EP0802329A2 - Einrichtung zur Belüftung eines Vorratstanks - Google Patents
Einrichtung zur Belüftung eines Vorratstanks Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0802329A2 EP0802329A2 EP97105577A EP97105577A EP0802329A2 EP 0802329 A2 EP0802329 A2 EP 0802329A2 EP 97105577 A EP97105577 A EP 97105577A EP 97105577 A EP97105577 A EP 97105577A EP 0802329 A2 EP0802329 A2 EP 0802329A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- storage tank
- inlet
- air
- compressed air
- pressure regulator
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B1/00—Installations or systems with accumulators; Supply reservoir or sump assemblies
- F15B1/26—Supply reservoir or sump assemblies
- F15B1/265—Supply reservoir or sump assemblies with pressurised main reservoir
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B21/00—Common features of fluid actuator systems; Fluid-pressure actuator systems or details thereof, not covered by any other group of this subclass
- F15B21/04—Special measures taken in connection with the properties of the fluid
- F15B21/044—Removal or measurement of undissolved gas, e.g. de-aeration, venting or bleeding
Definitions
- the invention relates to a device for venting a storage tank of a system operating with hydraulic fluid, in which changes in the level of the liquid occur in the storage tank, the latter having an inlet for dried air above the level of the liquid.
- the object of the invention is to provide dried air without using a special air dryer.
- the air entering the storage tank is dried in that the moisture is precipitated anyway when compressed air is generated.
- the pressure regulator By means of the pressure regulator, the compressed air is expanded to approximately atmospheric pressure and in this state is fed to the storage tank, in which a slight excess pressure can form.
- the inflow of relaxed air is therefore limited to the amount of liquid withdrawn from the storage tank.
- the compressed air source is designed as a branch from a compressed air generation system required outside the system. This can be particularly useful if the system is located in a device, for example a mobile construction machine with a compressed air braking device, in which a compressed air generation system must be present anyway.
- the inlet can also serve as an outlet for excess air in the storage tank. When liquid flows back into the storage tank, the excess air can escape in this way.
- an aerosol separator is inserted between the pressure regulator and the inlet.
- the aerosol separator can also be connected downstream of the outlet in order to filter out contaminants that are entrained in the liquid.
- a compact design of the device results from the fact that the pressure regulator, a compressed air inlet connection connected to the compressed air source, a connection serving as the inlet and outlet of the storage tank and an exhaust air outlet opening with an upstream pressure relief valve are combined in a unit which can be mounted on the storage tank.
- the device can thus be installed fully assembled in the system.
- a first check valve connected between the pressure regulator and the connection to the storage tank can also be provided in the structural unit, with the inflow of air bypassing the aerosol separator, and / or one between the connection to the storage tank and another Exhaust air outlet switched second check valve may be provided, in the open position of which outflowing air bypasses the aerosol separator.
- Another possibility using compressed air from a compressed air source in such storage tanks to avoid the formation of condensed water and the consequent premature aging of the liquid, corrosion, increased wear and, at appropriate temperatures, icing is by means of a compressed air operated ejector in the storage tank above it Outlet to a negative pressure generate, whereby air is sucked out of the storage tank, and connected in parallel to vent the inlet of the storage tank via a pressure regulator from the compressed air source.
- the negative pressure in the storage tank causes a lowering of the water vapor partial pressure and thus outgassing of the liquid.
- the air sucked out of the storage tank can contain aerosols which are separated out in an aerosol separator connected downstream of the ejector, which is followed by an exhaust air outlet opening.
- the storage tank is also ventilated via the pressure regulator via a vacuum relief valve, which prevents excessive vacuum from developing in the storage tank.
- a pressure relief valve leading to the exhaust air outlet can also be connected directly or indirectly to the storage tank, which, if a large amount of liquid suddenly flows back, allows air to flow out of the storage tank and thus prevents an undesirable increase in the pressure in the storage tank.
- a connection from the compressed air source, the pressure regulator, the vacuum relief valve, the ejector, the aerosol separator and the pressure relief valve can be combined to form one structural unit.
- a pressure regulator 2 is connected downstream of a compressed air source 1.
- an aerosol separator 3 which is connected via a line connection to an inlet 4 of a storage tank 5.
- the inlet 4 serves at the same time as the outlet of the storage tank 5, which is connected via the line connection and the aerosol separator 3 to a pressure relief valve 6, to which an exhaust air outlet opening 7 connects. Liquid is withdrawn from the storage tank 5 and liquid flows back into it, as indicated by arrows.
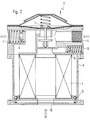
- the assembly 11 shown in FIG. 2 has in a housing 8 a compressed air inlet connection 9 which is connected to the compressed air source 1 and which is connected via the pressure regulator 2 to a space in the housing 8 enclosing the aerosol separator 3.
- the space formed within the aerosol separator 3 opens at the bottom into a connection 10 which serves as an inlet 4 to the storage tank 5 and also as an outlet from the storage tank 5.
- the space enclosing the aerosol separator 3 in the housing 8 is connected to the exhaust air outlet opening 7 via the pressure relief valve 6.
- a first check valve 12 is connected between the space enclosing the aerosol separator 3 in the housing 8 and the connection 10, and air flowing in bypasses the aerosol separator 3 when it is in the open position.
- a second check valve 14 is connected, in the open position of which air flowing out bypasses the aerosol separator 3.
- a compressed air source 21 is followed by a pressure regulator 22.
- This is followed by an ejector 23, which in turn is followed by an aerosol separator 24 and finally by an exhaust air outlet opening 27.
- a line connection branches off, which leads via a vacuum relief valve 31 to an inlet 25 of a storage tank 26.
- a pressure relief valve 28 is connected, which leads to an exhaust air outlet 29.
- an outlet 30 of the storage tank 26 is connected to the ejector 23, namely at its suction connection, via a further line connection. Liquid is withdrawn from the storage tank 26 and liquid flows back into it, as indicated by arrows.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Fluid Mechanics (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Jet Pumps And Other Pumps (AREA)
- Respiratory Apparatuses And Protective Means (AREA)
- Valves And Accessory Devices For Braking Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- Die Erfindung bezieht sich auf eine Einrichtung zur Belüftung eines Vorratstanks einer mit Druckflüssigkeit arbeitenden Anlage, bei der Änderungen des Niveaus der Flüssigkeit in dem Vorratstank auftreten, wobei letzterer über dem Niveau der Flüssigkeit einen Einlaß für getrocknete Luft aufweist.
- Bedingt durch Schwankungen von Druck, Temperatur und Luftfeuchtigkeit bildete sich in solchen Vorratstanks Kondenswasser, wenn nicht getrocknete Luft aus der Atmosphäre über den Einlaß in den Vorratstank eindringen würde. Dies hätte eine vorzeitige Alterung der Flüssigkeit, Korrosion, erhöhten Verschleiß und bei entsprechenden Temperaturen Vereisung zur Folge. Deshalb werden dem Einlaß bei bekannten Einrichtungen dieser Art Lufttrockner vorgeschaltet. Diese haben jedoch die Nachteile hoher Kosten, begrenzter Kapazität und schwieriger Regenerierbarkeit.
- Aufgabe der Erfindung ist es, getrocknete Luft ohne Verwendung eines besonderen Lufttrockners bereitzustellen.
- Diese Aufgabe ist bei einer Einrichtung der eingangs genannten Art dadurch gelöst, daß der Einlaß über einen Druckregler an eine Druckluftquelle angeschlossen ist.
- Die in den Vorratstank eintretende Luft ist hierbei dadurch getrocknet, daß die Feuchtigkeit bei der Erzeugung von Druckluft ohnehin ausgefällt wird. Mittels des Druckreglers wird die Druckluft annähernd auf Atmosphärendruck entspannt und in diesem Zustand dem Vorratstank zugeführt, in dem sich ein geringer Überdruck bilden kann.
- Das Einströmen entspannter Luft ist damit auf die Menge der aus dem Vorratstank abgezogenen Flüssigkeit begrenzt.
- Eine vorteilhafte Ausgestaltung der Einrichtung ergibt sich dadurch, daß die Druckluftquelle als Abzweigung von einer außerhalb der Anlage erforderlichen Drucklufterzeugungsanlage ausgebildet ist. Dies kann besonders dann sinnvoll sein, wenn sich die Anlage in einem Gerät, beispielsweise einer fahrbaren Baumaschine mit Druckluftbremseinrichtung, befindet, in dem ohnehin eine Drucklufterzeugungsanlage vorhanden sein muß.
- Der Einlaß kann zusätzlich als Auslaß für überschüssige Luft in dem Vorratstank dienen. Bei Rückströmen von Flüssigkeit in den Vorratstank kann dann die überschüssige Luft auf diesem Weg entweichen.
- Falls die aus der Druckluftquelle stammende, entspannte Luft eine Restfeuchtigkeit und/oder Verunreinigungen enthalten kann, ist es vorteilhaft, daß zwischen den Druckreger und den Einlaß ein Aerosolabscheider eingefügt ist. Der Aerosolabscheider kann auch dem Auslaß nachgeschaltet sein, um aus der Flüssigkeit stammende, mitgerissene Verunreinigungen auszufiltern.
- Eine kompakte Bauweise der Einrichtung ergibt sich dadurch, daß der Druckregler, ein an die Druckluftquelle angeschlossener Drucklufteintrittsanschluß, ein als Einlaß und Auslaß des Vorratstanks dienender Anschluß und eine Abluftaustrittsöffnung mit vorgeschaltetem Druckbegrenzungsventil in einer auf dem Vorratstank montierbaren Baueinheit zusammengefaßt sind. Die Einrichtung kann damit komplett montiert in die Anlage eingebaut werden.
- Bei Durchströmung des Aerosolabscheiders in der einen und/oder anderen Richtung besteht selbstverständlich die Gefahr, daß dieser sich durch Verunreinigungen zusetzt, wodurch die Einrichtung funktionsunfähig werden würde. Um dies zu vermeiden, kann in der Baueinheit zusätzlich ein zwischen den Druckregler und den Anschluß an den Vorratstank geschaltetes erstes Rückschlagventil vorgesehen sein, bei dessen Offen-Stellung einströmende Luft den Aerosolabscheider umgeht, und/oder ein zwischen den Anschluß an den Vorratstank und eine weitere Abluftaustrittsöffnung geschaltetes zweites Rückschlagventil vorgesehen sein, bei dessen Offen-Stellung abströmende Luft den Aerosolabscheider umgeht.
- Eine andere Möglichkeit unter Verwendung von Druckluft aus einer Druckluftquelle in solchen Vorratstanks die Bildung von Kondenswasser und die daraus folgende vorzeitige Alterung der Flüssigkeit, Korrosion, erhöhten Verschleiß und bei entsprechenden Temperaturen Vereisung zu vermeiden, besteht darin, mittels eines druckluftbetriebenen Ejektors in dem Vorratstank über dessen Auslaß einen Unterdruck zu erzeugen, wodurch Luft aus dem Vorratstank abgesaugt wird, und parallel geschaltet dazu den Einlaß des Vorratstanks über einen Druckregler aus der Druckluftquelle zu belüften. Der Unterdruck in dem Vorratstank bewirkt eine Absenkung des Wasserdampfpartialdruckes und damit ein Ausgasen der Flüssigkeit.
- Die aus dem Vorratstank abgesaugte Luft kann Aerosole enthalten, die in einem dem Ejektor nachgeschalteten Aerosolabscheider ausgeschieden werden, an den sich eine Abluftaustrittsöffnung anschließt.
- Die Belüftung des Vorratstanks über den Druckregler erfolgt zusätzlich über ein Unterdruck-Begrenzungsventil, das das Entstehen eines zu großen Unterdrucks in dem Vorratstank verhindert.
- An den Vorratstank kann außerdem ein zu dem Abluftaustritt führendes Druckbegrenzungsventil direkt oder indirekt angeschlossen sein, das bei plötzlichem Rückströmen einer größeren Menge an Flüssigkeit das Abströmen von Luft aus dem Vorratstank ermöglicht und damit einen unerwünschten Anstieg des Druckes in dem Vorratstank verhindert.
- Zur Vereinfachung der Montage dieser Einrichtung können ein Anschluß von der Druckluftquelle, der Druckregler, das Unterdruck-Begrenzungsventil, der Ejektor, der Aerosolabscheider und das Druckbegrenzungsventil zu einer Baueinheit zusammengefaßt sein.
- In der Zeichnung sind zwei Ausführungsbeispiele für Einrichtungen zur Belüftung eines Vorratstanks dargestellt, und zwar zeigt
- Fig. 1
- ein Schaltbild des ersten Ausführungsbeispiels,
- Fig. 2
- einen lotrechten Mittelschnitt einer Baueinheit zur Verwirklichung des ersten Ausführungsbeispiels,
- Fig. 3
- ein Schaltbild des zweiten Ausführungsbeispiels.
- In dem Schaltbild nach Fig. 1 ist einer Druckluftquelle 1 ein Druckregler 2 nachgeschaltet. Diesem ist ein Aerosolabscheider 3 nachgeschaltet, der über eine Leitungsverbindung mit einem Einlaß 4 eines Vorratstanks 5 verbunden ist. Der Einlaß 4 dient gleichzeitig als Auslaß des Vorratstanks 5, der über die Leitungsverbindung und den Aerosolabscheider 3 mit einem Druckbegrenzungsventil 6 verbunden ist, an das sich eine Abluftaustrittsöffnung 7 anschließt. Aus dem Vorratstank 5 wird Flüssigkeit abgezogen und in diesen strömt Flüssigkeit zurück, wie durch Pfeile angedeutet.
- Die in Fig. 2 dargestellte Baueinheit 11 weist in einem Gehäuse 8 einen an die Druckluftquelle 1 angeschlossenen Drucklufteintrittsanschluß 9 auf, der über den Druckregler 2 mit einem in dem Gehäuse 8 den Aerosolabscheider 3 umschließenden Raum in Verbindung steht. Der innerhalb des Aerosolabscheiders 3 gebildete Raum mündet unten in einen Anschluß 10 aus, der als Einlaß 4 zu dem Vorratstank 5 und auch als Auslaß von dem Vorratstank 5 dient. Der in dem Gehäuse 8 den Aerosolabscheider 3 umschließende Raum steht über das Druckbegrenzungsventil 6 mit der Abluftaustrittsöffnung 7 in Verbindung. Zwischen dem in dem Gehäuse 8 den Aerosolabscheider 3 umschließenden Raum und den Anschluß 10 ist ein erstes Rückschlagventil 12 geschaltet, bei dessen Offen-Stellung einströmende Luft den Aerosolabscheider 3 umgeht. Weiter ist zwischen den innerhalb des Aerosolabscheiders 3 gebildeten Raum und eine weitere Abluftaustrittsöffnung 13 ein zweites Rückschlagventil 14 geschaltet, bei dessen Offen-Stellung abströmende Luft den Aerosolabscheider 3 umgeht.
- In dem Schaltbild nach Fig. 3 ist einer Druckluftquelle 21 ein Druckregler 22 nachgeschaltet. Diesem ist ein Ejektor 23, diesem wiederum ein Aerosolabscheider 24 und diesem schließlich eine Abluftaustrittsöffnung 27 nachgeschaltet. Nach dem Druckregler 22 zweigt eine Leitungsverbindung ab, die über ein Unterdruck-Begrenzungsventil 31 zu einem Einlaß 25 eines Vorratstanks 26 führt. An diese Leitungsverbindung ist zwischen Einlaß 25 und Unterdruck-Begrenzungsventil 31 ein Druckbegrenzungsventil 28 angeschlossen, das zu einem Abluftaustritt 29 führt. An den Ejektor 23, und zwar an dessen Sauganschluß, ist schließlich über eine weitere Leitungsverbindung ein Auslaß 30 des Vorratstanks 26 angeschlossen. Aus dem Vorratstank 26 wird Flüssigkeit abgezogen und in diesen strömt Flüssigkeit zurück, wie durch Pfeile angedeutet.
Claims (9)
- Einrichtung zur Belüftung eines Vorratstanks einer mit Druckflüssigkeit arbeitenden Anlage, bei der Änderungen des Niveaus der Flüssigkeit in dem Vorratstank auftreten, wobei letzterer über dem Niveau der Flüssigkeit einen Einlaß für getrocknete Luft aufweist, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der Einlaß (4) über einen Druckregler (2) an eine Druckluftquelle (1) angeschlossen ist.
- Einrichtung nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Druckluftquelle (1) als Abzweigung von einer außerhalb der Anlage erforderlichen Drucklufterzeugungsanlage ausgebildet ist.
- Einrichtung nach Anspruch 1 oder 2, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der Einlaß (4) zusätzlich als Auslaß für überschüssige Luft in dem Vorratstank (5) dient.
- Einrichtung nach Anspruch 1, 2 oder 3, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß zwischen den Druckregler (2) und den Einlaß (4) ein Aerosolabscheider (3) eingefügt ist.
- Einrichtung nach Anspruch 3 und 4, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der Aerosolabscheider (3) auch dem Auslaß nachgeschaltet ist.
- Einrichtung nach den Ansprüchen 1 bis 5, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der Druckregler (2), ein an die Druckluftquelle (1) angeschlossener Drucklufteintrittsanschluß (9), ein als Einlaß (4) und Auslaß des Vorratstanks (5) dienender Anschluß (10) und eine Abluftaustrittsöffnung (7) mit vorgeschaltetem Druckbegrenzungsventil (6) in einer auf dem Vorratstank (5) montierbaren Baueinheit (11) zusammengefaßt sind.
- Einrichtung nach Anspruch 6, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß in der Baueinheit (11) zusätzlich ein zwischen den Druckregler (2) und den Anschluß (10) an den Vorratstank (5) geschaltetes erstes Rückschlagventil (12) vorgesehen ist, bei dessen Offen-Stellung einströmende Luft den Aerosolabscheider (3) umgeht.
- Einrichtung nach Anspruch 6, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß in der Baueinheit (11) zusätzlich ein zwischen den Anschluß (10) an den Vorratstank (5) und eine weitere Abluftaustrittsöffnung (13) geschaltetes zweites Rückschlagventil (14) vorgesehen ist, bei dessen Offen-Stellung abströmende Luft den Aerosolabscheider (3) umgeht.
- Einrichtung nach den Ansprüchen 7 und 8.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19615475A DE19615475A1 (de) | 1996-04-19 | 1996-04-19 | Einrichtung zur Belüftung eines Vorratstanks |
| DE19615475 | 1996-04-19 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0802329A2 true EP0802329A2 (de) | 1997-10-22 |
| EP0802329A3 EP0802329A3 (de) | 1998-02-11 |
| EP0802329B1 EP0802329B1 (de) | 2001-08-01 |
Family
ID=7791734
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP97105577A Expired - Lifetime EP0802329B1 (de) | 1996-04-19 | 1997-04-04 | Einrichtung zur Belüftung eines Vorratstanks |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0802329B1 (de) |
| DE (2) | DE19615475A1 (de) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102357974A (zh) * | 2011-09-28 | 2012-02-22 | 无锡锦和科技有限公司 | 自封式大通流量排气罐 |
| WO2016097512A1 (fr) * | 2014-12-17 | 2016-06-23 | Technoboost | Circuit hydraulique comprenant un reservoir tres basse pression mis en depression |
| CN120887127A (zh) * | 2025-09-30 | 2025-11-04 | 苏州杜尔气体化工装备有限公司 | 一种具有过滤干燥功能的储罐吸阀补气系统及其储罐 |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE10002118A1 (de) * | 2000-01-20 | 2001-07-26 | Mann & Hummel Filter | Ausgleichsbehälter eines Hydrauliksystems |
| RU2241865C2 (ru) * | 2002-12-31 | 2004-12-10 | Открытое акционерное общество "Красноярский проектно-конструкторский технологический институт комбайностроения" | Гидробак |
| DE102007052023A1 (de) * | 2007-10-31 | 2009-05-07 | Trw Automotive Gmbh | Hydraulikfluidspeicher sowie hydraulisches Servolenksystem mit einem solchen Hydraulikfluidspeicher |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2208451A (en) * | 1938-11-18 | 1940-07-16 | Gen Electric | Hydraulic mechanism |
| GB580604A (en) * | 1944-06-19 | 1946-09-13 | Automotive Prod Co Ltd | Improvements in or relating to liquid circulating systems |
| DE2618372A1 (de) * | 1976-04-27 | 1977-11-17 | Franz Walter | Kontinuierlich arbeitender druckmittelwandler |
| DE2650802C2 (de) * | 1976-11-03 | 1981-10-08 | Borsig Gmbh, 1000 Berlin | Gas-Öl-Antrieb |
| US4827719A (en) * | 1983-11-14 | 1989-05-09 | Paoluccio John A | Closed hydraulic system with drying means |
| DE8511057U1 (de) * | 1985-04-16 | 1985-10-03 | Bodendorfer, Gerhard, 7505 Ettlingen | Druckhaltekopf |
| HU201705B (en) * | 1988-11-04 | 1990-12-28 | Autoipari Kutato Fejlesztoe | Vehicle air dryer with control gear particularly for pressure air systems |
| DE4031494C2 (de) * | 1990-10-05 | 1994-07-21 | Bundesrep Deutschland | Hydraulikölbehälter |
-
1996
- 1996-04-19 DE DE19615475A patent/DE19615475A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
1997
- 1997-04-04 EP EP97105577A patent/EP0802329B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1997-04-04 DE DE59704163T patent/DE59704163D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102357974A (zh) * | 2011-09-28 | 2012-02-22 | 无锡锦和科技有限公司 | 自封式大通流量排气罐 |
| CN102357974B (zh) * | 2011-09-28 | 2016-02-03 | 无锡锦和科技有限公司 | 自封式大通流量排气罐 |
| WO2016097512A1 (fr) * | 2014-12-17 | 2016-06-23 | Technoboost | Circuit hydraulique comprenant un reservoir tres basse pression mis en depression |
| FR3030650A1 (fr) * | 2014-12-17 | 2016-06-24 | Technoboost | Circuit hydraulique comprenant un reservoir tres basse pression mis en depression |
| CN107107727A (zh) * | 2014-12-17 | 2017-08-29 | 技术推进公司 | 包括处于负压的极低压容器的液压回路 |
| CN107107727B (zh) * | 2014-12-17 | 2020-08-07 | 技术推进公司 | 包括处于负压的极低压容器的液压回路 |
| CN120887127A (zh) * | 2025-09-30 | 2025-11-04 | 苏州杜尔气体化工装备有限公司 | 一种具有过滤干燥功能的储罐吸阀补气系统及其储罐 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0802329A3 (de) | 1998-02-11 |
| DE59704163D1 (de) | 2001-09-06 |
| EP0802329B1 (de) | 2001-08-01 |
| DE19615475A1 (de) | 1997-10-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE3882782T2 (de) | Mehrfachölfilter für Verbrennungskraftmaschinen mit Anzeige der Verschmutzung der Filteroberfläche. | |
| DE102008023594A1 (de) | Kompressoreinheit | |
| DE3026203A1 (de) | Oelgekuehlter kompressor | |
| DE3032243C2 (de) | Druckregelventil für den Einbau in eine Entlüftungsleitung einer Brennkraftmaschine | |
| DE102020214814A1 (de) | Brennstoffzellensystem | |
| DE112018000542T5 (de) | Aufhängungsystem | |
| DE10048439C2 (de) | Dampfturbinenanlage und Verfahren zum Betreiben einer Dampfturbinenanlage | |
| EP0802329A2 (de) | Einrichtung zur Belüftung eines Vorratstanks | |
| DE2426378A1 (de) | Ventilplatte fuer kolbenkompressoren | |
| EP0659621A1 (de) | Druckbegrenzungseinrichtung | |
| EP0486726B1 (de) | Flüssigkeitsringpumpe | |
| DE102021109017A1 (de) | Wasserstoffgaszufuhrvorrichtung | |
| DE102018200681A1 (de) | Brennstoffzellensystem mit einer dem Verdichter zugeordneten Mitteldruckentnahme sowie Verwendung eines derartigen Brennstoffzellensystems | |
| WO2001044712A1 (de) | Verfahren zum ableiten von kondensat und kondensatableiter | |
| DE112018000942T5 (de) | Brennstoffzellenstapel unde Fahrzeug mit einem Brennstoffzellenstapel | |
| DE1962132C3 (de) | Entwässerungsvorrichtung für Druckluftanlagen, insbesondere Druckluftbremsanlagen, von Kraftfahrzeugen | |
| DE2855608A1 (de) | Doppelt wirkende vakuumpumpe | |
| DE19600377B4 (de) | Druckgasanlage mit einem Gastrockner | |
| DE3213236A1 (de) | Einrichtung mit einem lufttrockner fuer druckluftanlagen | |
| DE2940235C2 (de) | Einrichtung zum selbsttätigen Ergänzen des Schmieröls in der Kurbelwanne einer Brennkraftmaschine | |
| DE102019003386A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Rezirkulation von Abgas | |
| DE10359579B4 (de) | Vorrichtung und Verfahren zum Entfernen von Rückständen in einem Brennstoffzellensystem | |
| DE102022204160A1 (de) | Verfahren zum Betreiben eines mehrstufigen Luftverdichtungssystems, mehrstufiges Luftverdichtungssystem sowie Brennstoffzellensystem | |
| DE102020200611A1 (de) | Brennstoffzellensystem | |
| DE2843170A1 (de) | Anordnung in einem kompressor zur draenierung von fluessigkeit |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): CH DE FR GB IT LI SE |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): CH DE FR GB IT LI SE |
|
| RHK1 | Main classification (correction) |
Ipc: F15B 1/26 |
|
| RTI1 | Title (correction) | ||
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19980721 |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: MAHLE FILTERSYSTEME GMBH |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20000218 |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): CH DE FR GB IT LI SE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRE;WARNING: LAPSES OF ITALIAN PATENTS WITH EFFECTIVE DATE BEFORE 2007 MAY HAVE OCCURRED AT ANY TIME BEFORE 2007. THE CORRECT EFFECTIVE DATE MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM THE ONE RECORDED.SCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20010801 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59704163 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20010906 |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 20010917 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: IF02 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20080428 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20080422 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20080422 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed | ||
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20090404 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20091231 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090430 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090430 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090404 Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091222 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20080422 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20100511 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090405 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 59704163 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 59704163 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20111031 |