WO2015068490A1 - バルブ - Google Patents
バルブ Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015068490A1 WO2015068490A1 PCT/JP2014/075587 JP2014075587W WO2015068490A1 WO 2015068490 A1 WO2015068490 A1 WO 2015068490A1 JP 2014075587 W JP2014075587 W JP 2014075587W WO 2015068490 A1 WO2015068490 A1 WO 2015068490A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- valve
- chamber
- piston
- seat
- outer peripheral
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16F—SPRINGS; SHOCK-ABSORBERS; MEANS FOR DAMPING VIBRATION
- F16F9/00—Springs, vibration-dampers, shock-absorbers, or similarly-constructed movement-dampers using a fluid or the equivalent as damping medium
- F16F9/32—Details
- F16F9/34—Special valve constructions; Shape or construction of throttling passages
- F16F9/348—Throttling passages in the form of annular discs or other plate-like elements which may or may not have a spring action, operating in opposite directions or singly, e.g. annular discs positioned on top of the valve or piston body
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16F—SPRINGS; SHOCK-ABSORBERS; MEANS FOR DAMPING VIBRATION
- F16F9/00—Springs, vibration-dampers, shock-absorbers, or similarly-constructed movement-dampers using a fluid or the equivalent as damping medium
- F16F9/32—Details
- F16F9/34—Special valve constructions; Shape or construction of throttling passages
- F16F9/348—Throttling passages in the form of annular discs or other plate-like elements which may or may not have a spring action, operating in opposite directions or singly, e.g. annular discs positioned on top of the valve or piston body
- F16F9/3481—Throttling passages in the form of annular discs or other plate-like elements which may or may not have a spring action, operating in opposite directions or singly, e.g. annular discs positioned on top of the valve or piston body characterised by shape or construction of throttling passages in piston
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16F—SPRINGS; SHOCK-ABSORBERS; MEANS FOR DAMPING VIBRATION
- F16F9/00—Springs, vibration-dampers, shock-absorbers, or similarly-constructed movement-dampers using a fluid or the equivalent as damping medium
- F16F9/32—Details
- F16F9/34—Special valve constructions; Shape or construction of throttling passages
- F16F9/348—Throttling passages in the form of annular discs or other plate-like elements which may or may not have a spring action, operating in opposite directions or singly, e.g. annular discs positioned on top of the valve or piston body
- F16F9/3484—Throttling passages in the form of annular discs or other plate-like elements which may or may not have a spring action, operating in opposite directions or singly, e.g. annular discs positioned on top of the valve or piston body characterised by features of the annular discs per se, singularly or in combination
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16K—VALVES; TAPS; COCKS; ACTUATING-FLOATS; DEVICES FOR VENTING OR AERATING
- F16K31/00—Actuating devices; Operating means; Releasing devices
- F16K31/12—Actuating devices; Operating means; Releasing devices actuated by fluid
- F16K31/122—Actuating devices; Operating means; Releasing devices actuated by fluid the fluid acting on a piston
- F16K31/1223—Actuating devices; Operating means; Releasing devices actuated by fluid the fluid acting on a piston one side of the piston being acted upon by the circulating fluid
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16K—VALVES; TAPS; COCKS; ACTUATING-FLOATS; DEVICES FOR VENTING OR AERATING
- F16K31/00—Actuating devices; Operating means; Releasing devices
- F16K31/12—Actuating devices; Operating means; Releasing devices actuated by fluid
- F16K31/122—Actuating devices; Operating means; Releasing devices actuated by fluid the fluid acting on a piston
- F16K31/1226—Actuating devices; Operating means; Releasing devices actuated by fluid the fluid acting on a piston the fluid circulating through the piston
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a valve.
- the valve controls the flow direction and flow rate of fluid such as liquid and gas.
- the valve disclosed in JP2001-082526A is embodied as a piston valve of a shock absorber, and is held by a rod that enters and exits a cylindrical cylinder and is inserted into the cylinder so as to be movable in the axial direction.
- the piston valve includes a piston that is a valve disk that is formed in a cylinder and divides an expansion side chamber and a pressure side chamber filled with hydraulic oil, and an annular plate-like leaf valve that is stacked on both sides in the axial direction of the piston. It has. Furthermore, the piston is formed on both sides in the axial direction to form an annular boss portion that supports the leaf valve, a seat that is formed on the outer peripheral side of each boss portion, on which the leaf valve is seated, and an opening that is surrounded by each seat. And an extension side passage that communicates the extension side chamber and the opening on the compression side chamber side, and a pressure side passage that communicates the opening on the compression side chamber and the extension side chamber.
- the expansion side chamber When the expansion side chamber is pressurized during the extension of the shock absorber and the pressure in the expansion side chamber reaches the valve opening pressure of the leaf valve on the compression side chamber, the outer periphery of the leaf valve moves away from the seat on the compression side chamber side. Since the passage of the passage is allowed, the shock absorber generates an extension side damping force due to resistance when the hydraulic oil moves from the extension side chamber to the compression side chamber through the extension side passage.
- the compression side chamber is pressurized and the pressure side chamber pressure reaches the valve opening pressure of the leaf valve on the expansion side chamber during compression of the shock absorber, the outer periphery of the leaf valve is separated from the seat on the expansion side and the pressure side Since the passage of the passage is allowed, the shock absorber generates a compression side damping force due to the resistance when the hydraulic oil passes through the compression side passage and moves from the compression side chamber to the extension side chamber.
- the piston disclosed in JP2001-082526A is a molded piston integrated with a synthetic resin piston ring attached to the outer periphery thereof, and smoothly slides inside the cylinder by slidingly contacting the inner peripheral surface of the cylinder via the piston ring. Can be moved to.
- a piston ring is formed by vertically stacking pistons mounted on the outer periphery of an annular plate-shaped base material that will later become a piston ring, and sequentially pushing the piston into a heated mold. At the same time, the piston ring and the piston are integrated. At this time, a large force is applied to the piston and pushed into the mold.
- the overlapping piston bosses may not contact each other.
- the contact area of the piston may be extremely small.
- the problems associated with the deformation of the seat described above are handled by stacking the valve discs vertically, regardless of whether the valve disc is used for a shock absorber, the seat shape, the presence or absence of the piston ring, and the mounting method. In this case, this may occur when the boss portions cannot be brought into contact with each other and the outer diameters of the leaf valves that are seated on and off the seats are different.
- the object of the present invention is to suppress the deformation of the seat even when the bosses are not in contact with each other and the outer diameters of the leaf valves that are seated on and off the seats are different when the valve discs are stacked vertically. It is to provide a possible valve.
- a valve disk that divides one chamber and the other chamber, and an annular plate-shaped leaf valve that is stacked on the one chamber side and the other chamber side of the valve disk, respectively.
- the valve disc is formed on each of the one chamber side and the other chamber side to form an annular boss portion that supports the leaf valve, and on the outer peripheral side of each of the one chamber side and the other chamber side.
- a second passage that communicates with the opening, and at least one of the sheets on the one chamber side and the other chamber side is disposed so as to protrude from the boss portion, and the other chamber side Outside the seat
- the end is disposed on the outer peripheral side of the outer peripheral end of the leaf valve seated on the seat on the other chamber side, and the outer peripheral end of the seat on the other chamber side is the one in the radial direction of the valve disc.
- a valve is provided that is disposed at the same position as the outer peripheral end of the seat on the chamber side or on the outer peripheral side of the outer peripheral end of the seat on the one chamber side.
- FIG. 1 is a longitudinal sectional view showing a main part of a shock absorber provided with a piston valve (valve) according to an embodiment of the present invention.
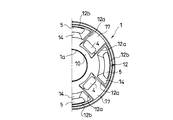
- FIG. 2A is a plan view showing a piston (valve disk) in the piston valve (valve) according to the embodiment of the present invention.
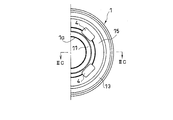
- FIG. 2B is a bottom view of the piston (valve disk) in the piston valve (valve) according to the embodiment of the present invention.
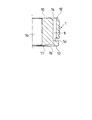
- 2C is a cross-sectional view taken along the line IIC-IIC in FIG. 2B.
- FIG. 3 is an enlarged view of a part of FIG. 2C.
- FIG. 1 is a longitudinal sectional view showing a main part of a shock absorber provided with a piston valve (valve) according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 2A is a plan view showing a piston (valve disk) in the piston valve (valve) according to the embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 2B is a bottom view of the piston (
- FIG. 4 shows that when the piston (valve disk) in the piston valve (valve) according to the embodiment of the present invention is coaxially overlapped, the boss portion and the seat of one of the overlapping pistons overlap the seat of the other piston. It is explanatory drawing which showed the state.
- FIG. 5 is an explanatory view showing a process of attaching a piston ring to a piston (valve disk) in the piston valve (valve) according to the embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 6A is a plan view showing a piston (valve disk) in a piston valve (valve) according to a comparative example.
- FIG. 6B is a bottom view of a piston (valve disk) in a piston valve (valve) according to a comparative example.
- FIG. 6C is a cross-sectional view taken along the line VIC-VIC in FIG. 6B.
- FIG. 7 shows a state where a piston (valve disk) in a piston valve (valve) according to a comparative example is overlapped on the same axis, and a boss portion of one piston and a seat overlap with a seat of the other piston. It is explanatory drawing.
- the valve according to the present embodiment is embodied as a piston valve V of the shock absorber D.
- the piston valve V includes a piston (valve disk) 1 that partitions an extension side chamber (one chamber) A and a pressure side chamber (other chamber) B, and rings that are stacked on the extension side chamber A side and the pressure side chamber B side of the piston 1, respectively.
- Plate-shaped leaf valves 2 and 3 are provided.
- the piston 1 is formed on the extending side chamber A side and the pressure side chamber B side, respectively, to form the annular boss portions 10 and 11 for supporting the leaf valves 2 and 3, and on the outer peripheral side of the boss portions 10 and 11, respectively.
- 2 and 3 seats 12 and 13, the opening portions 14 and 15 surrounded by the respective seats 12 and 13, and the extension side passages that communicate the extension side chamber A and the opening portion 15 on the compression side chamber B side (one side)
- a pressure side passage (the other passage) 5 that communicates the pressure side chamber B and the opening 14 on the extension side chamber A side.
- the sheet 13 on the compression side chamber B side is arranged at a position higher than the boss portion 11 on the same side, that is, so as to protrude.
- the outer peripheral end t3 of the seat 13 on the pressure side chamber B side is disposed on the outer peripheral side of the outer peripheral end t5 of the leaf valve 3 seated on the seat 13, and the seat 12 on the one chamber A side It is disposed at substantially the same position as the outer peripheral end t1.
- the “high position” in the piston 1 means that the piston 1 protrudes in the axial direction from the end face of the piston 1, and means that it is located on the side opposite to the piston from the comparative configuration.
- the “same side” in the piston 1 refers to the same end surface side of the piston 1 in the axial direction of the piston 1.
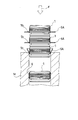
- the shock absorber D is, as shown in FIG. 1, a cylindrical cylinder C, a rod R that enters and exits the cylinder C, and a tip of the rod R that is held in the cylinder C in the axial direction.
- a movable piston valve V, an extension side chamber A formed on the rod R side of the piston valve V in the cylinder C, and a pressure side chamber B formed on the opposite rod side of the piston valve V in the cylinder C are provided.
- the extension side chamber A and the compression side chamber B are filled with hydraulic oil, but other fluids may be filled as long as a damping force can be generated.
- the shock absorber D includes a partition body such as a free piston or a bladder that divides an air chamber in which gas is enclosed and can be expanded and contracted, into the cylinder C.
- the change in the cylinder volume corresponding to the volume of the rod R entering and exiting C can be compensated.
- the configuration of the shock absorber D can be changed as appropriate.
- the shock absorber D includes an outer cylinder standing on the outer periphery of the cylinder C and is set to a double cylinder type.
- the reservoir is formed between the outer cylinder and the cylinder C and stores hydraulic oil. May be compensated.
- the shock absorber D includes a base valve that supplies the hydraulic oil corresponding to the volume of the rod entering and exiting the cylinder C from the reservoir to the cylinder C, and discharges the hydraulic oil from the cylinder C to the reservoir.
- This embodiment may be embodied.
- the shock absorber D is a single rod type shock absorber in which the rod R stands only on one side of the piston valve V, but the double rod type shock absorber in which the rod R stands on both sides of the piston valve V. It may be.
- the piston valve V includes an annular piston 1 that is a valve disk that partitions the expansion side chamber A and the pressure side chamber B, a plurality of annular plate-shaped leaf valves 2 stacked on the expansion side chamber A side of the piston 1, and a piston And a plurality of leaf valves 3 stacked on one pressure side chamber B side.
- tip part in the rod R and smaller diameter than the other part is each penetrated by the piston 1 and the center hole 1a, 2a, 3a of each leaf valve 2,3, and an attachment part A nut N is screwed to the tip of r1.
- the piston valve V is held at the tip of the rod R.
- the number of leaf valves 2 and 3 stacked on the extension side chamber A side and the pressure side chamber B side is not limited to the figure, and can be changed as appropriate.
- the piston 1 has a smaller diameter than the cylinder C. On the outer periphery of the piston 1, a plurality of irregularities 1b and 1c are formed. A piston ring 6 made of synthetic resin is integrally attached to the outer periphery of the piston 1 by using these irregularities 1b and 1c.
- the piston 1 in the present embodiment is a molded piston. The piston 1 is in sliding contact with the inner peripheral surface of the cylinder C through the piston ring 6 and can move smoothly in the axial direction in the cylinder 1.
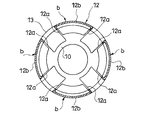
- the piston 1 includes an annular boss portion 10 formed on the extension side chamber A side which is the upper side in FIG. 2C and supporting the inner peripheral portion of the leaf valve 2 on the same side, and the boss portion 10 2 is formed on the pressure side chamber B side, which is the lower side in FIG. 2C, and the leaf on the same side.
- An annular boss portion 11 that supports the inner peripheral portion of the valve 3, a seat 13 that is formed on the outer peripheral side of the boss portion 11 and on which the outer peripheral portion of the leaf valve 3 is attached and detached, an opening 15 that is surrounded by the seat 13, and an extension A plurality of expansion side passages 4 communicating the side chamber A and the pressure side chamber B side opening 15, and a plurality of pressure side passages 5 communicating the pressure side chamber B and the expansion side chamber A side opening 14.
- the bosses 10 and 11 are support surfaces with which the leaf valves 2 and 3 abut, and the seats 12 and 13 are seat surfaces with which the leaf valves 2 and 3 are seated.
- the boss portion 10 on the extension side chamber A side is formed along the opening edge on the upper side in FIG. 2C of the center hole 1a.
- the sheet 12 formed on the outer peripheral side of the boss part 10 is formed in a petal shape, and connects the plurality of branch parts 12a radially extending from the boss part 10 to the outer peripheral side and the outer peripheral ends of the adjacent branch parts 12a.
- the boss part 10 and a plurality of arcuate arc parts 12b arranged at predetermined intervals are provided on the outer periphery of the part 10.
- the one branch part 12a is connected with the arc part 12b only with one branch part 12a among the branch parts 12a arrange
- Openings 14 are independently formed between the boss portion 10 on the extension side chamber A side, the arc portion 12b in the sheet 12 on the same side, and the pair of branch portions 12a connected by the arc portion 12b. Yes. A plurality of openings 14 are provided at predetermined intervals in the circumferential direction. Further, the leaf valve 2 on the extension side chamber A side is fixed to the rod R in a state in which the inner peripheral portion is seated on the boss portion 10 in the assembled state, and the outer peripheral portion is separable from the seat 12. For this reason, in the state where the outer peripheral portion of the leaf valve 2 is seated on the seat 12, the opening portion 14 is disconnected from the extension side chamber A by the leaf valve 2.
- the leaf valve 2 when the outer peripheral part of the leaf valve 2 bends to the anti-piston side and moves away from the seat 12, communication with the extension side chamber A is allowed. Since the pressure side passage 5 is connected to each opening 14 on the extension side chamber A side, the leaf valve 2 can allow or block the communication between the pressure side passage 5 and the extension side chamber A.
- the inner peripheral portion of the leaf valve 2 is not separated from the boss portion 10, but the assembly structure of the leaf valve 2 can be changed as appropriate.
- the inner peripheral portion of the leaf valve 2 may be separated from the boss portion 10.
- openings 17 are respectively formed between the pair of branch portions 12a that are not connected by the arc portion 12b in the sheet 12 on the same side on the outer peripheral side of the boss portion 10 on the extension side chamber A side.
- Each of the openings 17 is connected to the extending side passage 4. Even when the leaf valve 2 is seated on the seat 12, the communication between the opening 17 and the extension side chamber A is not blocked by the leaf valve 2. That is, the extension side passage 4 always communicates with the extension side chamber A through the opening 17.
- a plurality of openings 17 are provided at predetermined intervals in the circumferential direction.
- the boss portion 11 on the pressure side chamber B side is formed along the opening edge on the lower side in FIG. 2C of the center hole 1a.
- hub part 11 is formed in cyclic
- An annular opening 15 is formed between the boss 11 on the pressure side chamber B side and the sheet 13 on the same side. Further, the leaf valve 3 on the pressure side chamber B side is fixed to the rod R in a state in which the inner peripheral portion is seated on the boss portion 11 in the assembled state, and the outer peripheral portion can be separated from and seated on the seat 13. Therefore, the communication between the opening 15 and the pressure side chamber B is blocked by the leaf valve 3 when the outer peripheral portion of the leaf valve 3 is seated on the seat 13. On the other hand, when the outer peripheral portion of the leaf valve 3 bends to the anti-piston side and moves away from the seat 13, communication with the pressure side chamber B is allowed. Since the plurality of expansion side passages 4 are connected to the opening 15 on the compression side chamber B side, the leaf valve 3 can permit or block communication between the expansion side passage 4 and the compression side chamber B at the same time.
- the inner peripheral portion of the leaf valve 3 is not separated from the boss portion 11, but the assembly structure of the leaf valve 3 can be changed as appropriate.
- the inner peripheral portion of the leaf valve 3 may be separated from the boss portion 11.
- annular groove 1d is formed along the circumferential direction on the pressure side chamber B side of the outer periphery of the piston 1 with respect to the piston ring 6.
- the groove 1 d communicates with the pressure side passage 5. Even when the leaf valve 3 is seated on the seat 13, the groove 1 d is not blocked by the leaf valve 3 from the pressure side chamber B and is not blocked by the piston ring 6. . That is, the pressure side passage 5 is always in communication with the pressure side chamber B through the gap between the groove 1d and the cylinder C.
- the seat 13 on the pressure side chamber B side is disposed so as to protrude from the boss portion 11, and the initial deflection can be given to the leaf valve 3 seated on the seat 13.
- the shock absorber D in which the rod R is withdrawn from the cylinder C is extended, the extension side chamber A is pressurized, and the leaf valve 2 on the extension side chamber A side is pressed against the seat 12 on the same side so Block 5 Further, when the pressure in the expansion side chamber A reaches the valve opening pressure of the leaf valve 3 on the pressure side chamber B side, the outer peripheral portion of the leaf valve 3 bends to the anti-piston side and allows the expansion side passage 4 to communicate. Therefore, the shock absorber D generates an extension side damping force due to the resistance of the leaf valve 3 when the hydraulic oil passes through the extension side passage 4 and moves from the extension side chamber A to the compression side chamber B at the time of extension. To do. As described above, since the initial deflection is given to the leaf valve 3, the valve opening pressure of the leaf valve 3 can be increased.
- the shock absorber D in which the rod R enters the cylinder C, is compressed, the pressure side chamber B is pressurized, and the leaf valve 3 on the pressure side chamber B side is pressed against the seat 13 on the same side, so Cut off. Further, when the pressure in the pressure side chamber B reaches the valve opening pressure of the leaf valve 2 on the expansion side chamber A side, the outer peripheral portion of the leaf valve 2 bends to the anti-piston side, allowing the pressure side passage 5 to communicate. For this reason, the shock absorber D generates a compression-side damping force due to the resistance of the leaf valve 2 when the hydraulic oil passes through the compression-side passage 5 and moves from the compression-side chamber B to the expansion-side chamber A during compression.
- the inner peripheral end t4 of the sheet 13 on the compression side chamber B side is arranged on the inner peripheral side with respect to the inner peripheral end t2 of the arc portion 12b in the sheet 12 on the extension side chamber A side. Therefore, the outer diameter of the leaf valve 3 that is seated on the seat 13 on the pressure side chamber B side and can be opened when the shock absorber D is extended is made smaller than the outer diameter of the leaf valve 2, and the pressure receiving surface is made smaller. Therefore, the extension side damping force generated by the shock absorber D can be increased compared to the compression side damping force.
- the inner peripheral end t4 of the sheet 13 is an annular edge located on the innermost peripheral side in the sheet 13.
- the inner peripheral end t2 of the arc portion 12b is an arc-shaped edge located on the innermost side in the arc portion 12b.
- the outer peripheral end t3 of the seat 13 on the pressure side chamber B side is arranged on the outer peripheral side of the outer peripheral end t5 of the leaf valve 3 seated on the seat 13, and the outer peripheral end t3 of the seat 13 on the pressure side chamber B side is In the radial direction of the piston 1, it is arranged at the same position as the outer peripheral end of the arc portion 12 b that becomes the outer peripheral end t 1 of the sheet 12 on the extension side chamber A side.
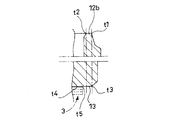
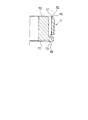
- FIG. 4 is an explanatory diagram showing a state in which the sheet 13 of the other piston 1 overlaps the boss 10 and the sheet 12 of one overlapping piston 1 when a plurality of pistons 1 are vertically stacked on the same axis.
- a hatched portion is shown in a portion b where one piston 1 and the other piston 1 are in contact with each other.
- the outer peripheral end t3 of the sheet 13 on the pressure side chamber B side is an annular edge located on the outermost side in the sheet 13.
- the outer peripheral end t1 of the sheet 12 on the extension side chamber A side is an outer peripheral end of the arc portion 12b in the sheet 12, and is an arcuate edge located on the outermost peripheral side in the arc portion 12b.
- the outer peripheral end t3 of the sheet 13 on the compression side chamber B side is the same position as the outer peripheral end t1 of the sheet 12 on the expansion side chamber A side in the radial direction of the piston 1 or on the outer peripheral side of the outer peripheral end t1.
- the entire arc portion 12b of one piston 1 can be brought into contact with the seat 13 of the other piston 1 without positioning in the circumferential direction.
- seat 13 of the other piston 1 can be contact
- FIG. 6A a piston valve (valve) according to a comparative example will be described with reference to FIGS. 6A, 6B, 6C, and 7.
- FIG. 6A, 6B, 6C, and 7 a piston valve (valve) according to a comparative example will be described with reference to FIGS. 6A, 6B, 6C, and 7.
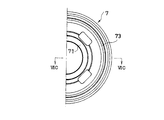
- a sheet 72 formed on the extending side chamber side of the piston 7 is formed in a petal shape.
- the piston 7 includes a plurality of branch portions 72a extending from the boss portion 70 on the same side to the outer peripheral side, and a plurality of arc-shaped arc portions 72b connecting the outer peripheral ends of the branch portions 72a.
- the sheet 73 formed on the pressure side chamber side of the piston 7 is formed in an annular shape, and is arranged on the outer periphery of the boss portion 71 on the same side with a predetermined distance from the boss portion 71.
- outer peripheral end t6 and the inner peripheral end t7 of the arc portion 72b on the extension side chamber side are arranged on the outer peripheral side with respect to the outer peripheral end t8 of the compression side chamber side sheet 73, and the compression side chamber side sheet 73 is on the same side boss. It is arranged at a position higher than the portion 71 (on the opposite piston side).
- the leaf valve can be formed with a small diameter, the pressure receiving surface can be made smaller, and the expansion side damping force can be made larger than the compression side damping force. Therefore, when a shock absorber equipped with a piston valve having the above-described structure is interposed between the vehicle body and the wheel, the shock absorber extends after a thrust input from the road surface is applied with a low compression side damping force. When turning to the process, high extension side damping force can be exhibited.
- FIG. 7 is an explanatory view showing a state in which the sheet 73 of the other piston 7 overlaps the boss 70 and the sheet 72 of one overlapping piston 7 when the plurality of pistons 7 are vertically stacked on the same axis.
- the part a to be shown is hatched.
- the piston (valve disk) 1 is a molded piston integrated with an annular piston ring 6 attached to the outer periphery thereof.
- the piston (valve disk) 1 can smoothly move in the cylinder C by sliding the piston ring 6 on the inner peripheral surface of the cylinder C.
- the attachment method of the piston ring 6 is not limited to the above, and can be appropriately changed.
- the valve disk may be other than the piston, and the piston ring 6 may be eliminated.
- seat 12 of the extending side chamber (one chamber) A side is formed in the petal shape, and adjoins the several branch part 12a extended in the outer peripheral side from the boss
- the outer diameter of the leaf valve 3 that is seated on and off the seat 13 on the other side is left as it is, and the outer peripheral end t3 of the piston 13 is the outer peripheral end t3.
- the sheet 12 extends to the same position as the outer peripheral end t1 of the seat 12 on one side or to the outer peripheral side of the outer peripheral end t1. It is extremely effective to increase the area.
- both the sheets 12 and 13 of the piston (valve disk) 1 can be appropriately changed.
- both the sheets 12 and 13 may be formed in a ring shape or a petal shape.
- the outer peripheral end t3 of the seat 13 on the pressure side chamber (other chamber) B side is disposed on the outer peripheral side with respect to the outer peripheral end t5 of the leaf valve 3 seated on the seat 13, and the extension side chamber (One chamber) It is disposed at substantially the same position as the outer peripheral edge t1 of the sheet 12 on the A side.
- the outer diameter of the leaf valve 3 that is seated on the seat 13 on the compression side chamber (the other chamber) B side is made equal to the leaf valve 2 that is seated on the seat 12 on the stretch chamber (one chamber) A side. Since it can be made smaller than the outer diameter, the extension side damping force can be made larger than the compression side damping force.
- the pressure side chamber (other chamber) B side sheet 13 is disposed at a position higher than the pressure side chamber B side (same side) boss portion 11, that is, protrudes.
- the sheet 12 on the side chamber (one chamber) A side may be arranged at a position higher than the boss portion 10 on the expansion chamber A side (same side), and both the sheets 12 and 13 on both sides are the same boss portion 10 on the same side.
- 11 may be arranged at a position higher than 11.
- the outer peripheral end t3 of the seat 13 on the pressure side chamber (other chamber) B side is the same position as the outer peripheral end t1 of the seat 12 on the extension side chamber (one chamber) A side in the radial direction of the piston 1 (valve disk). What is necessary is just to arrange
- the extension side chamber A is one chamber and the compression side chamber B is the other chamber, but the opposite may be possible.
- the compression side damping force can be made higher than the extension side damping force.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Fluid-Damping Devices (AREA)
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201480054170.6A CN105593561B (zh) | 2013-11-08 | 2014-09-26 | 阀 |
| DE112014005117.9T DE112014005117T5 (de) | 2013-11-08 | 2014-09-26 | Ventil |
| US15/029,645 US10167918B2 (en) | 2013-11-08 | 2014-09-26 | Valve |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013-232140 | 2013-11-08 | ||
| JP2013232140A JP5783647B2 (ja) | 2013-11-08 | 2013-11-08 | バルブ |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015068490A1 true WO2015068490A1 (ja) | 2015-05-14 |
Family
ID=53041273
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2014/075587 Ceased WO2015068490A1 (ja) | 2013-11-08 | 2014-09-26 | バルブ |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10167918B2 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP5783647B2 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN105593561B (enExample) |
| DE (1) | DE112014005117T5 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2015068490A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPWO2022168544A1 (enExample) * | 2021-02-02 | 2022-08-11 |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107191132B (zh) * | 2017-04-20 | 2019-10-22 | 黄金钗 | 封口套及伸缩梯 |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH03199732A (ja) * | 1989-12-27 | 1991-08-30 | Kayaba Ind Co Ltd | 油圧緩衝器のバルブ装置 |
| JP2001082526A (ja) * | 1999-09-17 | 2001-03-27 | Kayaba Ind Co Ltd | 油圧緩衝器用モールドピストンの製造方法 |
| JP2012229784A (ja) * | 2011-04-27 | 2012-11-22 | Hitachi Automotive Systems Ltd | 緩衝器 |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR1185696A (fr) * | 1957-11-04 | 1959-08-04 | Piston d'amortisseur | |
| US3088556A (en) * | 1957-12-09 | 1963-05-07 | Bourcier Christian Marie Louis | Shock absorbers |
| JP3009151B2 (ja) * | 1988-04-04 | 2000-02-14 | 株式会社ユニシアジェックス | 液圧緩衝器 |
| JP3471438B2 (ja) * | 1993-12-06 | 2003-12-02 | 株式会社ショーワ | 緩衝器のバルブ構造 |
| CN101857036B (zh) * | 2009-04-10 | 2012-07-25 | 萱场工业株式会社 | 铁道车辆用线性减震器 |
| JP5192441B2 (ja) * | 2009-05-20 | 2013-05-08 | カヤバ工業株式会社 | 減衰バルブ |
-
2013
- 2013-11-08 JP JP2013232140A patent/JP5783647B2/ja active Active
-
2014
- 2014-09-26 CN CN201480054170.6A patent/CN105593561B/zh active Active
- 2014-09-26 DE DE112014005117.9T patent/DE112014005117T5/de not_active Withdrawn
- 2014-09-26 US US15/029,645 patent/US10167918B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2014-09-26 WO PCT/JP2014/075587 patent/WO2015068490A1/ja not_active Ceased
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH03199732A (ja) * | 1989-12-27 | 1991-08-30 | Kayaba Ind Co Ltd | 油圧緩衝器のバルブ装置 |
| JP2001082526A (ja) * | 1999-09-17 | 2001-03-27 | Kayaba Ind Co Ltd | 油圧緩衝器用モールドピストンの製造方法 |
| JP2012229784A (ja) * | 2011-04-27 | 2012-11-22 | Hitachi Automotive Systems Ltd | 緩衝器 |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPWO2022168544A1 (enExample) * | 2021-02-02 | 2022-08-11 | ||
| WO2022168544A1 (ja) * | 2021-02-02 | 2022-08-11 | 日立Astemo株式会社 | 緩衝器 |
| JP7462804B2 (ja) | 2021-02-02 | 2024-04-05 | 日立Astemo株式会社 | 緩衝器 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2015094379A (ja) | 2015-05-18 |
| JP5783647B2 (ja) | 2015-09-24 |
| CN105593561B (zh) | 2017-09-01 |
| US20160230833A1 (en) | 2016-08-11 |
| US10167918B2 (en) | 2019-01-01 |
| CN105593561A (zh) | 2016-05-18 |
| DE112014005117T5 (de) | 2016-08-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9121524B2 (en) | Shock absorber | |
| CN103851119B (zh) | 压力阻尼装置 | |
| KR20110098630A (ko) | 완충기 | |
| WO2015068489A1 (ja) | バルブ | |
| CN101796323A (zh) | 具有全位移阀组件的减振器 | |
| JP5325763B2 (ja) | 緩衝器 | |
| WO2015068490A1 (ja) | バルブ | |
| CN107923469B (zh) | 缓冲器的阀构造 | |
| CN104903610A (zh) | 缓冲器 | |
| JP6628143B2 (ja) | 弁機構、減衰力発生装置、及び緩衝器 | |
| JP6628145B2 (ja) | 弁機構、減衰力発生装置、及び緩衝器 | |
| JP6628144B2 (ja) | 弁機構、減衰力発生装置、及び緩衝器 | |
| WO2020071165A1 (ja) | フロントフォーク | |
| JP5764054B2 (ja) | バルブ装置 | |
| WO2020026362A1 (ja) | 弁機構および緩衝器 | |
| JP6006621B2 (ja) | 緩衝器 | |
| JP2007333120A (ja) | 油圧緩衝器の減衰バルブ | |
| JP6401862B2 (ja) | ピストン | |
| JP2017145870A (ja) | 圧力緩衝装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 14860602 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15029645 Country of ref document: US |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 1120140051179 Country of ref document: DE Ref document number: 112014005117 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 14860602 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |