WO2014069129A1 - 放射線信号処理装置、放射線画像撮影システム、及び放射線信号処理方法 - Google Patents
放射線信号処理装置、放射線画像撮影システム、及び放射線信号処理方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2014069129A1 WO2014069129A1 PCT/JP2013/076131 JP2013076131W WO2014069129A1 WO 2014069129 A1 WO2014069129 A1 WO 2014069129A1 JP 2013076131 W JP2013076131 W JP 2013076131W WO 2014069129 A1 WO2014069129 A1 WO 2014069129A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- radiation
- irradiation
- signal
- signal processing
- dose
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05G—X-RAY TECHNIQUE
- H05G1/00—X-ray apparatus involving X-ray tubes; Circuits therefor
- H05G1/08—Electrical details
- H05G1/26—Measuring, controlling or protecting
- H05G1/30—Controlling
- H05G1/38—Exposure time
- H05G1/42—Exposure time using arrangements for switching when a predetermined dose of radiation has been applied, e.g. in which the switching instant is determined by measuring the electrical energy supplied to the tube
- H05G1/44—Exposure time using arrangements for switching when a predetermined dose of radiation has been applied, e.g. in which the switching instant is determined by measuring the electrical energy supplied to the tube in which the switching instant is determined by measuring the amount of radiation directly
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B6/00—Apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis; Apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis combined with radiation therapy equipment
- A61B6/42—Arrangements for detecting radiation specially adapted for radiation diagnosis
- A61B6/4208—Arrangements for detecting radiation specially adapted for radiation diagnosis characterised by using a particular type of detector
- A61B6/4233—Arrangements for detecting radiation specially adapted for radiation diagnosis characterised by using a particular type of detector using matrix detectors
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B6/00—Apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis; Apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis combined with radiation therapy equipment
- A61B6/54—Control of apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis
- A61B6/542—Control of apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis involving control of exposure
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a radiation signal processing apparatus, a radiation image capturing system, and a radiation signal processing method.
- radiation detectors such as FPD (Flat Panel Detector) that can arrange radiation sensitive layers on TFT (Thin Film Transistor) active matrix substrates and convert radiation dose into digital data (electrical signals) (referred to as “electronic cassettes”)
- FPD Fluor Deposition Detector
- TFT Thin Film Transistor
- electrospray cassettes a radiation image capturing apparatus that captures a radiation image represented by the amount of irradiated radiation using this radiation detector has been put into practical use.
- Some of such radiographic imaging apparatuses monitor radiation dose in order to control radiation start and stop.
- wireless communication In order to convey the detection result without error, it is exchanged with a digital signal.
- the radiation generator side makes a decision to stop the irradiation based on the cumulative amount of irradiated radiation
- the radiation imaging apparatus side sends information on the detected irradiation dose to the radiation generator side as needed during the radiation irradiation period. become.
- wirelessly exchanging digital signals it is naturally impossible to receive temporarily if the wireless strength is unstable, so the radiation generator side receives discrete information in terms of time.
- the cumulative amount of dose increases during the blank period between receiving dose information at a certain timing and receiving dose information at the next timing. I do not know. Therefore, when the dose information is received at the next timing, the necessary accumulated value may already be exceeded.
- the present invention has been made in consideration of the above facts, and an object thereof is to enable radiation irradiation stop control with high accuracy in a system that performs radiation irradiation stop control wirelessly.
- the radiation signal processing apparatus of the present invention captures an image corresponding to the irradiated radiation, detects the radiation dose, and outputs a signal representing the detection result from the radiation imaging apparatus.
- a receiving unit that receives a signal representing a detection result as a digital signal, and a digital signal that represents the detection result received by the receiving unit when the radiation imaging apparatus is irradiated with radiation and the radiation reaches a predetermined dose.
- Conversion means for converting the signal into an analog signal that can be recognized by the radiation irradiation apparatus that stops the radiation irradiation.
- the receiving means receives a signal representing the detection result of the radiation dose from the radiation imaging apparatus as a digital signal.
- the digital signal representing the detection result received by the receiving means is converted into an analog signal that can be recognized by the radiation irradiation apparatus. That is, by performing the conversion by the conversion means, the radiation irradiation stop control can be performed with high accuracy in a system that performs the radiation irradiation stop control wirelessly. In addition, radiation irradiation stop control can be performed by applying a radiation imaging apparatus capable of detecting the radiation irradiation amount to a system that performs radiation irradiation stop control using an ion chamber or the like.
- the receiving unit may receive the digital signal by wireless communication, and the converting unit may further output the analog signal to a radiation irradiation apparatus connected by wire.
- the receiving means may receive an irradiation stop notice signal indicating the irradiation time from the start of irradiation and the remaining irradiation time with respect to a predetermined appropriate irradiation time as the digital signal, or start of irradiation. May be received as the digital signal.
- the irradiation stop notice signal indicating the irradiation time from, the remaining irradiation time with respect to the predetermined appropriate irradiation time, and the unit of time may be received.
- the conversion means may obtain the voltage increase ⁇ per unit time from the digital signal, and convert the analog signal representing the voltage corresponding to the radiation dose by time integration.
- the conversion means can improve the accuracy of the signal by obtaining the voltage increase ⁇ per unit time based on the latest digital signal.
- the radiation imaging apparatus may transmit the irradiation stop notice signal that maximizes the voltage increase as the digital signal when the dose increases and stops immediately.
- a radiation imaging system having a function of detecting and outputting the dose of irradiated radiation and including a radiation image capturing device that captures a radiation image and the above-described radiation signal processing device may be configured. Good.
- the signal processing method of the radiographic imaging apparatus of the present invention captures an image corresponding to the irradiated radiation, and detects the radiation dose and outputs a signal representing the detection result from the radiographic imaging apparatus.
- a signal representing the result is received as a digital signal by the receiving means, and the received digital signal representing the detection result is irradiated to the radiation imaging apparatus and radiation irradiation is stopped when the radiation reaches a predetermined dose. It converts into an analog signal which can be recognized by the radiation irradiation apparatus.
- the signal representing the detection result of the radiation dose from the radiographic apparatus is received as a digital signal by the receiving means.
- the digital signal representing the received detection result is converted into an analog signal that can be recognized by the radiation irradiation apparatus. That is, by performing the conversion, the radiation irradiation stop control can be performed with high accuracy in a system that performs the radiation irradiation stop control wirelessly.
- radiation irradiation stop control can be performed by applying a radiation imaging apparatus capable of detecting the radiation irradiation amount to a system that performs radiation irradiation stop control using an ion chamber or the like.
- the digital signal may be received by wireless communication, and the analog signal may be further output to a radiation irradiation apparatus connected by wire.
- an irradiation stop notice signal indicating the irradiation time from the start of radiation irradiation and the remaining irradiation time with respect to a predetermined appropriate irradiation time may be received as the digital signal, or the irradiation time from the start of radiation irradiation And the irradiation stop notice signal showing the remaining irradiation time with respect to the predetermined appropriate irradiation time and the unit of time may be received as the digital signal.
- the voltage increase ⁇ per unit time may be obtained from the digital signal, and may be converted into an analog signal representing a voltage corresponding to the radiation dose by time integration. In this case, the accuracy of the signal can be improved by obtaining the voltage increase ⁇ per unit time based on the latest digital signal.
- the radiation imaging apparatus may transmit the irradiation stop notice signal that maximizes the voltage increase as the digital signal when the dose increases and stops immediately.
- the present invention may be a recording medium storing a program for causing a computer to execute the above-described radiation signal processing method.
- the present invention enables radiation irradiation stop control by applying a radiation imaging apparatus capable of detecting the amount of radiation irradiation to a related art system that performs radiation irradiation stop control using an ion chamber or the like. It has an excellent effect of being able to.
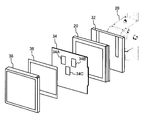
- FIG. 1 is a schematic configuration diagram of an outline of an overall configuration of an example of a radiographic image capturing system according to an embodiment. It is a figure which shows an example of the electronic cassette hold
- FIG. It is a flowchart which shows an example of the flow of a process performed by I / F for AEC of the radiographic imaging system concerning this Embodiment.
- FIG. 1 shows a schematic configuration diagram of an overall configuration of an example of a radiographic imaging system according to the present exemplary embodiment.
- the radiographic image capturing system 10 of the present embodiment has a function in which the electronic cassette 20 itself detects a radiation irradiation start (imaging start) and a radiation irradiation stop (imaging end).
- the radiographic imaging system 10 of the present exemplary embodiment is based on an instruction (imaging menu) input from an external system (for example, RIS: Radiology Information System: radiation information system) via the console 16. It has a function of taking a radiographic image by an operation such as the above.
- an instruction for example, RIS: Radiology Information System: radiation information system
- the radiographic image capturing system 10 of the present embodiment has a function of causing a doctor, a radiographer, or the like to interpret a radiographic image by displaying the captured radiographic image on the display 50 of the console 16 or the radiographic image interpretation device 18. It is what you have.
- the radiographic imaging system 10 of the present exemplary embodiment includes a radiation generation device 12, a control device 14, a console 16, a storage unit 17, a radiographic image interpretation device 18, and an electronic cassette 20.
- the radiation generator 12 includes a power source 22, a radiation irradiation controller 23, and a high voltage generator 24.
- the radiation irradiation control unit 23 has a function of irradiating the imaging target region of the subject 30 with the radiation X from the radiation irradiation source 25 based on the control of the radiation control unit 62 of the control device 14.
- the radiation irradiation control unit 23 according to the present embodiment supplies the current supplied from the power supply 22 to the high voltage generator 24, supplies the high voltage generated by the high voltage generator 24 to the radiation irradiation source 25, and generates radiation.
- X is generated.
- the power source 22 may be either an AC power source or a DC power source.
- the high voltage generator 24 may be any of a single-phase transformer system, a three-phase transformer system, an inverter system, and a capacitor system.
- the installation type radiation generator 12 is shown in FIG. 1, it is not restricted to this, The radiation generator 12 may be a mobile type.
- the radiation X transmitted through the subject 30 is applied to the electronic cassette 20 held on the wall stand 28.
- the electronic cassette 20 is attached to a back bracket 32 provided on a wall stand 28 fixed to a wall.
- a cover 38 is provided on the radiation irradiation side of the electronic cassette 20.
- an ion chamber 34 having a plurality of lighting fields 34A to 34C for detecting the radiation dose and a bucky / grid 36 for removing scattered light can be arranged.
- the electronic cassette 20 outputs not only the image information indicating the radiation image but also a signal for stopping the radiation irradiation, and can control the radiation irradiation stop even without the ion chamber 34.
- the ion chamber 34 can be omitted. Or you may be comprised so that irradiation of a radiation can also be stopped using the ion chamber 34.
- the electronic cassette 20 has a function of generating a charge corresponding to the dose of the radiation X transmitted through the subject 30, and generating and outputting image information indicating a radiation image based on the generated charge amount.
- dose refers to radiation intensity, for example, radiation applied at a predetermined tube voltage and a predetermined tube current per unit time.
- FIG. 2 shows an example in which the electronic cassette 20 is held on the wall stand 28. However, a configuration may be adopted in which a photographing stand for a subject to lie down is provided and the electronic cassette 20 is held on the photographing stand.
- image information indicating the radiation image output by the electronic cassette 20 is input to the console 16 via the control device 14.
- the console 16 has a function of controlling the radiation generator 12 and the electronic cassette 20 by using an imaging menu and various information acquired from an external system (RIS) through wireless communication (LAN: Local Area Network). Have. Further, the console 16 has a function of transmitting / receiving various information including image information of radiographic images to / from the control device 14 and a function of transmitting / receiving various information to / from the electronic cassette 20.
- the console 16 is configured as a server computer, and includes a control unit 49, a display driver 48, a display 50, an operation input detection unit 52, an operation panel 54, an I / O unit 56, an I / F unit 57, and an I / F unit 57.
- / F unit 58 is provided.
- the control unit 49 has a function of controlling the operation of the entire console 16, and includes a CPU, a ROM, a RAM, and an HDD.
- the CPU has a function of controlling the operation of the entire console 16, and various programs including a control program used by the CPU are stored in advance in the ROM.
- the RAM has a function of temporarily storing various data
- the HDD hard disk drive
- the display driver 48 has a function of controlling display of various information on the display 50.
- the display 50 according to the present embodiment has a function of displaying an imaging menu, a captured radiographic image, and the like.
- the operation input detection unit 52 has a function of detecting an operation state with respect to the operation panel 54.
- the operation panel 54 is used by a doctor, a radiographer, or the like to input operation instructions related to radiographic image capturing.
- the operation panel 54 includes, for example, a touch panel, a touch pen, a plurality of keys, a mouse, and the like. When configured as a touch panel, it may be configured the same as the display 50.
- the I / O unit 56 and the I / F unit 58 transmit and receive various types of information to and from the control device 14 and the radiation generation device 12 through wireless communication and wired communication, and also perform an image with the electronic cassette 20. It has a function of transmitting and receiving various information such as information.
- the I / F unit 57 has a function of transmitting / receiving various types of information to / from the RIS.
- the control unit 49, the display driver 48, the operation input detection unit 52, the I / F unit 58, and the I / O unit 56 are connected so that information can be exchanged with each other via a bus 59 such as a system bus or a control bus.
- a bus 59 such as a system bus or a control bus.
- the control unit 49 controls the display of various information on the display 50 via the display driver 48 and controls the transmission / reception of various information with the radiation generator 12 and the electronic cassette 20 via the I / F unit 58. Can be performed respectively.
- the control device 14 has a function of controlling the radiation generation device 12 and the electronic cassette 20 based on an instruction from the console 16 and stores the radiation image received from the electronic cassette 20 in the storage unit 17. And a function of controlling display on the display 50 of the console 16 and the radiographic image interpretation device 18.
- control device 14 includes a system control unit 60, a radiation control unit 62, a panel control unit 64, an image processing control unit 66, and an I / F unit 68.
- the system control unit 60 has a function of controlling the entire control device 14 and a function of controlling the radiographic imaging system 10.
- the system control unit 60 includes a CPU, ROM, RAM, and HDD.
- the CPU has a function of controlling the operation of the entire control device 14 and the radiographic imaging system 10, and various programs including a control program used by the CPU are stored in advance in the ROM.
- the RAM has a function of temporarily storing various data
- the HDD has a function of storing and holding various data.
- the radiation control unit 62 has a function of controlling the radiation irradiation control unit 23 of the radiation generator 12 based on an instruction from the console 16 or the like.
- the panel control unit 64 has a function of controlling the electronic cassette 20 based on an instruction from the console 16 or the like.
- the image processing control unit 66 has a function of performing various image processing on the radiation image.
- the system control unit 60, the radiation control unit 62, the panel control unit 64, and the image processing control unit 66 are connected to each other through a bus 69 such as a system bus or a control bus so as to be able to exchange information.
- the storage unit 17 of the present embodiment has a function of storing captured radiographic images and information related to the radiographic images.
- An example of the storage unit 17 is an HDD.
- the radiographic image interpretation device 18 of the present embodiment is a device having a function for the radiographer to interpret the radiographic image taken, and is not particularly limited, and includes a so-called radiogram interpretation viewer, a console, and the like.
- the radiological image interpretation apparatus 18 according to the present embodiment is configured as a personal computer, and, like the console 16 and the control apparatus 14, a CPU, ROM, RAM, HDD, display driver, display 40, operation input detection unit, An operation panel 42, an I / O unit, and an I / F unit are provided. In FIG. 1, only the display 40 and the operation panel 42 are shown in these configurations in order to avoid complicated description.
- the radiographic imaging system 10 has an automatic exposure control (AEC: Automatic exposure control) function (hereinafter referred to as an AEC function) for controlling the stop of radiation irradiation, and outputs a signal output from the electronic cassette 20.
- AEC Automatic exposure control
- the radiation irradiation control unit 23 controls the high voltage generator 24 to control the timing of stopping the irradiation of radiation from the radiation irradiation source 25.
- the electronic cassette 20 has a configuration for detecting the radiation dose.
- a dedicated sensor or the like may be provided, but in the present embodiment, a configuration in which a pixel for detecting the radiation dose is provided.
- FIG. 3 is a block diagram in which a part of the configuration related to the AEC function in the radiographic image capturing system 10 according to the present embodiment is extracted.
- the electronic cassette 20 outputs a digital irradiation stop notice signal.
- the irradiation time t and the appropriate irradiation time T from the start of irradiation are recalculated at 1 msec intervals (however, the accuracy of t and T is in increments of 0.1 msec, for example), and sent repeatedly, so If it can be received even once, radiation can be stopped, and the risk of overexposure is reduced. In addition, it is possible to stop the dose with higher accuracy by updating it with the latest one out of repeated reception.
- the AEC I / F 26 controls the irradiation stop of the radiation obtained from the electronic cassette 20 so that the irradiation stop control using the ion chamber 34 of the related art can be used.
- the signal (stop warning signal) is converted into an analog signal in the related art format.
- the analog signal converted by the AEC I / F 26 is output to the radiation generation apparatus 12, whereby the radiation stoppage of radiation can be controlled.
- the AEC I / F 26 and the radiation generator 12 are connected by wire to prevent the radiation irradiation from being stopped due to interference or the like. Further, the electronic cassette 20 and the AEC I / F 26 may be connected by wire.
- the AEC I / F 26 includes an AEC signal receiving unit 70, an AEC signal converting unit 72, and an AEC signal transmitting unit 74.
- FIG. 4 is a functional block diagram showing a schematic configuration of the AEC I / F 26.
- the AEC signal receiving unit 70 receives the digital irradiation stop notification signal wirelessly transmitted from the electronic cassette 20 and outputs the received digital irradiation stop notification signal to the AEC signal conversion unit 72.
- the AEC signal conversion unit 72 converts the digital irradiation stop notice signal into an analog unit voltage increase signal and integrates the time, thereby obtaining an analog signal (voltage) representing a voltage corresponding to the radiation dose detected by the electronic cassette 20. Signal) is output to the AEC signal transmitter 74.
- the AEC signal transmission unit 74 outputs an analog signal (voltage signal) obtained by the conversion of the AEC signal conversion unit 72 to the radiation irradiation control unit 23 of the radiation generation apparatus 12 connected by wire.
- the radiation irradiation control unit 23 receives an analog signal representing a voltage corresponding to the radiation dose similar to that in the related technology, so that the radiation dose is reduced using the radiation exposure stop system of the related technology. Radiation can be irradiated at the appropriate dose.
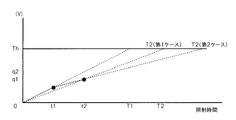
- the irradiation start time is set to 0, and the set of irradiation stop notification signals sent from the electronic cassette 20 is (t1, ⁇ t1), (t2, ⁇ t2), (t3, ⁇ t3),.
- incidental information such as an identification ID and an error code
- incidental information may be sent.
- the voltage increase ⁇ is calculated as follows, assuming that the irradiation time t1 from the start of irradiation until now is successful, t2 is reception failure, and t3 and t4 are reception success.
- black circle indicates successful reception
- white circle indicates reception failure.
- the voltage increase ⁇ (V / sec) per unit time, which is the same as the AEC of the related technology, is output as a unit voltage increase signal. That is, the voltage increase ⁇ is time-integrated, and stops when the integration amount reaches Thres.
- the voltage increase ⁇ can be obtained at one time without receiving it twice. It can be converted into an analog signal.
- Thres in the above calculation indicates a threshold value for the appropriate irradiation time T, and is adjusted at the time of installation and maintenance of the radiation generator 12 so as to stop at a constant output with uniform exposure as in the related art AEC. adjust. By doing so, it is possible to associate what (digit) the electronic cassette 20 is stopped with what (V) the radiation irradiation control unit 23 is stopped. For example, it is assumed that Thres (V) is Th (digit) as the electronic cassette 20.
- the absolute value of the irradiation time t differs depending on the shooting scene immediately after the start of irradiation, immediately before the end, subject (thickness), etc., but it is not possible to increase the number of bits in order to reliably transmit by radio. Therefore, the irradiation stop notice signal includes the unit of time as (t, ⁇ t, unit), so that the irradiation time t is longer or shorter, and the remaining irradiation time ⁇ t is the number of digits. Since the bit length of the irradiation stop notice signal can be minimized, the transmission cycle can be shortened repeatedly.
- FIG. 5B is a diagram for explaining how to obtain the remaining irradiation time ⁇ t or the appropriate irradiation time T.
- T is a known value because it is the time from the start of irradiation.
- Th is adjusted at the time of installation and maintenance of the radiation generator 12 as with the above-described threshold value Thres, and is adjusted to stop at a constant output with uniform exposure, as in the related art AEC. is there.
- the integrated pixel value q (digit) at each time is also a known value since it is a value detected by the electronic cassette 20.
- T2 (Th / q2) ⁇ t2 It becomes.
- the electronic cassette 20 side is updated every time because there is no information loss due to wireless disconnection.
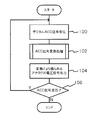
- FIG. 6 is a flowchart showing an example of the flow of processing performed in the AEC I / F 26 of the radiographic imaging system 10 according to the present exemplary embodiment.
- step 100 a digital AEC signal is received from the electronic cassette 20, and the process proceeds to step 102. That is, the AEC signal receiving unit 70 receives a digital irradiation stop notice signal output from the electronic cassette 20.
- the signal is converted into an analog voltage increase ⁇ (V / sec) per unit time, and the voltage increase ⁇ per unit time obtained is integrated over time to obtain a voltage corresponding to the radiation dose.
- An analog signal to be represented is obtained and the process proceeds to step 104.
- step 104 the converted analog signal (voltage signal) is output to the radiation irradiation control unit 23 of the radiation generator 12, and the process proceeds to step 106.
- the radiation irradiation control unit 23 can stop the radiation irradiation when the radiation irradiation amount reaches a predetermined amount, as in the related art AEC.
- step 106 it is determined whether or not an AEC signal has been received. If the determination is affirmative, the process returns to step 100 and the above-described processing is repeated. If the determination is negative, the series of processing ends. . Note that this determination determines whether or not the next AEC signal has been received, but depending on the wireless situation, the next AEC signal may not be received even though the irradiation stop dose is not reached. If the voltage increase [theta] has not reached the threshold value Thres, the process waits until the next AEC signal is received. Further, error processing (such as error notification) may be performed when a time during which the next AEC signal is not received even though the threshold Thres has not been reached has elapsed for a predetermined time or more.
- error processing such as error notification
- the digital irradiation stop notification signal output from the electronic cassette 20 is converted into an analog signal representing a dose by the AEC I / F 26 and output. Further, it is possible to perform complementary estimation between discrete dose information received in a jump by wireless communication, and it is possible to improve the accuracy of irradiation stop. In other words, it is possible to prevent the necessary accumulated value from being exceeded when the irradiation amount information is received, and the irradiation stop accuracy is good.
- the electronic cassette 20 can be used by directly using a system that performs AEC control using the ion chamber 34 or the like of related technology.
- the related art cassette can be used when the electronic cassette 20 cannot be used due to a failure or the like.
- the electronic cassette 20 for detecting the radiation dose can be applied to a related art system.
- a small communication load means that it is difficult to cause a delay in one-time wireless communication, which has a great advantage of stabilizing the system quality.
- the related art digital AEC signal irradiation control mechanism the more the transmission frequency is reduced, the larger the over amount will be when the cumulative amount is exceeded at a certain timing.
- the amount of over can be minimized while suppressing communication frequency and stabilizing communication quality.
- the AEC I / F 26 converts the digital irradiation stop notice signal into an analog signal (voltage signal) representing a voltage corresponding to the radiation dose, but it corresponds to the dose. You may make it convert into the analog signal (current signal) showing an electric current.
- the radiation in this embodiment is not particularly limited, and X-rays, ⁇ -rays, and the like can be applied.
- processing shown in the flowcharts in the above embodiments may be stored and distributed as various programs in various storage media.
- the configurations and operations of the radiographic imaging system 10, the radiation generator 12, the electronic cassette 20, and the like described in the present embodiment are merely examples, and can be changed according to the situation without departing from the gist of the present invention. It is.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- High Energy & Nuclear Physics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Toxicology (AREA)
- Measurement Of Radiation (AREA)
- Apparatus For Radiation Diagnosis (AREA)
- X-Ray Techniques (AREA)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201380056375.3A CN104768464B (zh) | 2012-11-02 | 2013-09-26 | 放射线信号处理装置、放射线图像摄影系统及放射线信号处理方法 |
| US14/692,746 US9674935B2 (en) | 2012-11-02 | 2015-04-22 | Radiation signal processing device, radiation imaging system, and radiation signal processing method |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012-242997 | 2012-11-02 | ||
| JP2012242997A JP6004898B2 (ja) | 2012-11-02 | 2012-11-02 | 放射線信号処理装置、放射線画像撮影システム、放射線信号処理方法、及び放射線信号処理プログラム |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US14/692,746 Continuation US9674935B2 (en) | 2012-11-02 | 2015-04-22 | Radiation signal processing device, radiation imaging system, and radiation signal processing method |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2014069129A1 true WO2014069129A1 (ja) | 2014-05-08 |
Family
ID=50627045
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2013/076131 Ceased WO2014069129A1 (ja) | 2012-11-02 | 2013-09-26 | 放射線信号処理装置、放射線画像撮影システム、及び放射線信号処理方法 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9674935B2 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6004898B2 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN104768464B (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2014069129A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6021403B2 (ja) * | 2012-04-19 | 2016-11-09 | キヤノン株式会社 | 放射線撮像装置 |
| JP6706136B2 (ja) | 2016-04-28 | 2020-06-03 | キヤノン株式会社 | 放射線撮像装置、放射線撮像システム、放射線撮像方法およびプログラム |
| CN112638258A (zh) * | 2018-09-19 | 2021-04-09 | 深圳帧观德芯科技有限公司 | 具有自动曝光控制的辐射检测器和自动曝光控制方法 |
| JP7551697B2 (ja) * | 2022-06-28 | 2024-09-17 | キヤノン株式会社 | 放射線撮影システム、放射線撮像装置、および放射線撮影システムの制御方法 |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH04105477A (ja) * | 1990-08-27 | 1992-04-07 | Hitachi Medical Corp | X線画像診断装置 |
| JP2008117641A (ja) * | 2006-11-06 | 2008-05-22 | Shimadzu Corp | X線撮影装置 |
| JP2012073230A (ja) * | 2010-08-31 | 2012-04-12 | Fujifilm Corp | 放射線撮影装置、及び放射線撮影システム |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4322619A (en) * | 1979-11-09 | 1982-03-30 | University Of Utah | Optical masking radiography |
| US6399950B1 (en) * | 2000-11-27 | 2002-06-04 | Shimadzu Corporation | Two-dimensional radiation detector |
| JP2006263339A (ja) | 2005-03-25 | 2006-10-05 | Konica Minolta Medical & Graphic Inc | 画像取得装置及び画像取得システム |
| JP4713952B2 (ja) * | 2005-06-02 | 2011-06-29 | 株式会社東芝 | X線透視撮影用自動露出制御装置 |
| US7313224B1 (en) * | 2006-06-22 | 2007-12-25 | General Electric Co. | Wireless integrated automatic exposure control module |
| JP2009034428A (ja) * | 2007-08-03 | 2009-02-19 | Konica Minolta Medical & Graphic Inc | X線撮影システム |
| JP5068128B2 (ja) * | 2007-09-28 | 2012-11-07 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 放射線画像撮影装置 |
| CN100581475C (zh) * | 2008-03-04 | 2010-01-20 | 西安交通大学 | 一种医用x射线ccd型数字摄像机 |
| JP5151676B2 (ja) * | 2008-05-20 | 2013-02-27 | コニカミノルタエムジー株式会社 | 放射線画像撮影システム |
| US8873712B2 (en) * | 2010-04-13 | 2014-10-28 | Carestream Health, Inc. | Exposure control using digital radiography detector |
| CN202143287U (zh) * | 2011-06-02 | 2012-02-08 | 赵建国 | X线曝光控制设备及x线曝光系统 |
-
2012
- 2012-11-02 JP JP2012242997A patent/JP6004898B2/ja active Active
-
2013
- 2013-09-26 WO PCT/JP2013/076131 patent/WO2014069129A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2013-09-26 CN CN201380056375.3A patent/CN104768464B/zh active Active
-
2015
- 2015-04-22 US US14/692,746 patent/US9674935B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH04105477A (ja) * | 1990-08-27 | 1992-04-07 | Hitachi Medical Corp | X線画像診断装置 |
| JP2008117641A (ja) * | 2006-11-06 | 2008-05-22 | Shimadzu Corp | X線撮影装置 |
| JP2012073230A (ja) * | 2010-08-31 | 2012-04-12 | Fujifilm Corp | 放射線撮影装置、及び放射線撮影システム |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US9674935B2 (en) | 2017-06-06 |
| CN104768464A (zh) | 2015-07-08 |
| JP2014090868A (ja) | 2014-05-19 |
| JP6004898B2 (ja) | 2016-10-12 |
| CN104768464B (zh) | 2018-12-18 |
| US20150230324A1 (en) | 2015-08-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN101849834B (zh) | 放射线成像设备及其暗电流校正方法 | |
| JP6326562B2 (ja) | X線システム | |
| CN102525506A (zh) | 射线图像检测设备及其控制方法 | |
| JP6004898B2 (ja) | 放射線信号処理装置、放射線画像撮影システム、放射線信号処理方法、及び放射線信号処理プログラム | |
| JP6890443B2 (ja) | 放射線撮影システム、放射線撮影方法、及びプログラム | |
| CN104605873A (zh) | X射线摄像设备以及控制x射线摄像的控制设备和方法 | |
| EP3266376A1 (en) | Radiographing system, dose index management method, and storage medium | |
| JP2024079839A (ja) | 放射線撮影装置、放射線撮影システム、制御装置及び照射停止方法 | |
| JP2011067543A (ja) | 放射線制御装置及び放射線撮影システム、並びに撮影条件設定方法 | |
| JP2014161454A (ja) | 放射線画像撮影装置及びその制御方法、並びにプログラム | |
| JP2010197679A (ja) | 放射線画像取得システム及び放射線画像検出カセッテ | |
| JP6433113B2 (ja) | 放射線撮影装置、放射線撮影システム、制御方法、及びプログラム。 | |
| JP6944268B2 (ja) | 放射線撮影装置、放射線撮影システム、放射線撮影装置の制御方法及びプログラム | |
| JP2014090869A (ja) | 放射線信号処理装置、放射線画像撮影システム、放射線信号処理方法、及び放射線信号処理プログラム | |
| JP2006026283A (ja) | 放射線撮影システム | |
| JP2009028367A (ja) | 放射線画像撮影システム | |
| US10498974B2 (en) | Radiation image capturing apparatus and radiation image capturing system | |
| JP2017094011A (ja) | 放射線撮影装置、放射線撮影システム、および放射線撮影装置の制御方法。 | |
| JP2008142093A (ja) | 放射線画像撮影システム及び放射線画像撮影用カセッテ | |
| CN108720854A (zh) | 放射线照射检测系统及放射线产生装置 | |
| JP2011098025A (ja) | 放射線画像生成システム | |
| JP2006122121A (ja) | 放射線画像撮影システム | |
| JP2010119513A (ja) | X線撮影システム | |
| JP6752353B2 (ja) | 放射線検出システム、放射線出力装置および放射線検出装置 | |
| JP2009226110A (ja) | 放射線画像撮影システム |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 13850125 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 13850125 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |