JP6974311B2 - 新規pd−1免疫調節剤 - Google Patents
新規pd−1免疫調節剤 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6974311B2 JP6974311B2 JP2018519261A JP2018519261A JP6974311B2 JP 6974311 B2 JP6974311 B2 JP 6974311B2 JP 2018519261 A JP2018519261 A JP 2018519261A JP 2018519261 A JP2018519261 A JP 2018519261A JP 6974311 B2 JP6974311 B2 JP 6974311B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- antigen
- cells
- seq
- binding protein
- cell
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 229940121354 immunomodulator Drugs 0.000 title description 4
- 239000002955 immunomodulating agent Substances 0.000 title 1
- 230000002584 immunomodulator Effects 0.000 title 1
- 210000001744 T-lymphocyte Anatomy 0.000 claims description 181
- 210000004027 cell Anatomy 0.000 claims description 166
- 108010019670 Chimeric Antigen Receptors Proteins 0.000 claims description 147
- 238000003782 apoptosis assay Methods 0.000 claims description 129
- 230000005522 programmed cell death Effects 0.000 claims description 129
- 108091000831 antigen binding proteins Proteins 0.000 claims description 121
- 102000025171 antigen binding proteins Human genes 0.000 claims description 121
- 230000027455 binding Effects 0.000 claims description 85
- 125000003275 alpha amino acid group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 68
- 239000013598 vector Substances 0.000 claims description 63
- 239000000427 antigen Substances 0.000 claims description 59
- 102000036639 antigens Human genes 0.000 claims description 59
- 108091007433 antigens Proteins 0.000 claims description 59
- 101000611936 Homo sapiens Programmed cell death protein 1 Proteins 0.000 claims description 45
- 150000007523 nucleic acids Chemical class 0.000 claims description 45
- 108010074708 B7-H1 Antigen Proteins 0.000 claims description 44
- 102000008096 B7-H1 Antigen Human genes 0.000 claims description 44
- 102000039446 nucleic acids Human genes 0.000 claims description 44
- 108020004707 nucleic acids Proteins 0.000 claims description 43
- 102100040678 Programmed cell death protein 1 Human genes 0.000 claims description 39
- 239000008194 pharmaceutical composition Substances 0.000 claims description 27
- 239000003446 ligand Substances 0.000 claims description 22
- 201000010099 disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 20
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 claims description 20
- 230000002401 inhibitory effect Effects 0.000 claims description 14
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 claims description 13
- 230000019491 signal transduction Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000011282 treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 229940124060 PD-1 antagonist Drugs 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000002519 immonomodulatory effect Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims 4
- 108010083359 Antigen Receptors Proteins 0.000 claims 1
- 102000006306 Antigen Receptors Human genes 0.000 claims 1
- 239000012634 fragment Substances 0.000 description 68
- 210000004881 tumor cell Anatomy 0.000 description 37
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 35
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 34
- 206010028980 Neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 30
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 24
- 238000000684 flow cytometry Methods 0.000 description 21
- 239000011324 bead Substances 0.000 description 20
- 241000699670 Mus sp. Species 0.000 description 18
- 230000035755 proliferation Effects 0.000 description 17
- 230000028327 secretion Effects 0.000 description 16
- 108010047041 Complementarity Determining Regions Proteins 0.000 description 15
- 101001117317 Homo sapiens Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 Proteins 0.000 description 14
- 108090000623 proteins and genes Proteins 0.000 description 14
- 102100024222 B-lymphocyte antigen CD19 Human genes 0.000 description 13
- 101000980825 Homo sapiens B-lymphocyte antigen CD19 Proteins 0.000 description 13
- 102000004169 proteins and genes Human genes 0.000 description 12
- 230000026683 transduction Effects 0.000 description 12
- 238000010361 transduction Methods 0.000 description 12
- 108091007741 Chimeric antigen receptor T cells Proteins 0.000 description 10
- 101000914514 Homo sapiens T-cell-specific surface glycoprotein CD28 Proteins 0.000 description 10
- 241000699666 Mus <mouse, genus> Species 0.000 description 10
- 230000006052 T cell proliferation Effects 0.000 description 10
- 102100027213 T-cell-specific surface glycoprotein CD28 Human genes 0.000 description 10
- 201000011510 cancer Diseases 0.000 description 10
- 238000003501 co-culture Methods 0.000 description 10
- 238000001262 western blot Methods 0.000 description 10
- 230000001965 increasing effect Effects 0.000 description 9
- 102100024216 Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 Human genes 0.000 description 8
- 230000009089 cytolysis Effects 0.000 description 8
- 108090000765 processed proteins & peptides Proteins 0.000 description 8
- 229940124597 therapeutic agent Drugs 0.000 description 8
- 238000002965 ELISA Methods 0.000 description 7
- 108010021625 Immunoglobulin Fragments Proteins 0.000 description 7
- 102000008394 Immunoglobulin Fragments Human genes 0.000 description 7
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 7
- 230000003993 interaction Effects 0.000 description 7
- 230000001404 mediated effect Effects 0.000 description 7
- 239000013642 negative control Substances 0.000 description 7
- 102100034458 Hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 2 Human genes 0.000 description 6
- 101001068133 Homo sapiens Hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 2 Proteins 0.000 description 6
- 101001137987 Homo sapiens Lymphocyte activation gene 3 protein Proteins 0.000 description 6
- 102000017578 LAG3 Human genes 0.000 description 6
- 229940122544 PD-1 agonist Drugs 0.000 description 6
- 230000005867 T cell response Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000003556 assay Methods 0.000 description 6
- 102000037865 fusion proteins Human genes 0.000 description 6
- 108020001507 fusion proteins Proteins 0.000 description 6
- 102000048776 human CD274 Human genes 0.000 description 6
- 102000048362 human PDCD1 Human genes 0.000 description 6
- 230000001177 retroviral effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 230000011664 signaling Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000010186 staining Methods 0.000 description 6
- 241001430294 unidentified retrovirus Species 0.000 description 6
- 208000023275 Autoimmune disease Diseases 0.000 description 5
- 108060003951 Immunoglobulin Proteins 0.000 description 5
- 102100024213 Programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 Human genes 0.000 description 5
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000028993 immune response Effects 0.000 description 5
- 102000018358 immunoglobulin Human genes 0.000 description 5
- 238000000338 in vitro Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000005764 inhibitory process Effects 0.000 description 5
- 210000005259 peripheral blood Anatomy 0.000 description 5
- 239000011886 peripheral blood Substances 0.000 description 5
- 102000004196 processed proteins & peptides Human genes 0.000 description 5
- 230000003248 secreting effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000008685 targeting Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000002560 therapeutic procedure Methods 0.000 description 5
- 102100029822 B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 101000864344 Homo sapiens B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 101001117312 Homo sapiens Programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 108010054477 Immunoglobulin Fab Fragments Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 102000001706 Immunoglobulin Fab Fragments Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 102100037850 Interferon gamma Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 108010074328 Interferon-gamma Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 108091028043 Nucleic acid sequence Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 239000000556 agonist Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000001270 agonistic effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000000259 anti-tumor effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 210000004369 blood Anatomy 0.000 description 4
- 239000008280 blood Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000003915 cell function Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000012875 competitive assay Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000021615 conjugation Effects 0.000 description 4
- 208000024908 graft versus host disease Diseases 0.000 description 4
- 230000004068 intracellular signaling Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000000178 monomer Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229920001184 polypeptide Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 230000002829 reductive effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000004083 survival effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 241000282412 Homo Species 0.000 description 3
- 108010067060 Immunoglobulin Variable Region Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 102000017727 Immunoglobulin Variable Region Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 108010076504 Protein Sorting Signals Proteins 0.000 description 3
- MTCFGRXMJLQNBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Serine Natural products OCC(N)C(O)=O MTCFGRXMJLQNBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 108010090804 Streptavidin Proteins 0.000 description 3
- GLNADSQYFUSGOU-GPTZEZBUSA-J Trypan blue Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].C1=C(S([O-])(=O)=O)C=C2C=C(S([O-])(=O)=O)C(/N=N/C3=CC=C(C=C3C)C=3C=C(C(=CC=3)\N=N\C=3C(=CC4=CC(=CC(N)=C4C=3O)S([O-])(=O)=O)S([O-])(=O)=O)C)=C(O)C2=C1N GLNADSQYFUSGOU-GPTZEZBUSA-J 0.000 description 3
- 230000003042 antagnostic effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000005557 antagonist Substances 0.000 description 3
- 210000000612 antigen-presenting cell Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 102000023732 binding proteins Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 108091008324 binding proteins Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229940079593 drug Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 239000003937 drug carrier Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000013604 expression vector Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000012642 immune effector Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000009169 immunotherapy Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000001727 in vivo Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000004806 packaging method and process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000002823 phage display Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 108020003175 receptors Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 102000005962 receptors Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 230000000638 stimulation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000006228 supernatant Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000003053 toxin Substances 0.000 description 3
- 231100000765 toxin Toxicity 0.000 description 3
- FWMNVWWHGCHHJJ-SKKKGAJSSA-N 4-amino-1-[(2r)-6-amino-2-[[(2r)-2-[[(2r)-2-[[(2r)-2-amino-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoyl]amino]hexanoyl]piperidine-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound C([C@H](C(=O)N[C@H](CC(C)C)C(=O)N[C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)N1CCC(N)(CC1)C(O)=O)NC(=O)[C@H](N)CC=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 FWMNVWWHGCHHJJ-SKKKGAJSSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 208000024893 Acute lymphoblastic leukemia Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 208000014697 Acute lymphocytic leukaemia Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 208000025321 B-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 108090000695 Cytokines Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102000004127 Cytokines Human genes 0.000 description 2
- DHMQDGOQFOQNFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycine Natural products NCC(O)=O DHMQDGOQFOQNFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004471 Glycine Substances 0.000 description 2
- HVLSXIKZNLPZJJ-TXZCQADKSA-N HA peptide Chemical compound C([C@@H](C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(O)=O)C(=O)N[C@@H](C(C)C)C(=O)N1[C@@H](CCC1)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(O)=O)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC=1C=CC(O)=CC=1)C(=O)N[C@@H](C)C(O)=O)NC(=O)[C@H]1N(CCC1)C(=O)[C@@H](N)CC=1C=CC(O)=CC=1)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 HVLSXIKZNLPZJJ-TXZCQADKSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 101710159910 Movement protein Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 206010061535 Ovarian neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 208000006664 Precursor Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia-Lymphoma Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 210000003719 b-lymphocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 238000012258 culturing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001461 cytolytic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 231100000433 cytotoxic Toxicity 0.000 description 2
- 231100000599 cytotoxic agent Toxicity 0.000 description 2
- 230000001472 cytotoxic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000003013 cytotoxicity Effects 0.000 description 2
- 231100000135 cytotoxicity Toxicity 0.000 description 2
- 239000002619 cytotoxin Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000002708 enhancing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 210000002950 fibroblast Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 208000010726 hind limb paralysis Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 210000000987 immune system Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 229940127121 immunoconjugate Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 229940072221 immunoglobulins Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 230000005917 in vivo anti-tumor Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000001802 infusion Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000003112 inhibitor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 108091008042 inhibitory receptors Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 230000000670 limiting effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000007774 longterm Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010369 molecular cloning Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004091 panning Methods 0.000 description 2
- 210000003819 peripheral blood mononuclear cell Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 230000002688 persistence Effects 0.000 description 2
- 208000017426 precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 230000002062 proliferating effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010188 recombinant method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000009885 systemic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 208000004736 B-Cell Leukemia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000025324 B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000003950 B-cell lymphoma Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 102100022005 B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 241000894006 Bacteria Species 0.000 description 1
- 238000011357 CAR T-cell therapy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 241000283707 Capra Species 0.000 description 1
- 101710112752 Cytotoxin Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000588724 Escherichia coli Species 0.000 description 1
- 208000032612 Glial tumor Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010018338 Glioma Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 108090000288 Glycoproteins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000003886 Glycoproteins Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 101000897405 Homo sapiens B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101100166600 Homo sapiens CD28 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101001002657 Homo sapiens Interleukin-2 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000914484 Homo sapiens T-lymphocyte activation antigen CD80 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000003812 Interleukin-15 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000172 Interleukin-15 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 206010025323 Lymphomas Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000004472 Lysine Substances 0.000 description 1
- KDXKERNSBIXSRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lysine Natural products NCCCCC(N)C(O)=O KDXKERNSBIXSRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 101100407308 Mus musculus Pdcd1lg2 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 206010029260 Neuroblastoma Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010061902 Pancreatic neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 108700030875 Programmed Cell Death 1 Ligand 2 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000007056 Recombinant Fusion Proteins Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010008281 Recombinant Fusion Proteins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108091081062 Repeated sequence (DNA) Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000040739 Secretory proteins Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108091058545 Secretory proteins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 201000009594 Systemic Scleroderma Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010042953 Systemic sclerosis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000033540 T cell apoptotic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 102100027222 T-lymphocyte activation antigen CD80 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 239000000370 acceptor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001413 amino acids Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 210000004102 animal cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- -1 antibody Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 238000011230 antibody-based therapy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010420 art technique Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005784 autoimmunity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008275 binding mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001574 biopsy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000000481 breast Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000000872 buffer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000004899 c-terminal region Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000002619 cancer immunotherapy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004113 cell culture Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000030833 cell death Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006037 cell lysis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000003679 cervix uteri Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000003153 chemical reaction reagent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000001072 colon Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000002860 competitive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004154 complement system Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012141 concentrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004163 cytometry Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000001151 cytotoxic T lymphocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000002019 disulfides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 231100000673 dose–response relationship Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 239000012636 effector Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008029 eradication Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000003238 esophagus Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000007717 exclusion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001747 exhibiting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- MHMNJMPURVTYEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N fluorescein-5-isothiocyanate Chemical compound O1C(=O)C2=CC(N=C=S)=CC=C2C21C1=CC=C(O)C=C1OC1=CC(O)=CC=C21 MHMNJMPURVTYEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000007850 fluorescent dye Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000005260 human cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000036737 immune function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003364 immunohistochemistry Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001506 immunosuppresive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011534 incubation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003834 intracellular effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001990 intravenous administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010253 intravenous injection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000003734 kidney Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000000670 ligand binding assay Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000004185 liver Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000011068 loading method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000004072 lung Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000002101 lytic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000036210 malignancy Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003211 malignant effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 208000015486 malignant pancreatic neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000007726 management method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010172 mouse model Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000035407 negative regulation of cell proliferation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 108700020942 nucleic acid binding protein Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000002773 nucleotide Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000003729 nucleotide group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000002515 oligonucleotide synthesis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000001672 ovary Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 201000002528 pancreatic cancer Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000008443 pancreatic carcinoma Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000003752 polymerase chain reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010837 poor prognosis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003389 potentiating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000002924 primary amino group Chemical group [H]N([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 238000011002 quantification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002285 radioactive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006798 recombination Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005215 recombination Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000003491 skin Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000002784 stomach Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 201000000596 systemic lupus erythematosus Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 229950008160 tanezumab Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 231100000419 toxicity Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 230000001988 toxicity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000003932 urinary bladder Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000002255 vaccination Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012646 vaccine adjuvant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940124931 vaccine adjuvant Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000010200 validation analysis Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K16/00—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies
- C07K16/18—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans
- C07K16/28—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans against receptors, cell surface antigens or cell surface determinants
- C07K16/2803—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans against receptors, cell surface antigens or cell surface determinants against the immunoglobulin superfamily
- C07K16/2818—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans against receptors, cell surface antigens or cell surface determinants against the immunoglobulin superfamily against CD28 or CD152
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K14/00—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K2239/00—Indexing codes associated with cellular immunotherapy of group A61K39/46
- A61K2239/31—Indexing codes associated with cellular immunotherapy of group A61K39/46 characterized by the route of administration
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K2239/00—Indexing codes associated with cellular immunotherapy of group A61K39/46
- A61K2239/38—Indexing codes associated with cellular immunotherapy of group A61K39/46 characterised by the dose, timing or administration schedule
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K2239/00—Indexing codes associated with cellular immunotherapy of group A61K39/46
- A61K2239/46—Indexing codes associated with cellular immunotherapy of group A61K39/46 characterised by the cancer treated
- A61K2239/48—Blood cells, e.g. leukemia or lymphoma
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K39/395—Antibodies; Immunoglobulins; Immune serum, e.g. antilymphocytic serum
- A61K39/39533—Antibodies; Immunoglobulins; Immune serum, e.g. antilymphocytic serum against materials from animals
- A61K39/39558—Antibodies; Immunoglobulins; Immune serum, e.g. antilymphocytic serum against materials from animals against tumor tissues, cells, antigens
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K39/46—Cellular immunotherapy
- A61K39/461—Cellular immunotherapy characterised by the cell type used
- A61K39/4611—T-cells, e.g. tumor infiltrating lymphocytes [TIL], lymphokine-activated killer cells [LAK] or regulatory T cells [Treg]
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K39/46—Cellular immunotherapy
- A61K39/462—Cellular immunotherapy characterized by the effect or the function of the cells
- A61K39/4621—Cellular immunotherapy characterized by the effect or the function of the cells immunosuppressive or immunotolerising
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K39/46—Cellular immunotherapy
- A61K39/463—Cellular immunotherapy characterised by recombinant expression
- A61K39/4631—Chimeric Antigen Receptors [CAR]
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K39/46—Cellular immunotherapy
- A61K39/464—Cellular immunotherapy characterised by the antigen targeted or presented
- A61K39/4643—Vertebrate antigens
- A61K39/46434—Antigens related to induction of tolerance to non-self
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K39/46—Cellular immunotherapy
- A61K39/464—Cellular immunotherapy characterised by the antigen targeted or presented
- A61K39/4643—Vertebrate antigens
- A61K39/4644—Cancer antigens
- A61K39/464402—Receptors, cell surface antigens or cell surface determinants
- A61K39/464411—Immunoglobulin superfamily
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K39/46—Cellular immunotherapy
- A61K39/464—Cellular immunotherapy characterised by the antigen targeted or presented
- A61K39/4643—Vertebrate antigens
- A61K39/4644—Cancer antigens
- A61K39/464402—Receptors, cell surface antigens or cell surface determinants
- A61K39/464411—Immunoglobulin superfamily
- A61K39/464412—CD19 or B4
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/51—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent
- A61K47/68—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment
- A61K47/6835—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment the modifying agent being an antibody or an immunoglobulin bearing at least one antigen-binding site
- A61K47/6849—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment the modifying agent being an antibody or an immunoglobulin bearing at least one antigen-binding site the antibody targeting a receptor, a cell surface antigen or a cell surface determinant
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K48/00—Medicinal preparations containing genetic material which is inserted into cells of the living body to treat genetic diseases; Gene therapy
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P35/00—Antineoplastic agents
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K14/00—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof
- C07K14/435—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof from animals; from humans
- C07K14/705—Receptors; Cell surface antigens; Cell surface determinants
- C07K14/70503—Immunoglobulin superfamily
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K14/00—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof
- C07K14/435—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof from animals; from humans
- C07K14/705—Receptors; Cell surface antigens; Cell surface determinants
- C07K14/70503—Immunoglobulin superfamily
- C07K14/7051—T-cell receptor (TcR)-CD3 complex
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K16/00—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies
- C07K16/18—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans
- C07K16/28—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans against receptors, cell surface antigens or cell surface determinants
- C07K16/2803—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans against receptors, cell surface antigens or cell surface determinants against the immunoglobulin superfamily
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K16/00—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies
- C07K16/18—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans
- C07K16/28—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans against receptors, cell surface antigens or cell surface determinants
- C07K16/30—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans against receptors, cell surface antigens or cell surface determinants from tumour cells
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N5/00—Undifferentiated human, animal or plant cells, e.g. cell lines; Tissues; Cultivation or maintenance thereof; Culture media therefor
- C12N5/06—Animal cells or tissues; Human cells or tissues
- C12N5/0602—Vertebrate cells
- C12N5/0634—Cells from the blood or the immune system
- C12N5/0636—T lymphocytes
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K35/00—Medicinal preparations containing materials or reaction products thereof with undetermined constitution
- A61K35/12—Materials from mammals; Compositions comprising non-specified tissues or cells; Compositions comprising non-embryonic stem cells; Genetically modified cells
- A61K2035/124—Materials from mammals; Compositions comprising non-specified tissues or cells; Compositions comprising non-embryonic stem cells; Genetically modified cells the cells being hematopoietic, bone marrow derived or blood cells
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K2039/505—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies comprising antibodies
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K2039/505—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies comprising antibodies
- A61K2039/507—Comprising a combination of two or more separate antibodies
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K38/00—Medicinal preparations containing peptides
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2317/00—Immunoglobulins specific features
- C07K2317/20—Immunoglobulins specific features characterized by taxonomic origin
- C07K2317/21—Immunoglobulins specific features characterized by taxonomic origin from primates, e.g. man
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2317/00—Immunoglobulins specific features
- C07K2317/50—Immunoglobulins specific features characterized by immunoglobulin fragments
- C07K2317/54—F(ab')2
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2317/00—Immunoglobulins specific features
- C07K2317/50—Immunoglobulins specific features characterized by immunoglobulin fragments
- C07K2317/55—Fab or Fab'
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2317/00—Immunoglobulins specific features
- C07K2317/50—Immunoglobulins specific features characterized by immunoglobulin fragments
- C07K2317/56—Immunoglobulins specific features characterized by immunoglobulin fragments variable (Fv) region, i.e. VH and/or VL
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2317/00—Immunoglobulins specific features
- C07K2317/50—Immunoglobulins specific features characterized by immunoglobulin fragments
- C07K2317/56—Immunoglobulins specific features characterized by immunoglobulin fragments variable (Fv) region, i.e. VH and/or VL
- C07K2317/565—Complementarity determining region [CDR]
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2317/00—Immunoglobulins specific features
- C07K2317/60—Immunoglobulins specific features characterized by non-natural combinations of immunoglobulin fragments
- C07K2317/62—Immunoglobulins specific features characterized by non-natural combinations of immunoglobulin fragments comprising only variable region components
- C07K2317/622—Single chain antibody (scFv)
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2317/00—Immunoglobulins specific features
- C07K2317/70—Immunoglobulins specific features characterized by effect upon binding to a cell or to an antigen
- C07K2317/73—Inducing cell death, e.g. apoptosis, necrosis or inhibition of cell proliferation
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2317/00—Immunoglobulins specific features
- C07K2317/70—Immunoglobulins specific features characterized by effect upon binding to a cell or to an antigen
- C07K2317/75—Agonist effect on antigen
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2317/00—Immunoglobulins specific features
- C07K2317/70—Immunoglobulins specific features characterized by effect upon binding to a cell or to an antigen
- C07K2317/76—Antagonist effect on antigen, e.g. neutralization or inhibition of binding
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2319/00—Fusion polypeptide
- C07K2319/01—Fusion polypeptide containing a localisation/targetting motif
- C07K2319/03—Fusion polypeptide containing a localisation/targetting motif containing a transmembrane segment
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2319/00—Fusion polypeptide
- C07K2319/33—Fusion polypeptide fusions for targeting to specific cell types, e.g. tissue specific targeting, targeting of a bacterial subspecies
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2319/00—Fusion polypeptide
- C07K2319/70—Fusion polypeptide containing domain for protein-protein interaction
- C07K2319/74—Fusion polypeptide containing domain for protein-protein interaction containing a fusion for binding to a cell surface receptor
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N2510/00—Genetically modified cells
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N2740/00—Reverse transcribing RNA viruses
- C12N2740/00011—Details
- C12N2740/10011—Retroviridae
- C12N2740/10041—Use of virus, viral particle or viral elements as a vector
- C12N2740/10043—Use of virus, viral particle or viral elements as a vector viral genome or elements thereof as genetic vector
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Cell Biology (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- Mycology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Proteomics, Peptides & Aminoacids (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Oncology (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- Gastroenterology & Hepatology (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Toxicology (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Hospice & Palliative Care (AREA)
- Peptides Or Proteins (AREA)
- Micro-Organisms Or Cultivation Processes Thereof (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Material From Animals Or Micro-Organisms (AREA)
- Medicines That Contain Protein Lipid Enzymes And Other Medicines (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Antibodies Or Antigens For Use As Internal Diagnostic Agents (AREA)
Description
本出願は、2016年6月16日に作成された配列表を包含し、ASCIIフォーマットにおけるそのファイルは、3314070AWO_SequenceListing_ST25.txtと命名され、そのサイズは104キロバイトである。そのファイルは、引用によりその全体が本出願に組み込まれる。
(A)配列番号10、配列番号21、配列番号32、配列番号43、配列番号53、配列番号61、配列番号72、配列番号83、配列番号94、配列番号103、配列番号114、配列番号125、配列番号133、配列番号142;その断片、およびその相同配列からなる群から選択されるアミノ酸配列を有する抗原結合領域;
(B)配列番号6および8;配列番号17および19;配列番号28および30;配列番号39および41;配列番号49および51;配列番号57および59;配列番号68および70;配列番号79および81;配列番号90および92;配列番号99および101;配列番号110および112;配列番号121および123;配列番号129および131;配列番号138および140;それらの断片、ならびにそれらの相同配列から選択されるアミノ酸配列をそれぞれ有する可変軽鎖(VL)および可変重鎖(VH)を含む抗原結合領域;または
(C)以下を含む抗原結合領域:
(i)アミノ酸配列QSISSY(配列番号1)、AASおよびQQSYSTPLT(配列番号2)をそれぞれ有する軽鎖相補性決定領域(LCCDR)LCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GFTSSSYW(配列番号4)、IKQDGSEK(配列番号5)およびARGGWSYDM(配列番号6)をそれぞれ有する重鎖相補性決定領域(HCCDR)HCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片またはそれらの相同配列;
(ii)アミノ酸配列SSNIGAGYA(配列番号12)、TNNおよびQSYDSSLSGVI(配列番号13)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GYTLTELS(配列番号14)、FDPEDGET(配列番号15)およびARAYYGFDQ(配列番号16)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片またはそれらの相同配列;
(iii)アミノ酸配列SSNIGNNA(配列番号23)、YNDおよびAAWDDSVNGYV(配列番号24)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GYTFTRFG(配列番号25)、ISVNNGNT(配列番号26)およびARYMYGRRDS(配列番号27)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片またはそれらの相同配列;
(iv)アミノ酸配列NIGSKS(配列番号34)、YDSおよびQVWDNHSDVV(配列番号35)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列RNKFSSYA(配列番号36)、ISGSGGTT(配列番号37)およびARWYSSYYDV(配列番号38)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片またはそれらの相同配列;
(v)アミノ酸配列NIGSKS(配列番号34)、YDSおよびQVWDSSSDYV(配列番号45)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GFTFSSYA(配列番号46)、ISGSGGST(配列番号47)およびARNYISMFDS(配列番号48)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片またはそれらの相同配列;
(vi)アミノ酸配列NIGSKS(配列番号34)、YDSおよびQVWDSSSDHV(配列番号55)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GFTFSSYA(配列番号46)、ISGSGGST(配列番号47)およびARGYSSYYDA(配列番号56)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片またはそれらの相同配列;
(vii)アミノ酸配列RSNIGENT(配列番号63)、SNNおよびAAWDDRLNGYV(配列番号64)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GYTFTNYG(配列番号65)、IGAQKGDT(配列番号66)およびARSQGVPFDS(配列番号67)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片またはそれらの相同配列;
(viii)アミノ酸配列RSNIGSNT(配列番号74)、NNNおよびATWDDSLNEYV(配列番号75)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GYTFTRYG(配列番号76)、ISGYNGNT(配列番号77)およびARHGYGYHGD(配列番号78)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片またはそれらの相同配列;
(ix)アミノ酸配列SSNIGAGYV(配列番号85)、HNNおよびQSYDSSLSGWV(配列番号86)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GFTFKDYY(配列番号87)、ISTSGNSV(配列番号88)およびARSPGHSDYDS(配列番号89)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片またはそれらの相同配列;
(x)アミノ酸配列NIGDKS(配列番号96)、YDSおよびQVWASGTDHPYVI(配列番号97)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GFTFSSYA(配列番号46)、ISGSGGST(配列番号47)およびARMYGSYTDM(配列番号98)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);およびそれらの断片または相同配列;
(xi)アミノ酸配列SSNIGYNY(配列番号105)、RNNおよびTSWDDSLSGYV(配列番号106)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GNAFTNFY(配列番号107)、INPSGTDLT(配列番号108)およびARQYAYGYSGFDM(配列番号109)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片またはそれらの相同配列;
(xii)アミノ酸配列QSVSNW(配列番号116)、AASおよびQQSYSTPIT(配列番号117)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GYTFTSYY(配列番号118)、INPNTGGS(配列番号119)およびARGDVTYDE(配列番号120)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片またはそれらの相同配列;
(xiii)アミノ酸配列NIGSKS(配列番号34)、YDDおよびQVWDINDHYV(配列番号127)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GFTFSSYA(配列番号46)、ISGSGGST(配列番号47)およびARSQASFMDI(配列番号128)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片またはそれらの相同配列;または
(xiv)アミノ酸配列NIGSKS(配列番号34)、DDSおよびQVWDSSSDQGV(配列番号135)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GFTFSSYA(配列番号46)、IGTGGGT(配列番号136)およびARGTGYDGDQ(配列番号137)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC)およびそれらの断片またはそれらの相同配列。
Fcに融合させたPD−1細胞外ドメイン(PD−1 ECD−Fcドメイン)であった。PD−1 ECDおよびhIgG1 FcをコードするDNA配列は、Genewiz,Inc.(South Plainfield,NJ)により合成された。DNA配列を次いでEurekaの所有する哺乳類発現ベクターにサブクローニングし、これを次いで融合タンパク質発現のためにHEK293細胞にトランスフェクトした。PD−1 ECD−Fc融合タンパク質を細胞が死滅した後にHEK293細胞培地から標準的FPLC方法によって精製した。
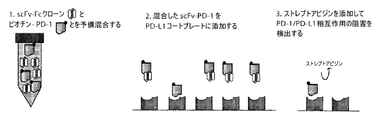
scFvがPD−1連結を阻害する能力を試験するために、scFv−Fcドメイン(scFv−Fc)融合タンパク質を作成し、ここで、scFvをマウスFc(マウスIgG1a)ドメインに連結させた。scFv−Fcクローンを次いで、ELISAプレートをヒトPD−1単量体でコーティングすることにより、PD−1に結合する能力について分析した。scFvのPD−1への結合をHRP−接合抗マウスIgG1 Fc二次抗体を用いて定量した。7つのすべての抗体は、用量依存的にPD1単量体に関して結合活性を示した(図1)。ET901 ScFv−Fc(マウスIgG1 Fc)を陰性対照として用いた。scFv−Fcクローンの結合親和性を順位付けしたところ、クローン31が弱く結合し、クローン26および27が最も強く結合した(31<23<40<18<16=27<26)。
PD−L1と相互作用するPD−1を阻害するscFv−Fcの能力を試験するために、模式的に図2Aに示す競合的リガンド−結合アッセイを行った。このアッセイにおいて、PD−L1−FcをELISAプレート上にコーティングした。ビオチン化−PD1−Fcを段階希釈したET901 ScFv−Fc(陰性対照)または抗PD1 ScFv−Fcと混合し、次いでPD−L1−Fcコートプレート中に添加した。プレート上にコーティングされたPD−L1へのPD−1−Fcの結合をHRP−接合ストレプトアビジンを介して可視化した(図2B)。同様の濃度のscFv−Fcを比較した場合(丸で囲む)、PD−1−PDL1相互作用を破壊する能力を順位付けしたところ、クローン40および23が最も弱く、クローン26が最も強い破壊能力を有していた(26>27=16>18>31>23=40、図2B)。
これらのクローンを次いで特異的T細胞機能を制御するそれらの能力について調べた。本発明者らは以前に、T細胞が腫瘍−特異的キメラ抗原受容体(CAR)を発現するようレトロウイルスにより形質導入されている、腫瘍−標的化T細胞を作成している。本発明者らは以前に、CARの発現が所与の抗原を標的化するT細胞機能を再指示したことを実証している(Brentjens,Santos et al,2007)。本発明者らの研究室において、本発明者らは、1928zと称するCD19に特異的なCARを用いてB細胞悪性腫瘍を標的とする(Brentjens,Santosら.2007)。本発明者らは以前に、CAR改変T細胞がインビトロおよびインビボおよび臨床研究において有意な抗腫瘍活性を示したことを実証している(Brentjens,Latoucheら.2003;Brentjens,Davilaら.2013;Davila,Riviereら.2014)。7つのscFvクローンが、アゴニスト性であるか(PD−1を刺激する)、アンタゴニスト性であるか(PD−1をブロックする)またはPD−1に対して有意な効果を有さないかを決定するために、本発明者らは、抗PD−1 scFv遺伝子の近位にマウスカッパリーダー配列を含めることにより分泌可能scFvを作成した(図3)。本発明者らは次いで、1928z CARの発現および形質導入されたヒト末梢血T細胞からの抗PD−1 scFvの分泌を誘導するために2シストロン性レトロウイルスベクターを作成した。
PD−1刺激がT細胞の増殖および機能を阻害する能力があるので、本発明者らは引き続いてT細胞増殖に対する抗PD−1 scFvの効果を特徴決定する探索を行った。これを達成するために、ヒトT細胞を健康ドナーの末梢血から単離し、以前に記載されている方法を用いて、CARを発現し、PD−1−特異的scFvを分泌するようレトロウイルス形質導入を介して改変した(Brentjens、Santosら.2007)。形質導入の後、改変されたT細胞をインビトロでの増殖についてモニターした(図4)。1928z CARを発現し、PD−1特異的scFvクローン23および27を分泌するT細胞は、1928z CARのみを発現するよう改変されたT細胞と同様に増殖した。CARを発現し、PD−1−特異的scFvクローン16、18、26、31または40を分泌するよう改変された細胞は増殖せず、これらのPD−1−特異的scFvクローンがアゴニスト性であり、潜在的にPD−1を刺激し、そしてT細胞増殖の低下をもたらしたことが示唆された。
増殖研究に加えて、本発明者らは、(CARを発現する、またはCARを発現し、PD−1−特異的scFvを分泌する)T細胞を、CD19+バーキットリンパ腫腫瘍細胞株、Rajiと共培養し、T細胞からのサイトカイン分泌のレベルを決定した。図5に示されるように、1928z CARを発現し、PD−1−特異的scFvクローン23または27を分泌するよう改変されたT細胞は、CARのみを発現するよう改変された細胞と比較してIFN−γの分泌の上昇を示し、これらのscFvクローンがPD−1シグナル伝達に関してアンタゴニスト性であったことが示唆された。1928z CARを発現し、PD−1−特異的scFvクローン16、18、26、31または40を分泌するよう改変された細胞は、CARのみにより改変された細胞と比較してより少ないIFN−γを分泌し、これらのscFvがPD−1に関してアゴニスト性であり、T細胞機能を阻害したことが示唆された。
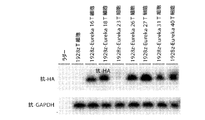
1928 CARおよびPD−1ブロッキングscFvを発現するよう改変されたヒトT細胞をフローサイトメトリーによって分析した。CARの発現の検証(図6)の後、scFvの存在を、細胞可溶化液における検出を可能とするようにゴルジ阻害剤で処理されたヒトT細胞から調製した可溶化液についての(scFv設計において組み込まれたHAタグに対して特異的な抗体を使用する)ウェスタンブロットを使用して決定した。1928z CARおよびクローン23を発現するよう改変されたヒトT細胞では、その他のクローンと比較してscFvタンパク質が有意に少なかった(図7)。これらの細胞を次いで、PD−1リガンドである、PD−L1/L2を発現するか、または発現しない、3T3マウス線維芽細胞(人工抗原提示細胞、aAPC)上に蒔いた。aAPCとの24時間の培養の後、ヒトT細胞を活性化させるために培養物にCD3/D28ビーズを添加した。ヒトT細胞、aAPCおよびビーズの培養の3日後、ヒトT細胞を数え上げて、PD−1リガンドの存在がヒトT細胞のビーズに駆動される増殖を阻害したか、または抗PD−1 scFvがT細胞増殖のPD−1リガンドに媒介される阻害を妨げたかを、決定した。1928z CARおよび抗PD−1 scFvクローン26および23を発現するよう改変されたT細胞では、抑制性リガンドを発現しないaAPCと比較してPD−L1/L2を発現するaAPC上での増殖が低下していた(図8)。一方、1928z CARおよび抗PD−1 scFvクローン27を発現するよう改変されたT細胞は、PD−L1/L2を発現するaAPC上での増殖が上昇していた。
当該技術分野において知られている組換え技術を使用して、PD−1特異的scFvから組換えヒトモノクローナル抗体を作成し、即ち、対応するscFvにおいてみられるものと同じ可変重および軽鎖を有する完全にヒトのIg分子を作った(上記表1〜14および図9を参照されたい)。これらのモノクローナル抗体のPD−1への結合をフローサイトメトリーを使用して実証した(図10を参照されたい)。
PD−L1/L2を発現するaAPC上でインキュベートされた、第1世代CARを発現するよう改変されたT細胞は、抗PD−1クローン27モノクローナル抗体が存在する場合、増殖する。第1世代CD19−特異的CAR(19z1)を発現するよう改変されたヒトT細胞を、抗PD−1モノクローナル抗体とともに24時間インキュベートし、次いでPD−L1/L2を発現するか、または発現しないaAPC上に置いた。aAPCによる24時間の刺激の後、細胞を次いでCD3/CD28ビーズにより刺激した。3日後、細胞を数え上げた。モノクローナル抗体なしでインキュベートした19z1 T細胞、対照抗体(901)およびクローン23および26モノクローナル抗体とともにインキュベートした19z1 T細胞は、抑制性リガンドなしのaAPC上(図11黒色バー)と比較して、PD−1リガンドを発現するaAPC上での増殖(図11白色バー)がより低かった。しかしながら、抗PD−1クローン27モノクローナル抗体とともにインキュベートした19z1 T細胞はPD−L1/L2 aAPC上でより高い程度に増殖した。示したデータは1回の実験の代表である。
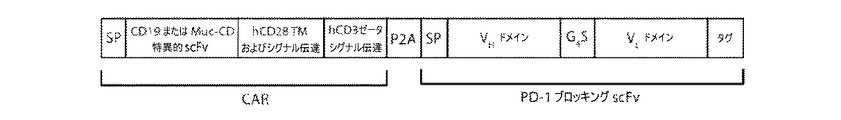
PD−1ブロッキングscFvである、E27を分泌するようさらに改変されたCAR T細胞の作成。CD19−特異的CAR(1928zと称する)または卵巣腫瘍抗原特異的CAR(4H1128zと称する)およびPD−1ブロッキングscFvである、E27をコードする2シストロン性レトロウイルスコンストラクトを作成した(図12A)。E27は、scFvの分泌を可能にするように、シグナルペプチドである、マウスIgKにより先行された。T細胞からいったん分泌されたscFvを検出するために、HA/Hisタグもまた含めた。ヒト末梢血T細胞に、CAR、1928z、またはCARおよびE27 PD−1ブロッキングscFv、1928z−E27をコードするレトロウイルスコンストラクトを形質導入した。形質導入の後、フローサイトメトリーを使用して、CD19−標的化CARに特異的に結合する、19E3と称する抗体を用いて、CARの発現を検出した(図12B)。形質導入されたヒトT細胞からの上清のウェスタンブロット分析を利用して、抗HA抗体を用いてPD−1ブロッキングscFvを検出した(図12C)。本発明者らはまた、CARおよび対照scFvである、B6を発現するよう改変されたT細胞からのscFv分泌を調べ、これは抗c−mycタグ抗体を用いて検出した。2つのCD19+腫瘍標的に対する標準的51Cr放出アッセイを行って、scFvの分泌が、CARがT細胞の細胞溶解能力を再指示する能力を妨げないことを確証した。CARのみ(1928zまたは4H1128z対照CAR)、CARおよびE27 scFv(1928z−E27または4H1128z−E27)、またはCARおよび対照scFv(1928z−B6H12.2または4H1128z−B6H12.2)のいずれかを発現するCAR T細胞を、51Cr標識化腫瘍細胞(RajiまたはNalm6)とともに4時間インキュベートした。CD19特異的CARを発現するT細胞は、腫瘍標的を同等のレベルで溶解することができ、卵巣−標的化CAR T細胞はRajiもNalm6も溶解することができなかった(図12D)。それゆえ、本発明者らは、scFvの分泌は、CARがT細胞溶解能力を再指示する能力を妨げなかったと結論する。
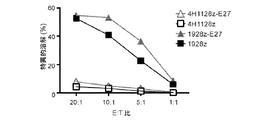
CARを発現し、PD−1ブロッキングscFvを分泌するよう改変されたT細胞は、PD−L1−PD−1相互作用からの阻害に、インビトロで耐える。CARのみ(1928z)、またはCARおよびPD−1ブロッキングscFv(1928z−E27)を発現するT細胞を3T3空細胞またはヒトPD−L1を発現するよう改変された3T3細胞上で培養した。3T3フィーダー細胞上での24時間の後、細胞を、1:3のビーズ:T細胞比にて培養物に添加したCD3/CD28ビーズにより刺激した。T細胞の増殖をトリパンブルーでの数え上げにより決定し、新しいビーズを2回培養物に添加した(矢印によって示す)。1928z T細胞は、3T3空フィーダー細胞上で増殖したが、しかし、3T3−PD−L1フィーダー細胞上では増殖しなかった。一方、1928z−E27 T細胞は、3T3空および3T3−PD−L1フィーダー細胞の両方の上で増殖し、PD−L1−PD−1に媒介される抑制に対する抵抗性が示された(図13A)。図13Aに示すように3T3空または3T3−PD−L1細胞上でインキュベートしたT細胞をフローサイトメトリーによって分析して、抑制性受容体である、PD−1、2B4およびLAG3についての発現を検出した。1928z細胞は、1928z−E27細胞よりも上昇したレベルのPD−1を発現した(示さず)。PD−1+細胞でゲートをかけた場合、2B4およびLAG3の分析により、1928z細胞は、1928z−E27細胞と比較してPD−1+、2B4+およびLAG3+細胞のより高い割合を有していたことが明らかになった(図13B)。形質導入されたT細胞を、様々なエフェクター対標的(E:T)比(1:1、1:3、1:5)で72時間、Raji−PDL1またはNalm6−PDL1腫瘍細胞とともに培養した。抗CD3および抗CD19抗体での染色後のフローサイトメトリーおよびビーズの数え上げを使用して、腫瘍標的の溶解およびT細胞の増殖を経時的にモニターした。1928z−E27細胞は、PDL1+腫瘍細胞とともに培養した場合、1928z T細胞と比較してより高いレベルで増殖し続けた(図13C)。形質導入されたT細胞を図13Cに示すようにNalm6−PDL1腫瘍細胞で刺激し、Nalm6−PDL1腫瘍細胞で1:5のT E:T比で再刺激した。48時間の共培養の後、フローサイトメトリーを使用して腫瘍標的の溶解を決定した。1928z−E27は、1928z細胞と比較して再刺激の際にPD−L1腫瘍標的を溶解する能力を保持していた(図13D)。
CARを発現し、PD−1ブロッキングscFvを分泌するよう改変されたT細胞のインビボ抗腫瘍効力を図14に示す。SCID−ベージュマウスに静脈内注入により0日目にRaji−PD−L1腫瘍細胞を接種した。1日目に、マウスに106のCAR+T細胞を静脈内に注入し、生存を臨床的にモニターした。後肢麻痺が生じるとマウスを安楽死させた。
PD−1ブロッキングmAb候補である、E27、E26およびE23を競合的結合アッセイにおいて使用して、様々な濃度で、ヒトには存在しないハプテンを標的とする対照mAbと比較してのPD−1のPD−L1への結合の妨害を検出した。E23、E26およびE27 mAbはすべてPD−1のPD−L1への結合を妨げた(図15A)。1928z CARとともに分泌可能scFvを発現するよう形質導入された293Glv9パッケージング細胞からのSNについての、抗HA抗体により染色したウェスタンブロット。E27 scFvが最高レベルで検出され、それゆえ残りの研究において使用した(図15C)。
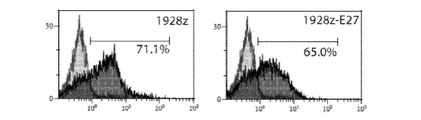
T細胞を、CARを発現し、PD−1ブロッキングscFvである、E27を分泌するよう共改変することができる。図16Aは、1928z CARのみ(1928z)または1928z CARおよびE27 PD−1ブロッキングscFv(1928z−E27)を形質導入した後の、1928z CARに特異的に結合する19E3 mAbによる染色の後での、同等のCAR発現を実証する代表的フローサイトメトリープロットである。図16Bは、抗HA mAbで染色した、1928zおよび1928z−E27 T細胞からのSNについてのウェスタンブロットを示し、約30kDaタンパク質が1928z−E27細胞においてのみ示され、E27 scFvが、1928z−E27を形質導入されたT細胞から分泌されるが、CARのみを形質導入されたT細胞からは分泌されないことを実証している。図16Cは、形質導入の後に、1928z T細胞と比較して1928z−E27 T細胞上でのより低いレベルのPD−1発現を実証する代表的フローサイトメトリーである。PD−1の発現は、1928z T細胞と比較して1928z−E27 T細胞上で統計的に有意により低かった。示されたデータは、4回の独立した実験からの平均+/−SEMである(図16D)。Raji腫瘍細胞の溶解はE27 scFvの分泌によって影響を受けなかったことを実証する4時間51Cr放出アッセイ。1928zおよび1928z−E27 T細胞はRaji腫瘍細胞を同等に溶解した。対照4H1128z−E27 T細胞は、4H1128z T細胞と比較してRaji細胞の溶解の上昇を媒介しなかった(図16E)。示したデータは、2回の独立した実験の代表である。
CARおよびE27の発現は、CD19+PD−L1+腫瘍細胞に関して、T細胞の増殖および溶解能力を保護する。Raji腫瘍細胞を、ヒトPD−L1を発現するようレトロウイルスにより改変し(Raji−PDL1)、PD−L1に対して特異的なmAbにより染色した。親Raji腫瘍(Raji)はPD−L1を発現せず、Raji−PDL1腫瘍細胞は高レベルのPD−L1を発現した(図17A)。図17Bは、1928z−E27 T細胞は、72時間の共培養の後のフローサイトメトリーにより決定して、1928z T細胞と比較してより多くのRaji−PDL1腫瘍細胞を溶解することを示す代表的フローサイトメトリープロットを示す。1928z−E27 T細胞は、1928z T細胞と比較して統計的に有意により多くのRaji−PDL1腫瘍細胞を溶解し、示されたデータは4回の独立した実験からの平均+/−SEMである(図17C)。1928z−E27 T細胞は、フローサイトメトリーおよびビーズの数え上げにより決定して、Raji−PDL1腫瘍細胞との共培養の後により多くの数に増殖し、示されたデータは4回の独立した実験からのT細胞の平均総数+/−SEMである(図17D)。図17Eは、Raji−PDL1腫瘍細胞との7日間の共培養の後の、1928z−E27 T細胞と比較して1928z T細胞上での上昇したPD−1発現を示す、代表的フローサイトメトリープロットを示す。1928z T細胞は、パーセンテージ陽性細胞およびPD−1染色の平均蛍光強度(MFI)に関して、1928z−E27 T細胞と比較して有意により多くのPD−1を発現する。示されたデータは、4回の独立した実験からの平均+/−SEMである(図17F)。図17Gは、7日間のRaji−PDL1との共培養の後に、1928z−E27細胞と比較して上昇したパーセンテージの2B4+PD−1+1928z T細胞を示す、代表的フローサイトメトリープロットを示す。1928z−E27 T細胞はまた、2B4+PD−1+集団について、より少ないBTLAおよびTIM3を発現する。示したデータは、3回の独立した実験の代表である。
E27は、PD−L1に関してCD3/CD28刺激T細胞の増殖能力を保護する。NIH3T3細胞をヒトPD−L1を発現するようレトロウイルスにより改変し(3T3−PDL1)、PD−L1に特異的なmAbにより染色した。親NIH3T3(3T3−空)は、PD−L1を発現せず、3T3−PDL1腫瘍細胞は、高レベルのPD−L1を発現した(図18A)。1928zおよび1928z−E27 T細胞を3T3−空または3T3−PDL1細胞とともに培養し、CD3/CD28ビーズにより刺激した。細胞を数え上げ、3、6、9および12日目に新しい3T3細胞上に再び蒔いた。1928z T細胞は3T3−空細胞と比較して3T3−PDL1細胞とともに培養した場合に増殖の低下を示した。1928z−E27細胞は、3T3−空または3T3−PDL1細胞上で培養した場合、同等の増殖を示した(図18B)。示したデータは、4回の独立した実験からの平均倍数増殖+/−SEMである。図18Cは、3T3−空細胞上で培養した1928z T細胞と比較して3T3−PDL1とともに培養した1928z T細胞上で2B4、PD−1、BTLAおよびTIM3の発現の上昇を示す、代表的フローサイトメトリープロットである。1928z−E27細胞は、3T3−空および3T3−PDL1とともに培養した場合、2B4、PD−1、BTLA−4およびTIM3の同等の発現を示した。示したデータは、3回の独立した実験の代表である。
E27 scFvを分泌するCAR T細胞は、抗腫瘍機能のインビボでの上昇を示す。SCID−ベージュマウスにRaji−PDL1腫瘍細胞を静脈内に接種し、翌日にCAR T細胞を静脈内に注入した。図19に示すように、1928z−E27 T細胞で処理されたマウスは1928z T細胞で処理されたマウスと比較して生存の向上を示した。1928z T細胞で処理したマウスは非処理マウスおよび無関係の抗原を標的としたCAR T細胞である、4H1128zおよび4H1128z−E27 T細胞で処理したマウスよりも長く生存した。示したデータは2回の独立した実験からのものである。
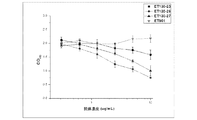
PD1/PDL1結合に対するブロッキング効果を確認するために、抗PD−1抗体ET130−23、ET130−26およびET130−27をELISAにより試験した。図20に示すように、ET901(陰性対照)は結合を示さず、一方、ET130−23、ET130−26およびET130−27は、0.031〜10μg/mlの濃度範囲にわたってPD1/PDL1結合に対してブロッキング効果を示した。
抗PD−1 scFvまたはモノクローナル抗体の適用を、scFvまたはモノクローナル抗体が免疫応答を弱め、自己免疫疾患を消失させる能力について調べる。これはまた、GVHDのマウスモデルを用いて調べることができる。ヒトT細胞の照射したNOD.SCID.IL−2Rγ−/−への注入の結果、ヒト細胞が生着し、ヒトT細胞がマウス組織を攻撃する重篤なGVHDが起こった。抗PD−1 scFvを分泌するT細胞(またはモノクローナル抗体の注入により増強されたT細胞)を対象に注入し、GVHDの発生を評価する。抗PD−1 scFv/mAbがアゴニスト性である場合、GVHD応答はヒトT細胞の抑制により阻害される。
例示的実施形態
1.以下の1つを含む組換え抗原結合性タンパク質またはその抗原結合性断片:
(A)配列番号10、配列番号21、配列番号32、配列番号43、配列番号53、配列番号61、配列番号72、配列番号83、配列番号94、配列番号103、配列番号114、配列番号125、配列番号133、配列番号142;その断片およびその相同配列からなる群から選択されるアミノ酸配列を含む抗原結合領域;
(B)配列番号6および8;配列番号17および19;配列番号28および30;配列番号39および41;配列番号49および51;配列番号57および59;配列番号68および70;配列番号79および81;配列番号90および92;配列番号99および101;配列番号110および112;配列番号121および123;配列番号129および131;配列番号138および140;それらの断片ならびにそれらの相同配列から選択されるアミノ酸配列をそれぞれ有する可変軽鎖(VL)および可変重鎖(VH)を含む抗原結合領域;
(C)以下を含む抗原結合領域:
(i)アミノ酸配列QSISSY(配列番号1)、AASおよびQQSYSTPLT(配列番号2)をそれぞれ有する軽鎖相補性決定領域(LCCDR)LCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GFTSSSYW(配列番号4)、IKQDGSEK(配列番号5)およびARGGWSYDM(配列番号6)をそれぞれ有する重鎖相補性決定領域(HCCDR)HCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片ならびにそれらの相同配列;
(ii)アミノ酸配列SSNIGAGYA(配列番号12)、TNNおよびQSYDSSLSGVI(配列番号13)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GYTLTELS(配列番号14)、FDPEDGET(配列番号15)およびARAYYGFDQ(配列番号16)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片ならびにそれらの相同配列;
(iii)アミノ酸配列SSNIGNNA(配列番号23)、YNDおよびAAWDDSVNGYV(配列番号24)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GYTFTRFG(配列番号25)、ISVNNGNT(配列番号26)およびARYMYGRRDS(配列番号27)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片ならびにそれらの相同配列;
(iv)アミノ酸配列NIGSKS(配列番号34)、YDSおよびQVWDNHSDVV(配列番号35)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列RNKFSSYA(配列番号36)、ISGSGGTT(配列番号37)およびARWYSSYYDV(配列番号38)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片ならびにそれらの相同配列;
(v)アミノ酸配列NIGSKS(配列番号34)、YDSおよびQVWDSSSDYV(配列番号45)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GFTFSSYA(配列番号46)、ISGSGGST(配列番号47)およびARNYISMFDS(配列番号48)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片ならびにそれらの相同配列;
(vi)アミノ酸配列NIGSKS(配列番号34)、YDSおよびQVWDSSSDHV(配列番号55)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GFTFSSYA(配列番号46)、ISGSGGST(配列番号47)およびARGYSSYYDA(配列番号56)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片ならびにそれらの相同配列;
(vii)アミノ酸配列RSNIGENT(配列番号63)、SNNおよびAAWDDRLNGYV(配列番号64)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GYTFTNYG(配列番号65)、IGAQKGDT(配列番号66)およびARSQGVPFDS(配列番号67)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片ならびにそれらの相同配列;
(viii)アミノ酸配列RSNIGSNT(配列番号74)、NNNおよびATWDDSLNEYV(配列番号75)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GYTFTRYG(配列番号76)、ISGYNGNT(配列番号77)およびARHGYGYHGD(配列番号78)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片ならびにそれらの相同配列;
(ix)アミノ酸配列SSNIGAGYV(配列番号85)、HNNおよびQSYDSSLSGWV(配列番号86)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GFTFKDYY(配列番号87)、ISTSGNSV(配列番号88)およびARSPGHSDYDS(配列番号89)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片ならびにそれらの相同配列;
(x)アミノ酸配列NIGDKS(配列番号96)、YDSおよびQVWASGTDHPYVI(配列番号97)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GFTFSSYA(配列番号46)、ISGSGGST(配列番号47)およびARMYGSYTDM(配列番号98)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片ならびにそれらの相同配列;
(xi)アミノ酸配列SSNIGYNY(配列番号105)、RNNおよびTSWDDSLSGYV(配列番号106)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GNAFTNFY(配列番号107)、INPSGTDLT(配列番号108)およびARQYAYGYSGFDM(配列番号109)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片ならびにそれらの相同配列;
(xii)アミノ酸配列QSVSNW(配列番号116)、AASおよびQQSYSTPIT(配列番号117)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GYTFTSYY(配列番号118)、INPNTGGS(配列番号119)およびARGDVTYDE(配列番号120)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片ならびにそれらの相同配列;
(xiii)アミノ酸配列NIGSKS(配列番号34)、YDDおよびQVWDINDHYV(配列番号127)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GFTFSSYA(配列番号46)、ISGSGGST(配列番号47)およびARSQASFMDI(配列番号128)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片ならびにそれらの相同配列;または
(xiv)アミノ酸配列NIGSKS(配列番号34)、DDSおよびQVWDSSSDQGV(配列番号135)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GFTFSSYA(配列番号46)、IGTGGGT(配列番号136)およびARGTGYDGDQ(配列番号137)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC);それらの断片ならびにそれらの相同配列。
2.前記タンパク質が抗体である、実施形態1に記載の組換え抗原結合性タンパク質。
3.前記抗体がヒト抗体である、実施形態2に記載の組換え抗原結合性タンパク質。
4.前記抗体またはその抗原結合性断片がインタクトなIg、Fab、F(ab’)2、Fv、またはscFvである、実施形態2に記載の組換え抗原結合性タンパク質。
5.前記抗原結合性タンパク質がPD−1アゴニストである、実施形態1に記載の抗原結合性タンパク質。
6.前記抗原結合性タンパク質がPD−1アンタゴニストである、実施形態1に記載の抗原結合性タンパク質。
7.前記抗原結合性タンパク質がキメラ抗原受容体(CAR)である、実施形態1に記載の抗原結合性タンパク質。
8.実施形態1から7のいずれか一項に記載の抗原結合性タンパク質をコードする核酸。
9.実施形態8に記載の核酸を含むベクター。
10.実施形態1から7のいずれか一項に記載の抗原結合性タンパク質、実施形態8に記載の核酸または実施形態9に記載のベクターを含む細胞。
11.治療薬に接合した実施形態1から7のいずれか一項に記載の抗原結合性タンパク質。
12.前記治療薬が、薬物、毒素、放射性同位元素、タンパク質、またはペプチドである、実施形態11に記載の抗原結合性タンパク質。
13.実施形態1から7のいずれか一項に記載の抗原結合性タンパク質、実施形態8に記載の核酸、実施形態9に記載のベクター、実施形態10に記載の細胞または実施形態11もしくは12に記載の抗原結合性タンパク質を含む、医薬組成物。
14.医薬上許容され得る担体をさらに含む、実施形態13に記載の医薬組成物。
15.対象におけるT細胞応答を上昇させる方法であって、治療上有効量の、実施形態1から7のいずれか一項に記載の抗原結合性タンパク質またはその抗原結合性断片、実施形態8に記載の核酸、実施形態9に記載のベクター、実施形態10に記載の細胞、実施形態11もしくは12のいずれかに記載の抗原結合性タンパク質または実施形態13もしくは14のいずれかに記載の医薬組成物を、前記対象に投与することを含む、方法。
16.前記抗原結合性タンパク質またはその抗原結合性断片が、PD−1によって媒介されるシグナル伝達を阻害する、低下させる、調節する、または消失させる、実施形態15に記載の方法。
17.PD1−陽性疾患を有する対象を治療する方法であって、治療上有効量の、実施形態1から7のいずれか一項に記載の抗原結合性タンパク質またはその抗原結合性断片、実施形態8に記載の核酸、実施形態9に記載のベクター、実施形態10に記載の細胞、実施形態11もしくは12のいずれかに記載の抗原結合性タンパク質または実施形態13もしくは14のいずれかに記載の医薬組成物を、前記対象に投与することを含む、方法。
18.前記抗原結合性タンパク質またはその抗原結合性断片が、それに連結した細胞毒性部分を有する接合体である、実施形態17に記載の方法。
19.前記PD−1陽性疾患が癌である、実施形態17または18に記載の方法。
20.実施形態1から7のいずれか一項に記載の組換え抗PD1抗原結合性タンパク質またはその抗原結合性断片、実施形態8に記載の核酸、実施形態9に記載のベクター、実施形態10に記載の細胞、実施形態11もしくは12のいずれかに記載の抗原結合性タンパク質または実施形態13もしくは14のいずれかに記載の医薬組成物の、PD1リガンドに対するPD1の結合を阻害することによるPD1−陽性疾患の治療のための、使用。
21.前記PD1−陽性疾患が癌である、実施形態20に記載の使用。
22.実施形態1から7のいずれか一項に記載の組換え抗PD1抗原結合性タンパク質またはその抗原結合性断片、実施形態8に記載の核酸、実施形態9に記載のベクター、実施形態10に記載の細胞、実施形態11もしくは12のいずれかに記載の抗原結合性タンパク質または実施形態13もしくは14のいずれかに記載の医薬組成物の、PD−1シグナル経路を阻害することによる免疫調節のための、使用。
23.組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質をコードする核酸およびキメラ抗原受容体をコードする核酸を含むベクターであって、前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質が、前記キメラ抗原受容体と同一ではない、ベクター。
24.実施形態23に記載のベクターを含む、細胞。
25.組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質をコードする核酸およびキメラ抗原受容体をコードする核酸を含む細胞であって、前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質が、前記キメラ抗原受容体と同一ではない、細胞。
26.組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質およびキメラ抗原受容体を含む細胞であって、前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質が、前記キメラ抗原受容体と同一ではない、細胞。
27.前記キメラ抗原受容体がPD−1に特異的に結合するものではない、実施形態23から26のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞。
28.前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質が抗体である、実施形態23から27のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞。
29.前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質がヒト抗体である、実施形態23から28のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞。
30.前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質が、インタクトなIg、Fab、F(ab’)2、Fv、またはscFvである、実施形態23から29のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞。
31.前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質がPD−1アゴニストである、実施形態23から30のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞。
32.前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質がPD−1アンタゴニストである、実施形態23から30のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞。
33.前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質が分泌可能タンパク質である、実施形態23から32のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞。
34.前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質が、実施形態1に記載の抗原結合領域を含む、実施形態23から33のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞。
35.前記キメラ抗原受容体がCD−19に特異的に結合する、実施形態23から34のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞。
36.前記キメラ抗原受容体がヒトT細胞膜に挿入されることができる、実施形態23から35のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞。
37.前記細胞がT細胞である、実施形態24から36のいずれか一項に記載の細胞。
38.実施形態23から37のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞を含む、医薬組成物。
39.医薬上許容され得る担体をさらに含む、実施形態38に記載の医薬組成物。
40.対象におけるT細胞応答を上昇させる方法であって、治療上有効量の、実施形態23から37のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞、または実施形態38もしくは39の医薬組成物を前記対象に投与することを含み、前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質がPD−1アンタゴニストである、方法。
41.前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質が、PD−1によって媒介されるシグナル伝達を阻害する、低下させる、調節する、または消失させる、実施形態40に記載の方法。
42.対象におけるT細胞応答を低下させる方法であって、治療上有効量の実施形態23から37のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞、または実施形態38もしくは39に記載の医薬組成物を、前記対象に投与することを含み、前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質がPD−1アゴニストである、方法。
43.PD1−陽性疾患を有する対象を治療する方法であって、治療上有効量の、実施形態23から37のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞、または実施形態38もしくは39に記載の医薬組成物を、前記対象に投与することを含む、方法。
44.PD1−陽性疾患を有する対象を治療する方法であって、前記対象の少なくとも1つのT細胞に、組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質をコードする核酸およびキメラ抗原受容体をコードする核酸を形質導入することを含み、前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質が、前記キメラ抗原受容体と同一ではない、方法。
45.前記キメラ抗原受容体がPD−1に特異的に結合するものではない、実施形態44に記載の方法。
46.前記PD1−陽性疾患が癌である、実施形態42から45のいずれか一項に記載の方法。
47.実施形態23から37のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞、または実施形態38もしくは39に記載の医薬組成物の、PD1リガンドへのPD1の結合を阻害することによるPD1−陽性疾患の治療のための、使用。
48.前記PD1−陽性疾患が癌である、実施形態47に記載の使用。
49.実施形態23から37のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞、または実施形態38もしくは39に記載の医薬組成物の、PD−1シグナル経路を阻害することによる免疫調節のための、使用。
50.実施形態5に記載の抗原結合性タンパク質、実施形態23から37のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞、または実施形態38もしくは39に記載の医薬組成物の、自己免疫疾患の治療のための使用であって、前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質がPD−1アゴニストである、使用。
51.前記抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質およびキメラ抗原受容体の少なくとも1つが治療薬と接合している、実施形態23から37のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞。
52.前記治療薬が、薬物、毒素、放射性同位元素、タンパク質、またはペプチドである、実施形態51に記載のベクターまたは細胞。
53.前記抗原結合性タンパク質または前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質がPD−1アゴニストであり、前記PD1−陽性疾患が自己免疫疾患である、実施形態17および42から45のいずれか一項に記載の方法。
参考文献
Brentjens, R. J., M. L. Davila, et al. (2013). "CD19-targeted T cells rapidly induce molecular remissions in adults with chemotherapy-refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia." Sci Transl Med 5(177): 177ra138.
Brentjens, R. J., J. B. Latouche, et al. (2003). "Eradication of systemic B-cell tumors by genetically targeted human T lymphocytes co-stimulated by CD80 and interleukin-15." Nat Med 9(3): 279-286.
Brentjens, R. J., E. Santos, et al. (2007). "Genetically targeted T cells eradicate systemic acute lymphoblastic leukemia xenografts." Clin Cancer Res 13 (18 Pt 1): 5426-5435.
Davila, M. L., I. Riviere, et al. (2014). "Efficacy and toxicity management of 19-28z CAR T cell therapy in B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia." Sci Transl Med 6(224): 224ra225.
Claims (24)
- (A)配列番号53のアミノ酸配列を含む抗原結合領域;
(B)配列番号49および51のアミノ酸配列をそれぞれ有する可変軽鎖(VL)および可変重鎖(VH)を含む抗原結合領域;
(C)アミノ酸配列NIGSKS(配列番号34)、YDSおよびQVWDSSSDYV(配列番号45)をそれぞれ有するLCCDR1、LCCDR2およびLCCDR3を含む軽鎖(LC)ならびにアミノ酸配列GFTFSSYA(配列番号46)、ISGSGGST(配列番号47)およびARNYISMFDS(配列番号48)をそれぞれ有するHCCDR1、HCCDR2およびHCCDR3を含む重鎖(HC)を含む抗原結合領域;
の1つを含む組換え抗原結合性タンパク質であって、
前記抗原結合性タンパク質は分泌可能scFvを含み、前記分泌可能scFvはプログラム細胞死(PD−1)に特異的に結合し、PD−1とそのリガンドであるPD−L1との結合を阻害する、前記組換え抗原結合性タンパク質。 - 前記抗原結合性タンパク質がPD−1アンタゴニストである、請求項1に記載の抗原結合性タンパク質。
- 前記抗原結合性タンパク質がキメラ抗原受容体(CAR)である、請求項1に記載の抗原結合性タンパク質。
- 請求項1〜3のいずれか一項に記載の抗原結合性タンパク質をコードする核酸。
- 請求項4に記載の核酸を含むベクター。
- 請求項1〜3のいずれか一項に記載の抗原結合性タンパク質、請求項4に記載の核酸または請求項5に記載のベクターを含む細胞。
- 請求項1〜3のいずれか一項に記載の抗原結合性タンパク質、請求項4に記載の核酸、請求項5に記載のベクター、又は請求項6に記載の細胞を含む、医薬組成物。
- 請求項1〜3のいずれか一項に記載の組換え抗PD1抗原結合性タンパク質、請求項4に記載の核酸、請求項5に記載のベクター、請求項6に記載の細胞、または請求項7に記載の医薬組成物の、PD1リガンドへのPD1結合を阻害することによる、PD1−陽性疾患の治療のための医薬の製造への、使用。
- 請求項1〜3のいずれか一項に記載の組換え抗PD1抗原結合性タンパク質、請求項4に記載の核酸、請求項5に記載のベクター、請求項6に記載の細胞、または請求項7に記載の医薬組成物の、PD−1シグナル経路を阻害することによる、免疫調節のための医薬の製造への、使用。
- 請求項1〜3のいずれか一項に記載の組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質をコードする核酸およびキメラ抗原受容体をコードする核酸を含むベクターであって、前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質が、前記キメラ抗原受容体と同一ではない、ベクター。
- 請求項10に記載のベクターを含む細胞。
- 請求項1〜3のいずれか一項に記載の組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質をコードする核酸およびキメラ抗原受容体をコードする核酸を含む細胞であって、前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質が、前記キメラ抗原受容体と同一ではない、細胞。
- 請求項1〜3のいずれか一項に記載の組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質およびキメラ抗原受容体を含む細胞であって、前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質が、前記キメラ抗原受容体と同一ではない、細胞。
- 前記キメラ抗原受容体がPD−1に特異的に結合するものではない、請求項10〜13のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞。
- 前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質が抗体である、請求項10〜14のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞。
- 前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質がヒト抗体である、請求項10〜15のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞。
- 前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質がPD−1アンタゴニストである、請求項10〜16のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞。
- 前記組換え抗PD−1抗原結合性タンパク質が、請求項1に記載の抗原結合領域を含む、請求項10〜17のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞。
- 前記キメラ抗原受容体がCD−19に特異的に結合する、請求項10〜18のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞。
- 前記キメラ抗原受容体が、ヒトT細胞膜に挿入されることができる、請求項10〜19のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞。
- 前記細胞がT細胞である、請求項11〜20のいずれか一項に記載の細胞。
- 請求項10〜21のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞を含む、医薬組成物。
- 請求項10〜21のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞、または請求項22に記載の医薬組成物の、PD1リガンドへのPD1結合を阻害することによる、PD1−陽性疾患の治療のための医薬の製造への、使用。
- 請求項10〜21のいずれか一項に記載のベクターまたは細胞、または請求項22に記載の医薬組成物の、PD−1シグナル経路を阻害することによる、免疫調節のための医薬の製造への、使用。
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021117516A JP2021177768A (ja) | 2015-06-23 | 2021-07-16 | 新規pd−1免疫調節剤 |
Applications Claiming Priority (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201562183297P | 2015-06-23 | 2015-06-23 | |
| US62/183,297 | 2015-06-23 | ||
| US201562266398P | 2015-12-11 | 2015-12-11 | |
| US62/266,398 | 2015-12-11 | ||
| PCT/US2016/039015 WO2016210129A1 (en) | 2015-06-23 | 2016-06-23 | Novel pd-1 immune modulating agents |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021117516A Division JP2021177768A (ja) | 2015-06-23 | 2021-07-16 | 新規pd−1免疫調節剤 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2018518540A JP2018518540A (ja) | 2018-07-12 |
| JP2018518540A5 JP2018518540A5 (ja) | 2019-08-08 |
| JP6974311B2 true JP6974311B2 (ja) | 2021-12-01 |
Family
ID=56373127
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018519261A Active JP6974311B2 (ja) | 2015-06-23 | 2016-06-23 | 新規pd−1免疫調節剤 |
| JP2021117516A Ceased JP2021177768A (ja) | 2015-06-23 | 2021-07-16 | 新規pd−1免疫調節剤 |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021117516A Ceased JP2021177768A (ja) | 2015-06-23 | 2021-07-16 | 新規pd−1免疫調節剤 |
Country Status (11)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US11136392B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP3313883B1 (ja) |
| JP (2) | JP6974311B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR20180019725A (ja) |
| CN (2) | CN108337890B (ja) |
| AU (1) | AU2016281641B2 (ja) |
| CA (1) | CA3006224A1 (ja) |
| HK (1) | HK1254803A1 (ja) |
| IL (1) | IL256463A (ja) |
| TW (1) | TWI773647B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2016210129A1 (ja) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021177768A (ja) * | 2015-06-23 | 2021-11-18 | メモリアル スローン ケタリング キャンサー センター | 新規pd−1免疫調節剤 |
Families Citing this family (43)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA2986254A1 (en) | 2015-05-18 | 2016-11-24 | TCR2 Therapeutics Inc. | Compositions and methods for tcr reprogramming using fusion proteins |
| SG10201913303XA (en) | 2015-07-13 | 2020-03-30 | Cytomx Therapeutics Inc | Anti-pd-1 antibodies, activatable anti-pd-1 antibodies, and methods of use thereof |
| CN114605548A (zh) | 2015-09-01 | 2022-06-10 | 艾吉纳斯公司 | 抗-pd-1抗体及其使用方法 |
| KR20180054824A (ko) | 2015-09-29 | 2018-05-24 | 셀진 코포레이션 | Pd-1 결합 단백질 및 이의 사용 방법 |
| UA124925C2 (en) | 2015-10-02 | 2021-12-15 | Hoffmann La Roche | Bispecific antibodies specific for pd1 and tim3 |
| SG11201803520PA (en) | 2015-11-03 | 2018-05-30 | Janssen Biotech Inc | Antibodies specifically binding pd-1 and their uses |
| WO2017133175A1 (en) * | 2016-02-04 | 2017-08-10 | Nanjing Legend Biotech Co., Ltd. | Engineered mammalian cells for cancer therapy |
| EP3432924A1 (en) | 2016-03-23 | 2019-01-30 | Novartis AG | Cell secreted minibodies and uses thereof |
| US11446398B2 (en) | 2016-04-11 | 2022-09-20 | Obsidian Therapeutics, Inc. | Regulated biocircuit systems |
| BR112019004733A2 (pt) | 2016-09-19 | 2019-05-28 | Celgene Corp | métodos de tratamento de distúrbios imunes usando proteínas de ligação a pd-1 |
| US10766958B2 (en) | 2016-09-19 | 2020-09-08 | Celgene Corporation | Methods of treating vitiligo using PD-1 binding antibodies |
| CA3044593A1 (en) | 2016-11-22 | 2018-05-31 | TCR2 Therapeutics Inc. | Compositions and methods for tcr reprogramming using fusion proteins |
| MA50948A (fr) | 2016-12-07 | 2020-10-14 | Agenus Inc | Anticorps et procédés d'utilisation de ceux-ci |
| EP3557671A4 (en) * | 2016-12-19 | 2020-08-19 | Showa Denko K.K. | PROCEDURE FOR OPERATING A REDOX FLOW BATTERY |
| EP3596108A4 (en) | 2017-03-15 | 2020-12-23 | Pandion Operations, Inc. | TARGETED IMMUNOTOLERANCE |
| PE20191494A1 (es) | 2017-04-03 | 2019-10-21 | Hoffmann La Roche | Inmunoconjugados de un anticuerpo anti-pd-1 con un il-2 mutante o con il-15 |
| TWI690538B (zh) | 2017-04-05 | 2020-04-11 | 瑞士商赫孚孟拉羅股份公司 | 特異性結合至pd1至lag3的雙特異性抗體 |
| CA3053360A1 (en) * | 2017-04-05 | 2018-10-11 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Anti-lag3 antibodies |
| WO2018195348A1 (en) * | 2017-04-19 | 2018-10-25 | University Of Southern California | Compositions and methods for treating cancer |
| SG10201913656TA (en) | 2017-04-26 | 2020-03-30 | Eureka Therapeutics Inc | Cells expressing chimeric activating receptors and chimeric stimulating receptors and uses thereof |
| CN110809582B (zh) * | 2017-05-01 | 2023-12-22 | 儿童医疗中心有限公司 | 涉及抗pd1抗体试剂的方法以及组合物 |
| BR112019024127A2 (pt) | 2017-05-24 | 2020-06-23 | Pandion Therapeutics, Inc. | Imunotolerância alvejada |
| IL271833B2 (en) * | 2017-07-06 | 2024-09-01 | Merus Nv | Antibodies that regulate biological activity expressed by a cell |
| US11884934B2 (en) * | 2017-07-21 | 2024-01-30 | Washington University | Methods and compositions for T cell activation |
| US10174092B1 (en) | 2017-12-06 | 2019-01-08 | Pandion Therapeutics, Inc. | IL-2 muteins |
| US10946068B2 (en) | 2017-12-06 | 2021-03-16 | Pandion Operations, Inc. | IL-2 muteins and uses thereof |
| WO2019152743A1 (en) * | 2018-01-31 | 2019-08-08 | Celgene Corporation | Combination therapy using adoptive cell therapy and checkpoint inhibitor |
| WO2019161133A1 (en) | 2018-02-15 | 2019-08-22 | Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center | Foxp3 targeting agent compositions and methods of use for adoptive cell therapy |
| AR114127A1 (es) | 2018-03-02 | 2020-07-22 | Lilly Co Eli | Anticuerpos agonistas contra pd-1 y usos de estos |
| BR112020021271A2 (pt) | 2018-04-17 | 2021-01-26 | Celldex Therapeutics, Inc. | construtos bispecíficos e anticorpos anti- cd27 e anti-pd-l1 |
| CN112673093A (zh) * | 2018-07-04 | 2021-04-16 | 赛通免疫治疗公司 | 靶向flt3、pd-1和/或pd-l1的免疫疗法的组合物和方法 |
| CN111320690B (zh) * | 2018-12-17 | 2022-04-05 | 程联胜 | 一种抗人Tim3单克隆抗体及其应用 |
| CN111748580B (zh) * | 2019-03-28 | 2022-09-13 | 百奥泰生物制药股份有限公司 | 一种检测免疫检查点抗体活性的方法 |
| CN111892655B (zh) * | 2019-05-06 | 2022-10-28 | 四川大学 | 抗pd-1纳米抗体的筛选及应用 |
| EP3972992A4 (en) | 2019-05-20 | 2023-07-19 | Pandion Operations, Inc. | ANTI-MADCAM IMMUNE TOLERANCE |
| KR20220030956A (ko) | 2019-07-05 | 2022-03-11 | 오노 야꾸힝 고교 가부시키가이샤 | Pd-1/cd3 이중 특이성 단백질에 의한 혈액암 치료 |
| EP3996735A4 (en) * | 2019-07-12 | 2023-07-19 | The Research Foundation for The State University of New York | COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR BLOCKING AND BINDING CXCR4 TO MODULATE CELLULAR FUNCTION |
| TW202120550A (zh) | 2019-08-08 | 2021-06-01 | 日商小野藥品工業股份有限公司 | 雙特異性蛋白質 |
| CN112852740A (zh) * | 2019-11-27 | 2021-05-28 | 深圳市菲鹏生物治疗股份有限公司 | Car-t细胞和检测方法 |
| US11981715B2 (en) | 2020-02-21 | 2024-05-14 | Pandion Operations, Inc. | Tissue targeted immunotolerance with a CD39 effector |
| CN114437229B (zh) * | 2020-11-01 | 2024-03-12 | 复旦大学 | 携带pd-1単链抗体且靶向egfr抗原的car t免疫细胞的制备及其用途 |
| CN112812174A (zh) * | 2021-01-15 | 2021-05-18 | 新乡学院 | 猪pd-l14qn-af表位多肽及其应用 |
| CN115521378B (zh) * | 2021-07-23 | 2023-12-22 | 南京吉盛澳玛生物医药有限公司 | Pd-l1抗体及其用途 |
Family Cites Families (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4834976A (en) * | 1986-07-03 | 1989-05-30 | Genetic Systems Corporation | Monoclonal antibodies to pseudomonas aeruginosa flagella |
| ATE514713T1 (de) * | 2002-12-23 | 2011-07-15 | Wyeth Llc | Antikörper gegen pd-1 und ihre verwendung |
| NZ563193A (en) * | 2005-05-09 | 2010-05-28 | Ono Pharmaceutical Co | Human monoclonal antibodies to programmed death 1(PD-1) and methods for treating cancer using anti-PD-1 antibodies alone or in combination with other immunotherapeutics |
| CA2683370C (en) * | 2007-04-03 | 2022-12-13 | Micromet Ag | Cross-species-specific binding domain |
| EP2170959B1 (en) * | 2007-06-18 | 2013-10-02 | Merck Sharp & Dohme B.V. | Antibodies to human programmed death receptor pd-1 |
| CN107266584B (zh) * | 2011-07-29 | 2022-05-13 | 宾夕法尼亚大学董事会 | 转换共刺激受体 |
| EP2948475A2 (en) | 2013-01-23 | 2015-12-02 | AbbVie Inc. | Methods and compositions for modulating an immune response |
| CN103965363B (zh) * | 2013-02-06 | 2021-01-15 | 上海白泽生物科技有限公司 | 与pd-1和vegf高效结合的融合蛋白、其编码序列及用途 |
| RS60759B1 (sr) * | 2013-02-26 | 2020-10-30 | Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center | Sastavi i postupci za imunoterapiju |
| CN103242448B (zh) * | 2013-05-27 | 2015-01-14 | 郑州大学 | 一种全人源化抗pd-1单克隆抗体及其制备方法和应用 |
| CN104558177B (zh) * | 2013-10-25 | 2020-02-18 | 苏州思坦维生物技术股份有限公司 | 拮抗抑制程序性死亡受体pd-1与其配体结合的单克隆抗体及其编码序列与用途 |
| EP3227436A4 (en) * | 2014-12-05 | 2018-06-20 | Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center | Chimeric antigen receptors targeting fc receptor-like 5 and uses thereof |
| CN104479020B (zh) * | 2014-12-26 | 2019-08-02 | 上海复宏汉霖生物技术股份有限公司 | 一种抗pd-1人源抗体 |
| CA2986713A1 (en) * | 2015-05-22 | 2016-12-01 | Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center | T cell receptor-like antibodies specific for a prame peptide |
| EP3313883B1 (en) * | 2015-06-23 | 2023-12-06 | Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center | Novel pd-1 immune modulating agents |
| SG11201804656PA (en) * | 2015-12-04 | 2018-06-28 | Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center | Antibodies targeting fc receptor-like 5 and methods of use |
| CN109069627A (zh) * | 2016-01-14 | 2018-12-21 | 纪念斯隆-凯特琳癌症中心 | 对foxp3衍生肽特异性的t细胞受体样抗体 |
| CA3039992A1 (en) * | 2016-11-02 | 2018-05-11 | Jounce Therapeutics, Inc. | Antibodies to pd-1 and uses thereof |
| JP2020536531A (ja) * | 2017-09-26 | 2020-12-17 | ロングウッド ユニバーシティーLongwood University | 免疫療法としてのpd1特異的キメラ抗原受容体 |
-
2016
- 2016-06-23 EP EP16736667.3A patent/EP3313883B1/en active Active
- 2016-06-23 CN CN201680037151.1A patent/CN108337890B/zh active Active
- 2016-06-23 AU AU2016281641A patent/AU2016281641B2/en active Active
- 2016-06-23 KR KR1020187002014A patent/KR20180019725A/ko active Search and Examination
- 2016-06-23 WO PCT/US2016/039015 patent/WO2016210129A1/en active Application Filing
- 2016-06-23 TW TW105119709A patent/TWI773647B/zh not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2016-06-23 CA CA3006224A patent/CA3006224A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2016-06-23 CN CN202111160281.3A patent/CN114133448A/zh active Pending
- 2016-06-23 JP JP2018519261A patent/JP6974311B2/ja active Active
-
2017
- 2017-12-20 US US15/849,107 patent/US11136392B2/en active Active
- 2017-12-20 IL IL256463A patent/IL256463A/en unknown
-
2018
- 2018-10-31 HK HK18113888.8A patent/HK1254803A1/zh unknown
-
2021
- 2021-07-16 JP JP2021117516A patent/JP2021177768A/ja not_active Ceased
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021177768A (ja) * | 2015-06-23 | 2021-11-18 | メモリアル スローン ケタリング キャンサー センター | 新規pd−1免疫調節剤 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3313883A1 (en) | 2018-05-02 |
| US20180127502A1 (en) | 2018-05-10 |
| WO2016210129A1 (en) | 2016-12-29 |
| TW201718648A (zh) | 2017-06-01 |
| KR20180019725A (ko) | 2018-02-26 |
| CN114133448A (zh) | 2022-03-04 |
| JP2021177768A (ja) | 2021-11-18 |
| US11136392B2 (en) | 2021-10-05 |
| IL256463A (en) | 2018-02-28 |
| AU2016281641B2 (en) | 2022-01-20 |
| CN108337890B (zh) | 2021-10-15 |
| JP2018518540A (ja) | 2018-07-12 |
| AU2016281641A1 (en) | 2018-02-08 |
| CN108337890A (zh) | 2018-07-27 |
| HK1254803A1 (zh) | 2019-07-26 |
| TWI773647B (zh) | 2022-08-11 |
| EP3313883B1 (en) | 2023-12-06 |
| CA3006224A1 (en) | 2016-12-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6974311B2 (ja) | 新規pd−1免疫調節剤 | |
| US12077583B2 (en) | Antibodies specific to human NECTIN4 | |
| JP7448896B2 (ja) | 抗cd33免疫療法によりがんを処置するための組成物および方法 | |
| US20240018257A1 (en) | Antibodies specific to human poliovirus receptor (pvr) | |
| EP3344658B1 (en) | Antibodies specific to human t-cell immunoglobulin and itim domain (tigit) | |
| CN110511278B (zh) | 抗b7-h6抗体、融合蛋白及其使用方法 | |
| US20210038646A1 (en) | Chimeric antigen receptors targeting the tumor microenvironment | |
| CA3143995A1 (en) | Anti-tigit antibodies | |
| JP7504142B2 (ja) | 抗cd19免疫療法によりがんを処置するための組成物および方法 | |
| KR20200092301A (ko) | 다중-특이적 항체 및 이를 제조하는 방법 및 이의 용도 | |
| JP2023554422A (ja) | がんの治療のための多重特異性抗体 | |
| JP2024012258A (ja) | Cd22に特異的なヒト化抗体およびそれを用いたキメラ抗原受容体 | |
| CN114616245A (zh) | 一种抗cd38的抗体及其用途 | |
| US12121579B2 (en) | Antibodies specific to human t-cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain (TIGIT) | |
| WO2024121414A1 (en) | Chimeric antigen receptor | |
| WO2023200873A2 (en) | Chimeric antigen receptor compositions and methods of using the same | |
| CN115335123A (zh) | 人4-1bb激动剂抗体及其使用方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20190624 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20190624 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20200707 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20201007 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20210316 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20210716 |
|
| C60 | Trial request (containing other claim documents, opposition documents) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: C60 Effective date: 20210716 |
|
| A911 | Transfer to examiner for re-examination before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A911 Effective date: 20210826 |
|
| C21 | Notice of transfer of a case for reconsideration by examiners before appeal proceedings |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: C21 Effective date: 20210831 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20211012 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20211104 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6974311 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |