EP3372998B1 - Sensor and method for measuring content of hydrogen in metal melt - Google Patents
Sensor and method for measuring content of hydrogen in metal melt Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP3372998B1 EP3372998B1 EP15908135.5A EP15908135A EP3372998B1 EP 3372998 B1 EP3372998 B1 EP 3372998B1 EP 15908135 A EP15908135 A EP 15908135A EP 3372998 B1 EP3372998 B1 EP 3372998B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- metal melt
- electrode
- sensor
- measured
- hydrogen content
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N27/00—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of electric, electrochemical, or magnetic means
- G01N27/26—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of electric, electrochemical, or magnetic means by investigating electrochemical variables; by using electrolysis or electrophoresis
- G01N27/403—Cells and electrode assemblies
- G01N27/406—Cells and probes with solid electrolytes
- G01N27/411—Cells and probes with solid electrolytes for investigating or analysing of liquid metals
- G01N27/4112—Composition or fabrication of the solid electrolyte
- G01N27/4114—Composition or fabrication of the solid electrolyte for detection of gases other than oxygen
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N33/00—Investigating or analysing materials by specific methods not covered by groups G01N1/00 - G01N31/00
- G01N33/0004—Gaseous mixtures, e.g. polluted air
- G01N33/0009—General constructional details of gas analysers, e.g. portable test equipment
- G01N33/0027—General constructional details of gas analysers, e.g. portable test equipment concerning the detector
- G01N33/0036—General constructional details of gas analysers, e.g. portable test equipment concerning the detector specially adapted to detect a particular component
- G01N33/005—H2
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N27/00—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of electric, electrochemical, or magnetic means
- G01N27/26—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of electric, electrochemical, or magnetic means by investigating electrochemical variables; by using electrolysis or electrophoresis
- G01N27/28—Electrolytic cell components
- G01N27/30—Electrodes, e.g. test electrodes; Half-cells
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N27/00—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of electric, electrochemical, or magnetic means
- G01N27/26—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of electric, electrochemical, or magnetic means by investigating electrochemical variables; by using electrolysis or electrophoresis
- G01N27/28—Electrolytic cell components
- G01N27/30—Electrodes, e.g. test electrodes; Half-cells
- G01N27/301—Reference electrodes
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N33/00—Investigating or analysing materials by specific methods not covered by groups G01N1/00 - G01N31/00
- G01N33/20—Metals
- G01N33/202—Constituents thereof
- G01N33/2022—Non-metallic constituents
- G01N33/2025—Gaseous constituents
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a hydrogen measurement sensing technology, in particular to a sensor and measurement method for measuring hydrogen content in metal melt.
- hydrogen is a harmful element in metal materials and can cause metal materials to produce defects such as hydrogen embrittlement, porosity and pinholes.
- Timely measurement of hydrogen content in metals and proper dehydrogenation after information feedback can avoid various hydrogen-induced defects in metal materials.
- EP0544281 TYK discloses a device for measuring hydrogen content in aluminum melt by a solid proton conductor.
- the hydrogen content of the metal melt of 1000 DEG C or below such as aluminum melt can be measured.
- the solid proton conductor hydrogen sensor can be used for measuring hydrogen content in gas
- the reference electrode and the electrode to be measured of the solid proton conductor sensor are both external porous electrodes.
- a reference compound with certain hydrogen partial pressure is stuffed into the reference electrode, or gas with certain hydrogen partial pressure is introduced, and the electrode to be measured is in contact with atmosphere to be measured, so that a concentration cell is obtained.
- a potentiometer is used for measuring the electromotive force of the concentration cell.
- the hydrogen partial pressure of the reference electrode is known (the hydrogen partial pressure of the reference electrode can be higher or lower than that of the electrode to be measured), so that the hydrogen partial pressure of the atmosphere to be measured can be calculated, and the hydrogen content is calculated.
- a solid proton conductor is used as the main body of the sensor probe, the solid proton conductor and the metal melt are isolated by a ceramic bushing, a ceramic cover or a porous material, and thereof, a gas chamber is created between the proton conductor and the metal melt.
- the hydrogen partial pressure of atmosphere in a porous material is equilibrium hydrogen partial pressure of the metal melt, and the hydrogen content in the aluminum melt can be obtained through calculation.
- US2005/0252789 proposes that a metal-hydrogen material with stable chemical stability such as ⁇ Ti- ⁇ Ti, ⁇ Zr- ⁇ Zr and ⁇ Hf- ⁇ Hf is taken as the reference compound of the sensor.
- the interface between the reference compound and the solid electrode can maintain chemical stability at higher temperature, influence of oxygen on the solid proton conductor is reduced, and stable hydrogen partial pressure is provided.
- the patent does not refer to the measurement method of hydrogen content in detail.
- US2009/0139876 discloses a device for measuring hydrogen content in metal melt by using a solid proton conductor and proposes a method for restoring the solid electrolyte of the proton conductor by using a water absorbing material such as AlN and BN.
- the equilibrium hydrogen partial pressure established between the metal melt and the gas chamber in the probe is measured by using the hydrogen concentration cell of the solid proton conductor.
- the method has the following disadvantages that: (1) time for establishing equilibrium between the metal melt and the gas chamber is long, which results in low sensor response speed; (2) the material for establishing the gas chamber in the sensor is usually the ceramic cover or fiber materials, water is easy to adhere to the surfaces of such materials, water reacts with the metal melt to produce a large amount of hydrogen during measurement, and the accuracy of measurement results is affected; and (3) during multiple measurement processes, the gas chamber is easy to block by metal and metal oxides adhered to the surface of the probe, so that establishment of equilibrium is slow, response speed is reduced and even measurement accuracy is affected. Further hydrogen sensors are known from EP2827137 A1 and JP2014160006 A .
- the present invention provides a sensor and measurement for measuring hydrogen content in metal melt.
- the invention is defined by the appended claims.
- a proton conductor in the sensor is in direct contact with the metal melt to form an electrode to be measured. It is not necessary to establish hydrogen solubility equilibrium with the metal melt via gas for the electrode to be measured, but the proton conductor is adopted to directly establish electrochemical equilibrium between a reference compound and hydrogen in the metal melt.
- a sensor for measuring hydrogen content in metal melt which comprises a solid proton conductor element, a reference electrode, a quasi-electrode to be measured, a reference compound, a through pipe and an insulating ceramic adhesive, wherein the through pipe and the solid proton conductor element are connected through the insulating ceramic adhesive to form an inner space, the surface located in the space, of the solid proton conductor element, is an inner surface, and the surface exposed outside is an outer surface; the reference porous electrode is coated to the inner surface of the solid proton conductor element, and the quasi-electrode to be measured is the outer surface of the solid proton conductor element; and the reference compound is gas, placed in the inner space and is in contact with the reference porous electrode.
- the quasi-electrode to be measured is in contact with metal melt during hydrogen measurement, and the contact surface forms the electrode to be measured.
- the sensor for measuring hydrogen content in metal melt also comprises gas guide pipe and a three-way clamp.
- the reference compound is gas
- the three-way clamp is connected with the upper part of the through pipe
- the gas guide pipe is inserted into the inner space formed by the through pipe, the insulating ceramic adhesive and the solid proton conductor element through the three-way clamp and is connected to the reference porous electrode;
- the bottom end of the gas guide pipe directly faces to the reference electrode and the solid proton conductor element, the bottom end of the gas guide pipe is a blind end, a side opening acts as a gas outlet which has the effect of preventing pressure change caused by the gas reference compound rushing at the reference porous electrode or the proton conductor element and improving measurement accuracy.
- the sensor for measuring hydrogen content in metal melt can also comprise a reference electrode cable.
- the reference electrode cable When the reference compound is a gas, the reference electrode cable is inserted into the through pipe through the three-way clamp, electrically connected with the reference porous electrode and externally connected to a measuring circuit; when, in examples not covered by the claimed invention, the reference compound is liquid or solid, a reference electrode cable penetrates through the insulating ceramic adhesive, is electrically connected with the reference porous electrode and is externally connected to the measuring circuit.
- the gas guide pipe is made of corundum, quartz, zirconium oxide, stainless steel, nickel-chromium alloy or iron-chromium-aluminum alloy.
- the sensor structure also comprises a reference electrode cable.
- the three-way clamp is made of stainless steel, copper, Teflon, nylon or polyurethane.
- the reference electrode cable is made of metal platinum, gold, silver, nickel-chromium alloy, iron-chromium-aluminum alloy or stainless steel.
- the sensor structure for measuring hydrogen content in metal melt comprises an inert material of Al 2 O 3 , YSZ or Y 2 O 3 ; and the inert material is stuffed between the reference compound and the insulating ceramic adhesive.
- the solid proton conductor element can adopt a tubular, spherical, flaky, discoid, cubic or cylindrical structure and is made of a perovskite or complex perovskite structure material.
- the reference electrode is made of silver, platinum or gold.
- the insulating ceramic adhesive is an alumina-based material.
- the reference compound is gas, liquid or solid, wherein the gas comprises Ar-H 2 , N 2 -H 2 , He-H 2 , O 2 -H 2 O or N 2 -NH 3 gas doped or undoped with one or more inert gases, the liquid comprises Li-LiH, and the solid comprises Y-H, Ti-H Zr-H or Sc-H.
- the insulating ceramic adhesive is used to seal the reference compound to the side of the reference electrode.
- the through pipe is made of corundum, quartz, graphite, stainless steel, Theron, SiC or LaCrO 3 and acts as a support and a gas path.
- f [H] is the activity coefficient of hydrogen in the metal melt
- w [H] is the percentage by mass of hydrogen in the metal melt.
- S 0 is the saturated solubility of hydrogen (ml/100 g), and K is a constant produced by unit transformation. Because the saturated solubility S 0 of most of metals is known thermodynamic data or thermodynamic data which can be calculated, the standard Gibbs free energy ⁇ G ⁇ for hydrogen dissolving in the metal melt can be calculated.
- the standard Gibbs free energy ⁇ G ⁇ for hydrogen dissolving in the metal melt is only related to the kind and the temperature of the metal melt and does not change along with hydrogen content in the metal melt, when hydrogen is saturated in the metal melt, the standard Gibbs free energy ⁇ G ⁇ for hydrogen dissolving in the metal melt is the same as that in unsaturation.
- the hydrogen content S of the metal melt can be calculated. According to different natures of the selected solid proton conductor and the metal melt to be measured, the formula (14) can be corrected according to experiment results.
- the sensor and measurement method for measuring hydrogen content in metal melt disclosed by the present invention have the beneficial effects that
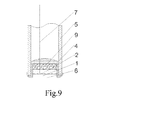
- 1 Solid proton conductor element; 2. Reference porous electrode; 3. Gas guide pipe; 4. Insulating ceramic adhesive; 5. Through pipe; 6. Quasi-electrode to be measured; 7. Reference electrode cable; 8. Solid reference compound; 9. Inert material; 100. Electrode to be measured; 101. Metal melt to be measured; 102. Corrosion-resistant electrode; 103. Cable; 104. Three-way clamp; 105. Gas outlet; 106; Gas inlet.
- the sensor for measuring hydrogen content in aluminum melt comprises a CaZr 0.9 In 0.1 O 3- ⁇ solid proton conductor element 1, a reference porous electrode 2, a quasi-electrode to be measured 6, a reference compound Ar-H 2 , a stainless steel gas guide pipe 3, a corundum through pipe 5, an alumina-based insulating ceramic adhesive 4 and a Teflon three-way clamp 104, wherein the solid proton conductor element 1 adopts a tubular structure and is made of perovskite, one end is sealed by the alumina-based insulating ceramic adhesive 4, the through pipe 5 and the solid proton conductor element 1 are connected through the insulating ceramic adhesive 4 to form an inner space, the surface located in the space, of the solid proton conductor element 1 is an inner surface, and the surface exposed outside is an outer surface; the reference porous electrode 2 is coated to the inner surface of the solid proton conductor element 1 and the alumina-based insulating ceramic adhesive 4, and the
- the reference porous electrode is made of porous platinum.
- the mole hydrogen content is 1.00%.
- S 0 is the saturated solubility of hydrogen (ml/100 g), and K is a constant produced by unit transformation. Because the saturated solubility S 0 of most of metals is known thermodynamic data or thermodynamic data which can be calculated, the standard Gibbs free energy ⁇ G ⁇ for hydrogen dissolving in the metal melt can be calculated.
- the standard Gibbs free energy ⁇ G ⁇ for hydrogen dissolving in the metal melt is only related to the kind and the temperature of the metal melt and does not change along with hydrogen content in the metal melt, when hydrogen is saturated in the metal melt, the standard free energy ⁇ G ⁇ for hydrogen dissolving in the metal melt is the same as that in unsaturation.
- the sensor for measuring hydrogen content in aluminum melt is the same as that in the embodiment 1, as shown in Figure 3 .
- the sensor structure also comprises a reference electrode cable 7 which is made of metal platinum.
- the reference electrode cable 7 is inserted into the quartz through pipe 5 through the copper three-way clamp 104, is connected to the gold reference porous electrode 2 and is externally connected to a measuring circuit;
- the gas guide pipe is made of corundum;
- the solid proton conductor element 1 is made of CaZr 0.9 Sc 0.1 O 3- ⁇ ;
- the three-way clamp 104 is made of copper;
- the through pipe is made of quartz;
- the reference porous electrode is made of porous gold.
- the method for measuring hydrogen content in metal melt by using the sensor comprises the following process steps of (1) inserting the sensor and a graphite corrosion-resistant electrode into the aluminum melt of 750 DEG C, and making sure that the solid proton conductor element is fully immersed into the aluminum melt, the quasi-electrode to be measured is in direct contact with the metal melt and the contact surface is the electrode to be measured; (2) connecting a potentiometer and the reference electrode cable to the graphite corrosion-resistant electrode through a platinum wire, and measuring the potential difference between the reference electrode and the electrode to be measured; and (3) calculating the stabilized hydrogen content S of the metal melt according to the measured potential difference, the temperature of the metal melt and the saturated solubility of hydrogen in the metal melt to be 0.113ml/100gAl.
- the sensor for measuring hydrogen content in aluminum melt is the same as that in the embodiment 1, as shown in Figure 4 .
- the difference lies in that: the solid proton conductor element 1 used in the sensor structure adopts a flaky structure; the through pipe 5 is made of stainless steel; one end being contact with the proton conductor 1, of the nickel-chromium gas guide pipe 3 is a blind end, a side opening is used as a gas outlet, and the vertical distance between the gas outlet and the top end of the solid proton conductor is 2-5 mm; the gas guide material is made of nickel-chromium alloy; and the reference gas is He-H 2 , and the mole hydrogen content is 1.00%.
- the method for measuring hydrogen content in metal melt by using the sensor comprises the following process steps of (1) inserting the sensor and a graphite corrosion-resistant electrode into the aluminum melt of 750 DEG C, and making sure that the solid proton conductor element is fully immersed into the aluminum melt, the quasi-electrode to be measured is in direct contact with the metal melt and the contact surface is the electrode to be measured; (2) connecting a potentiometer and the nickel-chromium gas guide pipe to the graphite corrosion-resistant electrode through a nickel-chromium wire, and measuring the potential difference between the reference electrode and the electrode to be measured; and (3) calculating the stabilized hydrogen content S of the aluminum melt according to the measured potential difference, the temperature of the metal melt and the saturated solubility of hydrogen in the metal melt to be 0.109ml/100gAl.
- the sensor for measuring hydrogen content in aluminum melt is the same as that in the embodiment 3, as shown in Figure 5 .
- the sensor structure also comprises a reference electrode cable 7 which is made of metal silver.
- the reference electrode cable 7 is inserted into the through pipe 5 through the stainless steel clamp 104, is connected with the porous silver reference porous electrode 2 and is externally connected to a measuring circuit;
- the through pipe 5 is made of quartz;
- the gas guide pipe is made of corundum;
- the reference porous electrode is made of porous silver;
- the reference gas is N 2 -H 2 , and the mole hydrogen content is 1.00%.
- the method for measuring hydrogen content in metal melt by using the sensor comprises the following process steps of (1) inserting the sensor and a graphite corrosion-resistant electrode into the aluminum melt of 750 DEG C, and making sure that the solid proton conductor element is fully immersed into the metal melt, the quasi-electrode to be measured is in direct contact with the metal melt and the contact surface is the electrode to be measured; (2) connecting a potentiometer and the reference electrode cable to the graphite corrosion-resistant electrode through a silver wire, and measuring the potential difference between the reference electrode and the electrode to be measured; and (3) calculating the stabilized hydrogen content S of the aluminum melt according to the measured potential difference, the temperature of the metal melt and the saturated solubility of hydrogen in the metal melt to be 0.130ml/100gAl.
- the sensor for measuring hydrogen content in aluminum melt is the same as that in the embodiment 3, as shown in Figure 6 .
- the difference lies in that: the solid proton conductor element 1 used in the sensor structure adopts a spherical structure.
- the method for measuring hydrogen content in metal melt by using the sensor comprises the following process steps of (1) inserting the sensor and a graphite corrosion-resistant electrode into the aluminum melt of 750 DEG C, and making sure that the solid proton conductor element is fully immersed into the aluminum melt, the quasi-electrode to be measured is in direct contact with the metal melt and the contact surface is the electrode to be measured; (2) connecting a potentiometer and the gas guide pipe to the graphite corrosion-resistant electrode through a stainless steel wire, and measuring the potential difference between the reference electrode and the electrode to be measured; and (3) calculating the stabilized hydrogen content S of the aluminum melt according to the measured potential difference, the temperature of the metal melt and the saturated solubility of hydrogen in the metal melt to be 0.123ml/100gAl.
- the sensor for measuring hydrogen content in aluminum melt is the same as that in the embodiment 5, as shown in Figure 7 .
- the difference lies in that: the sensor structure also comprises a reference electrode cable 7 which is made of stainless steel.
- the reference electrode cable 7 is inserted into the through pipe 5 through the Teflon three-way clamp 104, is connected to the reference porous electrode 2 and is externally connected to a measuring circuit; and the gas guide pipe is made of corundum.
- the method for measuring hydrogen content in metal melt by using the sensor comprises the following process steps of (1) inserting the sensor and a graphite corrosion-resistant electrode into the aluminum melt of 750 DEG C, and making sure that the solid proton conductor element is fully immersed into the aluminum melt, the quasi-electrode to be measured is in direct contact with the metal melt and the contact surface is the electrode to be measured; (2) connecting a potentiometer and the reference electrode cable to the corrosion-resistant electrode through a stainless steel wire, and measuring the potential difference between the reference electrode and the electrode to be measured; and (3) calculating the stabilized hydrogen content S of the aluminum melt according to the measured potential difference, the temperature of the metal melt and the saturated solubility of hydrogen in the metal melt to be 0.099ml/100gAl.
- the sensor for measuring hydrogen content in aluminum melt comprises a solid proton conductor element 1, a reference porous electrode 2, an electrode to be measured, a platinum-wire cable 7, a solid reference compound 8, a corundum through pipe 5, an alumina-based ceramic adhesive 4 and an Al 2 O 3 inert material 9, wherein the solid proton conductor element 1 adopts a tubular structure and is made of CaZr 0.9 In 0.1 O 3- ⁇ , one end is sealed by using the alumina-based ceramic adhesive 4, the through pipe 5 and the solid proton conductor element 1 are connected through the insulating ceramic adhesive 4 to form an inner space, the surface located in the inner space, of the solid proton conductor element 1 is an inner surface, and the surface exposed outside is an outer surface; the reference porous electrode 2 is coated to the inner surface of the solid proton conductor element 1, and the quasi-electrode 6 to be measured is the outer surface of the solid proton conductor element 1; the bottom of the solid proton conductor element 1 is stuffed with the Al 2
- the reference porous electrode is made of platinum.
- the reference compound is a Y-H system solid, and the mole hydrogen content in equilibrium atmosphere of the Y-H system solid at 750 DEG C is 0.11%.
- the method for measuring hydrogen content in metal melt by using the sensor comprises the following process steps of (1) inserting the sensor and a graphite corrosion-resistant electrode into the aluminum melt of 750 DEG C, and making sure that the solid proton conductor element 1 is fully immersed into the metal melt, the quasi-electrode to be measured is in direct contact with the metal melt and the contact surface is the electrode to be measured; (2) connecting a potentiometer and a platinum-wire cable to the graphite corrosion-resistant electrode through a platinum wire, and measuring the potential difference between the reference electrode and the electrode to be measured; and (3) calculating the stabilized hydrogen content S of the aluminum melt according to the measured potential difference, the temperature of the metal melt and the saturated solubility of hydrogen in the metal melt to be 0.107ml/100gAl.
- the sensor for measuring hydrogen content in aluminum melt is the same as that in the example 1, as shown in Figure 9 .
- the difference lies in that: the solid proton conductor element 1 used in the sensor structure adopts a flaky structure and is made of CaZr 0.9 Sc 0.1 O 3- ⁇ ; the inert material is Y 2 O 3 ; the reference compound is a Sc-H system solid, and the mole hydrogen content in equilibrium atmosphere of the Sc-H system solid at 750 DEG C is 0.25%.
- the method for measuring hydrogen content in metal melt by using the sensor comprises the following process steps of (1) inserting the sensor and a graphite corrosion-resistant electrode into the aluminum melt of 750 DEG C, and making sure that the solid proton conductor element is fully immersed into the aluminum melt, the quasi-electrode to be measured is in direct contact with the metal melt and the contact surface is the electrode to be measured; (2) connecting a potentiometer and a cable to the graphite corrosion-resistant electrode through a platinum wire, and measuring the potential difference between the reference electrode and the electrode to be measured; and (3) calculating the stabilized hydrogen content S of the aluminum melt according to the measured potential difference, the temperature of the metal melt and the saturated solubility of hydrogen in the metal melt to be 0.143ml/100gAl.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Electrochemistry (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Food Science & Technology (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Measuring Oxygen Concentration In Cells (AREA)
- Investigating And Analyzing Materials By Characteristic Methods (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201510770945.6A CN105319253B (zh) | 2015-11-12 | 2015-11-12 | 一种测量金属熔体中氢含量的传感器及测量方法 |
| PCT/CN2015/096049 WO2017080005A1 (zh) | 2015-11-12 | 2015-11-30 | 一种测量金属熔体中氢含量的传感器及测量方法 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP3372998A1 EP3372998A1 (en) | 2018-09-12 |
| EP3372998A4 EP3372998A4 (en) | 2018-09-19 |
| EP3372998B1 true EP3372998B1 (en) | 2020-11-18 |
Family
ID=55247105
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP15908135.5A Active EP3372998B1 (en) | 2015-11-12 | 2015-11-30 | Sensor and method for measuring content of hydrogen in metal melt |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10598629B2 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP3372998B1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6775012B2 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN105319253B (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2017080005A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105675652A (zh) * | 2016-02-19 | 2016-06-15 | 鸡西市天合科技有限公司 | 水稻田稻田水钾含量自动速测仪 |
| CN106770518A (zh) * | 2016-12-22 | 2017-05-31 | 东北大学 | 一种用于铝及铝合金熔体中的定氢装置及方法 |
| CN107247080B (zh) * | 2017-07-27 | 2020-01-24 | 中国原子能科学研究院 | 一种用于高温熔盐中氧离子的在线检测系统 |
| WO2021002199A1 (ja) * | 2019-07-01 | 2021-01-07 | 東京窯業株式会社 | 固体基準物質及び水素ガスセンサ |
| CN110655399B (zh) * | 2019-09-06 | 2022-01-11 | 钟祥市中原电子有限责任公司 | 一种钢水定氢探头用透气陶瓷头及其制备方法 |
| CN111024558B (zh) * | 2019-12-24 | 2021-05-18 | 东北大学 | 一种测量铝熔体中氢扩散系数的装置及方法 |
| US11549882B2 (en) * | 2020-02-21 | 2023-01-10 | The Regents Of The University Of Michigan | Reference electrode and electrochemical monitoring system |
| CN111289405B (zh) * | 2020-03-02 | 2022-07-01 | 哈尔滨理工大学 | 铝合金熔体氢分压惰性气体循环在线连续检测装置及其检测方法 |
| CN112129824B (zh) * | 2020-09-24 | 2021-11-30 | 东北大学 | 一种无损测量固体钢中氢含量的装置及方法 |
| CN114324535B (zh) * | 2022-01-05 | 2023-03-24 | 东北大学 | 一种可拆卸式金属熔体测氢传感器装置 |
| CN114373559B (zh) * | 2022-01-10 | 2024-09-27 | 中国原子能科学研究院 | 测定液态碱金属中的碳含量的系统及方法 |
| CN115184238A (zh) * | 2022-07-15 | 2022-10-14 | 中国人民解放军陆军炮兵防空兵学院 | 一种测量涂层结构材料氢同位素渗透的装置及方法 |
| CN115856055B (zh) * | 2022-12-06 | 2024-07-16 | 东北大学 | 一种测量镁熔体中氢含量的装置及方法 |
| CN115825371B (zh) * | 2022-12-06 | 2024-11-29 | 东北大学 | 一种测量金属中氢含量的装置及方法 |
| CN119510529A (zh) * | 2025-01-22 | 2025-02-25 | 浙江众氢科技有限公司 | 溶解氢的含量测量方法、测量装置以及计算机程序产品 |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014160006A (ja) * | 2013-02-19 | 2014-09-04 | Tokyo Yogyo Co Ltd | センサプローブ |
Family Cites Families (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS63269053A (ja) * | 1987-04-25 | 1988-11-07 | Tottori Univ | 溶融金属またはガス中に含有されている水素または水蒸気の濃度の測定装置用基準物質 |
| JP2578542B2 (ja) * | 1991-12-27 | 1997-02-05 | 東京窯業株式会社 | 溶融金属中の水素溶解量測定用センサプローブ |
| KR970003280B1 (ko) * | 1991-11-26 | 1997-03-17 | 도오교오 요오교오 가부시끼가이샤 | 용융금속중의 수소용해량 측정용 센서 프로우브 및 수소농도 측정방법 |
| US5490965A (en) * | 1994-01-24 | 1996-02-13 | Hewlett-Packard Company | Method for closing holes in ceramic substrates |
| JPH0829375A (ja) * | 1994-07-12 | 1996-02-02 | Tokyo Yogyo Co Ltd | 溶融金属中の水素溶解量測定用センサ |
| JP3878875B2 (ja) * | 2002-03-29 | 2007-02-07 | 三井造船株式会社 | 酸素濃度計 |
| GB0221393D0 (en) * | 2002-09-14 | 2002-10-23 | Univ Cambridge Tech | Hydrogen sensing apparatus and method |
| US7396443B2 (en) * | 2003-02-17 | 2008-07-08 | Dongsub Park | Solid-state electrochemical hydrogen probe for the measurement of hydrogen content in the molten aluminum |
| JP3095929U (ja) * | 2003-02-17 | 2003-08-29 | 株式会社エバニユー | 運動用ボール空気入れ |
| DE102004022763B3 (de) * | 2004-05-05 | 2005-09-15 | Heraeus Electro-Nite International N.V. | Messeinrichtung zur Bestimmung der Sauerstoffaktivität in Metall- oder Schlackeschmelzen |
| GB0520777D0 (en) * | 2005-10-12 | 2005-11-23 | Environmental Monitoring And C | Improved apparatus and method for measuring hydrogen concentration |
| CN101071119A (zh) * | 2007-06-15 | 2007-11-14 | 东北大学 | 一种测氢传感器及固体电解质的制备方法 |
| JP4433489B2 (ja) * | 2007-08-10 | 2010-03-17 | 昭和ホールディングス株式会社 | ソフトテニスボール用空気入れポンプ |
| KR101325508B1 (ko) * | 2012-03-14 | 2013-11-07 | 한국과학기술원 | 고체 산소이온 전도체와 고체 수소이온 전도체의 접합구조를 가진 용융금속 내 수소 측정 센서 |
| JP2015086093A (ja) * | 2013-10-29 | 2015-05-07 | 株式会社ノリタケカンパニーリミテド | セラミック積層体およびその製造方法 |
-
2015
- 2015-11-12 CN CN201510770945.6A patent/CN105319253B/zh active Active
- 2015-11-30 WO PCT/CN2015/096049 patent/WO2017080005A1/zh not_active Ceased
- 2015-11-30 US US15/774,205 patent/US10598629B2/en active Active
- 2015-11-30 JP JP2018517620A patent/JP6775012B2/ja active Active
- 2015-11-30 EP EP15908135.5A patent/EP3372998B1/en active Active
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014160006A (ja) * | 2013-02-19 | 2014-09-04 | Tokyo Yogyo Co Ltd | センサプローブ |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN105319253B (zh) | 2019-08-06 |
| US10598629B2 (en) | 2020-03-24 |
| JP6775012B2 (ja) | 2020-10-28 |
| WO2017080005A1 (zh) | 2017-05-18 |
| JP2018533727A (ja) | 2018-11-15 |
| EP3372998A1 (en) | 2018-09-12 |
| US20180328881A1 (en) | 2018-11-15 |
| EP3372998A4 (en) | 2018-09-19 |
| CN105319253A (zh) | 2016-02-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP3372998B1 (en) | Sensor and method for measuring content of hydrogen in metal melt | |
| Hersch | Trace monitoring in gases using galvanic systems | |
| JP2018533727A5 (enExample) | ||
| EP0562801B1 (en) | Oxygen measuring probe | |
| Gauthier et al. | Progress in the Development of Solid‐State Sulfate Detectors for Sulfur Oxides | |
| US6090268A (en) | CO gas sensor and CO gas concentration measuring method | |
| CN112129824B (zh) | 一种无损测量固体钢中氢含量的装置及方法 | |
| Ding et al. | In-situ measurement of dissolved H2 in aqueous fluid at elevated temperatures and pressures | |
| US20050252789A1 (en) | Hydrogen sensing apparatus and method | |
| Stromatt | Studies on the Electroreduction of Uranyl (VI) in Molten Equimolar KCl‐NaCl by Chronopotentiometric and Electrode Impedance Measurements | |
| JPH01129156A (ja) | 水素用電気化学的センサー | |
| CN210269703U (zh) | 一种用于控制气氛中极低氧含量并测量其氧分压的装置 | |
| JP4671565B2 (ja) | 隔膜型電極 | |
| JP2000275209A (ja) | 水素センサ | |
| CN110261459B (zh) | 一种用于控制气氛中极低氧含量并测量其氧分压的装置 | |
| US4065371A (en) | Electrochemical carbon meter | |
| Alberti et al. | Use of solid state protonic conductors for oxygen potentiometric sensor at room temperature | |
| JPH02128154A (ja) | 熱処理炉用酸素センサ | |
| Ghetta et al. | Control and monitoring of oxygen content in molten metals. Application to lead and lead-bismuth melts | |
| GB1208209A (en) | Method and system for determining the oxygen content in liquids | |
| CN115856055B (zh) | 一种测量镁熔体中氢含量的装置及方法 | |
| Chen et al. | Study on Polarization Parameters of Micro Dissolved Oxygen Sensor | |
| JP4514737B2 (ja) | pH電極 | |
| US20060254908A1 (en) | Electrochemical solid electrolyte sensor for the detection of oxygen, hydrocarbons and moisture in vacuum environments | |
| JP4496195B2 (ja) | 照合電極 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE INTERNATIONAL PUBLICATION HAS BEEN MADE |
|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: REQUEST FOR EXAMINATION WAS MADE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20180606 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| A4 | Supplementary search report drawn up and despatched |
Effective date: 20180821 |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: G01N 27/411 20060101AFI20180815BHEP Ipc: G01N 27/406 20060101ALI20180815BHEP |
|
| DAV | Request for validation of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: EXAMINATION IS IN PROGRESS |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20190502 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R079 Ref document number: 602015062374 Country of ref document: DE Free format text: PREVIOUS MAIN CLASS: G01N0027406000 Ipc: G01N0027411000 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: G01N 33/00 20060101ALN20200904BHEP Ipc: G01N 27/406 20060101ALI20200904BHEP Ipc: G01N 27/411 20060101AFI20200904BHEP |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20200924 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 602015062374 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 1336303 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20201215 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MK05 Ref document number: 1336303 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MP Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210219 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210218 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210318 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210218 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210318 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG9D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20201130 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20201130 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 602015062374 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20201130 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20201130 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20210819 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20201130 Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210318 Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20201130 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 602015062374 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: STRAUS, ALEXANDER, DIPL.-CHEM.UNIV. DR.PHIL., DE |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20241108 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20241106 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20241125 Year of fee payment: 10 |