるため、0.3%以上含有させることが好ましい。オーステナイト安定化能は、Niの約半分であるが、Niに比べて安価な元素である。しかし、過剰な添加は析出物起因の耐食性低下や、耐酸化性の低下に起因する表面の光沢むらを引き起こすため、上限を2.0質量%以下とする。好ましくは0.5〜1.5%である。
Moは必要に応じて添加される元素であり、Crにも増して耐食性を向上させる効果があるため、0.3%以上含有させることが好ましい。しかし、Crと同様に、複相化焼鈍時は、フェライトに濃化し、フェライトとマルテンサイトの耐食性差を拡大する。また、高価な元素であり、製造コストの上昇の原因ともなるため、その上限を2.0質量%以下とする。好ましくは0.5〜1.2%である。
Alは脱酸剤として効果的な添加成分である。脱酸効果を得るためには0.01%以上の添加が好ましい。しかし、多量に含有するとクラスタ状の高融点酸化物を形成してスラブの表面疵の原因となる。更に、溶接性も悪くなるため、その含有量は0.1質量%以下とする。好ましくは、0.02〜0.05質量%である。
下記(a)式で表わされる値γpは、1000〜1150℃のフェライト相とオーステナイト相の二相域における、オーステナイト相の最大量を表す指標であり、概ね体積分率をパーセンテージで表わした値と一致する。複相化焼鈍後、或いは更に冷間圧延や時効処理を加えた後の硬度がビッカース硬さで200を超えるために必要なマルテンサイト量を得るために、γpの式を60以上、95以下にすることが必要である。60未満ではフェライトとマルテンサイトの複相組織において十分な硬さが得られない。更に、20〜60では、熱延時の熱間加工性が低下して、耳割れを生じることもある。また、95%超では加工性が低下するために95以下とした。
γp =420C+470N+23Ni+7Mn+9Cu−11.5Cr−11.5Si−12Mo−7Sn−49Ti−47Nb−52Al+189・・・式(a)
表3に記載したNO.B1〜B31が本発明例であり、NO.b32〜b52が比較例である。本発明に規定される成分範囲の冷間圧延鋼帯に複相化焼鈍を行うことによって、耐食性、耐気性、材質に優れた材料を得ることができる。更に、熱延板の幅端部における耳割れが極めて少なく、優れた端面性状を示した。
Claims (8)
- 質量%で、
C:0.02〜0.20%、
Si:0.10〜1.0%、
Mn:0.20〜2.0%、
P:0.040%以下、
S:0.010%以下、
Cr:15.0〜18.0%、
Ni:0.5〜2.5%、
Sn:0.05〜0.30、
N:0.010〜0.10%を含み、下記(a)式で定義される値γp が60〜95の範囲にあり、残部がFeの組成をもち、フェライトおよびマルテンサイトの複相組織を有することを特徴とするビッカース硬さが200HV以上の複相組織ステンレス鋼鋼板。
γp =420C+470N+23Ni+7Mn+9Cu−11.5Cr−11.5Si−12Mo−7Sn−49Ti−47Nb−52Al+189・・・式(a) - 更に、質量%で、B:0.0003〜0.0050%以下、Cu:0.30〜2.0%,Mo:0.30〜2.0%,Al:0.01〜0.1%の1種または2種以上を含む、請求項1に記載の複相組織ステンレス鋼鋼板。
- 質量%で、
C:0.02〜0.20%、
Si:0.10〜1.0%、
Mn:0.20〜2.0%、
P:0.040%以下、
S:0.010%以下、
Cr:15.0〜18.0%、
Ni:0.5〜2.5%、
Sn:0.05〜0.30、
N:0.010〜0.10%を含み、下記(a)式で定義される値γp が60〜95の範囲にあり、残部がFeの組成をもち、フェライトおよびマルテンサイトの複相組織を有することを特徴とするビッカース硬さが200HV以上の複相組織ステンレス鋼鋼帯。
γp =420C+470N+23Ni+7Mn+9Cu−11.5Cr−11.5Si−12Mo−7Sn−49Ti−47Nb−52Al+189・・・式(a) - 更に、質量%で、B:0.0003〜0.0050%以下、Cu:0.30〜2.0%,Mo:0.30〜2.0%,Al:0.01〜0.1%の1種または2種以上を含む、請求項3に記載の複相組織ステンレス鋼鋼帯。
- 請求項1または請求項2記載のステンレス冷延鋼板の製造方法であって、フェライトおよびオーステナイトの二相域である850〜1100℃に加熱した後で冷却し、室温でフェライトおよびマルテンサイトの複相組織にする複相化焼鈍を施すことを特徴とする、複相組織ステンレス鋼板の製造方法。
- 更に、圧延率:1〜30%の調質圧延と時効温度:250〜300℃の時効処理のどちらか一方、または両方を行うことを特徴とする、請求項5に記載の複相組織ステンレス鋼板の製造方法。
- 請求項3または請求項4記載のステンレス冷延鋼帯の製造方法であって、フェライトおよびオーステナイトの二相域である850〜1100℃に加熱した後で冷却し、室温でフェライトおよびマルテンサイトの複相組織にする複相化焼鈍を施すことを特徴とする、複相組織ステンレス鋼帯の製造方法。
- 更に、圧延率:1〜30%の調質圧延と時効温度:250〜300℃の時効処理のどちらか一方、または両方を行うことを特徴とする、請求項7に記載の複相組織ステンレス鋼帯の製造方法。
Priority Applications (9)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011050003A JP5744575B2 (ja) | 2010-03-29 | 2011-03-08 | 複相組織ステンレス鋼鋼板および鋼帯、製造方法 |
| ES11762915T ES2713046T3 (es) | 2010-03-29 | 2011-03-29 | Chapa de acero inoxidable y banda de acero inoxidable de estructura de fase dual y método de producción de chapa de acero inoxidable y banda de acero inoxidable |
| TW100110755A TWI475116B (zh) | 2010-03-29 | 2011-03-29 | Multi-phase stainless steel sheet and strip, and the like |
| PCT/JP2011/058483 WO2011122697A1 (ja) | 2010-03-29 | 2011-03-29 | 複相組織ステンレス鋼板及び鋼帯並びにそれらの製造方法 |
| EP11762915.4A EP2554702B1 (en) | 2010-03-29 | 2011-03-29 | Dual phase structure stainless steel sheet and steel strip, and method for producing the dual phase structure stainless steel sheet and steel strip |
| KR1020127024762A KR101474626B1 (ko) | 2010-03-29 | 2011-03-29 | 복상 조직 스테인리스 강판 및 강대 및 그들의 제조 방법 |
| US13/637,690 US9074271B2 (en) | 2010-03-29 | 2011-03-29 | Dual-phase stainless steel sheet and steel strip and method of production |
| BR112012024400-0A BR112012024400B1 (pt) | 2010-03-29 | 2011-03-29 | Tira ou chapa de aço inoxidável duplex com microestrutura ferrítica-martensítica e método para sua produção |
| CN201180011390.7A CN102782171B (zh) | 2010-03-29 | 2011-03-29 | 多相组织不锈钢板及钢带及它们的制造方法 |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010074809 | 2010-03-29 | ||
| JP2010074809 | 2010-03-29 | ||
| JP2011050003A JP5744575B2 (ja) | 2010-03-29 | 2011-03-08 | 複相組織ステンレス鋼鋼板および鋼帯、製造方法 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2011225970A JP2011225970A (ja) | 2011-11-10 |
| JP5744575B2 true JP5744575B2 (ja) | 2015-07-08 |
Family
ID=44712384
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011050003A Active JP5744575B2 (ja) | 2010-03-29 | 2011-03-08 | 複相組織ステンレス鋼鋼板および鋼帯、製造方法 |
Country Status (9)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9074271B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP2554702B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5744575B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR101474626B1 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN102782171B (ja) |
| BR (1) | BR112012024400B1 (ja) |
| ES (1) | ES2713046T3 (ja) |
| TW (1) | TWI475116B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2011122697A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (27)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101632516B1 (ko) * | 2011-10-21 | 2016-06-21 | 닛폰 스틸 앤드 스미킨 스테인레스 스틸 코포레이션 | 2상 스테인리스강, 2상 스테인리스강 주조편 및 2상 스테인리스강 강재 |
| KR101463315B1 (ko) | 2012-12-21 | 2014-11-18 | 주식회사 포스코 | 경도와 저온 충격특성이 우수한 스테인리스 열연강판 |
| JP5924459B1 (ja) * | 2014-09-05 | 2016-05-25 | Jfeスチール株式会社 | ステンレス冷延鋼板用素材 |
| JP6417252B2 (ja) * | 2014-09-17 | 2018-11-07 | 新日鐵住金ステンレス株式会社 | ブレーキディスク用マルテンサイト系ステンレス鋼とその製造方法 |
| AT516453B1 (de) * | 2014-11-03 | 2018-02-15 | Berndorf Band Gmbh | Metallische Bänder und deren Herstellungsverfahren |
| WO2017011751A1 (en) | 2015-07-15 | 2017-01-19 | Ak Stell Properties, Inc. | High formability dual phase steel |
| JP6093063B1 (ja) * | 2016-03-09 | 2017-03-08 | 日新製鋼株式会社 | 加工性に優れた高強度ステンレス鋼材とその製造方法 |
| ES2862309T3 (es) * | 2016-04-12 | 2021-10-07 | Jfe Steel Corp | Lámina de acero inoxidable martensitico |
| CN105839023A (zh) * | 2016-05-09 | 2016-08-10 | 林淑录 | 一种海洋钻井平台钻井水系统用合金材料及其制备方法 |
| DE102016109253A1 (de) * | 2016-05-19 | 2017-12-07 | Böhler Edelstahl GmbH & Co KG | Verfahren zum Herstellen eines Stahlwerkstoffs und Stahlwerksstoff |
| CN105970117A (zh) * | 2016-05-25 | 2016-09-28 | 浙江大大不锈钢有限公司 | 一种低Ni抗硫化腐蚀不锈钢及其制造方法 |
| KR101903182B1 (ko) * | 2016-12-23 | 2018-10-01 | 주식회사 포스코 | 강도 및 내산성이 우수한 페라이트계 스테인리스강 및 이의 제조 방법 |
| WO2019226197A1 (en) * | 2018-05-25 | 2019-11-28 | Kingston William R | Impact resistant high strength steel |
| JP2019157203A (ja) * | 2018-03-13 | 2019-09-19 | 日鉄日新製鋼株式会社 | 耐食性および加工性に優れた複相ステンレス鋼とその製造方法 |
| CN111270129A (zh) * | 2018-12-05 | 2020-06-12 | 兴化市聚鑫不锈钢有限公司 | 用于矿山液压设备的新型合金耐磨材料 |
| KR102670275B1 (ko) * | 2019-09-03 | 2024-05-30 | 닛테츠 스테인레스 가부시키가이샤 | 마르텐사이트계 스테인리스 강판 및 마르텐사이트계 스테인리스강 부재 |
| TWI776112B (zh) * | 2019-12-20 | 2022-09-01 | 日商日鐵不銹鋼股份有限公司 | 冷加工性優異之高硬度、高耐蝕性用途之麻田散鐵系不鏽鋼及其製造方法 |
| JP7770757B2 (ja) * | 2020-02-05 | 2025-11-17 | 日本製鉄株式会社 | ロール成形用フェライト系ステンレス鋼材 |
| KR102872533B1 (ko) * | 2020-05-28 | 2025-10-20 | 닛테츠 스테인레스 가부시키가이샤 | 페라이트·오스테나이트 2상계 스테인리스 강재 및 내식성 부재 |
| CN115667560B (zh) * | 2020-06-19 | 2024-03-15 | 杰富意钢铁株式会社 | 合金管及其制造方法 |
| TWI738528B (zh) * | 2020-09-25 | 2021-09-01 | 中國鋼鐵股份有限公司 | 用於鍍鎳處理之淺亮紋理之低碳鋼帶之製備方法 |
| JP7564695B2 (ja) * | 2020-12-03 | 2024-10-09 | 日鉄ステンレス株式会社 | 拡散接合性及び溶接性に優れる複相ステンレス鋼 |
| JP7645115B2 (ja) * | 2021-03-26 | 2025-03-13 | 日鉄ステンレス株式会社 | 写像性および耐疵付き性に優れる鏡面仕上げ複相ステンレス鋼およびその製造方法 |
| CN113981328B (zh) * | 2021-09-18 | 2022-05-24 | 四川大学 | 表面自发连续生成三氧化二铝膜的含铝奥氏体不锈钢及其制备方法 |
| CN113913707A (zh) * | 2021-09-27 | 2022-01-11 | 鹰普(中国)有限公司 | 一种奥氏体耐热不锈钢材料性能提升方法 |
| CN116949371A (zh) * | 2023-06-19 | 2023-10-27 | 杭州碱泵有限公司 | 一种双相不锈钢、制备方法及应用 |
| CN118291886A (zh) * | 2024-03-11 | 2024-07-05 | 山西太钢不锈钢股份有限公司 | 一种煤矿机械用三相不锈钢 |
Family Cites Families (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS637338A (ja) | 1986-06-27 | 1988-01-13 | Nisshin Steel Co Ltd | 面内異方性の小さい高延性高強度の複相組織クロムステンレス鋼板または鋼帯の製造法 |
| JPH07100824B2 (ja) | 1987-01-03 | 1995-11-01 | 日新製鋼株式会社 | 延性に優れた高強度複相組織クロムステンレス鋼帯の製造法 |
| JPH0463912A (ja) * | 1990-07-02 | 1992-02-28 | Sakae Nakao | 内燃機関の吸気圧縮装置 |
| JPH07138704A (ja) | 1993-11-12 | 1995-05-30 | Nisshin Steel Co Ltd | 高強度高延性複相組織ステンレス鋼およびその製造方法 |
| JP3602201B2 (ja) * | 1995-05-24 | 2004-12-15 | 日新製鋼株式会社 | 高強度複相組織ステンレス鋼帯又は鋼板の製造方法 |
| US5843246A (en) * | 1996-01-16 | 1998-12-01 | Allegheny Ludlum Corporation | Process for producing dual phase ferritic stainless steel strip |
| JPH09263912A (ja) * | 1996-03-29 | 1997-10-07 | Nisshin Steel Co Ltd | 打抜き加工用高強度複相組織クロムステンレス鋼板およびその製造方法 |
| JP4390961B2 (ja) * | 2000-04-04 | 2009-12-24 | 新日鐵住金ステンレス株式会社 | 表面特性及び耐食性に優れたフェライト系ステンレス鋼 |
| JP4524850B2 (ja) * | 2000-04-27 | 2010-08-18 | Jfeスチール株式会社 | 延性および歪時効硬化特性に優れた高張力冷延鋼板および高張力冷延鋼板の製造方法 |
| JP2002105601A (ja) | 2000-09-27 | 2002-04-10 | Nisshin Steel Co Ltd | 高強度複相ステンレス鋼及びその製造方法 |
| IT1316030B1 (it) * | 2000-12-18 | 2003-03-26 | Acciai Speciali Terni Spa | Procedimento per la fabbricazione di lamierini a grano orientato. |
| JP3961341B2 (ja) * | 2002-05-10 | 2007-08-22 | 日新製鋼株式会社 | 溶接構造物用高強度複相ステンレス鋼板の製造法 |
| JP4470701B2 (ja) | 2004-01-29 | 2010-06-02 | Jfeスチール株式会社 | 加工性および表面性状に優れた高強度薄鋼板およびその製造方法 |
| CA2777715C (en) * | 2006-05-09 | 2014-06-03 | Nippon Steel & Sumikin Stainless Steel Corporation | Ferritic stainless steel excellent in resistance to crevice corrosion |
| CN101121995A (zh) * | 2007-09-06 | 2008-02-13 | 朱育民 | 新马氏体系不锈钢材料及其制备方法和应用 |
| CN103498113B (zh) * | 2008-03-26 | 2016-03-09 | 新日铁住金不锈钢株式会社 | 焊接热影响区的耐蚀性和韧性良好的合金节省型双相不锈钢 |
-
2011
- 2011-03-08 JP JP2011050003A patent/JP5744575B2/ja active Active
- 2011-03-29 TW TW100110755A patent/TWI475116B/zh active
- 2011-03-29 US US13/637,690 patent/US9074271B2/en active Active
- 2011-03-29 KR KR1020127024762A patent/KR101474626B1/ko active Active
- 2011-03-29 CN CN201180011390.7A patent/CN102782171B/zh active Active
- 2011-03-29 ES ES11762915T patent/ES2713046T3/es active Active
- 2011-03-29 EP EP11762915.4A patent/EP2554702B1/en active Active
- 2011-03-29 WO PCT/JP2011/058483 patent/WO2011122697A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2011-03-29 BR BR112012024400-0A patent/BR112012024400B1/pt active IP Right Grant
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20130014864A1 (en) | 2013-01-17 |
| CN102782171A (zh) | 2012-11-14 |
| ES2713046T3 (es) | 2019-05-17 |
| EP2554702A1 (en) | 2013-02-06 |
| BR112012024400A2 (pt) | 2016-05-24 |
| EP2554702B1 (en) | 2018-12-12 |
| TWI475116B (zh) | 2015-03-01 |
| KR20120126112A (ko) | 2012-11-20 |
| EP2554702A4 (en) | 2016-07-27 |
| WO2011122697A1 (ja) | 2011-10-06 |
| TW201202444A (en) | 2012-01-16 |
| KR101474626B1 (ko) | 2014-12-18 |
| CN102782171B (zh) | 2014-09-03 |
| JP2011225970A (ja) | 2011-11-10 |
| US9074271B2 (en) | 2015-07-07 |
| BR112012024400B1 (pt) | 2018-04-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5744575B2 (ja) | 複相組織ステンレス鋼鋼板および鋼帯、製造方法 | |
| CA3099932C (en) | High-strength double-sided stainless steel clad sheet and manufacturing method therefor | |
| KR101617115B1 (ko) | 열연 강판 및 그 제조 방법 | |
| JP5687624B2 (ja) | ステンレス鋼、この鋼から製造された冷間圧延ストリップ、及びこの鋼から鋼板製品を製造する方法 | |
| JP6779320B2 (ja) | 強度及び成形性に優れたクラッド鋼板及びその製造方法 | |
| JP7339339B2 (ja) | 冷間加工性及びssc抵抗性に優れた超高強度鋼材及びその製造方法 | |
| CN105200341A (zh) | 一种抗拉强度大于1000MPa的经济型双相不锈钢及其制造方法 | |
| JP7183410B2 (ja) | 極低温靭性及び延性に優れた圧力容器用鋼板及びその製造方法 | |
| CN112789365B (zh) | 具有改善的强度的奥氏体不锈钢 | |
| CN104726789A (zh) | 低镍不锈钢 | |
| JP4606113B2 (ja) | 比例限界応力の高いオーステナイト系ステンレス鋼材および製造法 | |
| US20200392609A1 (en) | Utility ferritic stainless steel with excellent hot workability and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP7366246B2 (ja) | 極低温横膨張に優れた圧力容器用鋼板及びその製造方法 | |
| CN118326282B (zh) | 一种奥氏体不锈钢板带及其制造方法 | |
| CN116018421A (zh) | 具有优异的生产率和成本降低效果的高强度奥氏体不锈钢及其生产方法 | |
| JP2023547090A (ja) | 熱的安定性に優れた高強度鋼板及びその製造方法 | |
| EP4606923A1 (en) | High-strength austenitic stainless steel and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP7648620B2 (ja) | 熱間成形用鋼材、熱間成形部材及びこれらの製造方法 | |
| US20250051894A1 (en) | Austenitic stainless steel and manufacturing method therefor | |
| KR101301386B1 (ko) | 열연 상소둔 생략에 의한 니켈이 첨가된 마르텐사이트계스테인레스강의 제조방법 | |
| JP2024535926A (ja) | ベイナイト鋼およびその作製方法 | |
| JP2016194136A (ja) | 製造安定性に優れた高強度高延性鋼板、及びその製造方法、並びに高強度高延性鋼板の製造に用いられる冷延原板 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20131106 |
|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20140421 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20141225 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150129 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20150407 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20150430 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5744575 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| S533 | Written request for registration of change of name |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313533 |
|
| R371 | Transfer withdrawn |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R371 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| S533 | Written request for registration of change of name |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313533 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313111 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |