WO2021187218A1 - 制振用成形品及び制振用成形品用の樹脂組成物の製造方法 - Google Patents
制振用成形品及び制振用成形品用の樹脂組成物の製造方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2021187218A1 WO2021187218A1 PCT/JP2021/009138 JP2021009138W WO2021187218A1 WO 2021187218 A1 WO2021187218 A1 WO 2021187218A1 JP 2021009138 W JP2021009138 W JP 2021009138W WO 2021187218 A1 WO2021187218 A1 WO 2021187218A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- olefin
- inorganic filler
- vibration
- vibration damping
- molded product
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L67/00—Compositions of polyesters obtained by reactions forming a carboxylic ester link in the main chain; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers
- C08L67/02—Polyesters derived from dicarboxylic acids and dihydroxy compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L81/00—Compositions of macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming in the main chain of the macromolecule a linkage containing sulfur with or without nitrogen, oxygen or carbon only; Compositions of polysulfones; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers
- C08L81/04—Polysulfides
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K3/00—Use of inorganic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K3/34—Silicon-containing compounds
- C08K3/346—Clay
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K9/00—Use of pretreated ingredients
- C08K9/04—Ingredients treated with organic substances
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L81/00—Compositions of macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming in the main chain of the macromolecule a linkage containing sulfur with or without nitrogen, oxygen or carbon only; Compositions of polysulfones; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers
- C08L81/02—Polythioethers; Polythioether-ethers
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K3/00—Use of inorganic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K3/18—Oxygen-containing compounds, e.g. metal carbonyls
- C08K3/20—Oxides; Hydroxides
- C08K3/22—Oxides; Hydroxides of metals
- C08K2003/2237—Oxides; Hydroxides of metals of titanium
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L23/00—Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers
- C08L23/02—Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers not modified by chemical after-treatment
- C08L23/04—Homopolymers or copolymers of ethene
- C08L23/08—Copolymers of ethene
- C08L23/0846—Copolymers of ethene with unsaturated hydrocarbons containing atoms other than carbon or hydrogen
- C08L23/0869—Copolymers of ethene with unsaturated hydrocarbons containing atoms other than carbon or hydrogen with unsaturated acids, e.g. [meth]acrylic acid; with unsaturated esters, e.g. [meth]acrylic acid esters
- C08L23/0884—Epoxide-containing esters
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L2310/00—Masterbatches
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16F—SPRINGS; SHOCK-ABSORBERS; MEANS FOR DAMPING VIBRATION
- F16F1/00—Springs
- F16F1/36—Springs made of rubber or other material having high internal friction, e.g. thermoplastic elastomers
- F16F1/3605—Springs made of rubber or other material having high internal friction, e.g. thermoplastic elastomers characterised by their material
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a molded product having vibration damping properties used for home appliances, automobiles, etc., and to a molded product having vibration damping properties even better than existing materials.
- Resin damping materials are effective in reducing noise and vibration, and efforts are being made to knead raw materials with excellent damping characteristics into the resin.
- Document 1 shows that a resin composition containing a polymer material composed of a thermoplastic resin component and an elastomer component and an inorganic filler is excellent in rigidity and vibration damping property.
- Document 2 shows that a resin containing an ethylene-glycidyl methacrylate-styrene copolymer in polyester and polyolefin is a vibration damping material having excellent impact resistance and repetitive toughness.
- Document 3 describes vinyl polymers such as ternary copolymers of ⁇ -olefin, ⁇ , ⁇ -unsaturated carboxylic acid ester and glycidyl ester of ⁇ , ⁇ -unsaturated carboxylic acid, polyester resin and rubbery elastic resin.
- An improvement method has been proposed by using a resin composition containing at least four components of the inorganic layered compound.
- An object of the present invention is to provide a molded product that exerts a vibration damping effect more than ever before.
- An object of the present invention has been achieved by: 1.
- a vibration-damping molded product comprising a resin composition containing at least a thermoplastic resin A, an olefin-based elastomer B having a reactive functional group, and an inorganic filler C, wherein the inorganic filler C is coated with the olefin-based elastomer B.
- Anti-vibration molded product 2.
- a method for producing a resin composition for a vibration-damping molded product in which an olefin-based elastomer B and an inorganic filler C are melt-kneaded and then melt-kneaded by adding a thermoplastic resin A.
- the vibration-damping molded product of the present invention is a vibration-damping molded product comprising a resin composition containing at least a thermoplastic resin A, an olefin-based elastomer B having a reactive functional group, and an inorganic filler C. C is coated with the olefin-based elastomer B.
- thermoplastic resin A of the present invention a crystalline thermoplastic resin or an amorphous thermoplastic resin is preferably used.
- the crystalline thermoplastic resin include polyacetal resin (POM), polybutylene terephthalate resin (PBT), polyethylene terephthalate resin (PET), polyphenylene sulfide resin (PPS), polyamide resin (PA) and the like. Anything having melt molding processability may be used.
- thermoplastic resin A of the present invention can be produced by a conventional method.
- the olefin-based elastomer B having a reactive functional group of the present invention (hereinafter, also simply referred to as olefin-based elastomer B) is preferably an epoxy group-containing olefin-based copolymer, and at least a structural unit derived from ⁇ -olefin and ⁇ . , ⁇ -Unsaturated acid glycidyl ester-derived structural unit.
- ⁇ -olefin C2-4 olefins such as ethylene and propylene can be used, and ethylene and propylene are preferable.
- ⁇ , ⁇ -unsaturated acid glycidyl ester it is preferable to use glycidyl acrylate or glycidyl methacrylate.
- a third component such as C1-12 (meth) acrylic acid ester or vinyl acetate may be copolymerized.
- Olefin and glycidyl ester are 30 to 90 mol% in the copolymer, respectively. It can be adjusted in the range of 70 to 10 mol%, and the third component can contain the range of 0 to 30 mol%.
- an ethylene-glycidyl methacrylate copolymer (hereinafter, also referred to as EGMA) is particularly preferable.
- the ratio of glycidyl methacrylate to ethylene is not particularly limited, but the modified site of the copolymer is converted into the mass of each monomer, and the ratio to 100 parts by mass of the copolymer is 1 to 30 parts by mass, preferably 3.
- the range is preferably from 20 parts by mass, more preferably 8 to 15 parts by mass.
- Examples of the inorganic filler C contained in the molded product of the present invention include glass fiber, glass flakes, glass beads, silica, talc, mica, potassium titanate whisker, calcium titanate and the like, and mica, potassium titanate whisker and the like. Especially preferable.
- the fiber length of the inorganic filler (state before preparation into a composition by melt-kneading or the like) is preferably 0.01 to 10 mm, and the diameter is preferably 5 to 20 ⁇ m.
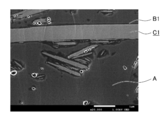
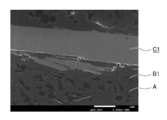
- the inorganic filler of the present invention is characterized in that its surface is coated with an olefin elastomer B. Whether or not it is coated can be known by observing the cross section of the molded product with SEM or by the following method (hereinafter, also referred to as a coating confirmation method).
- the inorganic filler coated with the olefin elastomer B can be produced by a coating treatment step in which the olefin elastomer B and the inorganic filler C are melt-kneaded.
- the inorganic filler having the surface coated with the olefin elastomer B is melt-kneaded with the thermoplastic resin A.
- the thermoplastic resin A and the excess olefin elastomer B that are not involved in the coating are removed with a solvent that can dissolve both the thermoplastic resin A and the olefin elastomer B. Then, the coated inorganic filler is measured by FT-IR.
- the resin composition for a molded product can be produced by subjecting the surface of the inorganic filler to the surface of the olefin elastomer B, then adding the thermoplastic resin A, and further melt-kneading.
- a molded product in which the inorganic filler coated with the olefin elastomer B is dispersed in the thermoplastic resin A can be obtained.
- the olefin-based elastomer B may be added to the coated olefin-based elastomer B at the time of melt-kneading with the thermoplastic resin A.
- the inorganic filler C is preferably contained in an amount of 20 to 200 parts by mass, more preferably 30 to 160 parts by mass, based on 100 parts by mass of the thermoplastic resin A.
- thermoplastic resins and thermosetting resins that is, burr suppressors, mold release agents, and lubrications, as long as the effects of the present invention are not impaired.
- Agents, plasticizers, flame retardants, colorants such as dyes and pigments, crystallization accelerators, crystal nucleating agents, various antioxidants, heat stabilizers, weather resistance stabilizers, corrosion inhibitors and the like may be blended.
- the molded product of the present invention is obtained by molding the resin composition for the molded product described above.
- the method for producing the molded product of the present invention is not particularly limited, and a known method can be adopted.
- the resin composition as described above can be put into an extruder, melt-kneaded and pelletized, and the pellets can be put into an injection molding machine equipped with a predetermined mold and injection-molded. ..
- C4 glass fiber ECS03T-747 manufactured by Nippon Electric Glass Co., Ltd.
- C5 glass fiber ECS03T-187 manufactured by Nippon Electric Glass Co., Ltd.
- the masterbatch was prepared by kneading B and C in the amounts shown in Tables 1 and 2 at a cylinder temperature of 190 ° C. and then pelletizing.
- a master batch pelletized with the thermoplastic resin A1 is kneaded at a cylinder temperature of 320 ° C. and then injection molded to be a test piece (200 mm ⁇ 10 mm ⁇ 1.6 mt).
- a master batch pelletized with the thermoplastic resin A2 was kneaded at a cylinder temperature of 260 ° C. and then injection molded to prepare a molded product (200 mm ⁇ 10 mm ⁇ 1.6 mt).
- the loss coefficient was obtained from the half width of the antiresonance point of the mechanical impedance by the central excitation method.
- the device used was a loss coefficient measuring device manufactured by Ono Sokki. The results are shown in Tables 1 and 2. Unless otherwise specified, the measurement was performed in a 23 ° C. and 50% RH atmosphere.
- the present invention is a molded product having excellent vibration damping properties.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Dispersion Chemistry (AREA)
- Compositions Of Macromolecular Compounds (AREA)
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US17/906,004 US12043737B2 (en) | 2020-03-17 | 2021-03-09 | Vibration-damping molded article and method for producing resin composition for vibration-damping molded article |
| JP2022508234A JP7393521B2 (ja) | 2020-03-17 | 2021-03-09 | 制振用成形品及び制振用成形品用の樹脂組成物の製造方法 |
| CN202180022082.8A CN115380069A (zh) | 2020-03-17 | 2021-03-09 | 减振用成形品和减振用成形品用的树脂组合物的制造方法 |
| EP21770854.4A EP4116368B1 (en) | 2020-03-17 | 2021-03-09 | Vibration-damping molded article and method for producing resin composition for vibration-damping molded article |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020-046358 | 2020-03-17 | ||
| JP2020046358 | 2020-03-17 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2021187218A1 true WO2021187218A1 (ja) | 2021-09-23 |
Family
ID=77771265
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2021/009138 Ceased WO2021187218A1 (ja) | 2020-03-17 | 2021-03-09 | 制振用成形品及び制振用成形品用の樹脂組成物の製造方法 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US12043737B2 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP4116368B1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP7393521B2 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN115380069A (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2021187218A1 (enExample) |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002356574A (ja) * | 2001-03-05 | 2002-12-13 | Sekisui Chem Co Ltd | 発泡性熱可塑性樹脂組成物、熱可塑性樹脂発泡体及び積層複合体 |
| JP2003292746A (ja) * | 2002-03-29 | 2003-10-15 | Kanegafuchi Chem Ind Co Ltd | 制振性樹脂組成物とそれを用いた成形品 |
| JP2006152020A (ja) * | 2004-11-25 | 2006-06-15 | Nippon Steel Corp | 樹脂組成物、樹脂シート並びに積層材料 |
| JP2008075087A (ja) * | 2007-10-02 | 2008-04-03 | Kaneka Corp | 制振性樹脂組成物とそれを用いた成形品 |
| JP2011148960A (ja) | 2010-01-25 | 2011-08-04 | Bridgestone Corp | ポリエステル樹脂組成物 |
| JP2012171989A (ja) * | 2011-02-17 | 2012-09-10 | Furukawa Electric Co Ltd:The | 制振樹脂組成物及びその製造方法 |
| JP2015203062A (ja) | 2014-04-14 | 2015-11-16 | 住友化学株式会社 | 樹脂組成物及びこれからなる制振部材 |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3960387B2 (ja) * | 2004-04-23 | 2007-08-15 | シーシーアイ株式会社 | 高分子組成物の製造方法 |
| JP4618057B2 (ja) * | 2004-12-07 | 2011-01-26 | マツダ株式会社 | 熱可塑性樹脂組成物及びその成形品並びに該成形品を用いた車両の外板部材 |
| JP2012171990A (ja) * | 2011-02-17 | 2012-09-10 | Furukawa Electric Co Ltd:The | 制振樹脂組成物及びその製造方法 |
| CN105793384A (zh) * | 2013-12-11 | 2016-07-20 | 株式会社可乐丽 | 密封剂 |
| US20190071554A1 (en) | 2016-03-17 | 2019-03-07 | Kao Corporation | Fan |
| WO2017188183A1 (ja) * | 2016-04-25 | 2017-11-02 | 花王株式会社 | 制振材料用のポリエステル樹脂成形組成物 |
| CN105949608A (zh) * | 2016-05-31 | 2016-09-21 | 江苏金发科技新材料有限公司 | 具备优良应力缓冲吸收的聚丙烯复合材料及其制备方法 |
| CN106046483B (zh) * | 2016-06-27 | 2020-06-16 | 湖北祥源新材科技股份有限公司 | 吸音隔热聚烯烃发泡片材及其制备方法 |
| WO2019107449A1 (ja) | 2017-11-29 | 2019-06-06 | 花王株式会社 | ポリプロピレン樹脂組成物 |
-
2021
- 2021-03-09 CN CN202180022082.8A patent/CN115380069A/zh active Pending
- 2021-03-09 EP EP21770854.4A patent/EP4116368B1/en active Active
- 2021-03-09 US US17/906,004 patent/US12043737B2/en active Active
- 2021-03-09 WO PCT/JP2021/009138 patent/WO2021187218A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2021-03-09 JP JP2022508234A patent/JP7393521B2/ja active Active
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002356574A (ja) * | 2001-03-05 | 2002-12-13 | Sekisui Chem Co Ltd | 発泡性熱可塑性樹脂組成物、熱可塑性樹脂発泡体及び積層複合体 |
| JP2003292746A (ja) * | 2002-03-29 | 2003-10-15 | Kanegafuchi Chem Ind Co Ltd | 制振性樹脂組成物とそれを用いた成形品 |
| JP2006152020A (ja) * | 2004-11-25 | 2006-06-15 | Nippon Steel Corp | 樹脂組成物、樹脂シート並びに積層材料 |
| JP4460426B2 (ja) | 2004-11-25 | 2010-05-12 | 新日本製鐵株式会社 | 樹脂組成物、樹脂シート並びに積層材料 |
| JP2008075087A (ja) * | 2007-10-02 | 2008-04-03 | Kaneka Corp | 制振性樹脂組成物とそれを用いた成形品 |
| JP2011148960A (ja) | 2010-01-25 | 2011-08-04 | Bridgestone Corp | ポリエステル樹脂組成物 |
| JP2012171989A (ja) * | 2011-02-17 | 2012-09-10 | Furukawa Electric Co Ltd:The | 制振樹脂組成物及びその製造方法 |
| JP2015203062A (ja) | 2014-04-14 | 2015-11-16 | 住友化学株式会社 | 樹脂組成物及びこれからなる制振部材 |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| See also references of EP4116368A4 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPWO2021187218A1 (enExample) | 2021-09-23 |
| US12043737B2 (en) | 2024-07-23 |
| EP4116368A1 (en) | 2023-01-11 |
| US20230109288A1 (en) | 2023-04-06 |
| EP4116368A4 (en) | 2023-08-16 |
| EP4116368B1 (en) | 2024-08-07 |
| CN115380069A (zh) | 2022-11-22 |
| JP7393521B2 (ja) | 2023-12-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4922124B2 (ja) | ポリ乳酸系樹脂組成物及びその成形体 | |
| JP2009256487A (ja) | ポリ乳酸組成物、その製造方法及びその成形体 | |
| CN106459578B (zh) | 结晶性聚酰胺类树脂组合物 | |
| JPWO2003022920A1 (ja) | ポリエチレン樹脂組成物 | |
| JPH02279745A (ja) | 強化ポリプロピレン樹脂組成物 | |
| KR20190064875A (ko) | 유리섬유 강화 폴리프로필렌 수지 조성물, 이의 제조방법 및 이를 포함하는 성형품 | |
| JP2022156073A (ja) | セルロース繊維強化ポリオレフィン系樹脂組成物及び樹脂成形品 | |
| WO2016080298A1 (ja) | エチレン-酢酸ビニル共重合体樹脂組成物、グラフト共重合体、熱可塑性樹脂組成物、及び樹脂成形品 | |
| CN109897285B (zh) | 包含甲硅烷基化的微纤化纤维素的聚丙烯复合树脂组合物及使用其的车辆柱装饰件 | |
| KR100387648B1 (ko) | 폴리프로필렌 수지 조성물 | |
| JP7393521B2 (ja) | 制振用成形品及び制振用成形品用の樹脂組成物の製造方法 | |
| JP7116423B2 (ja) | 樹脂組成物及び射出成形品 | |
| KR102187566B1 (ko) | 폴리프로필렌 수지 조성물 및 이의 성형품 | |
| JP5517849B2 (ja) | 樹脂組成物 | |
| KR20150067471A (ko) | 유리섬유 보강된 경량 폴리프로필렌 수지 조성물, 및 상기 조성물로 제조되는 성형품 | |
| KR20120077465A (ko) | 유리섬유 강화 열가소성 얼로이 수지 조성물 및 이를 이용한 성형품 | |
| JP2835596B2 (ja) | 高剛性制振性樹脂組成物 | |
| JP2022137334A (ja) | シリコーン接着用ポリブチレンテレフタレート樹脂組成物およびそれからなる成形品、ならびに複合成形品 | |
| JP2021075640A (ja) | 水を含む流体と接触し得る車両用冷却系部品 | |
| JP2023041360A (ja) | 成形品、成形品の製造方法および成形品の外観性向上方法 | |
| JPWO2018193893A1 (ja) | ポリオレフィン樹脂組成物及びポリオレフィン樹脂組成物成形体 | |
| JP2012188497A (ja) | 樹脂組成物 | |
| JPH11349801A (ja) | 熱可塑性樹脂組成物 | |
| JP2018130842A (ja) | ガラス繊維強化樹脂成形体の製造方法 | |
| JP2025154074A (ja) | 樹脂組成物、ペレット、および、成形品 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 21770854 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2022508234 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2021770854 Country of ref document: EP Effective date: 20221004 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |