EP1151857B1 - Gesteuerte Bebilderung und Löschung einer Druckform aus metallischem Titan - Google Patents
Gesteuerte Bebilderung und Löschung einer Druckform aus metallischem Titan Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1151857B1 EP1151857B1 EP01109311A EP01109311A EP1151857B1 EP 1151857 B1 EP1151857 B1 EP 1151857B1 EP 01109311 A EP01109311 A EP 01109311A EP 01109311 A EP01109311 A EP 01109311A EP 1151857 B1 EP1151857 B1 EP 1151857B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- printing
- printing form
- offset printing
- point
- titanium
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000007639 printing Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 90
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium Chemical compound [Ti] RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 title claims abstract description 52
- 239000010936 titanium Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 50
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 title claims abstract description 50
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 title claims 3
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 title description 14
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 29
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 11
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 11
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 9
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 9
- 229920003023 plastic Polymers 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 16
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 claims description 16
- 238000007645 offset printing Methods 0.000 claims description 16
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 14
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 11
- 230000002209 hydrophobic effect Effects 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 4
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 2
- 230000005670 electromagnetic radiation Effects 0.000 claims 2
- 239000004411 aluminium Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 10
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000011224 oxide ceramic Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229910052574 oxide ceramic Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphoric acid Chemical compound OP(O)(O)=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000012876 carrier material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000002048 anodisation reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000012217 deletion Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000037430 deletion Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000003595 spectral effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nickel Chemical compound [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfuric acid Chemical compound OS(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000002679 ablation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910000147 aluminium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005253 cladding Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000976 ink Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003446 memory effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229910001000 nickel titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000003973 paint Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 238000004549 pulsed laser deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910001369 Brass Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 206010073306 Exposure to radiation Diseases 0.000 description 1
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Magnesium Chemical compound [Mg] FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920002125 Sokalan® Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910010413 TiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000005299 abrasion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011149 active material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001298 alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000012670 alkaline solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000010407 anodic oxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008033 biological extinction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000010951 brass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012822 chemical development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007812 deficiency Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002848 electrochemical method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009713 electroplating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 description 1
- -1 ferrous metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000011888 foil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000005660 hydrophilic surface Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011147 inorganic material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000011031 large-scale manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000873 masking effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007769 metal material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000006259 organic additive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011368 organic material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001590 oxidative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007750 plasma spraying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004584 polyacrylic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000004760 silicates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000003980 solgel method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004544 sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000035882 stress Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003746 surface roughness Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008646 thermal stress Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001931 thermography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000005028 tinplate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007740 vapor deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920002554 vinyl polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000007704 wet chemistry method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009736 wetting Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41C—PROCESSES FOR THE MANUFACTURE OR REPRODUCTION OF PRINTING SURFACES
- B41C1/00—Forme preparation
- B41C1/10—Forme preparation for lithographic printing; Master sheets for transferring a lithographic image to the forme
- B41C1/1041—Forme preparation for lithographic printing; Master sheets for transferring a lithographic image to the forme by modification of the lithographic properties without removal or addition of material, e.g. by the mere generation of a lithographic pattern
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41N—PRINTING PLATES OR FOILS; MATERIALS FOR SURFACES USED IN PRINTING MACHINES FOR PRINTING, INKING, DAMPING, OR THE LIKE; PREPARING SUCH SURFACES FOR USE AND CONSERVING THEM
- B41N3/00—Preparing for use and conserving printing surfaces
- B41N3/006—Cleaning, washing, rinsing or reclaiming of printing formes other than intaglio formes
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a reusable printing form, in particular for use in offset printing, with a printing surface and a method for imaging a reusable printing form with a printing surface.
- the lithographic printing is based on utilizing the immiscibility of oil and water on the printing form, whereby the lipophilic solution or the ink or ink is captured by the image-forming areas and the water or hydrophilic solution by the non-image forming areas of the printing area.
- the suitably prepared printing surface is wetted with hydrophilic and lipophilic substance or solution, especially water and ink or paint
- the non-image areas preferentially retain the hydrophilic substance or solution and repel the lipophilic substances while the imagewise regions repel the lipophilic ones Take solution or ink or paint and repel the hydrophilic substances.
- the lipophilic substance is then suitably transferred to the surface of a material on which the image is to be fixed, for example, paper, cloth, polymers and the like.
- aluminum has been used as a substrate for printing plates.
- the aluminum is first subjected to a graining process and then a subsequent anodization process.
- the anodization serves to provide an anodic oxide layer whose adhesion is improved by the grain. Graining enhances the hydrophilic properties of the background of the printing plate.
- a strong acid such as sulfuric or phosphoric acid is usually used to subsequently make the surface hydrophilic by another method such as a thermal silicization method or so-called electrosilication.
- the aluminum support can be characterized as having a porous, demolition-resistant, hydrophilic surface, which is particularly adapted to lithographic printing, especially in the case of long print passes.
- hydrophilic barrier layers in particular of polyvinyl phosphoric acid, polyacrylic acid, silicates, zirconates, or titanates.
- a large number of radiation-sensitive materials are known which are suitable for generating images in the use of the lithographic printing process in that, after exposure and optionally required development and fixing, they provide an image-wise range which can be used for printing.
- photopolymerizable substances can be used for this purpose.
- the above-described arrangement is subjected to imagewise exposure by selectively supplying energy. This can be done for example by means of the exposure through a mask with UV light or by direct writing with a laser.
- the lithographic printing plates of the type described above are usually treated with a developing solution, which is typically an aqueous alkaline solution with organic additives.
- a developing solution typically an aqueous alkaline solution with organic additives.
- oxide ceramics which are present for example in the form of coatings on a printing plate, are used.
- zirconate in ceramic pure or provided with other additives form as the active material in the surface.
- the surface is spotwise exposed to laser radiation, ie, melted, and is thereby converted from a hydrophilic, stoichiometric to a lipophilic, substoichiometric state. This conversion to the substoichiometric state is accomplished by ablation of small amounts of the surface of the ceramic.
- the printing form can be erased by thermally oxidizing the surface.
- oxide ceramics as a printing surface, however, has significant deficiencies. Since oxide ceramics are much harder and more brittle than metals, stresses occur in and between the layers, leading to detachment from the substrate, be it a metal substrate or a film, in particular a polymer. In particular, by bending the substrate may cause cracks and chipping.
- the required temperatures are above the melting point of aluminum, which is used as a standard substrate of artwork, so that aluminum sheets can not be coated in this way.
- Layers that are applied by plasma spraying are at least a few hundred microns thick and too rough and inhomogeneous to be used as a printing surface.
- a printing plate In order to enable an even more economical printing with direct imaging printing machines in which the subject to be printed is imaged directly on a printing surface by means of a laser, or CtP systems (computer-to-plate systems), a printing plate must be used which can be deleted after printing and reprinted with another subject.
- a gravure form of a nickel-titanium alloy which has a shape memory effect.
- the gravure mold Before imaging, the gravure mold is subjected to plastic deformation by compression. In a selective heating, individual areas of the pressure surface return to their original height, while the unheated areas remain unchanged due to the low thermal conductivity of the nickel-titanium alloy, so that a relief-like structure for the gravure arises. Because the Gravure mold can be brought into their original shape by heating the entire work surface, the shape memory effect is repeatedly used. The gravure form is reusable.
- the object of the present invention is to propose a material for the printing plate surface, which has better surface and processing properties, so that it is suitable for multiple printing of different images on the same printing surface. At the same time the costs are reduced.
- a printing plate with a titanium-containing surface is proposed as the printing surface.
- a titanium-containing surface is understood to mean a metallic surface which consists entirely of metallic titanium or a titanium-containing alloy.
- the titanium content of the alloy ranges between 50 and 100%, preferably between 95 and 100%.
- this surface may be the untreated surface of a sheet of either titanium or a titanium-containing alloy.
- this surface may be formed as a thin layer which has been deposited on a support, such as a sheet, a plastic or a foil, by a suitable method, in particular by electroplating.
- the titanium-containing surface may also be present in the form of a coating of a plate or a printing cylinder.
- the titanium-containing surface changes its surface energy through a controlled supply of energy, such as by irradiation with electromagnetic energy and can be switched from a hydrophobic to a hydrophilic state.
- the polar and dispersive components of the surface energy in the exposed or unexposed state differ significantly from one another, so that the wetting differences can be used for offset printing.
- the metallic titanium surface according to the invention can thus be subjected to a controlled process for imaging and erasing.
- Two symmetrical methods are available for this purpose: selective pointwise hydrophilization with large-area hydrophilization and selective point-wise hydrophobing with large-area hydrophilization.
- a suitable laser or a light-emitting diode which emits in the ultraviolet spectral range, typically with a wavelength of less than 420 nm, is preferably used for this purpose.
- the printing plate can be combined with various types of heat and / or water or aqueous solution Additives, especially alcohols, preferably isopopanol, are treated. It can then be dried with hot air.
- pointwise hydrophilization can thus create an image be provided to the surface, which can be erased by large-scale hydrophobing.
- a large-area hydrophilization is carried out.
- a suitable light source typically a UV lamp
- a light source in the infrared spectral range preferably a laser
- an image can be provided on the surface by pointwise hydrophobing, which can be erased by extensive hydrophilization.
- the inventive method for imaging and deletion can be carried out both inside and outside of the printing unit or the printing press.
- An essential requirement is the imagewise exposure to radiation, for example, using ultraviolet light, which effectively converts the hydrophobic titanium layer or titanium-containing alloy layer to a hydrophilic state.
- the printing surface can also be exposed directly with digital information, for example by means of a laser beam.
- the laser equipped with a suitable control system can be used to write the background. Preference is given to lasers which emit in the ultraviolet spectral range.
- the printing surface of the printing device is suitably cleaned of ink or ink.
- the image can be deleted so that the printing surface can be reused.
- the imaging and deletion can be performed multiple times, since the printing surface is extremely durable and long abrasion resistant.
- the printing forme is in a preferred embodiment of an aluminum sheet, as it is used as a base material for conventional printing plates, deposited a metallic titanium layer, for example by electrochemical methods.
- the coated sheet can then be clamped onto the plate cylinder of a direct imaging printing press.
- the plate is first wetted with clean water, for example, with the help of an additional dampening unit and dried with hot air, so that it is placed in the hydrophobic state.
- the imaging is now carried out with a suitable laser head of the direct imaging printing machine which emits ultraviolet radiation. The required intensities are significantly lower than in a thermal imaging, since the material is not heated, but only - comparable to a film - must be exposed.
- the printing plate can now be printed like a conventional printing plate. After completion of an order, the plate then does not need to be changed, but must be restored only with water and hot air in the hydrophobic initial state.
- the use of a metallic titanium-containing surface offers a number of advantages.
- the metallic titanium coating of a sheet for the printing plate is less susceptible to bending than a printing plate having a ceramic surface.
- the production of metallic layers is much easier than that of ceramic, since on processes such.
- As galvanization can be used, which can be used over a large area.
- the surface roughness can be adjusted via the surface finish of the carrier sheet and / or the plastic carrier to create optimal conditions for offset printing. Since no material is removed from the printing plate when switching from the hydrophobic to the hydrophilic state and back, the plate is repeatedly erasable and writable. Since the titanium surface itself is hydrophilic or hydrophobic, it is no longer absolutely necessary to use the relatively expensive and anodized aluminum described above as the base material, but it is also possible, for example, to use a cheap tinplate.
- a printing device comprises a solid or monolithic printing cylinder, which consists partly or entirely of metallic titanium.
- a printing plate which partly consists of metallic titanium
- at least the outer pressure surface has such a composition.
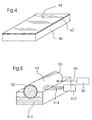
- a representative example of such a printing cylinder is shown in FIG.
- a solid pressure cylinder 10 is made entirely of metallic titanium and has an outer pressure surface 12 of metallic titanium.
- the cylinder 20 has a core 22, in particular of metal, of an alloy or a ceramic on which the metallic titanium surface has been applied as a layer or cladding 24 or deposited in a suitable manner, wherein an outer pressure surface 26 is provided.
- the metallic titanium layer or cladding 24 may be a hollow cylindrical sleeve or a pressure jacket, as shown in FIG.
- the sleeve 30 has a surface 32 made of a metallic titanium layer. The thickness of such sleeves varies in a wide range. In practical use, several centimeters have been proven.
- the cores of such printing plates generally consist of one or more metals, such as ferrous metals, nickel, brass, copper or magnesium or alloys thereof, or of non-metallic materials.
- the metal or alloy cores may be hollow or completely solid, or they may be one or more types of metal or alloys or non-metallic inorganic or organic materials.
- the titanium-containing layer applied to the above-described cores or carriers generally has a uniform thickness of several microns.
- the suitable carrier material 40 which consists of metal or a metal-containing alloy or ceramic, carries a layer which has a metallic titanium layer 42.
- the area 44 is used for printing.
- Such a plate can also be curved on a suitable printing unit or a suitable printing press, usually supported by rollers.
- Fig. 5 is simplified and schematically illustrated the inventive method for imaging and erasing the printing form according to the invention.
- the cylinder 50 carries a layer or sleeve or sheath 52 having the titanium-containing surface 54 which can be used for printing.
- the surface is selectively supplied with pointwise energy from the light source 56 through the outgoing beam 58 or over a large area from the energy source 512 through the radiation sector 514.
- this is a light source 56 which emits in the UV range and an energy source 512, in particular a heater for supplying heat.
- an IR laser is provided for the light source 56, and a UV lamp is provided as the power source 512.
- the water or aqueous solution 510 may aid in the process of hydrophobing.
- Such a device can be realized inside or outside a printing unit or a printing press in this scheme of appropriate topology or with additional elements such as applicator rollers, optics and the like.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Printing Plates And Materials Therefor (AREA)
- Thermal Transfer Or Thermal Recording In General (AREA)
- Printing Methods (AREA)
- Non-Silver Salt Photosensitive Materials And Non-Silver Salt Photography (AREA)
- Photosensitive Polymer And Photoresist Processing (AREA)
- Exposure And Positioning Against Photoresist Photosensitive Materials (AREA)
- Manufacture Or Reproduction Of Printing Formes (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE10021451A DE10021451A1 (de) | 2000-05-03 | 2000-05-03 | Gesteuerte Bebilderung und Löschung einer Druckform aus metallischem Titan |
| DE10021451 | 2000-05-03 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1151857A2 EP1151857A2 (de) | 2001-11-07 |
| EP1151857A3 EP1151857A3 (de) | 2001-11-14 |
| EP1151857B1 true EP1151857B1 (de) | 2006-06-28 |
Family
ID=7640591
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP01109311A Expired - Lifetime EP1151857B1 (de) | 2000-05-03 | 2001-04-12 | Gesteuerte Bebilderung und Löschung einer Druckform aus metallischem Titan |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6520088B2 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP1151857B1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP2001353974A (enExample) |
| AT (1) | ATE331617T1 (enExample) |
| DE (2) | DE10021451A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000155422A (ja) * | 1998-11-20 | 2000-06-06 | Fuji Photo Film Co Ltd | 平版印刷用原板及び平版印刷方法 |
| DE10115435B8 (de) * | 2001-03-29 | 2007-02-08 | Maschinenfabrik Wifag | Verfahren zur Erzeugung eines Druckbilds und/oder zur Löschung eines Druckbilds einer Nassoffset-Druckform mit fotothermisch veränderbarem Material |
| US20020189478A1 (en) * | 2001-06-14 | 2002-12-19 | Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. | Offset press |
| EP1266754A1 (en) * | 2001-06-14 | 2002-12-18 | Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. | Offset press and gapless printing plate |
| JP2003094599A (ja) * | 2001-07-17 | 2003-04-03 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | インプリンタ装置 |
| JP3609761B2 (ja) | 2001-07-19 | 2005-01-12 | 三洋電機株式会社 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| DE10227054B4 (de) * | 2002-06-17 | 2013-01-03 | Heidelberger Druckmaschinen Ag | Wiederverwendbare Druckform, Druckwerk und Druckmaschine damit sowie Verfahren zur Bebilderung der Druckform |
| US6851366B2 (en) | 2002-06-17 | 2005-02-08 | Heidelberger Druckmaschinen Ag | Reusable printing form |
| US7299749B2 (en) * | 2003-02-10 | 2007-11-27 | Fujifilm Corporation | Lithographic printing plate support and production method thereof |
| EP1831029A1 (en) * | 2004-12-22 | 2007-09-12 | Hille & Müller GmbH & Co. | Re-usable offset printing sheet and method for producing such a printing sheet |
| DE102006019801B4 (de) * | 2006-04-28 | 2012-01-19 | Koenig & Bauer Aktiengesellschaft | Zylinder einer Rotationsdruckmaschine |
| DE102008022860A1 (de) | 2008-05-08 | 2009-12-10 | Böhmer, Peter Arthur, Dipl.-Ing. (FH) | Wiederverwendbare Offset-Druckplatte |
| US20100101441A1 (en) * | 2008-10-24 | 2010-04-29 | Printing Research, Inc. | Offset Printing Transfer Cylinder Base Cover with Alignment Stripes for Precision Installation of a Flexible Jacket Cover also with Alignment Stripes |
| US8578853B2 (en) * | 2008-12-24 | 2013-11-12 | Printing Research, Inc. | Anti-marking jackets comprised of attachment structure and methods of using in offset printing |
| US8281716B2 (en) * | 2008-12-24 | 2012-10-09 | Printing Research, Inc. | Anti-marking jackets comprised of fluoropolymer and methods of using in offset printing |
| US8220388B2 (en) * | 2008-12-24 | 2012-07-17 | Printing Research, Inc. | Multiple layer anti-marking jackets and methods of using in offset printing |
| US8424453B2 (en) | 2010-09-01 | 2013-04-23 | Printing Research, Inc. | Apparatus and method for adjusting anti-marking jackets |
| US8677899B2 (en) | 2011-01-31 | 2014-03-25 | Printing Research, Inc. | Reversible anti-marking jackets and methods of using |
| US9346258B2 (en) | 2012-05-02 | 2016-05-24 | Printing Research, Inc. | Method for cleaning anti-marking jackets |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SU984878A1 (ru) * | 1980-08-11 | 1982-12-30 | за вители Ф. - ,. / с; | Способ изготовлени печатной формы |
| US4718340A (en) * | 1982-08-09 | 1988-01-12 | Milliken Research Corporation | Printing method |
| DE3938449A1 (de) * | 1989-11-18 | 1991-05-23 | Roland Man Druckmasch | Druckwerk |
| US5868074A (en) * | 1995-05-08 | 1999-02-09 | Flex Products, Inc. | Laser imageable direct-write printing member |
| US5743188A (en) | 1995-10-20 | 1998-04-28 | Eastman Kodak Company | Method of imaging a zirconia ceramic surface to produce a lithographic printing plate |
| US5870955A (en) * | 1997-03-05 | 1999-02-16 | Presstek, Inc. | Lithographic printing system with reusable support surfaces and lithographic constructions for use therewith |
| JPH11143055A (ja) * | 1997-11-14 | 1999-05-28 | Fuji Photo Film Co Ltd | 平版印刷版の作成方法及び平版印刷用原版 |
| US6079331A (en) * | 1997-10-24 | 2000-06-27 | Fuji Photo Film Co., Ltd. | Plate making device and printer and printing system using the plate making device |
| US5927206A (en) * | 1997-12-22 | 1999-07-27 | Eastman Kodak Company | Ferroelectric imaging member and methods of use |
| US5925496A (en) * | 1998-01-07 | 1999-07-20 | Eastman Kodak Company | Anodized zirconium metal lithographic printing member and methods of use |
| JP2000155422A (ja) * | 1998-11-20 | 2000-06-06 | Fuji Photo Film Co Ltd | 平版印刷用原板及び平版印刷方法 |
-
2000
- 2000-05-03 DE DE10021451A patent/DE10021451A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
2001
- 2001-04-12 AT AT01109311T patent/ATE331617T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2001-04-12 DE DE50110307T patent/DE50110307D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-04-12 EP EP01109311A patent/EP1151857B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-04-24 JP JP2001125824A patent/JP2001353974A/ja active Pending
- 2001-05-03 US US09/848,691 patent/US6520088B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20010042469A1 (en) | 2001-11-22 |
| DE50110307D1 (de) | 2006-08-10 |
| EP1151857A3 (de) | 2001-11-14 |
| DE10021451A1 (de) | 2001-11-08 |
| US6520088B2 (en) | 2003-02-18 |
| JP2001353974A (ja) | 2001-12-25 |
| EP1151857A2 (de) | 2001-11-07 |
| ATE331617T1 (de) | 2006-07-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1151857B1 (de) | Gesteuerte Bebilderung und Löschung einer Druckform aus metallischem Titan | |
| DE69733906T2 (de) | Dünnfilm-Bildaufzeichnungskonstruktionen mit anorganischen Metallschichten und optischen Interferenz-Strukturen | |
| EP1375136B1 (de) | Wiederverwendbare Druckform | |
| DE69604258T2 (de) | Flachdruckverfahren | |
| DE69330014T2 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Laserbeschriftung | |
| EP0963839B1 (de) | Druckmaschine und Druckverfahren | |
| DE69332092T2 (de) | Flachdruckplatten zur Bebilderung mittels Lasererosion | |
| DE69805385T2 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Herstellung einer Druckplatte und Drucker und Drucksystem die diese Vorrichtung verwenden | |
| DE69512321T2 (de) | Lithographische Druckplatten mit einer oleophilen bilderzeugenden Schicht | |
| DE69810733T2 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Herstellung einer Druckplatte und Drucker und Drucksystem die diese Vorrichtung verwenden | |
| DE19503951C2 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung für den Tiefdruck | |
| DE10360108A1 (de) | Herstellung einer wiederverwendbaren Druckform | |
| CH694159A5 (de) | Verfahren zum Gravieren von Gravurzylindern. | |
| DE69917126T2 (de) | Vorläufer für eine Flachdruckplatte sowie Verfahren zu deren Herstellung | |
| DE19507827C2 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung einer Druckform für den Offset- oder Tiefdruck | |
| DE69909711T2 (de) | Lithographische Druckplattenvorstufe und lithographisches Verfahren | |
| DE10126264A1 (de) | Tiefdruckzylinder, Verfahren zum Herstellen eines Tiefdruckzylinders und Verfahren zum Recyceln eines Tiefdruckzylinders | |
| DE10115435B4 (de) | Verfahren zur Erzeugung eines Druckbilds und/oder zur Löschung eines Druckbilds einer Nassoffset-Druckform mit fofothermisch veränderbarem Material | |
| EP1219417B1 (de) | Maskenerstellung zur Herstellung einer Druckform | |
| DE19602307A1 (de) | Druckmaschine | |
| DE69710867T2 (de) | Zylinder und Hülsen aus einer Zirconiumdioxidlegierung für lithografische Bilderzeugungs- und Druckverfahren | |
| EP1260360B1 (de) | Verfahren zum Aufbringen von Druckfarben auf einen Bedruckstoff | |
| DE19602289A1 (de) | Druckvorrichtung | |
| EP1354700B1 (de) | Verfahren zum Behandeln von erneut bebilderbaren Druckformen oder Druckformzylindern in Druckmaschinen | |
| CN102407652A (zh) | 用于使印刷过的印版重新成像的方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20011011 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Free format text: AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE TR |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20050322 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE TR |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT;WARNING: LAPSES OF ITALIAN PATENTS WITH EFFECTIVE DATE BEFORE 2007 MAY HAVE OCCURRED AT ANY TIME BEFORE 2007. THE CORRECT EFFECTIVE DATE MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM THE ONE RECORDED. Effective date: 20060628 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20060628 Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20060628 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 50110307 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20060810 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 20060829 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20060928 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20060928 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20061009 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20061128 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FD4D |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| PLAX | Notice of opposition and request to file observation + time limit sent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS2 |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: KOENIG & BAUER AG Effective date: 20070328 |
|
| NLR1 | Nl: opposition has been filed with the epo |
Opponent name: KOENIG & BAUER AG |
|
| PLBB | Reply of patent proprietor to notice(s) of opposition received |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS3 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20060929 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070412 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070430 |
|
| PLCK | Communication despatched that opposition was rejected |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNREJ1 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070412 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20060628 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20060628 |
|
| PLBN | Opposition rejected |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009273 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: OPPOSITION REJECTED |
|
| 27O | Opposition rejected |
Effective date: 20090817 |
|
| NLR2 | Nl: decision of opposition |
Effective date: 20090817 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20130429 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20130419 Year of fee payment: 13 Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20130427 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: V1 Effective date: 20141101 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20140430 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20140430 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20141101 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20140412 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20150424 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20150424 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20150423 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20160430 Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20160430 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20160412 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20161230 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20160502 Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20160412 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 50110307 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20171103 |