WO2019181964A1 - 直交軸減速機及び直交軸減速機を用いたロボット - Google Patents
直交軸減速機及び直交軸減速機を用いたロボット Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2019181964A1 WO2019181964A1 PCT/JP2019/011547 JP2019011547W WO2019181964A1 WO 2019181964 A1 WO2019181964 A1 WO 2019181964A1 JP 2019011547 W JP2019011547 W JP 2019011547W WO 2019181964 A1 WO2019181964 A1 WO 2019181964A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- orthogonal
- input shaft
- cylindrical member
- axis
- gear
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B25—HAND TOOLS; PORTABLE POWER-DRIVEN TOOLS; MANIPULATORS
- B25J—MANIPULATORS; CHAMBERS PROVIDED WITH MANIPULATION DEVICES
- B25J17/00—Joints
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16H—GEARING
- F16H1/00—Toothed gearings for conveying rotary motion
- F16H1/02—Toothed gearings for conveying rotary motion without gears having orbital motion
- F16H1/04—Toothed gearings for conveying rotary motion without gears having orbital motion involving only two intermeshing members
- F16H1/12—Toothed gearings for conveying rotary motion without gears having orbital motion involving only two intermeshing members with non-parallel axes
- F16H1/14—Toothed gearings for conveying rotary motion without gears having orbital motion involving only two intermeshing members with non-parallel axes comprising conical gears only
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16H—GEARING
- F16H57/00—General details of gearing
- F16H57/02—Gearboxes; Mounting gearing therein
- F16H57/029—Gearboxes; Mounting gearing therein characterised by means for sealing the gearboxes, e.g. to improve airtightness
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16H—GEARING
- F16H57/00—General details of gearing
- F16H57/02—Gearboxes; Mounting gearing therein
- F16H57/038—Gearboxes for accommodating bevel gears
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an orthogonal shaft speed reducer capable of increasing the inner diameter of a hollow portion of a cylindrical member and a robot using the orthogonal shaft speed reducer.
- Patent Document 1 discloses an orthogonal shaft type power transmission device in which a transmission member (bevel gear) is supported from the inner peripheral side via a bearing by a cylindrical member disposed through the center of the reduction gear. ing. According to this device, since the bevel gear is supported from the inner peripheral side by the cylindrical member, it is possible to reduce the shake of the input shaft.
- a transmission member bevel gear
- the present invention has been made in order to solve the above-described problems, and an orthogonal axis reduction device capable of increasing the inner diameter of a hollow portion by reducing the thickness of a cylindrical member, and a robot using the orthogonal axis reduction device
- the purpose is to provide.
- an orthogonal shaft reduction gear is engaged with a first reduction gear having a hollow input shaft, a first gear fixed to the input shaft, and the first gear.
- a second speed reduction portion comprising a second gear orthogonal to the axis of the input shaft, a housing containing the second speed reduction portion, and fixed to the housing, coaxially penetrates the input shaft and the first gear.
- the orthogonal shaft speed reducer according to claim 2 is the orthogonal shaft speed reducer according to claim 1, wherein the cylindrical member is a fixed portion including a flange portion and an inlay portion fixed to the casing. And the length of the spigot portion in the direction parallel to the axis of the input shaft is longer than the length of the flange portion in the direction orthogonal to the axis of the input shaft. .
- the orthogonal shaft reducer according to claim 3 is the orthogonal axis reducer according to claim 2, and further, the inlay portion of the cylindrical member includes a groove for arranging an O-ring. It is characterized by.
- the orthogonal shaft reducer according to claim 4 is the orthogonal axis reducer according to claim 2 or 3, wherein the cylindrical member further increases in outer diameter toward the fixed portion. It is characterized by.
- the orthogonal shaft reducer according to claim 6 is the orthogonal axis reducer according to any one of claims 1 to 5, wherein the cylindrical member is orthogonal to the axis of the input shaft. When viewed from the direction, it has a cylindrical shape in which no step is provided in a range overlapping the input shaft.
- the robot according to claim 7 is a robot having an indirect portion, wherein the indirect portion uses the orthogonal axis reducer according to any one of claims 1 to 6. Is.
- the cylindrical member does not pivotally support the first reduction gear portion or the first gear, the thickness of the cylindrical member can be reduced. For this reason, the internal diameter of the hollow part of a cylindrical member can be enlarged.
- the tubular member and the first reduction part or the first gear it is possible to reduce the size of the orthogonal axis reduction gear in the axial direction.
- the size of the flange portion can be reduced. For this reason, the size of the orthogonal shaft reduction gear can be reduced.
- the orthogonal shaft speed reducer since the outer diameter of the cylindrical member increases toward the fixed portion, the strength of the fixed portion of the cylindrical member increases. In addition, since the extra space inside the orthogonal shaft speed reducer can be narrowed, the lubricant enclosed inside is easily guided to the meshing portion such as the tooth surface of the first gear, and the lubricating performance is improved.
- the cylindrical member has a cylindrical shape in which no step is provided in a range overlapping the input shaft when viewed from the direction orthogonal to the axis of the input shaft.
- the thickness of the member can be reduced. For this reason, the internal diameter of the hollow part of a cylindrical member can be enlarged.
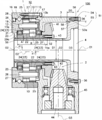
- FIG. 1 is a central longitudinal cross-sectional view of an orthogonal shaft reducer 100 which is a first embodiment of the orthogonal shaft reducer of the present invention.
- the orthogonal shaft speed reducer 100 includes a first speed reduction portion 1, a second speed reduction portion 2, a housing 3, and a tubular member 4.
- the first speed reduction unit 1 is connected to the housing 3, and the second speed reduction unit 2 is built in the housing 3.
- the cylindrical member 4 has one end fixed to the housing 3 and the other end arranged coaxially through the center of the first speed reduction unit 1.
- the first reduction gear unit 1 is an eccentric peristaltic type reduction unit in which the external gear 10 rotates eccentrically while meshing with the internal gear 11.
- the first reduction gear unit 1 includes a casing 12, a carrier 13, an external gear 10, and an input shaft 14a.
- the casing 12 has a cylindrical middle case 15 in which the internal gear 11 is integrally provided on the inner peripheral surface, and a cylindrical shape disposed on one end surface (the output side, the left side in FIG. 1) of the middle case 15 in the axial direction.
- the outer case 16 includes an inner case 15 and the outer case 16, which are connected to the other one in the axial direction (input) of the inner case 15 by a plurality of bolts 17, 17. 1 and the right side of FIG.
- the outer case 16 also serves as an outer ring of the cross roller bearing 18.
- the carrier 13 includes a first carrier member 13a and a second carrier member 13b.
- the first carrier member 13 a is rotatably supported on the inner side of the outer case 16 via a cross roller bearing 18.
- the first carrier member 13 a also serves as an inner ring of the cross roller bearing 18.
- an output portion 19 for transmitting power to the counterpart device is formed on one end face in the axial direction of the first carrier member 13a.
- a plurality of bolt holes (not shown) are formed in the output unit 19 and are connected to the counterpart device using the bolt holes.
- a circular inlay portion 20 is formed inside the output portion 19 for use in alignment with the counterpart device.
- the pin holes 25 are loosely inserted with pins 26 laid on the concentric circle centering on the axis O1 of the input shaft 14a in parallel with the axis. Both ends of the pin 26 are press-fitted into holes provided in the first carrier member 13a and the second carrier member 13b, and the first carrier member 13a and the second carrier member 13b can be integrally rotated by the pin 26. .
- a cylindrical metal 27 is integrally mounted on the loose insertion portion of the external gear 10 on the outer periphery of the pin 26.
- An oil seal 28 is disposed outside the cross roller bearing 18 between the outer case 16 and the first carrier member 13a.
- an oil seal 29 a is disposed outside the ball bearing 21 between the first carrier member 13 a and the tubular member 4.
- a portion of the first carrier member 13 a where the oil seal 29 a is disposed is formed to have the same diameter as the spigot portion 20.
- the internal space of the orthogonal shaft reduction gear 100 is sealed by the oil seal 28 and the oil seal 29a.
- the cylindrical member 4 is a cylindrical member formed of, for example, an aluminum alloy, and includes a fixed portion 51 fixed to the housing 3, a main body portion 52 that coaxially penetrates the first reduction gear 1 and the bevel gear 41. , And an intermediate portion 53a connecting between the fixed portion 51 and the main body portion 52.
- the cylindrical member 4 is fixed to the housing 3 only on the fixed portion 51 side, and the main body portion 52 side is only supported by the lip of the oil seal 29a and is not pivotally supported. That is, it is fixed to the housing 3 in a so-called cantilever state.
- the fixing portion 51 of the cylindrical member 4 includes a circular flange portion 54 and an inlay portion 55, and the inlay portion 55 is fitted to the inner periphery of the opening provided in the housing 3, and a plurality of flange portions 54 are provided. Are fixed to the housing 3 by bolts 56, 56.
- the axial length D5 of the spigot portion 55 is longer than the length D6 of the surface perpendicular to the axial direction of the flange portion 54.
- the inlay portion 55 is provided with a groove 57 over the entire circumference, and an O-ring 58 is disposed in the groove 57.
- An O-ring 58 seals between the opening of the housing 3 and the spigot 55 of the tubular member 4.
- a step, a groove, etc. is a cylindrical shape that is not provided with the shape.
- the distal end portion 59 of the cylindrical member 4 does not protrude beyond the end surface of the output portion 19 of the first carrier member 13a in the direction of the axis O1 of the input shaft 14a.
- each pin hole 25 also moves eccentrically and rotates.
- each pin hole 25 is formed to have a larger diameter than the pin 26 including the metal 27, each pin 26 is in a state in which it is inscribed in the pin hole 25.
- the eccentric component is relatively moved to absorb the eccentric component, and only the rotation component is extracted from each pin 26. Therefore, the first carrier member 13a and the second carrier member 13b rotate synchronously via the pin 26, and the rotation is transmitted from the output unit 19 to the counterpart device. At this time, the grease filled in the housing 3 is sealed by the oil seal 28 and the oil seal 29a.
- the cylindrical member 4 since the cylindrical member 4 does not support the input shaft 14a or the bevel gear 41, the radial load generated from the input shaft 14a or the bevel gear 41 is applied to the cylindrical member 4. It does not take. For this reason, the thickness of the main-body part 52 of the cylindrical member 4 can be made thin, and the internal diameter D1 of the main-body part 52 can be enlarged. Further, since there is no bearing or the like between the tubular member 4 and the input shaft 14a or the bevel gear 41, the size of the orthogonal shaft speed reducer 100 in the axial direction can be reduced.
- the ball bearings 21 and 21 that support the input shaft 14a are subjected to a vertical load (radial load) on the axis O1 of the input shaft by the bevel gear 41 and the bevel pinion 42 of the second reduction gear unit 2, but the ball bearing By reducing the distance between 21 and 21 and the bevel gear 41, the radial load can be reduced.
- the cylindrical member 4 does not pivotally support the input shaft 14a or the bevel gear 41, the distance of the ball bearings 21 and 21 and the bevel gear 41 can be shortened.
- the thickness of the fixing part 51 of the tubular member 4 can be increased. For this reason, even if the thickness of the main body 52 of the tubular member 4 is reduced, the strength of the tubular member 4 can be maintained and can be fixed to the housing 3 with high accuracy. For this reason, the internal diameter D1 of the main-body part 52 of the cylindrical member 4 can be enlarged.
- the groove 57 can be formed in the inlay portion 55. For this reason, compared with the case where a groove is formed in the flange portion 54, the outer diameter of the flange portion 54 can be reduced. For this reason, the magnitude
- the inner diameter of the tubular member 4 increases from the main body portion 52 toward the fixed portion 51, whereby the end portion of the hollow portion can be enlarged, and for example, an operation such as passing a cable through the hollow portion is facilitated.
- the inner periphery (inner diameter D3) of the fixed portion 51 is a cylindrical surface coaxial with the axis O1 of the input shaft 14a.
- the inner diameter gradually inclines toward the fixed portion or curves. May be larger.
- the inner periphery (inner diameter D1) and outer periphery (outer diameter D2) of the main body 52 of the cylindrical member 4 have a step or the like in a portion overlapping the input shaft 14a when viewed from the direction orthogonal to the axis O1 of the input shaft 14a. Since it is the cylindrical shape which is not provided, the thickness of the main-body part 52 can be made thinner. For this reason, the internal diameter D1 of the main-body part 52 of the cylindrical member 4 can be enlarged.
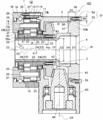
- the shape of the intermediate part 53b of the cylindrical member 4 differs from 1st Embodiment. Note that the configuration and operation of the orthogonal shaft speed reducer 100 excluding the shape of the intermediate portion 53b of the cylindrical member 4 are the same as those in the first embodiment described above, and thus detailed description thereof is omitted.
- the inner diameter D3 of the intermediate portion 53b of the cylindrical member 4 is larger than the inner diameter D1 of the main body portion 52. Further, the cylindrical member 4 has an outer diameter that increases from the main body portion 52 toward the fixed portion 51. The outer diameter D4 of the intermediate portion 53b is larger than the outer diameter D2 of the main body portion 52.
- the same effect as in the first embodiment is obtained. Further, since the outer diameter of the intermediate portion 53b of the cylindrical member 4 is increased, the strength of the intermediate portion 53b of the cylindrical member 4 is further increased. Further, since the extra space inside the housing 3 can be narrowed by increasing the outer diameter, the lubricant enclosed in the housing 3 is removed from the tooth surfaces of the bevel gear 41, the bevel pinion 42, and the like. It becomes easy to be guided to the meshing portion of the, and the lubrication performance is enhanced.
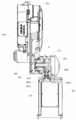
- a robot 200 using the orthogonal axis speed reducer of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS.
- the robot 200 includes a fixed base 201, a first arm 203, a second arm 204, and a hand unit 205.
- the first arm 203 is connected to an orthogonal shaft speed reducer 202 fixed to the upper end of the fixed base 201.
- the second arm 204 is connected to an orthogonal shaft reducer (not shown) housed at the upper end of the first arm 203.
- the hand unit 205 rotatably supports a gripping part (not shown) that grips a workpiece, and the gripping part is connected to an orthogonal shaft speed reducer (not shown) housed at the lower end of the second arm 204.
- the fixing base 201 is made of a material such as a substantially quadrangular columnar iron, and houses a power cord A, a motor 221 that rotates the first arm, and the like.
- the upper end of the fixed base 201 has a first opening 201a for wiring the power cord A to the orthogonal shaft reducer 202 side, and a second opening provided in the vicinity of the first opening 201a and the upper portion of the motor 221 facing the orthogonal shaft reducer 202 side. 201b.
- the orthogonal shaft reducer 202 has the lower end of the housing 3A fixed to the upper end of the fixed base 201.
- the lower end of the housing 3A has a first housing side opening 202a that communicates with the first opening 201a and a second housing side opening 202b that communicates with the second opening 201b.
- the right side of the housing 3A is a hollow portion for storing the power cord A and the like wired from the first housing side opening 202a.
- the end of the cylindrical member 4A is fixed to the upper wall and the lower wall of the left end portion of the housing 3A that forms the cavity.
- the rotation shaft of the motor 221 is disposed in the second housing side opening 202b, and the rotation shaft of the motor 221 is connected to the bevel pinion 42A of the orthogonal shaft speed reducer 202.
- the output unit 19 ⁇ / b> A of the orthogonal shaft speed reducer 202 is connected to the side wall at the lower right end of the first arm 203. Therefore, when the motor 221 rotates, the output unit 19A of the orthogonal shaft reduction gear 202 rotates, and the first arm 203 rotates with the rotation of the output unit 19A.
- the first arm 203 is formed of a material such as a substantially quadrangular columnar iron, and houses a motor (not shown) for driving the second arm 204 and an orthogonal shaft speed reducer (not shown).
- the output portion of the orthogonal shaft reducer housed in the first arm 203 is connected to the upper right wall of the second arm 204.
- the second arm 204 is formed of a material such as a substantially quadrangular columnar iron, and houses a motor (not shown) for driving the gripping portion and an orthogonal shaft speed reducer (not shown).
- the output part of the orthogonal shaft reducer housed in the second arm 204 rotatably supports the grip part of the hand part 205.
- the hand part 205 supports a gripping part (not shown) for gripping a workpiece so as to be openable and closable.
- the power cord A of the motor that rotates the second arm 204 passes through the hollow portion of the cylindrical member 4A via the first opening 201a and the first housing side opening 202a of the fixed base 201 and reaches the motor.
- the power cord A of the motor that rotates the gripping part passes through the hollow part of the cylindrical member of the orthogonal shaft reducer housed in the first arm 203 after passing through the hollow part of the cylindrical member 4A from the fixed base 201. To the motor.
- the robot 200 uses an orthogonal axis reduction gear
- the hollow portion of the cylindrical member 4A can be made larger than before, and thus a large number of power cords can be accommodated. Therefore, the orthogonal axis reduction gear of the present invention can be applied not only to the two arms shown in FIG. 3 but also to a multi-indirect robot having three or more arms.
- the material of the cylindrical member 4 is an aluminum alloy or the like, but the material may be a resin or the like. Since the cylindrical member 4 does not pivotally support the input shaft 14a or the first speed reduction unit 1, no load is applied to the cylindrical member 4 in principle. For this reason, a material such as a resin having a lower strength than an aluminum alloy may be used.
- the cylindrical member 4 may have both the outer diameter and the inner diameter expanded from the main body portion 52 toward the fixed portion 51. Further, the thickness may increase from the main body portion 52 toward the fixed portion 51 so that the thickness increases.
- the first gear of the present invention may be a hypoid gear
- the second gear may be a hypoid pinion
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Robotics (AREA)
- Gear Transmission (AREA)
- General Details Of Gearings (AREA)
- Retarders (AREA)
- Manipulator (AREA)
Abstract
【課題】筒状部材の内径を大きくすることができる直交軸減速機及び直交軸減速機を用いたロボットを得る。 【解決手段】中空の入力軸14a有する第1減速部1と、入力軸14aに固定されるベベルギア41、及びベベルギア41と噛み合い入力軸14aの軸線O1と直交する軸線O3を中心に回転するベベルピニオン42からなる第2減速部2と、第2減速部2を内蔵する筐体3と、筐体3に固定され、入力軸14a及びベベルギア41を同軸で貫通する筒状部材4と、を有する直交軸減速機100において、筒状部材4は、第1減速部1またはベベルギア41を軸支せず、筐体3に片持ち状態で固定される。
Description
本発明は、筒状部材の中空部の内径を大きくすることができる直交軸減速機及び直交軸減速機を用いたロボットに関するものである。
従来、特許文献1には、減速機の中央を貫通して配置される筒状部材により、伝達部材(ベベルギア)を内周側から軸受を介して支持した直交軸型の動力伝達装置が開示されている。この装置によれば、ベベルギアが筒状部材によって内周側から支持されるため、入力軸の軸ぶれを低減させることができる。
しかしながら、特許文献1の構成によれば、筒状部材が軸受を介してベベルギアを支持するため、筒状部材には、ある程度の強度が必要であり、筒状部材の肉厚も確保しなければならない。このため、筒状部材の中空部の内径が小さくなってしまうという問題があった。
本発明は、上述した問題点を解決するためになされたものであり、筒状部材の肉厚を薄くすることで中空部の内径を大きくできる直交軸減速機及び直交軸減速機を用いたロボットを提供することを目的とする。
この目的を達成するために、請求項1記載の直交軸減速機は、中空の入力軸を有する第1減速部と、前記入力軸に固定される第1ギア、及び前記第1ギアと噛み合い前記入力軸の軸線と直交する第2ギアからなる第2減速部と、前記第2減速部を内蔵する筐体と、前記筐体に固定され、前記入力軸及び前記第1ギアを同軸で貫通する筒状部材と、を備える直交軸減速機であって、前記筒状部材は、前記第1減速部または前記第1ギアを軸支せず、前記筐体に片持ちで固定されることを特徴とするものである。
また、請求項2記載の直交軸減速機は、請求項1に記載の直交軸減速機であって、更に、前記筒状部材は、前記筐体に固定されるフランジ部及びインロー部からなる固定部を有し、前記入力軸の軸線と直交する方向における前記フランジ部の長さよりも、前記入力軸の軸線と平行な方向における前記インロー部の長さのほうが長いことを特徴とするものである。
また、請求項3記載の直交軸減速機は、請求項2に記載の直交軸減速機であって、更に、前記筒状部材の前記インロー部は、Oリングを配置するための溝を備えることを特徴とするものである。
また、請求項4記載の直交軸減速機は、請求項2または3に記載の直交軸減速機であって、更に、前記筒状部材は、前記固定部に向かって外径が拡径することを特徴とするものである。
また、請求項5記載の直交軸減速機は、請求項2から4のいずれか1項に記載の直交軸減速機であって、更に、前記筒状部材は、前記固定部に向かって内径が拡径することを特徴とするものである。
また、請求項6記載の直交軸減速機は、請求項1から5のいずれか1項に記載の直交軸減速機であって、更に、前記筒状部材は、前記入力軸の軸線と直交する方向から見て、前記入力軸と重なる範囲には段差が設けられない円筒状であることを特徴とするものである。
また、請求項7記載のロボットは、間接部を有するロボットにおいて、前記間接部に前記請求項1から6のいずれか1項に記載の直交軸減速機を用いたロボットであることを特徴とするものである。
請求項1記載の直交軸減速機によれば、筒状部材が第1減速部または第1ギアを軸支しないため、筒状部材の肉厚を薄くできる。このため、筒状部材の中空部の内径を大きくすることができる。また、筒状部材と第1減速部または第1ギアとの間に軸受が無いため、直交軸減速機の軸方向の大きさを小さくすることができる。
また、請求項2記載の直交軸減速機によれば、インロー部を長くすることにより筒状部材の固定部の肉厚が厚くなり強度がアップする。また、筒状部材を精度よく筐体に固定することができる。このため、筒状部材における入力軸及び第1ギアを貫通する部分の肉厚を薄くすることができ、筒状部材の中空部の内径を大きくすることができる。
また、請求項3記載の直交軸減速機によれば、Oリングをインロー部に配置することにより、フランジ部にはOリングが不要となるため、フランジ部の大きさを小さくすることができる。このため、直交軸減速機のサイズを小さくすることができる。
また、請求項4記載の直交軸減速機によれば、筒状部材は固定部に向かって外径が拡径するため、筒状部材の固定部の強度がアップする。また、直交軸減速機の内部の余分な空間を狭くすることができるので、内部に封入された潤滑剤が第1ギアの歯面などの噛み合い部に導かれやすくなり、潤滑性能がアップする。
また、請求項5記載の直交軸減速機によれば、筒状部材は固定部に向かって内径が拡径するため、固定部付近の内径が大きくなる。このため、筒状部材の中空部にケーブル等を通す作業が容易になる。
また、請求項6記載の直交軸減速機によれば、筒状部材は、入力軸の軸線と直交する方向から見て入力軸と重なる範囲には段差が設けられない円筒状であるため、筒状部材の肉厚を薄くすることができる。このため、筒状部材の中空部の内径を大きくすることができる。
また、請求項7記載のロボットによれば、間接部に前記直交軸減速機を用いるので前述した何れの効果も有する。
[第1実施形態]
以下、本発明の第1実施形態について図面を参照して説明する。図1は、本発明の直交軸減速機の第1実施形態である直交軸減速機100の中央縦断面図である。
以下、本発明の第1実施形態について図面を参照して説明する。図1は、本発明の直交軸減速機の第1実施形態である直交軸減速機100の中央縦断面図である。
直交軸減速機100は、第1減速部1と、第2減速部2と、筐体3と、筒状部材4とからなる。第1減速部1は筐体3に連結され、第2減速部2は筐体3に内蔵されている。筒状部材4は、一端が筐体3に固定され、他端が第1減速部1の中心を同軸で貫通して配置される。
第1減速部1は、外歯歯車10が内歯歯車11と噛み合いながら偏心回転する偏心搖動型の減速部である。第1減速部1は、ケーシング12とキャリア13と外歯歯車10と入力軸14aとを備えている。ケーシング12は、内周面に内歯歯車11を一体に設けた円筒状の中ケース15と、中ケース15における軸方向の一方の端面(出力側、図1の左側)に配置される円筒状の外ケース16とから成り、中ケース15と外ケース16とは、中ケース15及び外ケース16に螺合される複数のボルト17,17・・により、中ケース15における軸方向の他方(入力側、図1の右側)から、筐体3と一体に結合されている。外ケース16はクロスローラベアリング18の外輪を兼ねている。
キャリア13は、第1キャリア部材13aと第2キャリア部材13bとで構成されている。第1キャリア部材13aは、外ケース16の内側にクロスローラベアリング18を介して回転可能に軸支されている。第1キャリア部材13aはクロスローラベアリング18の内輪を兼ねている。第1キャリア部材13aにおける軸方向の一方の端面には、相手側装置へ動力を伝達する出力部19が形成されている。出力部19には図示しない複数のボルト孔が形成され、該ボルト孔を利用して、相手側装置と連結される。また、出力部19の内側には、相手側装置との軸心合わせに使用するための円形のインロー部20が形成される。
ケーシング12の内側には、2個のボールベアリング21,21を介して、中空筒状の入力軸14aが、内歯歯車11の軸線と同軸で、第1キャリア部材13a及び第2キャリア部材13bに回転可能に軸支されている。入力軸14aにおいて、ボールベアリング21,21の間には、外径及び偏心量δ1が互いに等しく、偏心方向が互いに180度異なる位相となる一対の偏心部22,22が隣接して形成されている。各偏心部22,22には、全周に亘って配設される横断面円形状の複数のころ23,23・・からなるニードルベアリング24が設けられて、ニードルベアリング24を介して、外歯歯車10,10がそれぞれ回転可能に外装されている。入力軸14aにおける軸方向の入力側の端面には、複数のボルト孔が形成されている。入力軸14aにおける軸方向の出力側の端面位置は、出力側のボールベアリング21における出力側の端面位置と、略同一の位置になっている。
第1キャリア部材13aにおける軸方向の他方には、形状が同じ2枚の外歯歯車10,10が配置され、第1キャリア部材13aと第2キャリア部材13bとで2枚の外歯歯車10,10を挟むようになっている。外歯歯車10,10は、内歯歯車11の歯数よりも僅かに少ない歯数を有して内歯歯車11に偏心位置で内接している。外歯歯車10,10には、入力軸14aの軸線O1から偏心量δ1だけオフセットした軸線O2を中心とした同心円上に、複数の円形のピン孔25が、周方向に等間隔で形成されて、このピン孔25に、入力軸14aの軸線O1を中心とした同心円上で当該軸線と平行に架設されるピン26がそれぞれ遊挿されている。このピン26の両端は、第1キャリア部材13a及び第2キャリア部材13bに設けられた孔に圧入され、ピン26によって第1キャリア部材13a及び第2キャリア部材13bは一体に回転可能となっている。ピン26の外周における外歯歯車10の遊挿部分には、筒状のメタル27が一体に外装されている。
外ケース16と第1キャリア部材13aとの間でクロスローラベアリング18の外側には、オイルシール28が配置されている。また、第1キャリア部材13aと筒状部材4との間でボールベアリング21の外側には、オイルシール29aが配置されている。第1キャリア部材13aにおけるオイルシール29aが配置される部分は、インロー部20と同径に形成されている。オイルシール28及びオイルシール29aにより、直交軸減速機100の内部空間が封止されている。
第2減速部2は、直交軸型の減速部であり、第1ギアであるベベルギア41と、ベベルギア41に噛み合い入力軸14aの軸線O1と直交する軸線O3を中心に回転する第2ギアであるベベルピニオン42とを備え、筐体3に内蔵されている。ベベルギア41は、第1減速部1の入力軸14aの入力側の端部に連結されている。ベベルギア41は、複数のボルト43,43・・によって入力軸14aの端部に設けられたボルト孔に固定され、入力軸14aの軸線O1を中心として入力軸14aと一体に回転可能となっている。ベベルピニオン42は、ベベルギア41と噛み合う歯と反対側には、図示しないモータと連結可能な連結部44を備え、ボールベアリング45を介して筐体3の内側に回転自在に軸支されている。
筒状部材4は、例えばアルミ合金などで成型される円筒状の部材であり、筐体3に固定される固定部51と、第1減速部1及びベベルギア41を同軸で貫通する本体部52と、固定部51と本体部52との間をつなぐ中間部53aとからなる。筒状部材4は、固定部51側のみが筐体3に固定され、本体部52側はオイルシール29aのリップが当接するのみであり軸支はされていない。つまり、いわゆる片持ち状態で筐体3に固定されている。
筒状部材4の固定部51は、円形のフランジ部54とインロー部55とからなり、インロー部55が、筐体3に設けられた開口部の内周に嵌合し、フランジ部54は複数のボルト56,56・・によって筐体3に固定されている。なお、筒状部材4の固定部51において、インロー部55の軸方向長さD5は、フランジ部54の軸方向に垂直な面の長さD6よりも長くなっている。また、インロー部55には全周に亘って溝57が設けられ、溝57にはOリング58が配置されている。Oリング58によって、筐体3の開口部と筒状部材4のインロー部55との間が封止されている。
筒状部材4の固定部51と反対側には本体部52が形成される。本体部52の先端部59は、第1キャリア部材13aの内側に達し、先端部59の外周にはオイルシール29aのリップが当接する。筒状部材4の本体部52には、入力軸14aまたはベベルギア41を軸支するベアリング等が設けられず、入力軸14aの内周面から僅かな隙間Aを隔てて配置されている。筒状部材4の中間部53aには、本体部52の内径D1よりも大きな内径D3が形成されている。また、筒状部材4の本体部52のうち、入力軸14aの軸線O1と直交する方向から見て入力軸14a及びベベルギア41と重なる範囲Bには、内径D1及び外径D2に段差や溝等の形状が設けられない円筒状となっている。
筒状部材4の先端部59は、入力軸14aの軸線O1方向において、第1キャリア部材13aの出力部19の端面よりも突出しない。
以上のように構成された直交軸減速機100において、図示しないモータによってベベルピニオン42が回転すると、ベベルピニオン42に噛み合うベベルギア41が回転し、ベベルギア41に連結した入力軸14aが回転する。入力軸14aが回転することで、偏心部22,22がそれぞれ対称的に偏心運動し、各外歯歯車10,10を内歯歯車11に内接した状態で偏心及び自転運動する。このため、各ピン孔25も偏心及び自転運動するが、各ピン孔25はメタル27を含むピン26よりも大径に形成されているので、各ピン26はピン孔25に内接した状態で相対的に偏心運動して偏心成分を吸収し、各ピン26からは自転成分のみが取り出される。よって、ピン26を介して第1キャリア部材13a及び第2キャリア部材13bが同期回転し、出力部19から相手側装置に回転が伝達される。このとき、筐体3内に充填されたグリスは、オイルシール28及びオイルシール29aによって封止される。
このように、上記形態の直交軸減速機100によれば、筒状部材4が入力軸14aまたはベベルギア41を軸支しないため、筒状部材4には入力軸14aまたはベベルギア41から発生するラジアル荷重がかからない。このため、筒状部材4の本体部52の肉厚を薄くすることができ、本体部52の内径D1を大きくすることができる。また、筒状部材4と、入力軸14aまたはベベルギア41との間にベアリング等が無いため、直交軸減速機100の軸方向の大きさを小さくすることができる。
ここで、入力軸14aを支持するボールベアリング21,21には、第2減速部2のベベルギア41及びベベルピニオン42により入力軸の軸線O1に垂直方向の荷重(ラジアル荷重)が掛かるが、ボールベアリング21,21とベベルギア41との距離を短くすることで、当該ラジアル荷重を低減させることができる。上記形態では、筒状部材4が入力軸14aまたはベベルギア41を軸支しないため、ボールベアリング21,21とベベルギア41との距離を短くすることができる。
また、インロー部55の長さD5がフランジ部54の長さD6よりも長くなっているため、筒状部材4の固定部51の肉厚を厚くすることができる。このため、筒状部材4の本体部52の肉厚を薄くしても、筒状部材4の強度を保つことができ、筐体3に対して精度よく固定することができる。このため、筒状部材4の本体部52の内径D1を大きくすることができる。
また、インロー部55の長さD5が長いため、インロー部55に溝57を形成することができる。このため、溝をフランジ部54に形成した場合と比較して、フランジ部54の外径を小さくすることができる。このため、フランジ部54と結合される筐体3の大きさも小さくすることができ、直交軸減速機100のサイズを小さくすることができる。
また、筒状部材4の本体部52から固定部51に向かって内径が拡径することで、中空部の端部を大きくすることができ、例えば中空部にケーブルを通す等の作業が容易となる。なお、本実施形態では固定部51の内周(内径D3)は入力軸14aの軸線O1と同軸の筒状の面となっているが、内径は固定部に向けて徐々に傾斜したり、曲線的に大きくなっていてもよい。
また、筒状部材4の本体部52の内周(内径D1)及び外周(外径D2)は、入力軸14aの軸線O1と直交する方向から見て入力軸14aと重なる部分には段差等が設けられない円筒形状であるため、本体部52の肉厚をより薄くすることができる。このため、筒状部材4の本体部52の内径D1を大きくすることができる。
[第2実施形態]
次に、本発明の第2実施形態について図2を参照して説明する。第2実施形態では、筒状部材4の中間部53bの形状が第1実施形態とは異なる。尚、筒状部材4の中間部53bの形状を除く直交軸減速機100の構成と、動作とについては、上述の第1実施形態と同様なので、詳細な説明は省略する。
次に、本発明の第2実施形態について図2を参照して説明する。第2実施形態では、筒状部材4の中間部53bの形状が第1実施形態とは異なる。尚、筒状部材4の中間部53bの形状を除く直交軸減速機100の構成と、動作とについては、上述の第1実施形態と同様なので、詳細な説明は省略する。
筒状部材4の中間部53bの内径D3は、本体部52の内径D1よりも大きくなっている。また、筒状部材4は、本体部52から固定部51に向けて、外径が大きくなる。中間部53bの外径D4は、本体部52の外径D2よりも大きくなっている。
第2実施形態においても、第1実施形態と同様の効果を得る。また、筒状部材4の中間部53bの外径が大きくなっていることで、筒状部材4の中間部53bの強度がより強くなる。また、外径が大きくなることで、筐体3の内部の余分な空間を狭くすることができるこのため、筐体3の内部に封入された潤滑剤がベベルギア41やベベルピニオン42の歯面などの噛み合い部に導かれやすくなり、潤滑性能が高くなる。
本発明の直交軸減速機を用いたロボット200について図3、図4を用いて説明する。
ロボット200は、固定台201、第1アーム203、第2アーム204、及びハンド部205を備えている。第1アーム203は固定台201の上端に固定された直交軸減速機202と接続している。第2アーム204は第1アーム203の上端に収納した直交軸減速機(図示省略)と接続している。ハンド部205はワークを把持する把持部(図示省略)を回転可能に支持し、把持部は第2アーム204の下端に収納した直交軸減速機(図示省略)と接続している。
固定台201は略四角柱状の鉄等の材料で形成され且つ内部に電源コードA、第1アームを回転するモータ221等を収納している。固定台201の上端は電源コードAを直交軸減速機202側に配線する第1開口201aと、第1開口201a付近に設け且つモータ221の上部を直交軸減速機202側に臨ませる第2開口201bを有する。
直交軸減速機202は筐体3A下端を固定台201の上端に固定している。筐体3A下端は第1開口201aと連通する第1筐体側開口202aと、第2開口201bと連通する第2筐体側開口202bを有する。筐体3A右側部は第1筐体側開口202aから配線される電源コードA等を収納する空洞部となっている。空洞部を形成する筐体3A左端部分の上壁と下壁に筒状部材4Aの端部を固定している。第2筐体側開口202bにモータ221の回転軸を配置し、モータ221の回転軸は、直交軸減速機202のベベルピニオン42Aと接続している。直交軸減速機202の出力部19Aは第1アーム203の右側下端の側壁に接続している。従って、モータ221が回転すると、直交軸減速機202の出力部19Aが回転し、出力部19Aの回転に伴って第1アーム203が回転する。
第1アーム203は略四角柱状の鉄等の材料で形成し、内部に第2アーム204を駆動するモータ(図示省略)と直交軸減速機(図示省略)を収納している。第1アーム203に収納した直交軸減速機の出力部は第2アーム204の上端右壁に接続している。第1アーム203が収納したモータが回転すると、第1アーム203が収納した直交軸減速機の出力部が回転し、出力部の回転に伴って第2アーム204は回転する。
第2アーム204は略四角柱状の鉄等の材料で形成し、内部に把持部を駆動するモータ(図示省略)と直交軸減速機(図示省略)を収納している。第2アーム204に収納した直交軸減速機の出力部はハンド部205の把持部を回転可能に支持する。ハンド部205はワークを把持する把持部(図示省略)を開閉可能に支持している。第2アーム204が収納したモータが回転すると、第2アーム204が収納した直交軸減速機の出力部が回転し、出力部の回転に伴って把持部は回転する。
第2アーム204を回転するモータの電源コードAは固定台201の第1開口201a、第1筐体側開口202aを経由して筒状部材4Aの中空部を通過しモータに至る。把持部を回転するモータの電源コードAは固定台201から筒状部材4Aの中空部を通過した後、第1アーム203内に収納した直交軸減速機の筒状部材の中空部を通過してモータに至る。
ロボット200は、直交軸減速機を用いたので、筒状部材4Aの中空部を従来よりも大きくできるので、多数の電源コードを収納することができる。従って、本発明の直交軸減速機は図3に示した2つのアームだけではなく3つ以上のアームを備える多間接ロボットにも適用できる。
以上のように、本実施形態について説明したが、本発明は上記実施形態に限定されるものではなく、種々の変更が可能である。以下に、上記実施形態に加えうる変更の例について説明する。
例えば、本実施形態では、筒状部材4の材料はアルミ合金等としたが、材料は樹脂等であってもよい。筒状部材4は入力軸14aまたは第1減速部1を軸支しないため、筒状部材4には原則として荷重がかからない。このため、アルミ合金よりも強度が低い樹脂等の材料であってもよい。
また、例えば、筒状部材4は、本体部52から固定部51に向けて、外径と内径とのどちらも拡径していてもよい。また、本体部52から固定部51に向けて、肉厚が厚くなるように大きくなっていてもよい。
また、例えば、本発明の第1ギアはハイポイドギアであってもよく、第2ギアはハイポイドピニオンであってもよい。
100 直交軸減速機
200 ロボット
1 第1減速部
2 第2減速部
3 筐体
4 筒状部材
10 外歯歯車
11 内歯歯車
13 キャリア
14a 入力軸
19 出力部
20 インロー部
28,29a オイルシール
41 ベベルギア
42 ベベルピニオン
51 固定部
52 本体部
53a,53b 中間部
54 フランジ部
55 インロー部
57 溝
59 先端部
O1 入力軸の軸線
O3 第2軸線
A 隙間
B 入力軸と重なる範囲
D1 本体部の内径
D2 本体部の外径
D3 中間部の内径
D4 中間部の外径
D5 インロー部の長さ
D6 フランジ部の長さ
200 ロボット
1 第1減速部
2 第2減速部
3 筐体
4 筒状部材
10 外歯歯車
11 内歯歯車
13 キャリア
14a 入力軸
19 出力部
20 インロー部
28,29a オイルシール
41 ベベルギア
42 ベベルピニオン
51 固定部
52 本体部
53a,53b 中間部
54 フランジ部
55 インロー部
57 溝
59 先端部
O1 入力軸の軸線
O3 第2軸線
A 隙間
B 入力軸と重なる範囲
D1 本体部の内径
D2 本体部の外径
D3 中間部の内径
D4 中間部の外径
D5 インロー部の長さ
D6 フランジ部の長さ
Claims (7)
- 中空の入力軸を有する第1減速部と、
前記入力軸に固定される第1ギア、及び前記第1ギアと噛み合い前記入力軸の軸線と直交する第2ギアからなる第2減速部と、
前記第2減速部を内蔵する筐体と、
前記筐体に固定され、前記入力軸及び前記第1ギアを同軸で貫通する筒状部材と、
を備える直交軸減速機であって、
前記筒状部材は、前記第1減速部または前記第1ギアを軸支せず、前記筐体に片持ちで固定される
ことを特徴とする直交軸減速機。 - 前記筒状部材は、
前記筐体に固定されるフランジ部及びインロー部からなる固定部を有し、
前記入力軸の軸線と直交する方向における前記フランジ部の長さよりも、前記入力軸の軸線と平行な方向における前記インロー部の長さのほうが長い
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の直交軸減速機。 - 前記筒状部材の前記インロー部は、Oリングを配置するための溝を備えることを特徴とする請求項2に記載の直交軸減速機。
- 前記筒状部材は、前記固定部に向かって外径が拡径することを特徴とする請求項2または3に記載の直交軸減速機。
- 前記筒状部材は、前記固定部に向かって内径が拡径することを特徴とする請求項2から4のいずれか1項に記載の直交軸減速機。
- 前記筒状部材は、前記入力軸の軸線と直交する方向から見て、前記入力軸と重なる範囲には段差が設けられない円筒状であることを特徴とする請求項1から5のいずれか1項に記載の直交軸減速機。
- 間接部を有するロボットにおいて、前記間接部に前記請求項1から6のいずれか1項に記載の直交軸減速機を用いたロボット。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018053726A JP2019167966A (ja) | 2018-03-22 | 2018-03-22 | 直交軸減速機及び直交軸減速機を用いたロボット |
| JP2018-053726 | 2018-03-22 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2019181964A1 true WO2019181964A1 (ja) | 2019-09-26 |
Family
ID=67986201
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2019/011547 WO2019181964A1 (ja) | 2018-03-22 | 2019-03-19 | 直交軸減速機及び直交軸減速機を用いたロボット |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2019167966A (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2019181964A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022084176A (ja) | 2020-11-26 | 2022-06-07 | 住友重機械工業株式会社 | 歯車装置 |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6248492A (ja) * | 1985-08-29 | 1987-03-03 | フアナツク株式会社 | 工業用関節型ロボツトのケ−ブル処理構造 |
| JPH1194056A (ja) * | 1997-09-24 | 1999-04-09 | Kanzaki Kokyukoki Mfg Co Ltd | 車軸駆動ケース |
| JP2007085530A (ja) * | 2005-09-26 | 2007-04-05 | Nabtesco Corp | 中空減速機 |
| JP2013199981A (ja) * | 2012-03-23 | 2013-10-03 | Sumitomo Heavy Ind Ltd | 動力伝達装置 |
| JP2014100749A (ja) * | 2012-11-19 | 2014-06-05 | Yaskawa Electric Corp | ロボット |
| JP2016178728A (ja) * | 2015-03-18 | 2016-10-06 | 住友重機械工業株式会社 | ハイポイドギヤモータのシリーズおよびハイポイドギヤモータ |
| JP2017030138A (ja) * | 2015-07-28 | 2017-02-09 | 株式会社安川電機 | ロボットアーム |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6362686A (ja) * | 1986-08-30 | 1988-03-18 | フアナツク株式会社 | 多関節型ロボツト |
| JP5856478B2 (ja) * | 2011-12-28 | 2016-02-09 | 住友重機械工業株式会社 | 産業機械の旋回装置 |
-
2018
- 2018-03-22 JP JP2018053726A patent/JP2019167966A/ja active Pending
-
2019
- 2019-03-19 WO PCT/JP2019/011547 patent/WO2019181964A1/ja active Application Filing
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6248492A (ja) * | 1985-08-29 | 1987-03-03 | フアナツク株式会社 | 工業用関節型ロボツトのケ−ブル処理構造 |
| JPH1194056A (ja) * | 1997-09-24 | 1999-04-09 | Kanzaki Kokyukoki Mfg Co Ltd | 車軸駆動ケース |
| JP2007085530A (ja) * | 2005-09-26 | 2007-04-05 | Nabtesco Corp | 中空減速機 |
| JP2013199981A (ja) * | 2012-03-23 | 2013-10-03 | Sumitomo Heavy Ind Ltd | 動力伝達装置 |
| JP2014100749A (ja) * | 2012-11-19 | 2014-06-05 | Yaskawa Electric Corp | ロボット |
| JP2016178728A (ja) * | 2015-03-18 | 2016-10-06 | 住友重機械工業株式会社 | ハイポイドギヤモータのシリーズおよびハイポイドギヤモータ |
| JP2017030138A (ja) * | 2015-07-28 | 2017-02-09 | 株式会社安川電機 | ロボットアーム |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2019167966A (ja) | 2019-10-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5409397B2 (ja) | 歯車伝動装置 | |
| CN113547537B (zh) | 旋转轴组件和多关节机器人 | |
| CN110005759B (zh) | 偏心摆动型齿轮装置 | |
| KR200450505Y1 (ko) | 감속기 | |
| KR102123935B1 (ko) | 로봇 | |
| WO2010079683A1 (ja) | 歯車伝動装置 | |
| TWI656287B (zh) | Planetary gear reducer | |
| JP3186812U (ja) | 変速伝動ベアリング | |
| EP2479456A1 (en) | Eccentric oscillation gear device and method for producing eccentric oscillation gear device | |
| JP2023184669A (ja) | 歯車ユニット | |
| WO2019181964A1 (ja) | 直交軸減速機及び直交軸減速機を用いたロボット | |
| JP2010014177A (ja) | 偏心揺動型歯車伝動装置 | |
| JP2010084842A (ja) | 回転駆動装置、ロボットの関節構造及びロボットアーム | |
| TW202016450A (zh) | 撓曲嚙合式齒輪裝置 | |
| WO2018123895A1 (ja) | 減速装置、関節装置及びロボットアーム構造 | |
| JP5989148B2 (ja) | 減速機、及びこれを具えた直交型ギアモータ | |
| JP2020029914A (ja) | ハイポサイクロイド減速機 | |
| JP5130184B2 (ja) | 回転検出器付き減速装置 | |
| WO2019181965A1 (ja) | 減速機及び減速機シリーズの製造方法 | |
| JP6233805B2 (ja) | トラクション動力伝達装置 | |
| JP2016156436A (ja) | 減速装置 | |
| KR102345641B1 (ko) | 마찰 파동 감속기 | |
| JP2018009638A (ja) | 遊星歯車装置 | |
| JP2008208866A (ja) | 波動歯車減速機及び伝達比可変操舵装置 | |
| JP2009293714A (ja) | 歯車伝動装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 19771082 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 19771082 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |