JP2008192833A - 半導体装置の製造方法 - Google Patents
半導体装置の製造方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2008192833A JP2008192833A JP2007025861A JP2007025861A JP2008192833A JP 2008192833 A JP2008192833 A JP 2008192833A JP 2007025861 A JP2007025861 A JP 2007025861A JP 2007025861 A JP2007025861 A JP 2007025861A JP 2008192833 A JP2008192833 A JP 2008192833A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- solder
- bump
- connection
- semiconductor device
- semiconductor chip
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 113
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 31
- 229910000679 solder Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 194
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 36
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 11
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 55
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 claims description 20
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 claims description 20
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000009713 electroplating Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 6
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000007772 electroless plating Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000007689 inspection Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229910017944 Ag—Cu Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910020836 Sn-Ag Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910020888 Sn-Cu Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910020988 Sn—Ag Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910019204 Sn—Cu Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003014 reinforcing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003822 epoxy resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- -1 for example Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000155 melt Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920000647 polyepoxide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000011800 void material Substances 0.000 description 1
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/31—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process
- H01L24/32—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process of an individual layer connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/48—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/48—Manufacture or treatment of parts, e.g. containers, prior to assembly of the devices, using processes not provided for in a single one of the subgroups H01L21/06 - H01L21/326
- H01L21/4814—Conductive parts
- H01L21/4846—Leads on or in insulating or insulated substrates, e.g. metallisation
- H01L21/4853—Connection or disconnection of other leads to or from a metallisation, e.g. pins, wires, bumps
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/50—Assembly of semiconductor devices using processes or apparatus not provided for in a single one of the subgroups H01L21/06 - H01L21/326, e.g. sealing of a cap to a base of a container
- H01L21/56—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulation layers, coatings
- H01L21/563—Encapsulation of active face of flip-chip device, e.g. underfilling or underencapsulation of flip-chip, encapsulation preform on chip or mounting substrate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/28—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/10—Bump connectors ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L24/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L24/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K3/00—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing printed circuits
- H05K3/30—Assembling printed circuits with electric components, e.g. with resistor
- H05K3/32—Assembling printed circuits with electric components, e.g. with resistor electrically connecting electric components or wires to printed circuits
- H05K3/34—Assembling printed circuits with electric components, e.g. with resistor electrically connecting electric components or wires to printed circuits by soldering
- H05K3/341—Surface mounted components
- H05K3/3431—Leadless components
- H05K3/3436—Leadless components having an array of bottom contacts, e.g. pad grid array or ball grid array components
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/05—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of an individual bonding area
- H01L2224/0554—External layer
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/05—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of an individual bonding area
- H01L2224/0554—External layer
- H01L2224/0556—Disposition
- H01L2224/05568—Disposition the whole external layer protruding from the surface
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/05—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of an individual bonding area
- H01L2224/0554—External layer
- H01L2224/05573—Single external layer
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/11—Manufacturing methods
- H01L2224/114—Manufacturing methods by blanket deposition of the material of the bump connector
- H01L2224/1146—Plating
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/12—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/13—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/13001—Core members of the bump connector
- H01L2224/13099—Material
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/161—Disposition
- H01L2224/16151—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/16221—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/16225—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/161—Disposition
- H01L2224/16151—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/16221—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/16225—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
- H01L2224/16235—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation the bump connector connecting to a via metallisation of the item
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/27—Manufacturing methods
- H01L2224/27011—Involving a permanent auxiliary member, i.e. a member which is left at least partly in the finished device, e.g. coating, dummy feature
- H01L2224/27013—Involving a permanent auxiliary member, i.e. a member which is left at least partly in the finished device, e.g. coating, dummy feature for holding or confining the layer connector, e.g. solder flow barrier
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/28—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/29—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual layer connector
- H01L2224/29001—Core members of the layer connector
- H01L2224/29099—Material
- H01L2224/291—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/29101—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of less than 400°C
- H01L2224/29111—Tin [Sn] as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/28—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/29—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual layer connector
- H01L2224/29001—Core members of the layer connector
- H01L2224/29099—Material
- H01L2224/2919—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a polymer, e.g. polyester, phenolic based polymer, epoxy
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/31—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/32—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process of an individual layer connector
- H01L2224/321—Disposition
- H01L2224/32151—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/32221—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/32225—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/73—Means for bonding being of different types provided for in two or more of groups H01L2224/10, H01L2224/18, H01L2224/26, H01L2224/34, H01L2224/42, H01L2224/50, H01L2224/63, H01L2224/71
- H01L2224/732—Location after the connecting process
- H01L2224/73201—Location after the connecting process on the same surface
- H01L2224/73203—Bump and layer connectors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/73—Means for bonding being of different types provided for in two or more of groups H01L2224/10, H01L2224/18, H01L2224/26, H01L2224/34, H01L2224/42, H01L2224/50, H01L2224/63, H01L2224/71
- H01L2224/732—Location after the connecting process
- H01L2224/73201—Location after the connecting process on the same surface
- H01L2224/73203—Bump and layer connectors
- H01L2224/73204—Bump and layer connectors the bump connector being embedded into the layer connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/81009—Pre-treatment of the bump connector or the bonding area
- H01L2224/81026—Applying a precursor material to the bonding area
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/8119—Arrangement of the bump connectors prior to mounting
- H01L2224/81191—Arrangement of the bump connectors prior to mounting wherein the bump connectors are disposed only on the semiconductor or solid-state body
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/812—Applying energy for connecting
- H01L2224/8121—Applying energy for connecting using a reflow oven
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/8138—Bonding interfaces outside the semiconductor or solid-state body
- H01L2224/81399—Material
- H01L2224/814—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/818—Bonding techniques
- H01L2224/81801—Soldering or alloying
- H01L2224/81815—Reflow soldering
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/83—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a layer connector
- H01L2224/83009—Pre-treatment of the layer connector or the bonding area
- H01L2224/83051—Forming additional members, e.g. dam structures
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/0001—Technical content checked by a classifier
- H01L2924/00014—Technical content checked by a classifier the subject-matter covered by the group, the symbol of which is combined with the symbol of this group, being disclosed without further technical details
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01006—Carbon [C]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01013—Aluminum [Al]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01029—Copper [Cu]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01033—Arsenic [As]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01047—Silver [Ag]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/0105—Tin [Sn]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01075—Rhenium [Re]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01078—Platinum [Pt]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01079—Gold [Au]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/013—Alloys
- H01L2924/0132—Binary Alloys
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/013—Alloys
- H01L2924/0133—Ternary Alloys
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/013—Alloys
- H01L2924/014—Solder alloys
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/11—Device type
- H01L2924/14—Integrated circuits
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/15—Details of package parts other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/151—Die mounting substrate
- H01L2924/153—Connection portion
- H01L2924/1531—Connection portion the connection portion being formed only on the surface of the substrate opposite to the die mounting surface
- H01L2924/15311—Connection portion the connection portion being formed only on the surface of the substrate opposite to the die mounting surface being a ball array, e.g. BGA
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/15—Details of package parts other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/151—Die mounting substrate
- H01L2924/156—Material
- H01L2924/1579—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a polymer, e.g. polyester, phenolic based polymer, epoxy
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K2201/00—Indexing scheme relating to printed circuits covered by H05K1/00
- H05K2201/10—Details of components or other objects attached to or integrated in a printed circuit board
- H05K2201/10613—Details of electrical connections of non-printed components, e.g. special leads
- H05K2201/10621—Components characterised by their electrical contacts
- H05K2201/10674—Flip chip
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K2203/00—Indexing scheme relating to apparatus or processes for manufacturing printed circuits covered by H05K3/00
- H05K2203/04—Soldering or other types of metallurgic bonding
- H05K2203/043—Reflowing of solder coated conductors, not during connection of components, e.g. reflowing solder paste
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K2203/00—Indexing scheme relating to apparatus or processes for manufacturing printed circuits covered by H05K3/00
- H05K2203/04—Soldering or other types of metallurgic bonding
- H05K2203/0475—Molten solder just before placing the component
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K3/00—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing printed circuits
- H05K3/30—Assembling printed circuits with electric components, e.g. with resistor
- H05K3/32—Assembling printed circuits with electric components, e.g. with resistor electrically connecting electric components or wires to printed circuits
- H05K3/34—Assembling printed circuits with electric components, e.g. with resistor electrically connecting electric components or wires to printed circuits by soldering
- H05K3/3457—Solder materials or compositions; Methods of application thereof
- H05K3/3473—Plating of solder
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02P—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE PRODUCTION OR PROCESSING OF GOODS
- Y02P70/00—Climate change mitigation technologies in the production process for final industrial or consumer products
- Y02P70/50—Manufacturing or production processes characterised by the final manufactured product
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Wire Bonding (AREA)
- Internal Circuitry In Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Devices (AREA)
Abstract
【解決手段】半導体チップ12の電極パッド31に形成されたAuバンプ13と対向する配線基板11の接続パッド21の接続面21A及び側面21Bに、めっき法により、はんだ14を形成し、次いで、このはんだ14を溶融させて、接続パッド21の接続面21Aに凸形状とされたはんだ溜り15を形成し、その後、はんだ溜りが形成された接続パッド21の接続面21AにAuバンプ13を載置して、はんだ溜り15とAuバンプ13とを接合させた。
【選択図】図8
Description
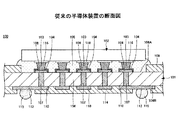
図8は、本発明の実施の形態に係る半導体装置の断面図である。
11 配線基板
12 半導体チップ
13 Auバンプ
14 はんだ
15 はんだ溜り
16 アンダーフィル樹脂
17 はんだボール
18 基板本体
18A 上面
18B 下面
19 貫通ビア
21 接続パッド
21A 接続面
21B 側面
23,29 ソルダーレジスト
23A,29A 開口部
24 配線
25 パッド
27 貫通孔
31 電極パッド
M1,M2 厚さ
Claims (4)
- 複数の電極パッドを有した半導体チップと、前記電極パッドと対向する接続パッドを有した配線基板と、を備え、
前記複数の電極パッドに設けられたAuバンプと、前記接続パッドに設けられたはんだとを接合させることにより、前記半導体チップと前記配線基板とをフリップチップ接続する半導体装置の製造方法であって、
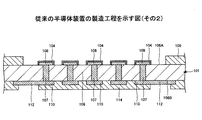
めっき法により、前記Auバンプと対向する前記接続パッドの接続面と、前記接続パッドの側面とに前記はんだを形成するはんだ形成工程と、
前記はんだを溶融させて、前記接続パッドの接続面に凸形状とされたはんだ溜りを形成するはんだ溜り形成工程と、
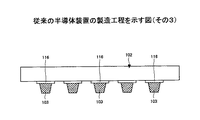
前記はんだ溜りが形成された前記接続面に前記Auバンプを載置することにより、前記はんだ溜りと前記Auバンプとを接合させる接合工程と、を含むことを特徴とする半導体装置の製造方法。 - 前記はんだ形成工程では、前記はんだを電解めっき法により形成することを特徴とする請求項1記載の半導体装置の製造方法。
- 前記はんだ溜り形成工程では、前記はんだを該はんだの融点以上で、かつ前記半導体チップの耐熱温度よりも低い温度で加熱することにより、前記はんだを溶融させることを特徴とする請求項1又は2記載の半導体装置の製造方法。
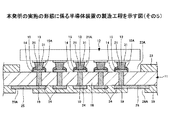
- 前記接合工程後に、前記半導体チップと前記配線基板との隙間を充填するようにアンダーフィル樹脂を形成するアンダーフィル樹脂形成工程を設けたことを特徴とする請求項1ないし3のうち、いずれか一項記載の半導体装置の製造方法。
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007025861A JP2008192833A (ja) | 2007-02-05 | 2007-02-05 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| KR1020080007383A KR20080073213A (ko) | 2007-02-05 | 2008-01-24 | 반도체 장치의 제조 방법 |
| US12/021,664 US7901997B2 (en) | 2007-02-05 | 2008-01-29 | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device |
| TW097104164A TW200836309A (en) | 2007-02-05 | 2008-02-04 | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007025861A JP2008192833A (ja) | 2007-02-05 | 2007-02-05 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2008192833A true JP2008192833A (ja) | 2008-08-21 |
| JP2008192833A5 JP2008192833A5 (ja) | 2010-02-25 |
Family
ID=39676522
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007025861A Pending JP2008192833A (ja) | 2007-02-05 | 2007-02-05 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US7901997B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP2008192833A (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR20080073213A (ja) |
| TW (1) | TW200836309A (ja) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012084681A (ja) * | 2010-10-12 | 2012-04-26 | Shinko Electric Ind Co Ltd | 電子部品装置及びその製造方法と配線基板 |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8143096B2 (en) * | 2008-08-19 | 2012-03-27 | Stats Chippac Ltd. | Integrated circuit package system flip chip |
| TWI559826B (zh) * | 2015-12-14 | 2016-11-21 | 財團法人工業技術研究院 | 接合結構及可撓式裝置 |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005217388A (ja) * | 2004-01-30 | 2005-08-11 | Phoenix Precision Technology Corp | 半導体パッケージ基板のプリ半田構造及びその製法 |
| JP2006100552A (ja) * | 2004-09-29 | 2006-04-13 | Rohm Co Ltd | 配線基板および半導体装置 |
| JP2007201469A (ja) * | 2006-01-23 | 2007-08-09 | Samsung Electro Mech Co Ltd | 半導体パッケージ用プリント基板及びその製造方法 |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3121734B2 (ja) | 1994-11-18 | 2001-01-09 | 新日本製鐵株式会社 | 半導体装置及び半導体装置バンプ用金属ボール |
| US20030001286A1 (en) * | 2000-01-28 | 2003-01-02 | Ryoichi Kajiwara | Semiconductor package and flip chip bonding method therein |
| JP3829325B2 (ja) * | 2002-02-07 | 2006-10-04 | 日本電気株式会社 | 半導体素子およびその製造方法並びに半導体装置の製造方法 |
| US20040084206A1 (en) * | 2002-11-06 | 2004-05-06 | I-Chung Tung | Fine pad pitch organic circuit board for flip chip joints and board to board solder joints and method |
| US7880317B2 (en) * | 2005-11-22 | 2011-02-01 | Sony Corporation | Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing semiconductor device |
-
2007
- 2007-02-05 JP JP2007025861A patent/JP2008192833A/ja active Pending
-
2008
- 2008-01-24 KR KR1020080007383A patent/KR20080073213A/ko not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2008-01-29 US US12/021,664 patent/US7901997B2/en active Active
- 2008-02-04 TW TW097104164A patent/TW200836309A/zh unknown
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005217388A (ja) * | 2004-01-30 | 2005-08-11 | Phoenix Precision Technology Corp | 半導体パッケージ基板のプリ半田構造及びその製法 |
| JP2006100552A (ja) * | 2004-09-29 | 2006-04-13 | Rohm Co Ltd | 配線基板および半導体装置 |
| JP2007201469A (ja) * | 2006-01-23 | 2007-08-09 | Samsung Electro Mech Co Ltd | 半導体パッケージ用プリント基板及びその製造方法 |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012084681A (ja) * | 2010-10-12 | 2012-04-26 | Shinko Electric Ind Co Ltd | 電子部品装置及びその製造方法と配線基板 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20080073213A (ko) | 2008-08-08 |
| TW200836309A (en) | 2008-09-01 |
| US7901997B2 (en) | 2011-03-08 |
| US20080188040A1 (en) | 2008-08-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101607790B1 (ko) | 반도체 장치 제조 방법 및 반도체 장치 | |
| JP2006279062A (ja) | 半導体素子および半導体装置 | |
| JP2007128982A (ja) | 半導体バンプ接続構造体及びその製造方法 | |
| JP5004549B2 (ja) | 電子部品の基板への搭載方法及びはんだ面の形成方法 | |
| JPH09260428A (ja) | 半導体装置及びその実装方法 | |
| JP2001085470A (ja) | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 | |
| JP5919641B2 (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法並びに電子装置 | |
| JP2015008254A (ja) | 回路基板、回路基板の製造方法、半導体装置の製造方法および実装基板の製造方法 | |
| JP2009009994A (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| JP2008192833A (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP2007243106A (ja) | 半導体パッケージ構造 | |
| JP2006351935A (ja) | 半導体チップ実装基板及びそれを用いた半導体装置 | |
| JP2010219507A (ja) | はんだバンプ、半導体チップ、半導体チップの製造方法、導電接続構造体、および導電接続構造体の製造方法 | |
| JP5113793B2 (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| JP2010123676A (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法、半導体装置 | |
| JP2004079891A (ja) | 配線基板、及び、配線基板の製造方法 | |
| JP4065264B2 (ja) | 中継基板付き基板及びその製造方法 | |
| JP4172238B2 (ja) | 電子部品の実装構造 | |
| JP2007048987A (ja) | フリップチップ実装方法 | |
| JP2008244277A (ja) | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 | |
| JP2007335652A (ja) | 半導体装置、回路基板及びそれらの製造方法 | |
| JPH10116927A (ja) | 接続端子及びその形成方法 | |
| JP2012028437A (ja) | 半導体装置とその製造方法 | |
| JP3078516B2 (ja) | 中継基板、ic搭載基板と中継基板の接続体、ic搭載基板と中継基板と取付基板とからなる構造体 | |
| JP4946965B2 (ja) | 電子部品実装装置及びその製造方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100106 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20100106 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20111109 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20111115 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20120313 |