JP2008218776A - 半導体装置 - Google Patents
半導体装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2008218776A JP2008218776A JP2007055247A JP2007055247A JP2008218776A JP 2008218776 A JP2008218776 A JP 2008218776A JP 2007055247 A JP2007055247 A JP 2007055247A JP 2007055247 A JP2007055247 A JP 2007055247A JP 2008218776 A JP2008218776 A JP 2008218776A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- lead
- inner leads
- differential signal
- pad
- interval
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/48—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor
- H01L23/488—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor consisting of soldered or bonded constructions
- H01L23/495—Lead-frames or other flat leads
- H01L23/49541—Geometry of the lead-frame
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/48—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor
- H01L23/488—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor consisting of soldered or bonded constructions
- H01L23/495—Lead-frames or other flat leads
- H01L23/49541—Geometry of the lead-frame
- H01L23/49558—Insulating layers on lead frames, e.g. bridging members
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/58—Structural electrical arrangements for semiconductor devices not otherwise provided for, e.g. in combination with batteries
- H01L23/60—Protection against electrostatic charges or discharges, e.g. Faraday shields
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/02—Bonding areas ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L24/06—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of a plurality of bonding areas
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L24/49—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of a plurality of wire connectors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2223/00—Details relating to semiconductor or other solid state devices covered by the group H01L23/00
- H01L2223/58—Structural electrical arrangements for semiconductor devices not otherwise provided for
- H01L2223/64—Impedance arrangements
- H01L2223/66—High-frequency adaptations
- H01L2223/6605—High-frequency electrical connections
- H01L2223/6638—Differential pair signal lines
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/05—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of an individual bonding area
- H01L2224/0554—External layer
- H01L2224/0555—Shape
- H01L2224/05552—Shape in top view
- H01L2224/05553—Shape in top view being rectangular
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/05—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of an individual bonding area
- H01L2224/0554—External layer
- H01L2224/05599—Material
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/481—Disposition
- H01L2224/48151—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/48221—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/48245—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being metallic
- H01L2224/48247—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being metallic connecting the wire to a bond pad of the item
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/481—Disposition
- H01L2224/48151—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/48221—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/48245—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being metallic
- H01L2224/48253—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being metallic connecting the wire to a potential ring of the item
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/49—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of a plurality of wire connectors
- H01L2224/491—Disposition
- H01L2224/4912—Layout
- H01L2224/49171—Fan-out arrangements
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/49—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of a plurality of wire connectors
- H01L2224/494—Connecting portions
- H01L2224/4943—Connecting portions the connecting portions being staggered
- H01L2224/49433—Connecting portions the connecting portions being staggered outside the semiconductor or solid-state body
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/85—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a wire connector
- H01L2224/8538—Bonding interfaces outside the semiconductor or solid-state body
- H01L2224/85399—Material
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L24/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/0001—Technical content checked by a classifier
- H01L2924/00014—Technical content checked by a classifier the subject-matter covered by the group, the symbol of which is combined with the symbol of this group, being disclosed without further technical details
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01004—Beryllium [Be]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01006—Carbon [C]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01015—Phosphorus [P]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01027—Cobalt [Co]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01033—Arsenic [As]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01082—Lead [Pb]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/11—Device type
- H01L2924/13—Discrete devices, e.g. 3 terminal devices
- H01L2924/1304—Transistor
- H01L2924/1306—Field-effect transistor [FET]
- H01L2924/13091—Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor [MOSFET]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/15—Details of package parts other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/181—Encapsulation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/19—Details of hybrid assemblies other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/1901—Structure
- H01L2924/1904—Component type
- H01L2924/19043—Component type being a resistor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/30—Technical effects
- H01L2924/301—Electrical effects
- H01L2924/30105—Capacitance
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/30—Technical effects
- H01L2924/301—Electrical effects
- H01L2924/30107—Inductance
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/30—Technical effects
- H01L2924/301—Electrical effects
- H01L2924/3011—Impedance
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Semiconductor Integrated Circuits (AREA)
- Lead Frames For Integrated Circuits (AREA)
Abstract
【解決手段】ダイパッド13の周りに複数のインナーリード14が設けられている。ダイパッド13と複数のインナーリード14との間の領域に、接地されたGNDリード16が設けられている。半導体チップ17と複数のインナーリード14は、複数のワイヤー21によりそれぞれ接続されている。半導体チップ17とGNDリード16はGNDワイヤー22により接続されている。GNDワイヤー22は複数のワイヤー21の間に配置されている。隣接するインナーリード14の先端の間隔が0.2mm以下である。
【選択図】図4
Description
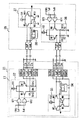
図1は、本発明の実施の形態1に係る半導体装置を示す平面図であり、図2はその側面図である。半導体チップ(後述)をモールド樹脂で封止したパッケージ本体11から複数のアウターリード12が出ている。
図9は、本発明の実施の形態2に係る半導体装置の要部を拡大した平面図である。実施の形態1では2本の差動信号用インナーリード14aの間隔を広げたのに対し、本実施の形態では、2個の差動信号用パッド18aの間隔を、複数のパッド18の最小間隔よりも広くしている。
図10は、本発明の実施の形態3に係る半導体装置のパッケージ本体の内部を示す平面図であり、図11は図10の要部を拡大した平面図である。本実施の形態3では2本の差動信号用インナーリード14aの間隔WAを、差動信号用インナーリード14aがアウターリードと連続する部分の間隔WBよりも広くしている。例えば、間隔WAを250μm、間隔WBを220μmとする。これにより、特性インピーダンスの不整合を小さくして信号の伝達特性が劣化するのを防ぐことができる。そして、全てのインナーリードの間隔を広くしているわけではないので、半導体装置の大型化を抑制することができる。
14 インナーリード
14a 差動信号用のインナーリード
14b 固定電位用インナーリード
15 T字型インナーリード
15a 第1リード部
15b 第2リード部
16 GNDリード
17 半導体チップ
18 パッド
18a 差動信号用のパッド
18b 固定電位用パッド
21 ワイヤー(第1ワイヤー)
22 GNDワイヤー
23 ワイヤー(第2ワイヤー)
24 リード押え
Claims (9)
- ダイパッドと、
前記ダイパッドの周りに設けられた複数のインナーリードと、
前記ダイパッドと前記複数のインナーリードとの間の領域に設けられ、接地されたGNDリードと、
前記ダイパッド上に搭載された半導体チップと、
前記半導体チップ上の複数のパッドと前記複数のインナーリードをそれぞれ接続する複数のワイヤーと、
前記複数のワイヤーの間に配置され、前記半導体チップ上のパッドと前記GNDリードを接続するGNDワイヤーとを有し、
隣接するインナーリードの先端の間隔が0.2mm以下であることを特徴とする半導体装置。 - ダイパッドと、
前記ダイパッドの周りに設けられた複数のインナーリード及びT字型インナーリードと、
前記ダイパッド上に搭載された半導体チップと、
前記半導体チップ上の複数のパッドと前記複数のインナーリードをそれぞれ接続する複数の第1ワイヤーと、
前記半導体チップ上のパッドと前記T字型インナーリードを接続する第2ワイヤーとを有し、
前記T字型インナーリードは、
前記ダイパッドと前記複数のインナーリードとの間の領域に設けられ前記複数のインナーリードの配列方向に延在する第1リード部と、
前記複数のインナーリードの間に設けられ前記第1リード部に接続された第2リード部とを有し、
前記第2ワイヤーは、前記T字型インナーリードの前記第1リード部にステッチボンドされていることを特徴とする半導体装置。 - 前記T字型インナーリードは、ワイヤボンディングの際にリード押えで押える部分の幅が、前記リード押えで押える部分の幅が一番細いインナーリードに比べて1.5倍以上であることを特徴とする請求項2に記載の半導体装置。
- 前記ダイパッドの周りに設けられた複数のインナーリードと、
前記ダイパッド上に搭載された半導体チップと、
前記半導体チップ上の複数のパッドと前記複数のインナーリードをそれぞれ接続する複数のワイヤーとを有し、
前記複数のインナーリードは、互いに隣接する2本の差動信号用インナーリードを含み、
前記2本の差動信号用インナーリードの間隔は、前記複数のインナーリードの最小間隔よりも広いことを特徴とする半導体装置。 - 前記複数のインナーリードは、前記差動信号用インナーリードに隣接する固定電位用インナーリードを含み、
前記差動信号用インナーリードと前記固定電位用インナーリードの間隔は、前記複数のインナーリードの最小間隔よりも広いことを特徴とする請求項4に記載の半導体装置。 - 前記複数のインナーリードは、前記差動信号用インナーリードに隣接する固定電位用インナーリードを含み、
前記2本の差動信号用インナーリードの間隔は、前記差動信号用インナーリードと前記固定電位用インナーリードの間隔よりも広いことを特徴とする請求項4に記載の半導体装置。 - 前記ダイパッドの周りに設けられた複数のインナーリードと、
前記ダイパッド上に搭載された半導体チップと、
前記半導体チップ上の複数のパッドと前記複数のインナーリードをそれぞれ接続する複数のワイヤーとを有し、
前記複数のパッドは、互いに隣接する2個の差動信号用パッドを含み、
前記2個の差動信号用パッドの間隔は、前記複数のパッドの最小間隔よりも広いことを特徴とする半導体装置。 - 前記複数のパッドは、前記差動信号用パッドに隣接する固定電位用パッドを含み、
前記差動信号用パッドと前記固定電位用パッドの間隔は、前記複数のパッドの最小間隔よりも広いことを特徴とする請求項7に記載の半導体装置。 - 前記複数のパッドは、前記差動信号用パッドに隣接する固定電位用パッドを含み、
前記2本の差動信号用パッドの間隔は、前記差動信号用パッドと前記固定電位用パッドの間隔よりも広いことを特徴とする請求項7に記載の半導体装置。
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007055247A JP2008218776A (ja) | 2007-03-06 | 2007-03-06 | 半導体装置 |
| TW097107439A TW200845342A (en) | 2007-03-06 | 2008-03-04 | Semiconductor device |
| CN2008100825992A CN101261973B (zh) | 2007-03-06 | 2008-03-05 | 半导体装置 |
| US12/073,384 US7763966B2 (en) | 2007-03-06 | 2008-03-05 | Resin molded semiconductor device and differential amplifier circuit |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007055247A JP2008218776A (ja) | 2007-03-06 | 2007-03-06 | 半導体装置 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2008218776A true JP2008218776A (ja) | 2008-09-18 |
| JP2008218776A5 JP2008218776A5 (ja) | 2010-04-08 |
Family
ID=39740812
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007055247A Pending JP2008218776A (ja) | 2007-03-06 | 2007-03-06 | 半導体装置 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US7763966B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP2008218776A (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN101261973B (ja) |
| TW (1) | TW200845342A (ja) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011134941A (ja) * | 2009-12-25 | 2011-07-07 | Fujitsu Semiconductor Ltd | 半導体装置及び実装構造 |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104851863B (zh) * | 2015-04-17 | 2017-11-28 | 华为技术有限公司 | 一种集成电路、引线键合封装芯片及倒装封装芯片 |
| WO2020012957A1 (ja) * | 2018-07-12 | 2020-01-16 | ローム株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5530210A (en) * | 1978-08-25 | 1980-03-04 | Hitachi Ltd | Transistor amplifier circuit |
| JPH0388356A (ja) * | 1989-08-31 | 1991-04-12 | Toshiba Corp | 集積回路及びその接続回路 |
| JP2001007458A (ja) * | 1999-06-18 | 2001-01-12 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 差動平衡信号伝送基板 |
| JP2001102488A (ja) * | 1999-09-28 | 2001-04-13 | Hitachi Cable Ltd | 半導体装置 |
| JP2002076235A (ja) * | 2000-08-30 | 2002-03-15 | Hitachi Ltd | 半導体装置 |
| JP2002084107A (ja) * | 2000-07-04 | 2002-03-22 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 伝送線路を有する多層配線基板 |
| JP2007043146A (ja) * | 2005-07-22 | 2007-02-15 | Marvell World Trade Ltd | 高速集積回路用のパッケージング |
Family Cites Families (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2580674B2 (ja) | 1988-02-08 | 1997-02-12 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 高周波用モールド型パッケージ |
| JPH0714976A (ja) | 1993-06-24 | 1995-01-17 | Shinko Electric Ind Co Ltd | リードフレーム及び半導体装置 |
| US5343074A (en) * | 1993-10-04 | 1994-08-30 | Motorola, Inc. | Semiconductor device having voltage distribution ring(s) and method for making the same |
| JP2866572B2 (ja) * | 1994-02-07 | 1999-03-08 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 半導体製造方法 |
| KR0148077B1 (ko) * | 1994-08-16 | 1998-08-01 | 김광호 | 분리된 다이 패드를 갖는 반도체 패키지 |
| US5949132A (en) * | 1995-05-02 | 1999-09-07 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Dambarless leadframe for molded component encapsulation |
| EP0848423B1 (en) * | 1996-07-03 | 2006-03-01 | Seiko Epson Corporation | Resin-encapsulated semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same |
| US6118173A (en) * | 1996-11-14 | 2000-09-12 | Nippon Steel Semiconductor Corporation | Lead frame and a semiconductor device |
| US5903050A (en) * | 1998-04-30 | 1999-05-11 | Lsi Logic Corporation | Semiconductor package having capacitive extension spokes and method for making the same |
| US6198163B1 (en) * | 1999-10-18 | 2001-03-06 | Amkor Technology, Inc. | Thin leadframe-type semiconductor package having heat sink with recess and exposed surface |
| US6538336B1 (en) * | 2000-11-14 | 2003-03-25 | Rambus Inc. | Wirebond assembly for high-speed integrated circuits |
| TW490826B (en) * | 2001-05-02 | 2002-06-11 | Siliconware Precision Industries Co Ltd | Semiconductor package device and its manufacture method |
| US6903448B1 (en) * | 2002-11-12 | 2005-06-07 | Marvell International Ltd. | High performance leadframe in electronic package |
| US6992377B2 (en) * | 2004-02-26 | 2006-01-31 | Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. | Semiconductor package with crossing conductor assembly and method of manufacture |
| JP2006220453A (ja) * | 2005-02-08 | 2006-08-24 | Denso Corp | 加速度センサ装置 |
| US7479680B2 (en) * | 2005-11-30 | 2009-01-20 | California Micro Devices | Method and apparatus that provides differential connections with improved ESD protection and routing |
| US8294249B2 (en) * | 2008-08-05 | 2012-10-23 | Integrated Device Technology Inc. | Lead frame package |
-
2007
- 2007-03-06 JP JP2007055247A patent/JP2008218776A/ja active Pending
-
2008
- 2008-03-04 TW TW097107439A patent/TW200845342A/zh unknown
- 2008-03-05 CN CN2008100825992A patent/CN101261973B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2008-03-05 US US12/073,384 patent/US7763966B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5530210A (en) * | 1978-08-25 | 1980-03-04 | Hitachi Ltd | Transistor amplifier circuit |
| JPH0388356A (ja) * | 1989-08-31 | 1991-04-12 | Toshiba Corp | 集積回路及びその接続回路 |
| JP2001007458A (ja) * | 1999-06-18 | 2001-01-12 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 差動平衡信号伝送基板 |
| JP2001102488A (ja) * | 1999-09-28 | 2001-04-13 | Hitachi Cable Ltd | 半導体装置 |
| JP2002084107A (ja) * | 2000-07-04 | 2002-03-22 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 伝送線路を有する多層配線基板 |
| JP2002076235A (ja) * | 2000-08-30 | 2002-03-15 | Hitachi Ltd | 半導体装置 |
| JP2007043146A (ja) * | 2005-07-22 | 2007-02-15 | Marvell World Trade Ltd | 高速集積回路用のパッケージング |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011134941A (ja) * | 2009-12-25 | 2011-07-07 | Fujitsu Semiconductor Ltd | 半導体装置及び実装構造 |
| US8811028B2 (en) | 2009-12-25 | 2014-08-19 | Fujitsu Semiconductor Limited | Semiconductor device and circuit board |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101261973B (zh) | 2011-12-21 |
| US7763966B2 (en) | 2010-07-27 |
| CN101261973A (zh) | 2008-09-10 |
| TW200845342A (en) | 2008-11-16 |
| US20080217750A1 (en) | 2008-09-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US20180197850A1 (en) | Semiconductor integrated circuit device | |
| US20060022703A1 (en) | Semiconductor device with bus terminating function | |
| US8767404B2 (en) | Decoupling capacitor circuitry | |
| US20130228867A1 (en) | Semiconductor device protected from electrostatic discharge | |
| US6396123B1 (en) | Semiconductor device provided with on-chip decoupling condenser utilizing CMP dummy patterns | |
| JP2008218776A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| US7250660B1 (en) | ESD protection that supports LVDS and OCT | |
| US8570075B2 (en) | Gate driver with digital ground | |
| US20190363060A1 (en) | Apparatuses and methods for pin capacitance reduction including bond pads and circuits in a semiconductor device | |
| US9609742B2 (en) | Electrical characteristics of package substrates and semiconductor packages including the same | |
| JP2006135302A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP2005086662A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| US7015588B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| KR20050092027A (ko) | 정전 방전 보호 장치, 다이오드, 입력 버퍼 및 정전 방전보호 방법 | |
| JP2017034052A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP2016219948A (ja) | 入出力インターフェース回路 | |
| US7538414B2 (en) | Semiconductor integrated circuit device | |
| US20100027171A1 (en) | Method and Apparatus for Forming I/O Clusters in Integrated Circuits | |
| US7361981B2 (en) | Pad layout | |
| US20050057872A1 (en) | Integrated circuit voltage excursion protection | |
| US20070200140A1 (en) | Electrostatic protection device for semiconductor circuit for decreasing input capacitance | |
| KR20120033884A (ko) | 정전기 방전 보호 회로 및 그 레이아웃 구조 | |
| KR100307046B1 (ko) | 패드의하부에캐패시터를구비하는반도체장치 | |
| EP1542360B1 (en) | Integrated circuit power supply circuit | |
| US6157205A (en) | Grounding scheme for a high-speed data channel |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100222 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20100222 |
|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A712 Effective date: 20100521 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20110713 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20110726 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20120124 |