EP0447619B1 - Warneinrichtung mit einer Messzelle und Alarmgebern zur Anzeige des Erschöpfungszustandes eines Gasfilters - Google Patents
Warneinrichtung mit einer Messzelle und Alarmgebern zur Anzeige des Erschöpfungszustandes eines Gasfilters Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0447619B1 EP0447619B1 EP90121361A EP90121361A EP0447619B1 EP 0447619 B1 EP0447619 B1 EP 0447619B1 EP 90121361 A EP90121361 A EP 90121361A EP 90121361 A EP90121361 A EP 90121361A EP 0447619 B1 EP0447619 B1 EP 0447619B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- gas filter
- flap piece
- warning arrangement
- warning
- arrangement according
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 230000029058 respiratory gaseous exchange Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 29
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 230000001960 triggered effect Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000002848 electrochemical method Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 18
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000003344 environmental pollutant Substances 0.000 description 4
- 231100000719 pollutant Toxicity 0.000 description 4
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 2
- LELOWRISYMNNSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydrogen cyanide Chemical compound N#C LELOWRISYMNNSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- UGFAIRIUMAVXCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon monoxide Chemical compound [O+]#[C-] UGFAIRIUMAVXCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chlorine atom Chemical compound [Cl] ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RWSOTUBLDIXVET-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dihydrogen sulfide Chemical compound S RWSOTUBLDIXVET-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910002091 carbon monoxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000460 chlorine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052801 chlorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000018109 developmental process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006056 electrooxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910000037 hydrogen sulfide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A62—LIFE-SAVING; FIRE-FIGHTING
- A62B—DEVICES, APPARATUS OR METHODS FOR LIFE-SAVING
- A62B18/00—Breathing masks or helmets, e.g. affording protection against chemical agents or for use at high altitudes or incorporating a pump or compressor for reducing the inhalation effort
- A62B18/08—Component parts for gas-masks or gas-helmets, e.g. windows, straps, speech transmitters, signal-devices
- A62B18/088—Devices for indicating filter saturation
Definitions
- the invention relates to a warning device with a measuring cell and alarm transmitters for displaying the state of exhaustion of a gas filter in connection with a breathing connection, the warning device being designed as a unit separate from the gas filter.
- Such a warning device is already known from DE-A-36 13 512.
- Optical and acoustic signal indicators are used in an electronic circuit arrangement as alarm devices, the measured value triggering the alarm being determined by means of an electrochemical measuring cell.
- the use of optical and acoustic signals as alarm devices can be ignored or overlooked by the device wearer in the event of noise or poor visibility.
- the object of the invention is therefore to create a warning device of the type mentioned at the outset which clearly and safely indicates to the device wearer the state of exhaustion of the gas filter even in the event of noise and poor visibility.
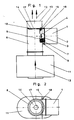
- the warning device 1 essentially consists of a housing 2 into which a measuring cell 3, an electronic circuit 4 connected to it in terms of circuitry, a battery 5, a pivotable mechanical device 6 with a permanent magnet 7 and an electromagnetic interrupter 7 a is arranged.
- the warning device 1 is flanged to an upright breathing tube 8 via a lateral opening 9 and is in flow connection with the breathing tube.
- the breathing tube 8 is designed as a functional part for the warning device 1 and has a stop element 10 against which the pivotable flap piece 14 bears in an end position.
- the breathing tube 8 with the warning device 1 is connected behind the latter in the flow direction 12 to indicate the state of exhaustion of a gas filter 11.
- the direction of flow 12 is synonymous with the direction of the inhaled air.
- the breathing tube 8 is connected in the flow direction with its opening 13 to a breathing tube, not shown in the drawing, with a breath connection.
- the mechanical device 6, which is controlled via the measuring cell 3 and the electronic circuit 4, closes the flow cross section of the breathing tube 8 with its pivotable flap piece 14 when the gas filter 11 is exhausted and thus shows the wearer of the gas filter 11 by increasing the breathing resistance.
- the mechanical device 6 consists essentially of a circular flap piece 14, an axis of rotation 15 which is fixed on the edge of the flap piece and a spring drive 16 which, when triggered, swings the flap piece into the breathing tube 8 against the stop element 10.
- the flap piece 14 has a slightly smaller diameter than the inside diameter of the breathing tube 8. Concentric to the circular flap piece 14, an opening 17 is machined into it, through which the device wearer can breathe when the flap piece 14 closes the flow cross section of the breathing tube 8 in the event of an indication of exhaustion. The remaining cross-section of the opening 17 then causes the device wearer to increase the inhalation resistance. At one end of the axis of rotation 15, a lever 18 is arranged, on which the device carrier can manually pivot the flap piece 14 blocking the flow cross section of the breathing tube 8 into the starting position, ie to rest against the permanent magnet 7, so that the full flow cross section of the breathing tube 8 can be inhaled is available again. The increased inhalation resistance is then lower again for the device wearer.
- the manual pivoting back of the flap piece 14 by means of the lever 18 corresponds to the acknowledgment of the triggered display of the state of exhaustion of the gas filter 11 which retains the harmful gases.
- the device carrier thus warned can then leave the pollutant-containing room for the time to replace the gas filter, with sufficient time.
- an electromotive drive (not shown in the drawing) for pivoting into the flow cross section of the breathing tube 8 can be provided on the flap piece 14, an acknowledgment switch (also not shown in the drawing) causing the flap piece 14 to pivot back electromotively.
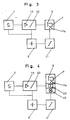
- Fig. 3 the electronic circuit arrangement of the warning device 1 is shown as a block diagram.
- the measuring cell 3 is a signal amplifier 19 and this a threshold switch 20 and as an alarm, the mechanical device 6 according to the invention with the permanent magnet 7 and the electromagnetic interrupter 7 a downstream.
- the battery 5 is provided with a battery monitor 21 for supplying power to the circuit arrangement.
- the switching threshold of the threshold switch 20 is set to the measurement signal corresponding to the measurement value which triggers the alarm corresponds to a certain harmful gas concentration, which indicates the end of the period of use of the gas filter 11.
- the measuring signal coming from the measuring cell 3 exceeds the set switching threshold (alarm threshold) of the threshold switch 20, its output is turned on and the electromagnetic interrupter 7 a is activated such that the magnet 7 is deactivated and the held flap piece 14 is released, which is then released by means of the
- the spring drive 16 swings suddenly into the breathing tube 8 and comes to rest against the stop 10 in the end position.
- the flap piece 14 closes the flow cross section of the breathing tube 8 and only the opening 17, which is worked in concentrically in the flap piece, remains as a passage for inhalation for the device wearer. Due to the relatively small opening 17, the inhalation resistance increases noticeably. This is then the sign for the equipment carrier that the gas filter 11 will be exhausted in a short time.
- FIG. 4 shows a block diagram of the warning device 1, in which, in addition to the flap device 6 described above and connected in parallel to it, a light-emitting diode 22 is provided as an optical alarm transmitter and a signal transmitter 23 as an acoustic alarm transmitter.
- An electrochemical measuring cell can be provided as the measuring cell 3, which works on the principle of electrochemical oxidation. It serves as a measuring element for the detection of harmful concentrations of harmful gas in the inhaled air, which can no longer be retained or removed by the gas filter 11 connected upstream of the measuring element in the event of being exhausted. In other words: the measuring element 3 measures a certain harmful pollutant concentration, which indicates that the pollutant retained in the gas filter 11 breaks through, which means that the gas filter is exhausted. Electrochemical measuring cells already exist for the detection of carbon monoxide, chlorine, hydrogen sulfide, hydrocyanic acid and oxygen, which can be used in the warning device 1 for the corresponding gas filter.
- a semiconductor sensor can be used as the measuring element, as a result of which a larger number of pollutants to be detected can advantageously be measured.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Pulmonology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Emergency Management (AREA)
- Respiratory Apparatuses And Protective Means (AREA)
- Fuel Cell (AREA)
- Sampling And Sample Adjustment (AREA)
- Burglar Alarm Systems (AREA)
- Investigating Or Analyzing Materials By The Use Of Fluid Adsorption Or Reactions (AREA)
Description
- Die Erfindung bezieht sich auf eine Warneinrichtung mit einer Meßzelle und Alarmgebern zur Anzeige des Erschöpfungszustandes eines Gasfilters in Verbindung mit einem Atemanschluß, wobei die Warneinrichtung als eine vom Gasfilter getrennte Einheit ausgebildet ist.
- Eine derartige Warneinrichtung ist bereits aus der DE-A-36 13 512 bekannt. Hierbei werden als Alarmgeber optische und akustische Signalanzeiger in einer elektronischen Schaltungsanordnung verwendet, wobei der den alarmauslösende Meßwert mittels einer elektrochemischen Meßzelle ermittelt wird. Die Verwendung von optischen und akustischen Signalen als Alarmgeber, kann vom Gerätträger bei Lärm oder bei schlechten Sichtverhältnissen überhört oder übersehen werden.
- Der Erfindung liegt deshalb die Aufgabe zugrunde, eine Warneinrichtung der eingangs genannten Art zu schaffen, die eindeutig und sicher dem Gerätträger auch bei Lärm und schlechter Sicht den Erschöpfungszustand des Gasfilters anzeigt.
- Diese Aufgabe wird durch die kennzeichnenden Merkmale des Patentanspruchs 1 gelöst.
- Vorteilhafte Weiterentwicklungen sind in den abhängigen Ansprüchen gekennzeichnet.
- Ein Ausführungsbeispiel des Erfindungsgegenstandes ist in der Zeichnung dargestellt. Es zeigen:
- Fig. 1
- eine Seitenansicht der Warneinrichtung, die in Strömungsrichtung hinter einem Gasfilter angeordnet ist,
- Fig. 2
- eine Draufsicht nach Fig. 1,
- Fig. 3
- eine Ausführung der Warneinrichtung als Blockschaltbild und
- Fig. 4
- eine andere Ausführung der Warneinrichtung als Blockschaltbild
- Wie aus den Figuren 1 und 3 ersichtlich ist, besteht die Warneinrichtung 1 im wesentlichen aus einem Gehäuse 2, in das eine Meßzelle 3, eine mit dieser schaltungstechnisch verbundene elektronische Schaltung 4, eine Batterie 5, eine schwenkbare mechanische Vorrichtung 6 mit einem Permanentmagnet 7 und ein elektromagnetischer Unterbrecher 7 a angeordnet ist. Die Warneinrichtung 1 ist an einem hochstehenden Atemrohr 8 über eine seitliche Öffnung 9 angeflanscht und steht mit dem Atemrohr in strömungsmäßiger Verbindung. Das Atemrohr 8 ist als ein Funktionsteil für die Warneinrichtung 1 ausgebildet und weist ein Anschlagelement 10 auf, gegen das in einer Endstellung das schwenkbare Klappenstück 14 anliegt. Das Atemrohr 8 mit der Warneinrichtung 1 ist zur Anzeige des Erschöpfungszustandes eines Gasfilters 11, hinter diesen in Strömungsrichtung 12 geschaltet. Die Strömungsrichtung 12 ist gleichbedeutend mit der Richtung der Einatemluft. Das Atemrohr 8 ist in Strömungsrichtung mit seiner Öffnung 13 an einen in der Zeichnung nicht dargestellten Atemschlauch mit Atemanschluß angeschlossen.
Die über die Meßzelle 3 und die elektronische Schaltung 4 gesteuerte mechanische Vorrichtung 6, verschließt mit ihrem schwenkbaren Klappenstück 14 im Erschöpfungsfall des Gasfilters 11 den Strömungsquerschnitt des Atemrohrs 8 und zeigt somit durch die Erhöhung des Einatemwiderstandes dem Gerätträger die Erschöfpung des Gasfilters 11 an. Die mechanische Vorichtung 6 besteht im wesentlichen aus einem kreisförmigen Klappenstück 14, einer Drehachse 15, die am Rande des Klappenstücks festgelegt ist und aus einem Federantrieb 16, der das Klappenstück im ausgelösten Zustand in das Atemrohr 8 gegen das Anschlagelement 10 einschwenkt. - Das Klappenstück 14 hat einen etwas geringeren Durchmesser als der Innendurchmesser des Atemrohres 8 ist. Konzentrisch zum kreisförmigen Klappenstück 14 ist in dieses eine Öffnung 17 eingearbeitet, durch die der Gerätträger atmen kann, wenn im anzeigenden Erschöpfungsfall das Klappenstück 14 den Strömungsquerschnitt des Atemrohres 8 verschließt. Der verbleibende Restquerschnitt der Öffnung 17 bewirkt dann spürbar für den Gerätträger die Vergrößerung des Einatemwiderstandes. An einem Ende der Drehachse 15 ist ein Hebel 18 angeordnet, an dem der Gerätträger das den Strömungsquerschnitt des Atemrohres 8 versperrende Klappenstück 14 in die Ausgangslage, d. h. zum Anliegen an den Permanentmagnet 7 manuell zurückschwenken kann, so daß der volle Strömungsquerschnitt des Atemrohrs 8 zum Einatmen wieder zur Verfügung steht. Der vergrößerte Einatemwiderstand ist dann wieder für den Gerätträger geringer. Das manuelle Zurückschwenken des Klappenstücks 14 mittels des Hebels 18 entspricht dem Quittieren der ausgelösten Anzeige des Erschöpfungszustandes des Schadgase zurückhaltenden Gasfilters 11. Der so gewarnte Gerätträger kann dann zum Auswechseln des Gasfilters, noch zeitlich ausreichend, den schadstoffhaltigen Raum verlassen.
In einer anderen Ausführung kann an dem Klappenstück 14 ein in der Zeichnung nicht dargestellter elektromotorischer Antrieb zum Einschwenken in den Strömungsquerschnitt des Atemrohrs 8 vorgesehen werden, wobei ein in der Zeichnung ebenfalls nicht dargestellter Quittierungsschalter das elektromotorische Zurückschwenken des Klappenstücks 14 bewirkt. - In Fig. 3 ist die elektronische Schaltungsanordnung der Warneinrichtung 1 als Blockschaltbild dargestellt. Der Meßzelle 3 ist ein Signalverstärker 19 und diesem ein Schwellwertschalter 20 sowie als Alarmgeber die erfindungsgemäße mechanische Vorrichtung 6 mit dem Permanentmagnet 7 und dem elektromagnetischen Unterbrecher 7 a nachgeschaltet. Zur Energieversorgung der Schaltungsanordnung ist die Batterie 5 mit einer Batterieüberwachung 21 vorgesehen. Die Schaltschwelle des Schwellwertschalters 20 ist auf das den alarmauslösenden Meßwert entsprechende Meßsignal eingestellt, das einer bestimmten Schadgaskonzentration entspricht, die das Ende der Gebrauchszeit des Gasfilters 11 anzeigt. Überschreitet beispielsweise das von der Meßzelle 3 kommende Meßsignal die eingestellte Schaltschwelle (Alarmschwelle) des Schwellwertschalters 20, so wird dessen Ausgang leitend und der elektromagnetische Unterbrecher 7 a derart aktiviert, daß der Magnet 7 deaktiviert wird und das festgehaltene Klappenstück 14 freigibt, das dann mittels des Federantriebs 16 schlagartig in das Atemrohr 8 einschwenkt und in der Endstellung gegen den Anschlag 10 zu liegen kommt. Das Klappenstück 14 verschließt den Strömungsquerschnitt des Atemrohrs 8 und es verbleibt lediglich die konzentrisch im Klappenstück eingearbeitete Öffnung 17 als Durchlaß zum Einatmen für den Gerätträger. Durch die verhältnismäßig kleine Öffnung 17 steigt der Einatemwiderstand merklich an. Das ist dann das Zeichen für den Gerätträger, daß das Gasfilter 11 in kurzer Zeit erschöpft sein wird.
- Fig. 4 zeigt ein Blockschaltbild der Warneinrichtung 1, in dem als Alarmgeber zusätzlich zu der vorstehend beschriebenen Klappenvorrichtung 6, zu dieser parallel geschaltet, eine Leuchtdiode 22 als optischer Alarmgeber und ein Signalgeber 23 als akustischer Alarmgeber vorgesehen ist.
Als Meßzelle 3 kann eine elektrochemische Meßzelle vorgesehen werden, die nach dem Prinzip der elektrochemischen Oxidation arbeitet. Sie dient als Meßelement zum Nachweis schädlicher Schadgaskonzentrationen in der Einatemluft, die von dem dem Meßelement vorgeschalteten Gasfilter 11 im Falle des Erschöpfungszustandes nicht mehr zurückgehalten bzw. entfernt werden kann. Mit anderen Worten: das Meßelement 3 mißt eine bestimmte schädliche Schadstoffkonzentration, die anzeigt, daß der im Gasfilter 11 zurückgehaltene Schadstoff durchbricht, was heißt, daß das Gasfilter erschöpft ist.
Elektrochemische Meßzellen gibt es bereits zum Nachweis von Kohlenmonoxid, Chlor, Schwefelwasserstoff, Blausäure und Sauerstoff, die in die Warneinrichtung 1 für die entsprechenden Gasfilter eingesetzt werden können. - Alternativ zu der oben genannten elektrochemischen Meßzelle kann ein Halbleiter-Sensor als Meßelement eingesetzt werden, wodurch vorteilhaft eine größere Anzahl von nachzuweisenden Schadstoffen gemessen werden kann.
Claims (11)
- Warneinrichtung mit einer Meßzelle und Alarmgebern zur Anzeige des Erschöpfungszustandes eines Gasfilters in Verbindung mit einem Atemanschluß, wobei die Warneinrichtung als eine vom Gasfilter getrennte Einheit ausgebildet und an ein in Strömungsrichtung hinter das Gasfilter (11) geschaltetes Atemrohr (8) angeordnet sowie mit diesem strömungsmäßig verbunden ist, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daßa) der Alarmgeber als eine mechanische Vorrichtung (6) ausgebildet ist, die ein schwenkbares Klappenstück (14) aufweist, das im von der Meßzelle gemessenen Erschöpfungszustand des Gasfilters (11) auslösbar ist und das Atemrohr (8) in Strömungsrichtung verschließt, undb) das Klappenstück (14) eine Öffnung (17) aufweist, durch die der Gerätträger atmet, wobei eine spürbare Vergrößerung des Einatemwiderstandes ein Indiz für den nahenden Erschöpfungszustand des Gasfilters (11) ist.
- Warneinrichtung nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Warneinrichtung (1) in einem Gehäuse (2) angeordnet ist, das an dem hochstehenden Atemrohr (8) über eine Öffnung (9) im Atemrohr angeschlossen ist.
- Warneinrichtung nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das Atemrohr (8) als ein Funktionsteil für die Warneinrichtung (1) ausgebildet ist, und ein Anschlagelement (10) an der dem Gasfilter (11) entgegengesetzten Ausgangsseite (13) aufweist, gegen das in einer Endstellung das schwenkbare Klappenstück (14) anliegt.
- Warneinrichtung nach den Ansprüchen 1 bis 3, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das Klappenstück (14) vorzugsweise als ein kreisförmiges Scheibenstück ausgebildet ist, das in einem Randbereich eine Drehachse (15) und einen Federaustrieb (16) aufweist.
- Warneinrichtung nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die mechanische Vorrichtung (6) einen Permanentmagnet (7) aufweist, an dem das schwenkbare Klappenstück (14) im Ruhezustand festgelegt ist.
- Warneinrichtung nach Anspruch 1 und 5, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der Permanentmagnet (7) einen Unterbrecher (7 a) aufweist, der mit einer elektronischen Schaltung (4) verbunden ist und im Alarmfall den Permanentmagneten derart deaktiviert, daß dieser das Klappenstück (14) freigibt, zum Einschwenken gegen das Anschlagelement (10) im Atemrohr (8).
- Warneinrichtung nach Anspruch 1 bis 6, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß an der mit dem Klappenstück (14) fest verbundenen Drehachse (15) ein Hebel (18) angeordnet ist, damit das Klappenstück nach Eintritt des Alarmfalls manuell zurückschwenkbar ist.
- Warneinrichtung nach den Ansprüchen 1 bis 3, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß an dem Klappenstück (14) vorzugsweise ein elektromotorischer Antrieb zum Einschwenken in den Strömungsquerschnitt des Atemrohrs (8) angeordnet ist, und daß ein Quittierungsschalter vorgesehen ist, der das Klappenstück elektromotorisch zurückschwenkt.
- Warneinrichtung mit einer elektronischen Schaltungsanordnung, die eine Meßzelle und einen nachgeschalteten Schwellwertschalter aufweist, dessen Schaltschwelle auf ein den alarmauslösenden Meßwert entsprechendes Meßsignal einstellbar ist, nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß an den Ausgang des Schwellwertschalters (20) der mit der mechanischen Vorrichtung (6) verbundene Permanentmagnet (7) mit dem elektromagnetischen Unterbrecher (7 a) geschaltet ist.
- Warneinrichtung nach Anspruch 1 und 8, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Meßzelle (3) vorzugsweise eine elektrochemische Meßzelle ist.
- Warneinrichtung nach Anspruch 1 und 8, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß für die Meßzelle (3) vorzugsweise ein Halbleiter-Sensor als Meßelement einsetzbar ist.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT90121361T ATE97824T1 (de) | 1990-03-21 | 1990-11-08 | Warneinrichtung mit einer messzelle und alarmgebern zur anzeige des erschoepfungszustandes eines gasfilters. |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE4009107 | 1990-03-21 | ||
| DE4009107A DE4009107A1 (de) | 1990-03-21 | 1990-03-21 | Warneinrichtung mit einer messzelle und alarmgebern zur anzeige des erschoefpungszustandes eines gasfilters |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0447619A1 EP0447619A1 (de) | 1991-09-25 |
| EP0447619B1 true EP0447619B1 (de) | 1993-12-01 |
Family
ID=6402758
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP90121361A Expired - Lifetime EP0447619B1 (de) | 1990-03-21 | 1990-11-08 | Warneinrichtung mit einer Messzelle und Alarmgebern zur Anzeige des Erschöpfungszustandes eines Gasfilters |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0447619B1 (de) |
| AT (1) | ATE97824T1 (de) |
| DE (2) | DE4009107A1 (de) |
| NO (1) | NO905329L (de) |
Families Citing this family (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AU645959B3 (en) * | 1993-11-05 | 1994-01-27 | Purecab (Australia) Pty Ltd | Respiratory filter indicator |
| US5666949A (en) * | 1994-10-24 | 1997-09-16 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Exposure indicator with continuous alarm signal indicating multiple conditions |
| US5659296A (en) * | 1994-10-24 | 1997-08-19 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Exposure indicating apparatus |
| DE29504087U1 (de) * | 1995-03-10 | 1995-08-10 | Palocz-Andresen, Michael, Dr.-Ing.habil., 20459 Hamburg | Mikro-Meßvorrichtung für die Erfassung der Beladung von Filtern |
| AUPN191095A0 (en) * | 1995-03-23 | 1995-04-27 | Safety Equipment Australia Pty Ltd | Positive air-purifying respirator management system |
| DE19650897A1 (de) * | 1996-12-07 | 1998-06-10 | T E M Tech Entwicklung Und Man | Apparat und Verfahren zur Erhöhung der Sicherheit von Atemschutzmasken |
| US6186140B1 (en) * | 1997-03-14 | 2001-02-13 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Respiratory filter element having a storage device for keeping track of filter usage and a system for use therewith |
| DE19911867C2 (de) * | 1999-03-17 | 2002-02-21 | T E M Techn Entwicklungen Und | Sensorsystem zur Detektion von Gasen und Dämpfen in Luft |
| DE50014087D1 (de) | 1999-03-17 | 2007-04-05 | T E M Techn Entwicklungen Und | Verfahren und sensorvorrichtung zur detektion von in luft enthaltenen gasen oder dämpfen |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US1676125A (en) * | 1928-07-03 | Device for indicating admixtures to gases and liquids | ||
| DE670550C (de) * | 1929-04-10 | 1939-01-20 | Bernh Draeger | Sauerstoffatemschutzgeraet |
| DE693685C (de) * | 1935-11-19 | 1940-07-17 | Auergesellschaft Akt Ges | Warnvorrichtung fuer Sauerstoffatemschutzgeraete |
| FR1353343A (fr) * | 1963-04-09 | 1964-02-21 | Avertisseur pour appareils protecteurs des voies respiratoires | |
| DE3613512C3 (de) * | 1986-04-22 | 1994-09-29 | Auergesellschaft Gmbh | Elektrische Warneinrichtung zur Anzeige des Erschöpfungszustandes eines Schadgase zurückhaltenden Gasfilters |
-
1990
- 1990-03-21 DE DE4009107A patent/DE4009107A1/de active Granted
- 1990-11-08 AT AT90121361T patent/ATE97824T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1990-11-08 DE DE90121361T patent/DE59003710D1/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1990-11-08 EP EP90121361A patent/EP0447619B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1990-12-10 NO NO90905329A patent/NO905329L/no unknown
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| ATE97824T1 (de) | 1993-12-15 |
| DE59003710D1 (de) | 1994-01-13 |
| EP0447619A1 (de) | 1991-09-25 |
| DE4009107A1 (de) | 1991-09-26 |
| NO905329D0 (no) | 1990-12-10 |
| DE4009107C2 (de) | 1993-06-09 |
| NO905329L (no) | 1991-09-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0246444A2 (de) | Warneinrichtung zur Anzeige des Erschöpfungszustandes eines Gasfilters | |
| DE69634169T2 (de) | Strombetriebenes luftreinigungs-beatmungs-management-system | |
| DE68909693T2 (de) | Angetriebenes Atemgerät. | |
| EP0447619B1 (de) | Warneinrichtung mit einer Messzelle und Alarmgebern zur Anzeige des Erschöpfungszustandes eines Gasfilters | |
| DE69015622T2 (de) | Verfahren zum nachweis von in der luft suspendierten allergenen. | |
| DE60209279T2 (de) | Tragbare Gasalarmvorrichtung | |
| DE69533138T2 (de) | Expositionsmelder | |
| DE60021016T2 (de) | Zellulares Telephongerät ausgerüstet mit einer Gaskomponentenmessfunktion | |
| DE60223527T2 (de) | Verfahren und messgerät zur messung der stickoxidkonzentration in der ausatemluft | |
| DE60300172T2 (de) | Vorrichtung und Methode zur Messung von Atemalkohol | |
| JPH10507664A (ja) | 暴露指示装置 | |
| DE1960517B2 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Aufrechterhalten atembarer Luft | |
| DE102008023523B4 (de) | Sicherheitsbekleidungsstück und Sicherheitssystem | |
| DE2906832A1 (de) | Verfahren und anordnung zur bestimmung der alkoholkonzentration des blutes durch messung der alkoholkonzentration der atemluft | |
| DE69718958T2 (de) | Überwachungsanordnung | |
| EP1165186B1 (de) | Verfahren und sensorvorrichtung zur detektion von in luft enthaltenen gasen oder dämpfen | |
| DE2428352A1 (de) | Anordnung zur bestimmung der alkoholkonzentration der (tiefen) lungenluft | |
| DE2800638A1 (de) | Messgeraet zur bestimmung des alkoholgehaltes in dem atem einer versuchsperson | |
| CN218852697U (zh) | 便携式呼气一氧化氮检测仪 | |
| DE19911869B4 (de) | Neuartige Atemschutzmaske mit Sensor-Mikrosystem und Verfahren zum Betreiben derselben | |
| DE2337988B2 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Bestimmung des Alkoholgehaltes in der Atemluft | |
| DE2147718B2 (de) | Kohlendioxid-warngeraet | |
| DE2909578A1 (de) | System zur erfassung der zeigerstellung eines messgeraetes | |
| EP3883469A1 (de) | Lungentestvorrichtung | |
| DE102023106966A1 (de) | Vorrichtung und verfahren zur durchführung eines hypoxie-trainings |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19901122 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE ES FR GB GR IT LI LU NL |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19930318 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE ES FR GB GR IT LI LU NL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 19931201 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 97824 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19931215 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59003710 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19940113 |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 19940114 |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: BA2A |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GR Ref legal event code: FG4A Free format text: 3010719 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Effective date: 19941108 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19941109 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19941130 Ref country code: LI Effective date: 19941130 Ref country code: CH Effective date: 19941130 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL Ref country code: GR Ref legal event code: MM2A Free format text: 3010719 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19950801 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19951103 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19951116 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19951120 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19951130 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Effective date: 19961108 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Effective date: 19961130 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FA2A Effective date: 19970325 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: AUERGESELLSCHAFT G.M.B.H. Effective date: 19961130 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Effective date: 19970601 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 19961108 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Effective date: 19970731 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee |
Effective date: 19970601 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES;WARNING: LAPSES OF ITALIAN PATENTS WITH EFFECTIVE DATE BEFORE 2007 MAY HAVE OCCURRED AT ANY TIME BEFORE 2007. THE CORRECT EFFECTIVE DATE MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM THE ONE RECORDED. Effective date: 20051108 |