EP0085626B1 - Composition and process for treating phosphated metallic surfaces - Google Patents
Composition and process for treating phosphated metallic surfaces Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0085626B1 EP0085626B1 EP83400204A EP83400204A EP0085626B1 EP 0085626 B1 EP0085626 B1 EP 0085626B1 EP 83400204 A EP83400204 A EP 83400204A EP 83400204 A EP83400204 A EP 83400204A EP 0085626 B1 EP0085626 B1 EP 0085626B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- composition
- titanium
- trivalent titanium
- process according
- trivalent
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired
Links
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 83
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 30
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium Chemical compound [Ti] RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 61
- 239000010936 titanium Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 52
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 51
- 238000011282 treatment Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 42
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 20
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 20
- 239000003973 paint Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- 239000012141 concentrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 10
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 46
- 239000003638 chemical reducing agent Substances 0.000 claims description 11
- 229910001868 water Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 8
- QIGBRXMKCJKVMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydroquinone Chemical compound OC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 QIGBRXMKCJKVMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- WQGWDDDVZFFDIG-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyrogallol Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC(O)=C1O WQGWDDDVZFFDIG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M Ilexoside XXIX Chemical compound C[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(CC[C@@]3(C(=CC[C@H]4[C@]3(CC[C@@H]5[C@@]4(CC[C@@H](C5(C)C)OS(=O)(=O)[O-])C)C)[C@@H]2[C@]1(C)O)C)C(=O)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)CO)O)O)O.[Na+] DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000010790 dilution Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000012895 dilution Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000007654 immersion Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000004094 surface-active agent Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000005868 electrolysis reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 229940079877 pyrogallol Drugs 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000003381 stabilizer Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 229930195733 hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000011065 in-situ storage Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000003609 titanium compounds Chemical class 0.000 abstract description 5
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 abstract description 4
- 238000002791 soaking Methods 0.000 description 25
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 24
- 239000008367 deionised water Substances 0.000 description 15
- 229910021641 deionized water Inorganic materials 0.000 description 15
- 238000005260 corrosion Methods 0.000 description 13
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical compound [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- 230000007797 corrosion Effects 0.000 description 12
- 239000008399 tap water Substances 0.000 description 11
- 235000020679 tap water Nutrition 0.000 description 11
- VYZAMTAEIAYCRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chromium Chemical compound [Cr] VYZAMTAEIAYCRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc Chemical compound [Zn] HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 229910052725 zinc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 9
- 239000011701 zinc Substances 0.000 description 9
- CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetone Chemical compound CC(C)=O CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 8
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 description 8
- ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Potassium Chemical compound [K] ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 238000004532 chromating Methods 0.000 description 7
- 229910052700 potassium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 239000011591 potassium Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000007921 spray Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 6
- RXCBCUJUGULOGC-UHFFFAOYSA-H dipotassium;tetrafluorotitanium;difluoride Chemical compound [F-].[F-].[F-].[F-].[F-].[F-].[K+].[K+].[Ti+4] RXCBCUJUGULOGC-UHFFFAOYSA-H 0.000 description 6
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 5
- 229910052804 chromium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 239000011651 chromium Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000005238 degreasing Methods 0.000 description 5
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nickel Chemical compound [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- XSTXAVWGXDQKEL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Trichloroethylene Chemical group ClC=C(Cl)Cl XSTXAVWGXDQKEL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229910052793 cadmium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- BDOSMKKIYDKNTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N cadmium atom Chemical compound [Cd] BDOSMKKIYDKNTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- JOPOVCBBYLSVDA-UHFFFAOYSA-N chromium(6+) Chemical compound [Cr+6] JOPOVCBBYLSVDA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000010960 cold rolled steel Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000008929 regeneration Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000011069 regeneration method Methods 0.000 description 4
- KWSLGOVYXMQPPX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2h-tetrazole Chemical compound FC(F)(F)C1=CC=CC(C2=NNN=N2)=C1 KWSLGOVYXMQPPX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Calcium Chemical compound [Ca] OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Carbonate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]C([O-])=O CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 3
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- QCWXUUIWCKQGHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zirconium Chemical compound [Zr] QCWXUUIWCKQGHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229910001430 chromium ion Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 3
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 3
- ACVYVLVWPXVTIT-UHFFFAOYSA-M phosphinate Chemical compound [O-][PH2]=O ACVYVLVWPXVTIT-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229910001379 sodium hypophosphite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052726 zirconium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonia Chemical compound N QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-O Ammonium Chemical compound [NH4+] QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-O 0.000 description 2
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-M Chloride anion Chemical compound [Cl-] VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorane Chemical compound F KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oxalic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(O)=O MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfuric acid Chemical compound OS(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 2
- 210000003298 dental enamel Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 238000007598 dipping method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 2
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229910000398 iron phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- WBJZTOZJJYAKHQ-UHFFFAOYSA-K iron(3+) phosphate Chemical compound [Fe+3].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O WBJZTOZJJYAKHQ-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 2
- 239000004922 lacquer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- ACVYVLVWPXVTIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N phosphinic acid Chemical class O[PH2]=O ACVYVLVWPXVTIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000005507 spraying Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 2
- XJDNKRIXUMDJCW-UHFFFAOYSA-J titanium tetrachloride Chemical compound Cl[Ti](Cl)(Cl)Cl XJDNKRIXUMDJCW-UHFFFAOYSA-J 0.000 description 2
- 239000002966 varnish Substances 0.000 description 2
- LRXTYHSAJDENHV-UHFFFAOYSA-H zinc phosphate Chemical compound [Zn+2].[Zn+2].[Zn+2].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O LRXTYHSAJDENHV-UHFFFAOYSA-H 0.000 description 2
- 229910000165 zinc phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- ZCZPJZYQBNOPLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3,5,6-tetramethylaniline Chemical compound CC1=CC(C)=C(C)C(N)=C1C ZCZPJZYQBNOPLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910000497 Amalgam Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- CPELXLSAUQHCOX-UHFFFAOYSA-M Bromide Chemical compound [Br-] CPELXLSAUQHCOX-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-M Fluoride anion Chemical compound [F-] KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 229910001335 Galvanized steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Magnesium Chemical compound [Mg] FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910021205 NaH2PO2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- GRYLNZFGIOXLOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nitric acid Chemical compound O[N+]([O-])=O GRYLNZFGIOXLOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910019142 PO4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 241000287107 Passer Species 0.000 description 1
- 229910010348 TiF3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910010340 TiFe Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000007513 acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052783 alkali metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000001340 alkali metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229940045714 alkyl sulfonate alkylating agent Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000004411 aluminium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910021529 ammonia Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002585 base Substances 0.000 description 1
- 208000002352 blister Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000003054 catalyst Substances 0.000 description 1
- ZCDOYSPFYFSLEW-UHFFFAOYSA-N chromate(2-) Chemical compound [O-][Cr]([O-])(=O)=O ZCDOYSPFYFSLEW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010411 cooking Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003599 detergent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- IRXRGVFLQOSHOH-UHFFFAOYSA-L dipotassium;oxalate Chemical compound [K+].[K+].[O-]C(=O)C([O-])=O IRXRGVFLQOSHOH-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 238000004090 dissolution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001962 electrophoresis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000008397 galvanized steel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009931 harmful effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 231100000086 high toxicity Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 230000003902 lesion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910017604 nitric acid Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- DCKVFVYPWDKYDN-UHFFFAOYSA-L oxygen(2-);titanium(4+);sulfate Chemical compound [O-2].[Ti+4].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O DCKVFVYPWDKYDN-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 230000002572 peristaltic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K phosphate Chemical compound [O-]P([O-])([O-])=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- 239000010452 phosphate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010791 quenching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000171 quenching effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004064 recycling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005070 sampling Methods 0.000 description 1
- -1 sodium alkyl sulfonates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000012279 sodium borohydride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910000033 sodium borohydride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910000348 titanium sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XROWMBWRMNHXMF-UHFFFAOYSA-J titanium tetrafluoride Chemical compound [F-].[F-].[F-].[F-].[Ti+4] XROWMBWRMNHXMF-UHFFFAOYSA-J 0.000 description 1
- 150000003754 zirconium Chemical class 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C22/00—Chemical surface treatment of metallic material by reaction of the surface with a reactive liquid, leaving reaction products of surface material in the coating, e.g. conversion coatings, passivation of metals
- C23C22/82—After-treatment
- C23C22/83—Chemical after-treatment
Definitions
- the subject of the invention is a method for the treatment, more precisely the "post-treatment" of phosphated metal surfaces, in particular when these surfaces must be subsequently coated with a layer of paint.
- the phosphating, including iron and zinc phosphating, of the metal surfaces in question i.e. surfaces of iron, steel, zinc, iron and galvanized steel substrates, d 'aluminum and alloys of the above metals, cadmium and others, aims to protect these surfaces against corrosion; these surfaces are then optionally covered with a layer of paint which may be based more particularly on lacquers, varnishes and enamels applied for example by immersion, electrophoresis, spraying and the like.
- These treatments which have the aim of further increasing the effectiveness of the protection against corrosion of previously phosphated metal surfaces, generally employ trivalent and / or hexavalent chromium ions in the form of chromium-based compositions or solutions of chromation. chromate applied in final or passivating rinse.
- the object of the invention is therefore, above all, to provide a process for the treatment of phosphated metal surfaces with the aid of a composition which, while giving these surfaces protection equivalent to that produced by the chromium plating solutions. 'prior art, no longer has the disadvantages of these.
- the treatment method according to the invention in which after phosphating of metal surfaces and before possible application of a layer of paint, the phosphated metal surface is treated by bringing said surface into contact with a composition comprising titanium, is characterized in that the composition comprises trivalent titanium at a concentration of 0.01 to 2 g / 1 and has a pH of 2 to 7, the temperature of the composition being less than 90 ° C, preferably included between 18 and 60 ° C.
- composition used in accordance with the method according to the invention contains trivalent titanium at a concentration of 0.2 to 0.6 g / I.
- the composition used in accordance with the process according to the invention is obtained by dilution with water from a concentrate which may contain, by way of indication, approximately 10 to 50 g of trivalent titanium per liter, this concentrate which is preferably kept away from oxygen in the air until the time of use, being diluted at that time with the quantity of water, preferably distilled or deionized, chosen to result in the concentration of trivalent titanium which corresponds to that of the composition used.
- the relatively low stability especially in dilute solution and in contact with the oxygen of the air of the compounds containing trivalent titanium, which rapidly oxidizes to tetravalent titanium, means that the composition used in the process in accordance with invention will generally be prepared at the time of use and regenerated if necessary during operation by reduction of tetravalent titanium formed of trivalent titanium.
- the process according to the invention is therefore characterized by the fact that the trivalent titanium to be comprised by the composition used is prepared in situ and before the application of the composition to the phosphated metal surfaces, by setting in contact with tetravalent titanium with a reduction means, the composition then being, during the process of treatment of phosphate surfaces, regenerated into. trivalent titanium by bringing into contact in particular a fraction derived from the composition with the abovementioned reduction means in such a way that the concentration of the composition in trivalent titanium compound is maintained in the proportion in particular from 0.2 to 0.6 g of trivalent titanium per liter, mentioned above.
- the process according to the invention is characterized in that the composition used is prepared from a concentrate and that the concentration of trivalent titanium of the composition thus obtained is maintained at the value effective by regeneration during operation in contact with a means of reducing tetravalent titanium to trivalent titanium.
- the above regeneration can take place continuously.
- Proposing therefore, to treat, in order to improve its resistance to corrosion, a phosphated metal surface which may possibly receive one or more layers of paint subsequently, this is done as follows or in an equivalent manner.
- said metallic surface which may be that of a metallic substrate based on iron, steel, zinc, galvanized iron or steel, aluminum, alloys of these metals, of cadmium and others, to a phosphating treatment comprising, after degreasing with the aid in particular of alkaline detergents, the action of a conventional acid phosphating composition with iron or zinc generally implemented hot and for several minutes by immersion or by sprinkling.
- the metal surface is treated in accordance with the method according to the invention using a composition which contains a trivalent titanium compound at a concentration of 0, 01 to 2 g, preferably 0.2 to 0.6 g of trivalent titanium per liter and has an acid pH of 2 to 7, preferably 2 to 5.
- the proportions of 0.2 to 0.6 g of trivalent titanium per liter correspond to a value of 4.17 10-3 to 1.25 - 10-2 gram atoms of trivalent titanium per liter.
- the pH can be adjusted using soda, ammonia, hydrofluoric acid, nitric acid and other acids or bases.
- the composition is used at a temperature below 90 ° C. and in particular chosen from the range from 18 to 60 ° C.
- the treatment preferably takes place by immersing the metal surface in the composition for a period generally between 10 and 60 seconds.
- composition can also be applied by spraying; this technique is less advantageous because of the sensitivity of trivalent titanium with respect to oxidation.
- the treatment is followed by rinsing with water and drying, in particular hot, of the metal surface before possible application of a paint which can be chosen from lacquers, varnishes, enamels and the like, applied by any process. suitable.
- the quality of the anti-corrosion protection conferred can be tested by the salt spray test which will be more particularly discussed in relation to the examples. This test is described in the American standards ASTM B 117 and ASTM D 1654-61. The assessment of the corrosion resistance conferred is made using a scale ranging from 0 (zero resistance) to 10 (very good corrosion resistance).
- the trivalent titanium compound can be chosen from the group comprising chloride, bromide, fluoride, oxalate and trivalent titanium sulfate which have been found to be particularly active.
- composition used in accordance with the invention must be regenerated to maintain its concentration of trivalent titanium at an effective value, this which can be achieved by contacting a reduction means, in particular a reducing agent.
- the treatment enclosure containing the composition can be made to include a bypass pipe in which the reducing agent is placed.
- the composition can be taken from the bottom of the enclosure, passed through the bypass pipe containing the reducing agent and reintroduced onto the surface of the bath constituting the composition.
- the immersion treatment is of the dynamic type with translation of the parts comprising the phosphated surfaces to be treated, it will be advantageously arranged so that the direction of the current created within the composition, as a result of the sampling in the bypass line, is contrary to the translational movement of the parts.
- the reduction means can be either a metallic or chemical reducing agent placed in a column, or an electrolysis cell, the column or cell being traversed by the composition to be regenerated continuously or discontinuously so that the titanium concentration trivalent is maintained at the effective value; the effects of the oxidation of the bath and / or of the regeneration are followed by simple volumetric redox dosing and the regeneration is started or stopped when the proportion of the composition in trivalent titanium goes beyond the limits indicated above.
- an inert electrode is used, the method being that used in redox batteries.
- test pieces made up of panels of "cold-rolled steel of current quality, thickness 8/10 mm and -measuring 150 mm x 70 mm, are carefully degreased using trichlorethylene then acetone; they are then subjected to a dip phosphating treatment.
- a commercial phosphating composition is used, in particular that known under the brand "Duridine 49" ® and the concentration of which is 3% by weight.
- This composition contains phosphating agents and surfactants.
- the duration of the quenching of the test pieces in the phosphating composition is 10 minutes.
- the coating obtained is an iron phosphate coating whose layer weight varies between 0.2 and 0.3 g / m2 .
- test pieces are divided into three sets of five.
- test pieces are then subjected to a 5% salt spray corrosion test at a temperature of 35 ° C. under the conditions specified in standard ASTM B 117. After 96 hours of exposure to this satin fog, the results obtained are examined. using ASTM D 1654-61. These results are shown in Table I below; they represent the means of the results of the three series of tests carried out with the three sets of fifteen test pieces.
- test specimens consisting of panels of "cold-rolled steel of standard quality, 8/10 mm thick, measuring 150 mm x 70 mm. These test pieces are carefully degreased using trichlorethylene and then acetone before undergoing a phosphating conversion treatment by soaking.
- This treatment is carried out with the same phosphating composition as in Example 1 and in the conditions described in this example.
- Curve C shown in FIG. 2 illustrates the variation in the content of the bath in grams of Ti (III) per liter of composition (ordinate axis) as a function of the time T expressed in minutes during which recycling is maintained (abscissa axis) in the conditions which have just been specified.
- test pieces are dried in an oven at 150 ° C. for 5 minutes, then the water-soluble paint of example 1 is applied to them by dipping while respecting the conditions described in this example.
- test pieces are then subjected to a 5% salt spray corrosion test at a temperature of 35 ° C. under the conditions specified in standard ASTM B 117. After 96 hours of exposure to said salt spray, the results obtained are examined in accordance with to ASTM D 1654-61. These results are shown in Table II below; they represent the averages of the results of the tests carried out on three sets of twenty-five test pieces.
- a zinc phosphate coating is obtained, the layer weight of which varies between 2 and 3 g / m 2 .
- the three sets of five test pieces are then treated respectively as the three sets of five test pieces of Example 1.
- Example 2 After drying and application of the water-soluble paint under the conditions of Example 1, the three series of test pieces are treated as described in standard ASTM B 117. After 384 hours of exposure to salt spray, the results are examined. obtained using ASTM 1654-61. These results are shown in Table III below; they represent the means of the results of three tests, that is to say tests carried out with three sets of three series of five test pieces.
- a zinc phosphate coating is obtained, the layer weight of which varies between 2 and 3 g / m 2 .
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Metallurgy (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Chemical Treatment Of Metals (AREA)
- Paints Or Removers (AREA)
Abstract
Description
L'invention a pour objet un procédé pour le traitement, plus précisément le « post-traitement » de surfaces métalliques phosphatées, notamment lorsque ces surfaces doivent être subséquemment revêtues d'une couche de peinture.The subject of the invention is a method for the treatment, more precisely the "post-treatment" of phosphated metal surfaces, in particular when these surfaces must be subsequently coated with a layer of paint.
La phosphatation, notamment la phosphatation au fer et au zinc, des surfaces métalliques en question, c'est-à-dire des surfaces de substrats à base de fer, d'acier, de zinc, de fer et d'acier galvanisés, d'aluminium et d'alliages des métaux qui précèdent, de cadmium et d'autres, a pour but de protéger ces surfaces contre la corrosion ; ces surfaces sont éventuellement recouvertes ensuite d'une couche de peinture qui peut être à base plus particulièrement de laques, vernis et émaux appliqués par exemple par immersion, électrophorèse, pistolage et autres.The phosphating, including iron and zinc phosphating, of the metal surfaces in question, i.e. surfaces of iron, steel, zinc, iron and galvanized steel substrates, d 'aluminum and alloys of the above metals, cadmium and others, aims to protect these surfaces against corrosion; these surfaces are then optionally covered with a layer of paint which may be based more particularly on lacquers, varnishes and enamels applied for example by immersion, electrophoresis, spraying and the like.
Il existe déjà des traitements de surfaces métalliques phosphatées, appelés couramment rinçages passivants ou rinçages de post-traitement.Treatments of phosphated metal surfaces already exist, commonly called passivating rinses or post-treatment rinses.
Ces traitements, qui ont pour but d'accroître encore l'efficacité de la protection contre la corrosion des surfaces métalliques préalablement phosphatées, mettent généralement en ceuvre des ions chrome trivalent et/ou hexavalent sous la forme de compositions ou solutions de chromatation à base de chromate appliquées en rinçage final ou passivant.These treatments, which have the aim of further increasing the effectiveness of the protection against corrosion of previously phosphated metal surfaces, generally employ trivalent and / or hexavalent chromium ions in the form of chromium-based compositions or solutions of chromation. chromate applied in final or passivating rinse.
Tout en donnant satisfaction du point de vue de l'amélioration de la protection contre la corrosion ainsi réalisée, ces traitements présentent néanmoins deux inconvénients majeurs résidant, dans l'ordre d'importance,
- - dans la haute toxicité - due aux ions chrome trivalent et hexavalent - des solutions de chromatation mises en oeuvre et des effluents subséquents dont le traitement visant à éliminer les ions gênants s'impose,
- - dans la forte coloration se traduisant par des taches jaunes visibles si la couche de peinture subséquemment appliquée est mince.
- - in the high toxicity - due to the trivalent and hexavalent chromium ions - chromating solutions used and subsequent effluents whose treatment aimed at removing the troublesome ions is necessary,
- - in the strong coloration resulting in visible yellow spots if the layer of paint subsequently applied is thin.
De nombreuses tentatives ont visé à remplacer le traitement de chromatage par des traitements à base de compositions exemptes de chrome.Many attempts have been made to replace the chromating treatment with treatments based on chromium-free compositions.
Il a ainsi été proposé d'appliquer aux surfaces préalablement phosphatées, notamment
- - des compositions renfermant des sels solubles de zirconium (voir FR-A- 2117256),
- - des compositions renfermant des sels fluorés de calcium, zinc, aluminium, de titane tétravalent, de zirconium, de nickel (voir FR-A- 2 232 615),
- - des compositions renfermant le titane tétravalent sous la forme de fluotitanate de potassium ou d'ammonium ou d'oxalate de potassium et de titanyle (voir FR-A- 2 339 683).
- - compositions containing soluble zirconium salts (see FR-A-2117256),
- - compositions containing fluorinated salts of calcium, zinc, aluminum, tetravalent titanium, zirconium, nickel (see FR-A- 2 232 615),
- - compositions containing tetravalent titanium in the form of potassium fluotitanate or ammonium or potassium oxalate and titanyl (see FR-A- 2 339 683).
Bien que ces traitements aient permis de supprimer les inconvénients dus à l'ion chrome et inhérents aux compositions qui en renferment, ils n'ont pas donné entièrement satisfaction en raison du fait que la protéction contre la corrosion qu'ils conféraient aux surfaces traitées, était très nettement inférieure à celle réalisée à l'aide des compositions de chromatage.Although these treatments have made it possible to eliminate the drawbacks due to the chromium ion and inherent in the compositions containing it, they have not been entirely satisfactory due to the fact that the protection against corrosion which they confer on the treated surfaces, was very much lower than that produced using the chromating compositions.
L'invention a donc pour but, surtout, de fournir un procédé pour le traitement des surfaces métalliques phosphatées à l'aide d'une composition qui, tout en conférant à ces surfaces une protection équivalente à celle réalisée par les solutions de chromatage de l'art antérieur, ne présente plus les inconvénients de celles-ci.The object of the invention is therefore, above all, to provide a process for the treatment of phosphated metal surfaces with the aid of a composition which, while giving these surfaces protection equivalent to that produced by the chromium plating solutions. 'prior art, no longer has the disadvantages of these.
Or, la Société demanderesse a eu le mérite de trouver que, de façon d'autant plus inattendue que les traitements de l'art antérieur mettant en oeuvre du titane tétravalent n'avaient pas été satisfaisants du point de vue de la protection conférée, le traitement à l'aide d'une composition à base d'un composé du titane trivalent et exempt de chrome conférait aux surfaces métalliques traitées une protection équivalente à celle réalisée avec les solutions de chromatage de l'art antérieur.However, the Applicant Company had the merit of finding that, all the more unexpectedly since the treatments of the prior art using tetravalent titanium had not been satisfactory from the point of view of the protection conferred, the treatment using a composition based on a trivalent titanium compound and free of chromium gave the treated metal surfaces protection equivalent to that achieved with the chromating solutions of the prior art.
Il s'ensuit que le procédé de traitement conforme à l'invention, dans lequel après phosphatation de surfaces métalliques et avant application éventuelle d'une couche de peinture, la surface métallique phosphatée est traitée par mise en contact de ladite surface avec une composition comprenant du titane, est caractérisé par le fait que la composition comprend du titane trivalent à une concentration de 0,01 à 2g/1 et présente un pH de 2 à 7, la température de la composition étant inférieure à 90 °C, de préférence comprise entre 18 et 60 °C.It follows that the treatment method according to the invention, in which after phosphating of metal surfaces and before possible application of a layer of paint, the phosphated metal surface is treated by bringing said surface into contact with a composition comprising titanium, is characterized in that the composition comprises trivalent titanium at a concentration of 0.01 to 2 g / 1 and has a pH of 2 to 7, the temperature of the composition being less than 90 ° C, preferably included between 18 and 60 ° C.
Plus particulièrement, la composition mise en ceuvre conformément au procédé selon l'invention renferme le titane trivalent à une concentration de 0,2 à 0,6 g/I.More particularly, the composition used in accordance with the method according to the invention contains trivalent titanium at a concentration of 0.2 to 0.6 g / I.
Plus particulièrement encore, la composition mise en oeuvre conformément au procédé selon l'invention est obtenue par dilution avec de l'eau à partir d'un concentré pouvant contenir, à titre indicatif, environ 10 à 50 g de titane trivalent par litre, ce concentré qui est maintenu de préférence à l'abri de l'oxygène de l'air jusqu'au moment de l'utilisation étant dilué à ce moment avec la quantité d'eau de préférence distillée ou déionisée, choisie pour aboutir à la concentration en titane trivalent qui correspond à celle de la composition mise en oeuvre.More particularly still, the composition used in accordance with the process according to the invention is obtained by dilution with water from a concentrate which may contain, by way of indication, approximately 10 to 50 g of trivalent titanium per liter, this concentrate which is preferably kept away from oxygen in the air until the time of use, being diluted at that time with the quantity of water, preferably distilled or deionized, chosen to result in the concentration of trivalent titanium which corresponds to that of the composition used.
La stabilité relativement faible, surtout en solution diluée et au contact de l'oxygène de l'air des composés renfermant du titane trivalent, qui s'oxyde rapidement en titane tétravalent, fait que la composition mise en oeuvre dans le procédé conforme à l'invention sera préparée en général au moment de son utilisation et régénérée si nécessaire en cours d'opération par réduction du titane tétravalent formé en titane trivalent.The relatively low stability, especially in dilute solution and in contact with the oxygen of the air of the compounds containing trivalent titanium, which rapidly oxidizes to tetravalent titanium, means that the composition used in the process in accordance with invention will generally be prepared at the time of use and regenerated if necessary during operation by reduction of tetravalent titanium formed of trivalent titanium.
Suivant un aspect particulier, le procédé conforme à l'invention est donc caractérisé par le fait que le titane trivalent devant être comporté par la composition mise en oeuvre est préparé in situ et avant l'application de la composition aux surfaces métalliques phosphatées, par mise en contact du titane tétravalent avec un moyen de réduction, la composition étant ensuite, au cours du procédé de traitement des surfaces phosphatées, régénérée en. titane trivalent par mise en contact notamment d'une fraction dérivée de la composition avec le susdit moyen de réduction de façon telle que la concentration de la composition en composé de titane trivalent soit maintenue à la proportion notamment de 0,2 à 0,6 g de titane trivalent par litre, susmentionnée.According to a particular aspect, the process according to the invention is therefore characterized by the fact that the trivalent titanium to be comprised by the composition used is prepared in situ and before the application of the composition to the phosphated metal surfaces, by setting in contact with tetravalent titanium with a reduction means, the composition then being, during the process of treatment of phosphate surfaces, regenerated into. trivalent titanium by bringing into contact in particular a fraction derived from the composition with the abovementioned reduction means in such a way that the concentration of the composition in trivalent titanium compound is maintained in the proportion in particular from 0.2 to 0.6 g of trivalent titanium per liter, mentioned above.
Suivant un autre aspect, le procédé conforme à l'invention est caractérisé par le fait que la composition mise en oeuvre est préparée à partir d'un concentré et que l'on maintient la concentration en titane trivalent de la composition ainsi obtenue à la valeur efficace par régénération en cours d'opération au contact d'un moyen de réduction du titane tétravalent en titane trivalent.According to another aspect, the process according to the invention is characterized in that the composition used is prepared from a concentrate and that the concentration of trivalent titanium of the composition thus obtained is maintained at the value effective by regeneration during operation in contact with a means of reducing tetravalent titanium to trivalent titanium.
La susdite régénération peut avoir lieu en continu.The above regeneration can take place continuously.
L'invention pourra encore être mieux comprise à l'aide du complément de description et des exemples ci-après, lesquels complément de description et exemples étant donnés en rapport avec des modes de réalisation avantageux.The invention will be able to be understood more clearly with the aid of the additional description and of the examples below, which further description and examples being given in relation to advantageous embodiments.
Se proposant, par conséquent, de traiter, en vue d'améliorer sa résistance à la corrosion, une surface métallique phosphatée devant éventuellement recevoir ultérieurement une ou plusieurs couches de peinture, on s'y prend comme suit ou de façon équivalente.Proposing, therefore, to treat, in order to improve its resistance to corrosion, a phosphated metal surface which may possibly receive one or more layers of paint subsequently, this is done as follows or in an equivalent manner.
On soumet tout d'abord et de façon en soi connue ladite surface métallique qui peut être celle d'un substrat métallique à base de fer, d'acier, de zinc, de fer ou d'acier galvanisés, d'aluminium, d'alliages de ces métaux, de cadmium et autres, à un traitement de phosphatation comportant après dégraissage à l'aide notamment de lessives alcalines, l'action d'une composition classique acide de phosphatation au fer ou au zinc mise en œuvre généralement à chaud et pendant plusieurs minutes par immersion ou par aspersion.First of all, and in a manner known per se, said metallic surface which may be that of a metallic substrate based on iron, steel, zinc, galvanized iron or steel, aluminum, alloys of these metals, of cadmium and others, to a phosphating treatment comprising, after degreasing with the aid in particular of alkaline detergents, the action of a conventional acid phosphating composition with iron or zinc generally implemented hot and for several minutes by immersion or by sprinkling.
Après rinçage, notamment à l'eau du robinet puis à l'eau déionisée, on traite la surface métallique conformément au procédé selon l'invention à l'aide d'une composition qui renferme un composé du titane trivalent à une concentration de 0,01 à 2 g, de préférence de 0,2 à 0,6 g de titane trivalent par litre et présente un pH acide de 2 à 7, de préférence de 2 à 5. After rinsing, in particular with tap water and then with deionized water, the metal surface is treated in accordance with the method according to the invention using a composition which contains a trivalent titanium compound at a concentration of 0, 01 to 2 g, preferably 0.2 to 0.6 g of trivalent titanium per liter and has an acid pH of 2 to 7, preferably 2 to 5.
Les proportions de 0,2 à 0,6 g de titane trivalent par litre correspondent à une valeur de 4,17 10-3 à 1,25 - 10-2 atomes-gramme de titane trivalent par litre.The proportions of 0.2 to 0.6 g of trivalent titanium per liter correspond to a value of 4.17 10-3 to 1.25 - 10-2 gram atoms of trivalent titanium per liter.
Le pH peut être ajusté à l'aide de soude, d'ammoniaque, d'acide fluorhydrique, d'acide nitrique et d'autres acides ou bases.The pH can be adjusted using soda, ammonia, hydrofluoric acid, nitric acid and other acids or bases.
La composition est mise en oeuvre à une température inférieure à 90 °C et notamment choisie dans la gamme de 18 à 60 °C.The composition is used at a temperature below 90 ° C. and in particular chosen from the range from 18 to 60 ° C.
Le traitement a lieu, de préférence, par immersion de la surface métallique dans la composition pendant une durée généralement comprise entre 10 et 60 secondes.The treatment preferably takes place by immersing the metal surface in the composition for a period generally between 10 and 60 seconds.
La composition peut également être appliquée par pulvérisation ; cette technique est moins avantageuse en raison de la sensibilité du titane trivalent à l'égard de l'oxydation.The composition can also be applied by spraying; this technique is less advantageous because of the sensitivity of trivalent titanium with respect to oxidation.
Le traitement est suivi d'un rinçage à l'eau et d'un séchage, notamment à chaud, de la surface métallique avant application éventuelle d'une peinture pouvant être choisie parmi les laques, vernis, émaux et autres, appliqués par tout procédé convenable.The treatment is followed by rinsing with water and drying, in particular hot, of the metal surface before possible application of a paint which can be chosen from lacquers, varnishes, enamels and the like, applied by any process. suitable.
Le rinçage avant application des peintures permet de diminuer le risque de cloquage de ces dernières.Rinsing before application of the paints reduces the risk of blistering of the latter.
La qualité de la protection anti-corrosion conférée peut être testée par l'essai au brouillard salin dont il sera plus particulièrement question en rapport avec les exemples. Ce test est décrit dans les normes américaines ASTM B 117 et ASTM D 1654-61. L'appréciation de la résistance à la corrosion conférée se fait à l'aide d'une échelle allant de 0 (résistance nulle) à 10 (très bonne résistance à la corrosion).The quality of the anti-corrosion protection conferred can be tested by the salt spray test which will be more particularly discussed in relation to the examples. This test is described in the American standards ASTM B 117 and ASTM D 1654-61. The assessment of the corrosion resistance conferred is made using a scale ranging from 0 (zero resistance) to 10 (very good corrosion resistance).
Le composé de titane trivalent peut être choisi dans le groupe comprenant le chlorure, le bromure, le fluorure, l'oxalate et le sulfate de titane trivalent qui se sont révélés particulièrement actifs.The trivalent titanium compound can be chosen from the group comprising chloride, bromide, fluoride, oxalate and trivalent titanium sulfate which have been found to be particularly active.
Avantageusement la composition mise en oeuvre conformément au procédé selon l'invention est préparée au départ à partir d'un concentré qui peut contenir environ 10 à 50 g de titane trivalent par litre et qui conduit à ladite composition par dilution avec la quantité convenable d'eau, de préférence déionisée pour éviter l'introduction d'agents polluants tels que le magnésium et le calcium ; ce concentré contient également les autres constituants éventuels de la composition mise en oeuvre conformément au procédé selon l'invention, à savoir notamment :
- - une faible quantité, notamment de l'ordre de 0,001 à 0,02 g/l d'agents tensio-actifs, en particulier du type organique tels que les alcoylsulfonates de sodium ou les hydrocarbures éthoxylés,
- - une faible proportion, notamment de 1 mg/I à 500 mg/I d'agents stabilisants, en particulier tels que le pyrogallol ou l'hydroquinone.
- a small amount, in particular of the order of 0.001 to 0.02 g / l of surface-active agents, in particular of the organic type such as sodium alkyl sulfonates or ethoxylated hydrocarbons,
- - A small proportion, in particular from 1 mg / I to 500 mg / I of stabilizing agents, in particular such as pyrogallol or hydroquinone.
En raison de la sensibilité du titane trivalent à l'égard de l'oxygène de l'air, le susdit concentré est maintenu à l'abri de l'air jusqu'au moment de son utilisation.Due to the sensitivity of trivalent titanium to oxygen in the air, the above-mentioned concentrate is kept protected from air until it is used.
Cette même sensibilité du titane trivalent fait que la composition mise en oeuvre conformément à l'invention doit être régénérée pour maintenir à une valeur efficace sa concentration en titane trivalent, ce qui peut être réalisé par mise en contact avec un moyen de réduction, notamment un agent réducteur.This same sensitivity of trivalent titanium means that the composition used in accordance with the invention must be regenerated to maintain its concentration of trivalent titanium at an effective value, this which can be achieved by contacting a reduction means, in particular a reducing agent.
Du point de vue pratique, on peut faire comporter à l'enceinte de traitement contenant la composition une conduite de dérivation dans laquelle on dispose l'agent réducteur.From the practical point of view, the treatment enclosure containing the composition can be made to include a bypass pipe in which the reducing agent is placed.
Si le traitement par immersion est du type statique, on peut prélever la composition au fond de l'enceinte, la faire passer par la conduite de dérivation contenant l'agent de réduction et la réintroduire à la surface du bain constituant la composition.If the immersion treatment is of the static type, the composition can be taken from the bottom of the enclosure, passed through the bypass pipe containing the reducing agent and reintroduced onto the surface of the bath constituting the composition.
Si le traitement d'immersion est du type dynamique avec translation des pièces comportant les surfaces phosphatées à traiter, on s'arrangera avantageusement pour que le sens du courant créé au sein de la composition, par suite du prélèvement dans la conduite de dérivation, soit contraire au mouvement de translation des pièces.If the immersion treatment is of the dynamic type with translation of the parts comprising the phosphated surfaces to be treated, it will be advantageously arranged so that the direction of the current created within the composition, as a result of the sampling in the bypass line, is contrary to the translational movement of the parts.
Le moyen de réduction peut être soit un agent réducteur métallique ou chimique disposé dans une colonne, soit une cellule d'électrolyse, la colonne ou la cellule étant traversée par la composition à régénérer en continu ou en discontinu de façon telle que la concentration en titane trivalent soit maintenue à la valeur efficace ; on suit les effets de l'oxydation du bain et/ou de la régénération par simple dosage volumétrique oxydo-réducteur et on met en route ou on stoppe la régénération lorsque la proportion de la composition en titane trivalent sort des limites indiquées plus haut.The reduction means can be either a metallic or chemical reducing agent placed in a column, or an electrolysis cell, the column or cell being traversed by the composition to be regenerated continuously or discontinuously so that the titanium concentration trivalent is maintained at the effective value; the effects of the oxidation of the bath and / or of the regeneration are followed by simple volumetric redox dosing and the regeneration is started or stopped when the proportion of the composition in trivalent titanium goes beyond the limits indicated above.
Les agents réducteurs utilisés peuvent être constitués :
- - lorsqu'il s'agit de réducteurs métalliques, par de l'amalgame solide de zinc, par des grains de cadmium, par des métaux de Raney, la réduction s'effectuant bien en milieu acide chlorhydrique ou sulfurique (0,5 à 2 N),
- - lorsqu'il s'agit de réducteurs chimiques, par des borohydrures ou hypophosphites de métaux alcalins du groupe comprenant NaBH4, KBH4, NaH2P02, H,0 ; l'emploi de ces agents se fait à chaud et nécessite la présence d'un catalyseur ; il permet notamment d'amener le fluotitanate de potassium (K2TiFe) en TiF3.
- - in the case of metallic reducing agents, with solid zinc amalgam, with cadmium grains, with Raney metals, the reduction taking place well in hydrochloric or sulfuric acid medium (0.5 to 2 NOT),
- - in the case of chemical reducers, with borohydrides or hypophosphites of alkali metals from the group comprising NaBH 4 , KBH 4 , NaH 2 P0 2 , H, 0; the use of these agents is done hot and requires the presence of a catalyst; it makes it possible in particular to bring potassium fluotitanate (K 2 TiF e ) to TiF 3 .
Quand la réduction est réalisée au moyen d'une électrolyse, on utilise une électrode inerte, le procédé étant celui utilisé dans les batteries redox.When the reduction is carried out by means of electrolysis, an inert electrode is used, the method being that used in redox batteries.
Compte tenu de l'exposé qui précède, il sera avantageux pour l'utilisateur de disposer simultanément de la composition de traitement mise en oeuvre dans le procédé selon l'invention et des moyens de réduction permettant de régénérer et évehtuellement de préparer ladite composition.In view of the foregoing description, it will be advantageous for the user to have simultaneously the treatment composition used in the process according to the invention and reduction means making it possible to regenerate and optionally to prepare said composition.
Les exemples qui suivent sont relatifs à des modes de réalisation préférés de l'invention et montrent, de par les résultats réunis, les avantages de cellemci.The examples which follow relate to preferred embodiments of the invention and show, by the results gathered, the advantages of cellemci.
Quinze éprouvettes constituées par des panneaux en « acier laminé à froid de qualité courante d'épaisseur 8/10 mm et-mesurant 150 mm x 70 mm, sont soigneusement dégraissées à l'aide de trichloréthylène puis d'acétone ; elles sont ensuite soumises à un traitement de phosphatation au trempé.Fifteen test pieces made up of panels of "cold-rolled steel of current quality, thickness 8/10 mm and -measuring 150 mm x 70 mm, are carefully degreased using trichlorethylene then acetone; they are then subjected to a dip phosphating treatment.
Pour ce traitement, on utilise une composition de phosphatation du commerce, notamment celle connue sous la marque « Duridine 49 » ® et dont la concentration est de 3 % en poids.For this treatment, a commercial phosphating composition is used, in particular that known under the brand "Duridine 49" ® and the concentration of which is 3% by weight.
Cette composition contient des agents phosphatants et des tensio-actifs.This composition contains phosphating agents and surfactants.
Son pH est de 4,8 à 4,9.Its pH is 4.8 to 4.9.
Elle est mise en oeuvre à 60 °C.It is implemented at 60 ° C.
La durée de la trempe des éprouvettes dans la composition de phosphatation est de 10 minutes.The duration of the quenching of the test pieces in the phosphating composition is 10 minutes.
Le revêtement obtenu est un revêtement de phosphate de fer dont le poids de couche varie entre 0,2 et 0,3 g/m2.The coating obtained is an iron phosphate coating whose layer weight varies between 0.2 and 0.3 g / m2 .
On divise les quinze éprouvettes dont la surface est ainsi phosphatée en trois séries de cinq.The fifteen test pieces, the surface of which is thus phosphated, are divided into three sets of five.
La première série ou Série (1) n'est soumise à aucun traitement destiné à accroître la protection contre la corrosion ; elle est simplement soumise à deux rinçages successifs, à savoir :
- - un rinçage à l'eau du robinet :
- - temps : 10 secondes au trempé
- - température : ambiante,
- - un rinçage à l'eau déionisée :
- - temps : 30 secondes au trempé
- - température : ambiante.
- - rinsing with tap water:
- - time: 10 seconds by soaking
- - ambient temperature,
- - rinsing with deionized water:
- - time: 30 seconds by soaking
- - ambient temperature.
La deuxième série ou Série (2) est soumise à un traitement de chromatage. On procède successivement à :
- - un rinçage à l'eau du robinet :
- - temps : 10 secondes au trempé
- - température : ambiante,
- - un rinçage final dans une solution chromique de pH égal à 3,4, qui est préparée avec de l'eau déionisée et qui contient 0,25 g/l de chrome hexavalent ainsi que 0,06 g/l de chrome trivalent :
- - temps : 30 secondes au trempé
- - température : ambiante,
- - un rinçage à l'eau déionisée :
- - temps : 5 secondes au trempé
- - température : ambiante.
- - rinsing with tap water:
- - time: 10 seconds by soaking
- - ambient temperature,
- - a final rinse in a chromic solution with a pH equal to 3.4, which is prepared with deionized water and which contains 0.25 g / l of hexavalent chromium as well as 0.06 g / l of trivalent chromium:
- - time: 30 seconds by soaking
- - ambient temperature,
- - rinsing with deionized water:
- - time: 5 seconds by soaking
- - ambient temperature.
La troisième série ou Série (3) est soumise au traitement conforme à l'invention. On procède successivement à :
- - un rinçage à l'eau du robinet :
- - temps : 10 secondes au trempé
- - température : ambiante,
- - un rinçage final dans une solution de chlorure de titane trivalent préparée à l'aide d'eau déionisée contenant 0,33 g/l de titane trivalent et dont le pH est ajusté avec de la soude à 3,4 :
- - temps : 30 secondes au trempé
- - température : ambiante,
- - un rinçage à l'eau déionisée :
- - temps : 5 secondes au trempé
- - température : ambiante.
- - rinsing with tap water:
- - time: 10 seconds by soaking
- - ambient temperature,
- - a final rinse in a solution of trivalent titanium chloride prepared using deionized water containing 0.33 g / l of trivalent titanium and whose pH is adjusted with sodium hydroxide to 3.4:
- - time: 30 seconds by soaking
- - ambient temperature,
- - rinsing with deionized water:
- - time: 5 seconds by soaking
- - ambient temperature.
Les quinze éprouvettes ainsi traitées sont séchées dans une étuve à 150 °C pendant 5 minutes, puis on leur applique au trempé une peinture hydrosoluble (notamment celle de marque BOUVET, référence : Primaire A6 noir satiné n° 63 04 44) en respectant les conditions stipulées par le fournisseur, à savoir :
- - viscosité : 25 à 30 secondes, mesurée à la coupe Ford n° 4,
- - pH : 8,8 à 9,2
- - temps d'égouttage : 10 minutes
- - temps et température de cuisson : 15 minutes à 160 °C.
- - viscosity: 25 to 30 seconds, measured with the Ford n ° 4 cut,
- - pH: 8.8 to 9.2
- - draining time: 10 minutes
- - cooking time and temperature: 15 minutes at 160 ° C.
On traite trois autres jeux de quinze éprouvettes dans les mêmes conditions.Three other sets of fifteen test pieces are treated under the same conditions.
Les éprouvettes sont ensuite soumises à un essai de corrosion au brouillard salin à 5% à une température de 35 °C dans les conditions spécifiées dans la norme ASTM B 117. Après 96 heures d'exposition à ce brouillard satin, on examine les résultats obtenus en utilisant la norme ASTM D 1654-61. Ces résultats sont indiqués dans le tableau I ci-dessous ; ils représentent les moyennes des résultats des trois séries d'essais effectués avec les trois jeux de quinze éprouvettes.
Ces résultats montrent que les éprouvettes traitées avec une composition à base de titane trivalent manifestent une résistance à la corrosion équivalente à un traitement de chromatage classique. Cette performance est d'autant plus remarquable que la présence d'ion chlorure apporté par le chlorure de titane (III) est bien connue pour son effet néfaste dans ce type de bain sur la tenue à la corrosion.These results show that the specimens treated with a composition based on trivalent titanium exhibit a corrosion resistance equivalent to a conventional chromating treatment. This performance is all the more remarkable since the presence of chloride ion provided by titanium chloride (III) is well known for its harmful effect in this type of bath on the resistance to corrosion.
On utilise vingt-cinq éprouvettes constituées par des panneaux en « acier laminé à froid de qualité courante d'épaisseur 8/10 mm et mesurant 150 mm x 70 mm. Ces éprouvettes sont soigneusement dégraissées à l'aide de trichloréthylène puis d'acétone avant de subir un traitement de conversion phosphatante au trempé.Twenty-five test specimens are used, consisting of panels of "cold-rolled steel of standard quality, 8/10 mm thick, measuring 150 mm x 70 mm. These test pieces are carefully degreased using trichlorethylene and then acetone before undergoing a phosphating conversion treatment by soaking.
Ce traitement est réalisé avec la même composition de phosphatation qu'à l'exemple 1 et dans les conditions décrites à cet exemple.This treatment is carried out with the same phosphating composition as in Example 1 and in the conditions described in this example.
Le revêtement obtenu est un revêtement de phosphate de fer dont le poids de couche varie entre 0,2 et 0,3 g/m2. On forme cinq séries de cinq éprouvettes qui sont traitées comme suit.
- Série (1) :
- - rinçage à l'eau du robinet :
- - temps : 10 secondes au trempé
- - température : ambiante,
-
- - rinçage à l'eau déionisée :
- - temps : 30 secondes au trempé
- - température : 60 °C.
- - rinçage à l'eau du robinet :
- Série (2) :
- - rinçage à l'eau du robinet :
- - temps : 10 secondes au trempé
- - température : ambiante,
- - chromatage dans une solution chromique préparée à partir d'eau déionisée qui contient 0,25 g/I de chrome hexavalent et 0,06 g/l de chrome trivalent et dont
le pH est 3,4 :- - temps : 30 secondes au trempé
- ― température : 60 °C,
- - rinçage à l'eau déionisée :
- - temps : 5 secondes au trempé
- - température : ambiante.
- - rinçage à l'eau du robinet :
- Série (3) :
- - rinçage à l'eau du robinet :
- - temps : 10 secondes au trempé
- - température: ambiante,
- - traitement par rinçage final dans une solution de fluotitanate de potassium préparée à partir d'eau déionisée qui contient 5 g/I de fluotitanate de potassium (soit environ 1 g/l de titane tétravalent) et dont le pH est ajusté à 4,5 avec de la soude :
- - temps : 30 secondes au trempé
- - température : 60 °C,
- - rinçage à l'eau déionisée :
- ― temps : 5 secondes au trempé
- - température : ambiante.
- - rinçage à l'eau du robinet :
- Série (4) :
- - rinçage à l'eau du robinet :
- - temps : 10 secondes au trempé
- - température : ambiante,
- - traitement par rinçage final dans une solution de fluotitanate de potassium et d'hypophosphite de sodium préparée à partir d'eau déionisée contenant 5 g/l de titane tétravalent et 10 g/I d'hypophosphite de sodium avec un pH ajusté à 4,5 avec de la soude :
- - temps : 30 secondes au trempé
- - température : 60 °C,
- - rinçage à l'eau déionisée :
- - temps : 5 secondes au trempé
- - température : ambiante.
- - rinçage à l'eau du robinet :
- Série (5) :
- - rinçage à l'eau du robinet :
- - temps : 10 secondes au trempé
- - température : ambiante,
- - traitement selon l'invention par rinçage final dans une solution de fluorure de titane trivalent contenant 0,3 g/I de titane trivalent. Cette solution est préparée par dissolution de 5 g de fluotitanate de potassium et 10 g d'hypophosphite de sodium (NaH2PO2, H20) dans un litre d'eau déionisée, chauffage de ce mélange à 60 °C et circulation en circuit fermé à l'aide d'une pompe péristaltique sur une colonne contenant 30 g de poudre de zinc.
- - rinçage à l'eau du robinet :
- Series (1):
- - rinsing with tap water:
- - time: 10 seconds by soaking
- - ambient temperature,
-
- - rinsing with deionized water:
- - time: 30 seconds by soaking
- - temperature: 60 ° C.
- - rinsing with tap water:
- Series (2):
- - rinsing with tap water:
- - time: 10 seconds by soaking
- - ambient temperature,
- - chromating in a chromic solution prepared from deionized water which contains 0.25 g / I of hexavalent chromium and 0.06 g / l of trivalent chromium and whose pH is 3.4:
- - time: 30 seconds by soaking
- - temperature: 60 ° C,
- - rinsing with deionized water:
- - time: 5 seconds by soaking
- - ambient temperature.
- - rinsing with tap water:
- Series (3):
- - rinsing with tap water:
- - time: 10 seconds by soaking
- - ambient temperature,
- - treatment by final rinsing in a potassium fluotitanate solution prepared from deionized water which contains 5 g / l of potassium fluotitanate (i.e. approximately 1 g / l of tetravalent titanium) and whose pH is adjusted to 4.5 with soda:
- - time: 30 seconds by soaking
- - temperature: 60 ° C,
- - rinsing with deionized water:
- - time: 5 seconds by soaking
- - ambient temperature.
- - rinsing with tap water:
- Series (4):
- - rinsing with tap water:
- - time: 10 seconds by soaking
- - ambient temperature,
- - treatment by final rinsing in a solution of potassium fluotitanate and sodium hypophosphite prepared from deionized water containing 5 g / l of tetravalent titanium and 10 g / I of sodium hypophosphite with a pH adjusted to 4, 5 with soda:
- - time: 30 seconds by soaking
- - temperature: 60 ° C,
- - rinsing with deionized water:
- - time: 5 seconds by soaking
- - ambient temperature.
- - rinsing with tap water:
- Series (5):
- - rinsing with tap water:
- - time: 10 seconds by soaking
- - ambient temperature,
- treatment according to the invention by final rinsing in a solution of trivalent titanium fluoride containing 0.3 g / l of trivalent titanium. This solution is prepared by dissolving 5 g of potassium fluotitanate and 10 g of sodium hypophosphite (NaH 2 PO 2 , H 2 0) in one liter of deionized water, heating this mixture to 60 ° C and circulating in closed circuit using a peristaltic pump on a column containing 30 g of zinc powder.
- - rinsing with tap water:
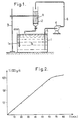
En respectant un débit de circulation de 0,7 I/heure, on obtient au bout d'une heure une solution de pH = 4,5 contenant 0,3 g/l de titane trivalent que l'on peut utiliser tel que (le schéma du montage utilisé est montré en figure 1 et la courbe d'obtention du titane trivalent en figure 2).By respecting a circulation rate of 0.7 I / hour, a solution of pH = 4.5 containing 0.3 g / l of trivalent titanium which can be used such as ( Diagram of the assembly used is shown in FIG. 1 and the curve for obtaining trivalent titanium in FIG. 2).
Le montage montré figure 1 comporte :
- - une enceinte 1 contenant des moyens de chauffage, par exemple une résistance chauffante 1a, ainsi que la
composition 1b dans laquelle est effectué le traitement, - - des moyens de réduction du titane tétravalent en titane trivalent comprenant un réducteur métallique R disposé à l'intérieur d'une colonne 2 fixée sur
un support 3 de façon à déboucher au-dessus de lacomposition 1b, - -
une pompe 4 reliée par unecanalisation 5 au fond de l'enceinte 1 et par unecanalisation 6 au sommet de la colonne 2 et propre à prélever dans l'enceinte 1 une fraction de lacomposition 1 b et de la faire passer parla colonne 2.
- an enclosure 1 containing heating means, for example a
heating resistance 1a, as well ascomposition 1b in which the treatment is carried out, - means for reducing tetravalent titanium to trivalent titanium comprising a metallic reducing agent R placed inside a
column 2 fixed on asupport 3 so as to open out abovecomposition 1b, - a
pump 4 connected by apipe 5 to the bottom of the enclosure 1 and by apipe 6 at the top of thecolumn 2 and suitable for taking from theenclosure 1 a fraction of thecomposition 1b and of the pass throughcolumn 2.
La courbe C montrée figure 2 illustre la variation de la teneur du bain en grammes de Ti(III) par litre de composition (axe des ordonnées) en fonction du temps T exprimé en minutes pendant lequel est maintenu le recyclage (axe des abscisses) dans les conditions qui viennent d'être précisées.Curve C shown in FIG. 2 illustrates the variation in the content of the bath in grams of Ti (III) per liter of composition (ordinate axis) as a function of the time T expressed in minutes during which recycling is maintained (abscissa axis) in the conditions which have just been specified.
Le traitement dans cette solution est comme suit :
- - temps : 30 secondes au trempé
- - température : 60 °C,
- - rinçage à l'eau déionisée :
- - temps : 5 secondes au trempé
- - température : ambiante.
- - time: 30 seconds by soaking
- - temperature: 60 ° C,
- - rinsing with deionized water:
- - time: 5 seconds by soaking
- - ambient temperature.
Les éprouvettes ainsi préparées sont séchées dans une étuve à 150°C pendant 5 minutes, puis on leur applique au trempé la peinture hydrosoluble de l'exemple 1 en respectant les conditions décrites à cet exemple.The thus prepared test pieces are dried in an oven at 150 ° C. for 5 minutes, then the water-soluble paint of example 1 is applied to them by dipping while respecting the conditions described in this example.
Les éprouvettes sont ensuite soumises à un essai de corrosion au brouillard salin à 5 % à une température de 35 °C dans les conditions spécifiées dans la norme ASTM B 117. Après 96 heures d'exposition audit brouillard salin, on examine les résultats obtenus conformément à la norme ASTM D 1654-61. Ces résultats sont indiqués dans le tableau Il ci-dessous ; ils représentent les moyennes des résultats des essais réalisés sur trois jeux de vingt-cinq éprouvettes.
Ces résultats montrent que, dès que la composition contient une quantité suffisante de titane trivalent, les performances anticorrosion deviennent équivalentes à celles d'un rinçage chromique classique.These results show that, as soon as the composition contains a sufficient amount of trivalent titanium, the anticorrosion performance becomes equivalent to that of a conventional chromic rinse.
Trois séries de cinq éprouvettes constituées par des panneaux en « acier laminé à froid de qualité courante d'épaisseur 8/10 mm et mesurant 150 x 70 mm, sont soigneusement dégraissées au trichloréthylène puis à l'acétone avant d'être soumises aux traitements suivants :
- - dégraissage au jet à l'aide d'une composition de dégraissage alcalin, notamment celle qui est commercialisée sous la marque « Ridoline 910 et dont
- - la concentration d'utilisation est de 1 % en poids,
- - la température d'application 60 °C et
- - la durée du traitement de 90 secondes,
- - la pression d'application étant de 1,5 bar,
- - rinçage à l'eau du robinet :
- - temps : 10 secondes au trempé
- - température : ambiante,
- - conversion phosphatante au jet à l'aide d'une solution de phosphatation, notamment celle commercialisée sous la marque « Granodine 16 dont
- - la concentration en agents phosphatants et tensio-actifs est de 1,6 % en volume,
- - la température d'application de 55 °C,
- - la durée d'application de 1 minute et
- - la pression de 0,8 bar.
- - jet degreasing using an alkaline degreasing composition, in particular that which is marketed under the brand "Ridoline 910 and of which
- - the use concentration is 1% by weight,
- - the
application temperature 60 ° C and - - the duration of the treatment of 90 seconds,
- - the application pressure being 1.5 bar,
- - rinsing with tap water:
- - time: 10 seconds by soaking
- - ambient temperature,
- - phosphating jet conversion using a phosphating solution, in particular that sold under the brand name “Granodine 16 including
- - the concentration of phosphating agents and surfactants is 1.6% by volume,
- - the application temperature of 55 ° C,
- - the duration of application of 1 minute and
- - the pressure of 0.8 bar.
On obtient un revêtement de phosphate de zinc dont le poids de couche varie entre 2 et 3 g/m2.A zinc phosphate coating is obtained, the layer weight of which varies between 2 and 3 g / m 2 .
Les trois séries de cinq éprouvettes sont alors traitées respectivement comme les trois séries de cinq éprouvettes de l'exemple 1.The three sets of five test pieces are then treated respectively as the three sets of five test pieces of Example 1.
Après séchage et application de la peinture hydrosoluble dans les conditions de l'exemple 1, les trois séries d'éprouvettes sont traitées de la façon décrite dans la norme ASTM B 117. Après 384 heures d'exposition au brouillard salin, on examine les résultats obtenus en utilisant la norme ASTM 1654-61. Ces résultats sont indiqués dans le tableau III ci-dessous ; ils représentent les moyennes des résultats de trois essais, c'est-à-dire des essais effectués avec trois jeux de trois séries de cinq éprouvettes.
Ces résultats confirment les conclusions formulées à l'exemple 1.These results confirm the conclusions made in Example 1.
On utilise toujours des éprouvettes constituées par des panneaux en « acier laminé à froid de qualité courante d'épaisseur 8/10 mm et mesurant 150 x 70 mm. Ces éprouvettes sont soigneusement dégraissées au trichloréthylène puis à l'acétone avant d'être traitées comme suit :
- - dégraissage au jet au moyen d'une composition de dégraissage alcalin dans les conditions de l'exemple 3,
- - rinçage à l'eau du robinet :
- - temps : 10 secondes au trempé
- - température : ambiante,
- - conversion phosphatante au jet dans les conditions de l'exemple 3.
- - degreasing with a jet using an alkaline degreasing composition under the conditions of Example 3,
- - rinsing with tap water:
- - time: 10 seconds by soaking
- - ambient temperature,
- - phosphating jet conversion under the conditions of Example 3.
On obtient un revêtement de phosphate de zinc dont le poids de couche varie entre 2 et 3 g/m2.A zinc phosphate coating is obtained, the layer weight of which varies between 2 and 3 g / m 2 .
On traite trois jeux de cinq séries de cinq éprouvettes dans les conditions de l'exemple 2.Three sets of five sets of five test pieces are treated under the conditions of Example 2.
On soumet toutes les éprouvettes au test du brouillard salin (norme ASTM B 117). Après 384 heures de brouillard salin, on examine les résultats obtenus, en utilisant les données de la norme ASTM D 1654-61. Ces résultats sont indiqués dans le tableau IV ci-dessous ; ils représentent les moyennes des résultats obtenus avec les trois jeux.
(Voir tableau IV page 9)All the test pieces are subjected to the salt spray test (standard ASTM B 117). After 384 hours of salt spray, the results obtained are examined, using data from standard ASTM D 1654-61. These results are shown in Table IV below; they represent the averages of the results obtained with the three games.
(See table IV page 9)
On dispose ainsi, et ce quel que soit le mode de réalisation adopté, d'une composition et d'un procédé de traitement des surfaces métalliques phosphatées dont les caractéristiques et les avantages résultent clairement de ce qui précède.Whatever the embodiment adopted, there is thus a composition and a method for treating phosphated metal surfaces, the characteristics and advantages of which are clearly apparent from the above.
Claims (9)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT83400204T ATE23574T1 (en) | 1982-01-29 | 1983-01-28 | COMPOSITION AND METHOD OF TREATMENT OF PHOSPHATEATED METAL SURFACES. |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR8201476A FR2520758A1 (en) | 1982-01-29 | 1982-01-29 | COMPOSITION AND METHOD FOR THE TREATMENT OF PHOSPHATE METAL SURFACES |
| FR8201476 | 1982-01-29 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0085626A1 EP0085626A1 (en) | 1983-08-10 |
| EP0085626B1 true EP0085626B1 (en) | 1986-11-12 |
Family
ID=9270495
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP83400204A Expired EP0085626B1 (en) | 1982-01-29 | 1983-01-28 | Composition and process for treating phosphated metallic surfaces |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US4497666A (en) |
| EP (1) | EP0085626B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JPS58136781A (en) |
| AT (1) | ATE23574T1 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA1197674A (en) |
| DE (1) | DE3367630D1 (en) |
| FR (1) | FR2520758A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AU2448684A (en) * | 1983-03-02 | 1984-09-06 | Parker Chemical Company | Metal treatment before phosphate coating |
| DE3400339A1 (en) * | 1984-01-07 | 1985-08-29 | Gerhard Collardin GmbH, 5000 Köln | METHOD FOR REPASSIVATING PHOSPHATED METAL SURFACES USING SOLUTIONS CONTAINING NICKEL AND / OR COPPER CATIONS |
| US5073196A (en) * | 1989-05-18 | 1991-12-17 | Henkel Corporation | Non-accelerated iron phosphating |
| DE4031817A1 (en) * | 1990-10-08 | 1992-04-09 | Henkel Kgaa | METHOD FOR PASSIVATING POST-TREATMENT OF PHOSPHATED METAL SURFACES |
| US5128211A (en) * | 1991-02-28 | 1992-07-07 | Diversey Corporation | Aluminum based phosphate final rinse |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE154542C (en) * | ||||
| US2970935A (en) * | 1959-03-02 | 1961-02-07 | Parker Rust Proof Co | Method of rinsing metallic surfaces with solutions containing hexavalent chromium |
| FR1388662A (en) * | 1962-10-15 | 1965-02-12 | Parker Ste Continentale | Method and solution for the treatment of metal surfaces provided with a chemical coating |
| DE1521879B2 (en) * | 1966-07-12 | 1975-08-28 | Metallgesellschaft Ag, 6000 Frankfurt | Process for applying phosphate coatings to iron and steel |
| US3695942A (en) * | 1970-12-02 | 1972-10-03 | Amchem Prod | Zirconium rinse for phosphate coated metal surfaces |
| US3895970A (en) * | 1973-06-11 | 1975-07-22 | Pennwalt Corp | Sealing rinse for phosphate coatings of metal |
| GB1461244A (en) * | 1974-06-17 | 1977-01-13 | Lubrizol Corp | Treatment of metal surfaces with trivalent chromium solutions |
| JPS5292836A (en) * | 1976-01-30 | 1977-08-04 | Nippon Packaging Kk | Zinc or its alloys subjected to chemical conversion |
| GB1586975A (en) * | 1976-07-05 | 1981-03-25 | Kansai Paint Co Ltd | Surface treatment of metals |
| US4165242A (en) * | 1977-11-21 | 1979-08-21 | R. O. Hull & Company, Inc. | Treatment of metal parts to provide rust-inhibiting coatings by phosphating and electrophoretically depositing a siccative organic coating |
| US4233088A (en) * | 1979-03-29 | 1980-11-11 | International Lead Zinc Research Organization, Inc. | Phosphatization of steel surfaces and metal-coated surfaces |
| US4281037A (en) * | 1980-08-08 | 1981-07-28 | Dap, Inc. | Cleaning and priming composition containing titanium acetylacetonate and method |
-
1982
- 1982-01-29 FR FR8201476A patent/FR2520758A1/en active Granted
-
1983
- 1983-01-28 EP EP83400204A patent/EP0085626B1/en not_active Expired
- 1983-01-28 US US06/462,088 patent/US4497666A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1983-01-28 DE DE8383400204T patent/DE3367630D1/en not_active Expired
- 1983-01-28 JP JP58012562A patent/JPS58136781A/en active Pending
- 1983-01-28 AT AT83400204T patent/ATE23574T1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1983-01-28 CA CA000420493A patent/CA1197674A/en not_active Expired
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| Gmelins Handbuch der anorganischen Chemie, vol. 41 (1951), pages 373, 413 * |
| Römpps Chemie-Lexikon (1977), pages 3608, 3609, 3612 * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| FR2520758A1 (en) | 1983-08-05 |
| EP0085626A1 (en) | 1983-08-10 |
| DE3367630D1 (en) | 1987-01-02 |
| ATE23574T1 (en) | 1986-11-15 |
| CA1197674A (en) | 1985-12-10 |
| US4497666A (en) | 1985-02-05 |
| JPS58136781A (en) | 1983-08-13 |
| FR2520758B1 (en) | 1984-04-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101412872B1 (en) | Replenishing compositions and methods of replenishing pretreatment compositions | |
| JPH05195247A (en) | Method of not incorporating chromium to protect aluminum and composition therefor | |
| CA2864109A1 (en) | Method for the surface treatment of parts made of an aluminum or magnesium alloy | |
| JP3875197B2 (en) | Method for applying a corrosion resistant coating | |
| JPS5811515B2 (en) | Composition for forming a zinc phosphate film on metal surfaces | |
| JPH0394074A (en) | Improved composition and method for imparting coating to metal surface | |
| EP3810833B1 (en) | Process for treating the surface of a part made of aluminium or aluminium alloy or of magnesium or magnesium alloy | |
| FR2512840A1 (en) | AQUEOUS ACID SOLUTIONS FOR ZINC PHOSPHATE COATINGS AND CONCENTRATES, METHODS OF COATING THEM USING THEM AND METAL ACTIVATION SOLUTIONS USED IN SUCH PROCESSES | |
| JPH02305972A (en) | Composition of phosphate treating liquid of metal and treatment thereof | |
| JPH11335865A (en) | Processing agent for forming protective coating film on metal and its formation | |
| EP0085626B1 (en) | Composition and process for treating phosphated metallic surfaces | |
| JP3372954B2 (en) | Method of phosphate treatment of steel strip or steel sheet with one side galvanized or zinc alloy-plated | |
| CA2442502C (en) | Method for treating metal surfaces by carboxylation | |
| JP5827792B2 (en) | Chemically treated iron-based materials | |
| US4812175A (en) | Passivation process and copmposition for zinc-aluminum alloys | |
| KR20140119762A (en) | Replenishing compositions and methods of replenishing pretreatment compositions | |
| EP0102284A1 (en) | Composition and process for the chemical conversion of metallic substrates | |
| JPH07173643A (en) | Method for phosphating metal surface and phosphating solution | |
| JPS6256579A (en) | Acidic aqueous solution and method for passivating surface of zinc or zinc/aluminum alloy | |
| US4316752A (en) | Oxalic acid treatment of carbon steel, galvanized steel and aluminum surfaces | |
| EP1252367B1 (en) | Method for oxalating the galvanized surface of sheet metal | |
| EP0826792A1 (en) | Bath and process for phosphating metal substrates, concentrates for preparing the bath and metal substrates treated according to the process | |
| FR2654440A1 (en) | PROCESS FOR THE CHEMICAL CONVERSION OF METAL SUBSTRATES, BATH USED IN THIS PROCESS AND CONCENTRATE FOR THE PREPARATION OF THE BATH. | |
| EP0298827A1 (en) | Mixed phosphatation solution and process | |
| BE561524A (en) | PROCESS FOR MANUFACTURING COATINGS FOR MAGNESIUM SURFACES |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE DE GB IT NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19840208 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE DE GB IT NL SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 23574 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19861115 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3367630 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19870102 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 19911219 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 19920121 Year of fee payment: 10 Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19920121 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19920128 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| ITTA | It: last paid annual fee | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19920131 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19920514 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Effective date: 19930128 Ref country code: AT Effective date: 19930128 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Effective date: 19930129 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Effective date: 19930131 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: CIE FRANCAISE DE PRODUITS INDUSTRIELS Effective date: 19930131 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Effective date: 19930801 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee | ||
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 19930128 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19931001 |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 83400204.0 Effective date: 19930810 |