WO2013046762A1 - 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、情報処理プログラム、及び記録媒体 - Google Patents
情報処理装置、情報処理方法、情報処理プログラム、及び記録媒体 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2013046762A1 WO2013046762A1 PCT/JP2012/058894 JP2012058894W WO2013046762A1 WO 2013046762 A1 WO2013046762 A1 WO 2013046762A1 JP 2012058894 W JP2012058894 W JP 2012058894W WO 2013046762 A1 WO2013046762 A1 WO 2013046762A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- product
- transaction
- target
- user
- information
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/01—Input arrangements or combined input and output arrangements for interaction between user and computer
- G06F3/048—Interaction techniques based on graphical user interfaces [GUI]
- G06F3/0481—Interaction techniques based on graphical user interfaces [GUI] based on specific properties of the displayed interaction object or a metaphor-based environment, e.g. interaction with desktop elements like windows or icons, or assisted by a cursor's changing behaviour or appearance
- G06F3/0482—Interaction with lists of selectable items, e.g. menus
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q30/00—Commerce
- G06Q30/06—Buying, selling or leasing transactions
- G06Q30/0601—Electronic shopping [e-shopping]
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a technical field of an information processing apparatus that performs processing related to deletion of a transaction object from a reference list that holds a reference to information related to the transaction object.
- Such a Web site there is a Web page on which information related to a transaction target is posted for each transaction target.
- a Web site may provide a function for a user to register an arbitrary transaction target in a reference list.
- the reference list is a list that holds references to information related to a transaction target such as a URL of information related to the transaction target.
- This reference list is called, for example, a favorite or a bookmark.
- the user registers, for example, an interest transaction object, a transaction object as a purchase candidate, a favorite transaction object, and the like in the reference list. Thereby, the information regarding the transaction object can be easily accessed from the reference list.
- the transaction target registered in the reference list may no longer be necessary for the user due to, for example, a change in the user's situation. Therefore, when the user sequentially registers transaction objects in the reference list, many transaction objects including the unnecessary transaction objects are registered in the reference list, and the reference list may be enlarged. Then, it may take time and effort for the user to search for a desired transaction target from the reference list and access information related to the transaction target. In order to prevent the enlargement of the reference list, it is necessary to organize the reference list. In this case, it is necessary for the user to search for unnecessary transaction objects from many transaction objects and delete them from the reference list. There is. This work may require labor.
- Patent Document 1 discloses a technique for collectively deleting URLs that the user has not accessed for a predetermined time among URLs registered in bookmarks.
- An object of the present invention is to provide an information processing apparatus, an information processing method, an information processing program, and a recording medium.
- the invention described in claim 1 is registered in a reference list that holds a reference to information on a transaction object when a predetermined operation related to selection of the transaction object is performed by a user. Based on the reference list information of the user stored in the storage means for storing the reference list information indicating the transaction target, related to the transaction target that is the target of the operation from among the transaction targets registered in the reference list Selecting means for selecting a transaction object to be deleted as a candidate for deletion from the reference list, and control means for presenting the deletion candidate selected by the selecting means.
- a transaction target related to a transaction target that is a target of a predetermined operation is presented, a highly probable transaction target that does not need to be registered in the reference list is presented as a deletion candidate. can do. Therefore, since it becomes easy to delete unnecessary transaction objects from the reference list, it is possible to support appropriately deleting transaction objects that do not need to be registered in the reference list from the reference list. Thereby, it is possible to prevent the reference list from being enlarged.
- the reference list from among the transaction objects searched in response to a request from the user as the reference list information Is stored in association with information indicating the transaction object registered in the search item and the search condition specified by the user for searching for the transaction object, and the selection means searches for the search object specified for the search.
- a transaction object that matches a transaction object whose condition is the object of the operation is selected as the deletion candidate.
- a transaction target that is searched under the same search condition as the search condition when a transaction target that is a predetermined operation target is searched and registered in the reference list is selected as a deletion candidate. Therefore, it is possible to present a transaction object having a high probability of not having to be registered in the reference list. That is, such a transaction object is highly likely to be a transaction object that has been compared as a purchase candidate together with a transaction object that is a target of a predetermined operation. When a predetermined operation is performed for any one of the plurality of transaction objects, there is a possibility that the comparison of purchase candidates is finished. Transaction objects that have been compared do not need to be registered in the reference list.
- the selection unit is configured to be in the same category as the transaction target that is the target of the operation among a plurality of transaction target categories.
- a transaction object to which the transaction belongs is selected as the deletion candidate.
- the present invention since a transaction object belonging to the same category as the transaction object that is the operation object is selected, it is possible to present a transaction object that has a high probability of not having to be registered in the reference list.
- the selection means is configured such that a stage in which the transaction target is used differs according to a transaction target attribute.
- a transaction target used in a stage prior to a stage in which the transaction target to be operated is used is selected as the deletion candidate.
- the transaction target used in the stage before the stage where the transaction target set as the target of the predetermined operation is used is selected, it is not necessary to register in the reference list.
- a transaction object with a high probability can be presented.
- the transaction object used in a stage prior to the stage where the transaction object is used is a transaction object that has already been used by the user, or a user is required. There is a probability that it is a transaction object that has been lost. Such trading objects do not need to be registered in the reference list.
- the storage means indicates a transaction object registered in the reference list as the reference list information.
- the information and the registration time of the transaction target in the reference list are stored in association with each other, and the selection unit is configured to register the registration time in the reference list at the same time as the transaction target of the operation.
- a certain transaction object is selected as the deletion candidate.
- a transaction target that is a target of a predetermined operation is registered in the reference list
- a transaction target registered at the same time as the registration time of the transaction target in the reference list is selected. Therefore, it is possible to present a transaction object having a high probability of not having to be registered in the reference list. That is, when a plurality of transaction objects are registered in the reference list at the same time, they may be registered as purchase candidates for comparison. When a predetermined operation is performed for any one of the plurality of transaction objects, there is a possibility that the comparison of purchase candidates is finished. Transaction objects that have been compared do not need to be registered in the reference list.
- the selecting unit is configured to display the transaction target information regarding the transaction target by the user, and the transaction target information. Based on the history stored in the history storage means that associates and stores information indicating the transaction target that has been viewed as the history, the browsing time of the transaction target information is the same as the transaction target that is the target of the operation. A transaction object that is a time is selected as the deletion candidate.
- the transaction target whose information is browsed at the same time as the browsing time of the information related to the transaction target that is a predetermined operation target is selected, it is not necessary to register in the reference list.
- a transaction object with a high probability can be presented. That is, when information on a plurality of transaction targets is browsed at the same time, the information may be browsed for comparison as a purchase candidate.
- a predetermined operation is performed for any one of the plurality of transaction objects, there is a possibility that the comparison of purchase candidates is finished.
- Transaction objects that have been compared do not need to be registered in the reference list.
- the selection means is determined to be a use time of a transaction target that is the target of the operation.
- a transaction object that is determined to be a use time in a season before the season is selected as the deletion candidate.
- the transaction target used in the season before the season in which the transaction target set as a predetermined operation target is used is selected, it is not necessary to register in the reference list.
- a transaction object with a high probability can be presented. That is, such a transaction object is highly likely to be less necessary for the user. Transaction objects that have become less necessary do not need to be registered in the reference list.
- the invention according to claim 8 is the information processing apparatus according to any one of claims 1 to 7, wherein the selection unit is a transaction target indicating relevance with the transaction target that is the target of the operation. For each attribute range determined in accordance with the attribute, among the transaction targets registered in the reference list, the transaction targets related to the transaction target that is the target of the operation from among the transaction targets included in the attribute range are It is selected as a deletion target, and the control unit presents the deletion target selected by the selection unit for each attribute range.
- deletion candidates are presented for each of the attribute ranges corresponding to the relevance with a transaction target that is a predetermined operation target. Accordingly, the user can select a range in which the number of deletion candidates is convenient for the user from among a plurality of attribute ranges as a range for determining whether or not to delete the deletion candidates. Therefore, it becomes easy to delete unnecessary transaction objects from the reference list.
- the invention according to claim 9 is an information processing method executed by the information processing apparatus, and holds a reference to information related to a transaction object when a user performs a predetermined operation related to selection of the transaction object. Based on the reference list information of the user stored in the storage means for storing the reference list information indicating the transaction object registered in the reference list, the operation object is selected from the transaction objects registered in the reference list. A selection step of selecting a transaction target related to the selected transaction target as a deletion candidate from the reference list, and a control step of presenting the deletion candidate selected in the selection step.
- the invention described in claim 10 is registered in a reference list that holds a reference to information related to a transaction object when a user performs a predetermined operation related to the selection of the transaction object. Based on the reference list information of the user stored in the storage means for storing the reference list information indicating the transaction target, the transaction target that is the target of the operation from among the transaction targets registered in the reference list It is made to function as a selection means for selecting a related transaction object as a deletion candidate from the reference list, and a control means for presenting the deletion candidate selected by the selection means.
- the invention described in claim 11 is registered in a reference list that holds a reference to information relating to a transaction object when a user performs a predetermined operation related to selection of the transaction object.
- the transaction target Based on the reference list information of the user stored in the storage means for storing the reference list information indicating the transaction target, the transaction target that is the target of the operation from among the transaction targets registered in the reference list
- An information processing program that functions as a selection unit that selects a related transaction object as a deletion candidate from the reference list and a control unit that presents the deletion candidate selected by the selection unit is recorded in a computer-readable manner. It is characterized by.
- a transaction target related to a transaction target that is a target of a predetermined operation is presented, a highly probable transaction target that does not need to be registered in the reference list is presented as a deletion candidate. can do. Therefore, since it becomes easy to delete unnecessary transaction objects from the reference list, it is possible to support appropriately deleting transaction objects that do not need to be registered in the reference list from the reference list. Thereby, it is possible to prevent the reference list from being enlarged.
- FIG. 1 It is a figure showing an example of outline composition of electronic commerce system S concerning one embodiment. It is a figure which shows the example of a screen display of a deletion candidate page. It is a block diagram which shows an example of schematic structure of the electronic commerce server 1 which concerns on one Embodiment.
- A is a figure which shows an example of the content registered into member information DB12a
- (b) is a figure which shows an example of the content registered into genre information DB12b
- (c) is store information DB12c.
- D is a figure which shows an example of the content registered into merchandise information DB12d
- (e) is an example of the content registered into browsing history DB12e.
- (F) is a figure which shows an example of the content registered into purchase history DB12f
- (g) is a figure which shows an example of the content registered into favorite information DB12g.
- the flowchart which shows the process example in the deletion candidate presentation control process of the system control part 14 of the electronic commerce server 1 in the case of making goods into which the goods page was browsed at the same time as the goods to be operated as goods related to the goods to be operated It is. It is a flowchart which shows the process example in the deletion candidate presentation control process of the system control part 14 of the electronic commerce server 1 in the case of making the goods registered into the favorite at the same time with the goods to be operated as the goods related to the goods to be operated. is there.
- (A) And (b) is a figure which shows the 1st example of the screen display of the deletion candidate page in a modification.
- A) And (b) is a figure which shows the 2nd example of the screen display of the deletion candidate page in a modification.
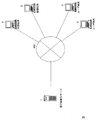
- FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating an example of a schematic configuration of an electronic commerce system S according to the present embodiment.
- the electronic commerce system S includes an electronic commerce server 1, a plurality of store terminals 2, and a plurality of user terminals 3.
- the electronic commerce server 1, each store terminal 2, and each user terminal 3 can transmit and receive data to and from each other using, for example, TCP / IP as a communication protocol via the network NW.
- the network NW is constructed by, for example, the Internet, a dedicated communication line (for example, a CATV (CommunityCommunAna Television) line), a mobile communication network (including a base station, etc.), a gateway, and the like.
- the electronic commerce server 1 (an example of an information processing apparatus in the present invention) is a server device that executes various processes related to an online shopping mall where an item can be purchased and an Internet auction.
- a user can purchase a desired product from a desired store by using the online shopping mall.
- the user can sell a product at an auction or bid for a product that is being sold.
- the electronic commerce server 1 transmits, for example, an online shopping mall or an auction Web page, or performs processing related to product search, purchase, exhibition, bidding, and the like. To do.
- the store terminal 2 is a terminal device used by an employee of a store opening a store in an online shopping mall.
- the store terminal 2 is used, for example, for registering information about products to be sold in an online shopping mall and confirming the order contents of products. Further, the store terminal 2 receives the Web page from the electronic commerce server 1 and displays it by accessing the electronic commerce server 1 based on an operation from an employee or the like.
- Software such as a browser and an e-mail client is incorporated in the store terminal 2.
- the user terminal 3 is a terminal device of a user who uses an online shopping mall or an auction.
- the user terminal 3 receives the Web page from the electronic commerce server 1 and displays it by accessing the electronic commerce server 1 based on an operation from the user.
- Software such as a browser and an e-mail client is incorporated in the user terminal 3.
- a favorite function is provided.
- the Favorites function by registering products sold on the online shopping mall as user favorites, it is possible to keep a reference to the product page in a user-specific list, and the user can easily access the product page of the favorite product. It is a function that enables browsing.
- the product page is a Web page on which detailed information regarding one product is displayed.
- a favorite product is also simply called a favorite.
- a hyperlink hereinafter referred to as “link”) displayed as “add to favorites” is displayed on the product page. When the user selects this link, the product whose information is displayed on the product page is registered in the user's favorites.
- the user can check the products registered in the favorites on the favorites page.
- the favorite page is a Web page on which a list of products registered in favorites is displayed, and is a dedicated Web page for each user.
- a link to a product page of a product registered as a favorite is embedded in the favorite page.
- the user selects a link of any product on the favorites page, the corresponding product page can be displayed.
- the user can designate a product that does not need to be registered from among the products registered in the favorites and delete it from the favorites.
- the electronic commerce server 1 provides support for deleting products that do not need to be registered from among products registered in favorites. Specifically, when a predetermined operation is performed on a product by a user in an online shopping mall or an auction, the electronic commerce server 1 selects a product related to the product targeted for the predetermined operation, Select as a candidate for deletion from favorites. Then, the electronic commerce server 1 causes the user terminal 3 to present the selected deletion candidate.
- the predetermined operation is referred to as “product selection related operation”.
- the product targeted for the product selection-related operation is referred to as “product targeted for operation” or “product targeted for operation”.
- the product selection related operation is a predetermined operation related to selection of a product. Specifically, the product selection related operation may be an operation performed after the user selects a product to be operated, or an operation accompanied by selection of a product by the user.
- the product selection related operations include, for example, an operation for registering a product as a favorite, an operation for deleting a product from the favorite, an operation for ordering (purchasing) a product, and an operation for listing the product in an auction.
- an operation for registering a product as a favorite an operation for deleting a product from the favorite
- an operation for ordering (purchasing) a product an operation for listing the product in an auction.
- the user may register products as favorites as candidates for purchase, for example.
- the product registered as a favorite is the product that is the operation target. Thereafter, it is assumed that the user registers a product related to this product as a favorite. In this case, for example, there is a probability that the purchase candidate is changed from a previously registered product to a later registered product. Accordingly, the previously registered product is a product that is no longer a purchase candidate. Products that are no longer candidates for purchase need not be registered in favorites.
- the operation of registering a product as a favorite is referred to as a “favorite registration operation”.
- a user may register a plurality of products as favorites in order to compare and consider them as candidates for purchase. Thereafter, it is assumed that the user deletes one of these products from the favorites.
- the product deleted from the favorites is the product that is the operation target.
- there is a possibility that it is not necessary to compare a plurality of products because the user has determined a product to be purchased from among the products that have been set as purchase candidates.
- Products that no longer need to be compared need not be registered in favorites.
- the operation for deleting a product from a favorite is referred to as a “favorite deletion operation”.
- Order operation A product related to the ordered product is presented as a deletion candidate regardless of whether or not the product for which the user has performed an ordering operation is registered in the user's favorites.
- the product exhibited here is the product that is the operation target. For example, there may be a case where a product that has become unnecessary due to the user purchasing another product is listed. In this case, there is a probability that the user does not need to purchase a product related to the exhibited product. Products that do not need to be purchased do not need to be registered in favorites. Note that the operation of listing a product is referred to as “exhibition operation”. Regardless of whether or not the product for which the user has performed an exhibition operation is registered in the user's favorites, products related to the exhibited product are presented as deletion candidates.
- the administrator of the electronic commerce system S may arbitrarily determine which of the illustrated operations is to be presented as a candidate for deletion from favorites.
- the electronic commerce server 1 may be configured so that the user can arbitrarily set which one of the illustrated operations is to be displayed as a candidate for deletion from favorites.
- the operation that is the product selection related operation is not limited to the above-described operation.
- products related to the operation target product for example, a product whose search condition matches the operation target product, a product whose genre matches the operation target product, and used before the operation target product.
- the reason why there is a probability that such a product does not need to be registered as a favorite when a product selection related operation is performed will be described.
- the user can specify a search condition in order to search for a product that is a purchase candidate in the online shopping mall.
- a search condition for example, a keyword, a product genre, and the like can be designated.
- the electronic commerce server 1 searches for products that satisfy the search condition.
- a search result page is displayed on the user terminal 3.
- the search result page is a Web page on which a list of searched products is displayed.
- the product page of the selected product is displayed.
- the product is registered as a favorite.
- a plurality of products searched under the same search condition are products that match the same keyword or products that belong to the same genre, and are therefore considered to have some relevance.
- a plurality of products searched under the same search condition are also products related to each other.
- the user compares a plurality of products as purchase candidates and determines a product to purchase. Therefore, when a product searched with the search conditions specified by the user is registered in favorites, deleted from favorites, purchased or listed, specified when searched for products registered in favorites. There is a possibility that a product whose search condition matches the search condition of the product to be operated is no longer a purchase candidate. For this reason, such a product does not need to be registered in a favorite, and therefore is a deletion candidate.
- the user may specify multiple search conditions. For example, a keyword and a genre are specified, or a plurality of keywords are specified. In this case, only products for which the product selection-related operation and all search conditions match may be presented as deletion candidates, or products for which at least one search condition matches are presented as deletion candidates. May be.
- the product genre is a range to which products of the same type, property, use, etc. belong, when the product is classified, for example, by type, property, use.
- the product genre is hierarchically defined with a tree structure. Specifically, each node of the tree structure corresponds to a genre.
- the depth of the node corresponds to the level (hierarchy) of the genre corresponding to the node.
- the depth of the node is a distance from a node located at the root (hereinafter referred to as “root node”). The larger the level value, the deeper the depth as the level, and the smaller the level value, the shallower the depth as the level.
- the genre corresponding to the child node of the root node is the level 1 genre.
- the genre of level 1 is the highest genre. For each level 1 genre, a genre corresponding to a child node is defined as a level 2 genre.
- the genre C2 corresponding to a child node of a certain genre C1 is referred to as a “child genre” of the genre C1.
- a child genre is also called a sub-genre.
- the genre C1 at this time is referred to as a “parent genre” of the genre C2.
- the child genre is a range to which similar products belong when the parent genre is further divided into a plurality of categories. Therefore, the child genre belongs to the parent genre.
- a genre corresponding to a descendant node for a certain genre is referred to as a “descendant genre”.
- the genre C3 is a child genre of the genre C2.
- the genres C2 and C3 are descendant genres of the genre C1.
- a genre corresponding to an ancestor node for a certain genre is referred to as an “ancestor genre”.
- Genres C1 and C2 are ancestor genres of genre C3.
- a plurality of products belonging to the same genre are products related to each other. Therefore, when a product is registered in favorites, deleted from favorites, purchased or listed, products that belong to the same genre as the product are likely to be products that do not need to be registered in favorites. is there.
- Each product basically has a genre defined at the lowest level (genre corresponding to a leaf node in a tree structure). That is, each product is divided into genres by the most detailed genre. Therefore, when the related products are determined based on whether the lowest genres into which the products are classified are the same, the range of the related products may be narrowed. In this case, for example, there may be a case where a product that is actually a comparison target as a purchase candidate by a user together with a product that has been previously operated is not presented as a deletion candidate. For example, it is assumed that there is a “seasonal home appliance” as a level 4 genre.
- fan and cold fan are child genres of “seasonal home appliances”, and “fan” and “cold fan” are the lowest genres.
- the product of the fan and the product of the cool fan are registered as favorites.
- the genre of each product is “fan” or “cold fan”, so among the products registered in favorites, the fan product is a candidate for deletion.
- the product of the cold air machine will not be presented.
- related products may be determined based on one or more genres at a higher level than the lowest genre in which the products are classified, that is, an ancestor genre. For example, in the above-described example, if it is determined whether or not the level 4 genre to which the operation target product belongs and the level 4 genre to which the product registered as a favorite belongs to the same genre, the fan product And refrigerator products belong to “seasonal home appliances”. Therefore, when a product selection-related operation is performed on a fan product, both the fan product and the cool fan product are presented as deletion candidates.
- the level of the genre for determining whether or not to belong to the same genre may be determined in advance for all genres, or may be determined according to the genre to which the operation target product belongs. Good.
- the electronic commerce server 1 is based on the number of products belonging to each genre from the level 1 genre to which the operation target product belongs to the lowest level genre among all the products sold in the online shopping mall. You may decide. Specifically, for example, the electronic commerce server 1 determines whether or not the genres at the level closest to the preset number among the genres from level 1 to the lowest level belong to the same genre. You may judge.
- the electronic commerce server 1 is based on the number of products belonging to each genre from the level 1 genre to which the operation target product belongs to the lowest level genre among all the products registered by the user as favorites. May be determined. Specifically, the electronic commerce server 1 is, for example, a genre at a level closest to a preset number of products registered in favorites among the genres from level 1 to the lowest level, and the same genre. It may be determined whether or not it belongs to.
- stages used in the process of things determined according to the genre May vary depending on product attributes. Examples of this process include a process in which the user grows (growth process), a process in which the user improves, learns, and advances things related to the product, and a process in which the story progresses.
- growth process a process in which the user grows
- the product used in the previous stage is a product that the user no longer needs or is already using. It is common to do. Products that the user does not need do not need to be registered in favorites.
- the product already used by the user is a product that does not need to be purchased, it is not necessary to register it as a favorite. Therefore, when a certain product is set as an operation target, a product used in a stage prior to the stage in which the product is used is determined as a deletion candidate assuming that the product is related to the operation target product.
- stage a is a stage before stage b.
- the product A is registered in a favorite as a purchase candidate, for example.
- the user registers the product B as a purchase candidate as a favorite, it is considered that the user intends to purchase the product used in stage b. Therefore, there is a probability that the product A used in the stage a is a product that does not need to be purchased by the user.
- the user when the user deletes the product B from the favorites, the user selects a product used in the stage b (including the case where the product is the product B) or a product used in a stage after the stage b. It is thought that it purchased.
- the product purchased by the user is a product that the user will use from now on. Accordingly, there is a possibility that the product A used in the stage before the stage where the product purchased by the user is used is a product that does not need to be purchased by the user. The same applies when the user purchases the product B.
- the product B when the user has exhibited the product B, there is a possibility that the product B is a product that is no longer necessary for the user because the user has entered a stage after the stage b. Therefore, there is a probability that the product A is a product that does not need to be purchased by the user.
- a specific example will be described below.
- a reference book for proficiency testing that measures a certain ability by score and a book such as a collection of questions may be issued depending on the target score.
- books for example, it is assumed that there are books for 600 points, 700 points, 800 points, and 900 points. In this case, a process of improving the user's ability is applied.
- the user starts to use a book for 800 points it is considered that the user has entered the stage of aiming for 800 points. In this case, there is a probability that the 600-point and 700-point books that are used in the previous stage are no longer needed by the user.
- Each shoe has its own size. This size corresponds to the length of the foot.
- a user growth process is applied. In the growth process of the user, the length of the user's foot increases, and the length of the foot generally does not decrease. Therefore, for example, when the user's foot length is 20 cm, the user needs a shoe to be worn when the user's foot length is less than 20 cm, that is, a shoe having a size of less than 20 cm. There is a probability that it will stop.
- Golf clubs may be sold according to their progress in golf. For example, it is assumed that there are golf clubs for beginners, intermediate players, and advanced players. In this case, the process of improving golf is applied. In the process of improving golf, the user is a beginner in the first stage. And if golf progresses, a user will become an intermediate person or an advanced person. Users who have become intermediate are not likely to return to beginners afterwards. Therefore, there is a probability that a user who has become an intermediate player does not need a golf club for beginners.
- Each group of books is given a volume number.
- the story progression process is applied.
- Such a book group is generally read sequentially from the first book in the course of the story. Therefore, when a user starts reading a book of a certain volume number, there is a probability that the user has already read a book of a volume number before that volume number. Therefore, since it is not necessary for the user to purchase these books, it is not necessary to register them as favorites.
- Products registered as favorites at the same time as the product to be operated the user may determine a plurality of products as purchase candidates and compare them. Conceivable. For this reason, products that are purchase candidates may be registered in a plurality of favorites at the same time. A plurality of products registered as favorites at the same time are products related to each other in that they are compared as purchase candidates. Therefore, when a certain product is deleted from the favorite or purchased, the product registered in the favorite at the same time as the product may be no longer a purchase candidate. Therefore, such a product does not need to be registered as a favorite.
- Seasonal products are products that are often used in specific seasons.
- the season here is not limited to, for example, one year divided by the characteristics of the weather, such as spring, summer, autumn, and winter.
- the period when things during the year are actively performed such as the examination season and the entrance season, is also included.
- the examination season and the entrance season is also included.
- seasonal products in that season are actively used, but seasonal products in the season before that season are not used much. In this respect, it is considered that there is a relationship between products that are used in different seasons.
- the product used in the season before the season in which the product is used may be less necessary for the user. . Products that are no longer necessary need not be registered in favorites.
- the season before a certain season may be, for example, a season immediately before a certain season or a season in a range from a certain season to six months ago.
- the administrator of the electronic commerce system S may arbitrarily determine which of the criteria described in (1) to (6) is used to select a related product.
- the administrator may arbitrarily determine which criterion is used to select a related product when any product selection-related operation is performed.
- the administrator may configure the electronic commerce server 1 so as to select related products by combining the above-mentioned criteria (1) to (6). For example, among the products of the same genre as the operation target product, a product registered as a favorite at the same time as the operation target product may be used as a related product.
- a product that was viewed at the same time as the product page of the product that was the operation target was viewed It may be a related product.
- the products related to the products to be operated are not limited to the products described in (1) to (6).
- a product that is the same as the operation target product and the same store as the seller may be used as a related product.
- an optional product when the product targeted for operation is the main product, and a main product when the product targeted for operation is the optional product may be used as related products.
- the optional items include consumables such as a replacement brush for the electric toothbrush that is the main product, and accessories such as a case that stores the mobile personal computer for the mobile personal computer that is the main product.
- Information indicating the relationship between the main product and the optional product may be stored in the storage unit 12, for example.
- the product code of the main product is posted on the product page of the optional product etc., that is, when the product code of the main product is included in the product information of the optional product etc.
- the product information Related products can be identified from
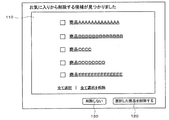
- FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a screen display example of a deletion candidate page.
- the screen of the user terminal 3 displays a deletion candidate page shown in FIG. Is displayed.
- the deletion candidate page is a Web page on which products selected as deletion candidates from favorites are presented.
- the deletion candidate page is a Web page for assisting deletion of a product that does not need to be registered as a favorite from among deletion candidates.
- a deletion candidate area 110 As shown in FIG. 2, a deletion candidate area 110, a deletion button 120, a non-deletion button 130, etc. are displayed on the deletion candidate page.
- a list of products that are candidates for deletion is displayed.
- product names of deletion candidates are displayed. This product name is a text link to a product page of a product that is a candidate for deletion. The user can confirm information on a product that is a deletion candidate by selecting a product name.
- a check box for selecting whether to delete the corresponding product from the favorite is displayed.
- a link for selecting or deselecting check boxes for all products is displayed.
- an image of a product that is a deletion candidate, a date of registration of the product that is a deletion candidate, and the like may be displayed.
- the delete button 120 When the user selects an unnecessary product from the deletion candidates and selects the delete button 120, the selected product is deleted from the user's favorites. On the other hand, when the user selects the non-delete button 130, the next Web page corresponding to the product selection related operation performed by the user is displayed without deleting the product from the favorites.
- the product selected as the deletion candidate may be presented to the user by a method other than the display of the Web page.
- the electronic commerce server 1 may be configured such that a pop-up window including display content similar to the display content shown in FIG.
- the electronic commerce server 1 may generate an e-mail having a list of products selected as candidates for deletion as a body, and transmit the generated e-mail to the user who performed the product selection-related operation.
- the user terminal 3 receives the electronic mail based on the user's operation and displays it on the screen.
- the name of a product that has become a deletion candidate is described for each line. The user replies to the received e-mail.
- the user displays a screen for creating a reply e-mail (hereinafter referred to as “reply mail”) so as to quote the text of the received e-mail.
- the user adds characters (for example, “delete”, “x”, etc.) indicating deletion to the line in which the product name of the product to be deleted from favorites is written in the body of the reply mail.
- a reply mail is transmitted from the user terminal 3 to the electronic commerce server 1.
- the electronic commerce server 1 deletes the item from the favorites based on the received reply mail text.
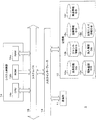
- FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing an example of a schematic configuration of the electronic commerce server 1 according to the present embodiment.
- the electronic commerce server 1 includes a communication unit 11, a storage unit 12, an input / output interface 13, and a system control unit 14.
- the system control unit 14 and the input / output interface 13 are connected via a system bus 15.
- the communication unit 11 is connected to the network NW and controls the communication state with the store terminal 2, the user terminal 3, and the like.
- the storage unit 12 (an example of a storage unit and a history storage unit in the present invention) is configured by, for example, a hard disk drive.
- databases such as a member information DB (database) 12a, a genre information DB 12b, a store information DB 12c, a product information DB 12d, a browsing history DB 12e, a purchase history DB 12f, and a favorite information DB 12g are constructed.
- FIG. 4A is a diagram showing an example of contents registered in the member information DB 12a.
- member information related to users who are registered as members in the electronic commerce system S is registered.
- user attributes such as user ID, password, nickname, name, date of birth, sex, postal code, address, telephone number, and e-mail address are registered in association with each user. Is done.
- the user ID is user identification information.
- FIG. 4B is a diagram showing an example of contents registered in the genre information DB 12b.
- Genre information relating to the genre of the product is registered in the genre information DB 12b.
- genre attributes such as a genre ID, a genre name, a genre level, a parent genre ID, a child genre ID list, and usage season information are registered in association with each genre.
- Genre information is set, for example, by an administrator of an online shopping mall.
- the genre ID is genre identification information defined by genre information.
- the parent genre ID is the genre ID of the parent genre of the genre defined by the genre information.
- the child genre ID list is a list of genre IDs of child genres of a genre defined by genre information.
- the child genre ID list is set when the genre defined by the genre information has a child genre.
- the use season information is information indicating a season in which products of a genre defined by genre information are determined to be actively used.
- the use season information is set when the product is a seasonal product.
- the genre information may be information indicating a season such as spring, summer, autumn, winter, or may be information indicating a start date to an end date of the season.
- FIG.4 (c) is a figure which shows an example of the content registered into store information DB12c.
- Store information related to stores that are open in the online shopping mall is registered in the store information DB 12c.
- store attributes such as store ID, store name, postal code, address, telephone number, e-mail address, and handling genre information are registered in the store information DB 12c in association with each store.
- the store ID is store identification information.
- the handling genre information is information indicating the genre of a product handled by the store (a product sold by the store).
- a genre ID is set for each genre of products handled by the store.
- FIG. 4D is a diagram showing an example of contents registered in the product information DB 12d.
- product information related to products sold in the online shopping mall is registered.
- product attributes such as product ID, store ID, product code, genre ID, product name, product image URL (Uniform Resource Locator), product description, product price, etc. are sold by the store.
- Each product to be registered is registered in association with each other.
- the product ID (an example of information indicating a transaction target in the present invention) is product identification information for managing a product sold by a store or the like.
- the store ID indicates the store from which the product is sold.
- the product code is a code number for identifying a product. Examples of the product code include a JAN (Japanese Article Number Code) code.
- the genre ID is the genre ID of the genre to which the product belongs.
- FIG. 4E is a diagram showing an example of contents registered in the browsing history DB 12e.
- the browsing history DB 12e browsing histories of product pages in the online shopping mall are registered.
- the product ID indicates the product for which the product page has been browsed.
- the browsing date and time (an example of browsing time in the present invention) indicates the date and time when the product page was browsed.
- the viewing date and time is the date and time when the electronic commerce server 1 transmits the product page to the user terminal 3.
- the user ID indicates a user who has viewed the product page.
- FIG. 4 (f) is a diagram showing an example of contents registered in the purchase history DB 12f.
- the purchase history of products by the user is registered. Specifically, an order code, a purchase date and time, a user ID, a product ID, a store ID, a product code, the number of purchases, and the like are registered in the purchase history DB 12f in association with each purchase of the product.
- the order code is order identification information given each time a product is ordered.
- the user ID indicates the purchased user.
- the product ID and the product code indicate the purchased product.
- the store ID indicates the store of purchase.
- the number of purchases is the number of products purchased.
- FIG. 4G is a diagram showing an example of contents registered in the favorite information DB 12g.
- favorite information related to user favorites an example of reference list information in the present invention
- a user ID indicates a user who has registered as a favorite.
- the product ID indicates a product registered as a favorite.
- the product ID is information corresponding to a reference to a product page of a product registered as a favorite.
- the actual reference information to the product page is a URL, but the URL of the product page can be specified from the product ID.
- the URL of the product page may be registered in the favorite information DB 12g together with the product ID or instead of the product ID.
- the registration date and time (an example of the registration time in the present invention) indicates the date and time when the registration to favorites was performed.
- the search condition is a condition designated by the user for searching for a product registered in a favorite.
- the storage unit 12 includes, for example, an order DB in which order contents in an online shopping mall are registered, an auction DB in which information on auctions is registered, information on products by product code (for example, official names of products, product names)
- An auction DB in which information on auctions is registered, information on products by product code (for example, official names of products, product names)
- a database such as a catalog DB in which genre IDs of genres, product specifications, etc.) are registered is also constructed.
- the storage unit 12 stores various types of data such as HTML (HyperText Markup Language) documents, XML (Extensible Markup Language) documents, image data, text data, and electronic documents for displaying Web pages.
- the storage unit 12 stores various setting values set by an administrator or the like.
- the storage unit 12 stores various programs such as an operating system, a WWW (World Wide Web) server program, a DBMS (Database Management System), and an electronic commerce management program.
- the electronic commerce management program is a program for executing various processes related to electronic commerce.
- the various programs may be acquired from other server devices or the like via the network NW, or may be recorded on a recording medium such as a DVD (Digital Versatile Disc) and read via the drive device. You may do it.
- the input / output interface 13 performs interface processing between the communication unit 11 and the storage unit 12 and the system control unit 14.
- the system control unit 14 includes a CPU 14a, a ROM (Read Only Memory) 14b, a RAM (Random Access Memory) 14c, and the like.
- the system control unit 14 functions as selection means and control means in the present invention by the CPU 14a reading and executing various programs.
- the electronic commerce server 1 may be composed of a plurality of server devices.
- a server device that performs processing related to favorites a server device that performs processing such as product search and ordering in an online shopping mall, a server device that performs processing related to auctions, and a server that transmits a Web page in response to a request from the user terminal 3
- a device, a server device that manages a database, and the like may be connected to each other via a LAN or the like.
- the system control unit 14 receives the user ID from the user terminal 3 at the time of login by the user, and stores the received user ID in the user terminal 3 as a cookie. Therefore, when the user is logged in, a cookie including the user ID is added to the request transmitted from the user terminal 3 to the electronic commerce server 1.
- the user ID included in the cookie added to the request received by the electronic commerce server 1 is referred to as “request user ID”.
- the user indicated by the requested user ID is referred to as “requested user”.
- the user designates a search condition for searching for a product on the Web page of the online shopping mall. Then, the user terminal 3 transmits a search request including the specified search condition to the electronic commerce server 1.
- the system control unit 14 holds the search condition included in the received search request in association with the requested user ID.
- the system control unit 14 searches for products that satisfy the search conditions included in the received search request. Specifically, when a keyword is set as the search condition, the system control unit 14 searches for a product including the keyword in at least one of the product name and the product description.
- the genre ID is set as the search condition, the system control unit 14 searches for products that belong to the genre corresponding to the genre ID.
- the system control unit 14 searches for products that satisfy the plurality of search conditions.
- the system control unit 14 When the system control unit 14 searches for a product, the system control unit 14 transmits a search result page on which a list of the searched products is displayed to the user terminal 3. When the user selects any product from the search result page displayed by the user terminal 3, the user terminal 3 transmits a request for the product page of the selected product to the electronic commerce server 1, and the electronic commerce server 1 The corresponding product page is transmitted to the user terminal 3.
- the user terminal 3 When the user selects a link displayed as “add to favorites” on the product page displayed by the user terminal 3, the user terminal 3 transmits a favorite registration request to the electronic commerce server 1.
- the favorite registration request is a message indicating a request to register a product whose information is displayed on the product page as a favorite.
- a product ID of a product to be registered as a favorite is set. This product ID is the product ID of the operation target product.
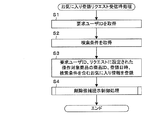
- FIG. 5 is a flowchart showing a processing example in the favorite registration request reception process of the system control unit 14 of the electronic commerce server 1 according to the present embodiment.
- the favorite registration request reception process is started when the electronic commerce server 1 receives a favorite registration request from the user terminal 3.
- the system control unit 14 acquires the requested user ID from the received favorite registration request (step S1). Next, the system control unit 14 acquires the search condition held in association with the requested user ID (step S2). Next, the system control unit 14 acquires the current date and time as the registration date and time. Then, the system control unit 14 registers the request user ID, the product ID of the operation target product set in the favorite registration request, the registration date and time, and the search condition in the favorite information DB 12g (step S3). Next, the system control unit 14 executes a deletion candidate presentation control process (step S4).
- deletion candidate presentation control process a product related to the operation target product is selected as a deletion candidate from the user's favorites, and a deletion candidate page on which the selected deletion candidate is displayed is transmitted to the user terminal 3. Details of the deletion candidate presentation control process will be described later.
- the system control unit 14 ends the favorite registration request reception process.
- the user performs an operation of listing a product. For example, the user sets the product name of the product to be exhibited, the description of the product, the genre of the product, and other information necessary for the listing, and selects and operates the button displayed as “Sell”. Then, the user terminal 3 transmits an exhibition request including the set information to the electronic commerce server 1.
- the system control unit 14 executes processing necessary for the exhibition. For example, the system control unit 14 registers information related to the auction in the auction DB and generates an auction page.
- the auction page is a Web page on which detailed information related to the auction of the exhibited product is displayed.
- the user can perform an operation of bidding a product on the auction page.
- the system control unit 14 specifies the exhibited product as the operation target product.
- the system control unit 14 specifies the product code of the exhibited product from the product name or genre of the exhibited product.
- the system control unit 14 executes a deletion candidate presentation control process.
- deletion candidate presentation control process will be described with reference to FIGS.
- the contents of the deletion candidate presentation control process differ depending on the criteria for selecting a product related to the operation target product. Therefore, below, it demonstrates for every reference
- the deletion candidate presentation control process described below is a process corresponding to operations (favorite registration operation, favorite deletion operation, order operation) that can specify the product ID of the operation target product. Therefore, supplementary description will be made as appropriate for the processing in the case where the exhibition operation is performed.
- FIG. 6 is a flowchart showing a processing example in the deletion candidate presentation control process of the system control unit 14 of the electronic commerce server 1 when a product whose search condition matches the product to be operated is a product related to the product to be operated. It is.
- the system control unit 14 searches the favorite information including the requested user ID from the favorite information DB 12g (step S11).
- the system control unit 14 includes, in the searched favorite information, whether there is favorite information including the request user ID and the product ID of the operation target product (hereinafter referred to as “favorite information of the operation target product”). It is determined whether or not (step S12). That is, the system control unit 14 determines whether the operation target product is registered in the request user's favorite. At this time, if the system control unit 14 determines that there is no favorite information of the operation target product (step S12: NO), the deletion candidate presentation control process is terminated. In this case, the deletion candidate page is not transmitted to the user terminal 3.
- the system control unit 14 acquires a search condition from the favorite information of the operation target product (step S13).
- the system control unit 14 initializes the deletion candidate list (step S14).
- the deletion candidate list is a list in which product IDs of products selected as deletion candidates are registered.
- the system control unit 14 selects one of the favorite information searched in step S11 (step S15).
- the system control unit 14 acquires the product ID included in the selected favorite information as the product ID of the candidate determination product that is the deletion candidate determination target (step S16).
- the system control unit 14 determines whether or not the product ID of the operation target product matches the product ID of the candidate determination product (step S17). At this time, if the system control unit 14 determines that they match (step S17: YES), the system control unit 14 proceeds to step S23.
- the candidate determination product is excluded from the deletion candidates. That is, the operation target product itself is excluded from deletion candidates. Note that when the product selection related operation is an order operation or an exhibition operation, the system control unit 14 may also include the operation target product itself as a deletion candidate.
- step S17 if the system control unit 14 determines that they do not match (step S17: NO), the system control unit 14 searches the purchase history DB 12f for a purchase history including the requested user ID and the product ID of the product to be operated (step S18). ). Next, the system control unit 14 determines whether there is a corresponding purchase history (step S19). That is, the system control unit 14 determines whether or not the requesting user has purchased the operation target product. At this time, if the system control unit 14 determines that there is a corresponding purchase history (step S19: YES), the system control unit 14 proceeds to step S23. That is, products that the user has purchased are excluded from deletion candidates.
- the system control unit 14 may also include products that the user has purchased as deletion candidates. Further, the system control unit 14 may determine whether or not to exclude a product that the user has purchased from deletion candidates based on the genre of the product.
- step S19: NO the system control unit 14 acquires a search condition from the favorite information of the selected candidate determination product.
- step S21 the system control unit 14 determines whether or not the search condition for the operation target product matches the search condition for the candidate determination product.
- step S21: NO the system control unit 14 proceeds to step S23. That is, the system control unit 14 excludes candidate determination products from deletion candidates.
- step S21 YES
- the system control unit 14 registers the product ID of the candidate determination product in the deletion candidate list (step S22). That is, the system control unit 14 selects the candidate determination product as a deletion candidate.
- the system control unit 14 proceeds to step S23.
- the system control unit 14 may set the candidate determination product as a deletion candidate when the search condition for the operation target product and the search condition for the candidate determination product all match, or select the candidate determination product when a part of the search condition matches. It may be a deletion candidate.
- step S23 the system control unit 14 determines whether there is favorite information not yet selected in the favorite information searched in step S11. At this time, if the system control unit 14 determines that there is favorite information that has not yet been selected (step S23: YES), the system control unit 14 selects one of the favorite information that has not yet been selected (step S24). Next, the system control unit 14 proceeds to step S16. The system control unit 14 selects deletion candidates from among the products registered in the requesting user's favorites as selection means by repeating the processing of steps S16 to S24.
- step S23: NO the control unit 14 determines that all favorite information has been selected.
- the control unit 14 determines that all favorite information has been selected (step S23: NO).
- step 25 the system control unit 14 acquires the product name of the deletion candidate product from the product information corresponding to the product ID registered in the deletion list.
- the system control unit 14 generates the URL of the product page of the product that is the candidate for deletion based on the product ID registered in the deletion list.
- the system control unit 14 generates an HTML document including a product name of a candidate product for deletion, a tag in which a URL of a product page is set, and the like.
- the system control unit 14 transmits the generated HTML document to the user terminal 3 that has transmitted the request. After completing this process, the system control unit 14 ends the deletion candidate presentation control process.
- the user terminal 3 displays a deletion candidate page as shown in FIG. 2, for example, based on the received HTML document. That is, the user terminal 3 presents deletion candidates to the user.
- the user selects a product to be deleted from favorites by operating a check box displayed in the deletion candidate area 110 of the deletion candidate page.
- the user terminal 3 transmits a favorite delete request including the product ID of the selected product to the electronic commerce server 1.
- the system control unit 14 deletes the favorite information including the requested user ID and the product ID of the operation target product from the favorite information DB 12g. At this time, the system control unit 14 does not execute the deletion candidate presentation control process.
- the user may order the product by displaying the product page from the search result page, instead of displaying the product page from the favorites and ordering the product.
- the operation target product may not be registered as a favorite.
- the search condition is specified by the user. Therefore, in step S12, the system control unit 14 searches for the search condition held in association with the requested user ID even if the operation target product is not registered in the favorites.
- the deletion candidate may be selected using the condition as a search condition for the operation target product.
- the system control unit 14 searches for a product whose operation code matches the product code among the products registered in the favorites. Then, the system control unit 14 executes the deletion candidate presentation control process using the product ID of the product whose product code matches the product to be operated as the product ID of the product to be operated.
- FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing a processing example in the deletion candidate presentation control process of the system control unit 14 of the electronic commerce server 1 when a product whose genre matches the product to be operated is a product related to the product to be operated. is there.
- the same steps as those in FIG. 6 are given the same step numbers.
- step S11 when the process of step S11 is completed, the system control unit 14 acquires the genre ID of the operation target product from the product information corresponding to the product ID of the operation target product (step S31). Next, the system control unit 14 proceeds to step S14.
- step S19 when it is determined that there is no corresponding purchase history (step S19: NO), the system control unit 14 acquires the genre ID of the candidate determined product from the product information corresponding to the product ID of the candidate determined product. (Step S32). Next, the system control unit 14 determines whether or not the genre ID of the operation target product matches the genre ID of the candidate determination product (step S33). That is, the system control unit 14 determines whether or not the operation target product and the candidate determination product are products belonging to the same genre. At this time, if the system control unit 14 determines that they do not match (step S33: NO), the system control unit 14 proceeds to step S23. On the other hand, when it judges with system control part 14 being in agreement (Step S33: YES), it registers goods ID of candidate judgment goods into a deletion candidate list (Step S22).
- the system control unit 14 may determine whether the genre ID of an ancestor of the genre indicated by the genre ID matches not the genre ID set in the product information. That is, the system control unit 14 determines whether or not the operation target product and the candidate determination product are products belonging to the same genre in a genre higher than the genre at the lowest level but in a genre higher than that genre. May be.
- the parent genre of the genre defined by the genre information can be specified by the parent genre ID included in the genre information registered in the genre information DB 12b. Therefore, the genre ID of the ancestor genre can be acquired from the genre information DB 12b using the parent genre ID as a clue.
- the system control unit 14 acquires a genre ID corresponding to the product code of the operation target product from the catalog DB in step S31.
- FIG. 8 is a processing example in the deletion candidate presentation control process of the system control unit 14 of the electronic commerce server 1 when the product used in the stage before the operation target product is a product related to the operation target product. It is a flowchart which shows. In FIG. 8, the same steps as those in FIG. 6 are given the same step numbers.
- the system control unit 14 acquires information indicating an attribute that can specify the stage at which the operation target product is used (step S41). For example, the system control unit 14 acquires the product name, product description, genre ID, and the like of the operation target product from the product information corresponding to the product ID of the operation target product. Next, the system control unit 14 specifies a process applied to the operation target product based on the information acquired from the product information. For example, when the operation target product is a shoe product, the system control unit 14 determines that the growth process of the user is applied. Further, for example, when the operation target product is a golf club product, the system control unit 14 determines that the process of improving the ability is applied. If the process to be applied cannot be specified, the system control unit 14 ends the deletion candidate presentation control process without selecting a deletion candidate.
- the system control unit 14 acquires information indicating the attribute of the product that can specify the stage in which the operation target product is used in the process. For example, in the case where the product to be operated is a book for an ability test that measures the ability with a score, the system control unit 14 indicates a score such as “600 points” or “700 points” from the product name or the product description. Get a string. For example, when the operation target product is a shoe product, genre classification may be performed based on the shoe size. Therefore, the system control unit 14 may acquire the shoe size based on the genre ID, or may acquire a character string indicating the shoe size from the product name or the product description.
- the system control unit 14 acquires a character string indicating a grade such as “Beginner” or “Intermediate” from the product name or the product description.
- the system control unit 14 acquires a character string indicating a volume number such as “Volume 1” or “Volume 2” from the product name or the product description. To do.
- the system control part 14 complete
- the system control unit 14 proceeds to step S14.
- step S19 when the system control unit 14 determines that there is no corresponding purchase history (step S19: NO), the system control unit 14 acquires information indicating an attribute that can specify the stage at which the candidate determination product is used (step S19). S42). This process is the same as the process of step S41 except that the product ID is different. The system control unit 14 cannot identify the process to be applied, the process applied to the operation target product is different from the process applied to the candidate determination product, or the product attribute If the information indicating “” cannot be acquired, the candidate determination product is excluded from the deletion candidates, and the process proceeds to step S23.
- the system control unit 14 determines whether or not the candidate determination product is used at a stage before the operation target product based on the information indicating the attribute of the product (step S43). For example, in the case of an ability test book that measures ability by score, the system control unit 14 determines that the candidate determination product is an operation target when the target score for the candidate determination product is lower than the target score for the operation target product. It is determined that the product is used at a stage before the product. In addition, for example, when the operation target product is a shoe, the system control unit 14 selects the candidate determination product as the operation target product when the size of the candidate determination product shoe is smaller than the size of the operation target product shoe. It is determined that it is used in an earlier stage.
- the system control unit 14 has a user ability class corresponding to the candidate determination product lower than a user ability class corresponding to the operation target product. In this case, it is determined that the candidate determination product is used at a stage prior to the operation target product. In addition, when the operation target product is a continuation book, the system control unit 14 determines that the candidate determination product is an operation target when the candidate determination product volume is smaller than the operation target product volume. It is determined that it is used at a stage before the product.
- step S43: NO If the system control unit 14 determines that the candidate determination product is not used in the stage before the operation target product (step S43: NO), the system control unit 14 proceeds to step S23. On the other hand, if the system control unit 14 determines that the candidate-determined product is used in a stage before the operation target product (step S43: YES), the product ID of the candidate-determined product is registered in the deletion candidate list. (Step S22).
- step S41 the system control unit 14 acquires the formal name, genre ID, specification, and the like of the product corresponding to the product code of the operation target product from the catalog DB. . And the system control part 14 acquires the information which shows the attribute which can specify the step in which the goods for operation are utilized based on the acquired information.
- FIG. 9 is a processing example in the deletion candidate presentation control process of the system control unit 14 of the electronic commerce server 1 when a product registered in the favorites at the same time as the operation target product is a product related to the operation target product. It is a flowchart which shows. In FIG. 9, the same steps as those in FIG. 6 are given the same step numbers.
- step S12 determines in step S12 that there is favorite information of the operation target product (step S12: YES)
- the system control unit 14 acquires the registration date and time from the favorite information of the operation target product. (Step S51).
- Step S14 the system control unit 14 proceeds to step S14.
- step S19 if the system control unit 14 determines that there is no corresponding purchase history (step S19: NO), the system control unit 14 acquires the registration date and time from the favorite information of the candidate determination product (step S52). Next, the system control unit 14 calculates the difference between the registration date / time of the operation target product and the registration date / time of the candidate determination product (step S53). Next, the system control unit 14 determines whether or not the absolute value of the calculated difference is equal to or less than a preset threshold value (step S54). That is, the system control unit 14 determines whether the candidate determination product is registered in the favorite at the same time as the operation target product is registered in the favorite.
- the range within the front and back threshold values from the registration date and time of the operation target product is a date and time determined to be the same period as the registration date and time of the operation target product.
- the administrator can arbitrarily set this threshold (for example, 1 hour, 1 day, 1 week, 1 month, etc.). If the system control unit 14 determines that the calculated absolute value of the difference is not equal to or less than the threshold (step S54: NO), the system control unit 14 proceeds to step S23. On the other hand, when the system control unit 14 determines that the absolute value of the calculated difference is equal to or smaller than the threshold (step S54: YES), the system control unit 14 registers the product ID of the candidate determination product in the deletion candidate list (step S22).
- FIG. 10 is a process in the deletion candidate presentation control process of the system control unit 14 of the electronic commerce server 1 in a case where a product whose product page is browsed at the same time as the product to be operated is a product related to the product to be operated. It is a flowchart which shows an example. In FIG. 10, the same steps as those in FIG. 6 are given the same step numbers.
- step S11 when the process of step S11 is completed, the system control unit 14 searches the browsing history DB 12e for a browsing history including the requested user ID and the product ID of the operation target product, and the searched browsing is performed.
- the browsing date and time is acquired from the history (step S61).
- step S14 the system control unit 14 proceeds to step S14.
- step S19 when the system control unit 14 determines that there is no corresponding purchase history (step S19: NO), the browsing history including the requested user ID and the product ID of the candidate determination product is read from the browsing history DB 12e. Search is performed, and the browsing date and time is acquired from the retrieved browsing history (step S62). Next, the system control unit 14 calculates the difference between the viewing date and time of the operation target product and the viewing date and time of the candidate determination product (step S63). Next, the system control unit 14 determines whether or not the calculated absolute value of the difference is equal to or less than a preset threshold value (step S64).
- the system control unit 14 determines whether or not the product page of the candidate determination product is browsed at the same time when the product page of the product to be operated is browsed.
- the range within the front and back thresholds from the browsing date of the product page of the operation target product is the date and time determined to be the same time as the browsing date of the product page of the operation target product.
- the administrator can arbitrarily set this threshold (for example, 1 hour, 1 day, 1 week, 1 month, etc.).
- step S64 YES
- the system control unit 14 registers the product ID of the candidate determination product in the deletion candidate list (step S22).
- FIG. 11 shows the deletion candidate presentation of the system control unit 14 of the electronic commerce server 1 when a product used in a season before the season in which the operation target product is used is a product related to the operation target product. It is a flowchart which shows the process example in a control process. In FIG. 11, the same steps as those in FIG. 6 are denoted by the same step numbers.
- step S71 the system control unit 14 determines whether or not the operation target product is a seasonal product. Specifically, the system control unit 14 acquires the genre ID from the product information corresponding to the product ID of the operation target product. Next, the system control unit 14 determines whether usage season information is set in the genre information corresponding to the acquired genre ID. At this time, if the use season information is not set in the genre information, the system control unit 14 determines that the operation target product is not a seasonal product (step S71: NO). In this case, the system control unit 14 ends the deletion candidate presentation control process.
- step S71 determines that the operation target product is a seasonal product. In this case, the system control unit 14 acquires the usage season information set in the genre information as the usage season information of the operation target product (step S72). Next, the system control unit 14 proceeds to step S14.
- step S19 when the system control unit 14 determines that there is no corresponding purchase history (step S19: NO), the system control unit 14 determines whether the candidate determination product is a seasonal product (step S73). This process is the same as the process of step S71 except that the product ID is different. At this time, if the system control unit 14 determines that the candidate determination product is not a seasonal product (step S73: NO), the system control unit 14 proceeds to step S23. On the other hand, if the system control unit 14 determines that the candidate-determined product is a seasonal product (step S73: YES), the system control unit 14 uses the use season information set in the genre information of the genre of the candidate-determined product as the candidate-determined product. Is acquired as use season information (step S74).
- the system control unit 14 determines whether the season in which the candidate determination product is used is a season before the season in which the operation target product is used based on the acquired use season information (Ste S75). At this time, when the system control unit 14 determines that the season in which the candidate determination product is used is not a season before the season in which the operation target product is used (step S75: NO), step S23 is performed. Migrate to On the other hand, when the system control unit 14 determines that the season in which the candidate determination product is used is a season before the season in which the operation target product is used (step S75: YES), the candidate determination product Is registered in the deletion candidate list (step S22).
- Favorites include, for example, products that the user is interested in, products that are candidates for purchase, products that the user likes, and the like. That is, the favorite can be considered to reflect the user's interest, demand, popularity, etc. for the product. And since products that are not interested in products that do not need to be registered in favorites are appropriately deleted, each user's favorites more accurately reflect the user's interests, demand, popularity, etc. It becomes. This means that your favorites are properly organized.
- the electronic commerce server 1 ranks each product based on the number of favorites registered. Specifically, the electronic commerce server 1 calculates the number of items registered in favorites for each product based on the favorite information registered in the favorite information DB 12g. Next, the electronic commerce server 1 ranks the products in the order of the largest number of registrations to favorites. Next, the electronic commerce server 1 generates a web page indicating the ranking of the number of favorite registrations.
- the electronic commerce server 1 may generate, for example, a Web page that shows rankings for all products, or a Web page that shows rankings for each genre. Then, in response to a request from the user terminal 3, the electronic commerce server 1 transmits a web page indicating the ranking.
- the ranking based on the number of sales may not accurately reflect the interest, demand, popularity, etc. of the user.
- the ranking based on the number of registrations to favorites since such factors are affected, the user's interest, demand, popularity, etc. can be accurately reflected.
- the electronic commerce server 1 predicts the demand for goods based on the number of favorites registered. Specifically, the electronic commerce server 1 calculates the number of items registered in favorites for the demand prediction target product based on the favorite information registered in the favorite information DB 12g. Next, the electronic commerce server 1 performs demand prediction that there is a demand for merchandise as the number of favorites registered increases. At this time, the electronic commerce server 1 may have a demand for one product for each registration to favorites.
- a product belonging to the same genre as the genre to which the demand prediction target product belongs is registered in a user's favorite.
- the genre of the product the magnitude of the demand for the product from the user who registers the product for which the demand is to be predicted as a favorite may be reduced. For example, it is common that only one product of a genre such as a refrigerator is purchased from one user at the same time. Therefore, when a plurality of items in the refrigerator are registered as favorites, it is registered for comparison as a purchase candidate, and it is estimated that one item is actually purchased.
- the online shopping mall server 1 calculates, for each user who has registered the demand prediction target product as a favorite, the number of registrations of the product of the genre to which the demand prediction target product belongs to the favorite, It is good also considering the demand with respect to the goods of this prediction object as 1 / the calculated number of registration.
- products of a genre such as clothes are products that may be purchased multiple times from one user at the same time. Therefore, for example, the online shopping mall server 1 receives a demand from each user who registers a demand prediction target product as a favorite regardless of the number of items registered in the genre to which the demand prediction target product belongs. May be set to 1, respectively.
- the electronic commerce server 1 may predict the size relationship of the demand between the plurality of products according to the size relationship of the number of registrations to favorites. .
- the electronic commerce server 1 performs a demand prediction such that “the product A is more demanded than the product B” when the number of registrations of the product A in the favorites is larger than the number of registrations of the product B in the favorites.
- the electronic commerce server 1 When the electronic commerce server 1 predicts demand, the electronic commerce server 1 transmits a Web page displaying the prediction result to the store terminal 2.
- the demand forecast based on the past number of sales cannot always predict the demand accurately. This is because, as described above, the number of sales is affected by factors such as the price of the product and the availability of the product. Moreover, it is because the past sales number has shown the consumption of the demand so far. In other words, if the number of past sales is large, most of the original demand may be consumed in the sales of the products so far. On the other hand, products that the user may purchase in the future are registered in the favorites. Therefore, it can be said that the favorite reflects the future demand more accurately than the past sales performance.
- the electronic commerce server 1 performs processing for recommending products sold in the online shopping mall to the user based on the number of registered favorites. This is because the user's interest in the product is reflected in the favorite. By properly organizing favorites, the proportion of products that do not need to be registered in favorites is reduced with respect to the entire favorites, so that appropriate recommendations can be made.
- the electronic commerce server 1 selects a product itself registered as a favorite as a recommended product, or selects a product related to the product registered as a favorite as a recommended product.
- a product related to the product registered as a favorite for example, a product whose genre is the same as the product registered as a favorite, or the product registered in the favorite and the store of the seller are the same.
- a recommended product for example, an e-mail recommending the selected product is transmitted to the user, or an advertisement for the recommended product is inserted into a web page of the online shopping mall, and the user terminal 3 to send.
- the system control unit 14 of the electronic commerce server 1 when the system control unit 14 of the electronic commerce server 1 performs a product selection-related operation by the user, the system control unit 14 selects a favorite based on the favorite information registered in the favorite information DB 12g. A product related to the product to be operated is selected from among the registered products as a candidate for deletion from favorites, and the selected deletion candidate is presented by the user terminal 3.
- the product attribute range indicating the relevance with the operation target product for determining whether or not the operation target product is related to the operation target is determined as one. It was done. Then, among the products registered in the favorites, a product within one defined range has been selected as a deletion candidate as a product related to the operation target product. However, a range of a plurality of attributes is determined according to the attribute of the product, and the electronic commerce server 1 selects a product related to the operation target product as a deletion candidate for each of the plurality of attribute ranges. The deletion candidates may be presented for each attribute range.
- a large number of products are included in the predetermined attribute range, a large number of products are presented to the user as deletion candidates. Then, since the user needs to find an unnecessary product from among a large number of deletion candidates, the operation of deleting the product from the favorites may be troublesome for the user.
- the user can select a range in which unnecessary products can be easily found. In addition, the user can select a range that the user thinks is related to the product that is the operation target from a plurality of attribute ranges.
- the attribute indicating relevance is the genre of the product.
- the range of products belonging to one level of the genre of the plurality of levels to which the operation target product belongs is set as the range of products related to the operation target product.
- a product that belongs to the same genre as the operation target product may be selected as a deletion candidate. That is, a product belonging to the same level 1 genre as the operation target product, a product belonging to the same level 2 genre as the operation target product, a product belonging to the same level 3 genre as the operation target product, and so on.
- the operation target is selected. Note that it is arbitrary from what level to what level the deletion candidate is selected.
- level 1 genre belongs to level 2 genre to which the operation target product belongs
- level 1 genre belongs to level 3 genre to which the operation target product belongs
- level 4 genre to which the operation target product belongs.
- Product 1 to product 10 belong
- product 1 to product 5 belong to the level 5 genre to which the operation target product belongs.
- 12 (a) and 12 (b) are diagrams showing a first example of screen display of the deletion candidate page in the modification. 12, elements similar to those in FIG. 2 are given the same reference numerals.
- the deletion candidate page shown in FIG. 12A is displayed on the user terminal 3.
- a deletion button 120, a non-deletion button 130, and the like are displayed on the deletion candidate page.
- the level name for example, “L1”, etc.
- the genre name for example, “AAAA”, etc.
- FIG. 2A level names and genre names from level 1 to level 5 are displayed.
- the number of extracted deletion candidates is displayed next to the level name. For example, in the level 3 genre, 30 deletion candidates are selected.
- a plus button 210 is displayed corresponding to each level name and genre name.
- a deletion candidate area 220 is displayed under the genre name corresponding to the selected plus button 210, as shown in FIG.
- the display contents of the deletion candidate area 220 are basically the same as the display contents of the deletion candidate area 110 shown in FIG.
- FIG. 12B a deletion candidate area 220 corresponding to the level 2 genre is displayed. Accordingly, in the deletion candidate area 220, the product names of the products 1 to 100 are displayed.
- the deletion candidate area 220 is displayed by selecting the plus button 210
- the selected plus button 210 changes to a minus button 230.
- the displayed deletion candidate area 220 is deleted from the screen. Then, the selected minus button 230 changes to a plus button 210. It is possible to display the deletion candidate area 220 for a plurality of levels.
- the user can display a list of deletion candidates for arbitrary levels of genres by selecting the plus button 210 or the minus button 230. Then, any product can be selected from the displayed deletion candidates and deleted from the favorites. For example, the user may select a genre at a level where the number of deletion candidates is such that it is easy to find unnecessary products, or a level that the user thinks that a product related to the operation target product belongs to The genre may be selected.
- FIG. 13A and FIG. 13B are diagrams showing a second example of the screen display of the deletion candidate page in the modified example.
- elements similar to those in FIG. 13 elements similar to those in FIG.
- the deletion candidate page shown in FIG. 13A is displayed on the user terminal 3.
- a deletion button 120, a non-deletion button 130, a deletion candidate area 310a, and the like are displayed on the deletion candidate page.
- products 1 to 200 are displayed as deletion candidates for the level 1 genre.
- the display contents of the deletion candidate area 310 are basically the same as the display contents of the deletion candidate area 110 shown in FIG.
- a plus button 320 is displayed.
- the deletion candidate area 310b to the deletion candidate area 310e are newly displayed in addition to the deletion candidate area 310a, as shown in FIG. 13B. Further, the plus button 320 is deleted from the screen, and the minus button 330 is displayed next to the deletion candidate area 310e.
- the deletion candidate area 310b products 1 to 100 are displayed as deletion candidates for the level 2 genre.
- the deletion candidate area 310c products 1 to 30 are displayed as deletion candidates for the level 3 genre.
- products 1 to 10 are displayed as deletion candidates for the level 4 genre.
- products 1 to 5 are displayed as deletion candidates for the level 5 genre.
- the display contents of the deletion candidate areas 310b to 310e are basically the same as the display contents of the deletion candidate area 110.
- the deletion candidate areas 310b to 310e are deleted from the screen, and the display state returns to that shown in FIG.
- the deletion candidate area 310b When the user selects the plus button 320 in the state shown in FIG. 13A, only the deletion candidate area 310b is newly displayed, and the plus button 320 and the minus button 330 are displayed next to the deletion candidate area 310b. You may make it do. Then, when the user selects the plus button 320 or the minus button 330, the deletion candidate area 310b may be deleted from the screen, or the deletion candidate area 310c may be newly displayed.
- the child genre to which the product that is the operation target among the child genres of the genre may be excluded from the selection range of deletion candidates.
- the products 101 to 200 are presented as deletion candidates corresponding to the level 1 genre.
- the products 31 to 100 are presented as deletion candidates corresponding to the level 2 genre.
- the products 11 to 30 are presented as deletion candidates corresponding to the level 3 genre.
- the products 6 to 10 are presented as deletion candidates corresponding to the level 4 genre.
- the products 1 to 5 are presented as deletion candidates corresponding to the level 5 genre.
- step S31 the system control unit 14 acquires the genre ID of the level 1 genre to which the operation target product belongs.
- step S32 the system control unit 14 acquires the genre ID of the level 1 genre to which the candidate determination product belongs.
- step S33 the system control unit 14 determines whether the genre ID of the level 1 genre of the operation target product matches the genre ID of the level 1 genre of the candidate determination product. If it is determined that they match (step S33: YES), the system control unit 14 registers the product ID of the candidate determination product in the deletion candidate list (step S22).
- step S23 If it is determined in step S23 that all the favorite information has been selected from the searched favorite information (step S23: NO), a product belonging to the same level 1 genre as the operation target product is set. Therefore, the system control unit 14 selects a product belonging to the same level 2 genre as the operation target product from among the products belonging to the same level 1 genre as the operation target product. In this way, the system control unit 14 selects a deletion target for each genre, for example, from a higher level genre to a lower level genre. In step S25, the system control unit 14 generates an HTML document of a deletion candidate page so that deletion candidates are displayed for each genre.
- the attributes of products for which deletion candidates can be selected for each of a plurality of ranges are not limited to genres.
- the present invention can be applied to favorites registration time, product page browsing time, and the like.
- the electronic commerce server 1 can make selections for each range, such as 1 hour before, after, 1 day before, 1 day before, 1 week before, 1 month before, etc. from the date and time of registration of the operation target product as a favorite. Further, the electronic commerce server 1 can make selections for each range, such as 1 hour before and after, 1 day before and after, 1 week before and after, 1 month before and after, etc. from the browsing date of the product page of the operation target product.
- the present invention can also be applied to a case where the stage in which the product is used differs depending on the attribute of the product.
- the electronic commerce server 1 has a range such as for beginners and intermediates, only for beginners, only for intermediates, etc., when the product to be operated is a golf club for advanced players. Selection can be made for each.
- the electronic commerce server 1 has the number of selected deletion candidates equal to or less than a preset threshold, and the number of deletion candidates.
- the deletion candidate may be presented only for the range closest to the threshold. For example, assume that the threshold is set to 20 in the above-described genre example. Then, the genre having the number of deletion candidates of 20 or less and closest to 20 is the level 4 genre. Therefore, products 1 to 10 are displayed as deletion candidates on the deletion candidate page.
- the user in the electronic commerce system S, can exhibit products for auction, and the display operation is a product selection related operation.
- the present invention may be applied not only to an auction listing but also to an operation in which a user starts selling a product as a product selection related operation.
- the user in the electronic commerce system S, the user may be able to sell new or used products.
- the transaction object in the present invention is applied to a product.
- the transaction target may be applied to the service.
- the present invention may be applied to a system capable of reserving a service as an electronic commerce system.
- service reservations include accommodation reservations for accommodation facilities, use reservations for competition facilities such as golf courses, and reservations for seats for transportation facilities.
- an operation for reserving a service is included in the predetermined operation in the present invention.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Finance (AREA)
- Accounting & Taxation (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Development Economics (AREA)
- Economics (AREA)
- Marketing (AREA)
- Strategic Management (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP12836773.7A EP2755181B1 (en) | 2011-09-30 | 2012-04-02 | Information processing device, information processing method, information processing program, and recording medium |
| CN201280047688.8A CN103843026B (zh) | 2011-09-30 | 2012-04-02 | 信息处理装置、信息处理方法 |
| US14/348,458 US9542077B2 (en) | 2011-09-30 | 2012-04-02 | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, information processing program, and recording medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011215973A JP5597613B2 (ja) | 2011-09-30 | 2011-09-30 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、情報処理プログラム、及び記録媒体 |
| JP2011-215973 | 2011-09-30 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2013046762A1 true WO2013046762A1 (ja) | 2013-04-04 |
Family
ID=47994832
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2012/058894 Ceased WO2013046762A1 (ja) | 2011-09-30 | 2012-04-02 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、情報処理プログラム、及び記録媒体 |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9542077B2 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP2755181B1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP5597613B2 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN103843026B (enExample) |
| TW (1) | TWI525566B (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2013046762A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3048576A4 (en) * | 2013-09-20 | 2017-01-25 | Sony Corporation | Information processing device |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5976216B2 (ja) * | 2013-06-28 | 2016-08-23 | 楽天株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及び情報処理プログラム |
| KR101629961B1 (ko) * | 2014-06-20 | 2016-06-13 | 네이버 주식회사 | 온라인 대화를 이용한 거래 방법 및 시스템 |
| CN105376286B (zh) * | 2014-08-29 | 2019-12-10 | 阿里巴巴集团控股有限公司 | 一种获取位置信息的方法及装置 |
| CN106294676B (zh) * | 2016-08-05 | 2017-05-31 | 张家口乐淘商贸有限公司 | 一种电子商务政务系统的数据检索方法 |
| JP6851894B2 (ja) * | 2017-04-24 | 2021-03-31 | 株式会社東芝 | 対話システム、対話方法及び対話プログラム |
| JP2020086675A (ja) * | 2018-11-19 | 2020-06-04 | Zホールディングス株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及び情報処理プログラム |
| JP7730408B1 (ja) * | 2024-12-13 | 2025-08-27 | 楽天グループ株式会社 | 管理装置、管理方法及びプログラム |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001209602A (ja) | 2000-01-27 | 2001-08-03 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Url処理装置、url登録方法、url削除方法および記録媒体 |
| JP2008146624A (ja) * | 2006-11-15 | 2008-06-26 | Sony Corp | コンテンツのフィルタリング方法、フィルタリング装置およびフィルタリングプログラム |
| US20080288492A1 (en) * | 2007-05-17 | 2008-11-20 | Microsoft Corporation | Assisted management of bookmarked web pages |
| JP2009217636A (ja) * | 2008-03-11 | 2009-09-24 | Fujitsu Ltd | 指定商品案内装置、指定商品案内方法、およびコンピュータプログラム |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6760746B1 (en) * | 1999-09-01 | 2004-07-06 | Eric Schneider | Method, product, and apparatus for processing a data request |
| JP4074428B2 (ja) * | 2000-12-28 | 2008-04-09 | 敏春 加藤 | 紹介方法、紹介システム |
| US7110968B2 (en) * | 2001-04-30 | 2006-09-19 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method for managing an electronic-commerce shopping cart |
| JP2006031655A (ja) * | 2004-07-16 | 2006-02-02 | Plusplus:Kk | インターネット商品販売システム、プログラム |
| US20060259867A1 (en) | 2005-05-13 | 2006-11-16 | Microsoft Corporation | System and method for automatic generation of browsing favorites |
| US8601374B2 (en) * | 2006-02-13 | 2013-12-03 | Google Inc. | Account administration for hosted services |
| US9594844B2 (en) * | 2007-11-08 | 2017-03-14 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Selectively deleting items that are not of interest to a user |
-
2011
- 2011-09-30 JP JP2011215973A patent/JP5597613B2/ja active Active
-
2012
- 2012-04-02 WO PCT/JP2012/058894 patent/WO2013046762A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2012-04-02 EP EP12836773.7A patent/EP2755181B1/en active Active
- 2012-04-02 CN CN201280047688.8A patent/CN103843026B/zh active Active
- 2012-04-02 US US14/348,458 patent/US9542077B2/en active Active
- 2012-09-28 TW TW101136033A patent/TWI525566B/zh active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001209602A (ja) | 2000-01-27 | 2001-08-03 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Url処理装置、url登録方法、url削除方法および記録媒体 |
| JP2008146624A (ja) * | 2006-11-15 | 2008-06-26 | Sony Corp | コンテンツのフィルタリング方法、フィルタリング装置およびフィルタリングプログラム |
| US20080288492A1 (en) * | 2007-05-17 | 2008-11-20 | Microsoft Corporation | Assisted management of bookmarked web pages |
| JP2009217636A (ja) * | 2008-03-11 | 2009-09-24 | Fujitsu Ltd | 指定商品案内装置、指定商品案内方法、およびコンピュータプログラム |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3048576A4 (en) * | 2013-09-20 | 2017-01-25 | Sony Corporation | Information processing device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2755181A4 (en) | 2015-05-06 |
| TW201331869A (zh) | 2013-08-01 |
| US20140237374A1 (en) | 2014-08-21 |
| EP2755181B1 (en) | 2023-09-13 |
| TWI525566B (zh) | 2016-03-11 |
| CN103843026A (zh) | 2014-06-04 |
| CN103843026B (zh) | 2017-09-08 |
| JP2013077107A (ja) | 2013-04-25 |
| JP5597613B2 (ja) | 2014-10-01 |
| EP2755181A1 (en) | 2014-07-16 |
| US9542077B2 (en) | 2017-01-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5597613B2 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、情報処理プログラム、及び記録媒体 | |
| JP4951404B2 (ja) | 商品レコメンド・システム | |
| JP5124680B1 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、情報処理プログラム及び記録媒体 | |
| US10776445B2 (en) | Apparatus and a method for reference list prioritization | |
| JP5686934B1 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、プログラム、記憶媒体 | |
| US20110106594A1 (en) | Expandable product feature and relation comparison system | |
| JP2010044584A (ja) | 商品広告配信装置、商品広告配信方法、及び商品広告配信制御プログラム | |
| WO2013145454A1 (ja) | 情報提供装置、情報提供方法、情報提供プログラム、及びそのプログラムを記憶するコンピュータ読取可能な記録媒体 | |
| JP5506104B2 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、及び情報処理プログラム | |
| JP6069599B1 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、プログラム | |
| JP5794881B2 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、及び情報処理プログラム | |
| WO2017203631A1 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、及び情報処理プログラム | |
| JP6896557B2 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、及び情報処理プログラム | |
| JP5275531B1 (ja) | 情報提供装置、情報提供方法、情報提供プログラム、及びそのプログラムを記憶するコンピュータ読取可能な記録媒体 | |
| JP6053093B1 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、プログラム | |
| JP2020087270A (ja) | 広告配信装置、制御方法及びプログラム | |
| WO2017090093A1 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、及び情報処理プログラム |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 12836773 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 14348458 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2012836773 Country of ref document: EP |