JP4789886B2 - Vacuum insulation and insulation box - Google Patents
Vacuum insulation and insulation box Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4789886B2 JP4789886B2 JP2007204400A JP2007204400A JP4789886B2 JP 4789886 B2 JP4789886 B2 JP 4789886B2 JP 2007204400 A JP2007204400 A JP 2007204400A JP 2007204400 A JP2007204400 A JP 2007204400A JP 4789886 B2 JP4789886 B2 JP 4789886B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- heat insulating
- organic fiber
- insulating material
- vacuum heat
- fiber
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 title claims description 30
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 claims description 113
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 claims description 55
- 239000011162 core material Substances 0.000 claims description 30
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000012212 insulator Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 239000005022 packaging material Substances 0.000 description 10
- -1 urethane Chemical compound 0.000 description 8
- 239000003365 glass fiber Substances 0.000 description 7
- 238000004064 recycling Methods 0.000 description 7
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 6
- JOYRKODLDBILNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl urethane Chemical compound CCOC(N)=O JOYRKODLDBILNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 229920000106 Liquid crystal polymer Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 239000004977 Liquid-crystal polymers (LCPs) Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000004743 Polypropylene Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229920005830 Polyurethane Foam Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 239000011888 foil Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229920000728 polyester Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 229920001155 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 239000011496 polyurethane foam Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 4
- 125000006850 spacer group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 239000003463 adsorbent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000002485 combustion reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000003475 lamination Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920000747 poly(lactic acid) Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000004626 polylactic acid Substances 0.000 description 3
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004760 aramid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920003235 aromatic polyamide Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 230000000712 assembly Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000000429 assembly Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000006260 foam Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000012784 inorganic fiber Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920000139 polyethylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000005020 polyethylene terephthalate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000009461 vacuum packaging Methods 0.000 description 2
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920000049 Carbon (fiber) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920003043 Cellulose fiber Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002292 Nylon 6 Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004372 Polyvinyl alcohol Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920006231 aramid fiber Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004917 carbon fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000428 dust Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920001903 high density polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004700 high-density polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002401 inhibitory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012774 insulation material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007794 irritation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000005001 laminate film Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002650 laminated plastic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000014759 maintenance of location Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000004400 mucous membrane Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000004806 packaging method and process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920001225 polyester resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004645 polyester resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002451 polyvinyl alcohol Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005057 refrigeration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011800 void material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004804 winding Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B3/00—Layered products comprising a layer with external or internal discontinuities or unevennesses, or a layer of non-planar shape; Layered products comprising a layer having particular features of form
- B32B3/02—Layered products comprising a layer with external or internal discontinuities or unevennesses, or a layer of non-planar shape; Layered products comprising a layer having particular features of form characterised by features of form at particular places, e.g. in edge regions
- B32B3/04—Layered products comprising a layer with external or internal discontinuities or unevennesses, or a layer of non-planar shape; Layered products comprising a layer having particular features of form characterised by features of form at particular places, e.g. in edge regions characterised by at least one layer folded at the edge, e.g. over another layer ; characterised by at least one layer enveloping or enclosing a material
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B5/00—Layered products characterised by the non- homogeneity or physical structure, i.e. comprising a fibrous, filamentary, particulate or foam layer; Layered products characterised by having a layer differing constitutionally or physically in different parts
- B32B5/02—Layered products characterised by the non- homogeneity or physical structure, i.e. comprising a fibrous, filamentary, particulate or foam layer; Layered products characterised by having a layer differing constitutionally or physically in different parts characterised by structural features of a fibrous or filamentary layer
- B32B5/12—Layered products characterised by the non- homogeneity or physical structure, i.e. comprising a fibrous, filamentary, particulate or foam layer; Layered products characterised by having a layer differing constitutionally or physically in different parts characterised by structural features of a fibrous or filamentary layer characterised by the relative arrangement of fibres or filaments of different layers, e.g. the fibres or filaments being parallel or perpendicular to each other
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B5/00—Layered products characterised by the non- homogeneity or physical structure, i.e. comprising a fibrous, filamentary, particulate or foam layer; Layered products characterised by having a layer differing constitutionally or physically in different parts
- B32B5/22—Layered products characterised by the non- homogeneity or physical structure, i.e. comprising a fibrous, filamentary, particulate or foam layer; Layered products characterised by having a layer differing constitutionally or physically in different parts characterised by the presence of two or more layers which are next to each other and are fibrous, filamentary, formed of particles or foamed
- B32B5/24—Layered products characterised by the non- homogeneity or physical structure, i.e. comprising a fibrous, filamentary, particulate or foam layer; Layered products characterised by having a layer differing constitutionally or physically in different parts characterised by the presence of two or more layers which are next to each other and are fibrous, filamentary, formed of particles or foamed one layer being a fibrous or filamentary layer
- B32B5/26—Layered products characterised by the non- homogeneity or physical structure, i.e. comprising a fibrous, filamentary, particulate or foam layer; Layered products characterised by having a layer differing constitutionally or physically in different parts characterised by the presence of two or more layers which are next to each other and are fibrous, filamentary, formed of particles or foamed one layer being a fibrous or filamentary layer another layer next to it also being fibrous or filamentary
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16L—PIPES; JOINTS OR FITTINGS FOR PIPES; SUPPORTS FOR PIPES, CABLES OR PROTECTIVE TUBING; MEANS FOR THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16L59/00—Thermal insulation in general
- F16L59/06—Arrangements using an air layer or vacuum
- F16L59/065—Arrangements using an air layer or vacuum using vacuum
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C3/00—Vessels not under pressure
- F17C3/02—Vessels not under pressure with provision for thermal insulation
- F17C3/08—Vessels not under pressure with provision for thermal insulation by vacuum spaces, e.g. Dewar flask
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B2262/00—Composition or structural features of fibres which form a fibrous or filamentary layer or are present as additives
- B32B2262/02—Synthetic macromolecular fibres
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B2307/00—Properties of the layers or laminate
- B32B2307/30—Properties of the layers or laminate having particular thermal properties
- B32B2307/304—Insulating
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B2509/00—Household appliances
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B2509/00—Household appliances
- B32B2509/10—Refrigerators or refrigerating equipment
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Thermal Insulation (AREA)
- Refrigerator Housings (AREA)
- Laminated Bodies (AREA)
Description
本発明は真空断熱材および断熱箱、特に、冷熱機器への使用に好適な真空断熱材および断熱箱に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a vacuum heat insulating material and a heat insulating box, and more particularly to a vacuum heat insulating material and a heat insulating box suitable for use in a cooling / heating apparatus.
従来、断熱材としてウレタンが用いられていたが、昨今、ウレタンよりも断熱性能が優れた真空断熱材が、ウレタンと併用して使用されるようになった。かかる真空断熱材は、冷蔵庫の他に、保温庫、車両空調機、給湯器などの冷熱機器にも使用されるものである。 Conventionally, urethane has been used as a heat insulating material, but nowadays, vacuum heat insulating materials having better heat insulating performance than urethane are used in combination with urethane. Such a vacuum heat insulating material is used not only for a refrigerator but also for a cooling device such as a heat insulation box, a vehicle air conditioner, and a water heater.
真空断熱材とは、ガスバリア性(空気遮断性に同じ)のアルミ箔でできた外包材の中に粉末、発泡体、繊維体などを芯材として挿入し、内部が数Paの真空度に保たれているものである。
真空断熱材の断熱性能が下がる原因の一つとして外気から進入する空気・水分の他に、芯材から発生するアウトガス、芯材そのものに存在する水分があるが、これらを吸着するために吸着剤が外包材の中に挿入されている。
真空断熱材の芯材としてシリカなどの粉末、ウレタンなどの発泡体、ガラスなどの繊維体などのものがあるが、現状は断熱性能の最も優れる繊維体のものが主流になっている。
A vacuum insulation material is a powder, foam, fiber, etc. inserted as a core material into an envelope made of aluminum foil with gas barrier properties (same as air barrier properties), and the inside is kept at a vacuum level of several Pa. It is what is leaning.
In addition to air and moisture entering from the outside air as one of the causes of the deterioration of the heat insulation performance of the vacuum heat insulating material, there are outgas generated from the core material and moisture present in the core material itself. Is inserted into the outer packaging.
There are powders such as silica, foams such as urethane, and fiber bodies such as glass as the core material of the vacuum heat insulating material. Currently, fiber bodies having the best heat insulation performance are mainly used.
繊維体のものには大きく分けて、無機繊維、有機繊維の2種類がある。
無機繊維には、ガラス繊維、炭素繊維などがある(例えば、特許文献1、8参照。)。
有機繊維には、ポリプロピレン繊維、ポリ乳酸繊維、アラミド繊維、LCP(液晶ポリマー)繊維、ポリエチレンテレフタレート繊維、ポリエステル繊維、ポリエチレン繊維、セルロース繊維などがある(例えば、特許文献2、7参照。)。
There are two types of fiber bodies: inorganic fibers and organic fibers.
Examples of inorganic fibers include glass fibers and carbon fibers (see, for example,
Examples of the organic fiber include polypropylene fiber, polylactic acid fiber, aramid fiber, LCP (liquid crystal polymer) fiber, polyethylene terephthalate fiber, polyester fiber, polyethylene fiber, and cellulose fiber (see, for example,
繊維体の形状には、綿状のもの、シートを積層したものなどがある(例えば、特許文献3、4参照。)。
また、繊維体の形状には、シートを繊維の配向が交互になるように積層したものもある(特許文献5、6参照。)。
Examples of the shape of the fibrous body include a cotton-like shape and a laminate of sheets (for example, see Patent Documents 3 and 4).
In addition, some fiber bodies are formed by laminating sheets so that fiber orientations alternate (see
従来の真空断熱には、ガラス繊維やポリエステル繊維が芯材として使用されている。
ガラス繊維は硬くて脆いため、真空断熱材の製造時に粉塵が飛び散り作業者の皮膚・粘膜などに付着すると刺激を受ける可能性があり、その取り扱い性、作業性が問題となっている。また、リサイクルの場面を考えた場合、例えば、冷蔵庫ではリサイクル工場で製品ごとに粉砕され、ガラス繊維はウレタン屑などに混じってサーマルリサイクルに供されるが、燃焼効率を落としたり、残渣となったりするなどリサイクル性が良くないという欠点がある。
In conventional vacuum insulation, glass fiber or polyester fiber is used as a core material.
Since glass fiber is hard and brittle, dust may scatter during the manufacture of vacuum heat insulating material and adhere to the skin, mucous membrane, etc. of the worker, which may cause irritation, and its handling and workability are problematic. Also, when considering the scene of recycling, for example, in a refrigerator, each product is pulverized in a recycling factory, and glass fiber is mixed with urethane scraps and used for thermal recycling. There is a disadvantage that recyclability is not good.
一方、ポリエステルなどの有機繊維は、取り扱い性、リサイクル性に優れるものの、断熱性能を表す指標である熱伝導率が、0.0030W/mK(特許文献7参照)であるのに対し、ガラス繊維では0.0013W/mK(特許文献8参照)となっており、断熱性能に劣るという欠点があった。 On the other hand, although organic fibers such as polyester are excellent in handleability and recyclability, the thermal conductivity, which is an indicator of heat insulation performance, is 0.0030 W / mK (see Patent Document 7), whereas in glass fibers, It was 0.0013 W / mK (refer to Patent Document 8), and there was a defect that the heat insulation performance was poor.
この発明は、上記のような課題を解決するためになされたものであって、取り扱い性と断熱性能に優れた真空断熱材、および該真空断熱材を具備する断熱箱を提供するものである。 The present invention has been made in order to solve the above-described problems, and provides a vacuum heat insulating material excellent in handleability and heat insulating performance, and a heat insulating box including the vacuum heat insulating material.
本発明に係る真空断熱材は、ガスバリア性容器の内部に芯材を収容して、内部を減圧状態にした真空断熱材であって、
前記芯材が、有機繊維をシート状に形成した第1の有機繊維集合体と、有機繊維をシート状に形成した第2の有機繊維集合体との積層構造であり、
前記第1の有機繊維集合体の厚さおよび前記第2の有機繊維集合体の厚さが、前記ガスバリア性容器の内部に減圧状態で収容された際、前記有機繊維の直径の1〜18倍であり、
前記第1の有機繊維集合体と前記第2の有機繊維集合体とが、互いに交わるように折り畳まれて積層され、
該積層された部分において、前記第1の有機繊維集合体の両面がそれぞれ前記第2の有機繊維集合体の同一の面に当接し、前記第2の有機繊維集合体の両面がそれぞれ前記第1の有機繊維集合体の同一の面に当接するものである。
The vacuum heat insulating material according to the present invention is a vacuum heat insulating material in which a core material is housed in a gas barrier container and the inside is in a reduced pressure state.
The core material is a laminated structure of a first organic fiber assembly in which organic fibers are formed in a sheet shape and a second organic fiber assembly in which organic fibers are formed in a sheet shape,
When the thickness of the first organic fiber aggregate and the thickness of the second organic fiber aggregate are accommodated in the gas barrier container in a reduced pressure state, the diameter of the organic fiber is 1 to 18 times. And
The first organic fiber aggregate and the second organic fiber aggregate are folded and laminated so as to cross each other,
In the laminated portion, both surfaces of the first organic fiber assembly are in contact with the same surface of the second organic fiber assembly, and both surfaces of the second organic fiber assembly are respectively in the first portion. In contact with the same surface of the organic fiber assembly.
したがって、本発明に係る真空断熱材は、シート状の有機繊維集合体を積層して構成されているので、取り扱い性およびリサイクル性に優れ、且つ、断熱性能に優れる。 Therefore, since the vacuum heat insulating material according to the present invention is configured by laminating sheet-like organic fiber aggregates, it is excellent in handling property and recyclability and excellent in heat insulating performance.
[実施の形態1:真空断熱材]
図1〜図4は本発明の実施形態1に係る真空断熱材を模式的に示すものであって、図1は芯材を薄く積層した斜視図、図2はシート1枚における繊維の配向を表した側面図、図3は厚みがある場合の繊維の配向具合を示す側面図、図4は真空断熱材の構成を示す分解斜視図である。
図4において、真空断熱材7は、空気遮断性を有するガスバリア性容器(以下、「外包材」と称す)4と、外包材4の内部に封入された芯材5およびガス吸着剤6と、を有している。そして、外包材4の内部は所定の真空度に減圧されている。
[Embodiment 1: Vacuum heat insulating material]
1 to 4 schematically show a vacuum heat insulating material according to
In FIG. 4, the vacuum
(積層構造)
図1において、芯材5は、シート状有機繊維集合体(以下、「繊維集合体」と称す)1を積層した積層構造を有している。
図2において、繊維集合体1は、所定の間隔を空けて配置された複数本の有機繊維2xと、有機繊維2xと直交する方向で、所定の間隔を空けて配置された複数本の有機繊維2yと、から形成されている。このとき、有機繊維2xと有機繊維2yとは点接触している。そして、繊維集合体1を薄く積層することで、伝熱方向への繊維の配向を抑えることができるので熱伝導率を下げることができる。
なお、以上は、有機繊維2xと有機繊維2yとが互いに直交する場合を示しているが、本発明はこれに限定するものではなく、互いに直角でない角度でもって交わってもよい。
(Laminated structure)
In FIG. 1, the
In FIG. 2, the
In addition, although the above has shown the case where the
(有機繊維)
真空断熱材7の芯材5を形成する有機繊維2に用いる材料として、実施の形態1ではポリエステルを用いたが、その他に、ポリプロピレン、ポリ乳酸、アラミド、LCP(液晶ポリマー)などを用いることができる。
ポリプロピレンは吸湿性が低いため、乾燥時間や真空引き時間を短縮でき生産性の向上が可能であり、固体熱伝導が小さいので真空断熱材の断熱性能の向上が期待できる。
また、ポリ乳酸には生分解性があるので、製品の使用後に解体、分別された芯材は埋め立て処理を行うこともできる。
また、アラミドやLCPは剛性が高いので、真空包装されて大気圧を受けたときの形状保持性が良く、空隙率を高めることができ断熱性能の向上が期待できるなどのメリットがある。
(Organic fiber)
As the material used for the
Since polypropylene has low hygroscopicity, drying time and evacuation time can be shortened and productivity can be improved. Since solid heat conduction is small, improvement in heat insulation performance of the vacuum heat insulating material can be expected.
Moreover, since polylactic acid is biodegradable, the core material disassembled and separated after use of the product can be subjected to landfill treatment.
In addition, since aramid and LCP have high rigidity, they have good merits such as good shape retention when vacuum-packed and subjected to atmospheric pressure, can increase the porosity, and can be expected to improve heat insulation performance.
(繊維集合体)
芯材5を形成する繊維集合体(有機繊維集合体、シート状集合体に同じ)1は、製造したい幅に対して横一列に並んだいくつものノズルから加熱溶融したポリエステル樹脂を、コンベア上に自由落下させ、コンベアを任意の速度で動かしながらローラーで加圧し巻き取って製造する。
繊維集合体1の嵩密度は溶融樹脂の吐出量とコンベアの速度により調整し、厚さの異なる繊維集合体を得ることができる。
(Fiber assembly)
A fiber assembly (same as an organic fiber assembly and a sheet-like assembly) 1 that forms the
The bulk density of the
なお、前記の方法で得た繊維集合体1は、有機繊維2同士がばらばらなため真空断熱材製造時の取り扱い性が悪い場合があるので、加圧時に、有機繊維2同士を加熱溶着しても良い、この際、過度の加圧、加熱溶着は、有機繊維2間の接触面積を増大し、伝熱の増加を招くため、接触面積をできるだけ少なくした方が良く、全面積の5%以下に抑えることが望ましい。
In addition, since the
次に、得られた繊維集合体1をA4サイズに裁断し、これを25層に積層して芯材5を形成した。なお、積層する枚数は、得られた繊維集合体1の厚さと製造したい真空断熱材7の厚さを元に任意に設定して良い。実施の形態1では繊維集合体1の繊維径は、これを成形するノズル径により調整し、約15μmとしたが、断熱性能上はより細い方が良く、理論的に繊維径は10μm以下が望ましい。
Next, the obtained
(外包材)
真空断熱材7の外包材4には、ナイロン(6μm)、アルミ蒸着PET(10μm)、アルミ箔(6μm)、高密度ポリエチレン(50μm)で構成されるガスバリア性のあるプラスチックラミネートフイルムを使用した。
その他に、ポリプロピレン、ポリビニルアルコール、ポリプロピレンの構成などのアルミ箔を含まないラミネートフイルムを用いると、ヒートブリッジによる断熱性能の低下を抑制できる。なお、4辺のうち3辺がシール包装機によってヒートシールされている。
(Outer packaging material)
As the outer packaging material 4 of the vacuum
In addition, when a laminate film that does not include an aluminum foil such as a configuration of polypropylene, polyvinyl alcohol, or polypropylene is used, it is possible to suppress a decrease in heat insulation performance due to a heat bridge. Of the four sides, three sides are heat sealed by a seal wrapping machine.
(製造方法)
真空断熱材7の製造は、袋である外包材4に芯材5を挿入し、残りの一辺の口が閉まらないように固定して恒温槽にて105℃の温度下で半日(約12時間)乾燥を行った後、真空包装後の残存ガスや経時的に放出される芯材5からのアウトガス、外包材4のシール層を通して進入する透過ガスを吸着するためのガス吸着剤6をフイルム袋内に挿入し、柏木式真空包装機(NPC社製;KT−650)にて真空引きを行った。真空引きは、チャンバー内真空度が1〜10Pa程度になるまで行い、そのままチャンバー内でフイルム袋の開口部をヒートシールして板状の真空断熱材7を得た。
(Production method)
The vacuum
(断熱性能)
次に、繊維集合体1の厚さの断熱性能に及ぼす影響を、本発明の繊維集合体1としての実施例1〜4と、比較のための比較例と、について説明する。
比較材は、実施例1〜4の繊維径(約15μm)と同じ径である綿状ポリエステルを芯材に用い、前記と同様の方法で真空断熱材を得た。
製作した実施例1〜4および比較例(いずれも真空断熱材)は、熱伝導率計「AutoΛ HC−073(英弘精機(株)製)」を用いて、上温度37.7℃、下温度10.0℃の温度差における熱伝導率を測定した。なお、測定は真空引き工程から1日経過後に測定した。
(Insulation performance)
Next, the influence which the thickness of the
The comparative material used the cotton-like polyester which is the same diameter as the fiber diameter (about 15 micrometers) of Examples 1-4 for the core material, and obtained the vacuum heat insulating material by the method similar to the above.
The manufactured Examples 1 to 4 and Comparative Example (both vacuum heat insulating materials) were measured using a thermal conductivity meter “AutoΛ HC-073 (manufactured by Eihiro Seiki Co., Ltd.)” with an upper temperature of 37.7 ° C. and a lower temperature. The thermal conductivity at a temperature difference of 10.0 ° C. was measured. The measurement was made after 1 day from the vacuuming step.
ここで、繊維集合体1の1枚の厚さは、真空断熱材7の厚さから外包材4の厚さの2倍を引いた後、積層枚数で割った値である。また、平均繊維径はマイクロスコープを用いて測定した100箇所の測定値の平均値とした。真空引き後の1枚厚さを平均繊維径で割った結果を表1に示す。
Here, the thickness of one
図5は、本発明の実施形態1に係る真空断熱材の断熱性能を説明する相関図であって、横軸は繊維集合体1の枚厚さを平均繊維径で割った数値、縦軸は断熱性能比である。なお、断熱性能比は、比較例の熱伝導率を実施例1〜4の熱伝導率で、それぞれ割った数値(実施例1〜4の熱伝導率を比較例の熱伝導率で割った値の逆数に同じ)である。
図5より、繊維集合体1の厚さが平均繊維径の18倍未満になると、綿状繊維を芯材にした比較例の場合よりも断熱性能が向上していることがわかる。これは、繊維集合体1の厚さが小さいほど繊維が断熱方向と直角方向である面方向に配向しやすく、すなわち断熱方向への真空断熱材7内の固体伝熱のパスが長くできるので、断熱性能が向上できたと考えられる。
また、繊維集合体1の厚さは、平均繊維径の1倍に近づけば近づくほど断熱性能がよくなる。よって、繊維集合体1の厚さは繊維径の1〜18倍がよいことがわかった。
なお、繊維集合体1の厚さが繊維径の8倍以下になると断熱性能が急に(極端に)向上するため、繊維集合体の厚さは平均繊維径の1〜8倍であることがより望ましい。
FIG. 5 is a correlation diagram for explaining the heat insulating performance of the vacuum heat insulating material according to
From FIG. 5, it can be seen that when the thickness of the
Moreover, the closer the thickness of the
In addition, when the thickness of the
[実施の形態2:真空断熱材]
図6および図7は、本発明の実施形態2に係る真空断熱材を形成する芯材の積層要領を模式的に示す斜視図である。
図6において、芯材5は、繊維集合体1を裁断せずに連続したシート状のまま折り畳みながら積層して形成される様子が表されている。
図7において、裁断せずに連続しているシート状の第1の繊維集合体1xと、裁断せずに連続しているシート状の第2の繊維集合体1yとを用い(両者をまとめて「繊維集合体1」と称す場合がある)、両者を交わるように配置して、それぞれの折り目に挟まれた範囲が一折り毎に重なるように、積層して形成される様子が表されている。
[Embodiment 2: Vacuum insulation]
6 and 7 are perspective views schematically showing a lamination procedure of core materials forming the vacuum heat insulating material according to
In FIG. 6, the
In FIG. 7, a sheet-like
すなわち、繊維集合体1を折りながら積層することで、裁断する手間が省け効率的に芯材5、引いては真空断熱材7を製造することができる。
ここで用いた繊維集合体1は、前記の製造方法で作ったものであるので、有機繊維2は長尺方向に配向している。このことに注目して、繊維集合体1同士が交わるように積層すると点接触に近づき断熱性能がより向上する。
That is, by laminating the
Since the
[実施の形態3:冷蔵庫]
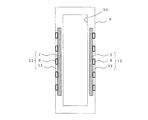
図8は、本発明の実施形態3に係る断熱箱を説明するものであって、冷蔵庫を模式的に示す正面視の断面図である。なお、実施の形態1、2と同じ部分にはこれと同じ符号を付し、一部の説明を省略する。
図8において、冷蔵庫100は、外箱9と、外箱9の内部に配置された内箱10と、外箱9と内箱10との隙間に配置された真空断熱材7およびポリウレタンフォーム11と、内箱10内に冷熱を供給する冷凍ユニット(図示しない)と、を有している。なお、外箱9および内箱10は、共通する面にそれぞれ開口部が形成され、当該開口部に開閉扉が設置されている(何れも図示しない)。
[Embodiment 3: Refrigerator]
FIG. 8 illustrates a heat insulating box according to the third embodiment of the present invention, and is a cross-sectional view in front view schematically illustrating a refrigerator. The same parts as those in the first and second embodiments are denoted by the same reference numerals, and a part of the description is omitted.
In FIG. 8, the refrigerator 100 includes an outer box 9, an
このとき、真空断熱材7の外包材4はアルミ箔を含んでいるため、該アルミ箔を通って熱が回り込むヒートブリッジが生じるおそれがある。このため、該ヒートブリッジの影響を抑制するため、真空断熱材7は樹脂成形品であるスペーサ8を用いて、外箱9の塗装鋼板から離して配設されている。なお、スペーサ8は後工程で断熱壁内に注入されるポリウレタンフォームにボイドが残らないように、流動を阻害しないための孔が、適宜設けられている。
すなわち、冷蔵庫100は、真空断熱材7、スペーサ8およびポリウレタンフォーム11によって形成された断熱壁12を有している。なお、断熱壁12が配置される範囲は限定するものではなく、外箱9と内箱10との間に形成される隙間の全範囲であっても一部であってもよく、また、前記開閉扉の内部に配置されてもよい。
At this time, since the outer packaging material 4 of the vacuum
That is, the refrigerator 100 has a
冷蔵庫100は、使用済みとなった場合、家電リサイクル法に基づき、各地のリサイクルセンターで解体・リサイクルされる。このとき、本発明の冷蔵庫100は、繊維集合体1(有機繊維2によって形成されている)からなる芯材5が配設された真空断熱材7を有するため、真空断熱材7を取り外すことなく破砕処理を行うことができ、サーマルリサイクルに際して燃焼効率を下げたり、残渣となったりすることがなく、リサイクル性が良い。
一方、真空断熱材を配設した冷蔵庫において、当該真空断熱材の芯材が無機粉末である真空断熱パネルの場合には、粉末が飛散してしまうため、箱体のまま破砕処理は行えず、大変な手間をかけて冷蔵庫箱体から真空断熱材を取り外さなければならない。
When the refrigerator 100 is used, it is dismantled and recycled at recycling centers in various places based on the Home Appliance Recycling Law. At this time, since the refrigerator 100 of the present invention has the vacuum
On the other hand, in the refrigerator in which the vacuum heat insulating material is arranged, in the case of the vacuum heat insulating panel in which the core material of the vacuum heat insulating material is an inorganic powder, the powder is scattered, so the crushing treatment cannot be performed as the box, It takes a lot of time to remove the vacuum insulation from the refrigerator box.
また、芯材がガラス繊維である真空断熱パネルの場合には、箱体のまま破砕処理は行えるものの、破砕後のガラス繊維はポリウレタンフォームの粉砕物に混じって、サーマルリサイクルに供されるが、この際、燃焼効率を低下させたり、燃焼後の残渣になったりするなどリサイクル性に難点がある。
なお、以上は、断熱箱として冷蔵庫を例示しているが、本発明はこれに限定されるものではなく、保温庫、車両空調機、給湯器などの冷熱機器あるいは温熱機器、さらには、所定の形状を具備する箱に替えて、変形自在な外袋および内袋を具備する断熱袋(断熱容器)であってもよい。
In addition, in the case of a vacuum insulation panel whose core material is glass fiber, although it can be crushed as it is in a box, the crushed glass fiber is mixed with polyurethane foam pulverized material and subjected to thermal recycling, At this time, there is a difficulty in recyclability such as lowering combustion efficiency or becoming a residue after combustion.
In addition, although the above has illustrated the refrigerator as a heat insulation box, this invention is not limited to this, Cold-heat equipment or thermal equipment, such as a heat retention box, a vehicle air conditioner, a water heater, Furthermore, predetermined | prescribed Instead of a box having a shape, a heat insulating bag (heat insulating container) having a deformable outer bag and an inner bag may be used.
以上より、本発明の真空断熱材および断熱箱は、取り扱い性、断熱性能およびリサイクル性に優れるから、各種機器に設置される真空断熱材として、さらに、各種形態の断熱箱ないし断熱容器として広く利用することができる。 As described above, since the vacuum heat insulating material and the heat insulating box of the present invention are excellent in handling property, heat insulating performance and recyclability, they are widely used as a heat insulating box or a heat insulating container in various forms as a vacuum heat insulating material installed in various devices. can do.
1:繊維集合体(シート状有機繊維集合体)、2:有機繊維、2x:有機繊維、2y:有機繊維、3:空隙、4:外包材、5:芯材、6:ガス吸着剤、7:真空断熱材、8:スペーサ、9:外箱、10:内箱、11:ポリウレタンフォーム、12:断熱壁、100:冷蔵庫。 1: fiber aggregate (sheet-like organic fiber aggregate), 2: organic fiber, 2x: organic fiber, 2y: organic fiber, 3: gap, 4: outer packaging material, 5: core material, 6: gas adsorbent, 7 : Vacuum heat insulating material, 8: spacer, 9: outer box, 10: inner box, 11: polyurethane foam, 12: heat insulating wall, 100: refrigerator.
Claims (5)
前記芯材が、有機繊維をシート状に形成した第1の有機繊維集合体と、有機繊維をシート状に形成した第2の有機繊維集合体との積層構造であり、
前記第1の有機繊維集合体の厚さおよび前記第2の有機繊維集合体の厚さが、前記ガスバリア性容器の内部に減圧状態で収容された際、前記有機繊維の直径の1〜18倍であり、
前記第1の有機繊維集合体と前記第2の有機繊維集合体とが、互いに交わるように折り畳まれて積層され、
該積層された部分において、前記第1の有機繊維集合体の両面がそれぞれ前記第2の有機繊維集合体の同一の面に当接し、前記第2の有機繊維集合体の両面がそれぞれ前記第1の有機繊維集合体の同一の面に当接することを特徴とする真空断熱材。 It is a vacuum heat insulating material in which a core material is housed in a gas barrier container and the inside is in a reduced pressure state,
The core material is a laminated structure of a first organic fiber assembly in which organic fibers are formed in a sheet shape and a second organic fiber assembly in which organic fibers are formed in a sheet shape,
When the thickness of the first organic fiber aggregate and the thickness of the second organic fiber aggregate are accommodated in the gas barrier container in a reduced pressure state, the diameter of the organic fiber is 1 to 18 times. And
The first organic fiber aggregate and the second organic fiber aggregate are folded and laminated so as to cross each other,
In the laminated portion, both surfaces of the first organic fiber assembly are in contact with the same surface of the second organic fiber assembly, and both surfaces of the second organic fiber assembly are respectively in the first portion. A vacuum heat insulating material which is in contact with the same surface of the organic fiber assembly.
該外箱の内部に配置された内箱と、
該外箱と前記内箱との隙間の全部または一部に、請求項1又は2に記載の真空断熱材が配置されていることを特徴とする断熱箱。 An outer box,
An inner box disposed inside the outer box;
A heat insulating box, wherein the vacuum heat insulating material according to claim 1 or 2 is disposed in all or part of a gap between the outer box and the inner box.
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007204400A JP4789886B2 (en) | 2007-08-06 | 2007-08-06 | Vacuum insulation and insulation box |
| GB0812583A GB2451614B (en) | 2007-08-06 | 2008-07-09 | Vacuum thermal insulating structure and thermal insulating case |
| CN2008101334786A CN101363566B (en) | 2007-08-06 | 2008-07-25 | Vacuum insulating structure |
| BE2008/0420A BE1018383A5 (en) | 2007-08-06 | 2008-07-25 | VACUUM THERMOSOLATING STRUCTURE AND THERMOISOLANT HOUSING. |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007204400A JP4789886B2 (en) | 2007-08-06 | 2007-08-06 | Vacuum insulation and insulation box |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009041592A JP2009041592A (en) | 2009-02-26 |
| JP2009041592A5 JP2009041592A5 (en) | 2009-08-13 |
| JP4789886B2 true JP4789886B2 (en) | 2011-10-12 |
Family
ID=39718233
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007204400A Expired - Fee Related JP4789886B2 (en) | 2007-08-06 | 2007-08-06 | Vacuum insulation and insulation box |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4789886B2 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN101363566B (en) |
| BE (1) | BE1018383A5 (en) |
| GB (1) | GB2451614B (en) |
Families Citing this family (22)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2538125A3 (en) | 2008-12-26 | 2013-02-20 | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation | Vacuum heat insulating material, heat insulating box using vacuum heat insulating material, refrigerator, refrigerating/air-conditioning apparatus, water heater, equipments, and manufacturing method of vacuum heat insulating material |
| JP5388603B2 (en) | 2009-01-29 | 2014-01-15 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Vacuum heat insulating material and heat insulating box equipped with the same |
| JP5236550B2 (en) * | 2009-03-30 | 2013-07-17 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Vacuum heat insulating material and manufacturing method thereof, and heat insulating box provided with the vacuum heat insulating material |
| JP2011027204A (en) * | 2009-07-28 | 2011-02-10 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Vacuum heat insulation material and insulation box provided with this vacuum heat insulation material |
| JP2011074934A (en) * | 2009-09-29 | 2011-04-14 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Vacuum thermal insulator and thermally insulating box including the vacuum thermal insulator |
| CN102575804A (en) * | 2009-10-16 | 2012-07-11 | 三菱电机株式会社 | Device for manufacturing core of vacuum heat insulation member and method for manufacturing vacuum heat insulation member, as well as vacuum heat insulation member and refrigerator |
| WO2011045947A1 (en) * | 2009-10-16 | 2011-04-21 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Vacuum heat insulation material and refrigerator |
| US9103482B2 (en) | 2009-10-19 | 2015-08-11 | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation | Vacuum heat insulating material, heat insulating box, refrigerator, refrigerating/air-conditioning apparatus, water heater, appliance, and manufacturing method of vacuum heat insulating material |
| JP5380313B2 (en) * | 2010-01-13 | 2014-01-08 | 日立アプライアンス株式会社 | Vacuum heat insulating material and refrigerator using the same |
| JP5424929B2 (en) * | 2010-02-19 | 2014-02-26 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Vacuum heat insulating material and heat insulating box provided with this vacuum heat insulating material |
| JP5448937B2 (en) * | 2010-03-03 | 2014-03-19 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Vacuum heat insulating material and heat insulating box provided with this vacuum heat insulating material |
| CN101963267A (en) * | 2010-10-09 | 2011-02-02 | 上海海事大学 | Air insulating structure of vacuum insulation panel and packaging method thereof |
| JP5664297B2 (en) * | 2011-02-04 | 2015-02-04 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Vacuum insulation and insulation box |
| SG194627A1 (en) * | 2011-05-30 | 2013-12-30 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Vacuum heat insulator and heat-insulating box formed using same |
| JP5798942B2 (en) * | 2011-09-12 | 2015-10-21 | 日立アプライアンス株式会社 | Vacuum heat insulating material and refrigerator and equipment using the same |
| JP5856091B2 (en) * | 2013-01-30 | 2016-02-09 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Heat insulation wall, refrigerator, equipment |
| JP5512011B2 (en) * | 2013-03-27 | 2014-06-04 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Vacuum insulation for insulation box |
| DE102013104712A1 (en) | 2013-05-07 | 2014-11-13 | Saint-Gobain Isover | Method for producing vacuum insulation panels |
| CN104373751A (en) * | 2013-08-12 | 2015-02-25 | 苏州维艾普新材料股份有限公司 | Different-length-diameter-ratio VIP (vacuum insulated panel) glass fiber core material |
| CN104373750A (en) * | 2013-08-12 | 2015-02-25 | 苏州维艾普新材料股份有限公司 | Laminated VIP (vacuum insulation panel) fiberglass core material |
| KR20210084534A (en) * | 2018-11-02 | 2021-07-07 | 라이프 테크놀로지스 코포레이션 | Thermal Insulation Packaging Systems and Related Methods |
| JP7287642B2 (en) * | 2018-12-27 | 2023-06-06 | アクア株式会社 | refrigerator |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB715174A (en) * | 1951-07-14 | 1954-09-08 | Gen Electric | Improvements in and relating to thermal insulation |
| US4055268A (en) * | 1975-11-18 | 1977-10-25 | Union Carbide Corporation | Cryogenic storage container |
| JP3298260B2 (en) * | 1993-10-05 | 2002-07-02 | ダイソー株式会社 | Chromatographic packing material |
| US5609934A (en) * | 1995-01-05 | 1997-03-11 | Schuller International, Inc. | Method of manufacturing heat bonded glass fiber insulation boards |
| JP4251463B2 (en) * | 1997-07-02 | 2009-04-08 | パナソニック株式会社 | Thermal insulation sheet and thermal insulation |
| DE19960694B4 (en) * | 1999-12-16 | 2005-02-10 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Process for producing an insulating body molding and Isolierkörperformteil for cryogenic insulation |
| JP2004251303A (en) * | 2003-02-18 | 2004-09-09 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Vacuum heat insulation material, freezing and cooling devices using vacuum heat insulation material |
| JP2006017151A (en) * | 2004-06-30 | 2006-01-19 | Fuji Electric Retail Systems Co Ltd | Vacuum heat insulating material |
| WO2006009146A1 (en) * | 2004-07-20 | 2006-01-26 | Kurashiki Boseki Kabushiki Kaisha | Vacuum heat insulation material |
| JP4012903B2 (en) * | 2004-11-30 | 2007-11-28 | 倉敷紡績株式会社 | Vacuum insulation |
| JP2006307921A (en) * | 2005-04-27 | 2006-11-09 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Vacuum thermal insulating material |
| JP2009228886A (en) * | 2008-03-25 | 2009-10-08 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Vacuum heat insulating material and heat insulating box using the same |
-
2007
- 2007-08-06 JP JP2007204400A patent/JP4789886B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2008
- 2008-07-09 GB GB0812583A patent/GB2451614B/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2008-07-25 CN CN2008101334786A patent/CN101363566B/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2008-07-25 BE BE2008/0420A patent/BE1018383A5/en active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| GB2451614A (en) | 2009-02-11 |
| CN101363566A (en) | 2009-02-11 |
| GB0812583D0 (en) | 2008-08-13 |
| BE1018383A5 (en) | 2010-10-05 |
| GB2451614B (en) | 2009-11-04 |
| JP2009041592A (en) | 2009-02-26 |
| CN101363566B (en) | 2012-06-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4789886B2 (en) | Vacuum insulation and insulation box | |
| JP5388603B2 (en) | Vacuum heat insulating material and heat insulating box equipped with the same | |
| JP5236550B2 (en) | Vacuum heat insulating material and manufacturing method thereof, and heat insulating box provided with the vacuum heat insulating material | |
| JP2011074934A (en) | Vacuum thermal insulator and thermally insulating box including the vacuum thermal insulator | |
| US9546481B2 (en) | Vacuum insulation material | |
| JP5362024B2 (en) | Vacuum heat insulating material, heat insulating box, refrigerator, refrigeration / air conditioning device, hot water supply device and equipment, and method for manufacturing vacuum heat insulating material | |
| JP3942189B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of vacuum insulation | |
| JP2011094807A (en) | Vacuum insulation material, and heat-insulating box, refrigerator, freezing/air-conditioning apparatus, hot-water supply device, and appliance each employing vacuum insulation material, and process for producing vacuum insulation material | |
| JP5111331B2 (en) | Vacuum heat insulating material and heat insulating box using this vacuum heat insulating material | |
| JP2010127421A (en) | Vacuum thermal-insulating material and thermal insulation box | |
| EP2105648B1 (en) | Vacuum heat insulating material and heat insulating box using the same | |
| JP2010281444A (en) | Heat insulating material | |
| JP5627773B2 (en) | Vacuum heat insulating material and heat insulating box using the same | |
| JP2010007806A (en) | Vacuum thermal insulation panel and thermal insulation box body with this | |
| JPWO2017029727A1 (en) | Vacuum insulation and insulation box | |
| JP4969555B2 (en) | Vacuum insulation and insulation box | |
| JP5968004B2 (en) | Refrigerator using vacuum heat insulating material and vacuum heat insulating material | |
| JP6793571B2 (en) | Vacuum heat insulating material, equipment equipped with it, and manufacturing method of vacuum heat insulating material | |
| JP5448937B2 (en) | Vacuum heat insulating material and heat insulating box provided with this vacuum heat insulating material | |
| EP2985376B1 (en) | Core material for vacuum insulator, comprising organic synthetic fiber, and vacuum insulator containing same | |
| KR102217150B1 (en) | Vacuum Insulation Material | |
| JP6184841B2 (en) | Vacuum insulation material and equipment using the same | |
| JP2011027204A (en) | Vacuum heat insulation material and insulation box provided with this vacuum heat insulation material | |
| JP2014077478A (en) | Vacuum heat insulation material and heat insulation box comprising the same | |
| JP2016142345A (en) | Manufacturing method of vacuum heat insulation material, vacuum heat insulation material and equipment including vacuum heat insulation material |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090629 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20090629 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20091116 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20091124 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100118 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100518 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100715 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20110104 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110126 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20110621 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20110719 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140729 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |