WO2014083754A1 - 熱交換器の固定構造 - Google Patents
熱交換器の固定構造 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2014083754A1 WO2014083754A1 PCT/JP2013/006212 JP2013006212W WO2014083754A1 WO 2014083754 A1 WO2014083754 A1 WO 2014083754A1 JP 2013006212 W JP2013006212 W JP 2013006212W WO 2014083754 A1 WO2014083754 A1 WO 2014083754A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- evaporator
- heat exchanger
- fixing
- vibration
- air conditioning
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28F—DETAILS OF HEAT-EXCHANGE AND HEAT-TRANSFER APPARATUS, OF GENERAL APPLICATION
- F28F9/00—Casings; Header boxes; Auxiliary supports for elements; Auxiliary members within casings
- F28F9/007—Auxiliary supports for elements
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60H—ARRANGEMENTS OF HEATING, COOLING, VENTILATING OR OTHER AIR-TREATING DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR PASSENGER OR GOODS SPACES OF VEHICLES
- B60H1/00—Heating, cooling or ventilating [HVAC] devices
- B60H1/00007—Combined heating, ventilating, or cooling devices
- B60H1/00021—Air flow details of HVAC devices
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60H—ARRANGEMENTS OF HEATING, COOLING, VENTILATING OR OTHER AIR-TREATING DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR PASSENGER OR GOODS SPACES OF VEHICLES
- B60H1/00—Heating, cooling or ventilating [HVAC] devices
- B60H1/00507—Details, e.g. mounting arrangements, desaeration devices
- B60H1/00514—Details of air conditioning housings
- B60H1/00521—Mounting or fastening of components in housings, e.g. heat exchangers, fans, electronic regulators
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60H—ARRANGEMENTS OF HEATING, COOLING, VENTILATING OR OTHER AIR-TREATING DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR PASSENGER OR GOODS SPACES OF VEHICLES
- B60H1/00—Heating, cooling or ventilating [HVAC] devices
- B60H1/00007—Combined heating, ventilating, or cooling devices
- B60H1/00021—Air flow details of HVAC devices
- B60H2001/00078—Assembling, manufacturing or layout details
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60H—ARRANGEMENTS OF HEATING, COOLING, VENTILATING OR OTHER AIR-TREATING DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR PASSENGER OR GOODS SPACES OF VEHICLES
- B60H1/00—Heating, cooling or ventilating [HVAC] devices
- B60H1/00007—Combined heating, ventilating, or cooling devices
- B60H1/00021—Air flow details of HVAC devices
- B60H2001/00114—Heating or cooling details
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28D—HEAT-EXCHANGE APPARATUS, NOT PROVIDED FOR IN ANOTHER SUBCLASS, IN WHICH THE HEAT-EXCHANGE MEDIA DO NOT COME INTO DIRECT CONTACT
- F28D1/00—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary conduit assemblies for one heat-exchange medium only, the media being in contact with different sides of the conduit wall, in which the other heat-exchange medium is a large body of fluid, e.g. domestic or motor car radiators
- F28D1/02—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary conduit assemblies for one heat-exchange medium only, the media being in contact with different sides of the conduit wall, in which the other heat-exchange medium is a large body of fluid, e.g. domestic or motor car radiators with heat-exchange conduits immersed in the body of fluid
- F28D1/04—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary conduit assemblies for one heat-exchange medium only, the media being in contact with different sides of the conduit wall, in which the other heat-exchange medium is a large body of fluid, e.g. domestic or motor car radiators with heat-exchange conduits immersed in the body of fluid with tubular conduits
- F28D1/053—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary conduit assemblies for one heat-exchange medium only, the media being in contact with different sides of the conduit wall, in which the other heat-exchange medium is a large body of fluid, e.g. domestic or motor car radiators with heat-exchange conduits immersed in the body of fluid with tubular conduits the conduits being straight
- F28D1/0535—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary conduit assemblies for one heat-exchange medium only, the media being in contact with different sides of the conduit wall, in which the other heat-exchange medium is a large body of fluid, e.g. domestic or motor car radiators with heat-exchange conduits immersed in the body of fluid with tubular conduits the conduits being straight the conduits having a non-circular cross-section
- F28D1/05366—Assemblies of conduits connected to common headers, e.g. core type radiators
- F28D1/05391—Assemblies of conduits connected to common headers, e.g. core type radiators with multiple rows of conduits or with multi-channel conduits combined with a particular flow pattern, e.g. multi-row multi-stage radiators
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28D—HEAT-EXCHANGE APPARATUS, NOT PROVIDED FOR IN ANOTHER SUBCLASS, IN WHICH THE HEAT-EXCHANGE MEDIA DO NOT COME INTO DIRECT CONTACT
- F28D21/00—Heat-exchange apparatus not covered by any of the groups F28D1/00 - F28D20/00
- F28D2021/0019—Other heat exchangers for particular applications; Heat exchange systems not otherwise provided for
- F28D2021/0068—Other heat exchangers for particular applications; Heat exchange systems not otherwise provided for for refrigerant cycles
- F28D2021/0071—Evaporators
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28D—HEAT-EXCHANGE APPARATUS, NOT PROVIDED FOR IN ANOTHER SUBCLASS, IN WHICH THE HEAT-EXCHANGE MEDIA DO NOT COME INTO DIRECT CONTACT
- F28D21/00—Heat-exchange apparatus not covered by any of the groups F28D1/00 - F28D20/00
- F28D2021/0019—Other heat exchangers for particular applications; Heat exchange systems not otherwise provided for
- F28D2021/008—Other heat exchangers for particular applications; Heat exchange systems not otherwise provided for for vehicles
- F28D2021/0085—Evaporators
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28F—DETAILS OF HEAT-EXCHANGE AND HEAT-TRANSFER APPARATUS, OF GENERAL APPLICATION
- F28F2265/00—Safety or protection arrangements; Arrangements for preventing malfunction
- F28F2265/30—Safety or protection arrangements; Arrangements for preventing malfunction for preventing vibrations
Definitions
- This disclosure relates to a heat exchanger fixing structure in which a refrigerant flows.
- the cooling evaporator in the vehicle air conditioning unit described in Patent Document 1 is incorporated in an air conditioning unit case with elastic members interposed at the four corners of the evaporator.
- This elastic member has a vibration absorbing action of the evaporator. More specifically, the vibration absorbing function is coupled to the compressor in the vehicle engine room via the refrigerant pipe, and this compressor is mounted on the vehicle engine and driven by the vehicle engine. Therefore, the compressor vibrates integrally with the vehicle engine. Further, the compressor itself vibrates due to the pulsation generated when the compressor discharges the refrigerant. The vibration of the compressor propagates to the evaporator located in the passenger compartment through the refrigerant pipe.
- the vibration propagated to the evaporator is absorbed by the elastic member, and the vibration of the evaporator is transmitted to the air conditioning unit case and amplified to become abnormal noise (noise). I try to suppress it.
- non-flow path constituent members other than the refrigerant flow path are supported by the case.
- the non-flow path component does not constitute a flow path for the heat exchange medium, so it is not directly vibrated by the pulsation of the heat exchange medium, and is not affected by the collision of the heat exchange medium. There is no direct vibration. By supporting the portion that is not directly excited in this way with the case, the vibration of the heat exchanger is hardly transmitted to the case.
- This disclosure is intended to provide a heat exchanger fixing structure capable of reducing the transmission of vibrations to the outside with a simple configuration.
- At least one of the surface surrounded by the first side and the third side and the surface surrounded by the second side and the third side is provided in at least one case.
- a fixing part for fixing is provided, and the fixing part is provided at a position excluding the four corners of the heat exchange surface and excluding a position corresponding to the abdomen of the natural vibration mode of the heat exchanger. This is a fixing structure of the heat exchanger.
- the heat exchanger is fixed to a case provided outside.
- the fixing part for fixing to the case is on at least one of the surface surrounded by the first side and the third side and the surface surrounded by the second side and the third side. , At least one is provided.
- the fixed portion is a position excluding the four corners of the heat exchange surface, and a position excluding a position corresponding to the abdomen of the natural vibration mode of the heat exchanger (hereinafter, simply referred to as “position excluding the abdomen”). ).
- position excluding the four corners and the abdomen are positions that do not vibrate easily.
- the abdomen is the most oscillating position, and the four corners have been found to be easily oscillated as well as the abdomen by the results of the applicant's earnest research.
- the fixing portion is provided so as to avoid such a position that easily vibrates, the portion that hardly vibrates is fixed to the case. Therefore, it becomes difficult for the vibration of the heat exchanger to be transmitted from the fixed portion to the case.
- vibration from the heat exchanger to the case can be suppressed with a simple configuration in which the position of the fixing portion is changed. As a result, noise caused by the vibration of the case due to the vibration of the heat exchanger can be suppressed.
- the evaporator 10 is disposed in a refrigeration cycle (not shown).
- the evaporator 10 is a heat exchanger that evaporates the refrigerant after being compressed to high temperature and high pressure by a compressor, radiated and cooled by a radiator, and decompressed to low temperature and low pressure by a decompression device.
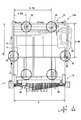
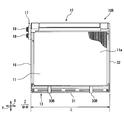
- the evaporator 10 of the present embodiment includes a core portion 11, an upper tank portion 12, a lower tank portion 13, and the like, and the constituent members are brazed and joined to each other.
- the core part 11 is configured by alternately laminating a plurality of flat tubes 14 and a plurality of corrugated fins 15. Further, side plates 16 are disposed outside the corrugated fins 15 that are the outermost sides on both sides in the stacking direction (X direction in FIG. 1).
- coolant which is an internal fluid of the core part 11 flows along the length direction (Y direction of FIG. 1) of the flat tube 14.
- FIG. The refrigerant flow direction is the width direction Y of the evaporator 10
- the ventilation direction in the core portion 11 is the thickness direction Z of the evaporator 10
- the width direction Y and the thickness direction Z are orthogonal to each other (stacking direction).
- the length direction X of the evaporator 10 is X
- the evaporator 10 is arranged in the vehicle with the width direction Y being the vertical direction.
- the flat tube 14 is a tube member formed by bending a thin aluminum strip, and the cross section perpendicular to the refrigerant flow direction is formed in a flat shape.
- the flat tube 14 may be formed by integrally forming a plurality of refrigerant passages extending in the longitudinal direction by extrusion molding of an aluminum material. Alternatively, two aluminum thin plates made of aluminum may be joined together in the middle.
- the plate thickness of the flat tube 14 is, for example, 0.2 mm.
- the corrugated fin 15 is a corrugated fin obtained by rolling a thin aluminum strip having a brazing material clad on both surfaces in a serpentine shape (wave shape).
- the corrugated fin 15 is formed by cutting and raising a plurality of louvers (not shown) for increasing the heat exchange efficiency.
- the plate thickness of the corrugated fin 15 is, for example, 0.05 mm.
- the side plate 16 constitutes a reinforcing member in the core portion 11, and is formed by pressing an aluminum flat plate made of a bare material in which a brazing material is not clad. Both end portions in the longitudinal direction (width direction Y) of the side plate 16 are formed in a flat plate shape. Further, the central portion is formed to have a U-shaped cross section that opens outward in the stacking direction of the flat tube 14 and the corrugated fin 15. The side plate 16 is brazed to the corrugated fin 15.
- the plate thickness of the side plate 16 is 1 mm, for example.
- the upper tank portion 12 is formed of a header tank on the anti-flat tube side divided into two in the longitudinal direction of the flat tube 14 and a header plate on the flat tube side.
- Each of the header tank and the header plate has a semicircular or rectangular cross-sectional shape, and is formed by pressing an aluminum flat plate.
- the brazing material is clad in advance on both sides of the header tank and the inner side of the header plate.
- the header tank and the header plate are fitted to each other and brazed to form a cylindrical body in which two internal spaces are arranged in the flow direction of the blown air (thickness direction Z of the evaporator 10).
- a cap formed by pressing an aluminum flat plate material is brazed to the opening at the longitudinal end of the upper tank 12 (both ends in the length direction X) so as to close the opening. ing.
- board thickness of the upper side tank part 12 and the lower side tank part 13 is 1 mm, for example.
- two separators that divide the respective internal spaces in the longitudinal direction of the upper tank portion 12 (length direction X of the evaporator 10) are provided at the substantially central portion in the length direction X of the upper tank portion 12. ) Is brazed. In the region of the upper tank portion 12 on the right side of the separator, the two internal spaces of the upper tank portion 12 arranged in the flow direction of the blown air communicate with each other through a plurality of communication paths (not shown). ing.
- the lower tank portion 13 has a structure similar to that of the upper tank portion 12 described above, and forms a cylindrical body constituted by a header tank and a header plate. And the cap is provided in the opening part of the both ends of the longitudinal direction. However, unlike the upper tank portion 12, a configuration corresponding to the separator and the communication path is not provided.
- a flat tube insertion port (not shown) and a side plate insertion port (not shown) have a length equal to the pitch of the flat tube 14 and the side plate 16 on the wall surface (wall surface of the header plate) on the core portion 11 side in the upper and lower tank portions. It is provided in the direction X.
- the longitudinal ends of the flat tubes 14 and the longitudinal ends of the side plates 16 are inserted into the respective insertion ports and brazed. Thereby, the flat tube 14 communicates with the internal space of the upper and lower tank portions 12 and 13, and the longitudinal end portion of the side plate 16 is supported and fixed to the upper and lower tank portions 12 and 13.
- connection block 17 (refrigerant inflow / outflow part) provided with the inflow port 18 into which a refrigerant
- the inflow port 18 communicates with the inside of the tank portion 12a on the downstream side of the air flow in FIG. 1 in the internal space of the upper tank portion 12, and the outflow port 19 is in the tank portion 12b on the upstream side of the air flow in FIG. Communicated with.
- the flat tube 14 is arranged so that the upstream flat tube row and the downstream flat tube row are arranged in two rows in the blown air flow as the external fluid, corresponding to the arrangement of the upper and lower tank portions 12 and 13. Yes.
- the evaporator 10 formed in this way after the refrigerant flows into the tank portion 12a on the downstream side of the air flow of the upper tank portion 12 from the inlet 18, the inside of the flat tube row on the downstream side of the air flow moves up and down. It turns and flows and returns to the right side area of FIG.
- the refrigerant flows from the upper tank portion 12a (right tank portion) on the downstream side of the air flow to the upper tank portion 12b (right tank portion) on the upstream side of the air flow, passes through the flat tube row on the upstream side of the air flow, Similarly, it makes a U-turn up and down and returns to the upper tank portion 12b on the upstream side of the air flow.
- This refrigerant finally flows out from the outlet 19.
- the evaporator 10 evaporates the refrigerant and cools the blown air by the latent heat of evaporation.
- the evaporator 10 is fixed in an air conditioning case constituting the vehicle air conditioner.
- the air conditioning case (not shown) has an air ventilation path inside, and an outside air inlet and an inside air inlet that are air intakes are formed on one side. On the other side of the ventilation path, a blow-off opening through which air that has been blown into the passenger compartment passes is formed.
- the air conditioning case is composed of a plurality of case members, and the material thereof is a resin molded product such as polypropylene.
- the evaporator 10 is arranged so as to cross the entire ventilation path in the air conditioning case, and all of the blown air passes therethrough.
- Such an evaporator 10 functions as a heat exchanger that cools the blown air before flowing into the cool air passage by the heat absorbing action of the refrigerant flowing inside during the cooling operation.
- the evaporator 10 has a rectangular parallelepiped shape as shown in FIG.
- a side extending in the length direction X of the evaporator 10 is a first side
- a side extending in the width direction Y is a second side 32
- a side extending in the thickness direction Z Is the third side 33.
- the length of the first side 31 is the largest and the length of the third side 33 is the smallest.
- the surface surrounded by the first side 31 and the second side 32 constitutes the surface of the core portion 11, and thus is a heat exchange surface 11 a through which air flows and exchanges heat with the refrigerant.
- the fixing structure of the evaporator 10 is configured by paying attention to noise caused by vibration propagation from the evaporator 10 to the air conditioning case, which is one of noise causes.
- the fixed structure is configured by paying attention to the natural vibration mode of the evaporator 10.
- the noise caused by the propagation from the evaporator 10 to the air conditioning case is limited to 1000 Hz or less.
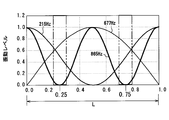
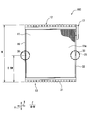
- the evaporator 10 has a natural vibration mode as shown in FIGS. 2 and 3, and the way of vibration varies depending on the vibration mode.
- the primary mode is 215 Hz
- the secondary mode is 241 Hz
- the third mode is 367 Hz
- the fourth mode is 677 Hz
- the fifth mode is 865 Hz.
- the vertical axis in FIG. 2 is a dimensionless value with the maximum amplitude value being 1, and is called a vibration level. 2 is based on the shape of the evaporator 10 regardless of the physical property values.
- the vibration excitation force (sum of vibration modes) in this vibration mode is as shown in FIG. That is, vibration transmission from the evaporator 10 to the air conditioning case can be minimized by holding a portion where the sum of the vibration modes is minimized.
- the large amplitude may be called the belly and the small amplitude may be called the node.
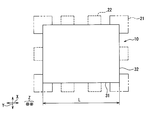
- the evaporator 10 is held at four corners (four corners).
- the belly in the evaporator 10 is held, vibration transmission from the evaporator 10 to the air conditioning case becomes large, and thus the NV (noise vibration) reduction is insufficient. Therefore, in the present embodiment, a structure that suppresses the position indicated by the broken line 22 shown in FIG. 4 is necessary to reduce NV.
- a surface surrounded by the first side 31 and the third side 33 (hereinafter, also referred to as “upper and lower surfaces”), and a second side 32 and the third side 33 are surrounded.
- a fixing part 30 for fixing to at least one case is provided on at least one of the surfaces (hereinafter, also referred to as “left and right surfaces”).
- two fixed portions 30 are provided on the lower surface of the upper and lower surfaces.
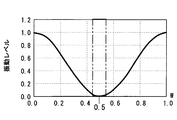
- the position of the fixing unit 30 is a position excluding the four corners on the heat exchange surface 11 a of the evaporator 10, and a position corresponding to the abdomen of the natural vibration mode of the evaporator 10. It is provided at the removed position (see FIG. 3).
- the fixed part 30 is arranged avoiding the center and both ends (four corners) of the first side 31.
- the fixing part 30 is provided at a position excluding the above-mentioned four corners, and the amplitude of the natural vibration mode of the evaporator 10 is smaller than the amplitude at the four corners.
- the preferable position of the fixing portion 30 is preferably a position that is 0.25 L ⁇ 0.05 L away from the end of the first side 31 and 0.75 L ⁇ if the length of the first side 31 is L. Provided at a position 0.05 L apart.
- 0.25L has a meaning of 0.25 ⁇ L, and has the same meaning when a number and L are described consecutively.
- the fixing portion 30 is provided in at least one of the range of 0.2L to 0.3L and the range of 0.7L to 0.8L from the end of the first side 31.
- the position of the fixing portion 30 corresponds to the area surrounded by the phantom line in FIG.
- the position where the fixing portion 30 is provided is a position where the combined vibration mode of 1000 Hz or less is the minimum (so-called node).
- the fixed part 30 is realized by a convex part protruding downward from the lower tank part 13.
- the evaporator 10 is fixed to the air conditioning case in a state where the fixing portion 30 is pressed against the inner wall of the air conditioning case.
- an elastic member such as rubber is interposed between the fixed portion 30 and the air conditioning case. By interposing the elastic member, vibration transmitted from the fixed portion 30 to the air conditioning case can be further attenuated.
- the evaporator 10 is in contact with the air conditioning case other than the fixed portion 30, the fixed portion 30 is fixed so that vibration is transmitted. Therefore, the other contact portions are in contact with each other as long as they are supported.
- the fixed part 30 is provided at a position where the vibration mode frequency of the evaporator 10 and the natural frequency of the wall surface vibration of the air conditioning case are different.
- the natural frequency of the air conditioning case varies depending on the location. If this natural frequency is provided at the same position as the vibration mode frequency of the evaporator 10, even if the vibration is attenuated and transmitted from the evaporator 10, if the natural frequency is the same as the natural frequency of the air conditioning case, the air conditioning case is large. It will vibrate. This is because the effect of reducing NV is reduced.
- the fixing structure of the embodiment is a structure in which the positions of 0.25L and 0.75L are fixed in the upper tank portion 12 and the lower tank portion 13, respectively.
- the fixing structure of the comparative example is a structure in which the four corners are fixed.
- the inertance was detected by using a piezoresistive vibration acceleration sensor (PCB, model number: 352C22) with the air conditioning case, the fixed portion 30 and the contact portion as detection positions.
- the experimental conditions in FIGS. 5 and 6 are the same.
- FIG. 5 shows the inertance at each frequency
- FIG. 6 shows the total inertance from 200 Hz to 1 kHz.
- the inertance of the example is smaller than that of the comparative example at any frequency.
- the example has a larger NV reduction effect than the comparative example.
- the total inertance from 200 Hz to 1 kHz is smaller in the example. Therefore, it can be seen that the example has a larger NV reduction effect than the comparative example.
- FIGS. 5 and 6 it is clear that the fixing structure of the evaporator 10 of the present embodiment has an NV reduction effect.
- the evaporator 10 of this embodiment is fixed to an air conditioning case provided outside.
- Two fixing portions 30 for fixing the evaporator 10 and the air conditioning case are provided on the surface surrounded by the first side 31 and the third side 33.
- the fixing part 30 is provided at a position excluding the four corners of the heat exchange surface 11a and excluding a position corresponding to the abdomen of the natural vibration mode of the evaporator 10.
- the positions excluding the four corners and the abdomen are positions that do not vibrate easily. In other words, the abdomen is the most vibrating position, and the four corners are also easy to vibrate. Since the fixing portion 30 is provided so as to avoid such a position that easily vibrates, the portion that does not vibrate is fixed to the air conditioning case.
- the vibration of the evaporator 10 is not easily transmitted from the fixed portion 30 to the air conditioning case.
- vibration from the evaporator 10 to the air conditioning case can be suppressed with a simple configuration in which the position of the fixing unit 30 is changed. As a result, noise caused by vibration of the air conditioning case due to vibration of the evaporator 10 can be suppressed.
- the fixing portion 30 is provided at a position excluding the four corners of the heat exchange surface 11a, and at a position where the amplitude of the natural vibration mode of the heat exchanger is smaller than the four corners.
- the position where the fixing portion 30 is provided is more preferably a position where the combined vibration mode of 1000 Hz or less is minimized.
- Noise due to propagation from the evaporator 10 to the vehicle air conditioner is limited to 1000 Hz or less. Therefore, the vibration transmitted to the air conditioning case can be further suppressed by fixing the position where the combined vibration mode of 1000 Hz or less is minimized.
- the fixed part 30 is provided at a position where the vibration mode frequency of the evaporator 10 and the natural frequency of the wall surface vibration of the air conditioning case are different.
- the natural frequency of the air conditioning case varies depending on the location. If this natural frequency is provided at the same position as the vibration mode frequency of the evaporator 10, even if the vibration is attenuated and transmitted from the evaporator 10, if the natural frequency is the same as the natural frequency of the air conditioning case, the air conditioning case is large. It will vibrate. Therefore, by providing the fixing unit 30 at a position where the vibration mode frequency of the evaporator 10 and the natural frequency of the wall surface vibration of the air conditioning case are different, the effect of reducing NV is reduced due to the natural frequency of the air conditioning case. This can be suppressed.
- the fixed part 30 is provided. As shown in FIG. 3, the position of 0.25L and the position of 0.75L are nodes. Since the fixing portion 30 is provided in the vicinity ( ⁇ 0.05 L) of the position of such a node, the effect of reducing NV can be achieved as described above.
- the vibration propagation to the vehicle air conditioner is achieved. It is suppressed.
- the NV of the vehicle air conditioner can be reduced by fixing the evaporator 10 at a position excluding the vicinity of the abdomen. Since the transmission of the main vibration mode of the evaporator 10 to the air conditioning case can be suppressed by pressing the node of the evaporator 10, the NV of the vehicle air conditioner can be reduced.
- FIG. 7 the vehicle air conditioner is shown, and the evaporator 10A is shown as an element constituting the vehicle air conditioner.
- the expansion valve 40 is integrally provided in the evaporator 10A.
- the evaporator 10A is connected to the outflow side of the expansion valve 40 of the refrigeration cycle apparatus, and the refrigerant decompressed by the expansion valve 40 flows toward the evaporator 10A.
- the present embodiment is characterized in that the fixing portions 30 are provided at six locations. Moreover, the structure of each fixing
- the fixing portion 30 is located at a position separated from the end of the first side 31 by 0.25 L ⁇ 0.05 L in each of the upper tank portion 12 and the lower tank portion 13, and 0.
- a fixing portion 30 is provided at a position separated by 75L ⁇ 0.05L. Since the position of the fixing portion 30 in the first side 31 is the same position as in the first embodiment described above, the same action and effect can be achieved.
- the fixing portion 30 is provided on each of the side plates 16 located at both ends in the length direction X. Specifically, if the length of the second side 32 is W, the fixing portion 30 is preferably provided at a position 0.5 W ⁇ 0.05 W away from the end of the second side 32.
- 0.5 W means 0.5 ⁇ W.
- the second side 32 is a position where a position of 0.5 W becomes a node in the second side 32. Since the fixing portion 30 is provided in the vicinity ( ⁇ 0.05 W) of the position of such a node, the effect of reducing NV can be achieved in the same manner as the position of the fixing portion 30 on the first side 31.
- the evaporator 10 can be fixed to an air-conditioning case more firmly.
- FIG. 9 is characterized in that the configuration of the fixing portion 30B is different from the evaporator 10 of the first embodiment described above.
- the fixing part 30B of the evaporator 10B of the present embodiment is realized by the convex part protruding outward from the lower tank part 13 as described above.
- the convex portion is configured to be covered with an elastic member, for example, an anti-vibration rubber.
- the elastic member can be reliably brought into contact with the air conditioning case.
- vibration transmitted from the fixed portion 30B to the air conditioning case can be further damped.
- FIG. 10 is characterized in that the position of the fixing unit 30 is different from that of the evaporator 10 of the first embodiment described above.
- the position of the fixing portion 30 of the present embodiment is provided on each of the side plates 16 located at both ends in the length direction X. Specifically, assuming that the length of the second side 32 is W, it is preferable that the position is 0.5 W ⁇ 0.05 W away from the end of the second side 32 (the position indicated by the virtual line 21 in FIG. 10). ) Is provided with a fixing portion 30.
- the second side 32 is a position where a position of 0.5 W becomes a node in the second side 32. Since the fixing portion 30 is provided in the vicinity ( ⁇ 0.05 W) of the position of such a node, the effect of reducing NV can be achieved.
- the number of fixing portions 30 is two.
- the number of the fixing portions 30 is not limited to two.
- the evaporator 10 constitutes the vehicle air conditioner, but is not limited to the vehicle, and may be an evaporator constituting a home air conditioner. Moreover, it is not restricted to an evaporator, A heat radiator and a condenser may be sufficient if it is a rectangular parallelepiped heat exchanger with which a refrigerant flows inside.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Air-Conditioning For Vehicles (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本開示の第1実施形態に関して、図1~図6を用いて説明する。蒸発器10は、図示しない冷凍サイクル中に配設されるものである。蒸発器10は、圧縮機で高温高圧に圧縮され、放熱器で放熱冷却され、減圧装置で低温低圧に減圧された後の冷媒を蒸発させる熱交換器である。本実施形態の蒸発器10は、図1に示すように、コア部11、上側タンク部12、下側タンク部13などを含み、各構成部材間が相互にろう付け接合されている。
次に、本開示の第2実施形態に関して、図7および図8を用いて説明する。図7では、車両用空調装置を示し、蒸発器10Aは車両用空調装置を構成する要素として示している。図7に示す車両用空調装置を構成する蒸発器10Aは、膨張弁40が一体に設けられている。蒸発器10Aは、冷凍サイクル装置の膨張弁40の流出側に接続され、その膨張弁40で減圧された冷媒が蒸発器10Aに向かって流れる。本実施形態は、固定部30が6箇所に設けられる点に特徴を有する。また各固定部30の構成は、前述の第1実施形態と同様に、凸部によって実現される。
次に、本開示の第3実施形態に関して、図9を用いて説明する。図9では、前述の第1実施形態の蒸発器10とは固定部30Bの構成が異なる点に特徴を有する。本実施形態の蒸発器10Bの固定部30Bは、前述のように下側タンク部13から外方に突出する凸部によって実現される。そして凸部は、弾性部材、たとえば防振ゴムで覆われて構成されている。
次に、本開示の第4実施形態に関して、図10を用いて説明する。図10では、前述の第1実施形態の蒸発器10とは固定部30の位置が異なる点に特徴を有する。本実施形態の固定部30の位置は、長さ方向Xの両端部に位置するサイドプレート16のそれぞれに設けられる。具体的には、第2の辺32の長さをWとすると、好ましくは、第2の辺32の端部から0.5W±0.05W離れた位置(図10の仮想線21で示す位置)に固定部30が設けられる。第2の辺32については、図8に示すように、0.5Wの位置が第2の辺32において節となる位置である。このような節の位置の近傍(±0.05W)に固定部30を設けるので、NV低減の効果を達成することができる。
以上、本開示の好ましい実施形態について説明したが、本開示は上述した実施形態に何ら制限されることなく、本開示の主旨を逸脱しない範囲において種々変形して実施することが可能である。
Claims (5)
- 内部を冷媒が流れる直方体形状の熱交換器(10,10A,10B,10C)をケースに固定するための固定構造であって、
前記直方体形状の前記熱交換器を構成する辺を、第1の辺(31)、第2の辺(32)および第3の辺(33)とした場合、前記第3の辺の長さが最も小さく、
前記第1の辺と前記第2の辺とで囲まれた面は、前記熱交換器の熱交換面(11a)であり、
前記第1の辺と前記第3の辺とで囲まれた面、および前記第2の辺と前記第3の辺とで囲まれた面の少なくともいずれか一方の面に、少なくとも1つの固定部(30,30B)を備え、
前記固定部は、前記熱交換面の四隅を除いた位置であって、前記熱交換器の固有振動モードの腹部に対応する位置を除いた位置に設けられる熱交換器の固定構造。 - 前記固定部は、前記熱交換面の前記四隅を除いた位置であって、前記熱交換器の前記固有振動モードの振幅が前記四隅における振幅よりも小さい位置に設けられる請求項1に記載の熱交換器の固定構造。
- 前記固定部が設けられる位置は、1000Hz以下の合成振動モードが最小となる位置である請求項1に記載の熱交換器の固定構造。
- 内部を冷媒が流れる直方体形状の熱交換器(10,10A,10B,10C)をケースに固定するための固定構造であって、
前記直方体形状の前記熱交換器を構成する辺を、第1の辺(31)、第2の辺(32)および第3の辺(33)とした場合、前記第1の辺の長さが最も大きく、かつ前記第3の辺の長さが最も小さく、
前記第1の辺と前記第2の辺とで囲まれた面は、前記熱交換器の熱交換面(11a)であり、
前記第1の辺と前記第3の辺とで囲まれた面に、少なくとも1つの固定部(30,30B)を備え、
前記第1の辺の長さをLとすると前記第1の辺の端部から、0.25L±0.05L離れた位置、および0.75L±0.05L離れた位置の少なくともいずれか一方に前記固定部が設けられる熱交換器の固定構造。 - 前記固定部は、前記熱交換器の振動モードの周波数と、前記ケースの壁面の固有振動数とが異なる位置に設けられる請求項1~4のいずれか1つに記載の熱交換器の固定構造。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US14/648,209 US20150300756A1 (en) | 2012-11-30 | 2013-10-21 | Fixing structure for heat exchanger |
| DE112013005735.2T DE112013005735T5 (de) | 2012-11-30 | 2013-10-21 | Befestigungsstruktur für einen Wärmetauscher |
| CN201380062581.5A CN104822554B (zh) | 2012-11-30 | 2013-10-21 | 热交换器的固定结构 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012262209A JP5920190B2 (ja) | 2012-11-30 | 2012-11-30 | 熱交換器の固定構造 |
| JP2012-262209 | 2012-11-30 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2014083754A1 true WO2014083754A1 (ja) | 2014-06-05 |
Family
ID=50827419
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2013/006212 WO2014083754A1 (ja) | 2012-11-30 | 2013-10-21 | 熱交換器の固定構造 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20150300756A1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5920190B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN104822554B (ja) |
| DE (1) | DE112013005735T5 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2014083754A1 (ja) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10113804B2 (en) | 2013-02-26 | 2018-10-30 | Denso Corporation | Heat exchanger and air conditioning device |
| WO2021079627A1 (ja) * | 2019-10-24 | 2021-04-29 | 株式会社デンソー | 車両用空調装置 |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6350373B2 (ja) | 2015-04-17 | 2018-07-04 | 株式会社デンソー | 蒸発器 |
| JP6804269B2 (ja) * | 2016-11-18 | 2020-12-23 | 三菱重工サーマルシステムズ株式会社 | 熱交換器 |
| CN110118174A (zh) * | 2019-04-22 | 2019-08-13 | 安徽大富重工机械有限公司 | 一种压缩机以及汽车空调系统 |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5846986U (ja) * | 1981-09-22 | 1983-03-30 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 多管式熱交換器 |
| JPH0342708U (ja) * | 1989-08-30 | 1991-04-23 | ||
| JP2000146217A (ja) * | 1998-11-12 | 2000-05-26 | Hitachi Ltd | 空気調和機の室内機 |
| JP2008247105A (ja) * | 2007-03-29 | 2008-10-16 | Denso Corp | 空調装置 |
Family Cites Families (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5784223A (en) * | 1980-11-13 | 1982-05-26 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | Vibration absorber of vehicle |
| JPS6288608A (ja) * | 1985-10-14 | 1987-04-23 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | 車輌用空気調和機のエバポレ−タユニツト |
| DE4102264C2 (de) * | 1991-01-26 | 2003-03-27 | Continental Teves Ag & Co Ohg | Hydraulische Servolenkung für Kraftfahrzeuge |
| JP3687150B2 (ja) * | 1995-05-17 | 2005-08-24 | 株式会社デンソー | 熱交換器支持装置 |
| JPH10269539A (ja) * | 1997-03-19 | 1998-10-09 | Fujitsu Ltd | ヘッドアームへのスプリングアーム取付構造および取付治具 |
| JP2002139289A (ja) * | 2000-06-08 | 2002-05-17 | Denso Corp | 熱交換器 |
| US6558137B2 (en) * | 2000-12-01 | 2003-05-06 | Tecumseh Products Company | Reciprocating piston compressor having improved noise attenuation |
| JP2003336935A (ja) * | 2002-05-21 | 2003-11-28 | Denso Corp | 熱交換器 |
| US7150604B2 (en) * | 2004-03-15 | 2006-12-19 | Carrier Corporation | Electric box for compressor assembly |
| FR2953774B1 (fr) * | 2009-12-11 | 2012-03-02 | Peugeot Citroen Automobiles Sa | Dispositif de fixation d'un echangeur de chaleur de vehicule automobile |
| CN201626282U (zh) * | 2010-03-12 | 2010-11-10 | 杨顺福 | 带减振器的汽车空调冷凝器 |
| JP2012001124A (ja) * | 2010-06-17 | 2012-01-05 | Japan Climate Systems Corp | 車両用空調装置 |
| CN201808425U (zh) * | 2010-09-30 | 2011-04-27 | 重庆长安汽车股份有限公司 | 一种商用车顶置蒸发器安装结构 |
-
2012
- 2012-11-30 JP JP2012262209A patent/JP5920190B2/ja active Active
-
2013
- 2013-10-21 DE DE112013005735.2T patent/DE112013005735T5/de not_active Ceased
- 2013-10-21 WO PCT/JP2013/006212 patent/WO2014083754A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2013-10-21 US US14/648,209 patent/US20150300756A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2013-10-21 CN CN201380062581.5A patent/CN104822554B/zh active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5846986U (ja) * | 1981-09-22 | 1983-03-30 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 多管式熱交換器 |
| JPH0342708U (ja) * | 1989-08-30 | 1991-04-23 | ||
| JP2000146217A (ja) * | 1998-11-12 | 2000-05-26 | Hitachi Ltd | 空気調和機の室内機 |
| JP2008247105A (ja) * | 2007-03-29 | 2008-10-16 | Denso Corp | 空調装置 |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10113804B2 (en) | 2013-02-26 | 2018-10-30 | Denso Corporation | Heat exchanger and air conditioning device |
| WO2021079627A1 (ja) * | 2019-10-24 | 2021-04-29 | 株式会社デンソー | 車両用空調装置 |
| JP2021066351A (ja) * | 2019-10-24 | 2021-04-30 | 株式会社デンソー | 車両用空調装置 |
| JP7200906B2 (ja) | 2019-10-24 | 2023-01-10 | 株式会社デンソー | 車両用空調装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN104822554B (zh) | 2017-06-09 |
| CN104822554A (zh) | 2015-08-05 |
| JP5920190B2 (ja) | 2016-05-18 |
| US20150300756A1 (en) | 2015-10-22 |
| DE112013005735T5 (de) | 2015-11-26 |
| JP2014108633A (ja) | 2014-06-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6051935B2 (ja) | 熱交換器 | |
| WO2014083754A1 (ja) | 熱交換器の固定構造 | |
| US20070084589A1 (en) | Evaporator | |
| JP5875918B2 (ja) | 車室内熱交換器及び車室内熱交換器のヘッダ間接続部材 | |
| KR101416358B1 (ko) | 차량용 열교환기 | |
| JP2013178007A (ja) | パラレルフロー型熱交換器及びそれを備えた機器 | |
| US10969180B2 (en) | Air-conditioning unit | |
| WO2014068842A1 (ja) | 冷媒蒸発器 | |
| JP6044477B2 (ja) | 車両用熱交換器 | |
| JP2003042597A (ja) | 一体型熱交換器 | |
| JP2013134016A (ja) | 熱交換器 | |
| JP2000213888A (ja) | 熱交換装置を備える熱ル―プを有する暖房、換気、または空気調和装置 | |
| JP2018189337A (ja) | 冷媒蒸発器およびその製造方法 | |
| US11148503B2 (en) | Evaporator with cool storage function | |
| JP2010065989A (ja) | 熱交換器用チューブ及び熱交換器 | |
| KR102371382B1 (ko) | 열교환기용 튜브 | |
| JP2018115775A (ja) | 熱交換器 | |
| KR101890867B1 (ko) | 증발기 | |
| JP6297808B2 (ja) | 熱交換器 | |
| KR100723809B1 (ko) | 열교환기 | |
| JP7426456B1 (ja) | 室内熱交換器及び空気調和機 | |
| KR20140095700A (ko) | 열교환기 | |
| JP2011169522A (ja) | 熱交換器 | |
| JPH10153358A (ja) | 積層型熱交換器 | |
| JP2019148389A (ja) | 蒸発器 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 13859150 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 14648209 Country of ref document: US |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 112013005735 Country of ref document: DE Ref document number: 1120130057352 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 13859150 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |