WO2017018071A1 - セグメント - Google Patents
セグメント Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2017018071A1 WO2017018071A1 PCT/JP2016/067174 JP2016067174W WO2017018071A1 WO 2017018071 A1 WO2017018071 A1 WO 2017018071A1 JP 2016067174 W JP2016067174 W JP 2016067174W WO 2017018071 A1 WO2017018071 A1 WO 2017018071A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- piece
- segment
- ring
- concrete
- plate
- Prior art date
Links
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 37
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 claims description 37
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 20
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 abstract description 17
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 abstract description 3
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 abstract description 3
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 abstract description 3
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000003014 reinforcing effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000009412 basement excavation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000002787 reinforcement Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004873 anchoring Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005266 casting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 1
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E02—HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING; FOUNDATIONS; SOIL SHIFTING
- E02D—FOUNDATIONS; EXCAVATIONS; EMBANKMENTS; UNDERGROUND OR UNDERWATER STRUCTURES
- E02D23/00—Caissons; Construction or placing of caissons
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E21—EARTH OR ROCK DRILLING; MINING
- E21D—SHAFTS; TUNNELS; GALLERIES; LARGE UNDERGROUND CHAMBERS
- E21D11/00—Lining tunnels, galleries or other underground cavities, e.g. large underground chambers; Linings therefor; Making such linings in situ, e.g. by assembling
- E21D11/04—Lining with building materials
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E21—EARTH OR ROCK DRILLING; MINING
- E21D—SHAFTS; TUNNELS; GALLERIES; LARGE UNDERGROUND CHAMBERS
- E21D5/00—Lining shafts; Linings therefor
- E21D5/06—Lining shafts; Linings therefor with iron or steel
- E21D5/10—Lining shafts; Linings therefor with iron or steel in the form of tubbing or of rings composed of profile elements
Definitions
- This invention relates to the segment which comprises a sunk structure.
- a ring body is constructed by connecting a plurality of segments, and a plurality of ring bodies are overlapped in the axial direction to be submerged in the ground.
- the sinking body is known.
- the segment constituting the sinking body includes a curved plate that becomes the wall surface of the sinking structure, a main girder provided at the upper end and lower end of the plate, and a joint provided at the left end and right end of the plate
- the segment which constructs the ring body provided with is known.
- the plate, the main beam, and the joint are all formed in a plate shape (see, for example, Patent Document 1).
- a sinking body in which a press-fit mold frame and a reinforcing bar as an inner frame and a steel structure as an outer frame are arranged from the inside is known. Concrete is driven into the space where the reinforcing bars are arranged between the press-fitting mold and the double frame of the steel structure. Only the steel structure is integrated with the reinforcing bar (see, for example, Patent Document 2).
- an object of the present invention is to provide a segment that can cope with a construction with a large cross section and can suppress a reduction in construction efficiency.
- the present invention is a segment constituting a subsidence structure embedded in the ground, wherein an outer piece forming an outer wall of the subsidence structure and an inner wall of the subsidence structure are formed.
- the piece formed of the concrete is provided with a connecting member for connecting the connecting piece.
- the connecting member is preferably embedded in the concrete in a state where a part of the connecting member is exposed between the outer piece and the inner piece.
- the connecting piece is connected to a portion exposed between the outer piece and the inner piece in the connecting member.
- the connecting member is provided with a distribution bar surrounding the connecting member.
- the connecting member is a steel material embedded in the concrete in a state where a part of the connecting member is exposed between the outer piece and the inner piece, a connecting piece that is provided in the steel material and connects the connecting piece, It is preferable to provide.
- the connecting piece is provided at both ends of the outer piece and the inner piece in the axial direction of the segment.
- the inner piece is made of concrete.
- the outer piece includes a plate forming a wall surface, main girders provided at the upper and lower ends of the plate, and ribs provided between the main girders, and the connecting piece is connected to the ribs. It is preferable that
- FIG. 4 is a sectional view of a segment on the IV-IV line in FIG. 2.
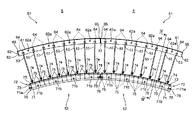
- FIG. 1 is a schematic front view of a part of a submerged structure 100 submerged in the ground, showing an example in which the subsidence structure 100 is applied to a shaft.
- FIG. 2 is a plan view partially showing two of the plurality of segments 5 constituting the double ring 44.
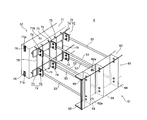
- FIG. 3 is a partial perspective view of the segment 5 as viewed obliquely from the outside in the radial direction toward the inside, and the outer piece 51 is depicted so as to be seen through.
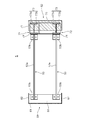
- 4 is a cross-sectional view of the segment 5 shown in FIG. 2 on the IV-IV line.
- the subsidence structure 100 is provided at an excavation start point or an intermediate point of a tunnel T built in the ground by a shield method or the like, and a space S inside the subsidence structure 100 is a shield machine. It becomes a conveyance path and a vent.
- the subsidence structure 100 includes a subsidence body 1 submerged in the ground, a bottom plate part 2 provided at the bottom inside the subsidence body 1, a subsidence anchor 3 used when subsiding the subsidence body 1 into the ground, It has.
- the sinking body 1 is constructed in a cylindrical shape, and is set in the ground so that its axis is along the vertical direction.
- the sinking body 1 is assembled by connecting a plurality of ring bodies 4 having an annular shape in plan view in the axial direction.
- the ring body 4 constituting the set-up body 1 is configured by stacking a blade ring 41, a guide ring 42, a workbench ring 43, and a double ring 44 in the vertical direction.
- the cutting edge ring 41 is a ring body provided at the lowermost end of the settling body 1 and has a cutting edge at the lower end thereof.
- the blade ring 41 has the tooth tip (tip) on the outside.
- a plurality of guide rings 42 are connected to the upper end of the blade ring 41 to guide the sinking of the sinking body 1.
- the work table ring 43 is connected to the upper end of the guide ring 42.
- the worktable ring 43 is formed such that the upper end surface is larger than the lower end surface, and the upper end surface is formed so as to project inside the worktable ring 43.
- the upper end surface of the work table ring 43 is formed to have a size that allows at least the double ring 44 to be placed thereon.
- the double ring 44 is connected to the upper end of the work table ring 43. Above the work table ring 43, a double ring 44 is provided in a plurality of stages.
- the guide ring 42 provided between the blade ring 41 and the work table ring 43 is formed so that the width of the end surface in the axial direction gradually increases from the blade ring 41 toward the work table ring 43. It is more preferable. That is, it is preferable that the upper guide ring 42 is formed such that the width of the upper end surface thereof is closer to the width of the work table ring 43.
- the segments of the upper ring 42 and the segments of the lower ring 41 are shifted in the circumferential direction of the rings 41 and 42 and arranged in a staggered manner. This arrangement also applies to the ring 42 and ring 43, the ring 43 and ring 44, and the rings 44 and 44.
- the ring body 4 is formed by connecting and assembling the segments 5 along the wall surface direction.
- the double ring 44 of the ring body 4 has a plurality of segments 5 connected to each other, and is finally formed into an annular shape.
- FIG. 2 shows a state where two segments 5 are connected.
- the segment 5 of the double ring 44 includes an outer piece 51 that forms the outer wall of the sinking structure 100, an inner piece 52 that forms the inner wall of the sinking structure 100, and a connecting piece that connects the outer piece 51 and the inner piece 52. 53.
- the outer piece 51 is erected on a rectangular plate 61 that is curved and formed in an arc shape that forms the outer wall surface of the double ring 44, and an outer edge along the curvature of the plate 61.
- ribs 64 provided on the inner surface side of the plate 61, and connecting members 65 provided at both ends in the circumferential direction of the plate 61. As shown in FIG.
- the outer piece 51 is installed above the blade ring 41. Specifically, the outer peripheral surfaces of the blade ring 41 and the outer piece 51 are on the same diameter of the sinking body 1. As a result, when the ring body 4 is submerged in the ground, a force is applied above the outer piece 51, so that the pressing force for substituting the ring body 4 is applied to the blade ring 41 via the outer piece 51. It can be transmitted efficiently.
- the material of the outer piece 51 is only required to have resistance against a load when buried in the ground, and is particularly preferably made of steel.
- the main beam 62 and the ribs 64 may both be joined to the plate 61 by welding, or a part thereof may be formed integrally with the plate 61.
- the joint 63 may be joined to the main beam 62 by welding, or a part thereof may be formed integrally with the main beam 62.
- the plate 61 forms the outer wall surface of the double ring 44 and is joined to the end face of the main girder 62 on the outer side in the radial direction of the double ring 44 so as to connect the two main girders 62.
- the main girder 62 is erected on the upper end and lower end of the plate 61.
- Each main girder 62 is formed with a plurality of through holes 62a through which bolts are inserted at predetermined intervals along the longitudinal (extending) direction.
- the through holes 62a of the two main girders 62 are formed so that the through holes 62a penetrate each other along the same axis parallel to the axis of the double ring 44, and the double rings 44 are stacked vertically.
- the through holes 62a of the main girders 62 are formed to face each other.
- the joint 63 is erected at one end on the left side of the main girder 62 between both ends of the two main girders 62.
- the joint 63 on the left side of the adjacent segment 5 is connected to the other end on the right side of the main girder 62 when the segments 5 are connected, so the joint 63 is not provided. Good.
- the rib 64 having both the function of increasing the rigidity of the outer piece 51 and the function of connecting the connecting piece 53 described later is the bending direction (longitudinal direction) of the plate 61.
- the ribs 64 are connected to the inner peripheral surface of the plate 61 by welding or the like at equal intervals in the circumferential direction from the central axis of each through hole 62a of the main girder 62.
- the rib 64 extends between the upper and lower main beams 62, 62 along the axial direction of the segment 5, but is provided with a connecting piece 53 described later. It may be provided corresponding to the position.
- the “axial direction of the segment 5” is the extending direction of the axial line passing through the center of the ring when the segments 5 are connected to form a double ring 44.
- the cross-sectional shape of the rib 64 orthogonal to the axial direction of the segment 5 is substantially L-shaped, the cross-sectional shape is limited as long as the rigidity of the segment 5 is increased and the connection with the connection piece 53 is possible. Not.
- the rib 64 is formed with a through hole for enabling connection with a connection piece 53 described later.
- Bolts are inserted into the through holes on the rib 64 side and the through holes on the connection piece 53 side, and the nuts are fastened to the inserted bolts, whereby the connection piece 53 and the ribs 64 are fastened together.
- the coupling tool 65 is provided at both ends in the circumferential direction of the plate 61 and extends over the width direction (short direction) of the plate 61.
- One end of the coupler 65 is joined to the plate 61 by welding or the like, and the other end is formed in a bowl shape.
- the segments 5 are connected to each other by engaging the connecting tool 65 and the tip of the plates 61 of the adjacent segments 5.
- the segment 5 is connected to the segment 5 adjacent in the circumferential direction by connecting the connector 65 to the flanged other end of the connector 65 of the segment 5 adjacent in the circumferential direction at the other end of the flange shape. Can do.
- the coupling tool 65 may be joined to the plate 61 as a separate member by welding, or may be formed integrally with the plate 61.
- the inner piece 52 includes a segment body 71 having a rectangular shape in plan view, which is curved in an arc shape, which forms the body of the inner piece 52, and a connecting member 72 provided in the segment body 71.
- the segment body 71 is made of concrete.
- the segment main body 71 accommodates a connector 76 described later on both end surfaces on the upper and lower sides in the axial direction passing through the center of the ring when the segments 5 are connected to form a double ring 44.
- a recess 71a is provided.
- the segment body 71 has a plurality of through-holes 71 b that penetrate in the axial direction of the double ring 44 and are arranged in parallel to each other at equal intervals.
- penetrate in the axial direction means that the through-hole 71 b extends from the upper end surface of the segment main body 71 to the lower end surface of the segment main body 71 through the web 73 b of the steel material 73 to be described later. It means to penetrate along the same parallel axis.
- a part of the connecting member 72 is embedded in the segment body 71 and the remaining part is exposed so as to protrude between the outer piece 51 and the inner piece 52, and the connecting piece 53 is connected to the connecting member 72. It is connected to the exposed part. More specifically, the connecting member 72 is exposed to the segment main body 71, that is, the portion embedded in the concrete, and not embedded, and protrudes into the space between the outer piece 51 and the inner piece 52.
- Steel member 73 having a portion (H-shaped steel in the present embodiment, see FIG. 4) and a steel connecting piece 74 provided on the exposed portion of steel member 73 and connected by connecting piece 53 described later. And.
- the steel material 73 is provided at two locations near the upper end and near the lower end in the axial direction of the segment 5, and extends in the circumferential direction of the segment body 71.
- the steel material 73 has two flange portions 73a and 73a and a web 73b that connects the two flange portions 73a and 73a.
- One flange part 73a and a part of the web 73b of the steel material 73 are embedded in the segment body 71, that is, in the concrete, and the other flange part 73a and the remaining part of the web 73b are connected to the outer piece 51 from the segment body 71. It protrudes toward and is exposed.
- the connecting piece 74 is spaced outside the flange portion 73 a where the upper and lower steel members 73 are exposed at a predetermined interval along the bending direction (longitudinal direction) of the segment body 71. It is erected on the surface facing the piece 51. Specifically, the connecting piece 74 is connected to the flange portion 73a by welding or the like. A through hole is formed in the connecting piece 74 for connection with a connecting piece 53 described later, and a bolt is inserted into the through hole on the connecting piece 74 side and the through hole on the connecting piece 53 side. The connecting piece 53 and the connecting piece 74 are fastened to each other by tightening a nut on the bolt.
- the two steel materials 73 and 73 are surrounded by a steel distribution bar 75. More specifically, the distribution bar 75 is a surface facing the outer piece 51 of the flange portions 73a and 73a exposed from the segment body 71 of the steel materials 73 and 73 provided at the upper end portion and the lower end portion, respectively.
- the flange portions 73a and 73a embedded in the segment main body 71 are wound around two steel materials 73 and 73 so as to be in contact with the surface facing the inner peripheral surface of the inner piece 52.
- the portion of the distribution bar 75 that extends along the axial direction of the segment 5 between the upper steel member 73 and the lower steel member 73 and that is exposed from the segment main body 71 and in the segment main body 71.
- the portions to be embedded are connected to each other at a predetermined location so as to fulfill a higher reinforcing function.
- connectors 76 and 76 are provided along a predetermined length in the axial direction of the segment 5. More specifically, the upper connecting member 76 extends from the upper end surface of the segment main body 71 to the surface facing the upper side of the web 73b of the upper steel material 73 on the upper side of the segment main body 71. The connector 76 extends below the segment body 71 from the lower end surface of the segment body 71 to a surface facing the lower side of the web 73b of the lower steel material 73.
- One end of the connector 76 is embedded in the segment main body 71, that is, in the concrete in the recess 71a, and the other end is exposed from the segment main body 71 and is formed in a bowl shape.
- the segments 5 are connected to each other by engaging the connecting tool 76 provided on the segment main body 71 of the adjacent segment 5 with the tips. That is, the segment 5 is connected to the segment 5 adjacent in the circumferential direction by connecting the connector 76 to the flanged other end of the connector 76 of the segment 5 adjacent in the circumferential direction at the other end of the flange shape. be able to.
- the plurality of connecting pieces 53 are provided between the outer piece 51 and the inner piece 52 to connect the two pieces 51, 52, and thereby the shear strength of the segment 5.
- the connecting piece 53 has one end connected to the rib 64 of the outer piece 51 and the other end connected to the connecting member 72 and the connecting piece 74 of the inner piece 52 to connect the outer piece 51 and the inner piece 52. is doing.
- the connecting pieces 53 are provided at the upper end portion and the lower end portion of the segment 5 in the axial direction of the segment 5, respectively.
- the connecting piece 53 includes a steel bar 53a and a steel rectangular plate 53b provided at both ends of the bar 53a.
- the plate material 53b is formed with a through hole that is concentric with the through hole formed in the rib 64 and the connecting piece 74 when connected.
- the plate member 53b, the rib 64, and the connecting piece 74 are connected to each other by inserting bolts into the concentrically aligned through holes and tightening the nuts to the bolts protruding to the opposite side of the insertion side. ing. That is, the connecting piece 53 connects the outer piece 51 and the inner piece 52 by connecting the plate member 53b to the rib 64 of the outer piece 51 and the connecting piece 74 of the inner piece 52 through bolts and nuts. Can do.
- the bottom plate part 2 serves as a foundation of the subsidence structure 100 and prevents underground water from flowing into the subsidence body 1.
- the bottom board part 2 is constructed by, for example, underwater concrete.
- the bottom board part 2 is constructed so that the upper surface thereof is substantially along the horizontal plane.
- the sinking anchor 3 takes a reaction force on the ground when the sinking body 1 is pushed into the ground by applying force to the ring body 4 from above the uppermost ring body 4 in the step of sinking the sinking body 1 into the ground. is there.
- the anchoring anchor 3 is embedded in and fixed to the ground excavated outside and below the settling position of the sinking body 1, and is connected to the fixing part 31. It has a connecting portion 32 that extends to the ground surface along the wall surface and is connected to a stationary portion (such as a base portion) of a sinking device (not shown) that pushes the ring body 4.
- the outer piece 51 and the inner piece 52 are connected by the connecting piece 53, so Also during construction, the outer piece 51 and the inner piece 52 can be separately created and transported to the construction site, and can be connected by the connecting piece 53 at the construction site to form the large segment 5. Thereby, it can respond to the construction in a large section and can suppress the fall of construction efficiency.
- the connecting piece 53 can be used as a shear reinforcement for the segment 5 and can prevent the outer piece 51 and the inner piece 52 from being displaced or inclined from each other.
- the inner piece 52 that faces the space S inside the settling structure 100 is formed of concrete, it is necessary to apply the antirust coating necessary for forming the inner piece 52 of steel to the inner piece 52. Therefore, the work load when creating the segment 5 can be greatly reduced.
- the inner piece 52 formed of concrete is provided with a connecting member 72 having a steel material 73 and a connecting piece 74 for connecting the connecting piece 53, so the inner piece 52, more specifically, While improving the rigidity of the segment main body 71 which consists of concrete, the connection of the connection piece 53 and the inner piece 52 can be made easy.
- the connecting piece 53 when the connecting piece 53 is provided at both ends of the segment 5 in the axial direction thereof, that is, on the upper side and the lower side, respectively, concrete is placed in the space between the outer piece 51 and the inner piece 52. Even if it exists, the relative movement of the outer piece 51 and the inner piece 52 can be suppressed, and the outer piece 51 and the inner piece 52 can always be maintained in the initial positional relationship. Further, since the connecting piece 53 includes the bar 53a and the plate members 53b provided at both ends thereof, the space between the outer piece 51 and the inner piece 52 is not completely partitioned, and the concrete casting is performed. It is possible to spread the concrete over the entire space between the outer piece 51 and the inner piece 52 just by placing the concrete from one place at the time of installation, and also to reduce the weight of the segment 5.
- the rigidity of the segment body 71 can be further increased by having the distribution bars 75 surrounding the steel material 73.
- the present invention is not limited to the above embodiment.
- the double ring 44 is not limited to a circular shape in plan view, and may be formed in an oval shape in plan view (oval shape) or a polygonal shape in plan view.
- the segment 5 may be a segment formed of concrete in the same manner as the inner piece 52 for the outer piece 51. Even when the outer piece 51 is made of concrete, after the settling body 1 is set, the anti-lifting anchor that prevents the settling body 1 from being lifted can be inserted into the through hole 71b.
- the steel 73 can increase the rigidity of the segment main body 71, and partially protrudes from the segment main body 71 into the space between the outer piece 51 and the inner piece 52 so that the connecting piece 53 can be connected. If it is, it is not restricted to H-section steel, You may have another cross-sectional shape. As long as the steel material 73 provides the segment body 71 with a predetermined rigidity, a plurality of steel materials may be provided at predetermined intervals.
- connecting piece 74 of the connecting member 72 is not limited to the case where it is provided on the steel material 73, and may be connected to the distribution bar 75 by welding or the like.
- the connecting piece 53 is not limited to the bar as described above, and may be a steel plate or the like along the axial direction of the segment 5.
- connection between the connection piece 53 and the rib 64 and the connection between the connection piece 53 and the connection piece 74 are not limited to a connection method using bolts and nuts as long as they are connected to each other.
- the connector 76 may be provided across the segment body 71 along the axial direction of the segment 5.
- the recess 71 a is provided along the axial direction of the segment 5 across the end surface on the circumferential side of the segment body 71.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mining & Mineral Resources (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- General Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Structural Engineering (AREA)
- Civil Engineering (AREA)
- Architecture (AREA)
- Geochemistry & Mineralogy (AREA)
- Geology (AREA)
- Paleontology (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Underground Structures, Protecting, Testing And Restoring Foundations (AREA)
- Lining And Supports For Tunnels (AREA)
Abstract
大断面での施工に対応することができ、施工効率の低下を抑制すること。 地中に埋設される沈設構造物を構成するセグメント(5)であって、沈設構造物の外壁を形成する外側ピース(51)と、沈設構造物の内壁を形成する内側ピース(52)と、外側ピース(51)と内側ピース(52)とを連結する連結ピース(53)と、を備え、外側ピース(51)及び内側ピース(52)の少なくとも一方がコンクリートにより形成されている。
Description
本発明は、沈設構造物を構成するセグメントに関する。
立坑や橋脚補強等の沈設構造物を地中に構築するために、複数のセグメントを連結してリング体を構築し、リング体をその軸線方向に重ねて複数連結した、地中に沈設される沈設体が知られている。
沈設体を地中に沈設する際には、施工場所の地表面上に刃口リングを設け、刃口リングの内側の地盤を掘削した後、刃口リングの上端を沈設装置によって地盤に向けて押圧し、刃口リングを地中に沈設していく。ある程度の深さまで刃口リングを沈設させた後、刃口リングの上端に別のリング体を連結し、リング体の内側を掘削し、リング体の上端を沈設装置によって地盤に向けて押圧し、リング体を地中に沈設していく。このように、複数のリング体の連結による沈設体の組み立てと、地盤の掘削及び沈設体の押圧とを順に繰り返すことで、沈設体を地中に沈設することができる。
沈設体を構成するセグメントとしては、沈設構造物の壁面となる湾曲形成されたプレートと、プレートの上端部及び下端部に設けられた主桁と、プレートの左端部及び右端部に設けられた継手とを備えるリング体を構築するセグメントが公知になっている。プレート、主桁及び継手は、全て板状に形成されている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。
また、沈設体として、内側から内枠として圧入型枠、鉄筋、外枠としてスチール構造体が配置された沈設体が公知になっている。圧入型枠、スチール構造体の二重枠の間の鉄筋が配置されている空間には、コンクリートが打ち込まれている。スチール構造体だけが、鉄筋と一体になっている(例えば、特許文献2参照)。
近年、大断面での沈設構造物の施工の需要が増加している。大断面の施工になると、沈設構造物を構成するセグメントも必要な断面性能を確保するために大きくする必要がある。
しかし、トラックやトレーラー等の輸送機器には、積載可能な大きさに制限があるため、従来の構造のセグメントを単に大きくするだけでは、セグメントを作成した後に施工現場まで運搬することが困難である。また、施工現場で一から沈設構造物を作成することは施工効率の低下を招き、好ましくない。
そこで、本発明は、上記問題に鑑みてなされたものであり、大断面での施工に対応することができ、施工効率の低下を抑制することができるセグメントを提供することを目的とする。
上記課題を解決するため、本発明は、地中に埋設される沈設構造物を構成するセグメントであって、前記沈設構造物の外壁を形成する外側ピースと、前記沈設構造物の内壁を形成する内側ピースと、前記外側ピースと前記内側ピースとを連結する連結ピースと、を備え、前記外側ピース及び前記内側ピースの少なくとも一方がコンクリートにより形成されていることを特徴とする。
前記コンクリートにより形成されているピースには、前記連結ピースを連結する連結部材が設けられていることが好ましい。
前記連結部材は、一部が前記外側ピースと前記内側ピースとの間に露出された状態で前記コンクリート内に埋設されていることが好ましい。
前記連結ピースは、前記連結部材における前記外側ピースと前記内側ピースとの間に露出した部分に連結されていることが好ましい。
前記連結部材に、該連結部材を取り囲む配力筋が設けられていることが好ましい。
前記連結部材は、一部が前記外側ピースと前記内側ピースとの間に露出された状態で前記コンクリート内に埋設される鋼材と、前記鋼材に設けられ、前記連結ピースを連結する連結片と、を備えることが好ましい。
前記連結ピースは、前記外側ピース及び前記内側ピースの、前記セグメントの軸線方向における両端部にそれぞれ設けられていることが好ましい。
前記内側ピースがコンクリートにより形成されていることが好ましい。
前記外側ピースは、壁面を形成するプレートと、前記プレートの上端部及び下端部に設けられた主桁と、これらの主桁間に設けられたリブとを備え、前記リブに前記連結ピースが連結されていることが好ましい。
本発明によれば、大断面での施工に対応することができ、施工効率の低下を抑制することができる。
本発明の好ましい実施の形態について、図面を参照しながら説明する。なお、以下に示す実施の形態は一つの例示であり、本発明の範囲において、種々の形態をとり得る。
図1は、地中に沈設された沈設構造物100の一部を断面視した概略正面図であり、沈設構造物100を立坑に適用した例を示している。図2は、二重リング44を構成する複数のセグメント5のうち部分的に2つを示す平面図である。図3は、セグメント5をその径方向外側から内側に向かって斜めに見た部分斜視図であり、外側ピース51を透視可能に描いた。図4は、図2に示すセグメント5のIV-IV線上における断面図である。
[沈設構造物の構成]
図1に示すように、沈設構造物100は、シールド工法等によって地中に構築されるトンネルTの掘削開始地点や中間地点等に設けられ、沈設構造物100の内側の空間Sがシールドマシンの搬送路や換気口となる。
沈設構造物100は、地中に沈設された沈設体1と、沈設体1の内側の底部に設けられた底盤部2と、沈設体1を地中に沈設する際に用いる沈設アンカー3と、を備えている。
図1に示すように、沈設構造物100は、シールド工法等によって地中に構築されるトンネルTの掘削開始地点や中間地点等に設けられ、沈設構造物100の内側の空間Sがシールドマシンの搬送路や換気口となる。
沈設構造物100は、地中に沈設された沈設体1と、沈設体1の内側の底部に設けられた底盤部2と、沈設体1を地中に沈設する際に用いる沈設アンカー3と、を備えている。
<沈設体>
図1に示すように、沈設体1は、円筒状に構築されており、その軸線が鉛直方向に沿うように地中に沈設される。沈設体1は、平面視円環状のリング体4をその軸線方向に複数連結して組み立てたものである。沈設体1を構成するリング体4は、刃口リング41と、ガイドリング42と、作業台リング43と、二重リング44とが上下方向に積み上げられて構成されている。
図1に示すように、沈設体1は、円筒状に構築されており、その軸線が鉛直方向に沿うように地中に沈設される。沈設体1は、平面視円環状のリング体4をその軸線方向に複数連結して組み立てたものである。沈設体1を構成するリング体4は、刃口リング41と、ガイドリング42と、作業台リング43と、二重リング44とが上下方向に積み上げられて構成されている。
刃口リング41は、沈設体1の最下端に設けられるリング体であり、その下端に刃口を有している。刃口リング41は、その歯先(先端)を外側に有している。ガイドリング42は、刃口リング41の上端に複数連結されて、沈設体1の沈設をガイドする。作業台リング43は、ガイドリング42の上端に連結されている。作業台リング43は、上端面が下端面よりも大きくなるように形成されており、上端面が作業台リング43の内側に張り出すように形成されている。作業台リング43の上端面は、少なくとも二重リング44が載置できる程度の大きさに形成されている。二重リング44は、作業台リング43の上端に連結されている。作業台リング43の上方には、二重リング44が複数段に亘って設けられている。
なお、刃口リング41と作業台リング43との間に設けられているガイドリング42は、刃口リング41から作業台リング43に向かうにつれて徐々に軸線方向の端面の幅が広がるように形成されているとより好ましい。すなわち、上方のガイドリング42になるほどその上端面の幅が作業台リング43の幅に近づくように形成されていることが好ましい。
上下に隣接するリング41,42において、上方のリング42の各セグメントと下方のリング41の各セグメントとは、互いにリング41,42の周方向にずれて千鳥状に配置されている。なお、この配置は、リング42とリング43、リング43とリング44、及びリング44,44においても同様である。リング体4は、セグメント5をその壁面方向に沿って連結して組み立てることにより形成される。
<二重リングのセグメント>
リング体4のうち二重リング44は複数のセグメント5が連結されており、最終的に環状に形成される。図2は、2つのセグメント5が連結された状態を示している。
二重リング44のセグメント5は、沈設構造物100の外壁を形成する外側ピース51と、沈設構造物100の内壁を形成する内側ピース52と、外側ピース51と内側ピース52とを連結する連結ピース53と、を備えている。
リング体4のうち二重リング44は複数のセグメント5が連結されており、最終的に環状に形成される。図2は、2つのセグメント5が連結された状態を示している。
二重リング44のセグメント5は、沈設構造物100の外壁を形成する外側ピース51と、沈設構造物100の内壁を形成する内側ピース52と、外側ピース51と内側ピース52とを連結する連結ピース53と、を備えている。
(外側ピース)
図2及び図3に示すように、外側ピース51は、二重リング44の外壁面をなす円弧状に湾曲形成された矩形状のプレート61と、プレート61の湾曲に沿った外縁に立設された2つの主桁62と、2つの主桁62の両端部間を結ぶように主桁62の長手方向における一端に立設された継手63と、2つの主桁62間を結ぶように継手63に平行にプレート61の内面側に設けられたリブ64と、プレート61の周方向における両端に設けられた連結具65と、を備えている。
図1に示すように、外側ピース51は、刃口リング41の上方に設置されている。具体的には、刃口リング41及び外側ピース51の外周面は、沈設体1の同一径上にある。これにより、リング体4を地中に沈設する際に、外側ピース51の上方に力を加えるので、リング体4を沈設させようとする押圧力を、外側ピース51を介して刃口リング41に効率よく伝達することができる。
外側ピース51の材質は、地中への埋設時の荷重に対する耐性を備えていればよく、特に鋼製であることが好ましい。
図2及び図3に示すように、外側ピース51は、二重リング44の外壁面をなす円弧状に湾曲形成された矩形状のプレート61と、プレート61の湾曲に沿った外縁に立設された2つの主桁62と、2つの主桁62の両端部間を結ぶように主桁62の長手方向における一端に立設された継手63と、2つの主桁62間を結ぶように継手63に平行にプレート61の内面側に設けられたリブ64と、プレート61の周方向における両端に設けられた連結具65と、を備えている。
図1に示すように、外側ピース51は、刃口リング41の上方に設置されている。具体的には、刃口リング41及び外側ピース51の外周面は、沈設体1の同一径上にある。これにより、リング体4を地中に沈設する際に、外側ピース51の上方に力を加えるので、リング体4を沈設させようとする押圧力を、外側ピース51を介して刃口リング41に効率よく伝達することができる。
外側ピース51の材質は、地中への埋設時の荷重に対する耐性を備えていればよく、特に鋼製であることが好ましい。
なお、主桁62及びリブ64は、いずれもプレート61に溶接によって接合されていてもよいし、一部がプレート61と一体に形成されていてもよい。また、継手63は、主桁62に溶接によって接合されていてもよいし、一部が主桁62と一体に形成されていてもよい。
プレート61は二重リング44の外壁面をなし、2つの主桁62の間を結ぶように、かつ二重リング44の径方向外側の、主桁62の端面に接合されている。
主桁62は、プレート61の上端部及び下端部に立設されている。各主桁62には、その長手(延在)方向に沿って所定の間隔をあけて、ボルトを挿通する複数の貫通孔62aが形成されている。ここで、両主桁62の貫通孔62aは、互いに貫通孔62aが二重リング44の軸線に平行な同一軸線上に沿って貫通するように形成されており、二重リング44を上下に積み重ねた際に、各主桁62の各貫通孔62a同士が対向するように形成されている。二重リング44同士を連結する際には、上下に隣接する二重リング44の主桁62同士を突き合わせ、双方の貫通孔62aにボルトを挿通してナットで締め付けることにより、隣接する二重リング44同士を連結し、沈設体1を構築することができる。
図2に示すように、継手63は、2つの主桁62の両端部の間において主桁62の左側の一端に立設されている。主桁62の右側の他端には、セグメント5同士を連結した際に、隣接するセグメント5の左側の継手63が接続するので継手63は設けられていないが、継手63が設けられていてもよい。
図2及び図3に示すように、外側ピース51の剛性を高める機能、及び後述する連結ピース53を連結する機能の2つの機能を兼備しているリブ64が、プレート61の湾曲方向(長手方向)に沿って所定の間隔をあけて、継手63に対して平行にプレート61の内周面に立設されている。具体的には、リブ64は主桁62の各貫通孔62aの中心軸線から周方向に等間隔あけて、プレート61の内周面に溶接等により連結されている。
図3に示すように、リブ64は、セグメント5の軸線方向に沿って、上側及び下側の主桁62,62の間に延在しているが、後述する連結ピース53が設けられている位置に対応して設けられていてもよい。
なお、ここで「セグメント5の軸線方向」とは、セグメント5を連結して二重リング44にした際の環の中心を通る軸線の延在方向のことである。
図3に示すように、リブ64は、セグメント5の軸線方向に沿って、上側及び下側の主桁62,62の間に延在しているが、後述する連結ピース53が設けられている位置に対応して設けられていてもよい。
なお、ここで「セグメント5の軸線方向」とは、セグメント5を連結して二重リング44にした際の環の中心を通る軸線の延在方向のことである。
なお、セグメント5の軸線方向に直交するリブ64の横断面形状は略L字形であるが、セグメント5の剛性を高め、連結ピース53との連結を可能にするのであれば、断面形状については限定されない。
リブ64には、後述する連結ピース53との連結を可能にするための貫通孔が形成されている。リブ64側の貫通孔と、連結ピース53側の貫通孔とにボルトが挿通されて、挿通されたボルトにナットを締め付けることにより、連結ピース53とリブ64とが互いに締結される。
連結具65は、プレート61の周方向における両端に設けられていて、プレート61の幅方向(短手方向)に亘って延在している。連結具65の一端はプレート61に溶接等によって接合されており、他端は鉤状に形成されている。セグメント5同士の連結は、隣接するセグメント5のプレート61における連結具65と先端部同士を噛み合わせて行う。つまりセグメント5は、連結具65を鉤状の他端において、周方向に隣接するセグメント5の連結具65の鉤状の他端と連結させることで、周方向に隣接するセグメント5に連結することができる。
なお、連結具65は別部材としてプレート61に溶接によって接合されていてもよいし、プレート61に一体に形成されていてもよい。
(内側ピース)
図2及び図3に示すように、内側ピース52は、内側ピース52の本体をなす円弧状に湾曲形成された平面視矩形状のセグメント本体71と、セグメント本体71に設けられている連結部材72と、を備えている。
セグメント本体71はコンクリートより形成されている。セグメント本体71は、セグメント5を連結して二重リング44にした際の環の中心を通る軸線方向において上側及び下側で周方向側の両端面に、後述する連結具76を収容するための凹部71aを備えている。また、セグメント本体71は、二重リング44の軸線方向に貫通するとともに互いに平行に等間隔に配置された複数の貫通孔71bを有する。ここで「軸線方向に貫通する」とは、貫通孔71bが、セグメント本体71の上端面から、後述する鋼材73のウェブ73bを貫通してセグメント本体71の下端面にまで、セグメント5の軸線に平行な同一軸線上に沿って貫通していることを意味する。
図2及び図3に示すように、内側ピース52は、内側ピース52の本体をなす円弧状に湾曲形成された平面視矩形状のセグメント本体71と、セグメント本体71に設けられている連結部材72と、を備えている。
セグメント本体71はコンクリートより形成されている。セグメント本体71は、セグメント5を連結して二重リング44にした際の環の中心を通る軸線方向において上側及び下側で周方向側の両端面に、後述する連結具76を収容するための凹部71aを備えている。また、セグメント本体71は、二重リング44の軸線方向に貫通するとともに互いに平行に等間隔に配置された複数の貫通孔71bを有する。ここで「軸線方向に貫通する」とは、貫通孔71bが、セグメント本体71の上端面から、後述する鋼材73のウェブ73bを貫通してセグメント本体71の下端面にまで、セグメント5の軸線に平行な同一軸線上に沿って貫通していることを意味する。
連結部材72は、その一部がセグメント本体71内に埋設され、残りの部分が外側ピース51と内側ピース52との間に突出するように露出していて、連結ピース53が、連結部材72の露出した部分に連結されている。より具体的には、連結部材72は、セグメント本体71、つまりコンクリート内に埋設されている部分、及び埋設されずに露出して、外側ピース51と内側ピース52との間の空間に突出している部分を有する鋼材73(本実施の形態においてはH形鋼、図4参照)と、鋼材73の露出している部分に設けられていて、後述する連結ピース53が連結する鋼製の連結片74と、を備えている。
図3に示すように、鋼材73は、セグメント5の軸線方向において上端部近傍及び下端部近傍の2箇所に設けられていて、セグメント本体71の周方向に延在している。
図4に示すように、鋼材73は、2つのフランジ部73a,73a及び2つのフランジ部73a,73aを結ぶウェブ73bを有している。
鋼材73の一方のフランジ部73a及びウェブ73bの一部はセグメント本体71内に、つまりコンクリート内に埋設されており、他方のフランジ部73a及びウェブ73bの残りの部分はセグメント本体71から外側ピース51に向かって突出して露出している。
図4に示すように、鋼材73は、2つのフランジ部73a,73a及び2つのフランジ部73a,73aを結ぶウェブ73bを有している。
鋼材73の一方のフランジ部73a及びウェブ73bの一部はセグメント本体71内に、つまりコンクリート内に埋設されており、他方のフランジ部73a及びウェブ73bの残りの部分はセグメント本体71から外側ピース51に向かって突出して露出している。
図3に示すように、連結片74は、セグメント本体71の湾曲方向(長手方向)に沿って所定の間隔をあけて、上側及び下側の鋼材73の露出しているフランジ部73aの、外側ピース51を向く面に立設されている。具体的には、連結片74はフランジ部73aに溶接等により連結されている。連結片74には、後述する連結ピース53との連結のために貫通孔が形成されており、連結片74側の貫通孔と、連結ピース53側の貫通孔とにボルトが挿通されて、挿通されたボルトにナットを締め付けることにより、連結ピース53と連結片74とは互いに締結される。
図4に示すように、2つの鋼材73,73は、鋼製の配力筋75によって取り囲まれている。より具体的には、配力筋75は、上端部及び下端部に設けられている鋼材73,73それぞれの、セグメント本体71から露出しているフランジ部73a,73aの、外側ピース51を向く面、及びセグメント本体71内に埋設されているフランジ部73a,73aの、内側ピース52の内周面を向く面に接するようにして、2つの鋼材73,73に巻き付けられている。
配力筋75の、上側の鋼材73と下側の鋼材73との間で、セグメント5の軸線方向に沿って延在している、セグメント本体71から露出している部分及びセグメント本体71内に埋設される部分は、所定の箇所で互いに連結されて、より高い補強機能を果たすようになっている。
配力筋75の、上側の鋼材73と下側の鋼材73との間で、セグメント5の軸線方向に沿って延在している、セグメント本体71から露出している部分及びセグメント本体71内に埋設される部分は、所定の箇所で互いに連結されて、より高い補強機能を果たすようになっている。
図3に示すように、セグメント本体71の周方向における両端部の上側及び下側には、セグメント5の軸線方向に所定の長さに沿って連結具76,76が設けられている。より具体的には、上側の連結具76は、セグメント本体71の上側で、セグメント本体71の上端面から上側の鋼材73のウェブ73bの上側を向く面にまで延在しており、下側の連結具76は、セグメント本体71の下側で、セグメント本体71の下端面から下側の鋼材73のウェブ73bの下側を向く面にまで延在している。
連結具76は、一端が凹部71aにおいてセグメント本体71内に、つまりコンクリート内に埋設されており、他端がセグメント本体71から露出して鉤状に形成されている。セグメント5同士の連結は、隣接するセグメント5のセグメント本体71に設けられた連結具76と先端部同士を噛み合わせて行う。即ち、セグメント5は、連結具76を鉤状の他端において、周方向に隣接するセグメント5の連結具76の鉤状の他端と連結させることで、周方向に隣接するセグメント5と連結することができる。
連結具76は、一端が凹部71aにおいてセグメント本体71内に、つまりコンクリート内に埋設されており、他端がセグメント本体71から露出して鉤状に形成されている。セグメント5同士の連結は、隣接するセグメント5のセグメント本体71に設けられた連結具76と先端部同士を噛み合わせて行う。即ち、セグメント5は、連結具76を鉤状の他端において、周方向に隣接するセグメント5の連結具76の鉤状の他端と連結させることで、周方向に隣接するセグメント5と連結することができる。
(連結ピース)
図2~図4に示すように、複数の連結ピース53は、外側ピース51と内側ピース52との間に設けられて両ピース51,52を連結しており、これにより、セグメント5のせん断強度を高めている。より具体的には、連結ピース53はその一端を外側ピース51のリブ64に、またその他端を内側ピース52の連結部材72、連結片74に連結して、外側ピース51及び内側ピース52を連結している。
図3及び図4に示すように、連結ピース53は、セグメント5の軸線方向においてセグメント5の上側端部及び下側端部にそれぞれ設けられている。
図4に示すように、連結ピース53は、鋼製の棒材53aと、この棒材53aの両端に設けられた鋼製の矩形状の板材53bと、を備えている。板材53bには、連結時にリブ64及び連結片74に形成された貫通孔と同心となる貫通孔が形成されている。セグメント5の組立て時に、板材53b、リブ64及び連結片74は、それぞれ同心に整合した貫通孔にボルトが挿入されて、挿入側とは反対側に突き出たボルトにナットを締め付けることによって互いに連結されている。つまり、連結ピース53はその板材53bを、ボルト及びナットを介して、外側ピース51のリブ64及び内側ピース52の連結片74に連結させることにより、外側ピース51と内側ピース52とを連結することができる。
図2~図4に示すように、複数の連結ピース53は、外側ピース51と内側ピース52との間に設けられて両ピース51,52を連結しており、これにより、セグメント5のせん断強度を高めている。より具体的には、連結ピース53はその一端を外側ピース51のリブ64に、またその他端を内側ピース52の連結部材72、連結片74に連結して、外側ピース51及び内側ピース52を連結している。
図3及び図4に示すように、連結ピース53は、セグメント5の軸線方向においてセグメント5の上側端部及び下側端部にそれぞれ設けられている。
図4に示すように、連結ピース53は、鋼製の棒材53aと、この棒材53aの両端に設けられた鋼製の矩形状の板材53bと、を備えている。板材53bには、連結時にリブ64及び連結片74に形成された貫通孔と同心となる貫通孔が形成されている。セグメント5の組立て時に、板材53b、リブ64及び連結片74は、それぞれ同心に整合した貫通孔にボルトが挿入されて、挿入側とは反対側に突き出たボルトにナットを締め付けることによって互いに連結されている。つまり、連結ピース53はその板材53bを、ボルト及びナットを介して、外側ピース51のリブ64及び内側ピース52の連結片74に連結させることにより、外側ピース51と内側ピース52とを連結することができる。
<底盤部>
図1に示すように、底盤部2は、沈設構造物100の基礎になると共に、地中の地下水が沈設体1の内側に湧き出すことを防止する。
底盤部2は、例えば、水中コンクリートによって構築されている。底盤部2は、その上面がほぼ水平面に沿うように構築されている。
図1に示すように、底盤部2は、沈設構造物100の基礎になると共に、地中の地下水が沈設体1の内側に湧き出すことを防止する。
底盤部2は、例えば、水中コンクリートによって構築されている。底盤部2は、その上面がほぼ水平面に沿うように構築されている。
<沈設アンカー>
沈設アンカー3は、沈設体1を地中に沈設する工程において、最上端のリング体4の上方からそのリング体4に力を加えて地中に押し込む際に、地盤に反力をとるものである。図1に示すように、沈設アンカー3は、沈設体1の沈設位置の外側かつ下方に掘削された地盤に埋設、固定される定着部31と、定着部31に連結され、沈設体1の外壁面に沿って地表まで延び、リング体4を押し込む沈設装置(図示せず)の不動部分(基礎部等)に連結される連結部32とを有している。
沈設アンカー3は、沈設体1を地中に沈設する工程において、最上端のリング体4の上方からそのリング体4に力を加えて地中に押し込む際に、地盤に反力をとるものである。図1に示すように、沈設アンカー3は、沈設体1の沈設位置の外側かつ下方に掘削された地盤に埋設、固定される定着部31と、定着部31に連結され、沈設体1の外壁面に沿って地表まで延び、リング体4を押し込む沈設装置(図示せず)の不動部分(基礎部等)に連結される連結部32とを有している。
以上のような、地中に埋設される沈設構造物100を構成するセグメント5によれば、外側ピース51と内側ピース52とを連結ピース53で連結する構成となっているので、大断面での施工に際しても、外側ピース51と内側ピース52とを別個に作成して施工現場に搬送し、施工現場で連結ピース53によって連結して大きなセグメント5を形成することができる。これにより、大断面での施工に対応することができ、施工効率の低下を抑制することができる。
また、連結ピース53は、セグメント5のせん断補強材として用いることができるほか、外側ピース51及び内側ピース52の相互のずれや傾きを防止することができる。
また、沈設構造物100の内側の空間Sを臨む内側ピース52がコンクリートにより形成されていることで、内側ピース52を鋼材により形成する場合に必要な防錆用の塗装を内側ピース52に施す必要がないので、セグメント5を作成する際の作業負担を大幅に軽減することができる。
また、連結ピース53は、セグメント5のせん断補強材として用いることができるほか、外側ピース51及び内側ピース52の相互のずれや傾きを防止することができる。
また、沈設構造物100の内側の空間Sを臨む内側ピース52がコンクリートにより形成されていることで、内側ピース52を鋼材により形成する場合に必要な防錆用の塗装を内側ピース52に施す必要がないので、セグメント5を作成する際の作業負担を大幅に軽減することができる。
また、コンクリートにより形成されている内側ピース52には、連結ピース53を連結するための鋼材73と連結片74とを有する連結部材72が設けられているので、内側ピース52、より具体的にはコンクリートよりなるセグメント本体71の剛性を高めるとともに、連結ピース53と内側ピース52との連結を容易にすることができる。
また、連結ピース53を、セグメント5の、その軸線方向における両端部に、つまり上側及び下側にそれぞれ設けることにより、外側ピース51と内側ピース52との間の空間にコンクリートを打設する場合であっても、外側ピース51及び内側ピース52の相対的な移動を抑制することができ、外側ピース51及び内側ピース52を常に初期の位置関係に維持することができる。また、連結ピース53は、棒材53aとその両端部に設けられた板材53bとを備えているので、外側ピース51と内側ピース52との間の空間が完全に仕切られることがなく、コンクリート打設時に一箇所からコンクリートを打設するだけで外側ピース51と内側ピース52との間の空間全域にコンクリートを行き渡らせることができるとともに、セグメント5の軽量化を図ることもできる。
また、鋼材73を取り囲む配力筋75を有することにより、セグメント本体71の剛性をさらに高めることができる。
<その他>
なお、本発明は、上記の実施の形態に限られるものではない。例えば、二重リング44は、平面視円形状に限らず、平面視長円形状(小判形状)、平面視多角形状に形成してもよい。
なお、本発明は、上記の実施の形態に限られるものではない。例えば、二重リング44は、平面視円形状に限らず、平面視長円形状(小判形状)、平面視多角形状に形成してもよい。
また、セグメント5は、外側ピース51も内側ピース52と同様にコンクリートから形成されたセグメントであってもよい。外側ピース51をコンクリートにより形成した場合であっても、沈設体1の沈設後に、沈設体1の浮き上がりを防止する浮上防止アンカーを貫通孔71bに挿通させることができる。
また、鋼材73は、セグメント本体71の剛性を高めることができ、かつ部分的にセグメント本体71から外側ピース51と内側ピース52との間の空間に突出して、連結ピース53が連結できるようになっていればH形鋼に限られず、他の断面形状を有していてもよい。鋼材73は、セグメント本体71に所定の剛性をもたらすのであれば、互いに所定の間隔をあけて複数の鋼材が設けられていてもよい。
また、連結部材72の連結片74は、鋼材73に設けられている場合に限られず、配力筋75に溶接等により連結されていてもよい。
また、連結ピース53は、上記のような棒材に限られることはなく、セグメント5の軸線方向に沿った鋼板等であってもよい。
また、連結ピース53とリブ64との連結、及び連結ピース53と連結片74との連結については、互いに連結されていればよく、ボルト及びナットによる連結方法には限られない。
また、連結具76は、セグメント5の軸線方向に沿ってセグメント本体71に亘って設けられていてもよい。このような実施の形態の場合、凹部71aは、セグメント本体71の周方向側の端面に亘って、セグメント5の軸線方向に沿って設けられている。
5 セグメント
51 外側ピース
52 内側ピース
53 連結ピース
61 プレート
62 主桁
64 リブ
71 セグメント本体
72 連結部材
73 鋼材
74 連結片
75 配力筋
76 連結具
100 沈設構造物
51 外側ピース
52 内側ピース
53 連結ピース
61 プレート
62 主桁
64 リブ
71 セグメント本体
72 連結部材
73 鋼材
74 連結片
75 配力筋
76 連結具
100 沈設構造物
Claims (9)
- 地中に埋設される沈設構造物を構成するセグメントであって、
前記沈設構造物の外壁を形成する外側ピースと、
前記沈設構造物の内壁を形成する内側ピースと、
前記外側ピースと前記内側ピースとを連結する連結ピースと、
を備え、
前記外側ピース及び前記内側ピースの少なくとも一方がコンクリートにより形成されていることを特徴とするセグメント。 - 前記コンクリートにより形成されているピースには、前記連結ピースを連結する連結部材が設けられていることを特徴とする請求項1に記載のセグメント。
- 前記連結部材は、一部が前記外側ピースと前記内側ピースとの間に露出された状態で前記コンクリート内に埋設されていることを特徴とする請求項2に記載のセグメント。
- 前記連結ピースは、前記連結部材における前記外側ピースと前記内側ピースとの間に露出した部分に連結されていることを特徴とする請求項2又は3に記載のセグメント。
- 前記連結部材に、該連結部材を取り囲む配力筋が設けられていることを特徴とする請求項2から4までのいずれか一項に記載のセグメント。
- 前記連結部材は、
一部が前記外側ピースと前記内側ピースとの間に露出された状態で前記コンクリート内に埋設される鋼材と、
前記鋼材に設けられ、前記連結ピースを連結する連結片と、
を備えることを特徴とする請求項2から5までのいずれか一項に記載のセグメント。 - 前記連結ピースは、前記外側ピース及び前記内側ピースの、前記セグメントの軸線方向における両端部にそれぞれ設けられていることを特徴とする請求項1から6までのいずれか一項に記載のセグメント。
- 前記内側ピースがコンクリートにより形成されていることを特徴とする請求項1から7までのいずれか一項に記載のセグメント。
- 前記外側ピースは、壁面を形成するプレートと、前記プレートの上端部及び下端部に設けられた主桁と、これらの主桁間に設けられたリブとを備え、
前記リブに前記連結ピースが連結されていることを特徴とする請求項8に記載のセグメント。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015147437A JP6545557B2 (ja) | 2015-07-27 | 2015-07-27 | セグメント |
| JP2015-147437 | 2015-07-27 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2017018071A1 true WO2017018071A1 (ja) | 2017-02-02 |
Family
ID=57884261
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2016/067174 WO2017018071A1 (ja) | 2015-07-27 | 2016-06-09 | セグメント |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6545557B2 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2017018071A1 (ja) |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5125315A (en) * | 1974-08-24 | 1976-03-01 | Chuo Fukuken Konsarutantsu Kk | Pc burotsukunitekochikusuru izutsu mataha senkannokutai |
| JPH09228379A (ja) * | 1996-02-22 | 1997-09-02 | Ishikawajima Constr Materials Co Ltd | 構造物の基礎 |
| JPH09291782A (ja) * | 1996-04-26 | 1997-11-11 | Nippon Steel Corp | 複数のセグメントを用いた柱状構造体 |
| JPH10205271A (ja) * | 1997-01-24 | 1998-08-04 | Kato Kensetsu:Kk | 沈設体用セグメントピースおよび沈設体の構築方法 |
| JP2003328369A (ja) * | 2002-05-09 | 2003-11-19 | Sumitomo Mitsui Construction Co Ltd | プレキャストコンクリート部材、これを用いたケーソンの構築方法及びトンネルの構築方法 |
| JP2004011327A (ja) * | 2002-06-10 | 2004-01-15 | Daiho Constr Co Ltd | ケーソン及びケーソン構築方法 |
-
2015
- 2015-07-27 JP JP2015147437A patent/JP6545557B2/ja active Active
-
2016
- 2016-06-09 WO PCT/JP2016/067174 patent/WO2017018071A1/ja active Application Filing
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5125315A (en) * | 1974-08-24 | 1976-03-01 | Chuo Fukuken Konsarutantsu Kk | Pc burotsukunitekochikusuru izutsu mataha senkannokutai |
| JPH09228379A (ja) * | 1996-02-22 | 1997-09-02 | Ishikawajima Constr Materials Co Ltd | 構造物の基礎 |
| JPH09291782A (ja) * | 1996-04-26 | 1997-11-11 | Nippon Steel Corp | 複数のセグメントを用いた柱状構造体 |
| JPH10205271A (ja) * | 1997-01-24 | 1998-08-04 | Kato Kensetsu:Kk | 沈設体用セグメントピースおよび沈設体の構築方法 |
| JP2003328369A (ja) * | 2002-05-09 | 2003-11-19 | Sumitomo Mitsui Construction Co Ltd | プレキャストコンクリート部材、これを用いたケーソンの構築方法及びトンネルの構築方法 |
| JP2004011327A (ja) * | 2002-06-10 | 2004-01-15 | Daiho Constr Co Ltd | ケーソン及びケーソン構築方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2017025645A (ja) | 2017-02-02 |
| JP6545557B2 (ja) | 2019-07-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101322122B1 (ko) | 버팀보용 강관 이음장치, 이를 이용한 흙막이 벽체 지지용 강관 버팀보 및 그 버팀보의 시공방법 | |
| JP2011117274A (ja) | 道路等の人工地盤及びその構築方法 | |
| JP2008111256A (ja) | 杭頭部の接合構造及び施工方法 | |
| KR100835777B1 (ko) | 콘크리트파일과 강관 파일의 이음장치 | |
| JP2017223072A (ja) | 鋼管の接合方法及び接合構造 | |
| JP2017223071A (ja) | 鋼製部材の接合方法及び接合構造 | |
| KR20100125162A (ko) | 건축용 파일의 조립식 두부보강장치 | |
| JP6253630B2 (ja) | 合成セグメント、リング及び沈設構造物 | |
| KR20100052847A (ko) | 말뚝연결장치 | |
| JP3899094B2 (ja) | 鋼管杭圧入による既存構造物の基礎補強工法 | |
| JP2016205119A (ja) | セグメント及び沈設構造物の構築方法 | |
| KR101773434B1 (ko) | 콘크리트 파일과 강관 파일 결합용 이음장치 | |
| KR20180007292A (ko) | Phc 말뚝 연결장치 | |
| WO2017018071A1 (ja) | セグメント | |
| JP4448816B2 (ja) | コンクリート製管体および推進工法 | |
| JP3162264U (ja) | 支持杭の構造 | |
| JP6893799B2 (ja) | 切梁火打接続構造および切梁火打接続ピース | |
| JP2009144424A (ja) | 支持杭の構造 | |
| JP4947650B2 (ja) | Pcウェル構造物の構築方法 | |
| JP4461153B2 (ja) | 杭の継ぎ手構造 | |
| JP6905813B2 (ja) | 合成セグメント及びリング体 | |
| JP4469300B2 (ja) | 接合金物 | |
| JP7543164B2 (ja) | 土留構造物 | |
| JP2006016777A (ja) | 回転圧入杭 | |
| JP7543170B2 (ja) | 鋼製土留パネル及び該鋼製土留パネルを用いた土留構造物 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 16830176 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 32PN | Ep: public notification in the ep bulletin as address of the adressee cannot be established |
Free format text: NOTING OF LOSS OF RIGHTS PURSUANT TO RULE 112(1) EPC (EPO FORM 1205 DATED 04/05/2018) |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 16830176 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |