EP4137752A1 - Verfahren und vorrichtung zur steuerung einer deckenmaschine, deckenmaschine und lesbares speichermedium - Google Patents
Verfahren und vorrichtung zur steuerung einer deckenmaschine, deckenmaschine und lesbares speichermedium Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP4137752A1 EP4137752A1 EP21818612.0A EP21818612A EP4137752A1 EP 4137752 A1 EP4137752 A1 EP 4137752A1 EP 21818612 A EP21818612 A EP 21818612A EP 4137752 A1 EP4137752 A1 EP 4137752A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- human
- angle
- air conditioner
- type air
- ceiling embedded
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F11/00—Control or safety arrangements
- F24F11/70—Control systems characterised by their outputs; Constructional details thereof
- F24F11/72—Control systems characterised by their outputs; Constructional details thereof for controlling the supply of treated air, e.g. its pressure
- F24F11/79—Control systems characterised by their outputs; Constructional details thereof for controlling the supply of treated air, e.g. its pressure for controlling the direction of the supplied air
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F1/00—Room units for air-conditioning, e.g. separate or self-contained units or units receiving primary air from a central station
- F24F1/0007—Indoor units, e.g. fan coil units
- F24F1/0011—Indoor units, e.g. fan coil units characterised by air outlets
- F24F1/0014—Indoor units, e.g. fan coil units characterised by air outlets having two or more outlet openings
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F1/00—Room units for air-conditioning, e.g. separate or self-contained units or units receiving primary air from a central station
- F24F1/0007—Indoor units, e.g. fan coil units
- F24F1/0043—Indoor units, e.g. fan coil units characterised by mounting arrangements
- F24F1/0047—Indoor units, e.g. fan coil units characterised by mounting arrangements mounted in the ceiling or at the ceiling
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F11/00—Control or safety arrangements
- F24F11/62—Control or safety arrangements characterised by the type of control or by internal processing, e.g. using fuzzy logic, adaptive control or estimation of values
- F24F11/63—Electronic processing
- F24F11/64—Electronic processing using pre-stored data
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F2120/00—Control inputs relating to users or occupants
- F24F2120/10—Occupancy
- F24F2120/12—Position of occupants
Definitions
- the present application relates to the technical field of an air conditioner, and in particular to a control method of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner, a device, a ceiling embedded-type air conditioner and a readable storage medium.
- the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner is installed on the ceiling of the room.
- the traditional ceiling embedded-type air conditioner can only swing back and forth or guide the airflow in a fixed angle, and cannot automatically adjust the direction of guiding airflow according to the position of the human, thus different actual needs cannot be met.
- the above content is only used to assist in understanding the technical solution of the present application and is not considered to be the prior art.
- the main objective of the present application is to provide a control method of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner, a device, a ceiling embedded-type air conditioner and a readable storage medium, to solve the problem that the existing ceiling embedded-type air conditioner cannot automatically adjust the direction of guiding airflow according to the position of the human.
- the present application provides a control method of a ceiling embedded-type air conditioner, applied to a ceiling embedded-type air conditioner including a millimeter wave human sense module and a plurality of individual deflectors, wherein the plurality of individual deflectors are configured to divide a blowing scope of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner into a corresponding plurality of blowing angle ranges, wherein the control method of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner includes:
- the determining the target swing angle according to the first angle, the first distance and the first included angle includes:
- the method before the detecting, by the millimeter wave human sense module, the first angle at which the human deviates from the angular bisector of the target blowing angle range corresponding to the target deflector, the first distance from the human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner, the first included angle between the connection line from the human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner and the plumb line, the method further includes:
- the method further includes:
- the method before the detecting, by the millimeter wave human sense module, the first angle at which the human deviates from the angular bisector of the target blowing angle range corresponding to the target deflector, the first distance from the human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner, the first included angle between the connection line from the human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner and the plumb line, wherein the target deflector is in the blowing to human mode, the method further includes:
- the method further includes:
- the present application further provides a control device of a ceiling embedded-type air conditioner, including: a memory, a processor and a control program of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner stored in the memory and running on the processor, wherein the control program of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner, when executed by the processor, can execute the control method of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner mentioned above.
- the present application further provides a ceiling embedded-type air conditioner, including a millimeter wave human sense module and N individual deflectors, wherein the N individual deflectors can divide a blowing scope of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner into N blowing angle ranges
- the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner includes: a memory, a processor and a control program of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner stored in the memory and running on the processor, wherein the control program of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner, when executed by the processor, can implement the control method of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner mentioned above.
- the present application also provides a computer readable storage medium, wherein a control program of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner is stored in the computer readable storage medium, the control program of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner, when executed by a processor, can implement the control method of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner mentioned above.
- the millimeter wave human sense module detects a first angle at which a human deviates from an angular bisector of a target blowing angle range corresponding to a target deflector, a first distance from the human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner, a first included angle between a connection line from the human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner and a plumb line.
- the target deflector is in a blowing to human mode.
- a target swing angle is determined according to the first angle, the first distance and the first included angle, and the target deflector is controlled according to the target swing angle to guide the airflow the human.
- the position of the human is detected by the millimeter wave human sense module, and the target deflector is controlled according to the target swing angle, to guide the airflow the human, to realize the effect of the airflow moving with a movement of the human, to improve the comfort of users.
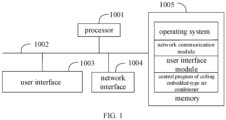
- FIG. 1 is a schematic structural view of a ceiling embedded-type air conditioner in a hardware operating environment according to some embodiments of the present application.
- the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner may include: a processor 1001 such as a central processing unit (CPU), a network interface 1004, a user interface 1003, a memory 1005 and a communication bus 1002.
- the communication bus 1002 is used to realize the connection communication among these components.
- the user interface 1003 may include a display, an input unit such as a keyboard.
- the user interface 1003 may further include a standard wired interface and a standard wireless interface.
- the network interface 1004 may include a standard wired interface, a standard wireless interface such as a Wi-Fi port.
- the memory 1005 can be a high-speed RAM memory or a non-volatile memory such a disk memory.
- the memory 1005 can be a storage device independent of processor 1001.
- the structure of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner shown in FIG.1 does not limit the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner and the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner may include more or fewer components than shown in FIG. 1 , or a combination of some components, or differently arranged components shown in FIG. 1 .
- the memory 1005 may include an operating system, a network communication module, a user interface module and a computer control program.
- the network interface 1004 is mainly used to connect to the background server for communication.
- the user interface 1003 is mainly used to connect to the client (user client) for communication.
- the processor 1001 can be used to call the control program of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner stored in memory 1005.
- the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner includes a memory 1005, a processor 1001 and a control program of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner stored in the memory 1005 and executable on the processor 1001.
- the processor 1001 when calling the control program of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner stored in memory 1005 executes the following operations:
- the determining the target swing angle according to the first angle, the first distance and the first included angle includes:
- the method before the detecting, by the millimeter wave human sense module, the first angle at which the human deviates from the angular bisector of the target blowing angle range corresponding to the target deflector, the first distance from the human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner, the first included angle between the connection line from the human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner and the plumb line, the method further includes:
- the method further includes: in response that no human is in the target blowing angle range, controlling the target deflector to guide the airflow in a preset swing angle.
- the method further includes:
- the method before the detecting, by the millimeter wave human sense module, the first angle of the human deviates from the angular bisector of the target blowing angle range corresponding to the target deflector, the first distance from the human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner, the first included angle between the connection line from the human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner and the plumb line, wherein the target deflector is in the blowing to human mode, the method further includes:
- the method further includes:
- the present application also provides a control method of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner.
- FIG.2 is a flowchart of the control method of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner according to some embodiments of the present application.
- the control method of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner can be applied to a ceiling embedded-type air conditioner equipped with a millimeter wave human sense module and a plurality of individual deflectors.
- the plurality of individual deflectors divide a blowing scope of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner into a corresponding plurality of blowing angle ranges.
- control method of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner includes: operation S 10, detecting, by the millimeter wave human sense module, a first angle at which a human deviates from an angular bisector of a target blowing angle range corresponding to a target deflector, a first distance from the human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner, a first included angle between a connection line from the human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner and a plumb line.
- the target deflector is in a blowing to human mode.
- the traditional ceiling embedded-type air conditioner can only swing back and forth or blow in a fixed angle, and cannot automatically adjust the direction of the airflow according to the position of the human, thus various actual needs cannot be met.
- the present application provides a control method of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner to detect the position information of the human by the millimeter wave human sense module, and determine an angle of a deflector according to the position information of the human, and can accurately determine the position information of the user, and control dynamically the deflector to swing according to the position of the user. In this way, the effect of the airflow moving with the movement of the human is realized and the comfort of the users is improved.
- the millimeter wave human sense module in the embodiment may include a millimeter wave radar.
- the millimeter wave radar is working in millimeter wave band.
- the millimeter wave generally refers to the wave in the frequency domain of 30 GHz ⁇ 300 GHz and the wavelength of 1 mm ⁇ 10 mm.
- the millimeter wave radar has a small size, a light weight and a high spatial resolution.
- the millimeter wave radar has a strong ability to penetrate fog, smoke, dust, and is in 24-hour service (except heavy rain days).
- the millimeter wave radar has a better ability in anti-interfering and anti-stealth than other microwave radars.
- the millimeter wave radar can identify very small targets and identify multiple targets at the same time.
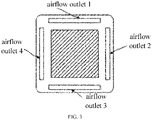
- the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner includes a plurality of independent deflectors, and each deflector is located in a separate outlet. Taking the center point of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner as a center of a circle, the plurality of independent deflectors divide the blowing scope of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner into a corresponding plurality of blowing angle ranges. Each deflector corresponds to a blowing angle range, and the complete blowing scope of each deflector can cover the corresponding blowing angle range. There are more than one deflector. It should be noted that when dividing the blowing angle ranges, the blowing scope can be averaged to be a corresponding plurality of blowing angle ranges, or can be divided in a certain rule. The specific division of the blowing scope is not limited herein.
- each deflector is independent in the embodiment, which can be realized by separately disposing each deflector on different machines.
- each deflector can support various airflow output modes simultaneously, which include but are not limited to any one of a standard mode, a swing mode, a blow avoiding human mode, a blow toward human mode and a custom mode.
- the blowing to human mode means that the deflector swings with the movement of the human, to guide the airflow to human.
- the deflector is regarded as a target deflector.
- the millimeter wave human sense module will detect the position information of the human in the blowing angle range corresponding to the target deflector.
- the position information of the human includes a first angle, a first distance and a first included angle.
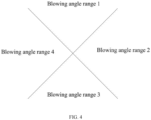
- Each blowing angle range refers to an angle on a horizontal plane, and the angle bisector of each angle refers to the angle bisector of the blowing angle range.
- the first angle ⁇ refers to an included angle between the connection line from the human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner and the angle bisector of the target blowing angle range corresponding to the target deflector.
- the first distance d 0 refers to a distance from the human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner, that is, a length of the connection line from the human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner.
- the first included angle ⁇ refers to an included angle between the connection line from the human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner and the plumb line.
- the feature point of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner can be set as a central point of the millimeter wave human sense module or a central point of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner.
- the millimeter wave human sense module detects the feature point of the human and the feature point of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner to determine a relative position of the human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner.
- the first angle refers to an angle at which the feature point of the human deviates from the angular bisector of the target blowing angle range corresponding to the target deflector.
- the first distance refers to a distance from the feature point of the human to the feature point of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner.
- the first included angle refers to an included angle between the connection line from the feature point of the human to the feature point of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner and the plumb line.
- the operation S20 is to determine a target swing angle of the target deflector according to the first angle, the first distance and the first included angle.
- the operation S20 includes: operation S21, determining a projection distance of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner and the human on the plumb line to be a perpendicular distance, according to the first distance d 0 and the first included angle ⁇ ; operation S22, determining a projection distance of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner and the human on the angular bisector to be a horizontal distance, according to the first distance d 0 and the first included angle ⁇ ; and operation S23, determining a target swing angle of the target deflector according to the perpendicular distance and the horizontal distance. It can be understood that the present application does not limit the execution sequence of the operation S21 and operation S22.
- the projection distance, i.e, the perpendicular distance h, of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner and the human on the plumb line can be determined according to the first distance d 0 , the first included angle ⁇ and a first formula.
- the projection distance, i.e, the horizontal distance, of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner and the human on the angular bisector can be determined according to the first distance d 0 , the first included angle ⁇ and a second formula.
- Operation S30 controlling the target deflector according to the target swing angle, to guide the airflow to the human.
- the target deflector after the target swing angle of the target deflector is determined, that is, the target deflector can be controlled to the target swing angle, to guide the airflow to the human.
- the millimeter wave human sense module may detect in real-time the position information of the human.
- the millimeter wave human sense module will obtain the first angle, the first distance and the first included angle again, then to determine a new swing angle of the target deflector according to the first angle, the first distance and the first included angle, to realize that the airflow moves with the movement of the human.
- the millimeter wave human sense module detects the first angle at which the human deviates from the angular bisector of the target blowing angle range corresponding to the target deflector, the first distance from the human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner, the first included angle between the connection line from the human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner and the plumb line.
- the first distance from the human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner is the length of the connection line from the human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner.
- the target deflector is in a blowing to human mode.
- a target swing angle is determined according to the first angle, the first distance and the first included angle and the target deflector is controlled to operate according to the target swing angle, to guide the airflow to the human.
- the position of the human is detected by the millimeter wave human sense module, and the target deflector is controlled to operate according to the target swing angle, to guide the airflow to the human, to realize the effect of the airflow moving with a movement of the human and to improve the comfort of users.
- control method of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner before the operation S10, the control method of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner further includes: operation S11, detecting the number of humans in the target blowing angle.
- the number of humans in the target blowing angle range can be detected by the millimeter wave human sense module.
- the operation S10 is executed.
- a heartbeat signal in the target blowing angle range can be detected by the millimeter wave human sense module, and the number of the humans can be determined according to the number of heartbeat signals, or a respiration signal in the target blowing angle range can be detected by the millimeter wave human sense module, and the number of the humans can be determined according to the number of respiration signals.
- the method before the operation S11, the method further includes: operation S12, in response to there being no humans in the target blowing angle range, controlling the target deflector to guide the airflow in a preset swing angle.
- the preset swing angle is previously set by a maintenance operator. At this angle, the deflector can achieve the maximum airflow output through the same fan speed. If there is no human in the target blowing angle range, it means that there is no human in the target blowing angle range, and there is no need to guide the airflow to move with the movement of the human. Therefore, the target deflector can be controlled to guide the airflow in the preset swing angle, to improve the efficiency of guiding airflow of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner.
- the method further includes:
- the millimeter wave human sense module in response to there being more than or equal to two humans in the target blowing angle range, detects the first angle at which each human in the target blowing angle range deviates from the angular bisector of the target blowing angle range corresponding to the target deflector, the first distance from each human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner, the first included angle between the connection line from each human to the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner and the plumb line.
- step S20 the swing angle of each human is obtained according to the position information of each human; swing angles are compared to determine a max-angle and a mini-angle of swing angles; and the target deflector is controlled to swing between the max-angle and the mini-angle to guide the airflow, to each human in the target blowing angle range, and the round-trip path of the target deflector is shortened, to shorten the round-trip time, and to avoid the airflow from being given to an unmanned area. In this way, the airflow is guided to the human as much and as fast as possible and the comfort of users is improved.
- control method of the air ceiling conditioner of the present application before the operation S 10, the method further includes:
- each deflector is independent.
- Each deflector can support different airflow output modes at the same time.
- the modes include but are not limited to any one of the standard mode, the swing mode, the blowing avoiding human mode, the blowing to human mode and the custom mode.
- the blowing to human mode refers to that the deflector swings following the movement of humans, to guide the airflow to the human.
- the custom mode refers to that the deflector guides the airflow according to the angle set by the user.
- the method further includes:
- the standard mode refers to that the deflector is fixed to guide the airflow in a preset swing angle, at this angle, the deflector can achieve a maximum airflow output through the same fan speed.
- the swing mode refers to that the deflector swings between a first limit angle and a second limit angle to guide the airflow.
- the limit angle is defined by a mechanical structure, so that the deflector can only swing between the first limit angle and the second limit angle.
- the blowing to human mode refers to that the deflector guides airflow in the first limit angle.
- the first limit angle is in a direction away from the human, so that a direction of guiding the airflow is away from the human.
- different deflectors can support different airflow output modes at the same time to meet the multiple airflow output requirements of the users.
- the present application also provides a computer readable storage medium, on which a control program of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner is stored, the operations realized when the control program of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner is executed by the processor can be referred to the above embodiments of the control method of the ceiling embedded-type air conditioner, which will not be repeated herein.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Fuzzy Systems (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Air Conditioning Control Device (AREA)
- Structures Of Non-Positive Displacement Pumps (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010503930.4A CN113757974B (zh) | 2020-06-04 | 2020-06-04 | 天花机控制方法、装置、天花机及可读存储介质 |
| PCT/CN2021/075858 WO2021244064A1 (zh) | 2020-06-04 | 2021-02-07 | 天花机控制方法、装置、天花机及可读存储介质 |
Publications (4)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP4137752A1 true EP4137752A1 (de) | 2023-02-22 |
| EP4137752A4 EP4137752A4 (de) | 2023-10-11 |
| EP4137752C0 EP4137752C0 (de) | 2025-06-18 |
| EP4137752B1 EP4137752B1 (de) | 2025-06-18 |
Family
ID=78783948
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP21818612.0A Active EP4137752B1 (de) | 2020-06-04 | 2021-02-07 | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur steuerung einer deckenmaschine, deckenmaschine und lesbares speichermedium |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP4137752B1 (de) |
| CN (1) | CN113757974B (de) |
| WO (1) | WO2021244064A1 (de) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116499112A (zh) * | 2022-01-21 | 2023-07-28 | 青岛海尔空调器有限总公司 | 用于控制空调导风板的方法及装置、空调、存储介质 |
| CN114754419B (zh) * | 2022-03-31 | 2023-11-17 | 青岛海尔空调器有限总公司 | 空调设备控制方法、装置、电子设备及存储介质 |
| CN115183434B (zh) * | 2022-08-22 | 2023-07-21 | 宁波奥克斯电气股份有限公司 | 空调控制方法、装置、空调器和计算机可读存储介质 |
| CN115451562B (zh) * | 2022-09-16 | 2024-07-30 | 宁波奥克斯电气股份有限公司 | 一种空调器摆风控制方法、控制装置和空调器 |
| CN115628477B (zh) * | 2022-10-31 | 2025-06-17 | 青岛海尔空调器有限总公司 | 顶装式空调、空调挡风板控制方法和装置 |
| CN115899837B (zh) * | 2022-12-01 | 2024-07-16 | 珠海格力电器股份有限公司 | 一种天井式空调器的控制方法、装置及天井式空调器 |
| CN119665402A (zh) * | 2023-09-21 | 2025-03-21 | 青岛海尔智慧楼宇科技有限公司 | 嵌入式空调器的控制方法、控制装置及嵌入式空调器 |
Family Cites Families (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006183974A (ja) * | 2004-12-28 | 2006-07-13 | Sanki Eng Co Ltd | 空調用吹出気流自動調整装置と空調用吹出気流の制御方法 |
| JP2015025564A (ja) * | 2013-07-24 | 2015-02-05 | パナソニック株式会社 | 空気調和機 |
| JP6386770B2 (ja) * | 2014-04-16 | 2018-09-05 | 日立ジョンソンコントロールズ空調株式会社 | 空気調和機 |
| JP6398463B2 (ja) * | 2014-08-22 | 2018-10-03 | ダイキン工業株式会社 | 空気調和装置 |
| CN104930662B (zh) * | 2015-06-25 | 2017-08-01 | 广东美的制冷设备有限公司 | 一种空调精准送风控制方法及系统 |
| CN105299829A (zh) * | 2015-10-27 | 2016-02-03 | 青岛海尔科技有限公司 | 一种调整空调运行的方法、装置及空调 |
| KR101823208B1 (ko) * | 2015-12-04 | 2018-01-29 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 공기 조화기 및 그 제어방법 |
| JP2018128155A (ja) * | 2017-02-06 | 2018-08-16 | 日立ジョンソンコントロールズ空調株式会社 | 空気調和機 |
| CN107631354A (zh) * | 2017-09-07 | 2018-01-26 | 青岛海尔空调器有限总公司 | 壁挂式空调室内机及其控制方法 |
| CN108397871B (zh) * | 2018-03-09 | 2021-05-28 | 广东美的制冷设备有限公司 | 空调器控制方法、装置、空调器和可读存储介质 |
| JP7230339B2 (ja) * | 2018-04-26 | 2023-03-01 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 空気調和装置 |
| CN109668279B (zh) * | 2018-12-19 | 2021-09-14 | 广东美的制冷设备有限公司 | 空调器的控制方法、空调器及存储介质 |
| CN109654697B (zh) * | 2018-12-29 | 2021-01-29 | 青岛海尔空调器有限总公司 | 防直吹空调的控制方法、装置、存储介质及计算机设备 |
| CN110848931A (zh) * | 2019-11-07 | 2020-02-28 | 海信(山东)空调有限公司 | 一种天花机的控制方法及天花机 |
| CN111237974B (zh) * | 2020-03-10 | 2021-03-16 | 珠海格力电器股份有限公司 | 人体定位装置及空调 |
-
2020
- 2020-06-04 CN CN202010503930.4A patent/CN113757974B/zh active Active
-
2021
- 2021-02-07 WO PCT/CN2021/075858 patent/WO2021244064A1/zh not_active Ceased
- 2021-02-07 EP EP21818612.0A patent/EP4137752B1/de active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2021244064A1 (zh) | 2021-12-09 |
| EP4137752C0 (de) | 2025-06-18 |
| CN113757974B (zh) | 2022-09-09 |
| CN113757974A (zh) | 2021-12-07 |
| EP4137752A4 (de) | 2023-10-11 |
| EP4137752B1 (de) | 2025-06-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP4137752B1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur steuerung einer deckenmaschine, deckenmaschine und lesbares speichermedium | |
| KR101886771B1 (ko) | 무선으로 서비스에 액세스하는 방법 및 장치 | |
| CN112367672B (zh) | 一种室内波束搜索与追踪方法、装置和电子设备 | |
| KR20200140866A (ko) | 다중 패널 ue에 대한 빔 표시 | |
| CN113965874A (zh) | 一种波束赋形信号发送方法及基站设备 | |
| WO2022100621A1 (zh) | 工作模式确定方法、装置、设备及存储介质 | |
| WO2022031477A1 (en) | Wireless communication network management for user devices based on real time mapping | |
| WO2022062714A1 (zh) | 抗干扰控制装置及其方法、终端设备、可读存储介质 | |
| EP3676626A1 (de) | Aus der ferne elektrisch neigbarer, streunender fokussierender passiver reflektor | |
| WO2019154063A1 (zh) | 检测系统和环境管理系统及其应用 | |
| WO2023134652A1 (zh) | 一种无线充电方法、装置和电子设备 | |
| WO2021191625A1 (en) | Uav and uav operator detector | |
| WO2022077267A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for communication management | |
| US20180239419A1 (en) | Wireless transceiver system using beam tracking | |
| CN114745669B (zh) | 跨区域活动感知方法及系统 | |
| JP7589811B2 (ja) | 制御装置、通信システム、制御方法、及びプログラム | |
| CN115334522A (zh) | 信号覆盖方法及系统 | |
| KR102743720B1 (ko) | 비행체 통제를 위한 지상 통신 장치, 동작 방법 및 컴퓨터 프로그램 | |
| JPH088814A (ja) | 移動無線通信方式 | |
| US20240251325A1 (en) | Control apparatus, communication system, control method and program | |
| US20210199959A1 (en) | Reducing interference between electromagnetic tracking systems | |
| CN107276644A (zh) | 阵列天线波束赋形方法和系统 | |
| KR102192557B1 (ko) | 송신 시스템, 송신 시스템 제어 장치 및 방법 | |
| WO2025179486A1 (en) | Cluster based object sensing | |
| CN115150842B (zh) | 一种通信方法以及相关设备 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE INTERNATIONAL PUBLICATION HAS BEEN MADE |
|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: REQUEST FOR EXAMINATION WAS MADE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20221117 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| DAV | Request for validation of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| A4 | Supplementary search report drawn up and despatched |
Effective date: 20230907 |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: F24F 11/64 20180101ALI20230901BHEP Ipc: F24F 1/0014 20190101ALI20230901BHEP Ipc: F24F 1/0047 20190101ALI20230901BHEP Ipc: F24F 11/54 20180101ALI20230901BHEP Ipc: F24F 120/12 20180101ALI20230901BHEP Ipc: F24F 11/65 20180101ALI20230901BHEP Ipc: F24F 11/79 20180101AFI20230901BHEP |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: F24F 11/64 20180101ALI20250324BHEP Ipc: F24F 1/0014 20190101ALI20250324BHEP Ipc: F24F 1/0047 20190101ALI20250324BHEP Ipc: F24F 11/54 20180101ALI20250324BHEP Ipc: F24F 120/12 20180101ALI20250324BHEP Ipc: F24F 11/65 20180101ALI20250324BHEP Ipc: F24F 11/79 20180101AFI20250324BHEP |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20250408 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 602021032549 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| U01 | Request for unitary effect filed |
Effective date: 20250710 |
|
| U07 | Unitary effect registered |
Designated state(s): AT BE BG DE DK EE FI FR IT LT LU LV MT NL PT RO SE SI Effective date: 20250717 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250919 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250918 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250618 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250918 |