WO2015194106A1 - 車両用目的地決定装置および車両用目的地決定システム - Google Patents
車両用目的地決定装置および車両用目的地決定システム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015194106A1 WO2015194106A1 PCT/JP2015/002783 JP2015002783W WO2015194106A1 WO 2015194106 A1 WO2015194106 A1 WO 2015194106A1 JP 2015002783 W JP2015002783 W JP 2015002783W WO 2015194106 A1 WO2015194106 A1 WO 2015194106A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- search
- destination
- condition
- unit
- vehicle
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01C—MEASURING DISTANCES, LEVELS OR BEARINGS; SURVEYING; NAVIGATION; GYROSCOPIC INSTRUMENTS; PHOTOGRAMMETRY OR VIDEOGRAMMETRY
- G01C21/00—Navigation; Navigational instruments not provided for in groups G01C1/00 - G01C19/00
- G01C21/26—Navigation; Navigational instruments not provided for in groups G01C1/00 - G01C19/00 specially adapted for navigation in a road network
- G01C21/34—Route searching; Route guidance
- G01C21/3407—Route searching; Route guidance specially adapted for specific applications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01C—MEASURING DISTANCES, LEVELS OR BEARINGS; SURVEYING; NAVIGATION; GYROSCOPIC INSTRUMENTS; PHOTOGRAMMETRY OR VIDEOGRAMMETRY
- G01C21/00—Navigation; Navigational instruments not provided for in groups G01C1/00 - G01C19/00
- G01C21/26—Navigation; Navigational instruments not provided for in groups G01C1/00 - G01C19/00 specially adapted for navigation in a road network
- G01C21/34—Route searching; Route guidance
- G01C21/36—Input/output arrangements for on-board computers
- G01C21/3605—Destination input or retrieval
- G01C21/362—Destination input or retrieval received from an external device or application, e.g. PDA, mobile phone or calendar application
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01C—MEASURING DISTANCES, LEVELS OR BEARINGS; SURVEYING; NAVIGATION; GYROSCOPIC INSTRUMENTS; PHOTOGRAMMETRY OR VIDEOGRAMMETRY
- G01C21/00—Navigation; Navigational instruments not provided for in groups G01C1/00 - G01C19/00
- G01C21/26—Navigation; Navigational instruments not provided for in groups G01C1/00 - G01C19/00 specially adapted for navigation in a road network
- G01C21/34—Route searching; Route guidance
- G01C21/36—Input/output arrangements for on-board computers
- G01C21/3605—Destination input or retrieval
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/20—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of structured data, e.g. relational data
- G06F16/29—Geographical information databases
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/90—Details of database functions independent of the retrieved data types
- G06F16/903—Querying
- G06F16/9032—Query formulation
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/90—Details of database functions independent of the retrieved data types
- G06F16/95—Retrieval from the web
- G06F16/953—Querying, e.g. by the use of web search engines
- G06F16/9537—Spatial or temporal dependent retrieval, e.g. spatiotemporal queries
Definitions
- the present disclosure relates to a vehicle destination determination device and a vehicle destination determination system that are used in a vehicle, input a search condition, obtain a search result, and determine a destination.
- Patent Document 1 There is known a technology that enables a search suitable for personal preference (Patent Document 1).
- the passengers can discuss each other against the destination search results obtained by each person, or the destination search results can be agreed by all As a result, there is a problem that it may take time to finally determine the destination, such as performing a destination search by changing the conditions again.
- the present disclosure has been made in view of the above points, and the purpose of the present disclosure is to determine a destination that can be agreed by a plurality of passengers with less effort when a plurality of passengers are on the vehicle.
- An object of the present invention is to provide a vehicular destination determination device and a vehicular destination determination system.
- a vehicle destination determination device includes a communication unit that is used in a vehicle and performs wireless communication with a portable terminal that is used by a passenger and has a destination search function in the vehicle, and a communication unit.
- a search condition acquisition unit that acquires destination search conditions from a mobile terminal, and a combination search condition that combines a plurality of destination search conditions acquired when the search condition acquisition unit acquires a plurality of destination search conditions
- a search unit that performs a destination search by AND search, and a search result output unit that outputs a search result of the destination search performed by the search unit using the combination search condition.
- a destination that can be agreed by the plurality of occupants can be determined with little effort.
- a vehicle destination determination system includes a vehicle destination determination device according to an aspect of the present disclosure and a mobile terminal.
- the mobile terminal transmits the destination search condition to the vehicle destination determination device each time the destination search condition is input, and the search unit of the vehicle destination determination device uses the search condition acquisition unit as the destination search condition.
- the search result output unit of the vehicle destination determination device performs a search obtained by the destination search via the communication unit each time the search unit performs a destination search.
- the number of records is output to the portable terminal, and the portable terminal includes a display unit, and displays the received number of retrieved items on the display unit each time the number of retrieved items is received.
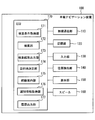
- FIG. 1 is a configuration diagram of a vehicle destination determination system according to an embodiment of the present disclosure.
- FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing a configuration of the in-vehicle navigation device of FIG.
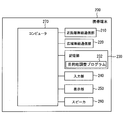
- FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing the configuration of the mobile terminal of FIG.
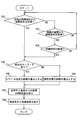
- FIG. 4 is a flowchart showing processing executed by the computer of the portable terminal in FIG. 3 in the first embodiment.
- FIG. 5 is a display example of step S12 in FIG.
- FIG. 6 is a flowchart showing a process executed by the ECU of the in-vehicle navigation device of FIG. 2 in the first embodiment.
- FIG. 1 is a configuration diagram of a vehicle destination determination system according to an embodiment of the present disclosure.
- FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing a configuration of the in-vehicle navigation device of FIG.
- FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing the configuration of the mobile terminal of FIG.
- FIG. 4 is a flowchart showing processing executed by the computer of the portable terminal in FIG.
- FIG. 7 is a display example of step S44 of FIG.
- FIG. 8 is a flowchart showing a part of processing executed by the ECU of the in-vehicle navigation device in the second embodiment.
- FIG. 9 is a display example of step S50 of FIG.
- FIG. 10 is a flowchart showing a part of processing executed by the ECU of the vehicle-mounted navigation device in the third embodiment.
- FIG. 11 is a display example of step S50 of FIG.
- FIG. 12 is a flowchart showing a part of processing executed by the ECU of the vehicle-mounted navigation device in the fourth embodiment.
- FIG. 13 is a flowchart showing a process executed by the ECU of the in-vehicle navigation device before FIG. 6 in the fourth embodiment.
- FIG. 13 is a flowchart showing a process executed by the ECU of the in-vehicle navigation device before FIG. 6 in the fourth embodiment.
- FIG. 14 is a display example of step S22 of FIG.
- FIG. 15 is a flowchart illustrating processing executed by the computer of the mobile terminal in the fifth embodiment.
- FIG. 16 is a flowchart showing processing executed by the computer in parallel with FIG.
- FIG. 17 is a display example of step S62 in FIG. 15 and step S72 in FIG.
- FIG. 18 is a flowchart showing a process executed by the ECU of the vehicle-mounted navigation device in the fifth embodiment.
- a vehicle destination determination system 1 includes the in-vehicle navigation device 100 and the mobile terminal 200 shown in FIG.
- the in-vehicle navigation device 100 has a function as a vehicle destination determination device.
- the in-vehicle navigation device 100 is fixed at a position where it can be operated from the driver's seat in the front part of the passenger compartment of the vehicle 300. Note that, unlike this, a navigation device that can be taken out of the vehicle 300 can be used.
- the portable terminal 200 is carried by a passenger who rides on the vehicle 300 and brought into the vehicle 300. In FIG. 1, three mobile terminals 200 a, 200 b, and 200 c are brought into the vehicle 300. When the portable terminals 200a, 200b, and 200c are not distinguished, the portable terminal 200 is simply used.
- the mobile terminal 200 is a smartphone, for example.
- the in-vehicle navigation device 100 and the mobile terminal 200 can communicate with each other wirelessly.
- the configurations of the in-vehicle navigation device 100 and the mobile terminal 200 will be described with reference to FIGS.
- the in-vehicle navigation device 100 includes a wireless communication unit 110, a storage unit 120, an input unit 130, a position detection unit 140, a display unit 150, a speaker 160, and an ECU 170.
- the wireless communication unit 110 performs wireless communication with the short-range wireless communication unit 210 (see FIG. 3) of the mobile terminal 200.
- the storage unit 120 is a rewritable storage unit such as a flash memory.
- the storage unit 120 stores road map data and search history. Therefore, the storage unit 120 corresponds to a search history storage unit.
- the search history includes the combination search condition used for the destination determination, the destination, the terminal ID of the mobile terminal 200 that acquired the destination search condition used to create the combination search condition, and the difference condition.
- the different condition is a condition that is different from the combination search condition in which all the destination search conditions acquired from the mobile terminal 200 are combined among the conditions constituting the combination search condition used for the destination determination.
- the input unit 130 is, for example, a touch panel or a mechanical switch, and can input a search condition and a determination instruction for determining a destination.
- the position detection unit 140 sequentially detects the current position of the vehicle 300.
- a GNSS receiver used in a GNSS that detects the position of its own device based on radio waves from a satellite is provided, and a current position is detected based on a signal received by the GNSS receiver.
- GNSS Global Navigation Satellite System
- the display unit 150 displays a road map around the current position.
- a search condition input screen In the destination search mode, a search condition input screen, a search result screen, and the like are displayed.
- the guidance sound for guiding the traveling direction of the vehicle 300 is output from the speaker 160 during the route guidance.
- the ECU 170 is a computer including a CPU, a ROM, a RAM, and the like, and the ECU 170 executes programs stored in the ROM while using the temporary storage function of the RAM, so that the ECU 170 functions as each unit illustrated in FIG. To do. That is, ECU 170 functions as search condition acquisition unit 171, search unit 172, search result output unit 173, destination determination unit 174, route guidance unit 175, identification information acquisition unit 176, and history output unit 177. Note that some or all of the functions executed by the ECU 170 may be configured in hardware by one or a plurality of ICs.
- the search condition acquisition unit 171 acquires the destination search condition transmitted from the mobile terminal 200 via the wireless communication unit 110. Also, the destination search condition input in the destination search performed by the in-vehicle navigation device 100 is acquired.
- the search unit 172 creates a combination search condition using the destination search condition acquired by the search condition acquisition unit 171 and performs a destination search. When there are a plurality of destination candidates that match the combination search condition, the destination search result includes a plurality of destination candidates.
- the processing of the search unit 172 will be described in detail later with reference to FIG.
- the search result output unit 173 outputs the search result of the destination search performed by the search unit 172 to the output destination device.
- the output destination device is the display unit 150 or the wireless communication unit 110.
- the search result is transmitted from the wireless communication unit 110 to the mobile terminal 200.
- the destination determination unit 174 determines a destination candidate designated by the user's destination determination operation from the destination candidates included in the search result obtained by the search by the search unit 172 as the destination.
- the route guide unit 175 Based on the current position sequentially detected by the position detection unit 140 and the road map data stored in the storage unit 120, the route guide unit 175 reaches the destination determined by the destination determination unit 174. Route guidance is performed as follows.
- the identification information acquisition unit 176 acquires the terminal ID of the portable terminal 200 that has transmitted the destination search condition, that is, identification information, via the wireless communication unit 110. This terminal ID is transmitted from the portable terminal 200 together with the destination search condition.
- the history output unit 177 outputs a search history in which the terminal ID of the mobile terminal 200 acquired by the identification information acquisition unit 176 matches the terminal ID stored in the storage unit 120 to the output destination device.
- the output destination device is the same as the output destination device described in the search result output unit 173, and is the display unit 150 or the wireless communication unit 110.
- the portable terminal 200 includes a short-range wireless communication unit 210, a wide-area wireless communication unit 220, a storage unit 230, an input unit 240, a display unit 250, a speaker 260, and a computer 270.
- the short-range wireless communication unit 210 has a communication range larger than the size of the passenger compartment, for example, a communication range of about 10 m to several tens of meters, and performs wireless communication with the wireless communication unit 110 of the in-vehicle navigation device 100.
- the wide area wireless communication unit 220 is connectable to a public communication line network and performs wireless communication with other communication devices connected via the public communication line network.
- the storage unit 230 is a rewritable storage unit such as a flash memory.
- the storage unit 230 stores a destination adjustment program 232.
- the input unit 240 is a touch panel, and is used when the user inputs search conditions and search condition transmission instructions.
- the display unit 250 is a thin display such as a liquid crystal display, and displays a search condition input screen and the like. Various notification sounds are output from the speaker 260.
- the computer 270 includes a CPU, a ROM, a RAM, and the like.
- the CPU executes the destination adjustment program 232 while using the temporary storage function of the RAM, the computer 270 executes the processing of FIG.
- the input of the destination adjustment program execution instruction is, for example, that a predetermined icon displayed on the display unit 250 is touch-operated.
- a search condition input screen 252 is displayed.
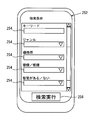
- FIG. 5 is an example of the search condition input screen 252.
- the search condition input screen 252 shown in FIG. 5 shows a condition input field 254 for inputting different destination search conditions.
- the condition input field 254 shown in FIG. 5 is a condition input field for inputting a keyword, genre, price range, smoking cessation or smoking, or whether there is a private room as a destination search condition. is there.
- a condition input field 254 for inputting other destination search conditions is also displayed.
- a search execution button 256 is also displayed on the search condition input screen 252.
- step S4 it is determined whether or not search execution is instructed by the user. This determination is made based on whether or not the search execution button 256 has been operated. If the search execution button 256 is operated, step S4 is set to YES, and if the search execution button 256 is not operated, step S4 is set to NO. If the determination in step S4 is NO, the process returns to step S2, and if YES, the process proceeds to step S6.
- step S6 it is determined whether the destination search condition has been input. If the destination search condition is input in at least one of the plurality of condition input fields 254, the determination in step S6 is YES, and if the destination search condition is not input in any of the condition input fields 254 Is NO in step S6. If the determination in step S6 is no, the process proceeds to step S8. If the determination is yes, the process proceeds to step S10.
- step S8 a message requesting input of destination search conditions is displayed on the display unit 250. After executing step S8, the process returns to step S2.
- step S10 a destination search is performed using the destination search conditions input at this time. Therefore, the mobile terminal 200 that executes the processing of FIG. 4 has a destination search function.
- an AND search is performed using all the destination search conditions input at this time.
- the destination search may be a process of transmitting the destination search condition to the server using the wide area wireless communication unit 220, performing an AND search at the server, and receiving the search result.
- the processing performed within 200 may be performed.
- step S12 the search result of the destination search performed in step S10 is displayed on the display unit 250.
- the displayed search results include the number of destination candidates that match the destination search condition, the names of the destination candidates, a transmission instruction button, a re-search button, and the like.
- step S14 it is determined whether or not a transmission instruction is issued by the user. This determination is made based on whether or not the transmission instruction button displayed on the display unit 250 has been operated. When the user sees the search result displayed on the display unit 250 and determines that the search result may be used for adjusting the destination with another person, the user presses the transmission instruction button. If it is determined that no transmission instruction has been given, the process proceeds to step S16.
- step S16 it is determined whether or not a re-search instruction has been issued by the user. This determination is made based on whether or not the re-search button displayed on the display unit 250 has been operated. When the user sees the search result displayed on the display unit 250 and determines that the destination search condition should be changed, the user presses the re-search button. If it is determined that a re-search instruction has not been issued, the process returns to step S14. If it is determined that a re-search instruction has been issued, the process returns to step S2.
- step S14 If it is determined in step S14 that a transmission instruction has been issued, the process proceeds to step S18.
- step S ⁇ b> 18 the short-range wireless communication unit 210 is used to transmit the destination search conditions used for the current destination search to the vehicle-mounted navigation device 100.
- destination search conditions are input in a plurality of condition input fields 254 and there are a plurality of destination search conditions used for the destination search, all destination search conditions are transmitted. Also, the terminal ID of the portable terminal 200 is transmitted together with the destination search condition.
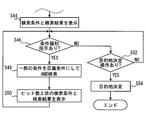
- step S44 is executed by the search result output unit 173, and the other steps are executed by the search unit 172.
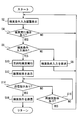
- step S30 it is determined whether the destination search conditions have been acquired from all the mobile terminals 200 brought into the vehicle 300.
- the in-vehicle navigation device 100 automatically recognizes the presence of the mobile terminal 200 brought into the vehicle 300. It has a function to do.
- step S30 it is determined whether or not the destination search condition has been acquired from all of the mobile terminals 200 that can be recognized as being brought into the vehicle 300. If the determination in step S30 is NO, the process proceeds to step S32. If YES, the process proceeds to step S36.
- step S32 it is determined whether or not destination search conditions have been acquired from a plurality of devices.
- the devices here include not only the mobile terminal 200 but also the in-vehicle navigation device 100. If judgment of step S32 is NO, it will return to step S30, and if it is YES, it will progress to step S34.
- step S34 it is determined whether or not a standby time has elapsed since it was first determined that destination search conditions were acquired from a plurality of devices. This determination is also performed even if it is determined that some users do not need to participate in destination adjustment and it is determined not to transmit the destination search condition from the mobile terminal 200 of the user. It is provided so that it can. If the determination in step S34 is NO, the process returns to step S30, and if YES, the process proceeds to step S36. Moreover, also when the judgment of step S30 becomes YES, it progresses to step S36.
- step S36 it is determined whether or not there is a keyword representing a point in the acquired destination search condition. If this determination is YES, the process proceeds to step S38, and if NO, the process proceeds to step S40.
- step S38 a point included as a keyword is determined as a base point of distance.
- step S40 the current position is determined as the base point of distance.
- a combined search condition is created by adding a condition that the distance from the base point is within the first distance to all the acquired search conditions, and each search condition included in the combined search condition is ANDed. Perform a destination search to search.
- the first distance is a distance such that there are many people who may move by car, and is set to, for example, about 50 km. This first distance may be changed by the user.
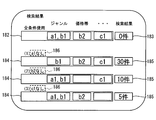
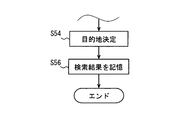
- step S44 the search result screen is displayed on the display unit 150.
- the search result screen includes all the search conditions used for the search in step S42 and the search results.
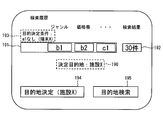
- FIG. 7 is an example of the search result screen.
- a search condition display field 180 is displayed, and the search condition display field 180 shows a combination search condition for performing a destination search.
- two search conditions a1 and b1 are set for the genre
- one search condition b2 is set for the price range
- c1 is set for another type of search condition. It is shown that.
- the search condition a1 is a search condition acquired from the mobile terminal 200a
- the search conditions b1 and b2 are search conditions acquired from the mobile terminal 200b
- the search condition c1 is a search condition acquired from the mobile terminal 200c.
- a search number display field 181 indicating the number of destination candidates corresponding to the combination search condition is displayed.
- destination candidates corresponding to the combination search condition are displayed in order from the shortest distance from the base point.
- the crew of the vehicle 300 looks at the search result screen and discusses, and sets one destination candidate as a route guidance destination.
- the search unit 172 creates a combination search condition that includes all destination search conditions acquired from a plurality of devices, and performs an AND search of the combination search condition as a destination search (S42). ).
- the destination search condition acquired from each device should be a condition for obtaining a destination candidate that matches the user's preference using each device. Therefore, the destination candidates included in the search result of the destination search that is AND-searched with the combination search conditions obtained by combining the destination search conditions acquired from a plurality of devices are a plurality of occupants with the destination search conditions set separately. Should be a destination candidate that suits everyone's taste.
- each passenger since the destination search is performed using a set of destination search conditions called combination search conditions, unlike when searching for destinations using different destination search conditions on each mobile terminal 200, each passenger There is no need to compare different destination search results. This also reduces the effort of determining a destination that a plurality of passengers can agree on.
- a condition that the distance from the base point is within the first distance is added to the combination search condition (S42).
- the distance is an important condition, but the destination search in the mobile terminal 200 may not include the distance condition. Therefore, in this embodiment, a distance condition is added to the acquired destination search condition. As a result, a search result that does not include a destination candidate that is far from the base point and is unlikely to be the final destination can be obtained, so that the final destination can be easily determined.
- the search unit 172 performs destination search by AND search of combination search conditions. Since this combination search condition is a search condition combining a plurality of destination search conditions, the combination search condition is a search condition combining destination search conditions used by a plurality of passengers. Therefore, the search result of the destination search under the combination search condition is likely to include destination candidates that can be agreed by a plurality of passengers.
- a search result that is highly likely to include a destination candidate that can be agreed by a plurality of passengers is obtained by a destination search under a combination search condition. Therefore, the passengers can discuss each other while comparing the destination search results obtained by each person, or perform the destination search again by changing the conditions so that a destination search result that everyone can agree to is obtained. The case decreases. Therefore, a destination that can be agreed by a plurality of passengers can be determined with little effort.
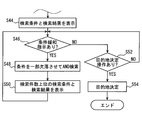
- step S46 and subsequent steps are executed following step S44.
- steps S46 and S48 are performed by the search unit 172
- step S50 is performed by the search result output unit 173
- steps S52 and S54 are performed by the destination determination unit 174.
- step S46 it is determined whether a condition relaxation instruction has been issued by the user.
- the condition relaxation instruction given by the user is determined by, for example, displaying a button for the user to instruct the condition relaxation on the search result screen and operating the button.
- the destination candidate included in the search result of the destination search performed in step S42 should be a destination candidate that suits the tastes of all the crew members. However, there may be zero destination candidates that match the preferences of all the crew members. Further, even if there are one or more destination candidates, when actually looking at the destination candidates, there is a possibility that the destination may be different from the expected destination. In these cases, the user issues a condition relaxation instruction. If the determination in step S46 is NO, the process proceeds to step S48.
- step S48 an AND search is executed by deleting some of the search conditions included in the combination search condition created in step S42.
- a new combination search condition is created by deleting one of the combination search conditions created in step S42.
- this new combination search condition one search condition to be deleted from the combination search condition created in step S42 is sequentially switched, and all search conditions are deleted once to create a new combination search condition.
- an AND search is performed using the new combination search condition.
- step S50 a predetermined number of combination search conditions and search results under the conditions are displayed on the display unit 150 in descending order of the number of destination candidates corresponding to the condition among the plurality of search results performed in step S48. .
- FIG. 9 is a display example displayed on the display unit 150 in step S50.
- the search performed by the combination search condition shown in the all condition display field 182 and the all condition display field 182 that are display fields indicating the combination search condition created in step S42.
- a search number display field 183 indicating the number of search cases is displayed.
- the missing search condition display field 184 and the search number display field 185 are displayed below the all condition display field 182 and the search number display field 183.
- the missing search condition display column 184 is a column for displaying the search conditions for the AND search performed in step S48.
- the search number display column 185 is a column for displaying the number of searches in the search performed under the search conditions shown in the missing search condition display column 184.
- the combination search condition shown in the missing search condition display field 184 is determined from the combination search condition shown in the all condition display field 182. You can see if the condition is missing. However, a missing condition display field 186 is provided above the missing search condition display field 184.
- the missing condition display field 186 includes a search condition (hereinafter, referred to as “combined search condition”) in which the combination search condition shown in the corresponding missing search condition display field 184 is missing from the search condition shown in the all condition display field 182. (Missing condition). The occupant can immediately determine the missing condition by looking at the missing condition display field 186.
- the combination condition shown in the uppermost missing search condition display field 184 shows that the missing condition is a1. Further, the combination search condition shown in the middle missing search condition display column 184 has a missing condition b2, and the combination condition shown in the bottom missing search condition display column 184 has a missing condition c1. I understand that.
- step S50 After executing step S50, the process returns to step S46.
- the search results displayed in step S50 have more search results than the search results obtained in step S42. Therefore, there is a high possibility that destination candidates that can be agreed by all of the plurality of crew members are included rather than the search result displayed in step S44.
- step S46 determines whether the destination candidate is displayed.
- step S48 a new combination search condition in which one search condition is missing is created and an AND search is performed.
- step S52 it is determined whether or not the occupant has performed a destination determination operation. If this judgment is NO, it will return to Step S46, and if it is YES, it will progress to Step S54.
- step S54 one destination determined based on the destination determination operation performed by the passenger is determined.
- an occupant can give a condition relaxation instruction.
- a condition relaxation instruction is issued (S46: YES)
- a part of the plurality of search conditions acquired by the search condition acquisition unit 171 is deleted to create a new combination search condition, and this new combination search is performed.
- An AND search is performed under conditions (S48).
- the search result of the AND search is displayed on the display unit 150 (S50).
- the search results displayed in step S50 have more search results than the search results displayed in step S44.
- step S44 there may be a case where the number of destination candidates is 0, or even if there are one or more destination candidates, it may feel that the destination is different from the expected destination. . Even in this case, by giving a condition relaxation instruction, it is possible to determine a destination that can be agreed by all of a plurality of passengers with little effort.
- a missing search condition display field 184 indicating the combination search condition used for the search is displayed in correspondence with the search number display field 185 indicating the search result.
- a missing condition display field 186 is also displayed. The occupant can easily determine which search condition is most effective by looking at the display contents of the missing search condition display field 184 and the missing condition display field 186. This facilitates smooth discussion between the passengers while viewing the screen displayed in step S50.
- the third embodiment is similar to the second embodiment.
- the process shown in FIG. 10 is executed instead of the process shown in FIG. FIG. 10 differs from FIG. 8 only in that step S49 is executed instead of step S48 in FIG.
- step S49 a part of the search conditions included in the combination search condition created in step S42 is changed to a broad sense condition, that is, broadened to be a new combination search condition. An AND search is executed under this new combination search condition.
- the search condition may be a superordinate condition.
- the genre “Chinese” includes a genre classification that includes the genre “Ramen”
- changing “Ramen” to a term having a higher concept of “Chinese” is a change to a broad sense.
- a search condition similar to the search condition that is, a condition to which a similar condition is added is also a broad sense condition. For example, adding a search condition in the price range of “1000 yen to 3000 yen” to the search condition of the price range “up to 1000 yen” is also a change to the broad sense condition.
- the search condition “1000 yen to 3000 yen” is a similar condition to the broadening target condition “up to 1000 yen”.
- AND search is performed with the combination search condition using “shopping mall” as the search condition.
- search condition changed to “”.
- search results of these two AND searches are combined with an OR condition.
- a broad sense condition corresponding to the search condition is set in advance.
- the broad-sense condition is changed.
- FIG. 11 is a display example displayed on the display unit 150 in step S50 in the third embodiment.
- a broad search condition display field 187 and a search number display field 188 are displayed below the all condition display field 182 and the search number display field 183.
- the broad search condition display column 187 is a column for displaying the search conditions performed in step S49
- the search number display column 188 is the number of searches in the search performed in the search conditions shown in the broad search condition display column 187. Is a column for displaying.
- a broad search condition display column 187 and a search number display column 188 are provided. Three of each are displayed.
- a broad sense condition display column 189 is provided on each broad sense search condition display column 187.
- this broad sense condition display field 189 what is the broad search condition for the search condition shown in the all condition display field 182 among the combination search conditions shown in the corresponding broad sense condition display field 187. It is shown whether there is.
- the broadest condition display column 189 at the top indicates that the search condition f is added to the genre search condition a1.
- the middle broad condition display field 189 indicates that the search condition g is added to the price range search condition b2.
- the lowermost broad condition display column 189 shows that the genre search condition b1 is superordinated to the search condition h.
- step S56 is executed.
- the search result is stored in the storage unit 120 as a search history.
- This search result includes the combination search condition used for the destination determination, the destination determined in step S54, the terminal ID of the mobile terminal 200 that acquired the destination search condition used for creating the combination search condition, and the difference condition.
- the different conditions are the search conditions shown in the missing condition display field 186 shown in FIG. 9 and the broad conditions shown in the broad condition display field 189 shown in FIG.
- the ECU 170 of the in-vehicle navigation device 100 executes the process shown in FIG. 13 before executing step S30 and subsequent steps shown in FIG.
- step S20 is executed by the identification information acquisition unit 176
- steps S21 and S22 are executed by the history output unit 177
- steps S23 and S24 are executed by the destination determination unit 174
- step S25 is executed by the search unit 172. Execute.
- step S20 the terminal ID of the mobile terminal 200 is acquired from all the mobile terminals 200 brought into the vehicle 300.
- step S21 it is determined whether or not a search history that matches the terminal ID acquired in step S20 is stored in the storage unit 120.
- match here means complete match. That is, if a plurality of terminal IDs are included in one search history, the search history exists when all of the plurality of terminal IDs match the terminal ID acquired in step S20. If the determination in step S21 is NO, the process proceeds to FIG.
- step S21 determines whether the search history matches the terminal ID acquired in step S20 among the search histories stored in the storage unit 120 is displayed on the display unit 150.
- FIG. 14 is a display example displayed in step S22.
- the search history is displayed at the top of the screen.
- a destination display column 190 is a column for displaying a destination
- the search condition display column 191 is a column for displaying a combination search condition used for destination determination.
- the search number display column 192 is a column for displaying the number of searches in the search performed under the combination search condition
- the different condition display column 193 is a column for displaying the different condition.
- the terminal name “terminal A” is also displayed. This indicates the mobile terminal 200 from which the different condition is a condition for changing the destination search condition acquired.
- a destination search button 195 operated by the passenger is displayed.
- step S23 it is determined whether or not the occupant has performed a destination determination operation. This determination is made based on whether or not the destination determination button 194 displayed on the display unit 150 has been operated. If this judgment is YES, it will progress to Step S24.
- step S24 the destination displayed in the destination display column 190 of the display unit 150, that is, the destination set in the past is set as the current goal.
- step S23 determines whether or not the passenger has issued a destination search instruction. This determination is made based on whether or not the destination search button 195 displayed on the display unit 150 has been operated. If this determination is NO, the process returns to step S23, and if YES, the process proceeds to S30 in FIG.
- the terminal IDs match, it is highly likely that the plurality of occupants who are currently on the vehicle 300 are the same occupants as when the destination included in the search history is determined. If all the passengers are the same, if the destination included in the search history is displayed, there is a possibility that the destination is set as the destination for route guidance again. Therefore, in the fourth embodiment, when the terminal ID of the mobile terminal 200 brought into the vehicle 300 matches the terminal ID included in the search history, the search history is displayed.
- the occupant can determine the destination without searching for the destination when he / she looks at the destination displayed in the destination display column 190 and determines that the destination is acceptable this time. Therefore, a destination that can be agreed by a plurality of passengers can be determined with less effort.
- the search history displayed on the display unit 150 includes a different condition.
- the different conditions are displayed in a different condition display field 193.
- This different condition means who the search condition is changed when a destination is determined in the past by a plurality of occupants in the vehicle 300 this time.
- a terminal name indicating which mobile terminal 200 is the destination search condition obtained by changing the different condition is also displayed. This terminal name clearly shows who has changed the search conditions when the destination is determined in the past.
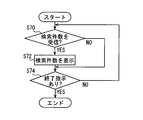
- the computer 270 of the mobile terminal 200 executes the processes of FIGS. 15 and 16 instead of the process of FIG. 15 and 16 are processed in parallel.
- the parallel processing if the computer 270 is multi-core, separate CPUs perform the processes of FIGS. 15 and 16, respectively. In the case of a single core, parallel processing is performed by time division processing.
- step S62 the search condition input screen 252a is displayed.
- FIG. 17 is an example of the search condition input screen 252a in the fifth embodiment.
- the search condition input screen 252a shown in FIG. 17 is different from the search condition input screen 252 shown in FIG. 5 in that the search execution button 256 of FIG. 5 is not displayed on the search condition input screen 252a.
- the search number display field 258 and the end button 259 are displayed.
- step S64 After displaying the search condition input screen 252a in step S62, it is determined in step S64 whether the search condition has been changed. If any one of the plurality of condition input fields 254 displayed on the search condition input screen 252a is changed, the determination in step S64 is YES. If the determination in step S64 is yes, the process proceeds to step S66. In step S ⁇ b> 66, the changed destination search condition, that is, all of the set search conditions are transmitted to the in-vehicle navigation device 100.
- the in-vehicle navigation device 100 Each time the in-vehicle navigation device 100 receives a destination search condition, the in-vehicle navigation device 100 performs a destination search and transmits the number of searches corresponding to the combination search condition to the mobile terminal 200. The processing of the in-vehicle navigation device 100 will be described in detail later with reference to FIG.
- step S68 it is determined whether or not the end button 259 has been operated. That is, in step S68, it is determined whether an end instruction has been issued. If this determination is NO, the process returns to step S64, and if YES, the process of FIG. 15 is terminated.
- step S ⁇ b> 70 it is determined whether the number of searches is received from the in-vehicle navigation device 100. If this judgment is YES, it will progress to Step S72.
- step S72 the number of searches received from the in-vehicle navigation device 100 is displayed in the search number display field 258.
- each occupant who operates the mobile terminal 200 deletes some search condition or sets some search condition in a broad sense. It can be determined that it must be changed.
- the number of items displayed in the search number display field 258 is large, it can be determined that a search condition should be added or that some search condition should be changed to a narrowly-defined search condition. That is, the search condition can be adjusted while viewing the number of searches displayed in the search number display field 258.
- the search results displayed on the display unit 150 of the in-vehicle navigation device 100 may be viewed. If a destination that can be agreed upon by a plurality of passengers can be determined by looking at the search result, the end button 259 is operated.
- step S70 determines whether or not the end button 259 has been operated. That is, in step S74, it is determined whether an end instruction has been issued. If this determination is NO, the process returns to step S70, and if YES, the process of FIG. 16 is terminated.
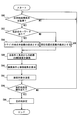
- step S80 it is determined whether or not the destination search condition has been acquired from any of the mobile terminals 200. If this determination is NO, this step S80 is repeated, and if it is YES, the process proceeds to step S82.
- Steps S82 to S90 are the same as steps S36 to S44 in FIG. 6, respectively.
- step S92 the number of searches obtained in step S88 is transmitted to all portable terminals 200 brought into the vehicle 300.
- step S94 it is determined whether or not the occupant has performed a destination determination operation. If this determination is NO, the process returns to step S80, and if YES, the process proceeds to step S96. In step S96, one destination determined based on the destination determination operation performed by the passenger is determined.
- the mobile terminal 200 transmits the destination search condition to the in-vehicle navigation device 100 every time the search condition is changed (S66), and the ECU 170 of the in-vehicle navigation device 100 acquires the destination search condition.
- a destination search is performed and the number of searches is transmitted to the mobile terminal 200 (S80 to S92).
- the search number transmitted from the vehicle-mounted navigation apparatus 100 is displayed on the display part 250 of the portable terminal 200 (S72).
- Each occupant operating the mobile terminal 200 can see the number of search items each time the search condition is changed, and can adjust the search conditions while viewing the number of search items. As a result, it is possible to quickly obtain a search result in which the number of search cases is appropriate and it is easy to determine a destination through discussion.
- each part is expressed as S2, for example.
- each part can be divided into a plurality of sub-parts, while the plurality of parts can be combined into one part.
- each part configured in this manner can be referred to as a circuit, a device, a module, and a means.
- Each of the above-mentioned plurality of parts or a combination thereof is not only (i) a software part combined with a hardware unit (for example, a computer), but also (ii) hardware (for example, an integrated circuit, As a part of the (wiring logic circuit), it can be realized with or without including the functions of related devices.
- the hardware unit can be configured inside a microcomputer.
- a combination search condition is created by adding a condition that the distance from the base point is within the first distance.
- the route guidance unit 175 performs route guidance
- the condition that the distance from the base point is within the first distance is added in place of the condition that the distance from the base point is within the second distance, and the combination is added.
- Search conditions may be created. Note that the distance from the guide route is not a straight-line distance, but a distance of a route that leaves the guide route and arrives at the destination candidate.
- the second distance may be set in advance, and the occupant may be able to change the distance.
- Modification 2 Unlike the above-described embodiment and Modification 1, the combination search condition may be created without adding the condition that the distance from the base point is within the first distance or the condition that the distance from the guide route is within the second distance. Good.
- Modification 4 when there is a condition relaxation instruction (S46: YES), some conditions are omitted, or some conditions are broadly defined. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and when the number of destination search searches is less than or equal to the minimum number, some of the conditions are automatically omitted, or the destination search is re-executed with some conditions in a broad sense. It may be executed (Modification 4). In this case, it is not necessary to display a search result in which the number of search destination searches is less than the minimum number.
- step S25 when the determination result of step S25 is YES, the process of FIG. 6 is executed, but instead, the process may proceed to step S44 of FIG. 8 or FIG.
- step S44 a search result screen with the combination search condition displayed in the search condition display field 191 is displayed.
- the search result screen displayed here may be the same as that shown in FIG.
- the destination included in the search history is determined as the current destination. Even if it is not set to, there is a possibility that the search is performed with the same combination search condition. Therefore, when the determination result in step S25 is YES, the search result screen with the combination search condition displayed in the search condition display field 191 is displayed.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Remote Sensing (AREA)
- Radar, Positioning & Navigation (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Navigation (AREA)
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/306,849 US10048079B2 (en) | 2014-06-19 | 2015-06-02 | Destination determination device for vehicle and destination determination system for vehicle |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014-126416 | 2014-06-19 | ||
| JP2014126416A JP6330508B2 (ja) | 2014-06-19 | 2014-06-19 | 車両用目的地決定装置および車両用目的地決定システム |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015194106A1 true WO2015194106A1 (ja) | 2015-12-23 |
Family
ID=54935118
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2015/002783 Ceased WO2015194106A1 (ja) | 2014-06-19 | 2015-06-02 | 車両用目的地決定装置および車両用目的地決定システム |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10048079B2 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6330508B2 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2015194106A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020060809A (ja) * | 2018-10-04 | 2020-04-16 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | エージェント装置 |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPWO2017149648A1 (ja) * | 2016-03-01 | 2018-12-20 | パイオニア株式会社 | 情報表示装置、情報表示方法、プログラム、及び、情報表示システム |
| JP6610426B2 (ja) * | 2016-05-20 | 2019-11-27 | アイシン・エィ・ダブリュ株式会社 | 検索システムおよび検索プログラム |
| JP6751117B2 (ja) * | 2018-07-20 | 2020-09-02 | ヤフー株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報提供方法及びプログラム |
| US20250130058A1 (en) * | 2023-10-19 | 2025-04-24 | Toyota Motor North America, Inc. | Vehicle modifications based on a determined destination |
Citations (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006195576A (ja) * | 2005-01-11 | 2006-07-27 | Toyota Motor Corp | 車載音声認識装置 |
| JP2008259043A (ja) * | 2007-04-06 | 2008-10-23 | Denso Corp | 車載システム及びプログラム |
| JP2009140316A (ja) * | 2007-12-07 | 2009-06-25 | Aisin Aw Co Ltd | 検索装置、ナビゲーション装置、及び検索プログラム |
| JP2009300389A (ja) * | 2008-06-17 | 2009-12-24 | Denso Corp | データ通信システムおよびこれに用いる第1車載装置、第2車載装置、およびデータ記憶装置 |
| JP2010164435A (ja) * | 2009-01-15 | 2010-07-29 | Fujitsu Ten Ltd | 車載装置 |
| JP2010190745A (ja) * | 2009-02-18 | 2010-09-02 | Equos Research Co Ltd | ナビゲーションシステム及びナビゲーション装置 |
| JP2010203844A (ja) * | 2009-03-02 | 2010-09-16 | Aisin Aw Co Ltd | 施設案内装置、施設案内方法及びコンピュータプログラム |
| JP2011080824A (ja) * | 2009-10-06 | 2011-04-21 | Clarion Co Ltd | ナビゲーション装置 |
| JP2012053593A (ja) * | 2010-08-31 | 2012-03-15 | Denso Corp | 情報提供装置、及び、情報提供システム |
| JP2012208369A (ja) * | 2011-03-30 | 2012-10-25 | Zenrin Datacom Co Ltd | 地図表示装置、地図表示方法、及びプログラム |
| JP2013190356A (ja) * | 2012-03-14 | 2013-09-26 | Fujitsu Ten Ltd | 車載装置、ナビゲーションシステム及び目的地選択方法 |
| JP2013195230A (ja) * | 2012-03-19 | 2013-09-30 | Panasonic Corp | ナビゲーション装置 |
Family Cites Families (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002123290A (ja) * | 2000-10-16 | 2002-04-26 | Pioneer Electronic Corp | 音声認識装置ならびに音声認識方法 |
| US6636799B2 (en) * | 2001-12-21 | 2003-10-21 | Motorola, Inc. | Method and apparatus for modification of vehicular navigation information |
| JP4153887B2 (ja) * | 2004-03-19 | 2008-09-24 | 株式会社日立製作所 | 移動体ナビゲーション装置、および、移動体ナビゲーション装置における目的地の検索方法 |
| US7523102B2 (en) * | 2004-06-12 | 2009-04-21 | Getty Images, Inc. | Content search in complex language, such as Japanese |
| JP5005331B2 (ja) | 2006-12-19 | 2012-08-22 | 富士重工業株式会社 | 筋力センサ |
| JP5243730B2 (ja) | 2007-04-24 | 2013-07-24 | 株式会社エヌ・ティ・ティ・ドコモ | 検索支援システム、検索支援方法 |
| JP2009140488A (ja) * | 2007-11-14 | 2009-06-25 | Fujitsu Ten Ltd | 車載装置および表示制御システム |
| JP4920663B2 (ja) * | 2007-12-11 | 2012-04-18 | ヤフー株式会社 | ディスプレイ連動装置及び方法 |
| WO2011020184A1 (en) * | 2009-08-21 | 2011-02-24 | William Spat | System and method for fulfilling requests using a mobile device |
| JP6082519B2 (ja) * | 2011-12-14 | 2017-02-15 | 株式会社デンソー | 案内経路決定装置および案内経路決定システム |
| JP2015052954A (ja) * | 2013-09-09 | 2015-03-19 | アルパイン株式会社 | データ識別管理装置およびデータ識別管理方法 |
| JP2015162801A (ja) * | 2014-02-27 | 2015-09-07 | パイオニア株式会社 | 通信装置、制御方法、プログラム、及び記憶媒体 |
| US20160349067A1 (en) * | 2015-05-29 | 2016-12-01 | Here Global B.V. | Ride Sharing Navigation |
-
2014
- 2014-06-19 JP JP2014126416A patent/JP6330508B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2015
- 2015-06-02 WO PCT/JP2015/002783 patent/WO2015194106A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2015-06-02 US US15/306,849 patent/US10048079B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006195576A (ja) * | 2005-01-11 | 2006-07-27 | Toyota Motor Corp | 車載音声認識装置 |
| JP2008259043A (ja) * | 2007-04-06 | 2008-10-23 | Denso Corp | 車載システム及びプログラム |
| JP2009140316A (ja) * | 2007-12-07 | 2009-06-25 | Aisin Aw Co Ltd | 検索装置、ナビゲーション装置、及び検索プログラム |
| JP2009300389A (ja) * | 2008-06-17 | 2009-12-24 | Denso Corp | データ通信システムおよびこれに用いる第1車載装置、第2車載装置、およびデータ記憶装置 |
| JP2010164435A (ja) * | 2009-01-15 | 2010-07-29 | Fujitsu Ten Ltd | 車載装置 |
| JP2010190745A (ja) * | 2009-02-18 | 2010-09-02 | Equos Research Co Ltd | ナビゲーションシステム及びナビゲーション装置 |
| JP2010203844A (ja) * | 2009-03-02 | 2010-09-16 | Aisin Aw Co Ltd | 施設案内装置、施設案内方法及びコンピュータプログラム |
| JP2011080824A (ja) * | 2009-10-06 | 2011-04-21 | Clarion Co Ltd | ナビゲーション装置 |
| JP2012053593A (ja) * | 2010-08-31 | 2012-03-15 | Denso Corp | 情報提供装置、及び、情報提供システム |
| JP2012208369A (ja) * | 2011-03-30 | 2012-10-25 | Zenrin Datacom Co Ltd | 地図表示装置、地図表示方法、及びプログラム |
| JP2013190356A (ja) * | 2012-03-14 | 2013-09-26 | Fujitsu Ten Ltd | 車載装置、ナビゲーションシステム及び目的地選択方法 |
| JP2013195230A (ja) * | 2012-03-19 | 2013-09-30 | Panasonic Corp | ナビゲーション装置 |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020060809A (ja) * | 2018-10-04 | 2020-04-16 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | エージェント装置 |
| JP7028130B2 (ja) | 2018-10-04 | 2022-03-02 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | エージェント装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20170045366A1 (en) | 2017-02-16 |
| JP6330508B2 (ja) | 2018-05-30 |
| US10048079B2 (en) | 2018-08-14 |
| JP2016004538A (ja) | 2016-01-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US20160033297A1 (en) | In-vehicle device, information distribution server, and facility information display method | |
| US10866107B2 (en) | Navigation system | |
| US10132638B2 (en) | Route search system, route search method, and computer program | |
| JP6330508B2 (ja) | 車両用目的地決定装置および車両用目的地決定システム | |
| JP2019046267A (ja) | 情報提供方法、情報提供システム、および情報提供装置 | |
| JP2012230001A (ja) | 経路探索システム及び経路探索方法 | |
| JP2009080337A (ja) | 広告情報配信システム、配信装置、及び、車載装置 | |
| JP2011185908A (ja) | ナビゲーション装置および目的地に関する情報の案内方法 | |
| JP2016200559A (ja) | コンテンツ起動制御装置、コンテンツ起動方法、およびコンテンツ起動システム | |
| JP7094610B2 (ja) | 情報表示システムおよび情報表示プログラム | |
| US20190078907A1 (en) | Navigation device | |
| WO2019130057A1 (ja) | 目的地の提案システム、提案装置及び提案方法 | |
| JP2016024166A (ja) | 電子装置、その周辺駐車場検索方法および周辺駐車場検索プログラム | |
| JP6578234B2 (ja) | 検索システム、検索方法、検索プログラム、記憶媒体 | |
| US11238517B2 (en) | Navigation server, navigation client and navigation system | |
| US10139240B2 (en) | Navigation device providing path information and method of navigation | |
| JP2016011905A (ja) | 案内システム、案内方法、サーバおよび電子装置 | |
| US10798219B2 (en) | Server and server client system | |
| JP6011299B2 (ja) | 車両用情報提供システム | |
| JP6270751B2 (ja) | ナビゲーション装置及びナビゲーション方法 | |
| JP2021067639A (ja) | 情報提供装置、情報提供方法、およびプログラム | |
| JP2020079783A (ja) | 地図表示システム、地図表示方法、及びプログラム | |
| JP5986765B2 (ja) | ナビゲーション装置 | |
| JPWO2018185809A1 (ja) | 走行支援装置及び走行支援方法 | |
| JP2018073362A (ja) | 施設検索装置、通信システム、施設検索方法及び施設検索プログラム |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 15809095 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15306849 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 15809095 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |