WO2021241685A1 - 吸収性物品 - Google Patents
吸収性物品 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2021241685A1 WO2021241685A1 PCT/JP2021/020195 JP2021020195W WO2021241685A1 WO 2021241685 A1 WO2021241685 A1 WO 2021241685A1 JP 2021020195 W JP2021020195 W JP 2021020195W WO 2021241685 A1 WO2021241685 A1 WO 2021241685A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- basis weight
- absorbent article
- convex portion
- low basis
- elastic member
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/45—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the shape
- A61F13/49—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the shape specially adapted to be worn around the waist, e.g. diapers, nappies
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/53—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium
- A61F13/534—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having an inhomogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad
- A61F13/535—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having an inhomogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad inhomogeneous in the plane of the pad, e.g. core absorbent layers being of different sizes
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/45—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the shape
- A61F13/49—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the shape specially adapted to be worn around the waist, e.g. diapers, nappies
- A61F13/49007—Form-fitting, self-adjusting disposable diapers
- A61F13/49009—Form-fitting, self-adjusting disposable diapers with elastic means
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/51—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the outer layers of the pads
- A61F13/511—Topsheet, i.e. the permeable cover or layer facing the skin
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/51—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the outer layers of the pads
- A61F13/511—Topsheet, i.e. the permeable cover or layer facing the skin
- A61F13/512—Topsheet, i.e. the permeable cover or layer facing the skin characterised by its apertures, e.g. perforations
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/53—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium
- A61F13/531—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having a homogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad
- A61F13/532—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having a homogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad inhomogeneous in the plane of the pad
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/53—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium
- A61F13/534—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having an inhomogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad
- A61F13/535—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having an inhomogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad inhomogeneous in the plane of the pad, e.g. core absorbent layers being of different sizes
- A61F2013/5355—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having an inhomogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad inhomogeneous in the plane of the pad, e.g. core absorbent layers being of different sizes with terraced core
Definitions
- the present invention relates to absorbent articles such as disposable diapers, urine absorbing pads, incontinence pads, and sanitary napkins.
- Absorbent articles such as disposable diapers generally include a sheet that comes into contact with the wearer's skin. From the viewpoint of touch and breathability, an absorbent article in which an uneven shape is formed on the skin-facing surface of such a sheet is known.
- Patent Document 1 in a surface sheet in which a first layer and a second layer are laminated, a first compression recess arranged in a predetermined pattern and a raised portion composed of the first layer are formed. .
- An absorbent article is described in which a second compression recess that does not reach the second layer is formed in the ridge.
- the applicant has previously obtained a fused portion in which the first nonwoven fabric and the second nonwoven fabric are fused to each other at the peripheral edge of the opening in the surface sheet containing the laminate of the first nonwoven fabric and the second nonwoven fabric.
- a plurality of convex portions of the first nonwoven fabric protruding in the direction away from the second nonwoven fabric are formed at a portion other than the fused portion, and the fused portion has a plurality of protruding portions protruding toward the sublayer, and the surface thereof is formed.
- Patent Document 2 proposes an absorbent article in which the sublayer is partially pressed by the protrusions when the sheet is pressed toward the sublayer side.
- the applicant has a non-elastic region in which the elastic member is not arranged between the elastic region in which the elastic member extending in the width direction is arranged and the absorbent core, and the surface sheet is formed.
- Patent Document 3 proposes an absorbent article in which the degree of is larger than that of the lateral groove portion.
- the present invention comprises a skin contact sheet which has an uneven region and the uneven region abuts on the wearer's skin in a wearing state, and has a vertical direction corresponding to the front-back direction of the wearer and a lateral direction orthogonal to the vertical direction.
- the uneven region has a first direction and a second direction orthogonal to the first direction, and a convex portion having a length longer in the first direction than the length in the second direction and a convex portion in the first direction or the second direction. It is preferable to have a plurality of concave portions located between the convex portions.
- the concave portion has a low basis weight portion in which the basis weight of the fiber material is smaller than that of the convex portion. It is preferable that the elastic member is arranged along the first direction on the non-skin facing surface side of the skin contact sheet.
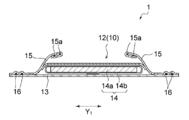
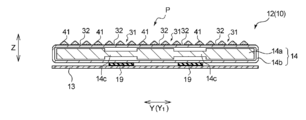
- FIG. 1 is a developed plan view schematically showing a skin-facing surface side (inner surface side) of a disposable diaper according to an embodiment of the absorbent article of the present invention in an unfolded and stretched state.
- FIG. 2 is a sectional view taken along line II-II of FIG.
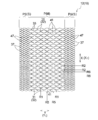
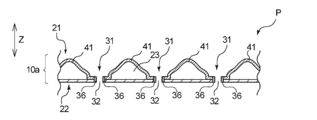
- FIG. 3 is a plan view showing the surface sheet (skin contact sheet) of the disposable diaper of the first embodiment.
- FIG. 4 is an enlarged plan view showing a part of the uneven region P of the skin contact sheet shown in FIG. 3 in an enlarged manner.
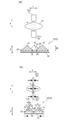
- 5A and 5B are a plan view and a cross-sectional view of a convex portion overlapping the elastic member in the skin contact sheet, and FIG. 5A is a view showing the convex portion before deformation.
- FIG. 5 (b) is a figure which shows the convex part after deformation.
- FIG. 6 is a cross-sectional view showing an example of the arrangement relationship between the uneven region of the skin contact sheet and the elastic member.
- FIG. 7 is a cross-sectional view showing another example of the arrangement relationship between the uneven region of the skin contact sheet and the elastic member.
- FIG. 8 is a cross-sectional view showing still another example of the arrangement relationship between the uneven region of the skin contact sheet and the elastic member.
- FIG. 9 is a diagram showing an example of the cross-sectional structure of the skin contact sheet according to still another embodiment.
- FIG. 10 is a view corresponding to FIG. 4 showing still another embodiment of the uneven region in the skin contact sheet.
- FIG. 11 is a view corresponding to FIG.
- FIG. 12 is a view corresponding to FIG. 4 showing still another embodiment of the uneven region in the skin contact sheet.
- FIG. 13 is a perspective view showing still another embodiment of the uneven region in the skin contact sheet.
- FIG. 14 is a partially broken perspective view showing a stretchable sheet that can be used for the elastic member according to the present invention.
- Patent Documents 1 to 3 do not disclose a technique for solving a problem that a convex portion is crushed by shrinkage of an elastic member.
- the present invention relates to an absorbent article capable of effectively suppressing the crushing of the convex portion due to the contraction of the elastic member without impairing the touch of the convex portion.
- the diaper 1 includes a liquid-permeable front surface sheet 12, a liquid-impermeable back surface sheet 13, and an absorber 14 arranged between the two sheets 12 and 13.
- the liquid impermeability is a concept including the impermeability of liquid, and includes the case where the back surface sheet 13 does not allow liquid to pass through at all and the case where the back surface sheet 13 is made of a water-repellent sheet or the like.
- the surface sheet 12 has uneven regions P and PS on the skin facing surface, but in FIGS. 1 and 2, the irregularities of the uneven regions P and PS are omitted.
- FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a developed and extended state of the diaper 1.
- the diaper 1 has a longitudinal direction X 1 corresponding to the longitudinal direction of the wearer, and a lateral Y 1 orthogonal to said longitudinal direction X 1.
- the diaper 1 is longitudinally X 1 of the full-length 3 equal parts, the front section A that is disposed on the front side of a wearer, the rear section B which is disposed on the rear side of the wearer when worn, And the inseam C located between the ventral side A and the dorsal side B.
- the diaper 1 is a deployable disposable diaper, and fastening tapes 17 are provided on both side edges of the dorsal side B, and a landing zone 18 for fastening the fastening tapes 17 to the outer surface of the ventral side A. Is provided.
- the "expanded and stretched state” of the diaper 1 means that the diaper 1 is in the unfolded state, and the elastic member of each part of the unfolded diaper 1 is stretched to eliminate the influence of the elastic member. It means the state of being unfolded until it becomes the same as the dimensions when it is unfolded in a plane.
- the "skin facing surface” is a surface facing the wearer's skin when wearing the diaper when focusing on the diaper or its constituent members (for example, an absorber), and the “non-skin facing surface” is the diaper. This is the surface that faces the wearer's skin when worn.
- the skin-facing surface is the surface relatively close to the wearer's skin
- the non-skin-facing surface is the surface relatively far from the wearer's skin.
- the absorber 14 in the diaper 1 includes an absorbent core 14a and a core wrap sheet 14b that encloses the absorbent core 14a.
- the absorbent core 14a can be composed of a fiber stack of liquid-absorbent fibers such as pulp fiber or a mixed fiber stack of the liquid-absorbent fiber and a water-absorbent polymer.
- the liquid-absorbent fiber include cellulosic hydrophilic fibers such as pulp fiber, rayon fiber, cotton fiber and cellulose acetate.
- a fiber made of a synthetic resin such as polyolefin, polyester, or polyamide, which has been hydrophilized with a surfactant or the like, can also be used.
- the core wrap sheet 14b for example, tissue paper or a water-permeable non-woven fabric is used.
- One core wrap sheet 14b may wrap the entire absorbent core 14a, or two or more core wrap sheets 14b may be combined to wrap the absorbent core 14a.
- the back sheet 13 a liquid-impermeable or water-repellent resin film, a laminated sheet of a resin film and a non-woven fabric, or the like is used.
- the three-dimensional gather forming sheet 15 having a three-dimensional gathers formed elastic members 15a are arranged, by the contraction of the stereo gathers forming elastic members 15a, crotch portion of the wearer state A three-dimensional gather is formed on C so as to stand up toward the wearer's skin side.
- the leg elastic member 16 is arranged in the extended state at the portion arranged around the leg in the inseam C, and due to the contraction thereof, the fit to the wearer's leg around the inseam C in the wearing state. Leg gathers are formed to improve.
- the stretching direction is the same as the longitudinal direction X 1 of the diaper 1.
- Waist flap portions WF is a portion consisting of members extending outwardly in the same direction X 1 than the edges of the longitudinal X 1 of the absorbent body 4.
- Waist flap portions WF in the present embodiment is composed of the absorbent body 4 of the end cuff-forming sheet 15b extending outward in the longitudinal direction X 1 from the edge, the topsheet 12 and the backsheet 13. These sheets are joined to each other by known joining means such as an adhesive, a heat seal, and an ultrasonic seal at the extending portion of the absorber 4 from the edge.
- the waist flap portion WF corresponds to the waist circumference of the wearer when the diaper 1 is worn.
- the waist flap portion WF of the rear section B, waist elastic member 19 are disposed under tension so as to extend in the transverse direction Y 1. Due to the contraction of the waist elastic member 19, waist gathers are formed on the portion arranged on the waist portion on the back side of the wearer. Waist elastic member 19 in the present embodiment, between the topsheet 12 and backsheet 13 in the waist flap portions WF, and is fixed in a stretched state along the transverse direction Y 1. The diaper 1 may have the waist elastic member 19 on the waist flap portion WF on the ventral side portion A. Waist elastic member 19 in the present embodiment, the stretching direction is the same as the transverse direction Y 1 of the diaper 1.
- the diaper 1 includes a skin contact sheet 10 that comes into contact with the wearer's skin when the diaper is worn.
- the skin contact sheet 10 has a concavo-convex region in which a plurality of convex portions and concave portions are formed, and the concavo-convex region, more specifically, the convex portion abuts on the wearer's skin in the wearing state.
- the surface sheet 12 is a skin contact sheet 10, and the surface sheet 12 has an uneven region on the skin facing surface.
- Topsheet 12 i.e. the skin contact sheet 10 of the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. 3, a pair of side regions located on either side of the central region M and the central region M located in the center of the lateral direction Y 1 S , S.
- Each of the central region M and the pair of side regions S and S has an uneven region, and the convex portions and the concave portions are formed in different arrangement patterns in both the central region M and S.
- the uneven region P in the central region M is referred to as a “central uneven region P”
- the uneven region PS in the side region S is referred to as a “side uneven region PS”.
- the skin contact sheet 10 of the present embodiment has a central uneven region P having a first direction Y and a second direction X orthogonal to the first direction Y.
- the first direction Y in this embodiment coincides with the transverse direction Y 1 of the diaper 1
- the second direction X coincides with the longitudinal direction X 1 of the diaper 1.
- the central uneven region P is formed over the entire area of the central region M.
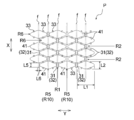
- the central uneven region P has a plurality of convex portions 41 having a length in the first direction Y longer than the length in the second direction X.
- the convex portion 41 long in the first direction Y is also referred to as a “long convex portion 41”.
- the uneven region P may have a plurality of long convex portions 41 and a plurality of concave portions 31 located between the long convex portions 41 in either the first direction Y or the second direction X.
- the long convex portion 41 of the present embodiment has a substantially elliptical shape in a plan view, its long axis direction coincides with the first direction Y, and its minor axis direction coincides with the second direction X.
- the central uneven region P is formed with the long convex portions 41 dispersed in the first direction Y and the second direction X.
- the long convex portions 41 are arranged in a staggered manner, and a vertical convex portion row R5 in which a plurality of long convex portions 41 are arranged along the second direction X is formed.
- a plurality of rows are formed in the first direction Y.
- the arrangement positions of the long convex portions 41 are deviated by half a pitch from the second direction X.
- the long convex portions 41 of the vertical convex portion rows R5 adjacent to each other in the first direction Y are arranged so that the portions of the long convex portions 41 overlap each other in the second direction X.
- the vertical convex portion rows R5 in which the positions of the long convex portions 41 in the second direction X coincide with each other are formed at equal intervals in the first direction Y.
- a plurality of lateral convex portion rows R6 in which a plurality of long convex portions 41 are arranged along the first direction Y are formed in a plurality of rows in the second direction X.
- the laterally convex portions R6 whose positions of the long convex portions 41 in the first direction Y coincide with each other are formed at equal intervals in the second direction X.
- the central uneven region P has a plurality of recesses 31 and 33 located between the long convex portions 41 in the first direction Y and the second direction X.
- the central uneven region P has two types of recesses 31 and 33 having different sizes.
- the concave portion 31 having a larger size is referred to as a "large concave portion 31”
- the concave portion 33 having a smaller size is referred to as a "small concave portion 33”.
- the central concavo-convex region P is between the edges of the long convex portions 41 in the vertical convex portion row R5 in the second direction X, and is the first of the long convex portions 41 in the lateral convex portion row R6.
- a large recess 31 is provided between the edges in the direction Y.
- the large concave portion 31 of the present embodiment has a low basis weight portion 32 having a smaller basis weight of the fiber material than the long convex portion 41.
- the low basis weight portion 32 may be a low volume fiber portion in which the basis weight of the fiber material is smaller than that of the long convex portion 41 and the fiber material is present, and the fiber material is not present and the skin contact sheet is present. It may be an opening that penetrates 10.
- the low basis weight portion 32 has the above-mentioned opening.
- the large recess 31 of the present embodiment has a high-density portion 35 in which the fiber material is densified by embossing or the like on the peripheral edge portion of the low basis weight portion 32 [see the cross-sectional view of FIG. 5 (a)]. ..
- the large recess 31 does not have to have the high density portion 35 on the peripheral edge portion of the low basis weight portion 32. In the plan views of FIGS. 4 and 5, the high-density portion 35 is not shown.
- the low basis weight portion 32 formed in the large recess 31 is also arranged in a staggered manner as shown in FIGS. 3 and 4. More specifically, in the plurality of low basis weight portions 32, the vertical direction low basis weight portion rows R1 arranged along the second direction X are intermittently formed in a plurality of rows in the first direction Y. In the vertical low basis weight section rows R1 adjacent to each other in the first direction Y, the arrangement position of the low basis weight section 32 is shifted in the second direction X by half a pitch. The plurality of rows of vertically low basis weight section rows R1 are formed at equal intervals in the first direction Y.
- the interval between the vertical low basis weight portion rows R1 in the first direction Y is such that the vertical low basis weight portion row R1 is used. It is the distance between the center lines that divide into two equal parts in the first direction Y.
- a plurality of horizontal low basis weight portion rows R2 in which a plurality of low basis weight portions 32 are arranged along the first direction Y are formed in a plurality of rows in the second direction X.
- FIG. 4 shows a region in which the vertical low basis weight section row R1 and the vertical convex section row R5 overlap in the first direction Y with reference numerals f.
- the long convex portion 41 and the large concave portion 31 are formed in a state of being alternately arranged in the first direction Y and the second direction X. That is, a plurality of vertical uneven rows R10 in which the long convex portions 41 and the large concave portions 31 are alternately arranged along the second direction X are formed along the first direction Y. Further, in the vertical uneven rows R10 adjacent to each other in the first direction Y, the arrangement position of the long convex portion 41 and the arrangement position of the large concave portion 31 are deviated by half a pitch in the second direction X.
- the central uneven region P of the present embodiment has a pair of small concave portions 33, 33 sandwiching the long convex portion 41 in the second direction X on both sides of the large concave portion 31 in the first direction Y.
- the pair of small recesses 33, 33 are in series along the second direction X, and a plurality of rows of the pair of small recesses 33, 33 are formed in the first direction Y at regular intervals.
- the positions of the small recesses 33 forming the row coincide with each other in the second direction X.
- elastic members are arranged along the first direction Y on the non-skin facing surface side of the skin contact sheet 10.
- the waist elastic member 19 is arranged in an extended state along the first direction Y on the non-skin facing surface side of the skin contact sheet 10 which is the surface sheet 12, and the waist elastic member 19 is arranged. Is adapted to exhibit elasticity along the first direction Y.
- the central uneven region P and the waist elastic member 19 overlap in the waist flap portion WF.
- the long convex portion 41 of the present embodiment has a portion a that overlaps the large concave portion 31 in the first direction Y [see FIG. 5 (a)].
- the waist elastic member 19 exhibiting elasticity in the first direction Y contracts, the central uneven region P is compressed in the first direction Y, and the skin contact sheet 10 is deformed.
- the portion a of the long convex portion 41 that overlaps the large concave portion 31 in the first direction Y is also compressed in the first direction Y.
- the long convex portion 41 compressed in the first direction Y is deformed so that the portion a overlapping the large concave portion 31 and the first direction Y bends inward [see FIG.
- the elongated convex portion 41 undergoes inward bending due to the contraction of the elastic member 19, and returns to the state before the inward folding due to the extension of the elastic member 19.
- the long convex portion 41 overlaps with the vertical low basis weight portion row R1 in the first direction Y.
- the large recess 31 has a low basis weight portion 32 having lower rigidity than other portions.
- the large recess 31 is easily compressed by the first direction Y due to the contraction of the elastic member 19 [see FIG. 5 (b)].
- the portion a of the long convex portion 41 that overlaps the large concave portion 31 in the first direction Y is also easily compressed by the same direction Y, so that the long convex portion 41 is more likely to be bent inward [FIG. 5 (FIG. 5).
- the inner bent portion a is located closer to the skin facing surface than the low basis weight portion 32.
- the elastic member 19 is located on the non-skin facing surface side with respect to the low basis weight portion 32.
- the inward bending occurs at a plurality of long convex portions 41.
- the uneven region P has a plurality of regions f in which the vertical low basis weight portion row R1 and the vertical convex portion row R5 overlap in the first direction Y.
- the elongation stress of the elastic member 19 is preferably 8 cN / 10 mm or more, more preferably 10 cN / 10 mm or more, and preferably 50 cN / 10 mm or less. It is preferably 40 cN / 10 mm or less, preferably 8 cN / 10 mm or more and 50 cN / 10 mm or less, and more preferably 10 cN / 10 mm or more and 40 cN / 10 mm or less.
- the elongation stress is measured by the following method.
- the basis weight of the fiber material in the low basis weight portion 32 is within the following range. Is preferable.
- the basis weight of the fiber material in the low basis weight portion 32 is preferably 10% or less, more preferably 20% or less, with respect to the basis weight of the fiber material in the long convex portion 41.
- the basis weight of the fiber material in the low basis weight portion 32 is preferably 30 g / m 2 or less, more preferably 20 g / m 2 or less.
- the inwardly bent portion a in the inwardly bent long convex portion 41 is formed by a valley portion v recessed inside the long convex portion 41 and a mountain portion m located on the skin facing surface side of the valley portion. [See FIG. 5 (b)]. From the viewpoint of facilitating the formation of the mountain portion m, it is preferable that the long convex portion 41 has a portion in which the constituent fibers of the skin contact sheet 10 are oriented along the second direction X. Since the portion oriented along the second direction X is less likely to receive a force for compressing the low basis weight portion 32, that is, a force for contracting in the first direction Y, it is easy to form a mountain portion m in the inwardly bent portion a.
- the long convex portion 41 has a portion in which the constituent fibers of the skin contact sheet 10 are oriented along the first direction Y. Since the portion oriented along the first direction Y is susceptible to a force for compressing the low basis weight portion 32, that is, a force for contracting in the first direction Y, it is easy to form a valley portion v in the inwardly bent portion a. From the viewpoint of forming the inwardly folded portion a more easily, the long convex portion 41 is oriented along the portion where the constituent fibers of the skin contact sheet 10 are oriented along the first direction Y and the portion along the first direction Y. It is preferable that the constituent fibers have portions oriented along the second direction X on both sides of the portion in the first direction Y.
- the orientation of the fibers on the sheet can be confirmed, for example, by the following method.
- the sheet to be evaluated is taken out from the absorbent article by peeling it off using a cold spray or the like.
- the taken-out sheet is cut into a rectangular shape in a plan view having a length of 2 cm along the second direction X and a length of 2 cm along the first direction Y using a cutter or the like, and this is used as a measurement piece.
- the measuring piece is cut out so as to include the long convex portion 41.
- a microscope for example, a digital microscope VHX-1000 manufactured by KEYENCE CORPORATION
- the long convex portion of the measuring piece is observed at a magnification of 60 to 200 times.
- the angle formed by the straight line connecting both ends and the first direction Y is measured. This measurement is performed for at least three observation regions, and the fiber orientation direction is obtained from the arithmetic mean value of the angles measured for a total of 30 or more fibers.
- the fiber orientation direction is determined to be oriented in the first direction Y when the angle formed with the first direction Y is 45 degrees or less, and is set to the second direction X when the angle formed with the first direction Y exceeds 45 degrees.
- Judge to be oriented In the measurement of fiber orientation, it is preferable to observe 10 or more fibers in the region at a magnification that can be confirmed.
- the long convex portion 41 satisfies the following formula (1) when the elastic member 19 is extended to the maximum.
- the length L1 of the long convex portion 41 in the first direction Y is the length L1 of the long convex portion 41 in the same direction Y. Maximum length (see FIG. 4).
- the H1 is measured using a thickness measuring device with a load of 0.05 kPa applied to the skin contact sheet 10.
- a thickness measuring instrument for example, a laser displacement meter (LK-080 manufactured by KEYENCE) can be used.
- La / H1 which is the ratio of La to H1
- La / H1 is preferably 1.5 or more, more preferably 2.0 or more, preferably 15.0 or less, more preferably 10.0 or less, and more preferable. Is 1.5 or more and 15.0 or less, more preferably 2.0 or more and 10.0 or less.
- L1 / L2 which is the ratio of L1 to L2, is preferably 1.5 or more, more preferably 1.8 or more, preferably 5.0 or less, more preferably 3.0 or less, and more preferable. Is 1.5 or more and 5.0 or less, more preferably 1.8 or more and 3.0 or less.
- the length of the long convex portion 41 in the second direction X is set to L2 (see FIG. 4), and the second When the length of the low basis weight portion 32 in the direction X is L5 (see FIG. 4), L5 / L2, which is the ratio of L5 to L2, is preferably 0.3 or more, more preferably 0.4 or more. It is preferably 0.8 or less, more preferably 0.7 or less, preferably 0.3 or more and 0.8 or less, and more preferably 0.4 or more and 0.7 or less.
- L6 / L2 which is the ratio of L6 to L2 is preferably 0.3 or more. , More preferably 0.4 or more, preferably 1.5 or less, more preferably 1.0 or less, and preferably 0.3 or more and 1.5 or less, more preferably 0.4 or more 1. It is 0 or less.
- the long convex portion 41 of the present embodiment has only one portion a overlapping the large concave portion 31 in the first direction, that is, an inwardly bent portion a in the second direction X.
- L1 see FIG. 4
- L10 the length of the inwardly bent portion a in the first direction Y
- L10 with respect to L1.
- the ratio of L10 / L1 is preferably 0.2 or more, more preferably 0.3 or more, preferably 0.8 or less, more preferably 0.7 or less, and preferably 0.2. It is 0.8 or more, more preferably 0.3 or more and 0.7 or less.
- the length L10 of the inwardly bent portion a in the first direction Y is the maximum length of the valley portion v in the inwardly bent long convex portion 41 along the first direction Y [see FIG. 5 (b)].
- L10 is the sum of the lengths of the plurality of inwardly bent portions a in the first direction Y.
- the dimensions of the long convex portion 41 and the low basis weight portion 32 are preferably within the following ranges.
- the length L1 (see FIG. 4) of the long convex portion 41 in the first direction Y is preferably 4.0 mm or more, more preferably 6.0 mm or more, and preferably 35.0 mm or less, more preferably 25. It is 0 mm or less, preferably 4.0 mm or more and 35.0 mm or less, and more preferably 6.0 mm or more and 25.0 mm or less.
- the length L2 (see FIG.
- the height H1 of the long convex portion 41 is preferably 0.5 mm or more, more preferably 0.8 mm or more, and preferably 4.0 mm or less, more preferably 3.0 mm or less. It is preferably 0.5 mm or more and 4.0 mm or less, and more preferably 0.8 mm or more and 3.0 mm or less.
- the length L6 (see FIG. 4) of the low basis weight portion 32 in the first direction Y is preferably 0.8 mm or more, more preferably 1.0 mm or more, and preferably 10.0 mm or less, more preferably 7. It is 0.0 mm or less, preferably 0.8 mm or more and 10.0 mm or less, and more preferably 1.0 mm or more and 7.0 mm or less.
- the length L5 (see FIG. 4) is preferably 0.8 mm or more, more preferably 1.0 mm or more, and preferably 10.0 mm or less, more preferably 7. It is 0.0 mm or less, preferably 0.8 mm or more and 10.0 mm or less, and more preferably 1.0 mm or more and 7.0 mm or less.
- the length L5 see FIG.
- the low basis weight portion 32 in the second direction X is preferably 0.8 mm or more, more preferably 1.0 mm or more, and preferably 6.0 mm or less, more preferably 4 It is 0.0 mm or less, preferably 0.8 mm or more and 6.0 mm or less, and more preferably 1.0 mm or more and 4.0 mm or less.
- the central uneven region P of the present embodiment has a small recess 33 together with a large recess 31 (see FIG. 3).
- the small recess 33 of the present embodiment has an opening as a low basis weight portion (not shown).
- the small recess 33 may not have a low basis weight portion.
- the central uneven region P may have a concave portion 33 that does not contribute to the inward bending of the long convex portion 41.
- the concave portion 33 that does not contribute to the inward bending of the long convex portion 41 does not have, for example, a concave portion having a length of less than 0.5 mm in the first direction Y or a low basis weight portion, and is consolidated by embossing or the like. Examples thereof include formed recesses.
- the waist elastic member 19 is stretchable along a lateral direction Y 1.
- the waist elastic member 19 and the central irregular region P is, the end portion of the diaper 1 in the longitudinal direction X 1, in particular overlaps with waist flap portion WF of the rear section B.
- the central uneven region P having the long convex portion 41 that can be folded inward is arranged around the waist (waist portion) of the wearer in the wearing state, so that the skin contact sheet 10 is the waist.
- the uneven region P maintains better air permeability and is less likely to cause stuffiness.
- the waist elastic member 19 is arranged in an extended state between the front surface sheet 12 which is the skin contact sheet 10 and the back surface sheet 13 in the waist flap portion WF.
- the surface sheet 12 and the waist elastic member 19 are overlapped with each other in direct contact with each other.
- Such a configuration is preferable in that the contraction force (elongation stress) of the elastic member 19 can be easily applied to the large concave portion 31 or the low basis weight portion 32, and the inward bending of the long convex portion 41 can be more easily generated.
- the skin contact sheet 10 and the elastic member arranged so as to exhibit elasticity along the first direction are in a state in which another member is interposed between the skin contact sheet 10 and the elastic member. May overlap with.
- the surface sheet 12 which is the skin contact sheet 10 and the surface sheet 12 exhibit elasticity along the first direction Y with the absorber 14 interposed therebetween.
- the arranged elastic member 19 may overlap with the arranged elastic member 19.
- the absorbent core 14a is the core low basis weight portion 14c having a low basis weight of the absorbent material.
- the core low basis weight portion 14c is a low product fiber in which the basis weight of the material for forming the absorbent core 14a is smaller than that of the portion other than the core low basis weight portion 14c in the absorbent core 14a and the forming material is present. It may be a portion, or it may be a penetration portion that does not have a forming material and penetrates the absorbent core 14a.
- the absorbent core 14a is the core low basis weight portion 14c.
- the basis weight of the absorbent material in the above is preferably more than 0%, more preferably 20% or more, and preferably 80% with respect to the basis weight of the absorbent material in the portion other than the core low basis weight portion 14c.
- it is more preferably 60% or less, preferably more than 0% and 80% or less, and more preferably 20% or more and 60% or less.
- the basis weight of the absorbent material in the core low basis weight portion 14c is preferably more than 0 g / m 2 and more preferably 40 g / g /.
- m is 2 or more, and preferably 500 g / m 2 or less, more preferably 400 g / m 2 or less, and preferably 0 g / m 2 ultra 500 g / m 2 or less, more preferably 40 g / m 2 or more 400 g / It is m 2 or less.
- the first direction Y of the long convex portion 41 and the extending direction of the elastic member 19 coincide with the lateral direction Y 1 of the diaper.
- the core low basis weight portion 14c extends in the longitudinal direction X 1.
- the first direction Y of Nagatotsu portion 41, the extending direction of the elastic member 19, and the extending direction of the core low basis weight portion 14c is coincident with the longitudinal direction X 1 of the diaper ..
- the fit of the skin contact sheet 10 can be further improved. Preferred in terms of points.
- the horizontal by the contraction of the stretchable elastic members 19 along the direction Y 1, may be one inner fold occurs inside the convex portion 41 can be folded in the irregular region P, the contraction of the longitudinally along the direction X 1 stretchable elastic member, the inner folding may occur on the convex portion 41 can be folded inside the irregular region P. That is, the first direction of the long convex portion 41 in the uneven region P may be made to coincide with the horizontal direction Y 1 of the diaper 1, or the first direction may be made to coincide with the vertical direction X 1. In the embodiment shown in FIG.
- the vertical direction X 1 stretchable elastic members along the irregular region P having a Nagatotsu portion 41 capable folded inner is overlapped at the center portion of the diaper 1 in the longitudinal direction X 1 It is more preferable that the diapers overlap with each other at the lower crotch C.
- the adhesion between the skin contact sheet 10 and the wearer's skin is more effectively suppressed, and the stuffiness caused by excrement such as urine absorbed by the absorber 14 and once absorbed by the absorber 14. It is possible to further suppress the so-called liquid return, in which the liquid is transferred to the surface sheet 12 side due to the influence of the wearer's body pressure or the like.
- the side uneven region PS has convex portions 47 and concave portions 37 arranged in a staggered pattern.
- the convex portion 47 in the side uneven region PS may cause inward bending due to the contraction of the elastic member, and may not cause inward bending due to the contraction of the elastic member.
- the convex portion 47 in the side uneven region PS has an inward fold, the above description of the central uneven region P is appropriately applied.
- FIGS. 1 to 8 show other embodiments of the skin contact sheet according to the present invention.
- the components different from the embodiments (first embodiment) shown in FIGS. 1 to 8 will be mainly described, and the same components are designated by the same reference numerals. And the explanation is omitted.
- the description of the first embodiment is appropriately applied to the components not particularly described.
- the skin contact sheet 10 of the first embodiment described above has a single-layer structure, and the inside of the long convex portion 41 is solid.
- the non-skin facing surface of the skin contact sheet 10 is flat in an extended state along the first direction Y.
- the "extended state along the first direction Y" means a state in which the skin contact sheet 10 having the convex portion 41 capable of inward folding is extended as follows.
- the unfolded diaper 1 is spread along the first direction Y until it reaches the design dimensions (the same as the dimensions when it is unfolded in a plane with the influence of the elastic member completely removed), and the diaper 1 comes into contact with the skin.
- the sheet 10 is marked with two marks at regular intervals L0 (eg, 100 mm) in the first direction Y.
- L0 regular intervals
- the skin contact sheet 10 is taken out from the diaper 1, and the skin contact sheet 10 is extended in the first direction Y until the distance between the two marks on the sheet 10 becomes the length of the fixed interval L0. This state is referred to as an "extended state along the first direction Y".
- the laminated first sheet 21 and the second sheet 22 are joined to each other at a plurality of joint portions 36 as shown in FIG. It may be a composite sheet.
- the first sheet 21 forms a long convex portion 41 protruding in a direction away from the second sheet 22 at a portion other than the concave portions 31 and 33.
- the surface of the composite sheet 10a formed by the second sheet 22, that is, the non-skin facing surface is flat.
- the inside of the long convex portion 41 is hollow and has a two-layer structure of the first sheet 21 and the second sheet 22, so that the force of the low basis weight portion 32 to compress is the first sheet. It is easy to concentrate on the 21 and the long convex portion 41 formed by the first sheet 21 is likely to be bent inward.
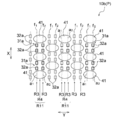
- the skin contact sheets 10b and 10c of the third and fourth embodiments shown in FIGS. 10 and 11 have different patterns of the uneven region P from the skin contact sheets 10 of the first embodiment.
- the long convex portions 41 are arranged in a staggered pattern, and four low basis weights are formed between the long convex portions 41 in the second direction X.
- a recess 31a having a portion 32a is formed.
- a plurality of vertical concavo-convex rows R11 in which the long convex portions 41 and the concave portions 31a are alternately arranged along the second direction X are formed along the first direction Y.
- the vertical concavo-convex rows R11 adjacent to each other in the first direction Y are offset from each other by half a pitch in the second direction X at the arrangement position of the long convex portion 41 and the arrangement position of the concave portion 31a.
- two sets of two low basis weight portions 32a (a pair of low basis weight portions 32a and 32a) arranged along the second direction X are arranged between the long convex portions 41 in the first direction Y. These four low basis weight portions 32a and the long convex portions 41 are alternately arranged along the second direction X.
- the vertical concavo-convex row R11 is a long-convex portion row R4 composed of a plurality of long-convex portions 41 intermittently arranged along the second direction X, and a pair of long-convex portions R4 arranged in the second direction X between the long-convex portions 41.
- the low basis weight portions 32a and 32a are composed of two rows of low basis weight portion rows R3 intermittently arranged along the same direction X.
- each long convex portion 41 forms a region f 1 and f 2 in which each of the two low basis weight portions 32a arranged in the first direction Y overlaps with the first direction Y. Have.
- the long convex portion 41 has two regions that overlap with the low basis weight portion 32a in the first direction Y.
- the elastic member 19 preferentially causes inward bending. That long convex portion 41 of the third embodiment has a plurality of inner folding portion a 1, a 2 in the first direction Y, by the contraction of the elastic members expressing stretchable in a first direction Y, folding the inner at a plurality of inner folding portion a 1, a 2, respectively occurs.
- Long protrusion 41 in the third embodiment had a inner fold portion a 1, a 2 of the two positions along the first direction Y, Nagatotsu unit 41 includes a first inner folding portion of three or more It may be held along one direction Y.
- the long convex portions 41 are arranged in a staggered pattern, and the large and low basis weight of a quadrangle is formed between the long convex portions 41 in the second direction X.
- a recess 31b having a portion 32b and four small low basis weight portions 32c located substantially diagonally outward of the large low basis weight portion 32b is formed.
- a plurality of vertical concavo-convex rows R13 in which the long convex portions 41 and the concave portions 31b are alternately arranged along the second direction X are formed along the first direction Y.
- the vertical concave-convex rows R13 adjacent to each other in the first direction Y are offset from each other by half a pitch in the second direction X at the arrangement position of the long convex portion 41 and the arrangement position of the concave portion 31b.
- the large low basis weight portion 32b and the long convex portion 41 are alternately arranged along the second direction X.
- the vertical concavo-convex row R13 is a long-convex portion row R8 composed of a plurality of long-convex portions 41 intermittently arranged along the second direction X, and a pair of long-convex portions R8 arranged in the second direction X between the long-convex portions 41.
- the long convex portion 41 in the longitudinal direction uneven rows R13 is, in the first direction Y, a large low basis weight portion 32b and the region f 4 overlaps the first direction Y, and two small low basis It has three places of the amount portion 32c and the area f 3 overlapped with the first direction Y, f 5. In these three areas f 3, f 4, f 5, as in the third embodiment, preferentially the inner bending occurs by the contraction of the elastic member 19.
- the inner folding portion a 3, a 4, a 5 has three positions along the first direction Y, the elastic members expressing stretchable in a first direction Y by contraction, these three inner bending portion a 3, a 4, a 5 inner fold in each occurs.
- the long convex portion 41 and the concave portion 31 are arranged in a scattered spot shape, but the long convex portion 41 and the concave portion 31 are continuous in one direction. You may.
- the skin contact sheet 10d of the fifth embodiment has a ridge-shaped surface facing the skin. Specifically, the continuous convex portion 41a forming the ridge extending in the first direction Y and the continuous concave portion 31d forming the groove extending in the same direction as the continuous convex portion 41a alternate along the second direction X. Is located in.
- the skin facing surface of the skin contact sheet 10d has a corrugated uneven shape when viewed in a direction orthogonal to the extending direction of the continuous convex portion 41a and the continuous concave portion 31d (not shown).
- the continuous recess 31d in the fifth embodiment intermittently has a plurality of low basis weight portions 32 along the first direction Y, and the low basis weight portion 32 in the continuous recess 31d adjacent to the second direction X.
- the arrangement positions match in the first direction Y. That is, a plurality of vertical concavo-convex rows R15 in which the continuous convex portions 41a and the low basis weight portions 32 of the continuous concave portions 31d are alternately arranged along the second direction X are formed along the first direction Y.
- each successive protrusions 41a in the longitudinal direction uneven rows R15 arranged along the second direction X includes a plurality of locations areas f 9 of the low basis weight portion 32 overlaps in the same first direction Y There is.
- bending the inner preferentially occurs by the contraction of the elastic member 19.
- That long convex portion 41 of the fifth embodiment has a plurality of inner folding portion a 9 along the first direction Y, by the contraction of the elastic members expressing stretchable in a first direction Y, the plurality inner fold occurs in each bending section a 9.
- the length L1 of the long convex portion in the first direction Y is the unit area of the continuous convex portion 41a (the continuous convex portion 41a). Assuming that the convex portion is per 30 mm square), the total length (30 mm) of the convex portion in the first direction Y is used.
- the length of the sum L10 of the inner folding portion a 9 in the first direction Y is when the continuous convex portion 41a assuming protrusions per unit area (30 mm square), present in the protrusions per the unit area the sum of the lengths in the first direction Y of the folded portion a 9 among the.
- protruding portions per unit area the number of inner folding portion a 9 in the convex portion is set within a range such that the maximum number.
- the skin contact sheet 10e has a plurality of long convex portions 41b and concave portions 31d protruding toward the skin facing surface side, and the long convex portions 41b are non-skin facing.
- the surface side is open to form a space.
- the back side of the recess 31d that is, the non-skin facing surface of the recess 31d protrudes toward the non-skin facing surface side, and when the skin contact sheet 10e is viewed from the non-skin facing surface side,
- the protruding portion on the back side of the concave portion 31d is a convex portion protruding toward the non-skin facing surface side.
- the recess 31d is open on the side facing the skin to form a space. These long convex portions 41b and concave portions 31d are arranged alternately and continuously along the entire surface of the skin contact sheet 10e along two different directions intersecting each other in a plan view.
- the recess 31d has the above-mentioned low-stacked fiber portion as the low basis weight portion 32d.
- the back sheet 13 and the absorber 14 those conventionally used for the absorbent article can be used without particular limitation.
- a liquid-impermeable resin film, a laminate of the resin film and a non-woven fabric, or the like can be used.
- the absorbent core 14a an aggregate of hydrophilic fibers such as wood pulp and a hydrophilized synthetic fiber, or an aggregate in which a water-absorbing polymer is retained can be used.
- the core wrap sheet 14b the same one as the surface sheet 12 can be used.
- the leak-proof cuff forming sheet 15b a water-repellent nonwoven fabric can be used.
- a liquid-permeable non-woven fabric conventionally used for absorbent articles can be used.
- the non-woven fabric include air-through non-woven fabric, spunbond non-woven fabric, spunlace non-woven fabric, meltblown non-woven fabric, resin bond non-woven fabric, needle punch non-woven fabric and the like. It is also possible to use a laminated body in which two or more kinds of these non-woven fabrics are combined.
- thermoplastic resin examples include polyolefins such as polyethylene and polypropylene, polyesters such as polyethylene terephthalate, polyamides such as nylon 6 and nylon 66, polyacrylic acid, polymethacrylic acid alkyl esters, polyvinyl chloride, and polyvinylidene chloride. These resins can be used alone or as a blend of two or more. Further, it can be used in the form of a composite fiber such as a core sheath type or a side-by-side type.
- Examples of the elastic members 15a, 16 and 19 described above include synthetic rubber such as styrene-butadiene, butadiene, isoprene and neoprene, natural rubber, EVA, elastic polyolefin and polyurethane.
- synthetic rubber such as styrene-butadiene, butadiene, isoprene and neoprene, natural rubber, EVA, elastic polyolefin and polyurethane.
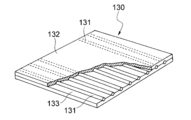
- the elastic sheet 130 may be used as the elastic members 15a, 16 and 19 described above.
- the stretchable sheet 130 is a non-woven fabric in which a plurality of elastic filaments 131 arranged so as to extend in one direction without intersecting each other are stretchable over their entire lengths in a substantially non-stretched state. It is joined to 132 and 133.
- Each elastic filament 131 is bonded to the first and second nonwoven fabrics 132 and 133.
- the first nonwoven fabric 132 and the second nonwoven fabric 133 may be of the same type or different types.
- the same type of nonwoven fabric as used herein means nonwoven fabrics having the same manufacturing process of the nonwoven fabric, types of constituent fibers of the nonwoven fabric, fiber diameters and lengths of the constituent fibers, thickness and basis weight of the nonwoven fabric, and the like. When at least one of these is different, it is said to be a different type of non-woven fabric.
- "Elasticity" means the original length when the force is released from the state where it can be stretched and is stretched 100% with respect to the original length (the length becomes 200% of the original length). It refers to the property of returning to a length of 125% or less.
- Each of the non-woven fabrics 132 and 133 is expandable.
- Each of the nonwoven fabrics 132 and 133 can be extended in the same direction as the elastic filament 131 extends.
- Stretchable means that (a) the constituent fibers of the non-woven fabrics 132 and 133 are elongated, and (b) the constituent fibers themselves are not elongated, but the fibers bonded at the intersections are separated from each other, or the fibers are separated from each other. This includes cases where the three-dimensional structure formed of a plurality of fibers is structurally changed due to bonding or the like, the constituent fibers are torn off, or the slack of the fibers is stretched, and the non-woven fabric as a whole is stretched.
- the nonwoven fabrics 132 and 133 may already be stretchable in the state of the original fabric before being joined to the elastic filament 131. Alternatively, it is not stretchable in the state of the original fabric before being joined to the elastic filament 131, but is processed so as to be stretchable after being joined to the elastic filament 131 so that it can be stretched. May be good. Specific methods for making the nonwoven fabric stretchable include heat treatment, inter-roll stretching, biting stretching with tooth grooves and gears, and tensile stretching with a tenter.
- Each elastic filament 131 is substantially continuous over the entire length of the elastic sheet 130.
- the elastic filament 131 contains an elastic resin.
- the elastic filaments 131 are arranged so as to extend in one direction without intersecting each other. However, it is permissible for the elastic filaments 131 to unintentionally intersect due to the unavoidable fluctuations in the manufacturing conditions of the stretchable sheet 130.
- the elastic filaments 131 may extend linearly or meander as long as they do not intersect each other.
- the above-mentioned elastic sheet 130 has a structure in which an elastic filament 131 is arranged between two stretchable non-woven fabrics 132 and 133, but instead of the elastic filament 131, one stretchable non-woven fabric is used on one surface.
- An elastic sheet having a structure in which the elastic filament 131 is arranged may be used. In this case, the elastic filament 131 is in an exposed state.
- the skin contact sheet of the present invention can be manufactured by using a known manufacturing method.
- the skin contact sheet 10 of the first embodiment is manufactured by a manufacturing method including a step of imparting an uneven shape to the sheet to form a concave portion and a convex portion, and a step of forming a low basis weight portion in the concave portion.
- a manufacturing method including a step of imparting an uneven shape to the sheet to form a concave portion and a convex portion, and a step of forming a low basis weight portion in the concave portion.
- a sheet is introduced between the embossed convex rolls and the flat rolls arranged so as to be opposed to each other to give an uneven shape, and then the concave portions having the uneven shape are subjected to ultrasonic treatment or the like to reduce the basis weight. Form a part.
- the composite sheet (skin contact sheet 10a) according to the second embodiment can be manufactured by the manufacturing method described in JP-A-2018-099883.
- a manufacturing method includes a step of imparting an uneven shape to the first sheet 21, a step of superimposing the second sheet 22 on the first sheet 21, and an ultrasonic wave applying ultrasonic vibration to both sheets 21 and 22.
- a processing step Provided with a processing step.
- the step of imparting the uneven shape the first sheet 21 is introduced into the meshing portion of both rolls while rotating the first roll and the second roll having the unevenness that meshes with each other on the peripheral surface portion, and the first roll is deformed into the uneven shape.
- the first sheet 21 deformed into an uneven shape is conveyed while being held on the first roll, and the second sheet 22 is superimposed on the first sheet 21 being conveyed.
- both sheets 21 and 22 that are overlapped are sandwiched between the convex portion of the first roll and the ultrasonic horn of the ultrasonic fusion machine, and ultrasonic vibration is applied to bring them into contact with the skin.
- a low basis weight portion 32 having an opening penetrating the sheet 10a is formed.
- a known cutting means capable of partially cutting the sheet deformed into an uneven shape can be used in addition to the ultrasonic treatment.
- the cutting means include a cutting device provided with a cutter roll and an anvil roll having a cutting blade having a shape corresponding to the contour of the opening on the outer peripheral surface of the cutter roll.
- the skin contact sheet 10 in the first embodiment has a central uneven region P and side uneven regions PS located on both sides thereof, but the entire surface of the skin contact sheet 10 is covered.
- the long convex portion 41 and the concave portions 31 and 33 having the same pattern as the central uneven region P may be formed.
- the uneven region P may have a region that overlaps with the elastic member 19 and a region that does not overlap with the elastic member 19.
- the convex portion in the region overlapping with the elastic member 19 and the convex portion in the region not overlapping with the elastic member 19 may have the same width or different widths in the first direction Y.
- the width of the convex portion in the region overlapping with the elastic member 19 in the first direction is smaller than the width of the convex portion in the region not overlapping with the elastic member 19 in the first direction.
- the shape of the low basis weight portion 32 can be any shape long in the first direction Y.
- examples of the shape of the low basis weight portion 32 include a rectangle, an ellipse, an oval, a triangle, a pentagon, a hexagon, a star, a heart, and the like.
- the absorbent article of the present invention may be a pants-type (pull-on type) disposable diaper instead of the deployable disposable diaper, and may be a pants-type or a normal non-pants-type sanitary napkin. It may be an incontinence pad, a panty liner, or the like.
- the present invention further discloses the following absorbent articles: ⁇ 1> Absorption having an uneven region, provided with a skin contact sheet in which the uneven region abuts on the wearer's skin in the wearing state, and has a vertical direction corresponding to the front-back direction of the wearer and a horizontal direction orthogonal to the vertical direction. It ’s a sex item,
- the uneven region has a first direction and a second direction orthogonal to the first direction, and a convex portion having a length longer in the first direction than the length in the second direction and a convex portion in the first direction or the second direction.
- the concave portion has a low basis weight portion in which the basis weight of the fiber material is smaller than that of the convex portion.
- An absorbent article in which an elastic member is arranged along a first direction on the non-skin facing surface side of the skin contact sheet.
- ⁇ 2> In the uneven region, a plurality of rows of low basis weight portions in which a plurality of the low basis weight portions are arranged along the second direction are intermittently formed in the first direction.
- the above-mentioned ⁇ The absorbent article according to 1>.
- ⁇ 3> The absorbent article according to ⁇ 2>, wherein the inner bent portion is located on the skin facing surface side with respect to the low basis weight portion.
- ⁇ 4> The absorption according to ⁇ 1>, wherein a plurality of rows of low basis weight portions in which a plurality of the low basis weight portions are arranged are intermittently formed in the first direction in the uneven region. Sex goods.
- ⁇ 5> The absorbent article according to ⁇ 2> or ⁇ 4>, wherein a plurality of rows of the low basis weight portions are formed at equal intervals in the first direction.
- ⁇ 6> The absorbent article according to any one of ⁇ 1> to ⁇ 5>, wherein the elastic member is arranged so as to exhibit elasticity along the first direction.
- ⁇ 7> The absorbent article according to any one of ⁇ 1> to ⁇ 6>, wherein the elongation stress of the elastic member is 8 cN / 10 mm or more and 50 cN / 10 mm or less, preferably 10 cN / 10 mm or more and 40 cN / 10 mm or less.
- the basis weight of the fiber material in the low basis weight portion is 10% or less, preferably 20% or less, with respect to the basis weight of the fiber material in the convex portion where the length in the first direction is longer than the length in the second direction.
- the length of the convex portion in the second direction is L2 and the length of the low basis weight portion in the first direction is L6, L6 / L2, which is the ratio of L6 to L2, is 0.3 or more, preferably 0.3 or more.
- the convex portion has one or a plurality of portions sandwiched between the low basis weight portions in the second direction along the first direction.
- L10 / L1 which is the ratio of L10 to L1 is 0.2 or more.
- ⁇ 15> The absorbent article according to any one of ⁇ 1> to ⁇ 14>, wherein the convex portion has a portion in which the constituent fibers of the skin contact sheet are oriented along the second direction.
- the skin contact sheet is a composite sheet in which the laminated first sheet and the second sheet are joined to each other at a plurality of joints.
- the first sheet forms the convex portion protruding in the direction away from the second sheet in a portion other than the concave portion.
- L1 / L2 which is the ratio of L1 to L2 is 1.5 or more and 5.0 or less.
- the absorbent article according to any one of ⁇ 1> to ⁇ 19> preferably 1.8 or more and 3.0 or less.
- the elastic member can be expanded and contracted along the lateral direction, and the elastic member can be expanded and contracted.
- the elastic member can be expanded and contracted along the vertical direction, and the elastic member can be expanded and contracted.
- ⁇ 23> Equipped with an absorbent core containing absorbent material, The absorbent core has a core low basis weight portion extending in the vertical direction and having a low basis weight of the absorbent material.
- the basis weight of the core low basis weight portion is more than 0% and 80% or less, more preferably 20% or more and 60% or less, based on the basis weight of the absorbent material in the portion other than the core low basis weight portion.
- ⁇ 25> Absorption basis weight of the core a low basis weight portion, 0 g / m 2 Ultra 500 g / m 2 or less, more preferably 40 g / m 2 or more 400 g / m 2 or less, according to ⁇ 23> or ⁇ 24> Sex goods.
- ⁇ 26> The absorbent article according to any one of ⁇ 1> to ⁇ 25>, wherein the elastic member is an elastic sheet in which a plurality of elastic filaments are bonded to an stretchable non-woven fabric.
- the uneven region has a region that overlaps with the elastic member and a region that does not overlap with the elastic member. Any of the above ⁇ 1> to ⁇ 26>, wherein the width of the convex portion in the region overlapping the elastic member in the first direction is smaller than the width of the convex portion in the region not overlapping the elastic member in the first direction.
- an absorbent article capable of effectively suppressing the crushing of the convex portion due to the contraction of the elastic member without impairing the touch of the convex portion.
- Such absorbent articles have good breathability.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Absorbent Articles And Supports Therefor (AREA)
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| GB2218186.1A GB2610963B (en) | 2020-05-27 | 2021-05-27 | Absorbent article |
| CN202180031572.4A CN115484910B (zh) | 2020-05-27 | 2021-05-27 | 吸收性物品 |
| DE112021002929.0T DE112021002929T5 (de) | 2020-05-27 | 2021-05-27 | Absorbierender Artikel |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020-091931 | 2020-05-27 | ||
| JP2020091931 | 2020-05-27 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2021241685A1 true WO2021241685A1 (ja) | 2021-12-02 |
Family
ID=78744926
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2021/020195 Ceased WO2021241685A1 (ja) | 2020-05-27 | 2021-05-27 | 吸収性物品 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7572913B2 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN115484910B (enExample) |
| DE (1) | DE112021002929T5 (enExample) |
| GB (1) | GB2610963B (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2021241685A1 (enExample) |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010227143A (ja) * | 2009-03-25 | 2010-10-14 | Uni Charm Corp | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2017153735A (ja) * | 2016-03-02 | 2017-09-07 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | パンツ型使い捨ておむつ |
| JP2019076499A (ja) * | 2017-10-25 | 2019-05-23 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6830800B2 (en) * | 1999-12-21 | 2004-12-14 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Elastic laminate web |
| JP4727267B2 (ja) * | 2005-03-25 | 2011-07-20 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品及び吸収性物品用表面シート |
| JP6239965B2 (ja) * | 2013-12-19 | 2017-11-29 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| WO2016158746A1 (ja) * | 2015-03-27 | 2016-10-06 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品の伸縮構造、及びパンツタイプ使い捨ておむつ |
| JP6726076B2 (ja) * | 2015-12-02 | 2020-07-22 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| GB2559933B (en) * | 2015-11-20 | 2021-09-22 | Kao Corp | Absorbent article |
| WO2017086327A1 (ja) * | 2015-11-20 | 2017-05-26 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP7023045B2 (ja) * | 2016-09-30 | 2022-02-21 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP6360542B2 (ja) | 2016-11-30 | 2018-07-18 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品及びそれに用いる立体開孔シートの製造方法 |
| JP7084130B2 (ja) | 2016-12-19 | 2022-06-14 | 花王株式会社 | 複合シートの製造方法及び製造装置 |
-
2021
- 2021-05-27 JP JP2021089183A patent/JP7572913B2/ja active Active
- 2021-05-27 DE DE112021002929.0T patent/DE112021002929T5/de active Pending
- 2021-05-27 CN CN202180031572.4A patent/CN115484910B/zh active Active
- 2021-05-27 GB GB2218186.1A patent/GB2610963B/en active Active
- 2021-05-27 WO PCT/JP2021/020195 patent/WO2021241685A1/ja not_active Ceased
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010227143A (ja) * | 2009-03-25 | 2010-10-14 | Uni Charm Corp | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2017153735A (ja) * | 2016-03-02 | 2017-09-07 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | パンツ型使い捨ておむつ |
| JP2019076499A (ja) * | 2017-10-25 | 2019-05-23 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN115484910B (zh) | 2023-08-29 |
| DE112021002929T5 (de) | 2023-03-09 |
| CN115484910A (zh) | 2022-12-16 |
| GB2610963B (en) | 2024-11-20 |
| JP7572913B2 (ja) | 2024-10-24 |
| JP2021186679A (ja) | 2021-12-13 |
| GB2610963A (en) | 2023-03-22 |
| GB202218186D0 (en) | 2023-01-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5368591B2 (ja) | シート部材、高密度領域含有シートの製造方法およびシート部材を使用した使い捨ておむつ | |
| JP5309022B2 (ja) | シート状部材の積層体 | |
| US10857043B2 (en) | Nonwoven fabric laminate, absorbent article having nonwoven fabric laminate, and process for producing nonwoven fabric laminate | |
| KR20170131423A (ko) | 흡수성 물품의 신축 구조, 및 팬티 타입 일회용 기저귀 | |
| EP2092923A1 (en) | Absorptive article | |
| JP6326222B2 (ja) | 使い捨てパンツ型おむつ | |
| CN110022819A (zh) | 具有多个弹性区域的一次性裤型吸收性物品 | |
| JP6442181B2 (ja) | パンツ型使い捨ておむつ | |
| WO2016013448A1 (ja) | パンツ型使い捨ておむつ | |
| JP6095207B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| EP3053561B1 (en) | Nonwoven fabric laminate and absorbent article having nonwoven fabric laminate | |
| JP4981539B2 (ja) | 高密度領域含有シートの製造方法および高密度含有シートを使用した使い捨ておむつ | |
| JP5932910B2 (ja) | パンツ型使い捨ておむつ | |
| JP2014104261A5 (enExample) | ||
| JP2017023782A (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6654671B2 (ja) | 使い捨て着用物品の伸縮構造、及びこの伸縮構造を有するパンツタイプ使い捨て着用物品 | |
| JP4757182B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP2015104605A (ja) | 使い捨てパンツ型おむつ | |
| JP6283208B2 (ja) | 使い捨てパンツ型おむつ | |
| WO2021241685A1 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP2015104607A (ja) | 使い捨てパンツ型おむつ | |
| JP3214474U (ja) | 使い捨てパンツ型おむつ | |
| RU2795254C1 (ru) | Впитывающее изделие | |
| JP7212584B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP7267069B2 (ja) | テープ式使い捨ておむつ |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 21813764 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 202218186 Country of ref document: GB Kind code of ref document: A Free format text: PCT FILING DATE = 20210527 |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 21813764 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |