EP2919993B2 - Système de surveillance pour l'orientation de groupes d'impression d'une machine à imprimer en ligne - Google Patents
Système de surveillance pour l'orientation de groupes d'impression d'une machine à imprimer en ligne Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2919993B2 EP2919993B2 EP13771100.8A EP13771100A EP2919993B2 EP 2919993 B2 EP2919993 B2 EP 2919993B2 EP 13771100 A EP13771100 A EP 13771100A EP 2919993 B2 EP2919993 B2 EP 2919993B2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- printing
- unit
- offset
- sensor unit
- print medium
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000007639 printing Methods 0.000 title claims description 186
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 title claims description 65
- 230000033001 locomotion Effects 0.000 claims description 40
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 38
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000012806 monitoring device Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000002699 waste material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000006978 adaptation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007812 deficiency Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007646 gravure printing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003550 marker Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007645 offset printing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002028 premature Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008054 signal transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010972 statistical evaluation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013519 translation Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41F—PRINTING MACHINES OR PRESSES
- B41F33/00—Indicating, counting, warning, control or safety devices
- B41F33/0081—Devices for scanning register marks
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41P—INDEXING SCHEME RELATING TO PRINTING, LINING MACHINES, TYPEWRITERS, AND TO STAMPS
- B41P2213/00—Arrangements for actuating or driving printing presses; Auxiliary devices or processes
- B41P2213/90—Register control
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41P—INDEXING SCHEME RELATING TO PRINTING, LINING MACHINES, TYPEWRITERS, AND TO STAMPS
- B41P2233/00—Arrangements for the operation of printing presses
- B41P2233/50—Marks on printed material
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41P—INDEXING SCHEME RELATING TO PRINTING, LINING MACHINES, TYPEWRITERS, AND TO STAMPS
- B41P2233/00—Arrangements for the operation of printing presses
- B41P2233/50—Marks on printed material
- B41P2233/52—Marks on printed material for registering
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a monitoring system for the alignment of printing units of a series printing machine, a correspondingly equipped series printing machine and a monitoring method for the alignment of printing units of a series printing machine.
- printing units are arranged in a row in the form of a series printing machine.
- the supply to the individual printing units takes place successively, so that there is a corresponding free conveying length of the printing medium between the individual printing units, which are responsible for different colors.
- the print medium is often made available by a paper roll and unrolled there and is in the form of a web.
- so-called printing markers are used.
- the print markers are part of the print image or are printed on the print medium on the side or on the edge of the print image.
- the exact position of the print image on the print medium can thus be determined by appropriate sensors, in particular sensor devices with sensor units for each printing unit. On the basis of this detection, the associated printing unit settings are aligned, that is to say in particular a mechanical displacement of the individual printing rollers in their axial direction.
- a disadvantage of known row printing machines and corresponding monitoring systems with sensor devices is that they are limited in terms of their detection width in order to be able to provide the necessary high speed with regard to detection at high printing speeds.
- different properties of the print medium may occur due to batch differences. These are in particular changes in the mechanical stability, preferably based on the tensile strength or the modulus of elasticity of the pressure medium. This variation can lead to so-called sheet travel. This means that the two lateral edges of the printing medium can withstand the pull applied by the printing machine to different degrees.
- a corresponding printing medium thus moves laterally, that is to say transversely to the conveying direction, along the respective printing units.
- This displacement error or this offset increases over the course of the entire in-line printing press, that is to say from printing unit to printing unit. Compared to small misalignments in the course of a batch in a feed roller, these are very large differences in the range of several millimeters. Due to the relatively small detection areas of the sensor unit, it can happen that the large misalignment when the roll is changed means that the print markers can no longer be recognized. In such a case, the machine stops and an operator of this in-line printing machine must manually readjust the corresponding offset data and accordingly align the printing units manually. By stopping the machine, however, at least the length section of the printing medium that is in the machine at this time arises as rejects or as so-called waste.
- the DE 10 2006 030 170 A1 also describes a generic system and a generic method.
- a monitoring system serves to align printing units of a series printing machine, in particular a gravure printing machine.
- Such a monitoring system has a sensor device with at least one sensor unit for each printing unit. These are designed to recognize the position of a print mark on the print medium. This information about the position of the print marker or print mark is used for the subsequent alignment of the printing unit.
- a monitoring system according to the invention is characterized in that at least one sensor unit arranged downstream of a first sensor unit can be moved transversely to the conveying direction of the pressure medium. The results The monitoring by the sensor device is used for the axial alignment of the respective printing unit.
- a controlled system is made available which adapts the respective printing unit to the recognized offset of the printing medium.
- the adaptation that is to say the coupling between the alignment of the respective printing unit and the sensor device, is preferably carried out electronically, in particular digitally.
- each sensor unit can be adjusted here.
- This relates in particular to so-called subordinate sensor units, in other words not the first sensor unit.
- This mobility is in particular translational mobility. Movability transverse to the conveying direction is to be understood in particular to mean movement essentially perpendicular to the conveying direction.
- an automatic or at least semi-automatic adaptation of the downstream sensor units can now be set to a high offset. If the first sensor unit detects a first offset in the first printing unit, which is in particular outside a standard offset in continuous operation, this offset can be used for repositioning the downstream movable sensor units. In the event of a roll change, that is to say if a significantly increased offset is to be expected, such a monitoring system can be put into a special programming so that an automated movement takes place transversely to the conveying direction of the downstream sensor units based on the recognized offset of the first sensor unit. This can reduce the likelihood that the downstream sensor units will no longer recognize the print markers of the preceding printing units.
- the downstream sensor units are moved in the direction of the offset, so that the sensor unit is in a suitable monitoring position at the time at which the offset printing mark is located in the downstream printing unit. Accordingly, the likelihood of the alignment of the printing units being made available by the information from the individual sensor units also in the case of a roll change is significantly increased in comparison with static sensor units in known monitoring systems. Due to the fact that the printing units can be aligned quickly and easily in this way even in the case of roll change situations, the roll change can be carried out in particular at a consistently high printing speed and above all without stopping and the production of rejects with regard to the printing medium.
- Print media that can be stored on a roll are particularly suitable as the print medium in the sense of the present invention. It can be z. B. paper or plastic, in particular PE or PET. Of course, the printing medium can be of one or more layers or of one or more layers.
- the sensor unit can be designed in a wide variety of ways for the recognition of the print mark. In particular, however, it has a possibility of generating a light spot and the associated evaluation optics in order to be able to carry out a corresponding position determination of the print mark on the print medium at a sufficiently high speed.
- the sensor unit also has associated control electronics and cabling, e.g. B. for the power supply or signal transmission.
- the signal forwarding can of course also take place wirelessly in order to make the mobility of the sensor unit even easier.
- the at least one movable sensor unit can be moved in translation by means of an actuator system, in particular with an electric motor.
- an electric motor e.g. B. the use of an air motor in the context of the present invention is also conceivable.
- An actuator system is used for the automatic or semi-automatic mobility of the sensor unit.
- a gear transmission can be made available in the form of a spindle gear in order to be able to ensure that the sensor unit can be adjusted precisely by means of the actuators.
- An electric motor can represent a particularly inexpensive and simple embodiment of such an actuator system.
- other transmission variants are also possible for the transmission of the force to the sensor unit for its translatory movement.
- Movable cable sleeves can be provided as a cable guide to the movable sensor unit.
- the sensor device and / or each sensor unit can have a corresponding control unit in order to carry out a monitoring method in whole or in part, as will be explained in more detail later.
- the at least one movable sensor unit can be moved along a guide, in particular along a guide rail.
- the guidance serves to predefine the movement path of the sensor unit.
- it is a translational guide or guide rail.
- a guide rail serves z. B. the sliding bearing movement of the sensor unit along this guide rail.
- the mechanical design of such a guide can of course be adjustable, so that preferably different large movement paths can be realized for each sensor unit.
- the movement of the sensor unit along Such a guide can also be designed as a traversing movement.
- another actuator in order to generate a movement of the sensor unit along the guide, in addition to the actuator system already described, e.g. B. in the form of an electric motor, another actuator, in particular lever kinematics, are used.
- the at least one movable sensor unit is designed to be movable as a function of an offset which has been recognized by the sensor unit arranged upstream of the pressure curve.
- This enables the movable sensor unit to be pre-positioned.
- This advance movement is based on a signal-communicating connection between at least two sensor units that are separate from one another, so that the detected offset of a pre-arranged sensor unit can be transmitted to the downstream movable sensor unit.
- This can be done in a simple control manner or in a closed control loop.
- the sensor unit and / or the sensor device can have a corresponding control unit for the execution of this signal communication or the corresponding control of the movement of the sensor unit.
- a preparation for the expected minimum offset takes place, so that, as has already been explained, an increase in the probability of the detection of the offset print mark is achieved.
- the at least one movable sensor unit has a possible movement path which is formed in the range of approximately ⁇ 2% based on the width of the printing medium transversely to the conveying direction. This specifies a possibility of a movement path that can compensate for a sufficient mobility with respect to the expected offset.
- printing widths of the printing medium come e.g. B. Values in the range between approx. 1000 and approx. 1500 mm in question. Approx. ⁇ 10 mm to approximately ⁇ 20 mm are particularly advantageous as possible movement paths.
- the individual movable sensor units are arranged in the center of the corresponding movement path.
- a control unit is provided for the execution of a monitoring method according to the invention which will be explained later. Accordingly, a monitoring system according to the invention has the same advantages as will be explained later with reference to a monitoring method according to the invention.
- the present invention also relates to a series printing machine with at least two printing units arranged in series for printing on a printing medium.
- a series printing machine according to the invention is characterized in that at least one monitoring device according to the present invention is provided for the alignment of the printing units. Accordingly, a series printing machine according to the invention brings with it the same advantages as have been explained in detail with reference to a monitoring system according to the invention.
- a monitoring method according to the invention is therefore used in particular in a series printing machine according to the invention, so that the same advantages can be achieved as have been explained in detail with reference to a series printing machine according to the invention and with reference to a monitoring system according to the invention.
- the subsequent sensor unit of the second printing unit can be pre-positioned. If an offset is detected in the first printing unit, the second sensor unit of the second printing unit can already be displaced in the direction of the recognized offset in preparation for this offset.
- This monitoring procedure is in particular a special procedure which is used when the print medium is changed. With high probabilities of delay, e.g. B. when generating a sheet run, the printing medium can be ensured in this way that even with a relatively large offset on the first printing unit, the other printing units are prepared for this large offset and can also recognize the print mark.
- This pre-positioning increases the security of the monitoring and thus reduces the likelihood of a machine stop. As has already been explained, this can significantly reduce the machine stop and the corresponding waste or so-called waste.
- An advantage can also be achieved if, in a monitoring method according to the invention, after detecting the offset of a printing mark on the printing medium in a first printing unit, all sensor units arranged downstream in the course of the printing transversely to the conveying direction of the printing medium in the direction of the detected Offset are moved. In a series printing machine with a large number of printing units, sensor units of the third, fourth and subsequent printing units can accordingly also be moved accordingly from the first detection of an offset on the first printing unit. This means that even large offsets with correspondingly smaller servomotors or less powerful actuators with regard to the high printing speed can be moved sufficiently quickly through the pre-positioning. This allows a reduction in the cost and the necessary installation space of the individual sensor units and the associated actuators. It can also be ensured that the in-line printing press can be operated at full printing speed even in the case of roll change situations.
- a monitoring method can be developed in such a way that the movement of the sensor unit of the second printing unit takes place at least by the amount of the recognized offset of the printing mark on the first printing unit.
- the minimum path of movement along the movement path is also predefined in this way. The movement therefore takes place at least by the recognized offset. It can be assumed that the offset increases in the same direction over the course of the printing press, that is to say from printing unit to printing unit.
- the pre-positioning by at least the amount of the recognized offset for the following printing unit thus allows the minimum positioning of the at least further offset to be expected for this second printing unit.
- a larger travel path than the amount of the detected offset can also be used.
- This increase in movement can e.g. B. on further information, e.g. B. on stored mean values using statistical evaluation methods.
- the increased travel path setting on the basis of a corresponding function of the recognized offset is also conceivable.
- a further advantage can be achieved if, in a monitoring method according to the invention, a sensor unit of a third printing unit is moved transversely to the conveying direction of the printing medium by an amount which is composed of the recognized offset and the recognized residual offset. At the latest after the print mark has passed through the second printing unit, both the offset and the detected residual offset are known. Accordingly, an expected residual offset for the own printing unit can be determined for the further displacement movements of the movable sensor units via the residual offset. Thus, the movable sensor units of the following printing units can be moved beyond the amount of the detected offset. This enables the subsequent sensor units to be positioned even more precisely in advance.
- the movement of the sensor unit of the second printing unit in the direction of the detected offset also takes place when no printing mark is detected on the second printing unit.
- the situation can arise that the print mark is not recognized by the sensor unit despite the pre-positioning on the second printing unit.
- the printing press does not necessarily have to be stopped completely here. Rather, the further movement of the sensor unit on the second printing unit can compensate for this deficiency again by means of the information about the direction of the detected offset and, after a short movement phase, can also recognize the printing mark on the second printing unit again.
- a monitoring method according to the invention a complete stop of the in-line printing machine and the corresponding rejects can be avoided even if the possibility of recognizing the print mark is lost.
- a monitoring method according to the invention can be developed in such a way that it is carried out as a special program for the duration of a roll change of the printing medium. Accordingly, other parameters for the positioning or movement of the individual sensor units can be used as the normal program.
- the measuring motor system ie the alignment of a light point and the evaluation using the corresponding optics, can differ from the normal program in the special program according to the present invention.
- the duration of the roll change is at least the length of time which is necessary to have the printing medium of the newly used roll completely within the in-line printing press.
- the special program is ended after the roll change has ended, in particular after a predetermined print length.
- a given print length can e.g. B. be one to two machine lengths of the print medium.
- the normal program already explained can continue to control or regulate. In particular, when returning to the normal program, the sensor devices or the sensor units remain at the positions at which they were or were positioned at the end of the special program of the monitoring method.
- the time offset to the first printing unit is taken into account in the sensor unit of the second printing unit.
- the respective downstream sensor unit remains in its previous position until, for example, the new material has reached this sensor unit when a roll is changed. The previous material will usually not yet have the sheet run. Thus, premature movement of the respective sensor unit could lead to the loss of the possibility of recognizing these print marks.
- the ratio of the printing length between the two printing units and the printing speed is in particular formed as a relation for the time offset.
- the time required for the movement of the sensor unit can also be taken into account.
- the downstream sensor units are moved around the detected offset with a time offset, in particular at precisely the right time, and are thus not only pre-positioned locally but also in time.
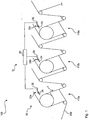
- a row printing machine 100 is shown schematically. Three printing units 110a, 110b and 110c are shown here.
- the pressure medium 200 is guided and conveyed along the conveying direction F via a multiplicity of deflecting rollers and pressure rollers.
- FIG. 1 it can be seen that this embodiment of the in-line printing press 100 is designed with a monitoring system 10 according to the invention.
- This has a control unit 40, which is connected in a signal-communicating manner to a respective sensor unit 22a, 22b and 22c of a sensor device 20.
- the sensor units 22a, 22b and 22c are each assigned to a printing group 100a, 100b and 100c.
- the individual sensor units 22a, 22b and 22c are essentially of identical design and have a guide 24 for translatory movement transverse to the conveying direction F.
- an actuator system 30 is provided in the form of an electric motor.
- the 2a to 2c show a possibility of carrying out a monitoring method according to the invention. They are shown schematically in particular according to the embodiment of a series printing machine 100 Fig. 1 based. All three are like that 2a to 2c to see a situation with three sensor units 22a, 22b and 22c, which correlate with associated printing units 100a, 100b and 100c (not shown). It can also be seen that a printing mark 210 is applied to a printing medium 200 (not shown in more detail).
- the method begins at the time of a roll change of the print medium 200. Due to the roll change and corresponding change due to batch differences in the elastic modulus of the print medium 200, the sensor unit 22a detects an offset V on the first printing unit 110a. When this offset V is determined, the two further sensor units 22b and 22c move automatically and automatically in the direction of this offset V and, in one embodiment of this monitoring method, even exactly by the amount of the offset V. The result shows Fig. 2b , so that the downstream sensor units 22b and 22c have already been pre-positioned by the offset V.
- the pre-positioning of the sensor unit 22b can now also be used to directly identify the residual offset R of the print mark 210.
- a movement of the third sensor unit 22c around this residual offset R now takes place. This can be carried out in an identical manner for further printing units, so that the loss of the possibility of recognizing the print mark 210 can be virtually excluded by the pre-positioning.
- Fig. 3 shows a possibility of how different print marks 210 can be arranged on the print medium 200. These have a straight edge in the direction of the conveying direction F at the beginning, that is to say at their upper end, and an oblique edge at their lower end. In this way, in addition to a positioning and alignment of the individual printing units 110a, 110b and 110c in the conveying direction F, an alignment transverse to the conveying direction F can also take place. About the relation between a light point of the sensor unit 22a and the oblique edge of the print mark 210 can this lateral offset V, which is the axial offset in relation to the respective printing unit, can be recognized. This determination result is used as an input variable for the controlled alignment of the respective printing group 110a, 110b and 110c.
- a separate print mark 210 can be applied to the printing medium for each individual printing unit 110a, 110b and 110c. Also recognizable in Fig. 3 is the freedom of movement along a movement path S for this sensor unit 22a. Here, a guide 24 in frame construction is provided, so that an even more precise pre-positioning along the movement path S is possible.
Landscapes
- Inking, Control Or Cleaning Of Printing Machines (AREA)
- Controlling Sheets Or Webs (AREA)
- Handling Of Sheets (AREA)
Claims (14)
- Système de surveillance (10) pour l'orientation d'unités d'impression (110a, 110b, 100c) d'une presse à imprimer en série (100), comprenant un dispositif de capteur (20) avec au moins une unité de capteur (22a, 22b, 22c) pour chaque unité d'impression (110a, 110b 100c) afin de détecter la position d'une marque d'impression (210) sur un support d'impression (200),
au moins une unité de capteur (22b, 22c), disposée en aval d'une première unité de capteur (22a) dans la direction de l'impression, étant mobile transversalement à la direction de convoyage (F) du support d'impression (200),
caractérisé en ce que
l'au moins une unité de capteur mobile (22b, 22c), disposée en aval, d'une unité d'impression 110b, 100c) disposée en aval, est conçue de manière mobile en fonction d'un décalage (V) qui a été détecté par l'unité de capteur (22a), disposée en amont dans la direction de l'impression, d'une unité d'impression (110a) disposée en amont. - Système de surveillance (10) selon la revendication 1,
caractérisé en ce que
l'au moins une unité de capteur mobile (22b, 22c) peut être déplacée en translation au moyen d'un actionneur (30), plus particulièrement d'un moteur électrique. - Système de surveillance (10) selon l'une des revendications précédentes,
caractérisé en ce que
l'au moins une unité de capteur mobile (22b, 22c) peut être déplacée le long d'un guidage (24), plus particulièrement le long d'un rail de guidage. - Système de surveillance (10) selon l'une des revendications précédentes,
caractérisé en ce que
l'au moins une unité de capteur mobile (22a, 22b) présente un trajet de déplacement possible (S) qui est conçu transversalement à la direction de convoyage (F) de l'ordre d'environ +- 2 % par rapport à la largeur du support d'impression (200) . - Système de surveillance (10) selon l'une des revendications précédentes,
caractérisé en ce que
une unité de contrôle (40) est conçu pour l'exécution d'un procédé de surveillance, plus particulièrement avec les caractéristiques d'une des revendications 7 à 13. - Presse à imprimer en série (100) avec au moins deux unités d'impression (110a, 110b, 110c) disposées en série pour l'impression d'un support d'impression (200),
caractérisé en ce que
pour l'orientation des unités d'impression (110a, 100b, 110c), est prévu au moins un dispositif de surveillance (10) avec les caractéristiques d'une des revendications 1 à 5. - Procédé de surveillance pour l'orientation d'unités d'impression (110a, 110b, 110c) d'une presse à imprimer en série (100), plus particulièrement avec les caractéristiques de la revendication 6, comprenant les étapes suivantes :- détection d'un décalage (V) d'une marque d'impression (210) sur le support d'impression (200) dans une première unité d'impression (110a),- déplacement d'une unité de capteur (22b) d'un dispositif de capteur (20) d'une deuxième unité d'impression (110b) transversalement à la direction de convoyage (F) du support d'impression (200) du décalage (V) détecté,- détection d'un décalage résiduel (R) de la marque d'impression (210) sur le support d'impression (200) dans la deuxième unité d'impression (110b).
- Procédé de surveillance selon la revendication 7,
caractérisé en ce que
après la détection d'un décalage (V) d'une marque d'impression (210) sur le support d'impression (200) dans la première unité d'impression (110a), toutes les unités de capteurs (22b, 22c) disposées en aval dans la direction d'impression sont déplacées transversalement à la direction de convoyage (F) du support d'impression (200) en direction du décalage (V) détecté. - Procédé de surveillance selon l'une des revendications 7 ou 8,
caractérisé en ce que
le déplacement de l'unité de capteur (22b) de la deuxième unité d'impression (110b) au moins de la valeur du décalage (V) détecté de la marque d'impression (210) a lieu au niveau de la première unité d'impression (110a). - Procédé de surveillance selon l'une des revendications 7 à 9,
caractérisé en ce que
une unité de capteur (22c) d'une troisième unité d'impression (110c) est déplacée transversalement à la direction de convoyage (F) du support d'impression (200) d'une valeur qui est constituée du décalage (V) détecté et du décalage résiduel (R) détecté. - Procédé de surveillance selon l'une des revendications 7 à 10,
caractérisé en ce que
le déplacement de l'unité de capteur (22b) de la deuxième unité d'impression (110b) en direction du décalage (V) détecté a également lieu lorsque aucune marque d'impression (210) n'est détectée au niveau de la deuxième unité d'impression (110b). - Procédé de surveillance selon l'une des revendications 7 à 11,
caractérisé en ce que
il est exécuté en tant que programme spécial pendant la durée d'un changement de rouleau du support d'impression (200). - Procédé de surveillance selon la revendication 12,
caractérisé en ce que
après la fin du changement de rouleau, plus particulièrement après une longueur d'impression prédéterminée, le programme spécial est terminé. - Procédé de surveillance selon l'une des revendications 7 à 13,
caractérisé en ce que
lors du déplacement de l'unité de capteur (22a) de la deuxième unité d'impression (110b), le décalage temporel par rapport à la première unité d'impression (110a) est pris en compte, plus particulièrement en tant que relation entre la longueur d'impression entre les deux unités d'impression (110a, 110b) et la vitesse d'impression.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102012110910.9A DE102012110910B4 (de) | 2012-11-13 | 2012-11-13 | Überwachungssystem für die Ausrichtung von Druckwerken einer Reihendruckmaschine |
| PCT/EP2013/070057 WO2014075841A1 (fr) | 2012-11-13 | 2013-09-26 | Système de surveillance pour l'orientation de groupes d'impression d'une machine à imprimer en ligne |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2919993A1 EP2919993A1 (fr) | 2015-09-23 |
| EP2919993B1 EP2919993B1 (fr) | 2017-03-22 |
| EP2919993B2 true EP2919993B2 (fr) | 2019-12-18 |
Family
ID=49293614
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP13771100.8A Active EP2919993B2 (fr) | 2012-11-13 | 2013-09-26 | Système de surveillance pour l'orientation de groupes d'impression d'une machine à imprimer en ligne |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2919993B2 (fr) |
| CN (1) | CN104853922B (fr) |
| DE (1) | DE102012110910B4 (fr) |
| ES (1) | ES2628370T5 (fr) |
| WO (1) | WO2014075841A1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11345139B2 (en) | 2015-04-10 | 2022-05-31 | Omet S.R.L. | System for registering the printing units of a rotary printing machine with manually-adjustable print register |
| JP6909063B2 (ja) * | 2017-06-15 | 2021-07-28 | 住友重機械工業株式会社 | 情報処理装置、印刷システム及び情報処理方法 |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3220093A1 (de) † | 1982-05-28 | 1983-12-01 | Licentia Patent-Verwaltungs-Gmbh, 6000 Frankfurt | Einrichtung zur farbdichtemessung an laufenden, bahnfoermigen druckmaterialien |
| EP0504486A1 (fr) † | 1991-03-20 | 1992-09-23 | HUECK & CIE | Procédé pour imprimer en registre en plusieurs couleurs, une bande de matériau, particulièrement un matériau mince |
Family Cites Families (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3811359C2 (de) | 1988-04-02 | 1994-06-16 | Heidelberger Druckmasch Ag | Vorrichtung zur Positionierung eines Meßkopfes für Passerabweichungen beim Offsetdruck |
| US5412577A (en) | 1992-10-28 | 1995-05-02 | Quad/Tech International | Color registration system for a printing press |
| DE4321179A1 (de) | 1993-06-25 | 1995-01-05 | Heidelberger Druckmasch Ag | Verfahren und Einrichtung zur Steuerung oder Regelung von Betriebsvorgängen einer drucktechnischen Maschine |
| IL113702A0 (en) | 1994-05-13 | 1995-08-31 | Advanced Vision Tech Ltd | General control for multiple color press devices |
| EP0882588B1 (fr) | 1997-06-02 | 2001-11-07 | Maschinenfabrik Wifag | Contrôle du repérage des cylindres dans une machine à imprimer rotative pour bandes |
| DE10261059B4 (de) * | 2002-12-24 | 2006-04-13 | Eltromat Gmbh | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Messen und Regeln eines Längs- und Seitenregisters sowie einer Druckbild-Parallelität eines Druckregisters in einer Mehrfarbendruckmaschine |
| DE10319770A1 (de) | 2003-05-02 | 2004-12-09 | Koenig & Bauer Ag | Verfahren zur Regelung der Farbdichte einer von einer Druckmaschine auf einem Druckträger aufgebrachten Farbe und Vorrichtung zur Regelung verschiedener für den Druckprozess einer Druckmaschine relevanter Parameter |
| DE10352619B4 (de) * | 2003-07-11 | 2012-09-27 | Koenig & Bauer Aktiengesellschaft | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Beeinflussung des Fan-Out-Effektes |
| TWI252809B (en) * | 2004-05-05 | 2006-04-11 | Bobst Sa | Method and device for initial adjustment of the register of the engraved cylinders of a rotary multicolour press |
| FI118759B (fi) * | 2005-07-01 | 2008-03-14 | Upm Kymmene Oyj | Menetelmä ja laitteisto painojäljen laadun tarkkailemiseksi |
| EP2269824B1 (fr) * | 2009-07-01 | 2012-09-12 | ELTROMAT GmbH | Procédé et dispositif de surveillance de l'ajustement du traitement de matériaux en forme de bandes dans des installations |
| DE102009046536B4 (de) * | 2009-11-09 | 2013-08-14 | Windmöller & Hölscher Kg | Rotationsdruckmaschine mit zumindest einem Farb- oder Druckwerk |
| CN202071485U (zh) * | 2011-05-24 | 2011-12-14 | 深圳扬丰印刷有限公司 | 一种放卷自动对准装置 |
| DE202011050286U1 (de) | 2011-05-30 | 2012-09-06 | Eltromat Gmbh | Druckmaschine mit Registermarkensensor |
| CN202192846U (zh) * | 2011-08-11 | 2012-04-18 | 湖北京山轻工机械股份有限公司 | 一种分压机根据纸边标记线横移精确纠偏装置 |
-
2012
- 2012-11-13 DE DE102012110910.9A patent/DE102012110910B4/de active Active
-
2013
- 2013-09-26 CN CN201380059409.4A patent/CN104853922B/zh active Active
- 2013-09-26 EP EP13771100.8A patent/EP2919993B2/fr active Active
- 2013-09-26 ES ES13771100T patent/ES2628370T5/es active Active
- 2013-09-26 WO PCT/EP2013/070057 patent/WO2014075841A1/fr active Application Filing
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3220093A1 (de) † | 1982-05-28 | 1983-12-01 | Licentia Patent-Verwaltungs-Gmbh, 6000 Frankfurt | Einrichtung zur farbdichtemessung an laufenden, bahnfoermigen druckmaterialien |
| EP0504486A1 (fr) † | 1991-03-20 | 1992-09-23 | HUECK & CIE | Procédé pour imprimer en registre en plusieurs couleurs, une bande de matériau, particulièrement un matériau mince |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2919993B1 (fr) | 2017-03-22 |
| CN104853922A (zh) | 2015-08-19 |
| EP2919993A1 (fr) | 2015-09-23 |
| DE102012110910A1 (de) | 2014-05-15 |
| CN104853922B (zh) | 2017-06-13 |
| ES2628370T5 (es) | 2020-06-29 |
| ES2628370T3 (es) | 2017-08-02 |
| DE102012110910B4 (de) | 2014-10-16 |
| WO2014075841A1 (fr) | 2014-05-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE102007049670B4 (de) | Verfahren zur Registerkorrektur bei einer Bearbeitungsmaschine sowie Bearbeitungsmaschine | |
| DE2701068A1 (de) | Schlitzvorrichtung fuer bahnenfoermiges material | |
| DE10052015A1 (de) | Bewegbarer Falzapparat und Falztrichteranordnung | |
| DE3606821C2 (fr) | ||
| EP2838822A1 (fr) | Dispositif de transport d'un substrat et système d'impression d'un substrat | |
| DE10236658B4 (de) | Schnittregister-Aufteilung | |
| EP4041537B1 (fr) | Appareil de pultrusion pour profiles courbes | |
| DE19936291B4 (de) | Bestimmung von Schnittlagen von Bahnsträngen in einer Rotationsdruckmaschine | |
| EP1619026B1 (fr) | Machine d'impression avec un dispositif de déclenchement d'un appareil de capture d'image et/ou d'illumination | |
| EP3802910A1 (fr) | Installation de revêtement sous vide et procédé pour munir un matériau en forme de bande d'un revêtement | |
| EP1388515B1 (fr) | Dispositif pour ajuster le répérage d'une découpeuse | |
| EP2919993B2 (fr) | Système de surveillance pour l'orientation de groupes d'impression d'une machine à imprimer en ligne | |
| DE102008048659A1 (de) | Vorrichtung und Verfahren zum Ausrichten von Bögen | |
| EP1867593A1 (fr) | Méthode et dispositif pour le traitement d'une bande en mouvement | |
| WO2019048232A1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif pour la fabrication d'un ruban adhésif | |
| DE102005045041B3 (de) | Vorrichtung und ein Verfahren zur Verwendung einer Vorrichtung zum Einziehen mindestens einer Materialbahn bzw. mindestens eines Bahnstrangs in einen Falzapparat | |
| DE1803179A1 (de) | Einrichtung zum Regeln der seitlichen Lage einer laufenden Materialbahn | |
| DE4203952C2 (de) | Verfahren zum Positionieren zweier Fühler bei einer Bahnlaufregeleinrichtung | |
| WO2007144185A1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif de traitement d'une bande de matière défilante | |
| DE102006057506A1 (de) | Verfahren zur Korrektur der Seitenposition eines Bedruckstoffes | |
| EP3098189A1 (fr) | Dispositif de separation d'une bande de materiau continue dans le sens de transport | |
| EP2470859B1 (fr) | Dispositif pour détecter au moins une position zéro | |
| DE102019121077A1 (de) | Drucksystem, insbesondere Tintenstrahldrucksystem, und Verfahren zum Schützen eines Druckkopfes beim Bedrucken eines Aufzeichnungsträgers | |
| EP1862303A2 (fr) | Unité de barres de retournement dans une machine rotative d'impression | |
| DE102008005392A1 (de) | Bahnspreizeinrichtung für eine Rotationsdruckmaschine und damit ausgerüstete Rotationsdruckmaschine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20150615 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| RIN1 | Information on inventor provided before grant (corrected) |
Inventor name: VOSSEBERG, MICHAEL Inventor name: DIL, BUELENT Inventor name: WESTHOF, FRANK Inventor name: BIETMANN, GUNDOLF Inventor name: BRINKMANN, CLEMENS Inventor name: NEUMANN, UDO Inventor name: BUECKER, HEINER |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20160603 |
|
| GRAJ | Information related to disapproval of communication of intention to grant by the applicant or resumption of examination proceedings by the epo deleted |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSDIGR1 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| INTC | Intention to grant announced (deleted) | ||
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20161007 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 877319 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20170415 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502013006747 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MP Effective date: 20170322 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170623 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170322 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170322 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170322 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170622 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2628370 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 Effective date: 20170802 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170322 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170322 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170622 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170322 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170322 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170322 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170322 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170322 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170322 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170724 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170722 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170322 Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170322 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R026 Ref document number: 502013006747 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| PLAX | Notice of opposition and request to file observation + time limit sent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS2 |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: MANROLAND WEB SYSTEMS GMBH Effective date: 20171221 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170322 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170322 |
|
| PLBB | Reply of patent proprietor to notice(s) of opposition received |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS3 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20170926 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170322 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20170930 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170926 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20180531 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170926 Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170926 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170930 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170930 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170930 Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20171002 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170322 |
|
| PLAB | Opposition data, opponent's data or that of the opponent's representative modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009299OPPO |
|
| R26 | Opposition filed (corrected) |
Opponent name: MANROLAND GOSS WEB SYSTEMS GMBH Effective date: 20171221 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20130926 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170322 |
|
| PUAH | Patent maintained in amended form |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009272 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 877319 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20180926 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: PATENT MAINTAINED AS AMENDED |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170322 |
|
| 27A | Patent maintained in amended form |
Effective date: 20191218 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B2 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R102 Ref document number: 502013006747 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180926 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: DC2A Ref document number: 2628370 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T5 Effective date: 20200629 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20170322 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Payment date: 20230905 Year of fee payment: 11 Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20230920 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20231018 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20240930 Year of fee payment: 12 |