EP0226907A2 - Relais - Google Patents
Relais Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0226907A2 EP0226907A2 EP86116890A EP86116890A EP0226907A2 EP 0226907 A2 EP0226907 A2 EP 0226907A2 EP 86116890 A EP86116890 A EP 86116890A EP 86116890 A EP86116890 A EP 86116890A EP 0226907 A2 EP0226907 A2 EP 0226907A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- core
- yoke
- piece
- tab
- coil
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H50/00—Details of electromagnetic relays
- H01H50/16—Magnetic circuit arrangements
- H01H50/36—Stationary parts of magnetic circuit, e.g. yoke
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H50/00—Details of electromagnetic relays
- H01H50/16—Magnetic circuit arrangements
- H01H50/36—Stationary parts of magnetic circuit, e.g. yoke
- H01H2050/365—Stationary parts of magnetic circuit, e.g. yoke formed from a single sheet of magnetic material by punching, bending, plying
Definitions
- the invention relates to a relay according to the preamble of claim 1.
- a relay has become known in various forms; All embodiments have in common that the core and the yoke form two different parts, which are therefore manufactured separately from one another and which are only connected to one another before the relay is assembled.
- the core is connected to the associated yoke via a rivet connection.
- this has the disadvantage that the connection between the core and the yoke in the area of the rivet connection can never be completely smooth, and this results in a slight air gap which increases the magnetic resistance in the flux circuit.
- the invention has for its object to develop a relay of the type mentioned so that the resistance in the magnetic flux circuit, consisting of core, yoke and armature, is further reduced.
- the invention is characterized in that the yoke and core consist of a one-piece U-shaped part.
- the yoke and core consist of a coherent, identical part, as a result of which the air gap described above, which can form in the connecting gap in the case of a two-part part, is avoided. Due to the one-piece construction of the yoke and core, the resistance in the magnetic flux circuit is substantially reduced and, consequently, the efficiency of the relay is improved.
- the core consists of a round-profiled metal part which merges on one side into a flat-profiled connecting flange, which in turn merges into a flat-profiled yoke.
- a round-profiled metal part which merges on one side into a flat-profiled connecting flange, which in turn merges into a flat-profiled yoke.
- Such a part is produced from a round material, the round-profiled core being produced by die-forming this round material. After this shaping, the flat material is bent in a U-shaped manner, after which the round-profiled core is opposite a yoke formed as a flat material.
- the yoke and core consist of a stamped part and this time the core is not flat-profiled by die forming, but only a multiple bending process takes place, after completion of which both the yoke and the core are made of a rectangularly profiled material (flat material ) are formed.
- the core which is still made of a flat material, is round-profiled by die forming.
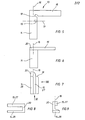
- Fig. 1 only the magnet system of a relay is shown, which in a conventional manner consists of a coil, the coil carrier has a central recess 2 into which a round-profiled core 7 is inserted.
- the round-profiled core 7 opens as shown in FIGS. 1, 2 and 3 in a rectangular profiled connecting flange 8, which in turn is bent through 90 degrees and opens into a yoke 6 with a rectangular profile.
- the armature 4 is pivotally mounted on the end face of the yoke 6 according to FIG. 1 and at its free, pivotable end there is an actuating pin 5 which actuates the contacts of the relay, which are not shown.
- the opposite side of the armature 4 lies as flush as possible on the end face 3 of the core 7.
- 1 - 3 show that the core and yoke consist of a one-piece part which is bent in a U-shape.
- a first bending edge 22 is located between the core 7 and the connecting flange 8, while a second bending edge 21 is located between the connecting flange 8 and the yoke 6.
- FIG. 4 shows an embodiment of the core and yoke that is improved compared to FIG. 1, because the end face 3 of the core 7 near the anchor has an enlarged area there, so that the contact area with the armature 4 is enlarged.
- a head part 10 is pushed onto the end face of the core 7, which is provided with an annular flange 12 and has an inner recess which is pressed onto the core 7 precisely flush.
- the end face 11 of the head part 10 is enlarged compared to the original end face 3 of the core 7.
- the head part 10 is integrally connected to the core 7 by inserting the core into the recess 2 of the coil 1 in the same manner as the head part 10 shows , mushroom-shaped, so that the head part 10 is integrally connected to the core 7.
- 5-9 show the second embodiment of a one-piece connection between a core 27 and a yoke 26.
- this embodiment is an angular stamped part 13, which consists of a flat material.
- a lower bracket 14 is connected in one piece to another bracket 15 at an angle of 90 degrees.
- a recess 18 is provided which extends approximately diagonally to the outer edge approximately to the center of the stamped part 13.
- this part is first bent in the region of the bending edge 17, so that the tab 15 protrudes vertically from the plane of the drawing according to FIG. 6, as shown in FIG. 6.
- the tab 15 is thus connected to the lower tab via a connecting flange 20, the connecting flange being formed by the corner between the tab 14 and the tab 15, which was divided by the recess 18.
- 5 also shows that a further recess 19 can be provided in the area of the bending edge 17 in order to facilitate bending in the area of the bending edge 17 during the transition from FIG. 5 to FIG. 6.
- a U-shaped part results from a flat material, wherein in a further process step the core 27 consisting of the flat material can still be profiled round by die forming.
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Electromagnets (AREA)
- Iron Core Of Rotating Electric Machines (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- Die Erfindung betrifft ein Relais nach dem Oberbegriff des Patentanspruchs l. Ein derartiges Relais ist in verschiedenartigen Ausführungsformen bekannt geworden; allen Ausführungsformen ist gemeinsam, daß der Kern und das Joch zwei verschiedene Teile bilden, die also getrennt voneinander hergestellt sind und die erst vor der Montage des Relais miteinander verbunden werden. Beispielsweise wird hierbei der Kern über eine Nietverbindung mit dem zugeordneten Joch verbunden. Damit besteht jedoch der Nachteil, daß der Anschluß zwischen Kern und Joch im Bereich der Nietverbindung nie vollständig glattflächig sein kann und damit sich ein geringfügiger Luftspalt ergibt, der den magnetischen Widerstand im Flußkreis erhöht.
- Der Erfindung liegt die Aufgabe zugrunde, ein Relais der eingangs genannten Art so weiterzubilden, daß der Widerstand im magnetischen Flußkreis, bestehend aus Kern, Joch und Anker, weiter verringert wird.
- Zur Lösung der gestellten Aufgabe ist die Erfindung dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß Joch und Kern aus einem werkstoffeinstückigen U-förmigen Teil bestehen.
- Erfindungsgemäß bestehen Joch und Kern aus einem zusammenhängenden, gleichen Teil, wodurch der vorher beschriebene Luftspalt, der sich bei einem zweistückigen Teil im Verbindungsspalt bilden kann, vermieden wird. Durch die werkstoffeinstückige Ausbildung von Joch und Kern ist also der Widerstand im magnetischen Flußkreis wesentlich verringert und demzufolge der Wirkungsgrad des Relais verbessert.
- In einer ersten Ausführungsform ist es nach dem Gegenstand des Anspruchs 2 vorgesehen, daß der Kern aus einem rundprofilierten Metallteil besteht, der an seiner einen Seite in ein flach profilierten Verbindungsflansch übergeht, der seinerseits in ein flach profiliertes Joch übergeht. Ein derartiges Teil wird aus einem Rundmaterial hergestellt, wobei der rundprofilierte Kern durch Gesenkumformen dieses Rundmaterials hergestellt wird. Nach diesem Umformen wird das Flachmaterial entsprechend U-förmig gebogen, wonach dem rundprofilierten Kern ein als Flachmaterial ausgebildetes Joch gegenüberliegt.
- In einer anderen Ausführungsform ist es vorgesehen, daß Joch und Kern aus einem Stanzteil bestehen und der Kern diesmal nicht durch Gesenkumformen flachprofiliert wird, sondern lediglich ein mehrmaliger Biegevorgang stattfindet, nach dessen Vollendung dann sowohl das Joch und der Kern aus einem rechteckig profilierten Material (Flachmaterial) gebildet sind.
- In einem weiteren Verfahrensschritt kann es jedoch vorgesehen sein, den noch aus einem Flachmaterial bestehenden Kern durch Gesenkumformen rundprofiliert auszubilden.
- Der Erfindungsgegenstand der vorliegenden Erfindung ergibt sich nicht nur aus dem Gegenstand der einzelnen Patentansprüche, sondern auch aus der Kombination der einzelnen Patentansprüche untereinander.
- Alle in den Unterlagen offenbarten Angaben und Merkmale, insbesondere die in den Zeichnungen dargestellte räumliche Ausbildung werden als erfindungswesentlich beansprucht, soweit sie einzeln oder in Kombination gegenüber dem Stand der Technik neu sind.
- Im folgenden wird die Erfindung anhand von mehrere Ausführungswege darstellenden Zeichnungen näher erläutert. Hierbei gehen aus den Zeichnungen und ihrer Beschreibung weitere erfindungswesentliche Merkmale und Vorteile der Erfindung hervor.
- Es zeigen:
- Figur 1: Schnitt durch ein Relais mit einem Joch und Kern in einer ersten Ausführungsform;
- Figur 2: Stirnansicht in Richtung des Pfeiles II in Fig. 1 unter Weglassung der Spule;
- Figur 3: Draufsicht auf das Teil nach Fig. 2 in Richtung des Pfeiles III in Fig. 2;
- Figur 4: der Kern nach Fig. 1 mit einem im Durchmesser erweiterten Kopf teil;
- Figur 5: Draufsicht auf ein Stanzteil zur Herstellung eines werkstoffeinstückigen Jochs mit Kern im Grundzustand;
- Figur 6: Draufsicht auf das Stanzteil nach Fig. 5 nach dem ersten Biegevorgang;
- Figur 7: Draufsicht auf das Stanzteil nach Fig. 6 nach dem zweiten Biegevorgang;
- Figur 8: Seitenansicht des Stanzteils nach Fig. 7 in Richtung des Pfeiles VIII;
- Figur 9: Stirnansicht des Stanzteils nach Fig. 7 in Richtung des Pfeiles IX.
- In Fig. 1 ist von einem Relais lediglich das Magnetsystem dargestellt, welches in herkömmlicher Weise aus einer Spule besteht, deren Spulenträger eine zentrische Ausnehmung 2 aufweist, in die ein rundprofilierter Kern 7 eingeschoben ist. Der rundprofilierte Kern 7 mündet gemäß den Darstellungen in Fig. 1, 2 und 3 in einen rechteckig profilierten Verbindungsflansch 8, der seinerseits um 90 Grad umgebogen ist und in ein gleichfalls rechteckig profiliertes Joch 6 einmündet. In nicht näher dargestellter Weise ist der Anker 4 schwenkbar an der Stirnseite des Jochs 6 gemäß Fig. 1 gelagert und an seinem freien, schwenkbaren Ende setzt ein Betätigungsstift 5 an, der die nicht näher dargestellten Kontakte des Relais betätigt.
- Die gegenüberliegende Seite des Ankers 4 liegt möglichst bündig an der Stirnfläche 3 des Kerns 7 an.
- Die Fig. 1 - 3 zeigen, daß Kern und Joch aus einem werkstoffeinstückigen Teil bestehen, welches U-förmig gebogen ist. Eine erste Biegekante 22 befindet sich dabei zwischen Kern 7 und Verbindungsflansch 8, während eine zweite Biegekante 21 sich zwischen Verbindungsflansch 8 und dem Joch 6 befindet.
- Die Fig. 4 zeigt eine gegenüber Fig. 1 verbesserte Ausführungsform von Kern und Joch, weil dort die ankernahe Stirnfläche 3 des Kerns 7 eine vergrößerte Fläche aufweist, so daß die Kontaktfläche zum Anker 4 vergrößert ist.
- Dies wird gemäß dem Ausführungsbeispiel nach Fig. 4 dadurch erreicht, daß auf die Stirnseite des Kerns 7 ein Kopfteil 10 aufgeschoben wird, welches mit einem Ringflansch 12 versehen ist und eine innere Ausnehmung aufweist, die genau bündig auf den Kern 7 aufgepreßt ist.
- Die Stirnfläche 11 des Kopfteils 10 ist gegenüber der ursprünglichen Stirnfläche 3 des Kerns 7 vergrößert.
- In einer anderen, nicht zeichnerisch dargestellten Ausführungsform ist es vorgesehen, daß das Kopfteil 10 werkstoffeinstückig mit dem Kern 7 dadurch verbunden ist, daß der Kern nach dem Einstecken in die Ausnehmung 2 der Spule 1 in der gleichen Art, wie es das Kopf teil 10 zeigt, pilzförmig umgeformt ist, so daß das Kopfteil 10 werkstoffeinstückig mit dem Kern 7 verbunden ist.
- Die Fig. 5 - 9 zeigen die zweite Ausführungsform einer werkstoffeinstückigen Verbindung zwischen einem Kern 27 und einem Joch 26.
- Gemäß Fig. 5 liegt dieser Ausführung ein winkelförmiges Stanzteil 13 gegenüber, was aus einem Flachmaterial besteht. Eine unter Lasche 14 ist im Winkel von 90 Grad mit einer weiteren Lasche 15 einstückig verbunden.
- Im Bereich der inneren Kante des winkelförmigen Teils ist eine Ausnehmung 18 vorgesehen, die sich etwa diagonal zur außenliegenden Kante etwa bis zur Mitte des Stanzteils 13 hin erstreckt.
- Gemäß Fig. 6 wird dieses Teil zunächst im Bereich der Biegekante 17 gebogen, so daß die Lasche 15 senkrecht aus der Zeichenebene nach Fig. 6 heraussteht, wie in Fig. 6 dargestellt.
- Die Lasche 15 nach Fig. 6 wird im Bereich der Biegekante 16 um 90 Grad gebogen, so daß sich die in Fig. 7 dargestellte Formgebung der Lasche 15 ergibt, die nun gemäß Fig. 8 parallel zur unteren Lasche 14 verläuft, jedoch ist die Breitseite der Lasche 15 um 90 Grad zur Breitseite der Lasche 14 verdreht, wie dies Fig. 9 zeigt.
- Die Lasche 15 hängt damit über einen Verbindungsflänsch 20 mit der unteren Lasche zusammen, wobei der Verbindungsflansch durch die Ecke zwischen der Lasche 14 und der Lasche 15 gebildet wurde, welche durch die Ausnehmung 18 abgeteilt wurde. Die Fig. 5 zeigt ferner, daß im Bereich der Biegekante 17 eine weitere Ausnehmung 19 vorgesehen werden kann, um das Biegen im Bereich der Biegekante 17 beim Übergang von der Fig. 5 auf die Fig. 6 zu erleichtern.
- Insgesamt ergibt sich gemäß den Fig. 8 und 9 ein U-förmiges Teil aus einem Flachmaterial, wobei in einem weiteren Verfahrensschritt der aus dem Flachmaterial bestehende Kern 27 durch Gesenkumformen noch rund profiliert werden kann.
Claims (4)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19853544532 DE3544532A1 (de) | 1985-12-17 | 1985-12-17 | Relais |
| DE3544532 | 1985-12-17 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0226907A2 true EP0226907A2 (de) | 1987-07-01 |
| EP0226907A3 EP0226907A3 (de) | 1989-08-30 |
Family
ID=6288613
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP86116890A Withdrawn EP0226907A3 (de) | 1985-12-17 | 1986-12-04 | Relais |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0226907A3 (de) |
| DE (1) | DE3544532A1 (de) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT402579B (de) * | 1991-10-07 | 1997-06-25 | Schrack Components Ag | Relais |
| EP0974994A1 (de) * | 1998-07-23 | 2000-01-26 | Bticino S.P.A. | Elektromagnet für einen Leitungsschutzschalter mit einem flachen Kern mit ein verdrillten Teil |
| CN106252161A (zh) * | 2016-08-31 | 2016-12-21 | 漳州宏发电声有限公司 | 一种只有铁芯的磁路系统及其继电器 |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5082899A (en) * | 1988-11-02 | 1992-01-21 | The Dow Chemical Company | Maleic anhydride-grafted polyolefin fibers |
| US5126199A (en) * | 1988-11-02 | 1992-06-30 | The Dow Chemical Company | Maleic anhydride-grafted polyolefin fibers |
| US5185199A (en) * | 1988-11-02 | 1993-02-09 | The Dow Chemical Company | Maleic anhydride-grafted polyolefin fibers |
| AT412926B (de) * | 2001-03-20 | 2005-08-25 | Moeller Gebaeudeautomation Kg | Joch für ein magnetsystem einer kurzschlussauslöseeinrichtung |
| CN110970268A (zh) * | 2018-09-30 | 2020-04-07 | 泰科电子(深圳)有限公司 | 电磁继电器 |
| CN110970266A (zh) * | 2018-09-30 | 2020-04-07 | 泰科电子(深圳)有限公司 | 电磁继电器 |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BE507613A (de) * | 1950-12-07 | |||
| DE1280409B (de) * | 1962-08-09 | 1968-10-17 | Siemens Ag | Elektromagnetisches Relais mit Klappanker |
| GB1007369A (en) * | 1963-08-08 | 1965-10-13 | Ericsson Telephones Ltd | Electromagnetic relay |
| DE2020150A1 (de) * | 1970-04-24 | 1971-12-02 | Gruner Kg Relais Fabrik | Elektromagnetisches Kleinrelais |
| DE2221702C3 (de) * | 1972-04-29 | 1975-11-27 | Paul & Siedler, 1000 Berlin | Elektromagnetisches Klappanker-Relais in Flachbauweise |
| GB1440359A (en) * | 1973-11-08 | 1976-06-23 | Plessey Co Ltd | Electromagnetic relay assemblies |
| FR2321181A1 (fr) * | 1975-08-11 | 1977-03-11 | Saparel | Relais sensible a collage sans aimant |
| DE3176825D1 (en) * | 1980-09-01 | 1988-09-01 | Fujitsu Ltd | Electromagnetic relay and method of manufacturing the same |
| ATA126182A (de) * | 1982-03-30 | 1987-06-15 | Schrack Elektronik Ag | Elektromagnetisches relais |
| DE8329097U1 (de) * | 1983-10-08 | 1984-01-12 | Eberle Anlagen KG, 8500 Nürnberg | Elektromagnetisches Relais |
-
1985
- 1985-12-17 DE DE19853544532 patent/DE3544532A1/de active Granted
-
1986
- 1986-12-04 EP EP86116890A patent/EP0226907A3/de not_active Withdrawn
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT402579B (de) * | 1991-10-07 | 1997-06-25 | Schrack Components Ag | Relais |
| EP0974994A1 (de) * | 1998-07-23 | 2000-01-26 | Bticino S.P.A. | Elektromagnet für einen Leitungsschutzschalter mit einem flachen Kern mit ein verdrillten Teil |
| CN106252161A (zh) * | 2016-08-31 | 2016-12-21 | 漳州宏发电声有限公司 | 一种只有铁芯的磁路系统及其继电器 |
| CN106252161B (zh) * | 2016-08-31 | 2019-03-05 | 漳州宏发电声有限公司 | 一种只有铁芯的磁路系统及其继电器 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE3544532C2 (de) | 1989-03-09 |
| EP0226907A3 (de) | 1989-08-30 |
| DE3544532A1 (de) | 1987-06-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0160121B1 (de) | Elektromagnet für elektrische Schaltgeräte, insbesondere Schütze | |
| DE69738308T2 (de) | Kontaktstift mit in entgegen gesetzter Richtung orientierte Verankerungsflügel und Steckerelement | |
| DE3883431T2 (de) | Elektrische Kontaktanordnung. | |
| DE3590369C2 (de) | ||
| DE4111054C2 (de) | ||
| DE69734859T2 (de) | Elektromagnetisches Relais | |
| DE69515968T2 (de) | Verbinderanordnung mit zusammenwirkenden Kontaktteilen und ein Verfahren zum Verbinden derselben | |
| DE69707369T2 (de) | Elektromagnetischer Schalter | |
| EP0536523B1 (de) | Anschlussklemme | |
| EP0226907A2 (de) | Relais | |
| DE2731001A1 (de) | Elektrische steckkontaktbuchse | |
| EP0451674B1 (de) | Einpresskontakt | |
| DE1515527C3 (de) | Elektrisches Kontaktglied | |
| DE69703277T2 (de) | Steckerelement | |
| DE3224933C2 (de) | Federkontakt für elektrische Steckverbindungen | |
| DE69913397T2 (de) | Schneidklemme | |
| DE69319259T2 (de) | Verbesserte Kontakte für den Anschluss von Spulenwicklungen | |
| DE2545180C3 (de) | Miniaturrelais | |
| EP0308819A2 (de) | Elektromagnetisches Relais | |
| DE3025814C2 (de) | Elektromagnetisches Relais | |
| DE3209198A1 (de) | Elektromagnetisches relais | |
| DE69204587T2 (de) | Elektrischer Kontaktstift für gedruckte Schaltungsplatten. | |
| DE3510638C1 (de) | Induktives Miniatur-Bauelement, insbesondere Miniatur-Spule sowie Verfahren zur Herstellung eines solchen Bauelements | |
| DE69103372T2 (de) | Spulenkörper mit winkelrechten Anschlussstiften. | |
| DE3784938T2 (de) | Elektrisches endglied. |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT CH DE FR GB IT LI |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19870724 |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT CH DE FR GB IT LI |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19900326 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn |
Effective date: 19901006 |
|
| RIN1 | Information on inventor provided before grant (corrected) |
Inventor name: SCHMITT, GERD |