JP7121908B2 - 電源システム - Google Patents
電源システム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7121908B2 JP7121908B2 JP2018222765A JP2018222765A JP7121908B2 JP 7121908 B2 JP7121908 B2 JP 7121908B2 JP 2018222765 A JP2018222765 A JP 2018222765A JP 2018222765 A JP2018222765 A JP 2018222765A JP 7121908 B2 JP7121908 B2 JP 7121908B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- sweep
- module
- battery module
- battery
- string
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M3/00—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output
- H02M3/02—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC
- H02M3/04—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC by static converters
- H02M3/10—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode
- H02M3/145—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal
- H02M3/155—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only
- H02M3/156—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators
- H02M3/158—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators including plural semiconductor devices as final control devices for a single load
- H02M3/1584—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators including plural semiconductor devices as final control devices for a single load with a plurality of power processing stages connected in parallel
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02J—CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS OR SYSTEMS FOR SUPPLYING OR DISTRIBUTING ELECTRIC POWER; SYSTEMS FOR STORING ELECTRIC ENERGY
- H02J1/00—Circuit arrangements for DC mains or DC distribution networks
- H02J1/10—Parallel operation of DC sources
- H02J1/102—Parallel operation of DC sources being switching converters
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02J—CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS OR SYSTEMS FOR SUPPLYING OR DISTRIBUTING ELECTRIC POWER; SYSTEMS FOR STORING ELECTRIC ENERGY
- H02J7/00—Circuit arrangements for charging or depolarising batteries or for supplying loads from batteries
- H02J7/02—Circuit arrangements for charging or depolarising batteries or for supplying loads from batteries for charging batteries from AC mains by converters
- H02J7/04—Regulation of charging current or voltage
- H02J7/06—Regulation of charging current or voltage using discharge tubes or semiconductor devices
-
- H02J7/56—
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M3/00—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output
- H02M3/02—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC
- H02M3/04—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC by static converters
- H02M3/10—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode
- H02M3/145—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal
- H02M3/155—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only
- H02M3/156—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators
- H02M3/158—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators including plural semiconductor devices as final control devices for a single load
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M1/00—Details of apparatus for conversion
- H02M1/0067—Converter structures employing plural converter units, other than for parallel operation of the units on a single load
- H02M1/0077—Plural converter units whose outputs are connected in series
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M3/00—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output
- H02M3/02—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC
- H02M3/04—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC by static converters
- H02M3/10—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode
- H02M3/145—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal
- H02M3/155—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only
- H02M3/156—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators
- H02M3/158—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators including plural semiconductor devices as final control devices for a single load
- H02M3/1584—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators including plural semiconductor devices as final control devices for a single load with a plurality of power processing stages connected in parallel
- H02M3/1586—Conversion of DC power input into DC power output without intermediate conversion into AC by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators including plural semiconductor devices as final control devices for a single load with a plurality of power processing stages connected in parallel switched with a phase shift, i.e. interleaved
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T10/00—Road transport of goods or passengers
- Y02T10/60—Other road transportation technologies with climate change mitigation effect
- Y02T10/70—Energy storage systems for electromobility, e.g. batteries
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Charge And Discharge Circuits For Batteries Or The Like (AREA)
- Secondary Cells (AREA)
Description
図1を参照して、本実施形態における電源システム1の全体構成について概略的に説明する。電源システム1は、上位の電力系統8に接続された配電装置5に対する電力の出力、および、配電装置5から入力される電力の蓄電の少なくともいずれか(以下、単に「電力の入出力」という場合もある)を行う。一例として、本実施形態では、配電装置5としてPCS(Power Conditioning Subsystem)が用いられている。PCSは、電力系統8から電源システム1等へ入力される電力および電源システム1等から電力系統8へ出力される電力を、電源システム1等と電力系統8との間で相互に変換する機能を有する。
図2を参照して、スイープモジュール20について詳細に説明する。スイープモジュール20は、電池モジュール30、電力回路モジュール40、およびスイープユニット(SU(Sweep Unit))50を備える。
ストリング10において実行されるスイープ制御について説明する。ここで、スイープ制御は、ストリング10の各電池モジュール30にスイープ動作をさせるための制御である。ストリング10において実行されるスイープ制御では、SCU11は、パルス状のゲート信号GSを出力する。また、ストリング10の複数のスイープモジュール20におけるスイッチング素子41,42は、適宜にオンとオフが切り替えられて駆動する。その結果、電池モジュール30のメインライン7に対する接続と、メインライン7からの切り離しが、スイープモジュール20毎に高速で切り替えられる。さらに、ストリング10は、上流側からX番目のスイープモジュール20に入力するゲート信号GSを、(X-1)番目のスイープモジュール20に入力するゲート信号GSに対して遅延させることができる。その結果、ストリング10に含まれるM個のスイープモジュール20のうち、メインライン7に接続されるm個(m<M)のスイープモジュール20が、順次切り替えられる。これにより、ストリング10に含まれた複数の電池モジュール30が、メインライン7に所定の順番で接続され、かつ、所定の順番で切り離される。そして、予め定められた数の電池モジュール30がメインライン7に常時接続されたような状態になる。かかるスイープ動作によって、ストリング10は、予め定められた数の電池モジュール30が直列に接続された1つの組電池として機能する。
図4を参照して、一部のスイープモジュール20に強制スルー動作を実行させ、他のスイープモジュール20にスイープ動作を実行させる場合の制御について説明する。前述したように、強制スルー動作の実行を指示されたスイープモジュール20は、電池モジュール30をメインライン7から切断した状態を維持する。図4に示す例では、No.2のスイープモジュール20に強制スルー動作を実行させる点が、図3に示す例とは異なる。つまり、図4に示す例では、1つのストリング10に含まれる5個のスイープモジュール20のうち、スイープ動作を実行させるスイープモジュール20の数(つまり、メインライン7への接続対象とするスイープモジュール20の数)Pが4個となっている。VH指令値、各々の電池モジュール30の電圧Vmod、および遅延時間DLは、図3に示す例と同じである。図4に示す例では、ゲート信号GSの周期Tは、「2.4μsec×4=9.6μsec」となる。ゲート信号GSのデューティー比は、約0.58となる。
図1を参照して、ストリング10および電源システム1の全体構成について詳細に説明する。前述したように、ストリング10は、SCU11と、メインライン7に電力回路モジュール40を介して直列に接続された複数のスイープモジュール20を備えている。さらに、ストリング10のメインライン7は、配電装置5から延びるバスライン9に接続されている。ストリング10は、メインライン7における配電装置5側(上流側)から順に、バスライン電圧検出部21、システム遮断器(システム遮断器は、適宜に、「SMR(System Main Relay)」と称される。)22、ストリングコンデンサ23、ストリング電流検出部24、ストリングリアクトル25、およびストリング電圧検出部26を備える。なお、一部の部材の配置を変更することも可能である。例えば、システム遮断器22は、ストリングコンデンサ23よりも下流側に設けられていてもよい。
図5を参照して、各々の電池モジュール30で発生するリンギングについて説明する。
図5は、スイープ制御を実行した場合の、ストリング10の電圧、ストリング10の電流、および、ストリング10に含まれる1つの電池モジュール30の電流の時間変化の一例を示すグラフである。図3および図4で例示したスイープ制御では、メインライン4に接続されるスイープモジュール20が順次切り替えられる。従って、ストリング10全体の電流および電圧は振動するが、上位システムから指令された値に近い値が維持される。
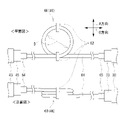
図6を参照して、本実施形態のインダクタ46(図2参照)として用いられるループ部60について説明する。本実施形態では、共振回路を形成するインダクタ46としてループ部60が用いられる。ループ部60は、電池回路モジュール40(図2参照)の入出力回路43と、電池モジュール30とを接続する配線61を、ループ状に形成した部位である。従って、共振回路を形成するために各種素子または機器(例えばリアクトル等)が用いられる場合に比べて、電源システム1の構成が簡素化される。ループ部60の形状を維持するために、ループ部60の少なくとも1つの箇所(本実施形態では2か所)には、配線を結束する結束バンド62が装着されている。なお、ループ部60のループの直径(本実施形態では内径)をDとする。
7 メインライン
10 ストリング
20 スイープモジュール
30 電池モジュール
31 電池
33 第2端子
40 電力回路モジュール
41 第1スイッチング素子
42 第2スイッチング素子
43 入出力回路
45 第1端子
46 インダクタ
47 コンデンサ
60 ループ部
61 配線
64 第1配線端子
65 第2配線端子
Claims (1)
- メインラインと、
前記メインラインに接続された複数のスイープモジュールと、
を有し、
前記スイープモジュールは、
少なくとも1つの電池を含む電池モジュールと、
前記電池モジュールを前記メインラインに接続するように構成された入出力回路と、
当該入出力回路に配置され、前記電池モジュールと前記メインラインとの接続および切断を切り替える、少なくとも1つのスイッチング素子と、
前記入出力回路に、前記電池モジュールと並列に取り付けられたコンデンサと、
前記入出力回路と前記電池モジュールを接続する配線と、
を有し、
前記複数のスイープモジュールは、前記スイッチング素子のオンとオフの交互駆動を制御するゲート信号を、定められた遅延時間毎に順に各々の前記入出力回路に出力することで、前記メインラインに接続する前記電池モジュールを順次切り替えるスイープ制御を実行するように構成されており、
前記配線は、ループが形成された状態で維持されており、
前記入出力回路は、前記配線を繋ぐ第1端子を有し、且つ、前記電池モジュールは、前記配線を繋ぐ第2端子を有しており、
前記配線は、前記第1端子に着脱可能に装着される第1配線端子、および、前記第2端子に着脱可能に装着される第2配線端子を有しており、
前記第1端子と前記第1配線端子の着脱を行うことによって前記入出力回路に接続する前記電池モジュールを前記ループが形成された配線と共に交換可能となり、且つ、前記第2端子と前記第2配線端子の着脱を行うことによって前記入出力回路に接続する前記電池モジュールを前記ループが形成された配線から離して交換可能となるように構成されている、
電源システム。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018222765A JP7121908B2 (ja) | 2018-11-28 | 2018-11-28 | 電源システム |
| US16/680,870 US11196252B2 (en) | 2018-11-28 | 2019-11-12 | Power supply system |
| CN201911099158.8A CN111245037B (zh) | 2018-11-28 | 2019-11-12 | 电源系统 |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018222765A JP7121908B2 (ja) | 2018-11-28 | 2018-11-28 | 電源システム |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2020089140A JP2020089140A (ja) | 2020-06-04 |
| JP7121908B2 true JP7121908B2 (ja) | 2022-08-19 |
Family
ID=70770470
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018222765A Active JP7121908B2 (ja) | 2018-11-28 | 2018-11-28 | 電源システム |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US11196252B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP7121908B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN111245037B (ja) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6960898B2 (ja) * | 2018-10-31 | 2021-11-05 | 株式会社豊田中央研究所 | 電源装置 |
| JP6960897B2 (ja) | 2018-10-31 | 2021-11-05 | 株式会社豊田中央研究所 | 電源装置 |
| JP6898904B2 (ja) | 2018-10-31 | 2021-07-07 | 株式会社豊田中央研究所 | 電源装置 |
| JP7089673B2 (ja) * | 2018-11-29 | 2022-06-23 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 電源システム |
| US11837905B2 (en) * | 2021-05-25 | 2023-12-05 | Cyberswitchingpatents, Llc | Battery charger system |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018182782A (ja) | 2017-04-03 | 2018-11-15 | 株式会社豊田中央研究所 | 電源装置 |
Family Cites Families (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4605952B2 (ja) * | 2001-08-29 | 2011-01-05 | 株式会社日立製作所 | 蓄電装置及びその制御方法 |
| JP2004336836A (ja) * | 2003-04-30 | 2004-11-25 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | モータ駆動装置 |
| US7446433B2 (en) * | 2004-01-23 | 2008-11-04 | American Power Conversion Corporation | Methods and apparatus for providing uninterruptible power |
| JP4101205B2 (ja) * | 2004-05-11 | 2008-06-18 | 松下電器産業株式会社 | 電池パック及び電源装置 |
| JP5486780B2 (ja) * | 2008-07-01 | 2014-05-07 | 株式会社日立製作所 | 電池システム |
| JP5417898B2 (ja) * | 2009-02-27 | 2014-02-19 | Tdk株式会社 | スイッチング電源装置 |
| DE102010027864A1 (de) * | 2010-04-16 | 2011-12-15 | Sb Limotive Company Ltd. | Batterie mit variabler Ausgangsspannung |
| JP2012209902A (ja) * | 2011-03-30 | 2012-10-25 | Semiconductor Components Industries Llc | 入出力回路 |
| KR101383167B1 (ko) * | 2011-10-20 | 2014-04-10 | 주식회사 엘지화학 | 안전성이 향상된 전지팩 |
| US9496749B2 (en) * | 2012-03-23 | 2016-11-15 | Hitachi Automotive Systems, Ltd. | Storage battery control device and electrical storage device |
| JP5982632B2 (ja) * | 2012-03-30 | 2016-08-31 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | 車載用電源回路およびそれを用いた車載電源ユニット |
| WO2014132321A1 (ja) * | 2013-02-26 | 2014-09-04 | 株式会社 日立製作所 | 電源装置 |
| WO2016081473A1 (en) * | 2014-11-17 | 2016-05-26 | Shibashis Bhowmik | Converter with phase-offset switching |
| JP6531745B2 (ja) | 2016-10-27 | 2019-06-19 | 株式会社豊田中央研究所 | 電源装置及び電源装置の制御方法 |
| US9784244B1 (en) * | 2017-03-29 | 2017-10-10 | Tarek O. Souryal | Energy collection pod |
| JP6805933B2 (ja) * | 2017-03-31 | 2020-12-23 | 株式会社豊田中央研究所 | 電源装置 |
| JP7100804B2 (ja) * | 2018-11-28 | 2022-07-14 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 電源システム |
-
2018
- 2018-11-28 JP JP2018222765A patent/JP7121908B2/ja active Active
-
2019
- 2019-11-12 CN CN201911099158.8A patent/CN111245037B/zh active Active
- 2019-11-12 US US16/680,870 patent/US11196252B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018182782A (ja) | 2017-04-03 | 2018-11-15 | 株式会社豊田中央研究所 | 電源装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN111245037B (zh) | 2023-08-08 |
| US11196252B2 (en) | 2021-12-07 |
| JP2020089140A (ja) | 2020-06-04 |
| CN111245037A (zh) | 2020-06-05 |
| US20200169081A1 (en) | 2020-05-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7121908B2 (ja) | 電源システム | |
| JP7022346B2 (ja) | 電源システム | |
| JP7129008B2 (ja) | 電源システム | |
| JP7100804B2 (ja) | 電源システム | |
| JP7145391B2 (ja) | 電源システム | |
| JP7025716B2 (ja) | 電源システム | |
| JP7145392B2 (ja) | 電源システム | |
| JP7089673B2 (ja) | 電源システム | |
| JP7216889B2 (ja) | 電源システム | |
| JP7054453B2 (ja) | 電源システム | |
| JP2021168556A (ja) | 電源システム | |
| JP2021151056A (ja) | 電源システム |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20210325 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20220106 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20220307 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20220707 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20220720 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 7121908 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |