EP0085626B1 - Zusammensetzung und Verfahren zur Behandlung von phosphatierten Metalloberflächen - Google Patents
Zusammensetzung und Verfahren zur Behandlung von phosphatierten Metalloberflächen Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0085626B1 EP0085626B1 EP83400204A EP83400204A EP0085626B1 EP 0085626 B1 EP0085626 B1 EP 0085626B1 EP 83400204 A EP83400204 A EP 83400204A EP 83400204 A EP83400204 A EP 83400204A EP 0085626 B1 EP0085626 B1 EP 0085626B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- composition
- titanium
- trivalent titanium
- process according
- trivalent
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired
Links
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 83
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 30
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium Chemical compound [Ti] RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 61
- 239000010936 titanium Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 52
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 51
- 238000011282 treatment Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 42
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 20
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 20
- 239000003973 paint Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- 239000012141 concentrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 10
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 46
- 239000003638 chemical reducing agent Substances 0.000 claims description 11
- 229910001868 water Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 8
- QIGBRXMKCJKVMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydroquinone Chemical compound OC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 QIGBRXMKCJKVMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- WQGWDDDVZFFDIG-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyrogallol Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC(O)=C1O WQGWDDDVZFFDIG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M Ilexoside XXIX Chemical compound C[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(CC[C@@]3(C(=CC[C@H]4[C@]3(CC[C@@H]5[C@@]4(CC[C@@H](C5(C)C)OS(=O)(=O)[O-])C)C)[C@@H]2[C@]1(C)O)C)C(=O)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)CO)O)O)O.[Na+] DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000010790 dilution Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000012895 dilution Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000007654 immersion Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000004094 surface-active agent Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000005868 electrolysis reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 229940079877 pyrogallol Drugs 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000003381 stabilizer Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 229930195733 hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000011065 in-situ storage Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000003609 titanium compounds Chemical class 0.000 abstract description 5
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 abstract description 4
- 238000002791 soaking Methods 0.000 description 25
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 24
- 239000008367 deionised water Substances 0.000 description 15
- 229910021641 deionized water Inorganic materials 0.000 description 15
- 238000005260 corrosion Methods 0.000 description 13
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical compound [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- 230000007797 corrosion Effects 0.000 description 12
- 239000008399 tap water Substances 0.000 description 11
- 235000020679 tap water Nutrition 0.000 description 11
- VYZAMTAEIAYCRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chromium Chemical compound [Cr] VYZAMTAEIAYCRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc Chemical compound [Zn] HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 229910052725 zinc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 9
- 239000011701 zinc Substances 0.000 description 9
- CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetone Chemical compound CC(C)=O CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 8
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 description 8
- ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Potassium Chemical compound [K] ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 238000004532 chromating Methods 0.000 description 7
- 229910052700 potassium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 239000011591 potassium Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000007921 spray Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 6
- RXCBCUJUGULOGC-UHFFFAOYSA-H dipotassium;tetrafluorotitanium;difluoride Chemical compound [F-].[F-].[F-].[F-].[F-].[F-].[K+].[K+].[Ti+4] RXCBCUJUGULOGC-UHFFFAOYSA-H 0.000 description 6
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 5
- 229910052804 chromium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 239000011651 chromium Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000005238 degreasing Methods 0.000 description 5
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nickel Chemical compound [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- XSTXAVWGXDQKEL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Trichloroethylene Chemical group ClC=C(Cl)Cl XSTXAVWGXDQKEL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229910052793 cadmium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- BDOSMKKIYDKNTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N cadmium atom Chemical compound [Cd] BDOSMKKIYDKNTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- JOPOVCBBYLSVDA-UHFFFAOYSA-N chromium(6+) Chemical compound [Cr+6] JOPOVCBBYLSVDA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000010960 cold rolled steel Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000008929 regeneration Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000011069 regeneration method Methods 0.000 description 4
- KWSLGOVYXMQPPX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2h-tetrazole Chemical compound FC(F)(F)C1=CC=CC(C2=NNN=N2)=C1 KWSLGOVYXMQPPX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Calcium Chemical compound [Ca] OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Carbonate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]C([O-])=O CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 3
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- QCWXUUIWCKQGHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zirconium Chemical compound [Zr] QCWXUUIWCKQGHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229910001430 chromium ion Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 3
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 3
- ACVYVLVWPXVTIT-UHFFFAOYSA-M phosphinate Chemical compound [O-][PH2]=O ACVYVLVWPXVTIT-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229910001379 sodium hypophosphite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052726 zirconium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonia Chemical compound N QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-O Ammonium Chemical compound [NH4+] QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-O 0.000 description 2
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-M Chloride anion Chemical compound [Cl-] VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorane Chemical compound F KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oxalic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(O)=O MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfuric acid Chemical compound OS(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 2
- 210000003298 dental enamel Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 238000007598 dipping method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 2
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229910000398 iron phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- WBJZTOZJJYAKHQ-UHFFFAOYSA-K iron(3+) phosphate Chemical compound [Fe+3].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O WBJZTOZJJYAKHQ-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 2
- 239000004922 lacquer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- ACVYVLVWPXVTIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N phosphinic acid Chemical class O[PH2]=O ACVYVLVWPXVTIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000005507 spraying Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 2
- XJDNKRIXUMDJCW-UHFFFAOYSA-J titanium tetrachloride Chemical compound Cl[Ti](Cl)(Cl)Cl XJDNKRIXUMDJCW-UHFFFAOYSA-J 0.000 description 2
- 239000002966 varnish Substances 0.000 description 2
- LRXTYHSAJDENHV-UHFFFAOYSA-H zinc phosphate Chemical compound [Zn+2].[Zn+2].[Zn+2].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O LRXTYHSAJDENHV-UHFFFAOYSA-H 0.000 description 2
- 229910000165 zinc phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- ZCZPJZYQBNOPLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3,5,6-tetramethylaniline Chemical compound CC1=CC(C)=C(C)C(N)=C1C ZCZPJZYQBNOPLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910000497 Amalgam Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- CPELXLSAUQHCOX-UHFFFAOYSA-M Bromide Chemical compound [Br-] CPELXLSAUQHCOX-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-M Fluoride anion Chemical compound [F-] KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 229910001335 Galvanized steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Magnesium Chemical compound [Mg] FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910021205 NaH2PO2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- GRYLNZFGIOXLOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nitric acid Chemical compound O[N+]([O-])=O GRYLNZFGIOXLOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910019142 PO4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 241000287107 Passer Species 0.000 description 1
- 229910010348 TiF3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910010340 TiFe Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000007513 acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052783 alkali metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000001340 alkali metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229940045714 alkyl sulfonate alkylating agent Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000004411 aluminium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910021529 ammonia Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002585 base Substances 0.000 description 1
- 208000002352 blister Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000003054 catalyst Substances 0.000 description 1
- ZCDOYSPFYFSLEW-UHFFFAOYSA-N chromate(2-) Chemical compound [O-][Cr]([O-])(=O)=O ZCDOYSPFYFSLEW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010411 cooking Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003599 detergent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- IRXRGVFLQOSHOH-UHFFFAOYSA-L dipotassium;oxalate Chemical compound [K+].[K+].[O-]C(=O)C([O-])=O IRXRGVFLQOSHOH-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 238000004090 dissolution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001962 electrophoresis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000008397 galvanized steel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009931 harmful effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 231100000086 high toxicity Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 230000003902 lesion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910017604 nitric acid Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- DCKVFVYPWDKYDN-UHFFFAOYSA-L oxygen(2-);titanium(4+);sulfate Chemical compound [O-2].[Ti+4].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O DCKVFVYPWDKYDN-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 230000002572 peristaltic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K phosphate Chemical compound [O-]P([O-])([O-])=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- 239000010452 phosphate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010791 quenching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000171 quenching effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004064 recycling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005070 sampling Methods 0.000 description 1
- -1 sodium alkyl sulfonates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000012279 sodium borohydride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910000033 sodium borohydride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910000348 titanium sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XROWMBWRMNHXMF-UHFFFAOYSA-J titanium tetrafluoride Chemical compound [F-].[F-].[F-].[F-].[Ti+4] XROWMBWRMNHXMF-UHFFFAOYSA-J 0.000 description 1
- 150000003754 zirconium Chemical class 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C22/00—Chemical surface treatment of metallic material by reaction of the surface with a reactive liquid, leaving reaction products of surface material in the coating, e.g. conversion coatings, passivation of metals
- C23C22/82—After-treatment
- C23C22/83—Chemical after-treatment
Definitions
- the subject of the invention is a method for the treatment, more precisely the "post-treatment" of phosphated metal surfaces, in particular when these surfaces must be subsequently coated with a layer of paint.
- the phosphating, including iron and zinc phosphating, of the metal surfaces in question i.e. surfaces of iron, steel, zinc, iron and galvanized steel substrates, d 'aluminum and alloys of the above metals, cadmium and others, aims to protect these surfaces against corrosion; these surfaces are then optionally covered with a layer of paint which may be based more particularly on lacquers, varnishes and enamels applied for example by immersion, electrophoresis, spraying and the like.
- These treatments which have the aim of further increasing the effectiveness of the protection against corrosion of previously phosphated metal surfaces, generally employ trivalent and / or hexavalent chromium ions in the form of chromium-based compositions or solutions of chromation. chromate applied in final or passivating rinse.
- the object of the invention is therefore, above all, to provide a process for the treatment of phosphated metal surfaces with the aid of a composition which, while giving these surfaces protection equivalent to that produced by the chromium plating solutions. 'prior art, no longer has the disadvantages of these.
- the treatment method according to the invention in which after phosphating of metal surfaces and before possible application of a layer of paint, the phosphated metal surface is treated by bringing said surface into contact with a composition comprising titanium, is characterized in that the composition comprises trivalent titanium at a concentration of 0.01 to 2 g / 1 and has a pH of 2 to 7, the temperature of the composition being less than 90 ° C, preferably included between 18 and 60 ° C.
- composition used in accordance with the method according to the invention contains trivalent titanium at a concentration of 0.2 to 0.6 g / I.
- the composition used in accordance with the process according to the invention is obtained by dilution with water from a concentrate which may contain, by way of indication, approximately 10 to 50 g of trivalent titanium per liter, this concentrate which is preferably kept away from oxygen in the air until the time of use, being diluted at that time with the quantity of water, preferably distilled or deionized, chosen to result in the concentration of trivalent titanium which corresponds to that of the composition used.
- the relatively low stability especially in dilute solution and in contact with the oxygen of the air of the compounds containing trivalent titanium, which rapidly oxidizes to tetravalent titanium, means that the composition used in the process in accordance with invention will generally be prepared at the time of use and regenerated if necessary during operation by reduction of tetravalent titanium formed of trivalent titanium.
- the process according to the invention is therefore characterized by the fact that the trivalent titanium to be comprised by the composition used is prepared in situ and before the application of the composition to the phosphated metal surfaces, by setting in contact with tetravalent titanium with a reduction means, the composition then being, during the process of treatment of phosphate surfaces, regenerated into. trivalent titanium by bringing into contact in particular a fraction derived from the composition with the abovementioned reduction means in such a way that the concentration of the composition in trivalent titanium compound is maintained in the proportion in particular from 0.2 to 0.6 g of trivalent titanium per liter, mentioned above.
- the process according to the invention is characterized in that the composition used is prepared from a concentrate and that the concentration of trivalent titanium of the composition thus obtained is maintained at the value effective by regeneration during operation in contact with a means of reducing tetravalent titanium to trivalent titanium.
- the above regeneration can take place continuously.
- Proposing therefore, to treat, in order to improve its resistance to corrosion, a phosphated metal surface which may possibly receive one or more layers of paint subsequently, this is done as follows or in an equivalent manner.
- said metallic surface which may be that of a metallic substrate based on iron, steel, zinc, galvanized iron or steel, aluminum, alloys of these metals, of cadmium and others, to a phosphating treatment comprising, after degreasing with the aid in particular of alkaline detergents, the action of a conventional acid phosphating composition with iron or zinc generally implemented hot and for several minutes by immersion or by sprinkling.
- the metal surface is treated in accordance with the method according to the invention using a composition which contains a trivalent titanium compound at a concentration of 0, 01 to 2 g, preferably 0.2 to 0.6 g of trivalent titanium per liter and has an acid pH of 2 to 7, preferably 2 to 5.
- the proportions of 0.2 to 0.6 g of trivalent titanium per liter correspond to a value of 4.17 10-3 to 1.25 - 10-2 gram atoms of trivalent titanium per liter.
- the pH can be adjusted using soda, ammonia, hydrofluoric acid, nitric acid and other acids or bases.
- the composition is used at a temperature below 90 ° C. and in particular chosen from the range from 18 to 60 ° C.
- the treatment preferably takes place by immersing the metal surface in the composition for a period generally between 10 and 60 seconds.
- composition can also be applied by spraying; this technique is less advantageous because of the sensitivity of trivalent titanium with respect to oxidation.
- the treatment is followed by rinsing with water and drying, in particular hot, of the metal surface before possible application of a paint which can be chosen from lacquers, varnishes, enamels and the like, applied by any process. suitable.
- the quality of the anti-corrosion protection conferred can be tested by the salt spray test which will be more particularly discussed in relation to the examples. This test is described in the American standards ASTM B 117 and ASTM D 1654-61. The assessment of the corrosion resistance conferred is made using a scale ranging from 0 (zero resistance) to 10 (very good corrosion resistance).
- the trivalent titanium compound can be chosen from the group comprising chloride, bromide, fluoride, oxalate and trivalent titanium sulfate which have been found to be particularly active.
- composition used in accordance with the invention must be regenerated to maintain its concentration of trivalent titanium at an effective value, this which can be achieved by contacting a reduction means, in particular a reducing agent.
- the treatment enclosure containing the composition can be made to include a bypass pipe in which the reducing agent is placed.
- the composition can be taken from the bottom of the enclosure, passed through the bypass pipe containing the reducing agent and reintroduced onto the surface of the bath constituting the composition.
- the immersion treatment is of the dynamic type with translation of the parts comprising the phosphated surfaces to be treated, it will be advantageously arranged so that the direction of the current created within the composition, as a result of the sampling in the bypass line, is contrary to the translational movement of the parts.
- the reduction means can be either a metallic or chemical reducing agent placed in a column, or an electrolysis cell, the column or cell being traversed by the composition to be regenerated continuously or discontinuously so that the titanium concentration trivalent is maintained at the effective value; the effects of the oxidation of the bath and / or of the regeneration are followed by simple volumetric redox dosing and the regeneration is started or stopped when the proportion of the composition in trivalent titanium goes beyond the limits indicated above.
- an inert electrode is used, the method being that used in redox batteries.
- test pieces made up of panels of "cold-rolled steel of current quality, thickness 8/10 mm and -measuring 150 mm x 70 mm, are carefully degreased using trichlorethylene then acetone; they are then subjected to a dip phosphating treatment.
- a commercial phosphating composition is used, in particular that known under the brand "Duridine 49" ® and the concentration of which is 3% by weight.
- This composition contains phosphating agents and surfactants.
- the duration of the quenching of the test pieces in the phosphating composition is 10 minutes.
- the coating obtained is an iron phosphate coating whose layer weight varies between 0.2 and 0.3 g / m2 .
- test pieces are divided into three sets of five.
- test pieces are then subjected to a 5% salt spray corrosion test at a temperature of 35 ° C. under the conditions specified in standard ASTM B 117. After 96 hours of exposure to this satin fog, the results obtained are examined. using ASTM D 1654-61. These results are shown in Table I below; they represent the means of the results of the three series of tests carried out with the three sets of fifteen test pieces.
- test specimens consisting of panels of "cold-rolled steel of standard quality, 8/10 mm thick, measuring 150 mm x 70 mm. These test pieces are carefully degreased using trichlorethylene and then acetone before undergoing a phosphating conversion treatment by soaking.
- This treatment is carried out with the same phosphating composition as in Example 1 and in the conditions described in this example.
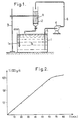
- Curve C shown in FIG. 2 illustrates the variation in the content of the bath in grams of Ti (III) per liter of composition (ordinate axis) as a function of the time T expressed in minutes during which recycling is maintained (abscissa axis) in the conditions which have just been specified.
- test pieces are dried in an oven at 150 ° C. for 5 minutes, then the water-soluble paint of example 1 is applied to them by dipping while respecting the conditions described in this example.
- test pieces are then subjected to a 5% salt spray corrosion test at a temperature of 35 ° C. under the conditions specified in standard ASTM B 117. After 96 hours of exposure to said salt spray, the results obtained are examined in accordance with to ASTM D 1654-61. These results are shown in Table II below; they represent the averages of the results of the tests carried out on three sets of twenty-five test pieces.
- a zinc phosphate coating is obtained, the layer weight of which varies between 2 and 3 g / m 2 .
- the three sets of five test pieces are then treated respectively as the three sets of five test pieces of Example 1.
- Example 2 After drying and application of the water-soluble paint under the conditions of Example 1, the three series of test pieces are treated as described in standard ASTM B 117. After 384 hours of exposure to salt spray, the results are examined. obtained using ASTM 1654-61. These results are shown in Table III below; they represent the means of the results of three tests, that is to say tests carried out with three sets of three series of five test pieces.
- a zinc phosphate coating is obtained, the layer weight of which varies between 2 and 3 g / m 2 .
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Metallurgy (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Chemical Treatment Of Metals (AREA)
- Paints Or Removers (AREA)
Claims (9)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT83400204T ATE23574T1 (de) | 1982-01-29 | 1983-01-28 | Zusammensetzung und verfahren zur behandlung von phosphatierten metalloberflaechen. |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR8201476A FR2520758A1 (fr) | 1982-01-29 | 1982-01-29 | Composition et procede pour le traitement de surfaces metalliques phosphatees |
| FR8201476 | 1982-01-29 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0085626A1 EP0085626A1 (de) | 1983-08-10 |
| EP0085626B1 true EP0085626B1 (de) | 1986-11-12 |
Family
ID=9270495
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP83400204A Expired EP0085626B1 (de) | 1982-01-29 | 1983-01-28 | Zusammensetzung und Verfahren zur Behandlung von phosphatierten Metalloberflächen |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US4497666A (de) |
| EP (1) | EP0085626B1 (de) |
| JP (1) | JPS58136781A (de) |
| AT (1) | ATE23574T1 (de) |
| CA (1) | CA1197674A (de) |
| DE (1) | DE3367630D1 (de) |
| FR (1) | FR2520758A1 (de) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AU2448684A (en) * | 1983-03-02 | 1984-09-06 | Parker Chemical Company | Metal treatment before phosphate coating |
| DE3400339A1 (de) * | 1984-01-07 | 1985-08-29 | Gerhard Collardin GmbH, 5000 Köln | Verfahren zur nachpassivierung von phosphatierten metalloberflaechen unter verwendung von nickel- und/oder kupfer-kationen enthaltenden loesungen |
| US5073196A (en) * | 1989-05-18 | 1991-12-17 | Henkel Corporation | Non-accelerated iron phosphating |
| DE4031817A1 (de) * | 1990-10-08 | 1992-04-09 | Henkel Kgaa | Verfahren zur passivierenden nachbehandlung von phosphatierten metalloberflaechen |
| US5128211A (en) * | 1991-02-28 | 1992-07-07 | Diversey Corporation | Aluminum based phosphate final rinse |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE154542C (de) * | ||||
| US2970935A (en) * | 1959-03-02 | 1961-02-07 | Parker Rust Proof Co | Method of rinsing metallic surfaces with solutions containing hexavalent chromium |
| FR1388662A (fr) * | 1962-10-15 | 1965-02-12 | Parker Ste Continentale | Procédé et solution pour le traitement des surfaces métalliques pourvues d'un revêtement chimique |
| DE1521879B2 (de) * | 1966-07-12 | 1975-08-28 | Metallgesellschaft Ag, 6000 Frankfurt | Verfahren zum Aufbringen von Phosphatüberzügen auf Eisen und Stahl |
| US3695942A (en) * | 1970-12-02 | 1972-10-03 | Amchem Prod | Zirconium rinse for phosphate coated metal surfaces |
| US3895970A (en) * | 1973-06-11 | 1975-07-22 | Pennwalt Corp | Sealing rinse for phosphate coatings of metal |
| GB1461244A (en) * | 1974-06-17 | 1977-01-13 | Lubrizol Corp | Treatment of metal surfaces with trivalent chromium solutions |
| JPS5292836A (en) * | 1976-01-30 | 1977-08-04 | Nippon Packaging Kk | Zinc or its alloys subjected to chemical conversion |
| GB1586975A (en) * | 1976-07-05 | 1981-03-25 | Kansai Paint Co Ltd | Surface treatment of metals |
| US4165242A (en) * | 1977-11-21 | 1979-08-21 | R. O. Hull & Company, Inc. | Treatment of metal parts to provide rust-inhibiting coatings by phosphating and electrophoretically depositing a siccative organic coating |
| US4233088A (en) * | 1979-03-29 | 1980-11-11 | International Lead Zinc Research Organization, Inc. | Phosphatization of steel surfaces and metal-coated surfaces |
| US4281037A (en) * | 1980-08-08 | 1981-07-28 | Dap, Inc. | Cleaning and priming composition containing titanium acetylacetonate and method |
-
1982
- 1982-01-29 FR FR8201476A patent/FR2520758A1/fr active Granted
-
1983
- 1983-01-28 US US06/462,088 patent/US4497666A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1983-01-28 EP EP83400204A patent/EP0085626B1/de not_active Expired
- 1983-01-28 DE DE8383400204T patent/DE3367630D1/de not_active Expired
- 1983-01-28 AT AT83400204T patent/ATE23574T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1983-01-28 JP JP58012562A patent/JPS58136781A/ja active Pending
- 1983-01-28 CA CA000420493A patent/CA1197674A/en not_active Expired
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| Gmelins Handbuch der anorganischen Chemie, vol. 41 (1951), pages 373, 413 * |
| Römpps Chemie-Lexikon (1977), pages 3608, 3609, 3612 * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPS58136781A (ja) | 1983-08-13 |
| DE3367630D1 (en) | 1987-01-02 |
| EP0085626A1 (de) | 1983-08-10 |
| CA1197674A (en) | 1985-12-10 |
| ATE23574T1 (de) | 1986-11-15 |
| FR2520758B1 (de) | 1984-04-27 |
| FR2520758A1 (fr) | 1983-08-05 |
| US4497666A (en) | 1985-02-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JPH05195247A (ja) | アルミニウムを保護するためのクロムを含まない方法および組成物 | |
| CA2864109A1 (fr) | Procede de traitement de surface de pieces en alliage d'aluminium ou de magnesium | |
| JP3875197B2 (ja) | 耐食被覆を施すための方法 | |
| JPH0394074A (ja) | 金属面へのコーテイング付与用改良組成物および付与方法 | |
| EP3810833B1 (de) | Verfahren zur oberflächenbehandlung eines teils aus aluminium oder einer aluminiumlegierung oder aus magnesium oder einer magnesiumlegierung | |
| FR2512840A1 (fr) | Solutions aqueuses acides pour revetements de phosphate de zinc et leurs concentres, procedes de revetement les mettant en oeuvre et solutions d'activation du metal utilisables dans ces procedes | |
| JPH02305972A (ja) | 金属の燐酸塩処理液組成物及びその処理方法 | |
| JPH11335865A (ja) | 金属の保護皮膜形成用処理剤と形成方法 | |
| EP0085626B1 (de) | Zusammensetzung und Verfahren zur Behandlung von phosphatierten Metalloberflächen | |
| JP3372954B2 (ja) | 片面を亜鉛鍍金または亜鉛合金鍍金した鋼帯板あるいは鋼板を燐酸塩処理する方法 | |
| CA2442502C (fr) | Procede de traitement par carboxylatation de surfaces metalliques | |
| JP5827792B2 (ja) | 化成処理鉄系材料 | |
| JP5061395B2 (ja) | 亜鉛又は亜鉛−ニッケル合金めっき用六価クロムフリー被膜形成剤及び形成方法 | |
| US4812175A (en) | Passivation process and copmposition for zinc-aluminum alloys | |
| EP0102284A1 (de) | Lösung und Verfahren zur chemischen Konversion metallischer Oberflächen | |
| JPH07173643A (ja) | 金属表面の燐酸塩処理方法及び処理液 | |
| JPS6256579A (ja) | 亜鉛または亜鉛−アルミニウム合金表面の不動態化用酸性水溶液および不動態化方法 | |
| US4316752A (en) | Oxalic acid treatment of carbon steel, galvanized steel and aluminum surfaces | |
| EP0298827B1 (de) | Lösung und Verfahren zur gemischten Phosphatisierung | |
| EP1252367B1 (de) | Verfahren zur oxalierung einer zinkbeschichteten bandoberfläche | |
| EP0826792A1 (de) | Bad und Verfahren zum Phosphatieren von Metallgegenständen, Konzentrate zur Herstellung des Bades und Metallgegenstanden behandelt nach dem Verfahren | |
| FR2654440A1 (fr) | Procede de conversion chimique de substrats metalliques, bain mis en óoeuvre dans ce procede et concentre pour la preparation du bain. | |
| BE561524A (fr) | Procede de fabrication de revetements pour les surfaces de magnesium | |
| US6723258B1 (en) | Method and composition for minimizing rust formation and improving paint adhesion of metal surfaces | |
| EP0187597B1 (de) | Zusammensetzung und Verfahren zum Beschichten von Metalloberflächen mit einer Konversionsschicht auf der Basis von Zinkphosphat |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE DE GB IT NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19840208 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE DE GB IT NL SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 23574 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19861115 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3367630 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19870102 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 19911219 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 19920121 Year of fee payment: 10 Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19920121 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19920128 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| ITTA | It: last paid annual fee | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19920131 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19920514 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Effective date: 19930128 Ref country code: AT Effective date: 19930128 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Effective date: 19930129 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Effective date: 19930131 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: CIE FRANCAISE DE PRODUITS INDUSTRIELS Effective date: 19930131 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Effective date: 19930801 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee | ||
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 19930128 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19931001 |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 83400204.0 Effective date: 19930810 |