WO2013111855A1 - 液滴形成装置および液滴形成方法 - Google Patents
液滴形成装置および液滴形成方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2013111855A1 WO2013111855A1 PCT/JP2013/051587 JP2013051587W WO2013111855A1 WO 2013111855 A1 WO2013111855 A1 WO 2013111855A1 JP 2013051587 W JP2013051587 W JP 2013051587W WO 2013111855 A1 WO2013111855 A1 WO 2013111855A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- plunger rod
- solenoid
- droplet forming
- chamber
- pressurized gas
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B05—SPRAYING OR ATOMISING IN GENERAL; APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05B—SPRAYING APPARATUS; ATOMISING APPARATUS; NOZZLES
- B05B1/00—Nozzles, spray heads or other outlets, with or without auxiliary devices such as valves, heating means
- B05B1/02—Nozzles, spray heads or other outlets, with or without auxiliary devices such as valves, heating means designed to produce a jet, spray, or other discharge of particular shape or nature, e.g. in single drops, or having an outlet of particular shape
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04B—POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS
- F04B17/00—Pumps characterised by combination with, or adaptation to, specific driving engines or motors
- F04B17/03—Pumps characterised by combination with, or adaptation to, specific driving engines or motors driven by electric motors
- F04B17/04—Pumps characterised by combination with, or adaptation to, specific driving engines or motors driven by electric motors using solenoids
- F04B17/042—Pumps characterised by combination with, or adaptation to, specific driving engines or motors driven by electric motors using solenoids the solenoid motor being separated from the fluid flow
- F04B17/044—Pumps characterised by combination with, or adaptation to, specific driving engines or motors driven by electric motors using solenoids the solenoid motor being separated from the fluid flow using solenoids directly actuating the piston
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B05—SPRAYING OR ATOMISING IN GENERAL; APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05C—APPARATUS FOR APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05C5/00—Apparatus in which liquid or other fluent material is projected, poured or allowed to flow on to the surface of the work
- B05C5/02—Apparatus in which liquid or other fluent material is projected, poured or allowed to flow on to the surface of the work the liquid or other fluent material being discharged through an outlet orifice by pressure, e.g. from an outlet device in contact or almost in contact, with the work
- B05C5/0208—Apparatus in which liquid or other fluent material is projected, poured or allowed to flow on to the surface of the work the liquid or other fluent material being discharged through an outlet orifice by pressure, e.g. from an outlet device in contact or almost in contact, with the work for applying liquid or other fluent material to separate articles
- B05C5/0212—Apparatus in which liquid or other fluent material is projected, poured or allowed to flow on to the surface of the work the liquid or other fluent material being discharged through an outlet orifice by pressure, e.g. from an outlet device in contact or almost in contact, with the work for applying liquid or other fluent material to separate articles only at particular parts of the articles
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B05—SPRAYING OR ATOMISING IN GENERAL; APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05C—APPARATUS FOR APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05C5/00—Apparatus in which liquid or other fluent material is projected, poured or allowed to flow on to the surface of the work
- B05C5/02—Apparatus in which liquid or other fluent material is projected, poured or allowed to flow on to the surface of the work the liquid or other fluent material being discharged through an outlet orifice by pressure, e.g. from an outlet device in contact or almost in contact, with the work
- B05C5/0225—Apparatus in which liquid or other fluent material is projected, poured or allowed to flow on to the surface of the work the liquid or other fluent material being discharged through an outlet orifice by pressure, e.g. from an outlet device in contact or almost in contact, with the work characterised by flow controlling means, e.g. valves, located proximate the outlet
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B05—SPRAYING OR ATOMISING IN GENERAL; APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05C—APPARATUS FOR APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05C5/00—Apparatus in which liquid or other fluent material is projected, poured or allowed to flow on to the surface of the work
- B05C5/02—Apparatus in which liquid or other fluent material is projected, poured or allowed to flow on to the surface of the work the liquid or other fluent material being discharged through an outlet orifice by pressure, e.g. from an outlet device in contact or almost in contact, with the work
- B05C5/0225—Apparatus in which liquid or other fluent material is projected, poured or allowed to flow on to the surface of the work the liquid or other fluent material being discharged through an outlet orifice by pressure, e.g. from an outlet device in contact or almost in contact, with the work characterised by flow controlling means, e.g. valves, located proximate the outlet
- B05C5/0237—Fluid actuated valves
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F02—COMBUSTION ENGINES; HOT-GAS OR COMBUSTION-PRODUCT ENGINE PLANTS
- F02M—SUPPLYING COMBUSTION ENGINES IN GENERAL WITH COMBUSTIBLE MIXTURES OR CONSTITUENTS THEREOF
- F02M51/00—Fuel-injection apparatus characterised by being operated electrically
- F02M51/06—Injectors peculiar thereto with means directly operating the valve needle
- F02M51/061—Injectors peculiar thereto with means directly operating the valve needle using electromagnetic operating means
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04B—POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS
- F04B17/00—Pumps characterised by combination with, or adaptation to, specific driving engines or motors
- F04B17/03—Pumps characterised by combination with, or adaptation to, specific driving engines or motors driven by electric motors
- F04B17/04—Pumps characterised by combination with, or adaptation to, specific driving engines or motors driven by electric motors using solenoids
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an apparatus and method for ejecting liquid material in the form of droplets, and more specifically, for example, an apparatus and method for causing a valve body to collide with a valve seat to separate the liquid material from the tip and fly and eject it in the form of droplets.
- Patent Document 1 there is a method in which the valve body is raised by air pressure and the valve body is lowered by the repulsive force of a spring.
- a piston attached to a valve body is slidably mounted in a drive chamber, and a spring (compression coil spring) is disposed above the piston, while an air chamber is formed below the piston. And connected to a compressed air source via a switching valve.
- a discharge chamber is provided at a lower portion of the drive chamber with a wall having a through hole through which the valve body is inserted, the valve body is provided movably, and a discharge port is provided on the lower surface of the discharge chamber. Further, the regulated liquid material is supplied to the discharge chamber from the storage container.
- the switching valve When the switching valve is operated to supply compressed air to the air chamber, the piston rises while the spring is contracted, and the discharge port closed by the valve element opens. Since the liquid material is in a state where pressure is applied, when the discharge port is opened, the liquid material is discharged out of the tip.
- the switching valve When the switching valve is released and the compressed air supplied to the air chamber is released into the atmosphere, the valve body descends due to the repulsive force of the contracted spring and comes into contact with the portion corresponding to the valve seat above the discharge port. Close the discharge port and stop quickly. As a result, the liquid material discharged from the tip of the discharge port is discharged as droplets.
- Patent Document 2 there is a method in which the valve body is raised by an electric solenoid and the valve body is lowered by (another) electric solenoid.
- an injection member is provided in a main container portion having a nozzle for discharging an adhesive, and two electric solenoids for driving the injection member are arranged on a concentric axis with the injection member above the main container.
- a flange portion is formed on the core rod of the second electric solenoid above the two electric solenoids, and a spring that constantly urges the ejection member toward the discharge prohibition position is engaged.
- the ejection member moves from the discharge prohibition position to the dischargeable position.
- the adhesive Since the adhesive is pressurized with compressed air, the adhesive is discharged from the nozzle, and an adhesive pool is formed at the tip of the nozzle. Then, when the second electric solenoid is operated, the biasing force of the spring is applied, the injection member moves from the dischargeable position to the discharge prohibition position, and the lower end portion of the injection member comes into contact with the bottom surface of the main container.
- the adhesive reservoir formed at the tip of the nozzle is jetted.
- the repulsive force of a spring gradually weakens in the process of extending from a contracted state to a natural state.
- this repulsive force becomes weak at the end of movement when the valve body (plunger rod) is lowered, and the force that the valve body closes the valve seat may become weak. there were.
- a sufficient force for the valve body to close the valve seat cannot be obtained in this method, and the liquid material is not separated from the tip of the discharge port and is not discharged.
- the present invention provides a droplet forming apparatus capable of giving a constant strong advance output to the valve body (plunger rod) without increasing the size of the apparatus, and that does not affect the backward operation time of the valve body. It aims to provide a method.
- the present invention comprises the following technical means.
- a liquid chamber that communicates with the nozzle and is supplied with a liquid material, a plunger rod whose tip moves forward and backward in the liquid chamber, a spring that applies a biasing force to the plunger rod, and a plunger rod that retreats.
- a droplet forming apparatus that includes a pressurizing chamber to which a pressurized gas to be actuated is supplied, a pressurizing source that supplies the pressurized gas to the pressurizing chamber, and a controller, A droplet forming apparatus having a magnetic field generating mechanism for applying an attractive force in the advancing direction when the rod approaches the most advanced position.
- the magnetic field generating mechanism includes a magnetic member provided on the plunger rod and a solenoid provided to face the magnetic member, and the controller In the advancing operation, the solenoid is energized to generate a magnetic field.
- the controller In the advancing operation, the solenoid is energized to generate a magnetic field.
- the controller In the second aspect, the controller energizes the solenoid during a time period including from the start of the plunger rod advance operation to the stop of the plunger rod advance operation.
- the solenoid has a recess that acts as a guide when the magnetic member enters.
- an adjustment mechanism for adjusting a fixed position of the magnetic member or the solenoid is provided, and the magnetic member and the solenoid contact each other, whereby the plunger rod It is characterized by defining the most advanced position.
- a sixth aspect of the invention includes the switching valve for controlling the flow rate of the pressurized gas flowing into the pressurizing chamber and the flow rate of the pressurized gas flowing out of the pressurizing chamber in any one of the first to fifth inventions. It is characterized by.
- a liquid chamber that communicates with the nozzle and is supplied with a liquid material, a plunger rod whose tip moves forward and backward in the liquid chamber, a spring that applies a biasing force to the plunger rod, and a plunger rod that retreats.
- a droplet forming apparatus that includes a pressurizing chamber to which an operating pressurized gas is supplied, a pressurizing source that supplies the pressurizing gas to the pressurizing chamber, and a controller, and that ejects droplets from the nozzles is used.
- a magnetic field generating mechanism that applies an attractive force in the advanced direction, and the plunger rod is retracted by flowing pressurized gas into the pressurized chamber.
- a suction force to act, a discharge step, the liquid droplet forming method characterized by having a city for discharging a liquid material in the liquid chamber.
- the magnetic field generating mechanism is composed of a magnetic member provided on the plunger rod and a solenoid provided opposite to the magnetic member.
- the controller In the discharge step, the controller However, when the plunger rod is advanced, the solenoid is energized to generate a magnetic field.
- a ninth invention is characterized in that, in the eighth invention, the controller energizes the solenoid during a time period including from the start of the plunger rod advance operation to the stop of the plunger rod advance operation.
- the solenoid has a concave portion that acts as a guide when the magnetic member enters, and the magnetic member enters the solenoid and guides in the discharging step.
- an adjustment mechanism for adjusting a fixed position of the magnetic member or the solenoid is provided, and the magnetic member and the solenoid are brought into contact with each other in the discharging step. The most advanced position of the plunger rod is defined.
- a switching valve for controlling a flow rate of the pressurized gas flowing into the pressurizing chamber and a flow rate of the pressurized gas flowing out of the pressurizing chamber, In the filling step, the switching valve is set to a first position for flowing pressurized gas into the pressurizing chamber, and in the discharging step, the switching valve is set to a second position for flowing pressurized gas from the pressurizing chamber. It is characterized by that.
- a strong advance output can be applied to the valve body (plunger rod) in a short time by using both the urging force of the spring and the propulsive force of the magnetic field generating mechanism. This makes it possible to precisely control droplets of the liquid material without increasing the size of the apparatus. Further, a high-viscosity liquid material that has conventionally been difficult to be ejected in droplets can be ejected in flight.
- the tact time can be shortened as much as the advancement time of the valve body is shortened.
- (a) represents the case where the position of the core member is adjusted
- (b) represents the case where the position of the solenoid is adjusted.
- (a) represents a signal to the switching valve
- (b) represents the position of the tip of the valve body.
- (a) shows the signal to the first solenoid
- (b) shows the signal to the second solenoid
- (c) shows the position of the tip of the valve body.
- FIG. 1 and 2 are schematic views of a droplet forming apparatus according to the present invention.
- FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating when the valve body is rising
- FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating when the valve body is descending.
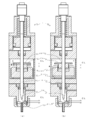
- a droplet forming apparatus 1 according to the present invention includes a main body 2 provided with a drive chamber for driving a valve body (plunger rod) 6 in the vertical direction, a plunger rod 6 disposed in the main body 2,
- the discharge unit 3 that discharges the liquid material 37 by the action of the driven plunger rod 6 is a main component.
- the drive chamber provided in the main body 2 includes a first drive chamber 4 for driving up and a second drive chamber 5 for driving down.
- the first drive chamber 4 is a space in which a piston 7 fixed to the plunger rod 6 is slidably arranged in the vertical direction.
- the first drive chamber 4 includes a spring chamber 9 and an air chamber 11 separated by the piston 7. Have.
- a spring chamber 9 is formed on the upper side of the piston 7 to accommodate a spring 8 for driving the plunger rod 6 downward. Air below the piston 7 is supplied with compressed air 10 for driving the plunger rod 6 upward.
- a chamber (pressurizing chamber) 11 is formed.
- the spring 8 is a compression coil spring.
- a stroke adjusting screw 12 for restricting the movement of the plunger rod 6 and adjusting a stroke, which is a moving distance, is provided on the upper portion of the spring chamber 9.
- the stroke of the plunger rod 6 is adjusted by turning the knob 13 exposed to the outside of the adjustment screw 12 and moving the tip 14 of the adjustment screw in the vertical direction to change the distance until the upper end of the plunger rod 6 collides. Do that.
- Compressed air 10 that flows into the air chamber 11 is allowed to flow from a compressed air source (pressurization source) 15 through an air inlet 17 of the first drive chamber 4 via a switching valve 16.
- the switching valve 16 includes an electromagnetic valve, a high-speed response valve, and the like, and is controlled to be opened and closed by a dispense controller 45 described later.
- a regulator 18 for adjusting pressure is provided between the compressed air source 15 and the switching valve 16.
- a seal member 19 is provided on the side surface of the piston 7, and a seal member 20 is provided at a portion where the plunger rod 6 below the air chamber 11 penetrates to prevent leakage of the compressed air 10 flowing into the air chamber 11.
- the second drive chamber 5 is a space in which the plunger rod 6 extends in the vertical direction.
- a solenoid 21 having a hole 28 through which the plunger rod 6 passes is fixed at the lower portion of the second drive chamber 5.
- the solenoid 21 is formed with a concave portion 23 on the upper surface so that the core member 22 made of a magnetic material can be fitted therein, and generates a magnetic field that acts on the plunger rod 6 in the advance direction in cooperation with the core member 22 It functions as a mechanism.
- the recess 23 serves as a guide for the core member 22 and the plunger rod 6 to reduce the blur of the central axis and to ensure that the plunger rod 6 contacts the valve seat 31 straightly.
- the plunger rod 6 is made of a nonmagnetic material.
- the core member 22 is a magnetic member made of, for example, cast steel or structural carbon steel that is attracted when the solenoid 21 is magnetized, and is attached to the plunger rod 6.
- the core member 22 has a flange-like portion 24 formed at the upper end.
- the tip 34 of the plunger rod comes into contact with the valve seat (valve seat) 31 first.
- the solenoid upper surface 25, the core member lower surface 26, and the solenoid recess bottom surface 27 do not contact each other. That is, there is a slight gap between the flange-like portion 24 and the solenoid upper surface 25.
- the flange-like portion 24 contacts the solenoid upper surface 25 and / or the core member lower surface 26 and the solenoid recessed portion bottom surface 27 contact each other, and serves to prevent the plunger rod 6 from descending beyond the set stroke. You may make it fulfill. In this form, discharge is performed in a state where the rod tip 34 does not contact the valve seat 31.
- the discharge part 3 has a liquid chamber 29 in which the plunger rod 6 can move up and down.
- a hole 30 through which the plunger rod 6 passes is provided in the upper part of the discharge part 3, and a valve seat 31 as a valve seat and a nozzle 32 for discharging the liquid material 37 are attached to a cylindrical lower part protruding downward.
- the valve seat 31 is provided with a communication hole 35 communicating with the liquid chamber 29 and the nozzle 32 through the center. Further, a mortar-shaped surface 33 is formed on the upper surface of the valve seat 31, and the liquid material 37 is discharged through the nozzles 32 by opening and closing the communication hole 35 by the rod tip 34 coming into contact with this surface.
- the valve seat 31 and the nozzle 32 are detachably fixed to the lower end of the liquid chamber 29 by a cap-shaped member 38, so that replacement is easy.
- the side surface of the liquid chamber 29 is provided with an introduction path 40 for receiving the supply of the liquid material 37 stored in the storage container 39, one end communicating with the liquid chamber 29, and the other end communicating with the communication channel 41.
- the storage container 39 receives supply of compressed gas from the compressed gas source 43, and the pressure can be adjusted by a dispense controller 45 described later.
- a seal member 44 is provided in a hole through which the plunger rod 6 passes above the liquid chamber 29 so that the liquid material 37 does not leak to the second drive chamber 5 side.
- the dispense controller 45 that manages and controls the switching valve 16 and solenoid 21 ON / OFF, the pressure of the compressed gas source 43, etc., and the above devices, signal lines (46, 47), gas pipes (48, 49). And is provided separately from the droplet forming apparatus 1.
- the configuration of the present invention described above can be easily realized by improving a conventional air spring type device.
- the present invention can be applied only by adding a magnetic field generating mechanism (solenoid) that gives a propulsive force to the plunger rod without changing a spring or the like. Therefore, improvement can be performed at low cost, and the apparatus does not become large.
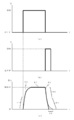
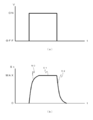
- FIG. 6 is a diagram showing the relationship between the operation timing of a conventional air spring system device (such as Patent Document 1) and the valve element tip position, and FIG. (B) represents the position of the tip of the valve body.
- a conventional air spring system device such as Patent Document 1
- FIG. (B) represents the position of the tip of the valve body.
- the conventional air spring type device when an operation start signal is transmitted to the switching valve (when turned ON), the valve is switched, compressed air flows into the air chamber, and the piston is lifted while compressing the spring. Accordingly, the plunger rod 6 opens the discharge port (reference numeral 50). Since the spring requires a greater force as it contracts, it has a curve in which the stroke change becomes gentle near the end of the backward movement operation as indicated by reference numeral 50.
- FIG. 7 is a diagram showing the relationship between the operation timing of the conventional droplet forming apparatus using a DC solenoid and the valve element tip position, and (a) is the first solenoid. (B) represents the signal to the second solenoid, and (c) represents the position of the tip of the valve body.
- the solenoid type device when an operation start signal is transmitted to the first solenoid (when turned ON), the solenoid is magnetized to move the core rod, and the injection member opens the nozzle accordingly (reference numeral 53).
- FIG. 3 is a diagram showing the operation timing of the droplet forming apparatus according to the present invention and the position of the tip of the valve body, where (a) is a signal to the switching valve, (b) is a signal to the solenoid, (c ) Represents the position of the tip of the valve body.
- the compressed air 10 flows into the air chamber 11 and the plunger rod 6 is moved backward. More specifically, when an operation start signal is transmitted to the switching valve 16 (when turned ON), the valve is switched and the compressed air 10 flows into the air chamber 11 and the piston 7 is lifted while compressing the spring 8.
- the plunger rod 6 opens the valve seat communication hole 35 and the nozzle 32 communicating therewith (reference numeral 56, see also FIG. 1). At this time, the power supply to the solenoid 21 is stopped, and no suction force (adsorption force) acts on the core member 22.
- the plunger rod 6 is advanced. More specifically, when the operation signal to the switching valve 16 is turned off (turned off) and the operation start signal is sent to the solenoid 21 (turned on), the valve is switched and the compressed air in the air chamber 11 is turned on. 10 starts to be released into the atmosphere, and the piston 7 starts to drop due to the repulsive force of the spring 8. Here, as the piston 7 descends, the force by the spring 8 becomes weaker. On the contrary, the suction force by the solenoid 21 becomes stronger. That is, the force that attracts the core member 22 attached to the plunger rod 6 by the magnetized solenoid 21 increases because the attracting force increases as the gap between the magnetic body and the magnet becomes smaller.
- the driving force can be applied from the beginning to the end of the movement without being attenuated. Then, the plunger rod 6 comes into contact with the valve seat 31 and closes the nozzle 32 (reference numeral 58, see also FIG. 2). In this way, by applying a stable driving force to the plunger rod 6 to close the communication hole 35, it is possible to precisely control the droplets of the liquid material 37 formed at the time of discharge.
- the above is the flow of a series of operations in one discharge according to the method of the present invention.
- the plunger rod 6 can be raised in a short time (reference numeral 59).
- a strong driving force can be obtained with a steep rise time due to the strong repulsive force of the spring 8 (reference numeral 60).
- the attractive force of the solenoid 21 becomes stronger, so that it is added to the force of the spring 8 and is stronger and faster than the force of the spring alone as shown in FIG.
- the liquid material is ejected (reference numerals 61 and 62).
- a strong force can be applied to the valve body in a short time by using the spring force and the solenoid force with good timing in the descending operation of the valve body to be carried.
- the piston 7 is lifted only by the force of the compressed air 10 without strengthening the spring itself, so that the valve body can be raised in a short time, leading to a reduction in tact time during continuous discharge.
- the present invention is suitable for continuous high-speed ejection (for example, 100 shots or more per second).
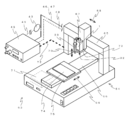
- the coating apparatus 63 can be configured by mounting the droplet forming apparatus 1 according to the present invention on the drive mechanism 64. An example is shown in FIG.
- the drive mechanism 64 includes an X drive mechanism 65 that can move in the direction of reference numeral 68, a Y drive mechanism 66 that can move in the direction of reference numeral 69, and a Z drive mechanism 67 that can move in the direction of reference numeral 70.
- a robot controller 71 for controlling the operation is provided inside the casing. The robot controller 71 is connected to the dispense controller 45 with a cable 72 and also transmits an operation signal to the dispense controller 45.
- a storage device that stores a coating program in which XYZ movement operation, discharge operation timing, and the like are routinely stored is included.
- the droplet forming apparatus 1 is supported by a holding unit 73 provided in the Z drive mechanism 67, and the Z drive mechanism 67 is provided on the X drive mechanism 65.
- the Y drive mechanism 66 is provided with a work table 75 on which the application object 74 is placed and fixed. Thereby, the nozzle 32 of the droplet forming apparatus 1 can be moved relative to the application object 74 in the XYZ directions (68, 69, 70). Since the droplet forming apparatus 1 is configured as shown in FIGS. 1 and 2, description thereof is omitted here.
- the droplet forming apparatus 1 is connected to a dispense controller 45 provided separately to manage and control the switching valve 16 and solenoid 21 ON / OFF, the pressure of the compressed gas source 43, and the like.
- a dispense controller 45 provided separately to manage and control the switching valve 16 and solenoid 21 ON / OFF, the pressure of the compressed gas source 43, and the like.
- the connection between the droplet forming apparatus 1 and the controller 45 is omitted from the broken lines 46, 47 (signal lines) and 48 (gas piping). Details of connection of signal lines, gas pipes and the like are as described with reference to FIGS.
- the switching valve 16 is connected to a compressed air source 15 (not shown) via a regulator 18.
- a basic operation procedure of the coating device 63 will be described.
- (1) the droplet forming apparatus 1 is installed and fixed to the holding unit 73 of the Z drive mechanism 67, and the wirings (46, 47) and the pipes (48, 49) are connected.
- (2) a coating program in which the XYZ movement operation, the discharge operation timing, and the like are routineized is created and stored in the robot controller 71.
- (3) the application object 74 is placed on the work table 75 and fixed.
- the stored application program is executed to perform application.
- the work content can be easily changed by changing the application program (2) according to the desired application form.
- the above is the basic operation flow of the droplet forming device 1 and the coating device 63.
- desired ejection can be performed at an accurate position. It is also possible to automate the work.
- a valve body (plunger rod) 6 is basically brought into contact with the valve seat 31 to form droplets, but a liquid material containing solid particles (for example, In the case of a solder paste, a phosphor paste, etc., the particles may be crushed by being brought into contact with each other, resulting in a problem that the quality of the material is impaired or the material is clogged with the nozzle.
- the droplet forming apparatus 1 according to the second embodiment shown in FIG. 5 is configured to perform discharge without bringing the valve body 6 into contact with the valve seat 31.
- the switching valve 16 and the storage container 39 are omitted.
- the valve body 6 is moved to the most advanced position by bringing the flange-like portion 24 of the core member 22 of the second drive chamber 5 and the upper surface 25 of the solenoid 21 into contact with each other.
- the valve seat 31 is not brought into contact.
- 5A shows a configuration for adjusting the position of the core member 22
- FIG. 5B shows a configuration for adjusting the position of the solenoid 21.
- the core member 22 is moved downward and fixed by the distance (reference symbol CL) between the rod tip 34 and the valve seat.
- the solenoid 21 is moved upward and fixed by the distance (reference symbol CL) between the rod tip 34 and the valve seat.
- the distance between the rod tip 34 and the valve seat is appropriately selected according to the conditions such as the liquid material to be used and the amount to be discharged at one time. For example, it may be obtained in advance by conducting an experiment or the like.
- the movement is performed in consideration of that amount.
- a mechanism for adjusting the solenoid 21 or the core member 22 a screw mechanism that can be used to know the distance moved from the rotation angle or a mechanism that inserts a spacer whose thickness is known in advance is used. Adjustments can be made.
- Coating device 64 Drive mechanism 65: X drive mechanism 66 Y drive mechanism 67: Z drive mechanism 68: X moving direction 69: Y moving direction 70: Z moving direction 71: robot controller 72: Cable 73: holder 74: object to be coated 75: worktable CL: Clearance
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Fluid Mechanics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Coating Apparatus (AREA)
- Application Of Or Painting With Fluid Materials (AREA)
- Nozzles (AREA)
Abstract
Description
第2の発明は、第1の発明において、前記磁界発生機構が、プランジャロッドに設けられた磁性部材と、磁性部材と対向して設けられたソレノイドとから構成され、前記コントローラが、プランジャロッドの進出動作時に、ソレノイドに通電し磁界を発生させることを特徴とする。
第3の発明は、第2の発明において、前記コントローラが、プランジャロッドの進出動作開始時からプランジャロッドの進出動作停止時までを含む時間帯に、ソレノイドへの通電を行うことを特徴とする。
第4の発明は、第2または3の発明において、前記ソレノイドが、前記磁性部材が進入することによりガイドとして作用する凹部を有することを特徴とする。
第5の発明は、第2ないし4のいずれかの発明において、前記磁性部材または前記ソレノイドの固定位置を調整する調整機構を備え、前記磁性部材と前記ソレノイドが当接することにより、前記プランジャロッドの最進出位置を規定することを特徴とする。
第6の発明は、第1ないし5のいずれかの発明において、前記加圧室に流入する加圧気体の流量および前記加圧室から流出する加圧気体の流量を制御する切換弁を備えることを特徴とする。
第8の発明は、第7の発明において、前記磁界発生機構が、プランジャロッドに設けられた磁性部材と、磁性部材と対向して設けられたソレノイドとから構成され、前記吐出工程において、前記コントローラが、プランジャロッドの進出動作時に、ソレノイドに通電し磁界を発生させることを特徴とする。
第9の発明は、第8の発明において、前記コントローラが、プランジャロッドの進出動作開始時からプランジャロッドの進出動作停止時までを含む時間帯に、ソレノイドへの通電を行うことを特徴とする。
第10の発明は、第8または9の発明において、前記ソレノイドが、前記磁性部材が進入することによりガイドとして作用する凹部を有し、前記吐出工程において、前記磁性部材が前記ソレノイドに進入しガイド作用を受けることを特徴とする。
第11の発明は、第8ないし10のいずれかの発明において、前記磁性部材または前記ソレノイドの固定位置を調整する調整機構を設け、前記吐出工程において、前記磁性部材と前記ソレノイドが当接することにより、前記プランジャロッドの最進出位置を規定することを特徴とする。
第12の発明は、第7ないし11のいずれかの発明において、前記加圧室に流入する加圧気体の流量および前記加圧室から流出する加圧気体の流量を制御する切換弁を設け、前記充填工程において、前記切換弁を加圧室に加圧気体を流入する第1の位置とし、前記吐出工程において、前記切換弁を加圧室から加圧気体を流出する第2の位置とすることを特徴とする。
第一に、スプリングによる付勢力と磁界発生機構の推進力を併用することで、弁体(プランジャロッド)に短時間で強い進出力を作用させることができる。これにより、装置を大型化させることなく、液体材料の滴を精密に制御することが可能となる。また、従来は滴状吐出が困難であった高粘度の液体材料についても飛翔吐出が可能となる。
図1および2に本発明に係る液滴形成装置の概略図を示す。図1は、弁体が上昇しているときを説明する図で、図2は、弁体が下降しているときを説明する図である。
本発明に係る液滴形成装置1は、弁体(プランジャロッド)6を上下方向に駆動させるための駆動室等が設けられた本体2と、本体2内に配設されたプランジャロッド6と、駆動されたプランジャロッド6の作用により液体材料37を吐出する吐出部3とを主要な構成要素とする。
第一駆動室4は、その内部にプランジャロッド6に固設されたピストン7が上下方向に摺動自在に配設された空間であり、ピストン7により分断されたバネ室9および空気室11を有する。ピストン7の上側にはプランジャロッド6を下降駆動させるためのスプリング8を収容するバネ室9が形成され、ピストン7の下側にはプランジャロッド6を上昇駆動させるための圧縮空気10を流入させる空気室(加圧室)11が形成されている。上記スプリング8には圧縮コイルばねを用いている。また、バネ室9上部にはプランジャロッド6の移動を規制し、移動距離であるストロークを調整するためのストローク調整ネジ12が設けられている。プランジャロッド6のストロークの調整は、調整ネジ12の外部に露出しているつまみ部13を回し、調整ネジの先端14を上下方向に移動させて、プランジャロッド6上端と衝突するまでの距離を変えることで行う。
別の実施形態として、ツバ状部24がソレノイド上面25と接触し、および/または、コア部材下面26とソレノイド凹部底面27が接触し、設定ストローク以上にプランジャロッド6が下降することを防ぐ役割を果たすようにしてもよい。この形態では、ロッド先端34がバルブシート31に当接しない状態で吐出が行われる。
次に、本発明に係る液滴形成装置の動作について、従来装置の動作と比較しながら説明する。まず、(1)、(2)で従来装置の動作について説明し、続いて(3)で本発明の動作を説明する。なお、以下で説明する各図において、横軸は時間(t)を表し、縦軸は、信号の場合は電圧(V)、弁体先端の場合は弁座からの位置(St)を表す。
図6は、従来のエア・スプリング方式装置(特許文献1など)の動作タイミングと弁体先端位置との関係を表した線図で、(a)は切換弁への信号、(b)は弁体先端の位置をそれぞれ表す。
従来のエア・スプリング方式の装置は、切換弁へ動作開始信号が送信されると(ONになると)、弁が切り換わって圧縮空気が空気室へ流入し、スプリングを圧縮しながら、ピストンを持ち上げ(後退させ)、それに伴いプランジャロッド6が吐出口を開放する(符号50)。スプリングは縮まるほど大きな力が必要となるため、符号50のように、後退動作終わり付近でストローク変化が緩やかになる曲線となっている。設定時間経過後(符号51)、切換弁への動作信号が切られると(OFFになると)、弁が切り換わって空気室内の圧縮空気を大気中へ放出し始め、スプリングの反発力によってピストンが下がり、そしてプランジャロッド6が吐出口を閉鎖する(符号52)。このように閉鎖することで液体材料が滴状になって吐出される。ピストン下降時(進出時)において、符号52のような曲線となっているのは、ピストンが下降し始めたときはスプリングの反発力が強く、下降速度も速いが、下降し終わる頃にはスプリングが伸びてきて反発力が弱く、下降速度も遅くなってきているためである。以上が、従来のエア・スプリング方式による一回の吐出における一連の動作の流れである。
なお、より強い付勢力を得るためにスプリングを強化した場合には、符号50の曲線はより緩やかなものとなる。
次いで、図7は、DCソレノイドを用いた従来の液滴形成装置の動作タイミングと弁体先端位置との関係を表した線図で、(a)は第一のソレノイドへの信号、(b)は第二のソレノイドへの信号、(c)は弁体先端の位置をそれぞれ表す。
従来のソレノイド方式の装置は、第一のソレノイドへ動作開始信号が送信されると(ONになると)、ソレノイドが磁化されて芯棒を移動させ、それに伴い噴射用部材がノズルを開放する(符号53)。設定時間経過後(符号54)、第一のソレノイドへの動作信号が切られ(OFFになり)、第二のソレノイドへ動作開始信号が送信されると(ONになると)、第二のソレノイドが芯棒を移動させ、そして噴射用部材がノズルを閉鎖する(符号55)。このように閉鎖することで液体材料(例えば、接着剤)が滴状になって吐出される。以上が、従来のソレノイド方式による一回の吐出における一連の動作の流れである。
上記二つの従来方式装置の説明を踏まえ、本発明に係る液滴形成装置の動作について説明する。図3は、本発明に係る液滴形成装置の動作タイミングと弁体先端の位置を示した線図であり、(a)は切換弁への信号、(b)はソレノイドへの信号、(c)は弁体先端の位置をそれぞれ表す。
まず、空気室11へ圧縮空気10を流入し、プランジャロッド6を後退させる。より詳細には、切換弁16へ動作開始信号が送信されると(ONになると)、弁が切り換わって圧縮空気10が空気室11へ流入し、スプリング8を圧縮しながら、ピストン7を持ち上げ、それに伴いプランジャロッド6がバルブシート連通孔35とそれに通ずるノズル32を開放する(符号56、併せて図1も参照)。この際、ソレノイド21への電力供給は停止されており、コア部材22に吸引力(吸着力)は作用していない。
また、弁体の上昇動作において、スプリング自体は強化することなく圧縮空気10の力のみでピストン7を持ち上げるので、短時間で弁体を上昇させることができ、連続吐出時のタクトタイム短縮につながる。本発明は、連続高速吐出(例えば1秒間に100ショット以上)に好適である。
本発明に係る液滴形成装置1を駆動機構64へと搭載して塗布装置63を構成することができる。図4にその一例を示す。
まず、準備として、(1)液滴形成装置1をZ駆動機構67の保持部73へ設置、固定し、配線(46、47)、配管(48、49)を接続する。加えて、(2)XYZ移動動作や吐出動作タイミングなどをルーチン化した塗布プログラムを作成し、ロボットコントローラ71に記憶させる。準備を終えたら、(3)塗布対象物74をワークテーブル75に載置し、固定する。そして、(4)記憶させた塗布プログラムを実行し、塗布を行う。ここで、続けて複数の塗布対象物74に塗布を行う場合は、上記(3)および(4)を繰り返せばよい。また、所望とする塗布形態に応じて(2)の塗布プログラムを変更することで、簡単に作業内容の変更を行うことができる。
Claims (12)
- ノズルと連通し、液体材料が供給される液室と、先端部が液室内を進退動するプランジャロッドと、プランジャロッドに付勢力を与えるスプリングと、プランジャロッドを後退させるよう作用する加圧気体が供給される加圧室と、加圧室に加圧気体を供給する加圧源と、コントローラと、を備え、ノズルから液滴を飛翔吐出する液滴形成装置において、
プランジャロッドが最進出位置に近づいた際に、進出方向への吸引力を作用させる磁界発生機構を有することを特徴とする液滴形成装置。 - 前記磁界発生機構が、プランジャロッドに設けられた磁性部材と、磁性部材と対向して設けられたソレノイドとから構成され、
前記コントローラが、プランジャロッドの進出動作時に、ソレノイドに通電し磁界を発生させることを特徴とする請求項1の液滴形成装置。 - 前記コントローラが、プランジャロッドの進出動作開始時からプランジャロッドの進出動作停止時までを含む時間帯に、ソレノイドへの通電を行うことを特徴とする請求項2の液滴形成装置。
- 前記ソレノイドが、前記磁性部材が進入することによりガイドとして作用する凹部を有することを特徴とする請求項2または3の液滴形成装置。
- 前記磁性部材または前記ソレノイドの固定位置を調整する調整機構を備え、前記磁性部材と前記ソレノイドが当接することにより、前記プランジャロッドの最進出位置を規定することを特徴とする請求項2ないし4のいずれかの液滴形成装置。
- 前記加圧室に流入する加圧気体の流量および前記加圧室から流出する加圧気体の流量を制御する切換弁を備えることを特徴とする請求項1ないし5のいずれかの液滴形成装置。
- ノズルと連通し、液体材料が供給される液室と、先端部が液室内を進退動するプランジャロッドと、プランジャロッドに付勢力を与えるスプリングと、プランジャロッドを後退させるよう作用する加圧気体が供給される加圧室と、加圧室に加圧気体を供給する加圧源と、コントローラと、を備え、ノズルから液滴を飛翔吐出する液滴形成装置を用いた液滴形成方法において、
プランジャロッドが最進出位置に近づいた際に、進出方向への吸引力を作用させる磁界発生機構を設け、
加圧気体を加圧室に流入させることによりプランジャロッドを後退させ、液室に液体材料を流入させる充填工程、
加圧室内の加圧液体を開放することによりプランジャロッドを進出させると共に、磁界発生機構によりプランジャロッドに進出方向への吸引力を作用させ、液室内の液体材料を吐出する吐出工程、とを有することを特徴とする液滴形成方法。 - 前記磁界発生機構が、プランジャロッドに設けられた磁性部材と、磁性部材と対向して設けられたソレノイドとから構成され、
前記吐出工程において、前記コントローラが、プランジャロッドの進出動作時に、ソレノイドに通電し磁界を発生させることを特徴とする請求項7の液滴形成方法。 - 前記コントローラが、プランジャロッドの進出動作開始時からプランジャロッドの進出動作停止時までを含む時間帯に、ソレノイドへの通電を行うことを特徴とする請求項8の液滴形成方法。
- 前記ソレノイドが、前記磁性部材が進入することによりガイドとして作用する凹部を有し、
前記吐出工程において、前記磁性部材が前記ソレノイドに進入しガイド作用を受けることを特徴とする請求項8または9の液滴形成方法。 - 前記磁性部材または前記ソレノイドの固定位置を調整する調整機構を設け、
前記吐出工程において、前記磁性部材と前記ソレノイドが当接することにより、前記プランジャロッドの最進出位置を規定することを特徴とする請求項8ないし10のいずれかの液滴形成方法。 - 前記加圧室に流入する加圧気体の流量および前記加圧室から流出する加圧気体の流量を制御する切換弁を設け、
前記充填工程において、前記切換弁を加圧室に加圧気体を流入する第1の位置とし、
前記吐出工程において、前記切換弁を加圧室から加圧気体を流出する第2の位置とすることを特徴とする請求項7ないし11のいずれかの液滴形成方法。
Priority Applications (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US14/374,726 US9821323B2 (en) | 2012-01-27 | 2013-01-25 | Droplet forming device and droplet forming method |
| EP13740917.3A EP2808093B1 (en) | 2012-01-27 | 2013-01-25 | Droplet forming device and droplet forming method |
| CN201380007028.1A CN104169008B (zh) | 2012-01-27 | 2013-01-25 | 液滴形成装置及液滴形成方法 |
| KR1020147023687A KR102003809B1 (ko) | 2012-01-27 | 2013-01-25 | 액적 형성 장치 및 액적 형성 방법 |
| HK15102242.5A HK1201781A1 (en) | 2012-01-27 | 2015-03-05 | Droplet forming device and droplet forming method |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012015736A JP5917925B2 (ja) | 2012-01-27 | 2012-01-27 | 液滴形成装置および液滴形成方法 |
| JP2012-015736 | 2012-01-27 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2013111855A1 true WO2013111855A1 (ja) | 2013-08-01 |
Family
ID=48873566
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2013/051587 WO2013111855A1 (ja) | 2012-01-27 | 2013-01-25 | 液滴形成装置および液滴形成方法 |
Country Status (8)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9821323B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP2808093B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5917925B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR102003809B1 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN104169008B (ja) |
| HK (1) | HK1201781A1 (ja) |
| TW (1) | TWI565528B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2013111855A1 (ja) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104324854A (zh) * | 2014-10-06 | 2015-02-04 | 温州碧戈之都鞋业有限公司 | 一种点胶鞋类机构 |
| WO2019181812A1 (ja) * | 2018-03-20 | 2019-09-26 | 武蔵エンジニアリング株式会社 | 液体材料吐出装置 |
Families Citing this family (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6452147B2 (ja) * | 2015-01-19 | 2019-01-16 | 武蔵エンジニアリング株式会社 | 液体材料吐出装置 |
| KR101588017B1 (ko) * | 2015-08-31 | 2016-01-25 | 이구환 | 고압력 분사용 디스펜서노즐 |
| JP6140864B2 (ja) * | 2016-04-07 | 2017-05-31 | 武蔵エンジニアリング株式会社 | 液滴形成装置および液滴形成方法 |
| JP5946597B1 (ja) * | 2016-04-20 | 2016-07-06 | 新倉工業株式会社 | 噴霧ノズル装置 |
| US10137471B2 (en) * | 2016-07-27 | 2018-11-27 | Newpark Mats & Integrated Services, LLC | Systems for reinforcing a multi-panel support mat |
| US9937514B2 (en) * | 2016-09-13 | 2018-04-10 | Nordson Corporation | Fluid applicator having a valve module with a floating member and the valve module |
| JP6778426B2 (ja) * | 2016-09-20 | 2020-11-04 | 武蔵エンジニアリング株式会社 | 液体材料吐出装置 |
| JP6772725B2 (ja) * | 2016-09-29 | 2020-10-21 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 流体吐出装置および流体を吐出する方法 |
| JP2018051478A (ja) * | 2016-09-29 | 2018-04-05 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 流体吐出装置および流体を吐出する方法 |
| WO2018117113A1 (ja) * | 2016-12-22 | 2018-06-28 | 武蔵エンジニアリング株式会社 | 液体吐出装置、同吐出装置を備える塗布装置およびその塗布方法 |
| CN206382185U (zh) * | 2017-01-13 | 2017-08-08 | 合肥鑫晟光电科技有限公司 | 一种用于点胶设备的滴胶装置 |
| JP7100373B2 (ja) * | 2017-05-31 | 2022-07-13 | 武蔵エンジニアリング株式会社 | 液体材料塗布方法および当該方法を実施するための装置 |
| DE102018222731A1 (de) * | 2018-12-21 | 2020-06-25 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Verfahren zum Betreiben einer Pumpe und System mit einer solchen Pumpe |
| JP6959385B2 (ja) * | 2020-03-26 | 2021-11-02 | アサヒビール株式会社 | 容器詰飲料の製造方法 |
| CN112431930A (zh) * | 2020-11-23 | 2021-03-02 | 石家庄禾柏生物技术股份有限公司 | 一种密封阀及包含该密封阀的出液结构 |
| CN115155979B (zh) * | 2022-09-07 | 2022-11-25 | 常州铭赛机器人科技股份有限公司 | 磁胶出胶精度高的螺杆阀及其出胶控制方法 |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS55137262U (ja) * | 1979-03-20 | 1980-09-30 | ||
| JPH1157594A (ja) * | 1997-08-19 | 1999-03-02 | Nordson Kk | 液状体の吐出塗布方法 |
| JP2003280015A (ja) * | 2002-02-27 | 2003-10-02 | Lg Phillips Lcd Co Ltd | 液晶滴下装置及び液晶滴下量の制御方法 |
| JP2004028312A (ja) * | 2002-06-28 | 2004-01-29 | Advance Denki Kogyo Kk | 手動閉じ機構を備えたエア操作弁 |
| JP3886211B2 (ja) | 1997-06-06 | 2007-02-28 | 松下電器産業株式会社 | 部品装着用接着剤塗布ヘッド、部品装着用接着剤塗布装置、及び部品装着用接着剤塗布方法 |
| JP4663894B2 (ja) | 2001-03-27 | 2011-04-06 | 武蔵エンジニアリング株式会社 | 液滴の形成方法および液滴定量吐出装置 |
Family Cites Families (22)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4978074A (en) * | 1989-06-21 | 1990-12-18 | General Motors Corporation | Solenoid actuated valve assembly |
| US5218999A (en) * | 1990-05-17 | 1993-06-15 | Mitsubishi Denki K.K. | Solenoid valve |
| US5405050A (en) | 1993-10-27 | 1995-04-11 | Nordson Corporation | Electric dispenser |
| CH689735A5 (de) * | 1994-05-09 | 1999-09-30 | Balzers Hochvakuum | Vakuumventil. |
| US5743960A (en) | 1996-07-26 | 1998-04-28 | Bio-Dot, Inc. | Precision metered solenoid valve dispenser |
| US5738728A (en) | 1996-07-26 | 1998-04-14 | Bio Dot, Inc. | Precision metered aerosol dispensing apparatus |
| US5916524A (en) | 1997-07-23 | 1999-06-29 | Bio-Dot, Inc. | Dispensing apparatus having improved dynamic range |
| US5741554A (en) | 1996-07-26 | 1998-04-21 | Bio Dot, Inc. | Method of dispensing a liquid reagent |
| CN1093782C (zh) * | 1996-07-26 | 2002-11-06 | 拜奥-多特公司 | 将液体分配到一种基材上的方法和装置 |
| USRE38281E1 (en) | 1996-07-26 | 2003-10-21 | Biodot, Inc. | Dispensing apparatus having improved dynamic range |
| US5765513A (en) * | 1996-11-12 | 1998-06-16 | Ford Global Technologies, Inc. | Electromechanically actuated valve |
| US6161722A (en) * | 1998-10-29 | 2000-12-19 | Nordson Corporation | Liquid dispensing device and methods utilizing a magnetically coupled valve stem |
| EP1099483B1 (en) * | 1999-11-11 | 2009-02-11 | Allegro Technologies Limited | Liquid droplet dispensing |
| US6874662B2 (en) * | 2002-03-21 | 2005-04-05 | Lg. Philips Lcd Co., Ltd. | Liquid crystal dispensing apparatus |
| EP2095885B1 (en) * | 2003-07-14 | 2017-08-02 | Nordson Corporation | Apparatus for dispensing discrete amounts of viscous material |
| JP2010022881A (ja) | 2007-03-30 | 2010-02-04 | Musashi Eng Co Ltd | 液材吐出装置および液材吐出方法 |
| KR101592443B1 (ko) * | 2007-05-18 | 2016-02-18 | 무사시 엔지니어링 가부시키가이샤 | 액체 재료 토출 방법 및 장치 |
| US20090107398A1 (en) * | 2007-10-31 | 2009-04-30 | Nordson Corporation | Fluid dispensers and methods for dispensing viscous fluids with improved edge definition |
| EP2182531B1 (en) * | 2008-10-29 | 2014-01-08 | Sauer-Danfoss ApS | Valve actuator |
| JP2010172795A (ja) * | 2009-01-27 | 2010-08-12 | Toyota Motor Corp | コーティング塗布治具及びコーティング塗布装置 |
| JP5780746B2 (ja) * | 2010-12-14 | 2015-09-16 | 芝浦メカトロニクス株式会社 | 塗布液の塗布装置 |
| JP2012135702A (ja) * | 2010-12-24 | 2012-07-19 | Shibaura Mechatronics Corp | 液滴塗布装置 |
-
2012
- 2012-01-27 JP JP2012015736A patent/JP5917925B2/ja active Active
-
2013
- 2013-01-24 TW TW102103059A patent/TWI565528B/zh active
- 2013-01-25 EP EP13740917.3A patent/EP2808093B1/en active Active
- 2013-01-25 KR KR1020147023687A patent/KR102003809B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2013-01-25 WO PCT/JP2013/051587 patent/WO2013111855A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2013-01-25 CN CN201380007028.1A patent/CN104169008B/zh active Active
- 2013-01-25 US US14/374,726 patent/US9821323B2/en active Active
-
2015
- 2015-03-05 HK HK15102242.5A patent/HK1201781A1/xx unknown
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS55137262U (ja) * | 1979-03-20 | 1980-09-30 | ||
| JP3886211B2 (ja) | 1997-06-06 | 2007-02-28 | 松下電器産業株式会社 | 部品装着用接着剤塗布ヘッド、部品装着用接着剤塗布装置、及び部品装着用接着剤塗布方法 |
| JPH1157594A (ja) * | 1997-08-19 | 1999-03-02 | Nordson Kk | 液状体の吐出塗布方法 |
| JP4663894B2 (ja) | 2001-03-27 | 2011-04-06 | 武蔵エンジニアリング株式会社 | 液滴の形成方法および液滴定量吐出装置 |
| JP2003280015A (ja) * | 2002-02-27 | 2003-10-02 | Lg Phillips Lcd Co Ltd | 液晶滴下装置及び液晶滴下量の制御方法 |
| JP2004028312A (ja) * | 2002-06-28 | 2004-01-29 | Advance Denki Kogyo Kk | 手動閉じ機構を備えたエア操作弁 |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104324854A (zh) * | 2014-10-06 | 2015-02-04 | 温州碧戈之都鞋业有限公司 | 一种点胶鞋类机构 |
| CN106334655A (zh) * | 2014-10-06 | 2017-01-18 | 陈卡丹 | 一种点胶鞋类机构的工作方法 |
| WO2019181812A1 (ja) * | 2018-03-20 | 2019-09-26 | 武蔵エンジニアリング株式会社 | 液体材料吐出装置 |
| JPWO2019181812A1 (ja) * | 2018-03-20 | 2021-05-13 | 武蔵エンジニアリング株式会社 | 液体材料吐出装置 |
| JP7161234B2 (ja) | 2018-03-20 | 2022-10-26 | 武蔵エンジニアリング株式会社 | 液体材料吐出装置 |
| US11833335B2 (en) | 2018-03-20 | 2023-12-05 | Musashi Engineering, Inc. | Liquid material ejecting apparatus |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2808093A4 (en) | 2016-05-18 |
| TW201338870A (zh) | 2013-10-01 |
| TWI565528B (zh) | 2017-01-11 |
| CN104169008B (zh) | 2016-12-14 |
| JP2013154277A (ja) | 2013-08-15 |
| HK1201781A1 (en) | 2015-09-11 |
| US20140346253A1 (en) | 2014-11-27 |
| US9821323B2 (en) | 2017-11-21 |
| EP2808093A1 (en) | 2014-12-03 |
| JP5917925B2 (ja) | 2016-05-18 |
| CN104169008A (zh) | 2014-11-26 |
| EP2808093B1 (en) | 2021-04-21 |
| KR102003809B1 (ko) | 2019-07-25 |
| KR20140122253A (ko) | 2014-10-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5917925B2 (ja) | 液滴形成装置および液滴形成方法 | |
| JP4663894B2 (ja) | 液滴の形成方法および液滴定量吐出装置 | |
| US9701143B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for discharging liquid material | |
| JP5986727B2 (ja) | 液体材料の吐出装置および方法 | |
| JP6285909B2 (ja) | 液体材料吐出装置、その塗布装置および塗布方法 | |
| JP6140864B2 (ja) | 液滴形成装置および液滴形成方法 | |
| JP2013017945A (ja) | 液滴吐出装置および方法 | |
| JP2013154277A5 (ja) | ||
| CN103230849B (zh) | 一种基于磁致伸缩执行器的开关流量控制型微滴喷射装置 | |
| JP6285510B2 (ja) | 液体材料の吐出装置および方法 | |
| CN216936815U (zh) | 一种电磁式喷射点胶阀 | |
| CN118179778A (zh) | 一种喷管撞击式高粘度流体按需喷射装置及方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 13740917 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 14374726 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2013740917 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20147023687 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |