EP2155563B1 - Maschine mit direktantrieb zur behandlung von behälter - Google Patents
Maschine mit direktantrieb zur behandlung von behälter Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2155563B1 EP2155563B1 EP08758850.5A EP08758850A EP2155563B1 EP 2155563 B1 EP2155563 B1 EP 2155563B1 EP 08758850 A EP08758850 A EP 08758850A EP 2155563 B1 EP2155563 B1 EP 2155563B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- motor
- drive
- housing
- unit
- rotor
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Not-in-force
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B67—OPENING, CLOSING OR CLEANING BOTTLES, JARS OR SIMILAR CONTAINERS; LIQUID HANDLING
- B67C—CLEANING, FILLING WITH LIQUIDS OR SEMILIQUIDS, OR EMPTYING, OF BOTTLES, JARS, CANS, CASKS, BARRELS, OR SIMILAR CONTAINERS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; FUNNELS
- B67C3/00—Bottling liquids or semiliquids; Filling jars or cans with liquids or semiliquids using bottling or like apparatus; Filling casks or barrels with liquids or semiliquids
- B67C3/02—Bottling liquids or semiliquids; Filling jars or cans with liquids or semiliquids using bottling or like apparatus
- B67C3/22—Details
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65C—LABELLING OR TAGGING MACHINES, APPARATUS, OR PROCESSES
- B65C9/00—Details of labelling machines or apparatus
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B67—OPENING, CLOSING OR CLEANING BOTTLES, JARS OR SIMILAR CONTAINERS; LIQUID HANDLING
- B67B—APPLYING CLOSURE MEMBERS TO BOTTLES JARS, OR SIMILAR CONTAINERS; OPENING CLOSED CONTAINERS
- B67B3/00—Closing bottles, jars or similar containers by applying caps
Definitions
- the invention relates to a treatment machine for containers, for.
- bottles cans or similar containers, for example, filled with a beverage, cleaned, provided with a label, equipped with a closure or comparable treatment routines are subjected, with at least one drive unit with regular electric drive motor and motor housing, further with a to the drive unit connected to a Manlpulatiansussi, and having a drive housing which accommodates the Antrlebsritt and at least one bearing for Manipulationselnheit, wherein the motor housing is also the Antrlebsgephase and forms a combined single motor / Antrlebsgephaseuse, and wherein the motor / drive housing at least one driven by the drive motor Has mounting flange as a bearing for direct connection of the manipulation unit.
- the EP 1 174 345 A1 with a treatment machine in which a drive unit is used in conjunction with a turntable.
- Such turntables are not used in a restrictive manner in order to move past the containers resting thereon at various treatment positions, for example on a labeling unit for transferring labels to the respective container, to brushing and / or pressing stations, etc.
- the known machine has a control unit and an actuator, which are housed in a common housing and can be replaced as a complete assembly.
- the drive unit can be completely replaced and thus examined independently of the treatment machine in question and optionally replaced.
- the invention is based on the technical problem of further developing such a handling machine for containers in such a way that the costs, the design complexity and the number of required components are further reduced.
- the invention proposes a treatment machine for containers, for. As bottles, cans or the like according to claim 1 before.
- the motor housing for receiving the drive motor also acts as a drive housing, thus forming the only combined motor / drive housing. Consequently, the combined motor / drive housing in question is not only set up for receiving the drive motor, but also has the bearing for the manipulation unit and optionally further devices and units in its interior. According to an advantageous embodiment, the aforementioned bearing is formed by at least one fastening flange driven by the drive motor, which is set up for the direct connection of the manipulation unit.
- the combined motor / drive housing has the mentioned driven mounting flange as a bearing.
- the combined motor / drive housing next to the drive motor and the bearing at least one sensor receives, which detects engine characteristics such as speed, rotation angle, engine temperature, etc. of the drive motor and transmitted to a control unit as needed.
- Dabel is universally universal using the combined single motor / drive housing, and thus the combined motor / drive unit as a whole.
- the described combined motor / drive unit can be used in conjunction with, for example, starwheels, as described in the EP 1 174 345 A1 to be discribed.
- the application in a capping machine according to the DE 103 52 016 B3 is of course conceivable and is encompassed by the inventive concept.
- the combination with a cleaning machine after the DE 197 03 369 A1
- the combined motor / drive unit with single motor / drive housing can replace any preferably rotary drive in a container handling machine.
- a linear actuator control can also be combined with the combined motor / drive unit in such a way that its mainly rotational movement is converted into a linear movement, for example with the aid of a rack drive or comparable gear arrangements.
- the combined single motor / drive housing of the motor / drive unit equipped with at least one hollow bore can be used for direct coupling with a drive shaft of the manipulation unit.
- the drive shaft of the manipulation unit in question requires no additional support (more), since this is provided by the mounting of the driven mounting flange in the motor / drive housing.
- the driven mounting flange is suitable for direct connection of the manipulation unit, for example via the inserted into the hollow bore and rotatably connected to the mounting flange drive shaft.
- the combined motor / drive unit with additional cooling z. B. water cooling
- This cooling is used primarily for the drive motor when needed.
- the drive motor with a brake, z. B. pneumatic brake be equipped.
- both the cooling and the brake are - again - included in the combined single motor / drive housing.
- a so-called reluctance motor As an electric drive motor, a so-called reluctance motor has proven to be favorable.
- a reluctance motor is a special design of an electric motor in which an associated rotor consists in particular of a soft magnetic material (eg iron) or such Has material and the corresponding stator contains the required magnetic coils.
- the rotor is neither equipped with permanent magnets nor energized. He has rather pronounced poles of the soft magnetic material. Accordingly, the operation is similar to an electric linear drive and works practically smoothly.
- the drive motor is a rotary, slotless synchronous motor, in which the magnetic coils of the stator are fastened on a flat iron ring.
- the equipped with a magnetic ring made of iron rotor is arranged taking into account an air gap compared to the stator.
- the drive motor has a high dynamic and a great flexibility in its construction and can cover a wide torque range up to several 1000 Nm.
- this design ensures that the combined motor / drive unit or the associated single motor / drive housing can be equipped at all with the already mentioned hollow bore for coupling to the drive shaft of the manipulation unit. Because both the stator and the rotor are each advantageously designed as a hollow cylinder and define in this way the already mentioned hollow bore in its interior, which is not mandatory.
- the invention also provides the use of an electric drive motor with motor housing as the drive unit according to claim 6.
- a treatment machine for container 1 is shown.
- the containers 1 are in the embodiment and not limiting bottles 1.
- cans or other vessels in the manner to be described below can be treated.
- Treatment means in the context of the invention, any manipulation of loading container 1, for example, his equipment with a in the Fig. 2 indicated label 2 in the context of the labeling machine shown, the attachment of a closure 3, as the Fig. 3 indicates or also the cleaning of the respective container 1 in the context of a cleaning machine, not shown, such as the object of the DE 197 03 369 A1 is.
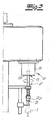
- a drive unit 4 with drive motor 5 and motor housing 6 is realized.
- a manipulation unit 7 is connected to the drive unit 4.
- the manipulation unit 7 is within the scope of the labeling machine Fig. 2 around a star wheel, whereas the manipulation unit 7 in the variant according to Fig. 3 is designed as a screw shaft or has such a container side which has a screw head 7a, which in turn attaches the closure 3 on the bottle 1.
- the drive unit 4 is accommodated in a drive housing 6, which according to the invention is at the same time the motor housing 6.
- the drive unit 4 has at least one bearing 8 for the manipulation unit 7 or for its connection.
- the bearing 8 is a fastening flange 8 which is driven rotatively by means of the drive motor 5.
- the fastening flange 8 is suitable for the direct connection of the manipulation unit 7.
- the fastening flange 8 closes off the cylindrical combined motor / drive housing 6 at the head in the manner of a cover.
- the manipulation unit 7 is directly connected to the mounting flange 8. While the motor / drive housing 6 is designed stationary and fixed by means of a fastening anchor 12 on an unspecified basis, in contrast, the mounting flange 8, driven by means of the drive motor 5 rotates.
- the motor housing 6 at the same time assumes the function of the drive housing 6, d. H. Motor housing 6 and drive housing 6 are congruent and form the combined single motor / drive housing 6. Consequently, this is a combined motor / drive unit 4, 5 with a single combined motor / drive housing. 6
- a sensor 9 In the interior of the single combined motor / drive housing 6 is in addition to the drive motor 5 additionally at least one sensor 9. With the help of this only in Fig. 1 indicated sensor 9 can detect the speed of the drive motor 5. In addition, the sensor 9 can also determine the angle of rotation of the drive motor 5 and its temperature. Associated data of the sensor 9 are connected to an externally connected and only in Fig. 1 indicated control unit 10 transmitted. The control unit 10 is usually used to control the entire treatment machine according to the Fig. 2 and 3 , This is not shown in detail.
- the combined motor / drive unit 4, 5 and, consequently, the only motor / drive housing 6 has at least one hollow bore 11.
- a drive shaft of the manipulation unit 7 can be added. This becomes immediate when looking at the Fig. 2 and 3 clearly where the drive shaft of the manipulation unit 7 each (non-rotatably) in the hollow bore 11 of the combined motor / drive unit 4, 5 is inserted.
- the hollow bore 11 is found in cup-shaped mounting flange 8, which is driven by the drive motor 5 rotatably. Consequently, the drive shaft rotatably in the hollow bore 11 of the mounting flange 8 wedged for the star wheel after Fig. 2 or the screw shaft according to the Fig. 3 when actuated by the drive motor 5 is rotated.
- the drive motor 5 or the combined motor / drive unit 4, 5 may with an additional and not explicitly shown cooling, z. B. water cooling, be equipped. It is also within the scope of the invention to provide a supplementary brake for the drive motor 5. Both the cooling and the brake are accommodated in the single combined motor / drive housing 6.
- the drive motor 5 used is a reluctance motor, that is to say an electric motor whose rotor 5a is made of soft magnetic material or has such material in the form of iron magnets attached thereto in the example.
- a stator 5b which contains only indicated magnetic coils.
- the operation of the reluctance motor is comparable to that of a linear electric motor.
- a rotating field is generated, which the rotor 5a follows with its iron magnets and rotates synchronously with the rotating field.
- the attachment flange 8 connected to the rotor 5a is also set in rotation, which is followed by the connected manipulation unit 7.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Connection Of Motors, Electrical Generators, Mechanical Devices, And The Like (AREA)
- Labeling Devices (AREA)
Description
- Die Erfindung betrifft eine Behandlungsmaschine für Behälter, z. B. Flaschen, Dosen oder vergleichbare Gefäße, die beispielsweise mit einem Getränk gefüllt, gereinigt, mit einem Etikett versehen, mit einem Verschluss ausgerüstet oder vergleichbaren Behandlungsroutinen unterzogen werden, mit zumindest einer Antriebseinheit mit regelmäßig elektrischem Antriebsmotor sowie Motorgehäuse, ferner mit einer an die Antriebseinheit angeschlossenen Manlpulatianseinheit, und mit einem Antriebsgehäuse, welches die Antrlebseinheit aufnimmt und wenigstens ein Lager für die Manipulationselnheit aufweist, wobei das Motorgehäuse zugleich das Antrlebsgehäuse ist und ein kombiniertes einziges Motor-/Antrlebsgehäuse formt, und wobei das Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse zumindest einen vom Antriebsmotor angetriebenen Befestigungsflansch als Lager zum unmittelbaren Anschluss der Manipulationseinheit aufweist.
- Im Rahmen der gattungsbildenden
WO 2005/115848 A2 , die eine Behandlungsmaschine gemäß dem Oberbegriff des Anspruchs 1 offenbart, ist eine Abtriebswelle das Antriebsmotors konzentrisch zur Drehachse eines Drehtellers angeordnet. Außerdem ist das obere Ende der Abtriebswelle in eine Aufnahmeeinheit gesteckt. Das wiederum obere Ende der Aufnahmeeinheit weist einen Drehteller auf. Daraus resultiert ein relativ ausladender und wenig kompakter Aufbau. Denn das Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse verfügt über eine ausgeprägte Ausdehnung In axialer Richtung. - Vergleichbares gilt für die ebenfalls gattungsgemäße
EP 1 596 488 A2 . Auch in diesem Fall ist die erforderliche Abtriebswelle des Antriebsmotores konzentrisch zur Drehachse eines Drehtellers angeordnet Als Folge hiervon stellt sich erneut ein ausladender Aufbau insbesondere In axialer Richtung ein. - Ganz abgesehen davon befasst sich die
EP 1 174 345 A1 mit einer Behandlungsmaschine, bei welcher eine Antriebseinheit in Verbindung mit einem Drehteller zum Einsatz kommt. Solche Drehteller werden nicht einschränkend eingesetzt, um die auf diesen aufstehenden Behälter an verschiedenen Behandlungspositionen vorbeizubewegen, beispielsweise an einem Etikettieraggregat zur Übergabe von Etiketten an den jeweiligen Behälter, an Anbürst- und/oder Andrückstationen usw.. - Zu diesem Zweck verfügt die bekannte Maschine über eine Steuer- und Regeleinheit sowie einen Stellantrieb, die in einem gemeinsamen Gehäuse untergebracht sind und sich als komplette Baugruppe austauschen lassen. Das hat sich bewährt, weil die Steuer- und Regeleinheit inklusive Stellantrieb funktionssicher in dem fraglichen Antriebsgehäuse untergebracht ist, Folglich Betriebsstörungen vermieden werden. Außerdem kann im Falle einer Funktionsstörung die Antriebseinheit komplett ausgetauscht und folglich unabhängig von der fraglichen Behandlungsmaschine untersucht und gegebenenfalls ersetzt werden.
- Ausgehend von diesem bewährten Stand der Technik besteht aktuell ein Bedürfnis danach, eine weitere konstruktive Vereinfachung zu erzielen und die Anzahl der verwendeten Bauteile und Baugruppen noch weiter zu verringern. Hier setzt die Erfindung ein.
- Der Erfindung liegt das technische Problem zugrunde, eine derartige Behendlungamaschine für Behälter so weiterzuentwickeln, dass die Kosten, der konstruktive Aufwand und die Anzahl der erforderlichen Bauteile noch weiter verringert sind.
- Zur Lösung dieser technischen Problemstellung schlägt die Erfindung eine Behandlungsmaschine für Behälter, z. B. Flaschen, Dosen oder dergleichen gemäß Anspruch 1 vor.
- Im Rahmen der Erfindung fungiert folglich das Motorgehäuse zur Aufnahme des Antriebsmotors zugleich als Antriebsgehäuse, bildet also das einzige kombinierte Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse. Folglich ist das fragliche kombinierte Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse nicht nur zur Aufnahme des Antriebsmotors eingerichtet, sondern weist auch das Lager für die Manipulationseinheit sowie gegebenenfalls weitere Einrichtungen und Aggregate in seinem Inneren auf. Nach vorteilhafter Ausgestaltung wird das vorgenannte Lager von zumindest einem seitens des Antriebsmotors angetriebenen Befestlgungsflansch gebildet, welcher zum unmittelbaren Anschluss der Manipulationseinheit eingerichtet ist. Das kombinierte Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse weist den erwähnten angetriebenen Befestigungsflansch als Lager auf. - Zusätzlich hat es sich bewährt, wenn das kombinierte Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse neben dem Antriebsmotor und dem Lager wenigstens noch einen Sensor aufnimmt, welcher Motoreigenschaften wie Drehzahl, Drehwinkel, Motortemperatur etc. des Antriebsmotors erfasst und bei Bedarf an eine Steuereinheit übermittelt.
- Auf diese Weise wird ein neuartiger Antrieb zur Verfügung gestellt, welcher sämtliche wesentlichen Eigenschaften und Funktionen einer Antriebseinheit in einer Behandlungsmaschine für Behälter übernimmt und zu deren Realisierung auf lediglich ein einziges kombiniertes Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse zurückgreift. D. h., im Rahmen der Erfindung werden gerade nicht ein separates Motorgehäuse und Antriebsgehäuse wie beispielsweise beim Stand der Technik nach der
EP 1 174 345 A1 verfolgt, sondern übernimmt das Motorgehäuse zugleich die Funktion des Antriebsgehäuses. - Auf diese Weise wird eine besonders kompakte und kostengünstige Bauweise erreicht. Außerdem lassen sich zahlreiche Bauteile einsparen, wie ein zusätzliches Antriebsgehäuse, ein ergänzendes Lager am Antriebsgehäuse zum Anschluss der Manipulationseinheit, Befestigungsmittel zur Anbringung der Manipulationseinheit an dem betreffenden Lager des Antriebsgehäuses, Dichtungen etc..
- Gleichzeitig wind der Bauraum verringert und werden geringere Fertigungskosten als bisher beobachtet. Dabel ist die Anwendung des kombinierten einzigen Motor-/Antriebsgehäuses und folglich der kombinierten Motor-/Antriebselnheit insgesamt universell. Tatsächlich lässt sich die beschriebene kombinierte Motor-/Antriebseinheit in Verbindung mit beispielsweise Sternrädern einsetzen, wie sie in der
EP 1 174 345 A1 beschrieben werden. Auch die Anwendung bei einer Verschließmaschine entsprechend derDE 103 52 016 B3 ist selbstverständlich denkbar und wird vom Erfindungsgedanken umfasst. Ebenso die Kombination mit einer Reinigungsmaschine nach derDE 197 03 369 A1 . - Letztendlich kann die kombinierte Motor-/Antriebseinheit mit einzigem Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse Jeden vorzugsweise rotativen Antrieb in einer Behandlungsmaschine für Behälter ersetzen. Auch ein linearer Stelitrleb kann mit der kombinierten Motor-/Antriebseinheit dergestalt kombiniert werden, dass seine hauptsächlich rotative Bewegung In eine lineare Bewegung umgewandelt wird, belspielsweise mit Hilfe eines Zahnstangenantriebes oder vergleichbaren Getriebeanordnungen.
- Dabei hat es sich ergänzend als besonders günstig erwiesen, dass das kombinierte einzige Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse der Motor-/Antriebseinheit mit zumindest einer Hohlbohrung ausgerüstet ist. Denn diese Hohlbohrung kann zur direkten Kopplung mit einer Antriebswelle der Manipulationseinheit genutzt werden. D. h., die fragliche Antriebswelle der Manipulationseinheit benötigt keine zusätzliche Lagerung (mehr), da diese durch die Lagerung des angetriebenen Befestigungsflansches im Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse zur Verfügung gestellt wird. Der angetriebene Befestigungsflansch eignet sich zum unmittelbaren Anschluss der Manipulationseinheit, beispielsweise über die in die Hohlbohrung eingesteckte und mit dem Befestigungsflansch drehfest verbundene Antriebswelle.
- Ergänzende Optionen bestehen darin, dass die kombinierte Motor-/Antriebseinheit mit einer zusätzlichen Kühlung, z. B. Wasserkühlung, ausgerüstet wird. Diese Kühlung wird primär für den Antriebsmotor bei Bedarf genutzt. Zusätzlich kann der Antriebsmotor mit einer Bremse, z. B. pneumatischen Bremse, ausgerüstet werden. Sowohl die Kühlung als auch die Bremse werden selbstverständlich - wiederum - in dem kombinierten einzigen Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse aufgenommen.
- Als elektrischer Antriebsmotor hat sich ein sogenannter Reluktanzmotor als günstig erwiesen. Bei einem solchen Reluktanzmotor handelt es sich um eine spezielle Bauform eines Elektromotors, bei welchem ein zugehöriger Rotor aus insbesondere weichmagnetischem Material (z. B. Eisen) besteht bzw. solches Material aufweist und der korrespondierende Stator die erforderlichen Magnetspulen enthält. Der Rotor ist weder mit Permanentmagneten bestückt noch wird er bestromt. Er besitzt vielmehr ausgeprägte Pole aus dem weichmagnetischem Material. Dementsprechend ist die Funktionsweise ähnlich wie bei einem elektrischen Linearantrieb und funktioniert praktisch reibungslos. In vorteilhafter Ausgestaltung handelt es sich bei dem Antriebsmotor um einen rotativen nutenlosen Synchronmotor, bei welchem die Magnetspulen des Stators auf einem flachen Eisenring befestigt sind. Demgegenüber ist der mit einem Magnetring aus Eisen ausgerüstete Rotor unter Berücksichtigung eines Luftspaltes im Vergleich zum Stator angeordnet.
- Auf diese Weise verfügt der Antriebsmotor über eine hohe Dynamik und eine große Flexibilität hinsichtlich seiner Konstruktion und kann einen weiten Drehmomentbereich bis zu mehreren 1000 Nm abdecken. Außerdem gewährleistet diese Bauform, dass die kombinierte Motor-/Antriebseinheit bzw. das zugehörige einzige Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse überhaupt mit der bereits angesprochenen Hohlbohrung zur Kopplung mit der Antriebswelle der Manipulationseinheit ausgerüstet werden kann. Denn sowohl der Stator als auch der Rotor sind jeweils vorteilhaft hohlzylindrisch ausgebildet und definieren auf diese Weise die bereits angesprochene Hohlbohrung in ihrem Innern, die jedoch nicht zwingend ist.
- Gegenstand der Erfindung ist auch die Verwendung eines elektrischen Antriebsmotors mit Motorgehäuse als Antriebseinheit nach Anspruch 6.
- Im Folgenden wird die Erfindung anhand einer lediglich ein Ausführungsbeispiel darstellenden Zeichnung näher erläutert; es zeigen:
- Fig. 1
- die erfindungsgemäße kombinierte Motor-/Antriebseinheit schematisch im Schnitt,
- Fig. 2
- eine Anwendung der kombinierten Motor-/Antriebseinheit bei einer Behandlungsmaschine für Behälter, vorliegend einer Etikettiermaschine und
- Fig. 3
- einen anderen Anwendungsfall bei einer Behandlungsmaschine, die als Verschließmaschine ausgeführt ist.
- In den
Fig. 2 und3 ist jeweils eine Behandlungsmaschine für Behälter 1 dargestellt. Bei den Behältern 1 handelt es sich im Ausführungsbeispiel und nicht einschränkend um Flaschen 1. Tatsächlich können auch Dosen oder andere Gefäße in der nachfolgend noch zu beschreibenden Art und Weise behandelt werden. Behandlung meint im Rahmen der Erfindung jede Manipulation am Be-hälter 1, beispielsweise seine Ausrüstung mit einem in derFig. 2 angedeuteten Etikett 2 im Rahmen der dargestellten Etikettiermaschine, die Anbringung eines Verschlusses 3, wie dieFig. 3 andeutet oder auch die Reinigung des jeweiligen Behälters 1 im Rahmen einer nicht dargestellten Reinigungsmaschine, wie sie beispielsweise Gegenstand derDE 197 03 369 A1 ist. - Diese sämtlichen Behandlungen bzw. die einzelnen Behandlungsmaschinen zeichnen sich dadurch aus, dass eine Antriebseinheit 4 mit Antriebsmotor 5 und Motorgehäuse 6 realisiert ist. An die Antriebseinheit 4 ist eine Manipulationseinheit 7 angeschlossen. Bei der Manipulationseinheit 7 handelt es sich im Rahmen der Etikettiermaschine nach
Fig. 2 um ein Sternrad, wohingegen die Manipulationseinheit 7 bei der Variante nachFig. 3 als Schraubwelle ausgeführt ist bzw. eine solche aufweist, welche behälterseitig einen Schraubkopf 7a aufweist, der seinerseits den Verschluss 3 auf der Flasche 1 anbringt. - Die Antriebseinheit 4 wird in einem Antriebsgehäuse 6 aufgenommen, weiches erfindungsgemäß zugleich das Motorgehäuse 6 ist. Zusätzlich weist die Antriebseinheit 4 wenigstens ein Lager 8 für die Manipulationseinheit 7 bzw. zu deren Anschluss auf.
- Im Rahmen des Ausführungsbeispiels handelt es sich bei dem Lager 8 um einen mit Hilfe des Antriebsmotors 5 rotativ angetriebenen Befestigungsflansch 8. Der Befestigungsflansch 8 ist zum unmittelbaren Anschluss der Manipulationseinheit 7 geeignet. Im Übrigen schließt der Befestigungsflansch 8 das zylindrische kombinierte Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse 6 kopfseitig in der Art eines Deckels ab. Tatsächlich ist die Manipulationseinheit 7 unmittelbar mit dem Befestigungsflansch 8 verbunden. Während das Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse 6 ortsfest ausgelegt und mit Hilfe eines Befestigungsankers 12 an einer nicht näher spezifizierten Basis festgelegt ist, rotiert demgegenüber der Befestigungsflansch 8, und zwar angetrieben mit Hilfe des Antriebsmotors 5.
- Wie bereits ausgeführt, übernimmt das Motorgehäuse 6 zugleich die Funktion des Antriebsgehäuses 6, d. h. Motorgehäuse 6 und Antriebsgehäuse 6 sind deckungsgleich und formen das kombinierte einzige Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse 6. Folgerichtig handelt es sich vorliegend um eine kombinierte Motor-/Antriebseinheit 4, 5 mit einzigem kombinierten Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse 6.
- Im Innern des einzigen kombinierten Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse 6 findet sich neben dem Antriebsmotor 5 zusätzlich noch wenigstens ein Sensor 9. Mit Hilfe dieses lediglich in
Fig. 1 angedeuteten Sensors 9 lässt sich die Drehzahl des Antriebsmotors 5 erfassen. Ergänzend kann der Sensor 9 auch den Drehwinkel des Antriebsmotors 5 bestimmen sowie dessen Temperatur. Zugehörige Daten des Sensors 9 werden an eine extern angeschlossene und lediglich inFig. 1 angedeutete Steuereinheit 10 übermittelt. Die Steuereinheit 10 dient üblicherweise zur Steuerung der gesamten Behandlungsmaschine entsprechend denFig. 2 und3 . Das ist im Detail jedoch nicht dargestellt. - Anhand der Schnittdarstellung in
Fig. 1 erkennt man, dass die kombinierte Motor-/Antriebseinheit 4, 5 und folgerichtig das einzige Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse 6 zumindest eine Hohlbohrung 11 aufweist. In dieser Hohlbohrung 11 kann eine Antriebswelle der Manipulationseinheit 7 aufgenommen werden. Das wird unmittelbar beim Betrachten derFig. 2 und3 deutlich, wo die Antriebswelle der Manipulationseinheit 7 jeweils (drehfest) in die Hohlbohrung 11 der kombinierten Motor-/Antriebseinheit 4, 5 eingesteckt ist. Denn die Hohlbohrung 11 findet sich im topfförmig gestalteten Befestigungsflansch 8, welcher durch den Antriebsmotor 5 rotativ angetrieben wird. Folglich wird auch die drehfest in der Hohlbohrung 11 des Befestigungsflansches 8 verkeilte Antriebswelle für das Sternrad nachFig. 2 bzw. die Schraubwelle entsprechend derFig. 3 bei Beaufschlagung des Antriebsmotors 5 in Rotationen versetzt. - Der Antriebsmotor 5 bzw. die kombinierte Motor-/Antriebseinheit 4, 5 mag mit einer zusätzlichen und nicht ausdrücklich dargestellten Kühlung, z. B. Wasserkühlung, ausgerüstet werden. Ebenso liegt es im Rahmen der Erfindung, für den Antriebsmotor 5 eine ergänzende Bremse vorzusehen. Sowohl die Kühlung als auch die Bremse werden in dem einzigen kombinierten Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse 6 aufgenommen.
- Als Antriebsmotor 5 kommt vorliegend ein Reluktanzmotor zum Einsatz, also ein Elektromotor, dessen Rotor 5a aus weichmagnetischem Material hergestellt ist bzw. solches Material in Gestalt von daran angebrachten Eisenmagneten im Beispielfall aufweist. Mit dem Rotor 5a ist der rotativ angetriebene Befestigungsflansch 8 und folglich auch die bereits angesprochene Antriebswelle für das Sternrad (
Fig. 2 ) bzw. die Schraubwelle (Fig. 3 ) verbunden. - Zu dem Rotor 5a des Antriebsmotors 5 korrespondiert ein Stator 5b, welcher lediglich angedeutete Magnetspulen enthält. Die Funktionsweise des Reluktanzmotors ist vergleichbar mit derjenigen eines elektrischen Linearmotors. Tatsächlich wird in den Magnetspulen des Stators 5b ein Drehfeld erzeugt, welchem der Rotor 5a mit seinen Eisenmagneten folgt und sich synchron mit dem Drehfeld dreht. Als Folge hiervon wird auch der an den Rotor 5a angeschlossene Befestigungsflansch 8 in Drehungen versetzt, welchen die angeschlossene Manipulationseinheit 7 folgt.
Claims (6)
- Behandlungsmaschine für Behälter (1), z. B. Flaschen (1), Dosen oder dergleichen, mit zumindest einer Antriebseinheit (4) mit Antrlebsmotor (5) sowie Motorgehäuse (6), ferner mit einer an die Antriebseinheit (4) angeschlossenen Manipulationseinheit (7), und mit einem Antriebsgehäuse (6), welches die Antriebseinheit (4) aufnimmt und wenigstens ein Lager (8) für die Manipulationseinheit (7) aufweist, wobei- das Motorgehäuse (6) zugleich das Antriebsgehäuse (6) ist und ein kombiniertes einziges Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse (6) formt, und wobei- das Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse (6) zumindest einen vom Antriebsmotor (5) angetriebenen Befestigungsflansch (8) als Lager (8) zum unmittelbaren Anschluss der Manipulationseinheit (7) aufweist,dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass- der Antriebsmotor (5) als Reluktanzmotor mit hoher Dynamik und großer Flexibilität hinsichtlich seiner Konstruktion ausgebildet ist und einen weiten Drehmomentbereich bis zu mehreren 1000 Nm abdeckt und dazu mit einem Rotor (5a) und einem Stator (5b) ausgebildet ist,- wobei der Rotor (5a) ausgeprägte Pole aus einem weichmagnetischem Material besitzt und- der korrespondierende Stator (5b) die erforderlichen Magnetspulen enthält, und wobei- der Stator (5b) sowie der Rotor (5a) des Antriebsmotors (5) jeweils hohlzylindrisch ausgebildet sind und- hierdurch in ihrem Innern eine Hohlbohrung (11) zur drehfesten Kopplung mit einer Antriebswelle der Manipulationseinheit (7) definieren.
- Behandlungsmaschine nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das kombinierte Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse (6) neben dem Antriebsmotor (5) wenigstens einen Sensor (9) aufnimmt, welcher Motorelgenschaften wie Drehzahl, Drehwinkel, Temperatur etc. des Antriebsmotors (5) erfasst.
- Behandlungsmaschine nach Anspruch 1 oder 2, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass der Befestigungsflansch (8) das Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse (6) kopfseitig in der Art eines Deckels abschließt.
- Behandlungsmaschine nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 3, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass zusätzlich eine Kühlung vorgesehen ist.
- Behandlungsmaschine nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 4, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass dem Antriebsmotor (5) eine Bremse zugeordnet Ist.
- Verwendung eines elektrischen Antriebsmotors (5) mit Motorgehäuse (6) als Antriebseinheit (4) mit kombiniertem einzigen Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse (6) zum direkten Anschluss an eine Manipulationseinheit (7) im Zuge der Behandlung von Behältern, zum Beispiel Flaschen (1), Dosen oder dergleichen, in zugehörigen Behandlungsmaschinen, wobei das Motor-/Antriebsgehäuse (6) zumindest einen vom Antriebsmotor (5) angetriebenen Befestigungsflansch (8) als Lager (8) zum unmittelbaren Anschluss der Manipulationseinheit (7) aufweist, und der Antriebsmotor (5) als Reluktanzmotor mit hoher Dynamik und großer Flexibilität hinsichtlich seiner Konstruktion ausgebildet ist und einen weiten Drehmomentbereich bis zu mehreren 1000 Nm abdeckt und dazu mit einem Rotor (5a) und einem Stator (5b) ausgebildet ist, wobei der Rotor (5a) ausgeprägte Pole aus einem weichmagnetischem Material besitzt und der korrespondierende Stator (5b) die erforderlichen Magnetspulen enthält, und wobei der Stator (5b) sowie der Rotor (5a) des Antriebsmotors (5) jeweils hohlzylindrisch ausgebildet sind und hierdurch in ihrem Innern eine Hohlbohrung (11) zur drehfesten Kopplung mit einer Antriebswelle der Manipulationseinheit (7) definieren.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| SI200831513T SI2155563T1 (sl) | 2007-05-31 | 2008-05-29 | Stroj z neposrednim pogonom za obdelavo vsebnikov |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE200710025522 DE102007025522A1 (de) | 2007-05-31 | 2007-05-31 | Maschine mit Direktantrieb zur Behandlung von Behältern |
| PCT/EP2008/004267 WO2008145363A1 (de) | 2007-05-31 | 2008-05-29 | Maschine mit direktantrieb zur behandlung von behälter |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2155563A1 EP2155563A1 (de) | 2010-02-24 |
| EP2155563B1 true EP2155563B1 (de) | 2015-09-16 |
Family
ID=39730854
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP08758850.5A Not-in-force EP2155563B1 (de) | 2007-05-31 | 2008-05-29 | Maschine mit direktantrieb zur behandlung von behälter |
Country Status (8)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2155563B1 (de) |
| JP (1) | JP5449141B2 (de) |
| CN (1) | CN101678910B (de) |
| BR (1) | BRPI0813106A2 (de) |
| DE (1) | DE102007025522A1 (de) |
| RU (1) | RU2429171C1 (de) |
| SI (1) | SI2155563T1 (de) |
| WO (1) | WO2008145363A1 (de) |
Families Citing this family (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102008038146A1 (de) * | 2008-08-18 | 2010-02-25 | Krones Ag | Vorrichtung zum Behandeln von Behältern |
| DE102009009822A1 (de) * | 2009-02-20 | 2010-08-26 | Krones Ag | Vorrichtung zum Verschließen von Behältnissen mit berührungsloser Drehmomentenerzeugung |
| DE202009019170U1 (de) | 2009-09-07 | 2017-07-07 | Krones Ag | Vorrichtung zum Herstellen von Kunstoffflaschen |
| DE102009055301A1 (de) | 2009-12-23 | 2011-06-30 | Krones Ag, 93073 | Behältertransporteur |
| DE102010027337A1 (de) | 2010-07-15 | 2012-01-19 | Khs Gmbh | Behandlungsmaschine für Behälter |
| DE102011003118A1 (de) | 2011-01-25 | 2012-07-26 | Krones Aktiengesellschaft | Verschließeinrichtung |
| DE102011103837A1 (de) | 2011-06-01 | 2012-12-06 | Khs Gmbh | Behandlungsmaschine für Behälter |
| JP5500144B2 (ja) * | 2011-09-07 | 2014-05-21 | 株式会社安川電機 | 回転電機 |
| DE102012000881A1 (de) | 2011-12-14 | 2013-06-20 | Khs Gmbh | Behandlungsmaschine für Behälter |
| EP2610187B1 (de) * | 2011-12-30 | 2016-12-28 | Krones AG | Vorrichtung zum Transferieren von Ausstattungsteilen für die Behälteretikettierung |
| DE102012204721A1 (de) * | 2012-03-23 | 2013-09-26 | Schaeffler Technologies AG & Co. KG | Direktantrieb für eine Rotationsmaschine, insbesondere für eine Behälterbehandlungsmaschine |
| DE102012209905A1 (de) * | 2012-06-13 | 2013-12-19 | Krones Ag | Verschließer für Behälter |
| DE102012209970A1 (de) * | 2012-06-14 | 2013-12-19 | Krones Ag | Monotec-sternsäulen mit umluftkühler |
| DE102013218438A1 (de) * | 2013-09-13 | 2015-03-19 | Krones Ag | Rundläufermaschine mit Direktantrieb |
| CN104743345B (zh) * | 2013-12-31 | 2017-05-17 | 楚天科技股份有限公司 | 双列瓶体排列输送方法及装置 |
| DE102014100733A1 (de) * | 2014-01-23 | 2015-07-23 | Krones Ag | Kühlsystem für Behälterbehandlungsanlagen |
| DE102015216089B4 (de) | 2014-09-11 | 2024-06-06 | Baumüller Nürnberg GmbH | Dosiervorrichtung, Getränke-Abfüllanlage und Verwendung einer Dosiervorrichtung |
| JP6785691B2 (ja) | 2017-03-13 | 2020-11-18 | 住友重機械工業株式会社 | 駆動装置 |
| DE102019119596A1 (de) * | 2019-07-19 | 2021-01-21 | Khs Gmbh | Füllmaschine zum Füllen von Behältern mit einem flüssigen Füllgut und Verfahren zum Kühlen einer Antriebs- und/oder Getriebeeinheit einer Füllmaschine |
| CN111646419B (zh) * | 2020-06-09 | 2021-07-16 | 王锦 | 一种生物试剂的装取装置 |
Family Cites Families (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE1970339U (de) | 1967-07-17 | 1967-10-12 | Rheinische Draht Und Kabelwerk | Schweisszange. |
| JPH0297248A (ja) * | 1988-09-08 | 1990-04-09 | Ntn Corp | 回転角検出機能付ddモータ |
| US5281296A (en) * | 1991-07-30 | 1994-01-25 | Markem Corporation | Label applicator |
| DE9217784U1 (de) * | 1992-12-29 | 1993-04-08 | Schneider, Friedhelm, 5226 Reichshof | Füllrohr für hochviskose Flüssigkeiten |
| DE19703369A1 (de) | 1997-01-30 | 1998-08-06 | Khs Masch & Anlagenbau Ag | Vorrichtung zum Transportieren von Gefäßen |
| DE29724886U1 (de) * | 1997-09-15 | 2005-04-14 | Krones Ag | Maschine zum Behandeln von Gefäßen |
| JP4196433B2 (ja) * | 1998-07-09 | 2008-12-17 | 日本精工株式会社 | 密閉型アクチュエータ |
| IT1304700B1 (it) * | 1998-12-23 | 2001-03-28 | Antas S P A | Apparecchiatura per la lavorazione del vetro con sistema a giostraperfezionato e suo metodo di controllo |
| DE10034907A1 (de) | 2000-07-18 | 2002-01-31 | Khs Masch & Anlagenbau Ag | Maschine zum Behandeln von Flaschen, Dosen o. dgl. Behälter |
| DE10352016B3 (de) | 2003-11-07 | 2005-08-11 | Khs Maschinen- Und Anlagenbau Ag | Verschließmaschine zum Verschließen von Gefäßen |
| DE102004024136B4 (de) * | 2004-05-14 | 2023-08-10 | Khs Gmbh | Antriebsmotor mit integrierten Wellenverbindungselementen |
| DE202004021791U1 (de) * | 2004-05-29 | 2011-02-10 | Krones Ag | Maschine zum Ausrichten und Ausstatten von Gegenständen |
| EP1864911B1 (de) * | 2006-06-06 | 2012-09-05 | Sidel Holdings & Technology S.A. | Motor und Trägerplatte in einer Etikettiermaschine |
| DE102006039090A1 (de) * | 2006-08-19 | 2008-02-21 | Khs Ag | Antrieb für Rotationsmaschinen |
-
2007
- 2007-05-31 DE DE200710025522 patent/DE102007025522A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
2008
- 2008-05-29 WO PCT/EP2008/004267 patent/WO2008145363A1/de active Application Filing
- 2008-05-29 JP JP2010509733A patent/JP5449141B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2008-05-29 CN CN200880017484.3A patent/CN101678910B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2008-05-29 SI SI200831513T patent/SI2155563T1/sl unknown
- 2008-05-29 BR BRPI0813106A patent/BRPI0813106A2/pt not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2008-05-29 EP EP08758850.5A patent/EP2155563B1/de not_active Not-in-force
- 2008-05-29 RU RU2009149433/12A patent/RU2429171C1/ru not_active IP Right Cessation
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| RU2429171C1 (ru) | 2011-09-20 |
| WO2008145363A1 (de) | 2008-12-04 |
| CN101678910A (zh) | 2010-03-24 |
| CN101678910B (zh) | 2013-12-18 |
| SI2155563T1 (sl) | 2015-11-30 |
| EP2155563A1 (de) | 2010-02-24 |
| BRPI0813106A2 (pt) | 2018-06-05 |
| JP5449141B2 (ja) | 2014-03-19 |
| RU2009149433A (ru) | 2011-07-10 |
| DE102007025522A1 (de) | 2008-12-04 |
| JP2010527858A (ja) | 2010-08-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2155563B1 (de) | Maschine mit direktantrieb zur behandlung von behälter | |
| EP2338813B1 (de) | Behältertransporteur | |
| EP1529751B1 (de) | Verschliessmaschine zum Verschliessen von Gefässen | |
| EP2479136A2 (de) | Verschließeinrichtung | |
| DE102007057857A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Verschließen von Behältern | |
| DE2151916A1 (de) | Magnetische Lagerung | |
| DE202004021791U1 (de) | Maschine zum Ausrichten und Ausstatten von Gegenständen | |
| WO2010081515A2 (de) | Behälterbehandlungsmaschine | |
| WO2011141236A2 (de) | Antriebsvorrichtung für dreh- und linearbewegungen mit entkoppelten trägheiten | |
| EP2221272A2 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Verschließen von Behältnissen mit berührungsloser Drehmomentenerzeugung | |
| DE10024327A1 (de) | Antrieb eines rotierenden Bauteils einer Druckmaschine und Verfahren zum Trennen eines Antriebes | |
| EP2105404A2 (de) | Vortisch für Behälterbehandlungsmaschinen sowie Behälterbehandlungsmaschine | |
| EP1082225B1 (de) | Walze für eine rotationsdruckmaschine | |
| EP0689277B1 (de) | Anordnung eines Elektromotors zum Antrieb eines Drehkörpers | |
| EP2714528B1 (de) | Behandlungsmaschine für behälter | |
| EP1728574A1 (de) | Spannvorrichtung einer Werkzeugmaschine | |
| EP2593370B1 (de) | Behandlungsmaschine für behälter | |
| DE102009032231A1 (de) | Direktantrieb für hin und her gehende Bewegung | |
| DE102017105509A1 (de) | Verschließmaschine | |
| WO2017005472A1 (de) | Antriebsanordnung für eine schwenkbrücke | |
| DE102008061848A1 (de) | Vorrichtung und Verfahren zum Verschließen von Behältern mit einem Verschluss | |
| DE3844288C1 (de) | ||
| DE10032815A1 (de) | Steuerkurvenunabhängiger Antrieb für Falzkomponenten | |
| WO2011047893A1 (de) | Vorrichtungen in einem druckwerk einer druckmaschine | |
| DE29921343U1 (de) | Verschließvorrichtung zum Aufschrauben von Verschlußkappen auf Behälter |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20100104 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL BA MK RS |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: KHS GMBH Owner name: SCHAEFFLER KG Owner name: INA DRIVES & MECHATRONIC GMBH & CO. OHG |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20100916 |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: KHS GMBH Owner name: INA DRIVES & MECHATRONIC GMBH & CO. OHG Owner name: SCHAEFFLER TECHNOLOGIES AG & CO. KG |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: SCHAEFFLER TECHNOLOGIES AG & CO. KG Owner name: KHS GMBH |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: KHS GMBH Owner name: SCHAEFFLER TECHNOLOGIES GMBH & CO. KG |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: KHS GMBH Owner name: SCHAEFFLER TECHNOLOGIES AG & CO. KG |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20150625 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: E. BLUM AND CO. AG PATENT- UND MARKENANWAELTE , CH Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 749596 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20151015 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502008013388 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MP Effective date: 20150916 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150916 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150916 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151217 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151216 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150916 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150916 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150916 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150916 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150916 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150916 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150916 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160116 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150916 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150916 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160118 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150916 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502008013388 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20160617 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150916 Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20160531 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160529 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20160529 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20160529 Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20160529 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150916 Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20080529 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150916 Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150916 Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150916 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150916 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20180522 Year of fee payment: 11 Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20180523 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20180530 Year of fee payment: 11 Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20180522 Year of fee payment: 11 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20180522 Year of fee payment: 11 Ref country code: SI Payment date: 20180504 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 502008013388 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 749596 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20190529 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20190529 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20190531 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20190531 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20190530 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20190529 Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20191203 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20190531 |