WO2015141660A1 - 薬剤払出し装置 - Google Patents
薬剤払出し装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015141660A1 WO2015141660A1 PCT/JP2015/057842 JP2015057842W WO2015141660A1 WO 2015141660 A1 WO2015141660 A1 WO 2015141660A1 JP 2015057842 W JP2015057842 W JP 2015057842W WO 2015141660 A1 WO2015141660 A1 WO 2015141660A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- medicine
- container
- drug
- information
- dispensing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65B—MACHINES, APPARATUS OR DEVICES FOR, OR METHODS OF, PACKAGING ARTICLES OR MATERIALS; UNPACKING
- B65B1/00—Packaging fluent solid material, e.g. powders, granular or loose fibrous material, loose masses of small articles, in individual containers or receptacles, e.g. bags, sacks, boxes, cartons, cans, or jars
- B65B1/30—Devices or methods for controlling or determining the quantity or quality or the material fed or filled
- B65B1/32—Devices or methods for controlling or determining the quantity or quality or the material fed or filled by weighing
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65B—MACHINES, APPARATUS OR DEVICES FOR, OR METHODS OF, PACKAGING ARTICLES OR MATERIALS; UNPACKING
- B65B37/00—Supplying or feeding fluent-solid, plastic, or liquid material, or loose masses of small articles, to be packaged
- B65B37/04—Supplying or feeding fluent-solid, plastic, or liquid material, or loose masses of small articles, to be packaged by vibratory feeders
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65B—MACHINES, APPARATUS OR DEVICES FOR, OR METHODS OF, PACKAGING ARTICLES OR MATERIALS; UNPACKING
- B65B57/00—Automatic control, checking, warning, or safety devices
- B65B57/005—Safety-devices
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65B—MACHINES, APPARATUS OR DEVICES FOR, OR METHODS OF, PACKAGING ARTICLES OR MATERIALS; UNPACKING
- B65B59/00—Arrangements to enable machines to handle articles of different sizes, to produce packages of different sizes, to vary the contents of packages, to handle different types of packaging material, or to give access for cleaning or maintenance purposes
- B65B59/04—Machines constructed with readily-detachable units or assemblies, e.g. to facilitate maintenance
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a drug dispensing device that dispenses powdered medicine for each dose.
- the powder medicine packaging device is an apparatus for individually packaging powder medicine or the like for each dose. If the powder medicine packaging device is used, it is possible to automate most of the work of packaging powder medicines one by one.
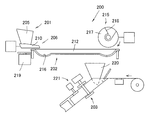
- the powder medicine packaging apparatus 200 disclosed in Patent Document 1 is an apparatus for individually packaging powder medicines for each dose. As shown in FIG. 25, the medicine supply apparatus 201, the powder medicine distribution apparatus 202, and the medicine packaging are contained therein. Device 203. As shown in FIGS. 25 and 26, the medicine supply device 201 disclosed in Patent Document 1 includes an input hopper 205 and a powder feeder 206. As shown in FIG. 26, the powder feeder 206 is provided with two piezoelectric elements 207 and 208 under the trough 210, and vibrates the trough 210.
- the powder distribution device 202 includes a distribution tray 212 and a scraping device 215.
- the distribution tray 212 has an arc-shaped cross section, and has an annular groove 216 in plan view. Distribution tray 212 is rotated at a constant speed by motor 219.
- the scraping device 215 has a disk 217 that moves up and down and rotates, and a scraping plate 218 is provided on the disk 217.
- the medicine packaging device 203 is composed of a packaging hopper 220 and a packaging device 221 as shown in FIG.
- the weighed 60 grams of powdered medicine is put into the feeding hopper 205 of the medicine supply device 201.
- the piezoelectric elements 207 and 208 (FIG. 26) of the powder feeder 206 are energized to vibrate the trough 210, and the distribution tray 212 is rotated at about 20 to 30 revolutions per minute.
- the powder charged in the charging hopper 205 falls from the opening at the lower end of the charging hopper 205 to the trough 210 of the powder feeder 206.
- the trough 210 vibrates, the powder slowly moves to the tip side and is rectified. Further, the rectification progresses while moving on the trough 210, and the flow of the medicine becomes a laminar flow state.
- the distribution of the drug in a cross section perpendicular to the flow is constant, and the distance that the drug travels per unit time is also constant.
- 60 grams of powder is evenly dispersed and slowly moves toward the tip side at a constant rate per hour.
- the powder that moves at the top reaches the tip of the trough 210, and the powder that moves at the top falls from the tip of the trough 210 into the groove 216 of the distribution tray 212. Further, the powder that follows will fall to the distribution tray 212 by a certain amount per hour. Finally, the last powder falls into the distribution tray 212 and all 60 grams of powder enters the groove 216.
- the distribution tray 212 rotates at a predetermined speed, the powder falling from the trough 210 is evenly distributed in the grooves 216 of the distribution tray 212. That is, the powder feeder 206 gradually drops the powder onto the distribution tray 212 and the distribution tray 212 rotates at a constant speed, so that the powder is evenly distributed in the grooves 216 of the distribution tray 212.
- the rotation of the distribution tray 212 is once stopped. Thereafter, the disk 217 of the scraping device 215 is dropped into the groove 216 of the distribution tray 212. Thereafter, the distribution tray 212 is rotated by an angle corresponding to the number of distribution. In the above example, 60 grams of powder is divided into 60 packets, so the distribution tray 212 is rotated by (60/360) degrees, and the powder is applied to the front side of the disk 217 by (60/360) degrees. Gather. Then, the disk 217 is rotated, and the powder for (60/360) degrees is scraped out of the distribution tray 212 by the scraper 218 and put into the packaging hopper 220. The powder falling from the packaging hopper 220 is packaged by the packaging device 221.
- the drug weighing system disclosed in Patent Document 2 includes a drug weighing device for weighing a drug and a powder packaging device for distributing and packaging the drug.
- the powder medicine packaging device has substantially the same configuration as that described above, and also has RFID (Radio). Frequency An RFID reader that reads information from an identification tag is provided.
- the drug weighing device employed in the invention of Patent Document 2 is provided with a barcode reader in addition to a weighing platform as a weighing means, and is accommodated in a prescription or a medicine bottle from a barcode attached to a prescription or a medicine bottle label. The type of the applied drug can be read.
- the medicine weighing device includes an RFID reader / writer, and can read information from the RFID tag and write information to the RFID tag.
- the drug weighing device has a touch panel. The touch panel functions as display means and input means.
- a drug sheet is used for weighing drugs.
- the medicine sheet functions as a tray for temporarily putting medicine, and an RFID tag is attached to the medicine sheet.
- the pharmacist moves the drug sheet on which the weighed drug is placed to the powder packaging device, and puts the drug into the charging hopper of the powder packaging device. Also, information related to dispensing is read into the medicine packaging device from the RFID tag of the medicine sheet.
- the powder medicine packaging device packages the powder according to the information obtained from the RFID tag. Therefore, after that, the medicine put into the hopper is divided and packaged one by one by the powder medicine packaging device.
- Patent Document 3 discloses a powder medicine packaging device having a function of automatically cleaning the distribution tray 212.
- the medicine supply device 201 employed in the prior art powder packaging device 200 is configured by the charging hopper 205 and the powder feeder 206 as described above.
- the medicine is put into the charging hopper 205, falls from the opening at the lower end of the charging hopper 205 to the trough 210 of the powder feeder 206, moves on the trough 210, and drops from the tip of the trough 210 to the groove 216 of the distribution tray 212. .
- the medicine when the medicine is packaged, the medicine may pass through not only the distribution tray 212 but also the charging hopper 205 and the trough 210, and the medicine may remain in the charging hopper 205 and the trough 210. Therefore, in order to completely prevent contamination of the medicine, not only the distribution tray 212 but also the charging hopper 205 and the trough 210 must be cleaned. However, this work is troublesome and improvement has been desired.
- the present invention focuses on the above-described problems of the prior art, and has an object to provide a medicine dispensing device that has a function of reducing human error during weighing and that does not require cleaning of the charging hopper and trough. It is what.
- An aspect for solving the above-described problem is a drug dispensing device including a separate main body device, a drug weighing device, and a drug container, wherein the drug weighing device detects the weight of the drug.
- a container vibration which has a detection means, a dispensing information reading means for reading information related to dispensing, an information writing means and / or a weighing apparatus side information reading means, and the main body device places and vibrates the drug container
- a medicine distribution device that divides the powder into a predetermined amount and divides the powder into a plurality of parts, a body-side information reading means, and a medicine container comprises a medicine reservoir for temporarily storing medicine, It has a medicine discharge part that opens laterally when placed on the container shaking table, an information recording member and / or a container identification member, and information related to dispensing is sent to the main body device in association with the medicine container.
- a drug dispensing device according to symptoms.
- the medicine dispensing device of the present invention includes a main body device and a medicine weighing device.
- the drug weighing device has substantially the same function as the drug weighing device disclosed in Patent Document 2, and includes a weight detection unit that detects the weight of the drug, a dispensing information reading unit that reads information related to dispensing, It has information writing means and / or weighing device side information reading means.
- the main unit does not have the charging hopper and the trough that have been adopted in the prior art, and a container shaking table is installed instead.
- the medicine dispensing apparatus of the present invention includes a medicine container.
- the medicine container has an information recording member and / or a container identification member.
- the medicine container has a medicine reservoir part for temporarily storing medicines, and a medicine discharge part that opens laterally when placed on the container shaking table of the main unit.
- the medicine dispensing apparatus according to the present invention, the weighed medicine is put into the medicine container, and the medicine container is placed on the container shaking table of the main body apparatus as it is. Then, the medicine container is vibrated by the container shaking table and dropped directly from the medicine discharge section onto the medicine dispensing device.
- the medicine dispensing apparatus according to the present invention drops medicine directly from the medicine container, and has no charging hopper and trough in the first place. Therefore, there is no need to clean the charging hopper and trough.
- the weight detection unit of the drug weighing device has a container mounting unit for mounting the drug container, and the weight detection unit detects the weight of the drug introduced from the drug input unit to the drug reservoir storage unit of the drug container.
- the medicine container has a medicine input part that opens upward when placed on the container placement part of the medicine weighing device.
- the drug can be weighed by loading the drug from the drug loading unit in a state where the drug is loaded on the container mounting unit of the drug weighing device.
- the medicine container has an information recording member, the information recording member can rewrite information, the medicine weighing device has information writing means, and information related to dispensing by the information writing means is recorded in the information recording means. It is desirable that information recorded on the member and recorded on the information recording member is read by the main body side information reading means so that information related to the dispensing is sent to the main body device in association with the medicine container.
- the main body side information reading means is a receiving means for receiving a signal
- the medicine container has a container identification member
- the medicine weighing apparatus has a weighing apparatus side information reading means
- the weighing apparatus side information reading means uses the medicine.
- Information specifying the container is read, information relating to dispensing and information specifying the drug container are transmitted from the drug weighing device, and the information is directly or indirectly transmitted to the main body device, and the main body side information reading means
- the information related to the dispensing by being received in the configuration may be transmitted to the main body device in association with the medicine container.
- the information related to the dispensing sent to the main body device in association with the drug container includes information related to the weight of the drug detected by the weight detection means.
- the main body device has a packaging device for packaging the medicine and printing means, and information related to the prescription is printed by the printing means.
- the main body device has display means and can display information related to the dispensing sent to the main body device in association with the medicine container on the display means.
- the medicine dispensing apparatus of the present invention it is possible to reduce human errors during weighing. Further, according to the medicine dispensing device of the present invention, the worker is released from the cleaning operation of the charging hopper and the trough.
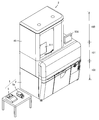
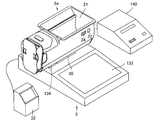
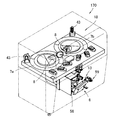
- FIG. 1 is a perspective view of a main body device, a drug weighing device, and a manual drug container of a drug dispensing device according to an embodiment of the present invention.
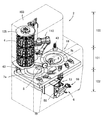
- FIG. 2 is a perspective view showing the inside of the main body device of FIG. It is a perspective view of the chemical
- FIG. 10 is an exploded perspective view of the container shaking table of FIG. 9.
- FIG. 10 is a vertical perspective view of the container shaking table of FIG. 9. It is a vertical side view of the container shaking table of FIG.
- FIG. 2 is a side view conceptually showing a part of a medicine dividing device of the main body device of FIG.
- FIG. 2 is a side view conceptually showing a part of a medicine dividing device of the main body device of FIG.
- FIG. 21 It is a perspective view which shows the state which mounted the manual type medicine container in the medicine weighing device. It is a flowchart which shows operation
- the medicine dispensing apparatus 1 includes a main body apparatus 2, a medicine weighing apparatus (medicine inspection system) 3, and a manual medicine container 5a.
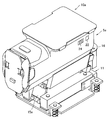
- the main body device 2 includes a powder dispensing device 18 and a drug packaging device 6 as in the powder packaging device 200 disclosed in Patent Document 1 (see FIGS. 2, 13, and 14).
- the powder distribution device 18 includes distribution dishes 7a and 7b and a scraping device 8, and can divide the supplied powder into doses.
- medical agent packaging apparatus 6 can be packaged for every dose.
- the medicine packaging device 6 has a printing means 13 built in, and can perform predetermined printing on the packaging bag.
- a medicine feeder 10a having a structure as shown in FIG. 4 is employed in place of the medicine supply apparatus 201 disclosed in Patent Document 1.
- the medicine feeder 10a includes a container shaking table 11 and a manual medicine container 5a.
- the container shaking table 11 constituting the medicine feeder 10a and the manual medicine container 5a are separate, and the electromagnet 12 (see FIG. 9) provided on the container shaking table 11 is acted to integrate both. be able to.
- the container shaking table 11 is vibrated by the vibrating means 15a and 15b.
- An RFID reader 16 serving as a main body side information reading unit is attached to the container vibration table 11.
- the container shaking table 11 is installed in the vicinity of the distribution dishes 7a and 7b as shown in FIGS.
- the main device 2 has a touch panel 106 as shown in FIG.
- the touch panel 106 serves as both display means and input means.
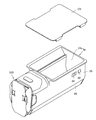
- the manual medicine container 5a is a container as shown in FIGS. 5, 6 and 7, and the container body 25 is open on the upper surface side and the distal end side.
- the manual medicine container 5a has a bottom, and has a medicine reservoir 9 for temporarily storing medicine.
- a rectifying member 17a is provided inside the manual medicine container 5a. That is, the manual medicine container 5a has a medicine discharge part 20a that opens in the lateral direction with reference to the posture placed on the container vibration table 11. The opening on the upper surface side functions as a medicine input part 21a.
- An RFID tag 22 as an information recording member is attached to the outer surface of the manual medicine container 5a.
- a fixed iron plate portion 26 is attached to the bottom of the manual medicine container 5a.
- a barcode 24 is also provided in addition to the RFID tag 22.
- the bar code 24 is a container identification member that identifies the manual drug container 5a.
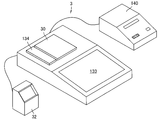
- the drug weighing device 3 is substantially the same as that disclosed in Patent Document 2 described above, and as shown in FIG. 16, a balance table (container placement unit) 30, an RFID reader / writer 134, and a barcode reader 32. And a touch panel 133.
- the barcode reader 32 functions as a dispensing information reading unit and a contained medicine confirmation unit, and in the embodiment of the present invention, the dispensing information described in the prescription is also stored in the medicine weighing device using the barcode reader 32. 3 is read by the control unit 131. Then, the pharmacist places the manual medicine container 5a on the balance table (container mounting part) 30, and directly introduces the medicine into the manual medicine container 5a from the medicine input part 21 of the manual medicine container 5a and measures the medicine. .
- the type of medicine contained in the medicine bottle is read from the barcode attached to the medicine bottle or the like (not shown) by the barcode reader 32 and it is confirmed that there is no mistake in the prescribed medicine. it can.
- Information on the prescription, the name of the pharmacist, and the type and amount of the weighed drug are written to the RFID tag 22 of the manual drug container 5a by the RFID reader / writer 134 of the drug weighing device. That is, the RFID reader / writer 134 functions as information writing means.
- the manual medicine container 5 a is moved manually or using a robot, and the manual medicine container 5 a is placed on the container vibration table 11 of the main body device 2.
- an RFID reader 16 as a main body side information reading means is provided in the vicinity of the container vibration table 11, and dispensing information is read into the main body device 2 by the RFID reader 16.
- the read dispensing information is displayed on the touch panel 106 provided in the main device 2. Therefore, the pharmacist can check the dispensing information displayed on the touch panel 106.
- this is displayed on the touch panel 106.
- the pharmacist can examine the displayed content and operate the touch panel 106 to instruct the main device 2 of work items and the like. That is, it is possible to instruct additional work and change work contents by using the touch panel 106.
- the kind and amount of the medicine described in the prescription and the kind and amount of the medicine contained in the manual medicine container 5a are different.
- the main body device 2 it may be necessary to put the remaining medicine into the distribution tray 7.
- a plurality of types of drugs are packed in the same package, and there are cases where drugs are put into the distribution tray 7 from a plurality of manual-type drug containers 5a.
- the pharmacist operates the touch panel 106 to operate the main body device 2 so as to perform an operation in accordance therewith.
- the support screen for the medicine filling operation is displayed on the screen of the touch panel 106 in advance. A filling operation may be performed.
- a predetermined operation is instructed from the touch panel 106 also when powder and tablets are combined. For example, when a main body device having a function of dispensing a solid medicine such as a tablet is adopted, or when a main body device having a “handing function” for individually packing tablets or the like is adopted, the touch panel 106 can be used. A predetermined operation is instructed.
- the pharmacist operates the touch panel 106 to cause the main body device 2 to perform the necessary operation. Furthermore, there is a case where the medicine required for the packing is not accommodated in the container-type drug container 4 or is insufficient, and the container-type drug container 4 needs to be newly filled. The pharmacist operates the touch panel 106 to cause the main body device 2 to perform necessary operations.
- the pharmacist's prescription inspection and a predetermined additional instruction are completed and the pharmacist operates the touch panel 106 to input a confirmation signal
- the confirmation signal is to touch a predetermined display portion of the touch panel 106
- the confirmation display is arbitrary. For example, a display such as “confirmation” and “work start” can be considered.
- the pharmacist creates a chance to start the packaging at his own will.
- the distribution tray 7 is rotated, and at the same time, the container shaking table 11 is vibrated.
- the manual-type medicine container 5a on the container vibration table 11 vibrates, and the internal powder slowly moves to the medicine discharge section 20 side, and finally falls from the medicine discharge section 20 to the distribution tray 7.
- the powder is dropped directly onto the distribution dish 7 from the manual medicine container 5a without passing through a conventional trough. Then, when all the powder has been dropped, the rotation of the distribution tray 7 is stopped. Thereafter, in accordance with the dispensing information read by the RFID reader 16, the powder in the distribution tray 7 is divided into a predetermined number, the drug is scraped out by the scraping device 8, put into the drug packaging device 6, and individually packaged. Predetermined characters are printed on the bag.
- the manual medicine container 5a is removed from the container shaking table 11.
- the medicine dispensing apparatus 1 of the present embodiment vibrates the manual medicine container 5a and directly inputs the powder into the distribution tray 7 from the manual medicine container 5a. Therefore, the trough 210 does not have the trough 210 as in the prior art. There is no need to clean.
- the manual medicine container 5a is placed on the balance table 30 of the medicine weighing device 3 and the medicine is loaded therein.
- the sheet is placed on the balance table 30 and the medicine is weighed.
- the medicine may be transferred from the sheet to the manual medicine container 5a.
- the RFID tag 22 as an information recording member writable in the manual medicine container 5 a is provided, dispensing information is recorded on the information recording member, and dispensing information is transmitted from the information recording member to the main body device 2.
- the manual medicine container 5a has an RFID tag 22 as an information recording member, the RFID tag 22 can rewrite information, and the medicine weighing device 3 is an RFID reader / writer as information writing means.
- the medicine weighing device 3 is an RFID reader / writer as information writing means.
- information related to the dispensing is recorded on the RFID tag 22 by the RFID reader / writer 134, and the information recorded on the RFID tag 22 is read by the RFID reader 16 which is the main body side information reading means.
- Information is sent to the main unit 2 in association with the manual medicine container 5a.
- the dispensing information may be directly transmitted from the medicine weighing device 3 to the main body device 2 by wire or wirelessly. Further, the dispensing information may be transmitted from the drug weighing device 3 to the main body device 2 via another central control device or the like.
- the main body device 2 is provided with a receiving means for receiving a signal as the main body side information reading means. Further, a bar code 24 provided on the manual medicine container 5a is used. Then, the drug weighing device 3 reads the information specifying the manual drug container 5a by causing the barcode reader 32 to function as the weighing device side information reading means.
- the main body device 2 is provided with a container confirmation means for recognizing the container identification member.
- the container confirmation means is, for example, a barcode reader.
- the RFID tag 22 provided on the manual medicine container 5a may be used as a container identification member, and the RFID reader 16 may be used as a container confirmation means.
- the barcode reader 32 reads information specifying the manual drug container 5a, and associates the information related to dispensing with the information specifying the manual drug container 5a to measure the drug.
- the information is transmitted from the device 3 and the main device 2 receives this information.
- the manual drug container 5a is individually identified by the container confirmation means of the main body device 2, and the drug is divided and packaged in accordance with the dispensing information related to the manual drug container 5a.
- a medicine dispensing device 1 described below includes a main body device 2, a medicine weighing device 3, a housed medicine container 4, and a manual medicine container 5a.
- the container-type medicine container 4 is an accessory member and is not directly related to the present invention.
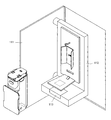
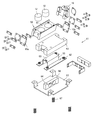
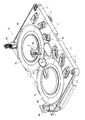
- the main body device 2 of the present embodiment is surrounded by a housing 40, and the inside thereof is divided into a medicine shelf area 100, a medicine division area 101, and a medicine packaging area 102.
- a container storage device 103 (FIG. 2) for installing the containing medicine container 4 is provided in the medicine shelf region 100.
- the container storage device 103 includes a vertical drum member 105 that rotates in a substantially horizontal direction, and a plurality of container installation devices (not shown) are provided on the outer peripheral surface of the drum member 105. In the container storage device 103, a large number of storage type drug containers 4 as shown in FIG. 8 are stored. Housed in the container storage device 103 is a container-type medicine container 4 of a type that does not have a medicine input portion as shown in FIG.
- the drum member 105 is rotated by a motor (not shown), and the desired container-type medicine container 4 is brought close to the robot 110 and attached / detached by the robot 110.
- a door member 111 is provided in the housing 40 of the medicine shelf region 100.
- the door member 111 is opened and closed by a hinge as shown in FIG. 3, and is a wing type door.
- a medicine container temporary placement portion 112 is provided inside the door member 111.
- a main body side information reading means (door portion) 113 such as an RFID reader is provided on the inner side of the door member 111.
- a robot 110 is provided in an area from the drug shelf area 100 to the drug division area 101.
- the medicine division area 101 is an area where the powder distribution device 18 is provided. As shown in FIGS. 2 and 13, the medicine division area 101 has a table member 38, and is an area where two distribution trays 7 a and 7 b are embedded in the table member 38. A table 11 and a cleaning device 43 are arranged. Further, a scraping device 8 is provided in the medicine division region 101.
- the table member 38 is provided with a medicine injection opening 68.
- the distribution trays 7a and 7b are members provided with a drug insertion groove 45 on the upper surface side.
- the medicine feeding groove 45 is also referred to as “R groove” and has a circular arc cross-sectional shape.
- the medicine charging groove 45 is in the vicinity of the outer edge of the distribution trays 7a and 7b.
- the distribution dishes 7a and 7b can be rotated at a constant speed by a dish rotation mechanism (not shown). It can also be rotated by a predetermined angle.
- the scraping device 8 includes a drive unit (not shown), a scraping arm 46 shown in FIG. 14, and a scraping mechanism 47 provided at the tip of the scraping arm 46.
- the cleaning device 43 has a cleaning arm 50 that protrudes from the table member 38 in a cantilevered manner and whose tip side is raised and lowered by power, and a cleaning brush 51 is provided at the tip.
- the table member 38 is provided with a container vibration table 11.
- a container vibration table 11 In the present embodiment, there are three sets of container shaking tables 11 around the distribution trays 7a and 7b.
- the structure of the container shaking table 11 is as shown in FIGS.
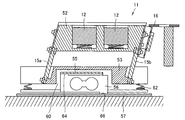
- the container shaking table 11 directly or indirectly determines the weight of the placing table 52 on which the housed medicine container 4 and the manual medicine container 5a are placed, and the medicine container (the housed medicine container 4 and the manual medicine container 5a). Weight measuring means for measuring.
- the container shaking table 11 is provided with an electromagnet 12 as a container holding means for temporarily fixing the drug container to the container shaking table 11. More specifically, the container holding means is an electromagnet having a structure called a self-holding solenoid.
- the self-holding solenoid is a combination of a permanent magnet and an electromagnet, and always exerts an attractive force mainly by the permanent magnet.
- the electromagnet is energized to generate a magnetic force in the direction opposite to that of the permanent magnet, thereby canceling the magnetic force of the permanent magnet.
- the manual medicine container 5a can be placed on the container vibration table 11, and the medicine can be discharged from the manual medicine container 5a by vibrating the container vibration table 11. Further, the weight change of the manual medicine container 5a at that time is detected by the weight measuring means.
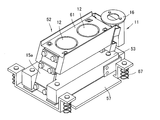
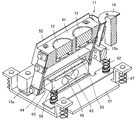
- the container vibration table 11 includes a mounting table 52, vibration units 15a and 15b, an intermediate table 53, a vibration isolation table 55, a vibration isolation member 62, a weight measurement unit 56, and a foundation member 57 from above. It is constituted by.
- An RFID reader 16 is provided in the vicinity of the mounting table 52.
- the mounting table 52 is a block-shaped mounting table.
- the appearance shape of the mounting table 52 is as shown in FIGS. 9 to 12, and is a substantially rectangular parallelepiped.
- An electromagnet 12 is built in the mounting surface 61.
- the vibration means 15a and 15b are piezoelectric elements.
- the intermediate platform 53 has a substantially “H” shape in plan view. There is a large cavity 60 inside the intermediate platform 53, and the back surface of the intermediate platform 53 is largely open.
- the vibration isolator 55 is a plate having a central portion protruding and a space provided inside.
- vibration means 15 a and 15 b are provided between the mounting table 52 and the intermediate table 53.
- the vibration means 15a and 15b exist between the mounting table 52 and the intermediate table 53, and the mounting table 52 is not supported in any part other than the vibration means 15a and 15b. Therefore, the mounting table 52 has a structure that is supported hollowly from the intermediate table 53 by the vibration means 15a and 15b.
- a vibration isolating table 55 is disposed below the intermediate table 53.
- the intermediate base 53 has a structure that is supported hollowly from the vibration isolation table 55 by the vibration isolation member 62.
- a weight measuring means 56 is arranged at the lower part of the vibration isolator 55, and a foundation member 57 is arranged at the lower part thereof.
- most of the weight measuring means 56 is in a ridge 63 provided at the center of the vibration isolation table 55, and the upper installation surface 64 of the weight measurement means 56 is the vibration isolation table 55. Is connected to the inner surface of the top surface of the ridge 63.
- the lower installation surface 66 of the weight measuring means 56 is attached to the base member 57.
- the base member 57 is attached to the vicinity of the distribution trays 7a and 7b in the medicine division region 101 via the vibration isolation member 67 as in the previous embodiment.
- the medicine packaging device 6 is built in the medicine packaging area 102.
- the medicine packaging device 6 is a machine for packaging a medicine for each dose, similarly to the known one, and is constituted by a packaging paper supply device and a packaging device as is well known. In addition, a medicine hopper for feeding medicine into the packaging part is provided.
- the medicine packaging device 6 is a device having a packaging paper supply device 58, a packaging device 59 and a printing means 13 as a basic configuration.
- the wrapping paper supply device 58 is a part that supplies sheet-shaped sealing paper to the wrapping unit.
- the packaging device 59 is a part that bends a sheet-like wrapping paper and introduces powder into the wrapping paper, and then fuses the sides of the sheet to form a bag.
- the wrapping paper supply device 58, the wrapping device 59, and the printing unit 13 employed in the present embodiment are all well-known and will not be described in detail.
- the manual medicine container 5a is a medicine container of a type having a medicine input part 21 a.
- the manual medicine container 5a includes a container body 25, a fixing iron plate portion 26, a discharge side cover member 120, an input side cover member 121, an RFID tag (information recording member) 22, and a barcode 24.
- the container body 25 is a vertically long container made of a resin, and one end in the longitudinal direction is opened to constitute the medicine discharge part 20a. In addition, there is a large opening on the side surface of the container body 25, and the opening functions as the medicine charging part 21a.
- the medicine discharge unit 20 a provided in the container body 25 is open in the horizontal direction with reference to the posture placed on the container vibration table 11. Moreover, the chemical
- the drug discharge unit 20a opens in the horizontal direction, and the drug input unit 21b opens upward.
- the medicine charging portion 21a has a flange portion 28 formed around the opening.
- the input side lid member 121 is attached to the flange portion 28.
- An RFID tag (information recording member) 22 and a barcode 24 are attached to the outer side surface of the container body 25.
- the discharge-side lid member 120 includes a lid body 125, a movable lid 124, a rectifying coil 126, and a comb-like rectifying member 130. Further, a desiccant 182 is disposed on the discharge-side lid member 120 as shown in FIG.
- the movable lid portion 124 has a knob portion 147, and the movable lid portion 124 is opened by pressing the knob portion 147. And the movable cover part 124 is maintained in the opened state.
- the discharge side lid member 120 is attached to the medicine discharge part 20a of the container body 25 as shown in FIG.
- the fixing iron plate portion 26 is a steel plate containing a magnetic component such as ferrite.
- the fixing iron plate portion 26 is an outer peripheral portion of the container body 25 and is attached to the peripheral wall lower surface 27.
- the surface on which the fixing iron plate portion 26 is attached and the surface on which the medicine injection portion 21a is provided face each other.
- the container-type medicine container 4 is an accessory part of the present invention, and does not directly affect the operational effects of the present invention.
- the housed medicine container 4 is a medicine container of a type that does not have a medicine input part.
- the container-type medicine container 4 is provided with a transporting iron plate portion 157 in the container body 25.
- the transporting iron plate portion 157 is divided into two small transporting iron plate portions 157a and 157b.
- the iron plate portion 157 for transportation is made of a steel plate containing a magnetic component such as ferrite. Since the other configuration of the container-type drug container 4 is the same as that of the manual drug container 5a, the description thereof is omitted.
- a pair of medicine feeders 10a is configured by the medicine container (the housed medicine container 4 or the manual medicine container 5a) and the container shaking table 11. That is, the medicine container (the housed medicine container 4 or the manual medicine container 5a) and the container shaking table 11 are separate, and when the powder medicine is packaged, they are combined to form the medicine feeder 10a.
- the main body device 2 employed in the present embodiment can selectively use the housed medicine container 4 and the manual medicine container 5a.
- the storage-type medicine container 4 is filled with a specific medicine in advance and is stored in the container storage device 103 in the medicine shelf region 100.
- medicines according to a prescription for a specific patient are put one by one by a pharmacist.
- the present invention is characterized in that a manual type drug container 5a is used.
- the manual medicine container 5 a is installed on the container shaking table 11 without being stored in the container storage device 103.
- the medicine feeder 10a has a function of fixing the manual medicine container 5a to the container vibration table 11 by the electromagnet 12 built in the mounting table 52, and discharging the powder by vibrating the manual medicine container a5.
- the drug weighing device includes weighing means, prescription information reading means, stored drug information reading means, information writing means, and control means.
- the weighing means measures the drug.
- the prescription etc. information reading means reads prescription etc. information including prescription drug identification information for identifying one or a plurality of prescription medicines recorded in the prescription.
- the contained medicine information reading means is a medicine container such as a medicine bottle.
- the stored medicine information of the stored medicine identification information for identifying the stored medicine recorded in is read from a medicine bottle or the like.
- the control means selects the prescription drug as a weighing target and weighs the prescription drug. A target weighing screen is displayed on the display means. Further, necessary information is written into the RFID tag 22 of the manual medicine container 5a by the information writing means.
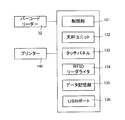
- the drug weighing device 3 includes a control unit 131, a balance unit 132, a touch panel 133, an RFID reader / writer 134, a data storage unit 135, a USB port 136, a barcode reader 32, a printer 140, and the like.
- the main body of the drug weighing device 3 is integrally provided with at least a balance table 30, a control unit 131, a balance unit 132, and a touch panel 133.
- the control unit 131 is a computer that includes a CPU, a ROM, a RAM (such as an EEPROM), and the like, and controls the drug weighing device 3 in an integrated manner.
- the CPU is a processor that executes various arithmetic processes according to various programs.
- the ROM is a non-volatile memory in which a program executed by the CPU is stored in advance.
- the RAM is a volatile memory or a non-volatile memory used for development of various programs by the CPU and temporary storage of data in various arithmetic processes.
- the balance unit 132 has a stainless steel balance table 30 and is a weighing means for weighing the drug placed on the balance table 30.
- the balance unit 132 is a balance unit that is also used in a well-known electronic balance including a balance circuit, a force coil, a current / voltage conversion circuit, an A / D conversion circuit, and the like.
- the weight of the medicine weighed by the balance unit 132 is input to the control unit 131 as digital data.
- a pharmacist or the like places a manual medicine container 5a on the balance table 30 and then puts the medicine into the manual medicine container 5a when weighing the medicine with the medicine weighing device 3.
- the manual medicine container 5a is provided with the RFID tag 22 as a recording medium on which various kinds of information are read and written.
- the RFID tag 22 is provided at a position where data can be read and written by the RFID reader / writer 134 when the manual medicine container 5 a is placed on the balance table 30.
- the balance unit 132 sets a value obtained by subtracting the weights of the manual medicine container 5a and the RFID tag 22 set in advance as a medicine weighing value.
- the touch panel 133 detects and detects an operation of a display unit such as a liquid crystal panel or an organic EL panel that displays various screens and various information according to a control instruction from the control unit 131 and an operation key displayed on the display unit. And a detection unit that inputs a signal to the control unit 131. That is, the touch panel 133 also serves as a display unit and an input unit in the drug weighing device 3. Specifically, the control unit 131 causes the touch panel 133 to display the weighing value weighed by the balance unit 132.
- a display unit such as a liquid crystal panel or an organic EL panel that displays various screens and various information according to a control instruction from the control unit 131 and an operation key displayed on the display unit.
- a detection unit that inputs a signal to the control unit 131. That is, the touch panel 133 also serves as a display unit and an input unit in the drug weighing device 3.
- the control unit 131 causes the touch panel 133 to display the weighing value weighed by the balance unit 132.
- the RFID reader / writer 134 records information on an RFID tag or an RFID label or reads information from the RFID tag or RFID label using RFID wireless communication technology.
- the RFID reader / writer 134 is provided adjacent to the balance table 30 and is used to read / write information from / to the RFID tag 22 when the manual medicine container 5a is placed on the balance table 30. .
- the RFID reader / writer 134 may be incorporated in the drug weighing device 3.
- the data storage unit 135 is a USB memory or other recording medium that stores various data such as a control program such as a drug weighing program executed by the control unit 131 and a pharmaceutical agent master, and is attached to and detached from the drug weighing device 3. Is possible.
- the drug weighing program is software that causes a computer such as the control unit 131 to execute each processing step of a drug weighing process (see FIG. 18) described later.
- an audit program for auditing whether or not the weighing value of the drug is within the range of a normal dose (a proper amount to be taken once a day or once) for each drug by the control unit 131. Therefore, the drug weighing device 3 can perform both of the drug weighing and the normal dose audit without using another information processing apparatus such as a computer.
- the drug master includes drug code, drug name, JAN code (or RSS), drug bottle code, classification (dosage form: powdered medicine, tablet, liquid medicine, topical medicine, etc.), specific gravity, drug type (ordinary drug, poisonous drug, Narcotics, powerful drugs, antipsychotics, therapeutic drugs, etc.), formulation changes, excipients, precautions, normal dose (corresponding to appropriate amount information), and information on prohibition of simultaneous use.
- the JAN code is information corresponding to the stored medicine name recorded in the medicine bottle supplied from the pharmaceutical manufacturer, and the JAN code is recorded (described) in the medicine bottle by the barcode.
- the medicine bottle code is the information corresponding to the stored medicine name recorded in the medicine bottle when the medicine in the medicine box supplied from the pharmaceutical manufacturer is subdivided into medicine bottles. Is recorded by barcode.
- the control unit 131 can obtain the stored medicine name corresponding to each barcode by referring to the pharmaceutical agent master.
- the normal dose is an appropriate amount to be taken on a daily or once basis corresponding to each drug.
- the simultaneous dosing prohibition information is information relating to a medicine that is determined in advance corresponding to each medicine and prohibited from being taken at the same time.
- the barcode reader 32 reads information from a one-dimensional barcode such as a JAN code or RSS and a two-dimensional code such as a QR code (registered trademark).
- a one-dimensional barcode such as a JAN code or RSS
- a two-dimensional code such as a QR code (registered trademark).
- the control unit 131 uses the barcode reader 32, a QR code (registered trademark) in which prescription information including one or more prescription drug names recorded (described) in the prescription is recorded. ) And other two-dimensional codes.
- the prescription information includes prescription delivery date, patient ID, patient name, patient date of birth, drug information (medicine code, drug name, dose, dosage form information “pills, powders and other oral medicines, ointments, etc. Medicine "), usage information (such as after meals three times a day), and the like.
- the control unit 131 uses the barcode reader 32 to record (describe) the stored medicine information including the stored medicine name recorded (described) in the medicine bottle with a barcode. Read from JAN code or vial code.
- the control unit 131 when executing the reading process corresponds to the stored medicine information reading unit.
- the method for reading the prescription information and the stored medicine information from the prescription or the medicine bottle is not limited to using a barcode, and may use a character recognition technique or an image recognition technique.
- an information recording medium such as an RFID tag or an RFID label is provided in the medicine bottle, and the contained medicine information including the name of the medicine contained in the medicine bottle is recorded on the information recording medium.
- prescription information including the prescription drug name recorded in the prescription is recorded on the information recording medium.
- prescription information may be input to a receipt computer or the like in advance, transmitted from the receipt computer or the like to the drug weighing device 3 via a LAN (wired / wireless), and received by the drug weighing device 3.
- the printer 140 prints out print data input from the control unit 131 via the USB port 136. Specifically, the printer 140 is used for printing a weighing result by the drug weighing device 3 and the like.
- the medicine dispensing device 1 can execute fully automatic packaging using the housed medicine container 4 and manual packaging using the manual medicine container 5a.
- the medicine dispensing device 1 of the present embodiment is characterized by the latter manual packaging.
- manual packaging using the manual medicine container 5a will be described.
- the manual packing operation procedure is roughly divided into “drug weighing operation” and “drug packing operation”.
- the drug weighing operation is an operation performed using the drug weighing device 3
- the drug packaging operation is an operation performed using the main body device 2.
- the main body device 2 has two types of drug containers. In the present embodiment, a manual drug container 5a is used.
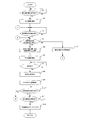
- the flowchart shows an example of a procedure of a drug weighing process executed by the control unit 131 in accordance with the drug weighing program in the drug weighing device 3.
- the drug weighing process is a process executed by the control unit 131 when the drug weighing device is turned on.
- the prescription, delivery date, patient ID, patient name, patient birth date, drug information (medicine code, drug name, dose, dosage form information “tablet, powdered and other oral medicines, ointments, etc.”
- drug information (medicine code, drug name, dose, dosage form information “tablet, powdered and other oral medicines, ointments, etc.”
- dispensing information such as “medicine”
- usage information (such as after every meal three times a day) is recorded in a two-dimensional code will be described as an example.
- the prescription drug name includes three types of drugs, drug A, drug B, and drug C. It is assumed that the above three types of medicines are not contained in the containing medicine container 4 housed in the container storage device 103.
- an empty manual drug container 5 a is placed on the balance table 30.
- the loading side lid member 121 of the manual drug container 5a is removed in advance, and the drug loading part 21a is opened.
- the medicine charging part 21a is opened upward.
- the control unit 131 of the drug weighing device 3 waits for reading of prescription information (step 1).
- the pharmacist operates the barcode reader 32 of the drug weighing device 3 to read dispensing information from the two-dimensional code attached to the prescription.
- the control unit 131 advances the process to step 2.
- the dispensing information read from the two-dimensional code includes prescription delivery date, patient ID, patient name, patient birth date, drug information (drug code, drug name, dose, dosage form information “tablet, powder, etc. Or other external medicines such as ointments, ointments, etc.), usage information (such as after meals three times a day), and the like.
- step 2 the control unit 131 displays a prescription screen (not shown) on the touch panel 133 based on the prescription information read in step 1.
- the prescription screen displays the dispenser name, patient name, age, weight, prescription days, fractions, drug name, dosage form, prescription amount, and the like.
- step 3 the control unit 131 waits for reading of the contained medicine name (NO side of step 3). Specifically, when the stored medicine information indicated by the JAN code or the medicine bottle code recorded in the medicine bottle is read by the bar code reader 32, the control unit 131 determines that the name of the medicine contained has been read. . When the pharmacist holds the JAN code or medicine bottle code of the medicine bottle over the barcode reader 32 and the barcode reader 32 reads the JAN code or medicine bottle code (YES side of step 3), the control unit 131 Shifts the process to step 4.
- step 4 the control unit 131 branches the process according to the collation result between the stored drug name in the stored drug information read in step 3 and the stored drug name in the prescription information read in step 1. Specifically, in step 4, the control unit 131 determines whether the stored medicine name corresponds to one of the prescription medicine names.
- step 5 if the stored medicine name corresponds to one of the prescription drug names (YES side of step 4), the process proceeds to step 5, and if the stored drug name does not correspond to any of the prescription drug names (step) 4 (NO side), the process proceeds to step 13.
- step 5 the control unit 131 selects a prescription drug name that matches the contained drug name among prescription drug names included in the prescription information as a weighing target. That is, when the stored medicine name corresponds to one of the prescription medicine names, the prescription medicine name to be weighed is automatically selected from the prescription medicine names included in the prescription information.
- the pharmacist can check the stored drug name and the prescription drug name in the drug weighing device 3 only by making the barcode reader 32 read the JAN code or the drug bottle code recorded in the drug bottle, and the drug to be weighed. Can be realized. Accordingly, when a plurality of prescription drug names are included in the prescription information, the operation for selecting the prescription drug name to be weighed can be omitted, and the dispensing efficiency by the doctor or pharmacist can be improved. .
- step 6 the control unit 131 causes the touch panel 133 to display a weighing screen (not shown) for weighing a drug having a prescription drug name corresponding to the stored drug name from the prescription information. At this time, the control unit 131 displays the measured value of the drug by the balance unit 132 and the target value of the measured drug of the prescription drug name on the weighing screen.
- the target value “0.9 g” that is the prescription amount of “drug A” and the actual weighing value “0.0 g” by the balance unit 132 are displayed.
- step 7 the control part 131 waits for completion of the measurement of the said prescription drug name (NO side of step 7). Specifically, the control unit 131 determines that the weighing of the prescription drug name is completed by operating a determination key (not shown) displayed on the weighing screen. When the control unit 131 determines that the weighing of the prescription drug name is complete (YES in step 7), the control unit 131 shifts the process to step 8. In addition, the control part 131 memorize
- RAM storage part 135
- step 8 the control unit 131 causes the touch panel 133 to display a progress screen (not shown) indicating the progress of the weighing of the prescription drug name in the prescription information.
- Step 9 the control unit 131 writes the dispensing information and the weighing result (an example of the weighing drug information) to the RFID tag 22 of the manual drug container by the RFID reader / writer 134.
- Dispensing information includes prescription delivery date, patient ID, patient name, patient date of birth, drug information (drug code, drug name, dose, dosage form information “internal medicine such as tablets and powders, topical medicines such as ointments) "), Information recorded in a prescription, such as usage information (such as after meals three times a day).
- the weighing result includes the name of the drug to be weighed, the weighing target value, the actual weighing value, the collation result between the prescription drug name and the stored drug name.
- the prescription drug name included in the prescription information is replaced with the generic drug name and weighed, information to that effect is also included in the weighing result.
- the control unit 131 may record only a part of prescription information on the RFID tag 22.
- the control unit 131 may store at least the drug name to be weighed in the RFID tag 22.
- the medicine weighing device 3 and the main body device 2 are communicably connected via a communication network such as a LAN or the Internet, and the control unit 131 may transmit information not recorded in the RFID 22 to the main body device 2. Conceivable.
- the main device 2 receives and stores the transmitted information by a control device (not shown).
- simple fixed information (such as an identification number of information) stored in the drug weighing device 3 in association with prescription information and weighing results. Can be recorded in the RFID tag 22.
- the main body device 2 requests the medicine weighing device 3 to transmit the prescription information and the weighing result corresponding to the fixed information.
- the prescription information and the weighing result corresponding to the fixed information are transmitted from the drug weighing device 3 to the main body device 2 via the communication network.
- the main device 2 receives and stores the transmitted information by a control device (not shown).
- step 8 and step 9 may be executed in reverse or in substantially parallel order. That is, immediately after it is determined in step 7 that weighing is completed, prescription information and weighing results may be recorded in the RFID tag 22 in step 9.
- step 10 the control unit 131 determines whether or not the next stored medicine name has been read by the barcode reader 32.
- the control part 131 judges that the next accommodated medicine name was read (YES side of step 10)
- it will transfer a process to step 4.
- the control unit 131 shifts the process to Step 11.
- step 11 the control unit 131 determines whether all weighings corresponding to the prescription information are completed. Specifically, when a completion key (not shown) is operated, or when weighing of all weighing target drugs included in the prescription information is completed, it is determined that all weighing related to the prescription information is completed. .
- step 11 a process will be transferred to step 12.
- the control part 131 makes a process transfer to step 10, when all the weighings regarding the said prescription etc. information are not completed (NO side of step 11).
- the control unit 131 determines in step 11 that the completion key (not shown) has been operated, the name of the prescription drug included in the prescription information, which is input of completion of weighing by the operation of the completion key. If there is a prescription drug name for which the completion of weighing is not input by the enter key, it can be displayed on the touch panel 133 to that effect. Thereby, it is possible to warn the pharmacist of forgetting to weigh.
- the control unit 131 determines whether or not the weighing of each prescription drug name is completed according to the information stored in the data storage unit 135 (RAM) in step 7.
- the control unit 131 when executing the display process corresponds to an incomplete display unit.
- the control part 131 may display a display with a character, an image, an audio
- the control unit 131 causes the printer 140 to print the prescription information and the weighing result in the subsequent step 12. Specifically, the patient name, the drug name to be weighed, the weighing target value, the actual weighing value in the drug weighing device 3, the prescription drug name and the contained drug name included in the prescription information read in Step 1 The collation result, weighing time, weighing operator, etc. are printed. That is, the control unit 131 causes the printer 140 to print only the record relating to the drug weighed in the drug weighing device 3.
- step 4 when the stored medicine name read in step 3 does not correspond to any of the prescription medicine names (NO side of step 4), the control unit 131 proceeds to step 13 and indicates that the medicine is different. A warning screen (not shown) is displayed on the touch panel 133, and the process returns to step 3. Thereby, it is possible to warn the pharmacist that the selection of the medicine bottle is wrong, and to prevent prescription of the wrong medicine.
- the pharmacist using the drug weighing device 3 can accurately and easily measure the drug according to the prescription by causing the barcode reader 32 to sequentially read the two-dimensional code of the prescription and the barcode of the drug bottle. It can be carried out.
- the medicine weighing device 3 collates the name of the contained medicine and the prescription medicine, and the prescription medicine to be weighed from which weighing is started. A name is selected. Therefore, when a plurality of prescription drug names are recorded in the prescription, the pharmacist can save the trouble of selecting the prescription drug name to be weighed.
- the “drug weighing operation” is completed through the above steps. Subsequent to this, “medicine packaging work” will be performed.
- the loading side lid member 121 is attached to the drug loading portion 21a of the manual drug container 5a by the hand of the pharmacist.
- the manual-type medicine container 5a is moved to the main body device 2 by the hand of the pharmacist, opens the door member 111 provided in the casing 40 of the medicine shelf section region 100 shown in FIG. 3). Thereafter, the packaging operation is automatically performed by the main body device 2. That is, information on the dispensing written in the RFID tag 22 of the manual medicine container 5a is read by the body side information reading means (door part) 113 such as an RFID reader provided inside the door member 111.
- the body side information reading means (door) 113 automatically determines the mounting destination of the manual medicine container 5a based on the read information.
- the body side information reading means (door) 113 automatically determines the mounting destination of the manual medicine container 5a based on the read information.
- two distribution dishes 7a and 7b are provided, it is determined which distribution dish 7a and 7b is used.
- three container shaking tables 11 are provided in the vicinity of each distribution tray 7a, 7b, so it is determined which of the container shaking tables 11 is to be fitted with the manual medicine container 5a.
- the manual medicine container 5a is placed on one of the container shaking tables 11 determined by the robot 110. That is, the robot 110 holding the manual medicine container 5 a goes directly to the container shaking table 11 without going to the container storage apparatus 103 and installs the manual medicine container 5 a in the container storage apparatus 103.
- the distribution trays 7a and 7b to be used may be selected depending on properties such as the color of the medicine.
- the RFID reader 16 is provided in the vicinity of the container vibration table 11, and information relating to dispensing is read also by the RFID reader 16 on the container vibration table 11 side.
- the powder is divided according to the information regarding the dispensing. That is, one of the distribution trays 7a and 7b rotates and simultaneously vibrates the container shaking table 11. As a result, the manual-type medicine container 5a on the container vibration table 11 vibrates, and the internal powder slowly moves to the medicine discharge section 20a, and finally falls from the medicine discharge section 20a to the distribution tray 7. That is, in the present embodiment, the powder is dropped directly onto the distribution dish 7 from the manual medicine container 5a without passing through a conventional trough. Then, when all the powder has been dropped, the rotation of the distribution tray 7 is stopped.
- the powder in the distribution tray 7 is divided into a predetermined number, the drug is scraped out by the scraping device 8, put into the drug packaging device 6, and individually packaged.
- predetermined characters are printed on the packaging bag.
- the groove cleaning operation is performed when all the medicines in the distribution trays 7a and 7b have been discharged. That is, the scraping arm 46 of the scraping device 8 shown in FIG. 14 is swung, the tip side is raised, and the scraping mechanism 47 is taken out from the distribution trays 7a and 7b. Subsequently, the cleaning arm 50 of the cleaning device 43 is rotated to lower the cleaning brush 51 provided at the tip, and the cleaning brush 51 is placed in the medicine feeding groove 45 of the distribution trays 7a and 7b. Then, the distribution trays 7a and 7b are rotated while the cleaning brush 51 is rotated.
- the cleaning arm 50 is rotated to raise the cleaning brush 51 provided at the tip, and the cleaning brush 51 is taken out from the medicine insertion groove 45 of the distribution trays 7a and 7b.
- the scraping portion cleaning operation is performed. That is, the turntable 48 built under the table is rotated, the entire scraping device 8 is turned, and the scraping mechanism 47 of the scraping device 8 is moved to the vicinity of the cleaning device 43. Then, the cleaning arm 50 of the cleaning device 43 is slightly inclined, the cleaning brush 51 is pressed against the scraping mechanism 47, and the cleaning brush 51 is rotated. As a result, the residual of the medicine stuck to the scraping mechanism 47 is scraped off by the cleaning brush 51 and enters the brush cover. The residual in the brush cover is sucked by the suction means. As a result, the scraping mechanism 47 is cleaned.
- the main unit used in the present embodiment does not have the trough 210 as in the prior art, it is not necessary to clean the trough 210.
- the main body device 2 has the container storage device 103 (FIG. 2) in which the container-type medicine container 4 is installed.
- the main body device 2 includes a robot 110.
- the container storage device 103 and the robot 110 are not indispensable, and may not have them like the main body device 170 shown in FIG.
- the RFID readers 16 serving as main body side information reading means are attached to the respective container vibration tables 11, but the RFID readers 16 are not necessarily provided for all. It suffices that an RFID reader is provided in any part of the main device 2 or the RFID reader is connected to the housing of the main device 2. Further, the RFID reader 16 may be provided in only one container vibration table 11.
- the main body device 170 shown in FIG. 24 is a main body device 170 that does not have the drug shelf region 100 or the robot 110, and the other configuration is the same as that of the main body device 2 described above, and thus detailed description thereof is omitted. .
- the pharmacist holds the manual medicine container 5a by hand and places the manual medicine container 5a on the container vibration table 11. Further, which distribution tray 7a, 7b is used and which container shaking table 11 is used is displayed on a touch panel (not shown) provided in the main body device 170. That is, the dispensing information is read into the main body device 170 by the RFID reader 16, and the dispensing information is displayed on the touch panel 106 provided in the main body device 2. In addition, the manual medicine container 5a is placed on any container shaking table 11. It is instructed whether to place it. The pharmacist places the manual medicine container 5a on the container shaking table 11 instructed according to the display.
- the manual drug container 5a with the input side lid member 121 has been disclosed as an example of the manual drug container.
- the manual medicine container 5a is suitable for a case where the robot 110 is used to move the manual medicine container 5a because the medicine inside does not spill even if it is conveyed in a vertical posture.
- the charging side lid member 121 is not necessary, and for example, a manual drug container 5b as shown in FIG. 20 is adopted. You can also.
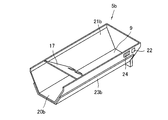
- the manual medicine container 5b is a container having a boat shape or a bowl shape as shown in FIG. 20, and has an upper surface side and a distal end side opened.
- the manual medicine container 5b has a bottom, and has a medicine reservoir 9 for temporarily storing medicine. Further, a rectifying member 17 is provided inside the manual medicine container 5b. That is, the manual medicine container 5b has a medicine discharge part 20b that opens laterally with reference to the posture placed on the container vibration table 11. The opening on the upper surface side functions as a medicine input part 21b. An RFID tag 22 as an information recording member is attached to the outer surface of the manual medicine container 5b. An iron plate 23b is attached to the bottom of the manual medicine container 5b.
- the operator directly holds the manual medicine container 5b by hand and moves the manual medicine container 5b to manually move the medicine.
- the container 5 b is placed on the container shaking table 11. After that, when the pharmacist's prescription inspection and a predetermined additional instruction are completed and the pharmacist operates the touch panel 106 to input a confirmation signal, the above-described packaging operation is started.
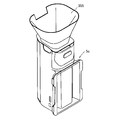
- FIG. 21 shows a modification of the manual drug container. That is, the manual medicine container 5c shown in FIG. 21 has a large opening (medicine charging part) 150 on the upper surface of the peripheral wall of the container body 25c, and a large lid 151 is provided in the opening 150.
- the large lid 151 can be opened to put the medicine inside.
- the shape of the top surface when the large lid 151 is turned over is made to match the shape of the bottom surface of the container body 5c. Since the bottom side when the large lid 151 is turned over is larger than the top surface, when the large lid 151 is turned over and placed on the desk, the large lid 151 maintains a stable posture. Therefore, as shown in FIG. 22, by removing the large lid 151, turning it over and placing it on the container body 25c, it can be used as a base for the container body 25c.
- the sheet or the like may be weighed on the balance table 30, and then the drug may be transferred from the sheet to the manual drug container.
- the manual drug container 5c shown in FIG. 21 adopts this method. Recommended if.
- a funnel member 355 may be mounted on the lid member 120 side to transfer the medicine.
- the medicine dispensing device 1 of the present embodiment also has a function of performing fully automatic packaging using the housed medicine container 4.
- fully automatic packaging is performed using the containment drug container 4.
- the storage-type drug container 4 is filled with a specific drug in advance and stored in the container storage device 103 in the drug shelf region 100.
- the container shaking table 11 employed in the present embodiment includes weight measuring means 56 that directly or indirectly measures the weight of the containing drug container 4.
- the main body device 2 employed in the above-described embodiment includes a container storage device 103.
- the above-described main body device 2 has a function of automatically selecting a container-type medicine container 4 in which a medicine is accommodated according to a prescription and further automatically weighing the medicine in the main body device 2.
- This function is demonstrated using the containment type drug container 4.
- a predetermined medicine is stored in advance in the storage-type medicine container 4 and the storage-type medicine container 4 filled with the medicine is stored in the container storage device 103.
- the drum member 105 of the container storage device 103 is rotated to bring the desired container type medicine container 4 closer to the robot 110.
- the robot 110 holds the container type drug container 4 and operates the arm or the like to place the container type drug container 4 on the container shaking table 11.
- medical agent container 4 is installed in the container vibration stand 11.
- the container shaking table 11 is vibrated.
- the powder in the container-type drug container 4 slowly moves, is discharged from the container-type drug container 4, and falls to the distribution trays 7a and 7b.
- the distribution trays 7a and 7b are rotated before and after the start of vibration.
- the weight of the container-type medicine container 4 is measured. Meanwhile, the weight of the container-type medicine container 4 is monitored, and the vibration of the container shaking table 11 is stopped when the total amount of powder drops reaches a desired weight.
- the original weight which is the weight of the container-type drug container 4 before discharging the drug
- the weight measuring means 56 when the powder is discharged from the container-type drug container 4 little by little, the container-shaped drug is measured by the weight measuring means 56.
- the weight of the container 4 is monitored.
- the current weight which is the current weight of the container-type drug container 4
- the weight measuring means 56 is not essential. This is because the total amount of the medicine to be distributed to the distribution trays 7a and 7b is weighed by the medicine weighing device 3 in advance, so that it is not necessary to stop the dispensing operation halfway. Therefore, it is only necessary to confirm whether or not the medicine is discharged by an optical sensor or the like, and it is sufficient to detect that all the medicine is discharged from the manual medicine container 5. That is, the weight measuring means 56, the container storage device 103, the robot 110, and the like included in the container shaking table 11 are not essential to the present invention. Moreover, in this embodiment, although the main body side information reading means is provided in both the door member 111 and the container shaking table 11, any one may be sufficient.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Medical Preparation Storing Or Oral Administration Devices (AREA)
- Basic Packing Technique (AREA)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020167023659A KR102349296B1 (ko) | 2014-03-18 | 2015-03-17 | 약제 불출장치 |
| JP2016508729A JP6601686B2 (ja) | 2014-03-18 | 2015-03-17 | 薬剤払出し装置 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014054486 | 2014-03-18 | ||
| JP2014-054486 | 2014-03-18 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015141660A1 true WO2015141660A1 (ja) | 2015-09-24 |
Family
ID=54144627
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2015/057842 Ceased WO2015141660A1 (ja) | 2014-03-18 | 2015-03-17 | 薬剤払出し装置 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (8) | JP6601686B2 (enExample) |
| KR (1) | KR102349296B1 (enExample) |
| TW (1) | TWI647150B (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2015141660A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2017111022A1 (ja) * | 2015-12-24 | 2017-06-29 | 株式会社タカゾノテクノロジー | 凹部形成装置及びこれを備えた薬剤供給装置、薬剤包装装置 |
| JP2019068934A (ja) * | 2017-10-06 | 2019-05-09 | 株式会社湯山製作所 | 薬品払出装置、薬品払出プログラム |
| JP2020006132A (ja) * | 2018-07-03 | 2020-01-16 | 株式会社トーショー | 散薬分包機 |
| JP2020062368A (ja) * | 2018-10-13 | 2020-04-23 | 株式会社トーショー | 散薬自動計量準備装置 |
| CN111372548A (zh) * | 2018-01-11 | 2020-07-03 | 株式会社汤山制作所 | 散剂称量装置和药剂分包系统 |
| JP2022009426A (ja) * | 2017-11-22 | 2022-01-14 | 株式会社タカゾノ | 粉粒体供給装置 |
| CN114795771A (zh) * | 2022-05-23 | 2022-07-29 | 徐宏女 | 一种实现药品多样化配置的配药装置 |
| JP2023056528A (ja) * | 2018-08-31 | 2023-04-19 | 株式会社タカゾノ | 散剤計量装置及び散剤計量分包装置 |
| JP2023115145A (ja) * | 2014-03-18 | 2023-08-18 | 株式会社湯山製作所 | 薬剤払出し装置 |
| JP2024023701A (ja) * | 2020-07-15 | 2024-02-21 | 株式会社タカゾノ | 薬剤分包装置 |
| JP2024071607A (ja) * | 2020-08-04 | 2024-05-24 | 株式会社タカゾノ | 薬剤供給装置 |
| JP2024105704A (ja) * | 2020-10-13 | 2024-08-06 | 株式会社タカゾノ | 薬剤分配装置 |
| WO2024228157A1 (de) * | 2023-05-03 | 2024-11-07 | Hmh Sytems Ag | Vorrichtung zum beschicken eines zuführsystem zur verpackung von medikamenten |
| JP2024169591A (ja) * | 2018-08-31 | 2024-12-05 | 株式会社タカゾノ | 散剤計量分包装置 |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110422347B (zh) * | 2019-07-25 | 2021-06-18 | 南通超科机器人有限公司 | 采用中心滑环装置通信的中药饮片集中煎药配药装置 |
| TWI758775B (zh) * | 2020-07-09 | 2022-03-21 | 科達製藥股份有限公司 | 取藥套組及其系統 |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008154783A (ja) * | 2006-12-22 | 2008-07-10 | Tosho Inc | 散薬調剤機 |
| JP5239297B2 (ja) * | 2007-07-03 | 2013-07-17 | 株式会社湯山製作所 | 薬剤包装装置 |
| WO2013154202A1 (ja) * | 2012-04-13 | 2013-10-17 | 株式会社湯山製作所 | 薬品秤量装置、薬品秤量システム、薬品秤量プログラム、記録媒体 |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6355001A (ja) * | 1986-08-25 | 1988-03-09 | 株式会社 東京商会 | 散剤分包機の作動装置 |
| JPH0242653Y2 (enExample) * | 1987-03-04 | 1990-11-14 | ||
| JPH0312159A (ja) * | 1989-06-09 | 1991-01-21 | Shoji Yuyama | 薬品の調剤分包システム |
| JP2893988B2 (ja) * | 1991-03-12 | 1999-05-24 | 神鋼電機株式会社 | 振動供給装置 |
| JPH11114020A (ja) * | 1997-10-17 | 1999-04-27 | Tosho:Kk | 散薬供給装置 |
| JP4057159B2 (ja) | 1998-09-10 | 2008-03-05 | 株式会社湯山製作所 | 散薬分配装置 |
| JP4877586B2 (ja) * | 2006-07-06 | 2012-02-15 | 株式会社湯山製作所 | 薬剤収納取出装置 |
| JP4450839B2 (ja) | 2007-02-19 | 2010-04-14 | 高園産業株式会社 | 薬剤分配装置 |
| JP5899544B2 (ja) * | 2011-12-12 | 2016-04-06 | 株式会社タカゾノテクノロジー | 薬剤分包機用のフィーダユニット及びそのトラフ |
| WO2015141660A1 (ja) | 2014-03-18 | 2015-09-24 | 株式会社湯山製作所 | 薬剤払出し装置 |
-
2015
- 2015-03-17 WO PCT/JP2015/057842 patent/WO2015141660A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2015-03-17 KR KR1020167023659A patent/KR102349296B1/ko active Active
- 2015-03-17 JP JP2016508729A patent/JP6601686B2/ja active Active
- 2015-03-18 TW TW104108671A patent/TWI647150B/zh active
-
2019
- 2019-03-25 JP JP2019056610A patent/JP6628118B2/ja active Active
- 2019-09-04 JP JP2019161189A patent/JP6796270B2/ja active Active
-
2020
- 2020-11-06 JP JP2020185753A patent/JP7096982B2/ja active Active
-
2022
- 2022-06-24 JP JP2022101516A patent/JP7308395B2/ja active Active
-
2023
- 2023-06-27 JP JP2023104860A patent/JP7478941B2/ja active Active
-
2024
- 2024-04-22 JP JP2024069249A patent/JP7624586B2/ja active Active
-
2025
- 2025-01-17 JP JP2025006571A patent/JP7770631B2/ja active Active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008154783A (ja) * | 2006-12-22 | 2008-07-10 | Tosho Inc | 散薬調剤機 |
| JP5239297B2 (ja) * | 2007-07-03 | 2013-07-17 | 株式会社湯山製作所 | 薬剤包装装置 |
| WO2013154202A1 (ja) * | 2012-04-13 | 2013-10-17 | 株式会社湯山製作所 | 薬品秤量装置、薬品秤量システム、薬品秤量プログラム、記録媒体 |
Cited By (27)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2023115145A (ja) * | 2014-03-18 | 2023-08-18 | 株式会社湯山製作所 | 薬剤払出し装置 |
| JP7770631B2 (ja) | 2014-03-18 | 2025-11-17 | 株式会社湯山製作所 | 薬剤払出し装置 |
| JP2025061417A (ja) * | 2014-03-18 | 2025-04-10 | 株式会社湯山製作所 | 薬剤払出し装置 |
| JP7624586B2 (ja) | 2014-03-18 | 2025-01-31 | 株式会社湯山製作所 | 薬剤払出し方法 |
| JP2024086992A (ja) * | 2014-03-18 | 2024-06-28 | 株式会社湯山製作所 | 薬剤払出し方法 |
| JP7478941B2 (ja) | 2014-03-18 | 2024-05-08 | 株式会社湯山製作所 | 薬剤払出し装置 |
| WO2017111022A1 (ja) * | 2015-12-24 | 2017-06-29 | 株式会社タカゾノテクノロジー | 凹部形成装置及びこれを備えた薬剤供給装置、薬剤包装装置 |
| JP2019068934A (ja) * | 2017-10-06 | 2019-05-09 | 株式会社湯山製作所 | 薬品払出装置、薬品払出プログラム |
| JP6996210B2 (ja) | 2017-10-06 | 2022-01-17 | 株式会社湯山製作所 | 薬品払出装置、薬品払出プログラム |
| JP2022009426A (ja) * | 2017-11-22 | 2022-01-14 | 株式会社タカゾノ | 粉粒体供給装置 |
| JP7140427B2 (ja) | 2017-11-22 | 2022-09-21 | 株式会社タカゾノ | 粉粒体供給装置 |
| JP7392246B2 (ja) | 2018-01-11 | 2023-12-06 | 株式会社湯山製作所 | 薬剤分包システム及び薬剤払い出し方法 |
| JP2023024530A (ja) * | 2018-01-11 | 2023-02-16 | 株式会社湯山製作所 | 薬剤分包システム及び薬剤払い出し方法 |
| CN111372548A (zh) * | 2018-01-11 | 2020-07-03 | 株式会社汤山制作所 | 散剂称量装置和药剂分包系统 |
| JP2020006132A (ja) * | 2018-07-03 | 2020-01-16 | 株式会社トーショー | 散薬分包機 |
| JP2024169591A (ja) * | 2018-08-31 | 2024-12-05 | 株式会社タカゾノ | 散剤計量分包装置 |
| JP7454886B2 (ja) | 2018-08-31 | 2024-03-25 | 株式会社タカゾノ | 散剤計量装置及び散剤計量分包装置 |
| JP2023056528A (ja) * | 2018-08-31 | 2023-04-19 | 株式会社タカゾノ | 散剤計量装置及び散剤計量分包装置 |
| JP2020062368A (ja) * | 2018-10-13 | 2020-04-23 | 株式会社トーショー | 散薬自動計量準備装置 |
| JP7621683B2 (ja) | 2020-07-15 | 2025-01-27 | 株式会社タカゾノ | 薬剤分包装置 |
| JP2024023701A (ja) * | 2020-07-15 | 2024-02-21 | 株式会社タカゾノ | 薬剤分包装置 |
| JP2024071607A (ja) * | 2020-08-04 | 2024-05-24 | 株式会社タカゾノ | 薬剤供給装置 |
| JP7718726B2 (ja) | 2020-08-04 | 2025-08-05 | 株式会社タカゾノ | 薬剤供給装置 |
| JP2024105704A (ja) * | 2020-10-13 | 2024-08-06 | 株式会社タカゾノ | 薬剤分配装置 |
| JP7718732B2 (ja) | 2020-10-13 | 2025-08-05 | 株式会社タカゾノ | 薬剤分配装置 |
| CN114795771A (zh) * | 2022-05-23 | 2022-07-29 | 徐宏女 | 一种实现药品多样化配置的配药装置 |
| WO2024228157A1 (de) * | 2023-05-03 | 2024-11-07 | Hmh Sytems Ag | Vorrichtung zum beschicken eines zuführsystem zur verpackung von medikamenten |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2020006196A (ja) | 2020-01-16 |
| JP2019115735A (ja) | 2019-07-18 |
| JP2022123133A (ja) | 2022-08-23 |
| JP2025061417A (ja) | 2025-04-10 |
| TWI647150B (zh) | 2019-01-11 |
| JP2023115145A (ja) | 2023-08-18 |
| JP6628118B2 (ja) | 2020-01-08 |
| KR20160133428A (ko) | 2016-11-22 |
| JP7096982B2 (ja) | 2022-07-07 |
| JP7308395B2 (ja) | 2023-07-14 |
| JP6796270B2 (ja) | 2020-12-09 |
| JP7770631B2 (ja) | 2025-11-17 |
| KR102349296B1 (ko) | 2022-01-10 |
| JPWO2015141660A1 (ja) | 2017-04-13 |
| JP7478941B2 (ja) | 2024-05-08 |
| TW201619005A (zh) | 2016-06-01 |
| JP6601686B2 (ja) | 2019-11-06 |
| JP2021013768A (ja) | 2021-02-12 |
| JP7624586B2 (ja) | 2025-01-31 |
| JP2024086992A (ja) | 2024-06-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7308395B2 (ja) | 薬剤払出し装置の動作方法 | |
| JP2019115735A5 (enExample) | ||
| JP7089683B2 (ja) | 薬品払出装置 | |
| JP7471560B2 (ja) | 薬品払出装置 | |
| JP6833183B2 (ja) | 散薬調剤業務支援システム | |
| TW201930149A (zh) | 散劑秤量裝置及藥劑分包系統 | |
| JP2024003040A (ja) | 薬剤分包装置 | |
| JP7212851B2 (ja) | 散薬調剤業務支援システム | |
| JP7718726B2 (ja) | 薬剤供給装置 | |
| JP7756951B2 (ja) | 薬剤供給装置 | |
| JP6833184B2 (ja) | 散薬調剤業務支援システム | |
| JP7412766B2 (ja) | 薬剤分包装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 15765506 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20167023659 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2016508729 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 15765506 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |