JP6683083B2 - Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof - Google Patents
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6683083B2 JP6683083B2 JP2016184257A JP2016184257A JP6683083B2 JP 6683083 B2 JP6683083 B2 JP 6683083B2 JP 2016184257 A JP2016184257 A JP 2016184257A JP 2016184257 A JP2016184257 A JP 2016184257A JP 6683083 B2 JP6683083 B2 JP 6683083B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- layer
- type
- forming
- semiconductor
- conductivity type
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims description 128
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 19
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 claims description 411
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 claims description 67
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 30
- 230000007480 spreading Effects 0.000 claims description 21
- 238000003892 spreading Methods 0.000 claims description 21
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 claims description 11
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000011229 interlayer Substances 0.000 claims description 11
- 238000000137 annealing Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000005468 ion implantation Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000000149 penetrating effect Effects 0.000 claims 2
- HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon carbide Chemical compound [Si+]#[C-] HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 66
- 229910010271 silicon carbide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 66
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 11
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 8
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 6
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 6
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 4
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Argon Chemical compound [Ar] XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007772 electrode material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000001020 plasma etching Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000002344 surface layer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000003213 activating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052786 argon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910003460 diamond Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010432 diamond Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005684 electric field Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 125000004435 hydrogen atom Chemical class [H]* 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000059 patterning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/76—Unipolar devices, e.g. field effect transistors
- H01L29/772—Field effect transistors
- H01L29/78—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate
- H01L29/7801—DMOS transistors, i.e. MISFETs with a channel accommodating body or base region adjoining a drain drift region
- H01L29/7802—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors
- H01L29/7813—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors with trench gate electrode, e.g. UMOS transistors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/30—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26
- H01L21/324—Thermal treatment for modifying the properties of semiconductor bodies, e.g. annealing, sintering
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0603—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions
- H01L29/0607—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration
- H01L29/0611—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices
- H01L29/0615—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices by the doping profile or the shape or the arrangement of the PN junction, or with supplementary regions, e.g. junction termination extension [JTE]
- H01L29/063—Reduced surface field [RESURF] pn-junction structures
- H01L29/0634—Multiple reduced surface field (multi-RESURF) structures, e.g. double RESURF, charge compensation, cool, superjunction (SJ), 3D-RESURF, composite buffer (CB) structures
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/08—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions with semiconductor regions connected to an electrode carrying current to be rectified, amplified or switched and such electrode being part of a semiconductor device which comprises three or more electrodes
- H01L29/0843—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices
- H01L29/0847—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices of field-effect transistors with insulated gate
- H01L29/0852—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices of field-effect transistors with insulated gate of DMOS transistors
- H01L29/0873—Drain regions
- H01L29/0878—Impurity concentration or distribution
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/08—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions with semiconductor regions connected to an electrode carrying current to be rectified, amplified or switched and such electrode being part of a semiconductor device which comprises three or more electrodes
- H01L29/0843—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices
- H01L29/0847—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices of field-effect transistors with insulated gate
- H01L29/0852—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices of field-effect transistors with insulated gate of DMOS transistors
- H01L29/0873—Drain regions
- H01L29/0886—Shape
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/10—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions with semiconductor regions connected to an electrode not carrying current to be rectified, amplified or switched and such electrode being part of a semiconductor device which comprises three or more electrodes
- H01L29/1095—Body region, i.e. base region, of DMOS transistors or IGBTs
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/40—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/41—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape, relative sizes or dispositions
- H01L29/417—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape, relative sizes or dispositions carrying the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/41725—Source or drain electrodes for field effect devices
- H01L29/41766—Source or drain electrodes for field effect devices with at least part of the source or drain electrode having contact below the semiconductor surface, e.g. the source or drain electrode formed at least partially in a groove or with inclusions of conductor inside the semiconductor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66007—Multistep manufacturing processes
- H01L29/66053—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having a semiconductor body comprising crystalline silicon carbide
- H01L29/66068—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having a semiconductor body comprising crystalline silicon carbide the devices being controllable only by the electric current supplied or the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched, e.g. three-terminal devices
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/12—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed
- H01L29/16—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed including, apart from doping materials or other impurities, only elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table
- H01L29/1608—Silicon carbide
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Composite Materials (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Junction Field-Effect Transistors (AREA)
Description
本発明は、半導体装置およびその製造方法に関し、特に炭化珪素(以下、SiCという)などのワイドバンドギャップ半導体を用いた半導体素子およびその製造方法に適用されると好適なものである。 The present invention relates to a semiconductor device and a method for manufacturing the same, and is particularly suitable for being applied to a semiconductor element using a wide band gap semiconductor such as silicon carbide (hereinafter referred to as SiC) and a method for manufacturing the same.
SiC半導体装置において、オン抵抗値の低減はスイッチング損失の低減などを図るために必要であるが、負荷短絡時に半導体素子に流れる電流値は、半導体素子のオン抵抗値に反比例して大きくなる。すなわち、オン抵抗値の小さい半導体素子ほど、負荷短絡時の飽和電流が大きな電流値となる。その結果、自己発熱により半導体素子の破損が発生し易くなるので、負荷短絡時におけるSiC半導体装置の耐量が低下することになる。このため、オン抵抗値の低減と負荷短絡時におけるSiC半導体装置の耐量向上はトレードオフの関係を有しているが、このトレードオフの関係の改善、つまり低オン抵抗値と低飽和電流の両立が望まれている。 In the SiC semiconductor device, the reduction of the on-resistance value is necessary to reduce the switching loss and the like, but the current value flowing through the semiconductor element at the time of load short circuit increases in inverse proportion to the on-resistance value of the semiconductor element. That is, the smaller the ON resistance value of the semiconductor element, the larger the saturation current at the time of load short circuit becomes. As a result, the semiconductor element is likely to be damaged due to self-heating, so that the withstand capability of the SiC semiconductor device at the time of load short circuit is reduced. Therefore, there is a trade-off relationship between the reduction of the on-resistance value and the improvement of the withstand capacity of the SiC semiconductor device at the time of load short-circuit. However, the improvement of this trade-off relationship, that is, a low on-resistance value and a low saturation current are compatible. Is desired.
これに対して、特許文献1において、低オン抵抗値と低飽和電流を両立させるために、p型ベース領域のうちのチャネル近傍の部分の不純物濃度とJFET部分の不純物濃度が異なった濃度となるようにした構造が提案されている。具体的には、深さ方向においてp型ベース領域の不純物濃度に勾配をつけ、チャネル近傍では不純物濃度が低く、下方になるにしたがって不純物濃度が高くなるようにしている。このような構成によれば、p型ベース領域の不純物濃度がチャネル近傍では低くされているため、低オン抵抗が実現できる。また、p型ベース領域のうちのJFET部分については所望の不純物濃度とすることで、隣り合うp型ベース領域間におけるn型ドリフト層がピンチオフされるようにでき、低飽和電流を実現できる。したがって、低オン抵抗値と低飽和電流を両立することが可能となる。
On the other hand, in
しかしながら、特許文献1のSiC半導体装置では、より低飽和電流として高い耐量が得られるように、p型ベース領域のうちのJFET部分の不純物濃度を濃くしたり、JFET部分において隣り合うp型ベース領域の間隔を狭くすると、JFET抵抗が増大する。このため、低オン抵抗値と低飽和電流を両立することができなくなる。
However, in the SiC semiconductor device of
本発明は上記点に鑑みて、低オン抵抗値と低飽和電流を両立することができる半導体装置およびその製造方法を提供することを目的とする。 In view of the above points, an object of the present invention is to provide a semiconductor device that can achieve both a low on-resistance value and a low saturation current, and a manufacturing method thereof.
上記目的を達成するため、請求項1に記載のSiC半導体装置は、半導体で構成された第1または第2導電型の基板(1)と、基板の上に形成され、基板よりも低不純物濃度とされた第1導電型の半導体からなるドリフト層(2)と、ドリフト層の上に形成された第2導電型の半導体からなる第2導電型領域(3、5、6、8、71)と、ドリフト層上に形成され、第2導電型領域に挟まれて配置されたJFET部(2a)と、第2導電型領域の上に形成され、ドリフト層よりも高濃度の第1導電型の半導体からなるソース領域(7)と、第2導電型領域の一部をチャネル領域として、該チャネル領域上に形成されたゲート絶縁膜(10)と、ゲート絶縁膜上に形成されたゲート電極(11)と、ゲート電極およびゲート絶縁膜を覆うと共にコンタクトホールが形成された層間絶縁膜(12)と、コンタクトホールを通じて、ソース領域に電気的に接続されたソース電極(13)と、基板の裏面側に形成されたドレイン電極(14)とを有した構成とされている。具体的には、ゲート電極に対してゲート電圧を印加すると共にドレイン電極に対して印加するドレイン電圧として通常作動時の電圧を印加することでチャネル領域を形成し、ソース領域およびJFET層を介して、ソース電極およびドレイン電極の間に電流を流す反転型の半導体素子とされている。このような構成において、JFET部と第2導電型領域との間には、ドレイン電圧として通常作動時の電圧が印加されているときには第2導電型領域からJFET部に伸びる空乏層の伸び量を抑制しつつJFET部を通じて電流を流し、ドレイン電圧として通常動作時の電圧よりも高い電圧が印加されると空乏層によってJFET部をピンチオフさせる空乏層調整層(20、30)が形成されている。
In order to achieve the above object, the SiC semiconductor device according to
このように、少なくともディープ層のうちの側面、つまりディープ層とJFET部との間に空乏層調整層を形成している。このため、通常作動時においては、空乏層調整層が空乏層の伸びを調整する層として機能し、JFET部内への空乏層の伸びを抑制することが可能になり、電流経路が狭くなることを抑制できるため、低オン抵抗を図ることが可能となる。 Thus, the depletion layer adjusting layer is formed at least on the side surface of the deep layer, that is, between the deep layer and the JFET portion. Therefore, during normal operation, the depletion layer adjustment layer functions as a layer that adjusts the extension of the depletion layer, and it is possible to suppress the extension of the depletion layer into the JFET portion, which narrows the current path. Since it can be suppressed, low on-resistance can be achieved.
また、負荷短絡などによってドレイン電圧が通常作動時の電圧よりも高くなると、ディープ層側から空乏層調整層へ伸びる空乏層が空乏層調整層の厚みよりも伸び、JFET部が即座にピンチオフされる。これにより、低飽和電流を維持することができ、負荷短絡等によるSiC半導体装置の耐量を向上することが可能となる。したがって、低オン抵抗値と低飽和電流を両立することができるSiC半導体装置とすることが可能となる。 Also, when the drain voltage becomes higher than the voltage during normal operation due to load short circuit, the depletion layer extending from the deep layer side to the depletion layer adjustment layer extends beyond the thickness of the depletion layer adjustment layer, and the JFET portion is immediately pinched off. . This makes it possible to maintain a low saturation current and improve the withstand capability of the SiC semiconductor device due to a load short circuit or the like. Therefore, it is possible to provide a SiC semiconductor device that can achieve both a low on-resistance value and a low saturation current.
なお、上記各手段の括弧内の符号は、後述する実施形態に記載の具体的手段との対応関係の一例を示すものである。 The reference numerals in parentheses of the above means indicate an example of the correspondence with the specific means described in the embodiments described later.
以下、本発明の実施形態について図に基づいて説明する。なお、以下の各実施形態相互において、互いに同一もしくは均等である部分には、同一符号を付して説明を行う。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. In each of the following embodiments, the same or equivalent portions will be denoted by the same reference numerals for description.
(第1実施形態)
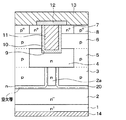
第1実施形態について説明する。本実施形態にかかるSiC半導体装置は、図1に示すように、半導体素子として縦型MOSFETが形成されたものである。縦型MOSFETは、SiC半導体装置のうちのセル領域に形成されており、そのセル領域を囲むように外周耐圧構造が形成されることでSiC半導体装置が構成されているが、ここでは縦型MOSFETのみ図示してある。なお、以下の説明では、図1の左右方向を幅方向とし、上下方向を厚み方向もしくは深さ方向として説明を行う。
(First embodiment)
The first embodiment will be described. As shown in FIG. 1, the SiC semiconductor device according to the present embodiment has a vertical MOSFET formed as a semiconductor element. The vertical MOSFET is formed in the cell region of the SiC semiconductor device, and the outer periphery breakdown voltage structure is formed so as to surround the cell region to configure the SiC semiconductor device. Only shown. In the following description, the left-right direction of FIG. 1 is the width direction and the up-down direction is the thickness direction or the depth direction.
SiC半導体装置には、SiCからなるn+型基板1が半導体基板として用いられている。n+型基板1の主表面上にSiCからなるn-型ドリフト層2が形成されている。n-型ドリフト層2は、n+型基板1から離れた位置において幅狭とされたJFET部2aと連結されており、このJFET部2aの両側にSiCからなるp型ディープ層3が形成されている。本実施形態の場合、JFET部2aは、後述するトレンチゲート構造の長手方向に沿って延設された短冊形状とされ、JFET部2aの周囲がp型ディープ層3とされている。
An n + type substrate 1 made of SiC is used as a semiconductor substrate in a SiC semiconductor device. An n −
これらn-型ドリフト層2およびJFET部2aとp型ディープ層3との間には高濃度n型層20が形成されている。本実施形態では、この高濃度n型層20が空乏層調整層として機能する。より詳しくは、高濃度n型層20は、少なくともp型ディープ層3のうちの側面、つまりp型ディープ層3とJFET部2aとの間に形成されている。本実施形態の場合は、n-型ドリフト層2の上面、つまりn-型ドリフト層2とp型ディープ層3の底部との間やn-型ドリフト層2のうちのJFET部2aとの境界位置にも高濃度n型層20が形成されている。
A high-concentration n-
n+型基板1は、表面が(0001)Si面とされ、例えばn型不純物濃度が5.9×1018/cm3とされ、厚さが100μmとされている。n-型ドリフト層2は、例えばn型不純物濃度が1.0×1016/cm3とされ、厚さが8.0μmとされている。また、JFET部2aについては、例えばn型不純物濃度が1.0×1016/cm3とされ、幅が0.1μmとされている。p型ディープ層3は、例えばp型不純物濃度が1.0×1018/cm3とされ、厚さが1.0μmとされている。高濃度n型層20は、n-型ドリフト層2よりも高濃度とされており、例えばn型不純物濃度が1.0×1018/cm3とされている。高濃度n型層20の厚さについては、p型ディープ層3の側面では0.05μm、n-型ドリフト層2の上面では0.07μmとされている。
The surface of the n + type substrate 1 is a (0001) Si surface, the n type impurity concentration is 5.9 × 10 18 / cm 3, and the thickness is 100 μm. The n −
また、JFET部2aおよびp型ディープ層3の上には、JFET部2aと連結され、かつ、JFET部2aよりも幅広とされたSiCからなるn型電流分散層4が形成されている。さらに、p型ディープ層3の上には、p型ディープ層3よりも幅が狭くされたSiCからなるp型連結層5が形成されている。
On the
n型電流分散層4は、後述するようにチャネルを通じて流れる電流が幅方向に拡散できるようにする層であり、JFET部2aよりも高濃度とされており、例えばn型不純物濃度が3×1017/cm3とされ、厚さが0.6μmとされている。また、p型連結層5は、p型ディープ層3と同じ濃度とされていても良いが、本実施形態ではp型ディープ層3よりも高濃度とされ、例えばp型不純物濃度が3×1017/cm3とされ、厚さが0.6μmとされている。
The n-type
n型電流分散層4およびp型連結層5の上にはSiCからなるp型ベース領域6が形成されており、p型連結層5を介してp型ベース領域6とp型ディープ層3とが連結されている。また、p型ベース領域6の上には、SiCからなるn+型ソース領域7およびp+型コンタクト領域8が形成されている。n+型ソース領域7は、p型ベース領域6のうちn型電流分散層4と対応する部分の上に形成されており、p+型コンタクト領域8は、p型ベース領域6のうちp型連結層5と対応する部分の上に形成されている。
A p-
p型ベース領域6は、p型ディープ層3よりも厚みが薄く、かつ、p型不純物濃度が低くされており、例えばp型不純物濃度が3×1017/cm3とされ、厚さが0.3μmとされている。また、n+型ソース領域7は、n型不純物濃度がn型電流分散層4よりも高濃度とされており、p+型コンタクト領域8は、p型不純物濃度がp型ベース領域6よりも高濃度とされている。
The p-
また、p型ベース領域6およびn+型ソース領域7を貫通してn型電流分散層4に達するように、例えば幅が0.8μm、深さがp型ベース領域6とn+型ソース領域7の合計膜厚よりも0.2〜0.4μm深くされたゲートトレンチ9が形成されている。このゲートトレンチ9の側面と接するように上述したp型ベース領域6およびn+型ソース領域7が配置されている。ゲートトレンチ9は、図1の紙面左右方向を幅方向、紙面法線方向を長手方向、紙面上下方向を深さ方向とするライン状のレイアウトで形成されている。また、図1には1本しか示していないが、ゲートトレンチ9は、複数本が紙面左右方向に等間隔に配置され、それぞれp型ディープ層3の間に挟まれるように配置されていてストライプ状とされている。例えば、ゲートトレンチ9のピッチとなるセルピッチ、つまり隣り合うゲートトレンチ9の配置間隔の半分となるハーフセルピッチは、例えば1.55μmとされている。ゲートトレンチ9の幅については任意であるが、ハーフセルピッチよりも小さくされている。
In addition, the p-
さらに、p型ベース領域6のうちゲートトレンチ9の側面に位置している部分を、縦型MOSFETの作動時にn+型ソース領域7とn型電流分散層4との間を繋ぐチャネル領域として、チャネル領域を含むゲートトレンチ9の内壁面にゲート絶縁膜10が形成されている。そして、ゲート絶縁膜10の表面にはドープドPoly−Siにて構成されたゲート電極11が形成されており、これらゲート絶縁膜10およびゲート電極11によってゲートトレンチ9内が埋め尽くされている。
Further, a portion of the p-
また、n+型ソース領域7およびp+型コンタクト領域8の表面やゲート電極11の表面には、層間絶縁膜12を介してソース電極13などが形成されている。ソース電極13は、複数の金属、例えばNi/Al等にて構成されている。そして、複数の金属のうち少なくともn型SiC、具体的にはn+型ソース領域7やn型ドープの場合のゲート電極11と接触する部分はn型SiCとオーミック接触可能な金属で構成されている。また、複数の金属のうち少なくともp型SiC、具体的にはp+型コンタクト領域8と接触する部分はp型SiCとオーミック接触可能な金属で構成されている。なお、ソース電極13は、層間絶縁膜12上に形成されることで電気的に絶縁されている。そして、層間絶縁膜12に形成されたコンタクトホールを通じて、ソース電極13はn+型ソース領域7およびp+型コンタクト領域8と電気的に接触させられている。
A
さらに、n+型基板1の裏面側にはn+型基板1と電気的に接続されたドレイン電極14が形成されている。このような構造により、nチャネルタイプの反転型のトレンチゲート構造の縦型MOSFETが構成されている。このような縦型MOSFETが複数セル配置されることでセル領域が構成されている。そして、このような縦型MOSFETが形成されたセル領域を囲むように図示しないガードリングなどによる外周耐圧構造が構成されることでSiC半導体装置が構成されている。
Further, on the back side of the n + -type substrate 1 n + -
このように構成される縦型MOSFETを有するSiC半導体装置は、ソース電圧Vsを0V、ドレイン電圧Vdを例えば1〜1.5Vとした状態で、ゲート電極11に対して例えば20Vのゲート電圧Vgを印加することで動作させられる。すなわち、ゲート電圧が印加されることにより、縦型MOSFETは、ゲートトレンチ9に接する部分のp型ベース領域6にチャネル領域が形成され、ドレイン−ソース間に電流が流れるという動作を行う。
In the SiC semiconductor device having the vertical MOSFET configured as described above, a gate voltage Vg of 20 V is applied to the
このとき、少なくともJFET部2aとp型ディープ層3との間に高濃度n型層20を配置していることから、この高濃度n型層20が空乏層調整層として機能することで、次の作動を行うことになる。
At this time, since the high-concentration n-
具体的には、図2の一点鎖線で示すように、ドレイン電圧Vdが例えば1〜1.5Vのように通常作動時に印加される電圧である場合には、p型ディープ層3側から高濃度n型層20へ伸びる空乏層は、高濃度n型層20の厚みよりも小さい幅しか伸びない。つまり、高濃度n型層20が空乏層の伸びをストップする層として機能する。このため、JFET部2a内への空乏層の伸びを抑制することが可能になり、電流経路が狭くなることを抑制できるため、低オン抵抗を図ることが可能となる。
Specifically, as shown by the alternate long and short dash line in FIG. 2, when the drain voltage Vd is a voltage applied during normal operation, such as 1 to 1.5 V, the high concentration is applied from the p-type
また、高濃度n型層20のうち空乏層が伸びていない部分については電流経路として機能する。そして、高濃度n型層20がJFET部2aよりもn型不純物濃度が高濃度になっており、低抵抗となっていることから、高濃度n型層20が電流経路として機能することで、さらに低オン抵抗化を図ることが可能となる。
The portion of the high concentration n-
また、負荷短絡などによってドレイン電圧Vdが通常作動時の電圧よりも高くなると、p型ディープ層3側から高濃度n型層20へ伸びる空乏層が高濃度n型層20の厚みよりも伸びる。そして、n型電流分散層4よりも先にJFET部2aが即座にピンチオフされる。このとき、高濃度n型層20の厚みおよびn型不純物濃度に基づいてドレイン電圧Vdと空乏層の幅との関係が決まる。このため、通常作動時のドレイン電圧Vdよりも少し高い電圧となったときにJFET部2aがピンチオフされるように、高濃度n型層20の厚みおよびn型不純物濃度を設定することで、低いドレイン電圧VdでもJFET部2aをピンチオフすることが可能となる。このように、ドレイン電圧Vdが通常作動時の電圧よりも高くなったときにJFET部2aが即座にピンチオフされるようにすることで、低飽和電流を維持することができ、負荷短絡等によるSiC半導体装置の耐量を向上することが可能となる。
Further, when the drain voltage Vd becomes higher than the voltage at the time of normal operation due to a load short circuit or the like, the depletion layer extending from the p-type
したがって、低オン抵抗値と低飽和電流を両立することができるSiC半導体装置とすることが可能となる。 Therefore, it is possible to provide a SiC semiconductor device that can achieve both a low on-resistance value and a low saturation current.
さらに、p型ディープ層3をp型ベース領域6よりもゲート電極11の中心線側に張り出させ、JFET部2aの幅が狭くなるようにしている。このため、ドレイン電圧Vdが高電圧になったとしても、下方からn-型ドリフト層2に伸びてくる空乏層の伸びがp型ディープ層3によって抑えられ、トレンチゲート構造に延伸することを防ぐことができる。したがって、ゲート絶縁膜10に掛かる電界を低下させることが可能となり、信頼性の高い素子とすることが可能となる。そして、このようにトレンチゲート構造への空乏層の延伸を防げるため、n-型ドリフト層2やJFET部2aのn型不純物濃度を比較的濃くすることができ、低オン抵抗化を図ることが可能となる。
Furthermore, the p-type
よって、低オン抵抗かつ高信頼性の縦型MOSFETを有するSiC半導体装置とすることが可能となる。 Therefore, a SiC semiconductor device having a vertical MOSFET with low on-resistance and high reliability can be obtained.
なお、本実施形態のSiC半導体装置は、ゲート電圧Vgを印加していないときには、チャネル領域が形成されていないため、ドレイン−ソース間に電流が流れないノーマリオフ型の半導体素子となる。しかしながら、JFET部2aについては、ゲート電圧Vgを印加していないときでもドレイン電圧Vdが通常作動時の電圧よりも高くならないとピンチオフしないため、ノーマリオン型となる。
The SiC semiconductor device of the present embodiment is a normally-off type semiconductor element in which no current flows between the drain and the source because the channel region is not formed when the gate voltage Vg is not applied. However, the
図3は、高濃度n型層20が備えられた本実施形態の構造と高濃度n型層20が備えられていない従来構造とについて、ドレイン電圧Vdに対するドレイン電流Idの特性であるVd−Id特性を比較した結果を示している。ゲート電圧を20Vとし、ドレイン電圧を変化させた場合の特性を示している。この図に示されるように、従来構造では、ドレイン電圧Vdが高いときのドレイン電流Id、つまり飽和電流値が大きな値であった。これに対して、本実施形態の構造では、ドレイン電圧Vdが高くなっても飽和電流値があまり大きな値にならず、例えば従来構造に対して1/5程度まで低下していた。
FIG. 3 shows Vd-Id which is a characteristic of the drain current Id with respect to the drain voltage Vd for the structure of the present embodiment provided with the high concentration n-
このように、本実施形態のSiC半導体装置によれば、ドレイン電圧Vdが高電圧になっても、ドレイン電流Idを低下させられる。このため、低飽和電流を実現することができる。 As described above, according to the SiC semiconductor device of the present embodiment, the drain current Id can be reduced even when the drain voltage Vd becomes high. Therefore, a low saturation current can be realized.
一方、図4は、本実施形態の構造と従来構造について、SiC半導体装置の通常作動範囲と想定されるドレイン電圧Vdの範囲でのVd−Id特性を比較した結果、すなわち図3中の通常作動範囲を拡大した図を示している。この図に示されるように、通常作動範囲では、本実施形態の構造もほぼ従来構造と同様の特性となった。具体的には、同じドレイン電圧Vdの際に、僅かながら従来構造の方が本実施形態の構造よりもドレイン電流Idが大きくなっていたが、殆ど同じ値となった。このことから、本実施形態の構造としても従来構造と同等のオン抵抗にできることが判る。 On the other hand, FIG. 4 shows a result of comparing the Vd-Id characteristics between the structure of the present embodiment and the conventional structure in the normal operation range of the SiC semiconductor device and the expected drain voltage Vd range, that is, the normal operation in FIG. The figure which expanded the range is shown. As shown in this figure, in the normal operating range, the structure of the present embodiment has almost the same characteristics as the conventional structure. Specifically, at the same drain voltage Vd, although the drain current Id was slightly larger in the conventional structure than in the structure of the present embodiment, it was almost the same value. From this, it is understood that the structure of the present embodiment can have the same on-resistance as the conventional structure.
したがって、上記したように、低オン抵抗値と低飽和電流を両立することができるSiC半導体装置とすることが可能となる。 Therefore, as described above, it is possible to provide a SiC semiconductor device that can achieve both a low on-resistance value and a low saturation current.
なお、本実施形態の場合、高濃度n型層20をn-型ドリフト層2のうちp型ディープ層3よりも下方部分の上面にも形成している。このため、p型ディープ層3からn-型ドリフト層2側に伸びる空乏層の伸び量も抑制され、よりオン抵抗の低減を図ることが可能となる。
In the case of this embodiment, the high-concentration n-
また、JFET部2aや高濃度n型層20などのn型不純物濃度や厚みの一例を示したが、これらについては一例を示したに過ぎない。例えば、JFET部2aや高濃度n型層20については、所望のピンチオフ条件を満たすようにn型不純物濃度や厚みを設定している。
Further, although examples of the n-type impurity concentration and thickness of the
具体的には、JFET部2aについては、例えば半導体素子の耐圧の10%でピンチオフする条件として設計されている。すなわち、JFET部2aのn型不純物濃度をNd1、厚みをW1、ピンチオフ電圧をVp1、素電荷をq1、誘電率をε1として次の数式1を満たすようにn型不純物濃度Nd1、厚みW1を設計している。
Specifically, the
(数1)Vp1=(q1×Nd1×W12)/2ε1<半導体素子の耐圧の10%
一方、高濃度n型層20については、例えば半導体素子の耐圧の0.1%でピンチオフしない条件として設計されている。すなわち、高濃度n型層20のn型不純物濃度をNd2、p型ディープ層3の側面上での厚みをW2、ピンチオフ電圧をVp2、素電荷をq2、誘電率をε2として次の数式2を満たすようにn型不純物濃度Nd2、厚みW2を設計している。
(Equation 1) Vp1 = (q1 × Nd1 × W1 2 ) / 2ε1 <10% of the breakdown voltage of the semiconductor element
On the other hand, the high-concentration n-
(数2)Vp2=(q2×Nd2×W22)/2ε2>半導体素子の耐圧の0.1%
次に、本実施形態にかかるnチャネルタイプの反転型のトレンチゲート構造の縦型MOSFETを備えたSiC半導体装置の製造方法について、図5および図6に示す製造工程中の断面図を参照して説明する。
(Equation 2 ) Vp2 = (q2 × Nd2 × W2 2 ) / 2ε2> 0.1% of the breakdown voltage of the semiconductor element
Next, referring to the cross-sectional views in the manufacturing process shown in FIG. 5 and FIG. 6, for the manufacturing method of the SiC semiconductor device provided with the vertical MOSFET of the n-channel type inverted trench gate structure according to the present embodiment. explain.
〔図5(a)に示す工程〕
まず、半導体基板として、n+型基板1を用意する。そして、エピタキシャル成長により、n+型基板1の主表面上にSiCからなるn-型ドリフト層2を形成したのち、n-型ドリフト層2の上にSiCからなる高濃度n型層20の一部を形成し、さらにSiCからなるp型ディープ層3を形成する。
[Step shown in FIG. 5 (a)]
First, an n + type substrate 1 is prepared as a semiconductor substrate. Then, the n −
〔図5(b)に示す工程〕
p型ディープ層3の上にJFET部2aと対応する位置を開口させた図示しないマスクを形成し、そのマスクを用いてp型ディープ層3を除去してトレンチ3aを形成し、トレンチ3aの底部においてn-型ドリフト層2を露出させる。
[Process shown in FIG. 5 (b)]
A mask (not shown) having an opening at a position corresponding to the
〔図5(c)に示す工程〕
p型ディープ層3のうちトレンチ3a以外の表面をマスクで覆ったままの状態で埋め込みエピタキシャル成長を行うことによって、高濃度n型層20とJFET部2aを形成する。例えば、n型層を濃度差を付けて形成し、成長初期時には高濃度、その後は低濃度で形成されるようにする。これにより、トレンチ3aの側面にまず高濃度n型層20が形成され、更にトレンチ3a内を埋め尽くすようにJFET部2aが形成される。この後、図示しないマスクを除去する。また、必要に応じて、p型ディープ層3や高濃度n型層20およびJFET部2aの表面の平坦化を行う。
[Process shown in FIG. 5 (c)]
The high-concentration n-
〔図5(d)に示す工程〕
p型ディープ層3や高濃度n型層20およびJFET部2aの表面にn型電流分散層4をエピタキシャル成長させる。
[Process shown in FIG. 5 (d)]
The n-type current spreading
〔図5(e)に示す工程〕
n型電流分散層4のうちJFET部2aや高濃度n型層20から離れた位置にp型不純物をイオン注入し、活性化することでp型連結層5を形成する。
[Process shown in FIG. 5 (e)]
A p-
〔図6(a)に示す工程〕
n型電流分散層4およびp型連結層5の上にp型ベース領域6およびn+型ソース領域7をエピタキシャル成長させる。
[Step shown in FIG. 6 (a)]
A p-
〔図6(b)に示す工程〕
n+型ソース領域7の一部にp型不純物をイオン注入することでp+型コンタクト領域8を形成する。
[Process shown in FIG. 6 (b)]
A p + -
〔図6(c)に示す工程〕
n+型ソース領域7などの上に図示しないマスクを形成したのち、マスクのうちのゲートトレンチ9の形成予定領域を開口させる。そして、マスクを用いてRIE(Reactive Ion Etching)などの異方性エッチングを行うことで、ゲートトレンチ9を形成する。
[Step shown in FIG. 6 (c)]
After forming a mask (not shown) on the n +
その後、マスクを除去してから例えば熱酸化を行うことによって、ゲート絶縁膜10を形成し、ゲート絶縁膜10によってゲートトレンチ9の内壁面上およびn+型ソース領域7の表面上を覆う。そして、p型不純物もしくはn型不純物がドープされたPoly−Siをデポジションした後、これをエッチバックし、少なくともゲートトレンチ9内にPoly−Siを残すことでゲート電極11を形成する。
After that, the mask is removed and then, for example, thermal oxidation is performed to form the
〔図6(d)に示す工程〕
ゲート電極11およびゲート絶縁膜10の表面を覆うように、例えば酸化膜などによって構成される層間絶縁膜12を形成する。また、層間絶縁膜12の表面上に図示しないマスクを形成したのち、マスクのうち各ゲート電極11の間に位置する部分、つまりp+型コンタクト領域8と対応する部分およびその近傍を開口させる。この後、マスクを用いて層間絶縁膜12をパターニングすることでp型ディープ層3およびn+型ソース領域7を露出させるコンタクトホールを形成する。そして、層間絶縁膜12の表面上に例えば複数の金属の積層構造により構成される電極材料を形成したのち、電極材料をパターニングすることでソース電極13を形成する。
[Step shown in FIG. 6 (d)]
An interlayer insulating
〔図6(e)に示す工程〕
n+型基板1の裏面側にドレイン電極14を形成する。これにより、本実施形態にかかるSiC半導体装置が完成する。
[Step shown in FIG. 6 (e)]
The
以上説明したように、本実施形態のSiC半導体装置では、少なくともp型ディープ層3のうちの側面、つまりp型ディープ層3とJFET部2aとの間に高濃度n型層20を形成している。
As described above, in the SiC semiconductor device of this embodiment, the high-concentration n-
このため、通常作動時においては、高濃度n型層20が空乏層の伸びをストップする層として機能し、JFET部2a内への空乏層の伸びを抑制することが可能になり、電流経路が狭くなることを抑制できるため、低オン抵抗を図ることが可能となる。また、負荷短絡などによってドレイン電圧Vdが通常作動時の電圧よりも高くなると、p型ディープ層3側から高濃度n型層20へ伸びる空乏層が高濃度n型層20の厚みよりも伸び、JFET部2aが即座にピンチオフされる。これにより、低飽和電流を維持することができ、負荷短絡等によるSiC半導体装置の耐量を向上することが可能となる。したがって、低オン抵抗値と低飽和電流を両立することができるSiC半導体装置とすることが可能となる。
Therefore, during normal operation, the high-concentration n-
なお、本実施形態で説明したSiC半導体装置において、縦型MOSFETは、JFET部2aがトレンチゲート構造の直下に位置した構造となっていると、電流経路を最短にできるため好ましい。しかしながら、マスクのアライメントずれなどにより、図7に示すように、トレンチゲート構造の直下からずれた位置にJFET部2aが位置した構造と有っていても、上記効果を得ることができる。
In the SiC semiconductor device described in the present embodiment, it is preferable that the vertical MOSFET has a structure in which the
(第2実施形態)
第2実施形態について説明する。本実施形態は、第1実施形態に対して高濃度n型層20の代わりになる層を備えるようにしたものであり、その他については第1実施形態と同様であるため、第1実施形態と異なる部分についてのみ説明する。
(Second embodiment)
The second embodiment will be described. The present embodiment is provided with a layer which replaces the high-concentration n-
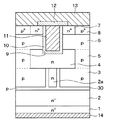
図8に示すように、本実施形態では、第1実施形態のSiC半導体装置に備えていた高濃度n型層20に代えて、低濃度p型層30を備えてある。本実施形態では、この低濃度p型層30が空乏層調整層として機能する。低濃度p型層30は、少なくともp型ディープ層3のうちの側面、つまりp型ディープ層3とJFET部2aとの間に形成されている。そして、本実施形態の場合は、n-型ドリフト層2の上面、つまりn-型ドリフト層2とp型ディープ層3の底部との間やn-型ドリフト層2とJFET部2aとの境界位置にも低濃度p型層30が形成されている。
As shown in FIG. 8, in the present embodiment, a low concentration p-
低濃度p型層30は、JFET部2aやp型ディープ層3よりも不純物濃度が低くされており、例えばp型不純物濃度が1.0×1017/cm3とされている。低濃度p型層30の厚さについては、p型ディープ層3の側面では0.05μm、n-型ドリフト層2の上面では0.07μmとされている。
The low-concentration p-
なお、低濃度p型層30のp型不純物濃度やp型ディープ層3の側面上での厚みについては、所望のピンチオフ条件を満たすように設計している。具体的には、低濃度p型層30については、例えば半導体素子の耐圧の0.1%でピンチオフしない条件として設計されている。すなわち、低濃度p型層30のp型不純物濃度をNa、p型ディープ層3の側面上での厚みをW3、ピンチオフ電圧をVp3、素電荷をq3、誘電率をε3として次の数式3を満たすようにn型不純物濃度Nd3、厚みW3を設計している。
The p-type impurity concentration of the low-concentration p-
(数3)Vp3=(q3×Na×W32)/2ε3>半導体素子の耐圧の0.1%
また、高濃度n型層20を低濃度p型層30に代えることに伴って、JFET部2aの不純物濃度を変更しており、n型不純物濃度を1.0×1017/cm3としている。なお、ここで説明するJFET部2aのn型不純物濃度についても、JFET部2aの厚みと共に、第1実施形態で説明した数式2を満たす設計とされている。
(Equation 3) Vp3 = (q3 × Na × W3 2 ) / 2ε3> 0.1% of the breakdown voltage of the semiconductor element
Further, the impurity concentration of the
このように、低濃度p型層30をJFET部2aとp型ディープ層3との間に配置した場合、JFET部2aと低濃度p型層30との不純物濃度差がJFET部2aとp型ディープ層3との不純物濃度差よりも少なくなる。このため、低濃度p型層30からJFET部2a側に伸びる空乏層の伸び量が抑制される。したがって、空乏層によってJFET部2a内での電流経路が狭められることを抑制することが可能となり、低オン抵抗を図ることが可能となる。よって、本実施形態の構成としても、第1実施形態と同様の効果を得ることが可能となる。
In this way, when the low-concentration p-
なお、本実施形態のSiC半導体装置の製造方法は、第1実施形態とほぼ同じである。すなわち、第1実施形態で説明した高濃度n型層20を形成する際に、それに代えて低濃度p型層30を形成する以外は、第1実施形態と同じ工程を行えば、本実施形態のSiC半導体装置を製造することができる。
The method of manufacturing the SiC semiconductor device of this embodiment is almost the same as that of the first embodiment. That is, when the high-concentration n-
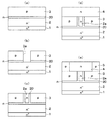
(第1、第2実施形態の変形例)
上記第1実施形態で説明した高濃度n型層20と第2実施形態で説明した低濃度p型層30を組み合わせて形成することもできる。例えば、図9に示すように、n-型ドリフト層2の上面に高濃度n型層20を備え、p型ディープ層3の側面に低濃度p型層30を備える。または、図10に示すように、n-型ドリフト層2の上面に低濃度p型層30を備え、p型ディープ層3の側面に高濃度n型層20を備える。これらの構造としても、第1、第2実施形態と同様の効果を得ることができる。
(Modifications of the first and second embodiments)
It is also possible to form the high-concentration n-
(第3実施形態)
第3実施形態について説明する。本実施形態は、第1、第2実施形態に対してスーパージャンクション構造を適用したものであり、その他については第1、第2実施形態と同様であるため、第1、第2実施形態と異なる部分についてのみ説明する。なお、ここでは第1実施形態のように高濃度n型層20を有する縦型MOSFETに対してスーパージャンクション構造を適用した場合について説明するが、第2実施形態のような低濃度p型層30を有する縦型MOSFETに対しても適用可能である。
(Third Embodiment)
A third embodiment will be described. In this embodiment, a super junction structure is applied to the first and second embodiments, and the other points are the same as those in the first and second embodiments, and therefore are different from the first and second embodiments. Only the part will be described. Note that, here, a case where the super junction structure is applied to the vertical MOSFET having the high-concentration n-
図11に示すように、本実施形態では、p型ディープ層3よりも下方において、n-型ドリフト層2側に伸びるp型カラム層40が備えられている。図11では、p型カラム層40がn+型基板1に接する構造としているが、n+型基板1から離れた構造であっても良い。
As shown in FIG. 11, in the present embodiment, a p-
このように、p型カラム層40を形成することで、n-型ドリフト層2をn型カラム層とするPN接合のスーパージャンクション構造が構成されている。このようなスーパージャンクション構造を有する縦型MOSFETに対しても、高濃度n型層20を形成している。このため、第1実施形態と同様の効果を得ることができる。
By thus forming the p-
なお、本実施形態の構造のSiC半導体装置も、基本的には第1実施形態のものと同様の製造方法によって製造できる。p型カラム層40については、n-型ドリフト層2に対してトレンチを形成したのち、埋め込みエピタキシャル成長を行い、さらにエッチバックしてp型カラム層40の表面の平坦化を行うことで形成できる。これ以外については、第1実施形態と同様の方法により、本実施形態のSiC半導体装置を製造できる。
The SiC semiconductor device having the structure of this embodiment can also be manufactured basically by the same manufacturing method as that of the first embodiment. The p-
(第4実施形態)
第4実施形態について説明する。本実施形態は、第1〜第3実施形態に対してソース電極13のコンタクト構造を変更したものであり、その他については第1〜第3実施形態と同様であるため、第1〜第3実施形態と異なる部分についてのみ説明する。なお、ここでは第1実施形態のように高濃度n型層20を有する縦型MOSFETに対してソース電極13のコンタクト構造を変更した場合について説明するが、第2実施形態のような低濃度p型層30を有する縦型MOSFETに対しても適用可能である。
(Fourth Embodiment)
A fourth embodiment will be described. In the present embodiment, the contact structure of the
図12に示すように、n+型ソース領域7を挟んでトレンチゲート構造の反対側にコンタクトトレンチ50が形成されている。そして、このコンタクトトレンチ50の底面においてp型ベース領域6の表層部にp+型コンタクト領域8が形成されている。このような構造は、n+型ソース領域7を形成した後に、エッチングによってコンタクトトレンチ50を形成し、その後にp+型コンタクト領域8を形成するためのイオン注入を行うことによって実現できる。
As shown in FIG. 12, a
このように、コンタクトトレンチ50によってn+型ソース領域7の一部を除去することで、ソース電極13とp型ベース領域6とのコンタクトを図るようにしても良い。
In this way, by removing a part of the n +
(第5実施形態)
第5実施形態について説明する。本実施形態は、第1〜第4実施形態に対してJFET部2aの上面レイアウトを変更したものであり、その他については第1〜第4実施形態と同様であるため、第1〜第4実施形態と異なる部分についてのみ説明する。なお、ここでは第1実施形態のように高濃度n型層20を有する縦型MOSFETに対してレイアウト構成を変更した場合について説明するが、第2実施形態のような低濃度p型層30を有する縦型MOSFETに対しても適用可能である。
(Fifth Embodiment)
A fifth embodiment will be described. In the present embodiment, the upper surface layout of the
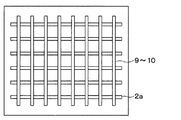
上記第1実施形態では、JFET部2aをトレンチゲート構造の長手方向に沿って短冊状に形成している。これに対して、本実施形態では、図13に示すように、トレンチゲート構造の長手方向に対して交差、ここでは直交するようにJFET部2aをレイアウトすることで、トレンチゲート構造とJFET部2aとが格子状にレイアウトされた構造としている。
In the first embodiment described above, the
このように、トレンチゲート構造とJFET部2aとが格子状のレイアウトとなるようにしても、第1実施形態と同様の効果を得ることができる。
In this way, even if the trench gate structure and the
(第5実施形態の変形例)
第5実施形態のように、トレンチゲート構造とJFET部2aとが格子状のレイアウトとなる場合に限らず、他のレイアウトとなるようにすることもできる。例えば、図14に示すように、JFET部2aを四角形などの枠体形状で構成し、各JFET部2aを格子状に並べた構造としても良い。
(Modification of Fifth Embodiment)
The layout is not limited to the case where the trench gate structure and the
(第6実施形態)
第6実施形態について説明する。本実施形態は、第1〜第5実施形態に対してトレンチゲート構造の縦型MOSFETに代えてプレーナ構造の縦型MOSFETとしたものであり、その他については第1〜第5実施形態と同様であるため、第1〜第5実施形態と異なる部分についてのみ説明する。なお、ここでは第1実施形態のように高濃度n型層20を有する縦型MOSFETに対してプレーナ構造とする場合について説明するが、第2実施形態のような低濃度p型層30を有する縦型MOSFETに対しても適用可能である。
(Sixth Embodiment)
A sixth embodiment will be described. In this embodiment, a vertical MOSFET having a planar structure is used instead of the vertical MOSFET having a trench gate structure as compared with the first to fifth embodiments. Others are the same as those in the first to fifth embodiments. Therefore, only parts different from the first to fifth embodiments will be described. Note that, here, a case where the vertical MOSFET having the high-concentration n-
具体的には、図15に示すようなプレーナ構造の縦型MOSFETを有するSiC半導体装置に対しても、高濃度n型層20を備える構造を適用できる。プレーナ構造の場合、n-型ドリフト層2の上にp型ベース領域6を形成し、p型ベース領域6の表層部にn+型ソース領域7を形成した構造とされる。また、p型ベース領域6に挟まれるようにJFET部2aが形成されている。そして、p型ベース領域6のうちn+型ソース領域7とJFET部2aとの間に位置している部分の表面側をチャネル領域として、チャネル領域上にゲート絶縁膜10を介してゲート電極11が形成された構造とされる。
Specifically, the structure including the high-concentration n-
このような構造においても、少なくともp型ベース領域6の側面に高濃度n型層20を備えることで、第1実施形態と同様の効果を得ることができる。
Even in such a structure, by providing the high-concentration n-
また、本実施形態の場合、高濃度n型層20をn-型ドリフト層2の上面にも形成している。このため、p型ベース領域6からn-型ドリフト層2側に伸びる空乏層の伸び量も抑制され、よりオン抵抗の低減を図ることが可能となる。
Further, in the case of this embodiment, the high concentration n-
(第7実施形態)
第7実施形態について説明する。本実施形態は、第1〜第6実施形態に対して高濃度n型層20や低濃度p型層30の形成方法を変更したものであり、その他については第1〜第6実施形態と同様であるため、第1〜第6実施形態と異なる部分についてのみ説明する。なお、ここでは第1実施形態のように高濃度n型層20を有する縦型MOSFETに対して本実施形態の製造方法を適用する場合について説明するが、第2実施形態のような低濃度p型層30を有する縦型MOSFETに対しても適用可能である。
(Seventh embodiment)
The seventh embodiment will be described. This embodiment is different from the first to sixth embodiments in the method of forming the high-concentration n-
本実施形態では、第1実施形態で説明した図5(c)に示す埋め込みエピタキシャル成長に代えて、他の手法によって高濃度n型層20を形成する。
In the present embodiment, instead of the buried epitaxial growth shown in FIG. 5C described in the first embodiment, the high concentration n-
具体的には、図16(a)に示すように、高濃度n型層20のうちp型ディープ層3よりも下方位置の部分を形成したのち、p型ディープ層3をエピタキシャル成長させる。続いて、図16(b)に示すように、p型ディープ層3の上にn型層60を形成する。n型層60についてはエピタキシャル成長によって形成しても良いが、ここではn型不純物をイオン注入することによって形成している。また、n型層60の不純物濃度については、高濃度n型層20と同じ程度となるようにしている。その後、図16(c)に示すように、p型ディープ層3に加えてn型層60を貫通するようにトレンチ3aを形成する。このトレンチ3aは、第1トレンチに相当する。そして、アニール処理、例えばエッチングガスとなる水素(H2)とアルゴン(Ar)の混合ガス雰囲気中において加熱する。これにより、図16(d)に示すように、溶融したn型層60がトレンチ3a内に垂れるように流動し、p型ディープ層3の側面などに付着して高濃度n型層20の残りの部分が形成される。この後は、第1実施形態で説明した各工程を実施することで、図1と同様の構造の縦型MOSFETを備えたSiC半導体装置を製造できる。
Specifically, as shown in FIG. 16A, after forming a portion of the high-concentration n-
このように、n型層60をp型ディープ層3の上に形成しておき、アニール処理によってn型層60を溶融させて流動させることで、p型ディープ層3の側面などに高濃度n型層20を形成するようにしても良い。
In this way, the n-
(第8実施形態)
第8実施形態について説明する。本実施形態は、第1〜第7実施形態に対してp型連結層5およびp+型コンタクト領域8の形成方法を変更したものであり、その他については第1〜第7実施形態と同様であるため、第1〜第7実施形態と異なる部分についてのみ説明する。なお、ここでは第1実施形態のように高濃度n型層20を有する縦型MOSFETに対して本実施形態の製造方法を適用する場合について説明するが、第2実施形態のような低濃度p型層30を有する縦型MOSFETに対しても適用可能である。
(Eighth Embodiment)
The eighth embodiment will be described. The present embodiment is different from the first to seventh embodiments in the method of forming the p-
まず、第1実施形態で説明した図5(a)〜(d)に示す工程まで行う。続いて、図17(a)に示すように、n型電流分散層4に対してp型連結層5を形成することなく、p型ベース領域6やn+型ソース領域7を形成し、更にトレンチゲート構造を形成する。この後、図17(c)に示すように、トレンチゲート構造から離れた位置において、n+型ソース領域7やp型ベース領域6およびn型電流分散層4を貫通してp型ディープ層3に達するトレンチ70を形成する。このトレンチ70は、第2トレンチに相当する。そして、図17(d)に示すように、埋め込みエピタキシャル成長によって、p型連結層5およびp+型コンタクト領域8として機能するp型層71を形成する。
First, the steps shown in FIGS. 5A to 5D described in the first embodiment are performed. Subsequently, as shown in FIG. 17A, the p-
このように、p型連結層5およびp+型コンタクト領域8として機能するp型層71をエピタキシャル成長によって形成するようにしても良い。
In this way, the p-
(他の実施形態)
本発明は上記した実施形態に限定されるものではなく、特許請求の範囲に記載した範囲内において適宜変更が可能である。
(Other embodiments)
The present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment, but can be appropriately modified within the scope described in the claims.
例えば、上記各実施形態は、互いに無関係なものではなく、組み合わせが明らかに不可な場合を除き、適宜組み合わせが可能である。 For example, the above embodiments are not unrelated to each other, and can be appropriately combined unless the combination is clearly impossible.
また、第1実施形態等では、p型ディープ層3をソース電極13に接続することでソース電位とする構造について説明した。これに対して、p型ディープ層3をp型ベース領域6から分離した構造とし、p型ディープ層3への電圧印加に伴ってJFET部2aの空乏層の伸び量を調整する第2ゲートとして機能させるようにしても良い。その場合、p型ディープ層3は、ゲート電極11に電気的に接続してゲート電圧が印加される構成としたり、ドレイン電極14に接続してドレイン電圧が印加される構成とすることができる。
Further, in the first embodiment and the like, the structure in which the p-type
また、JFET部2aの幅は一定である必要は無く、例えばドレイン電極14側の方に向かって徐々に幅が狭くなるような断面テーパ形状となっていても良い。
In addition, the width of the
また、各部の不純物濃度は一定でなくても良い。例えば、p型ディープ層3がドレイン電極14に近づくほどp型不純物濃度が低く、ソース電極13に近づくほどp型不純物濃度が高くなるような不純物濃度勾配を有した構造であっても良い。
Further, the impurity concentration of each part may not be constant. For example, a structure having an impurity concentration gradient such that the p-type impurity concentration is lower as the p-type
同様に、上記各実施形態で説明したSiC半導体装置を構成する各部の寸法や不純物濃度については一例を示したに過ぎない。各部の寸法や不純物濃度については、高濃度n型層20や低濃度p型層30およびJFET部2aのピンチオフ条件等に基づいて、適宜設定すれば良い。
Similarly, the dimensions and the impurity concentrations of the respective parts constituting the SiC semiconductor device described in the above embodiments are merely examples. The dimensions and the impurity concentration of each portion may be appropriately set based on the pinch-off conditions of the high-concentration n-
例えば、高濃度n型層20の幅を広くすることもできる。例えば、高濃度n型層20の幅を全域0.2μmとする場合、n型不純物濃度を3.0×1017/cm3とし、JFET部2aの幅を0.4μm、1.0×1018/cm3とすることができる。また、ハーフセルピッチを広くし、例えば3μmとすることもできる。また、n型電流分散層4やp型連結層5の厚みを薄くして不純物濃度を濃くする構成にでき、例えば厚みを0.4μmとし、それぞれのn型不純物濃度やp型不純物濃度を6.0×1017/cm3とすることもできる。また、p型ディープ層3の厚みを薄くして不純物濃度を濃くする構成にでき、例えば厚みを0.6μmとし、p型不純物濃度を2.0×1018/cm3とすることもできる。また、低濃度p型層30を備える構造についても、ここで示した一例と同寸法および同不純物濃度を適用できる。ただし、ここで挙げたものも一例であり、他の寸法、不純物濃度とすることもできる。
For example, the width of the high concentration n-
また、上記第1実施形態等では、第1導電型をn型、第2導電型をp型としたnチャネルタイプの縦型MOSFETを例に挙げて説明したが、各構成要素の導電型を反転させたpチャネルタイプの縦型MOSFETとしても良い。また、上記説明では、半導体素子として縦型MOSFETを例に挙げて説明したが、同様の構造のIGBTに対しても本発明を適用することができる。IGBTは、上記各実施形態に対してn+型基板1の導電型をn型からp型に変更するだけであり、その他の構造や製造方法に関しては上記各実施形態と同様である。
Further, in the above-described first embodiment and the like, an n-channel vertical MOSFET in which the first conductivity type is n-type and the second conductivity type is p-type is described as an example, but the conductivity type of each component is An inverted p-channel type vertical MOSFET may be used. Further, in the above description, the vertical MOSFET has been described as an example of the semiconductor element, but the present invention can be applied to an IGBT having a similar structure. The IGBT only changes the conductivity type of the n + -
また、上記実施形態では半導体装置としてSiC半導体装置を例に挙げて説明したが、Siを用いた半導体装置に対しても本発明を適用できるし、他のワイドバンドギャップ半導体装置、例えばGaN、ダイヤモンド、AlNなどを用いた半導体装置に対して上記各実施形態を適用することもできる。 In addition, although the SiC semiconductor device has been described as an example of the semiconductor device in the above embodiment, the present invention can be applied to a semiconductor device using Si, and other wide band gap semiconductor devices such as GaN and diamond. Each of the above embodiments can be applied to a semiconductor device using AlN, AlN, or the like.
2 n-型ドリフト層
2a JFET部
3 p型ディープ層
4 n型電流分散層
6 p型ベース領域
7 n+型ソース領域
10 ゲート絶縁膜
11 ゲート電極
13 ソース電極
14 ドレイン電極
2 n −
Claims (18)
前記基板の上に形成され、前記基板よりも低不純物濃度とされた第1導電型の半導体からなるドリフト層(2)と、
前記ドリフト層の上に形成された第2導電型の半導体からなる第2導電型領域(3、5、6、8、71)と、
前記ドリフト層上に形成され、前記第2導電型領域に挟まれて配置されたJFET部(2a)と、
前記第2導電型領域の上に形成され、前記ドリフト層よりも高濃度の第1導電型の半導体からなるソース領域(7)と、
前記第2導電型領域の一部をチャネル領域として、該チャネル領域上に形成されたゲート絶縁膜(10)と、
前記ゲート絶縁膜上に形成されたゲート電極(11)と、
前記ゲート電極および前記ゲート絶縁膜を覆うと共にコンタクトホールが形成された層間絶縁膜(12)と、
前記コンタクトホールを通じて、前記ソース領域に電気的に接続されたソース電極(13)と、
前記基板の裏面側に形成されたドレイン電極(14)とを有し、
前記ゲート電極に対してゲート電圧を印加すると共に前記ドレイン電極に対して印加するドレイン電圧として通常作動時の電圧を印加することで前記チャネル領域を形成し、前記ソース領域および前記JFET部を介して、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極の間に電流を流す反転型の半導体素子を備え、
前記JFET部と前記第2導電型領域との間には、前記ドレイン電圧として前記通常作動時の電圧が印加されているときには前記第2導電型領域から前記JFET部に伸びる空乏層の伸び量を抑制しつつ前記JFET部を通じて電流を流し、前記ドレイン電圧として前記通常作動時の電圧よりも高い電圧が印加されると前記空乏層によって前記JFET部をピンチオフさせる空乏層調整層(20、30)が形成されており、
前記第2導電型領域は、
前記ドリフト層の上に形成されたディープ層(3)と、
前記ディープ層に対して連結されていると共に前記ソース電極に接続され、前記チャネル領域が形成されるベース領域(6)と、を有し、
前記ディープ層は、前記ベース領域よりも前記ゲート電極の中心線側に張り出しており、
前記JFET部は、前記ディープ層に挟まれており、
前記空乏層調整層は、前記JFET部と前記ディープ層との間に形成されている半導体装置。 A first or second conductivity type substrate (1) made of a semiconductor;
A drift layer (2) formed on the substrate, the drift layer (2) made of a semiconductor of a first conductivity type and having an impurity concentration lower than that of the substrate;
A second conductivity type region (3, 5, 6, 8, 71) made of a second conductivity type semiconductor formed on the drift layer;
A JFET portion (2a) formed on the drift layer and sandwiched between the second conductivity type regions;
A source region (7) formed on the second conductivity type region and made of a first conductivity type semiconductor having a higher concentration than the drift layer;
A gate insulating film (10) formed on the channel region using a part of the second conductivity type region as a channel region;
A gate electrode (11) formed on the gate insulating film,
An interlayer insulating film (12) covering the gate electrode and the gate insulating film and having a contact hole formed therein;
A source electrode (13) electrically connected to the source region through the contact hole;
A drain electrode (14) formed on the back surface side of the substrate,
The channel region is formed by applying a gate voltage to the gate electrode and a voltage during normal operation as a drain voltage to be applied to the drain electrode, and through the source region and the JFET portion. And an inversion type semiconductor element for flowing a current between the source electrode and the drain electrode,
An extension amount of a depletion layer extending from the second conductivity type region to the JFET part when the voltage in the normal operation is applied as the drain voltage between the JFET part and the second conductivity type region. A depletion layer adjusting layer (20, 30) for pinching off the JFET section by the depletion layer when a current higher than the voltage during the normal operation is applied as the drain voltage while allowing a current to flow through the JFET section while suppressing the depletion layer. Has been formed ,
The second conductivity type region is
A deep layer (3) formed on the drift layer,
A base region (6) connected to the deep layer and connected to the source electrode to form the channel region,
The deep layer extends beyond the base region toward the center line of the gate electrode,
The JFET portion is sandwiched between the deep layers,
The semiconductor device , wherein the depletion layer adjusting layer is formed between the JFET portion and the deep layer .
前記ゲート絶縁膜および前記ゲート電極が前記ゲートトレンチ内に形成されることでトレンチゲート構造が構成されている請求項10に記載の半導体装置。 A gate trench (9) is formed penetrating the source region and the base region to reach the current spreading layer,
The semiconductor device according to claim 10 , wherein a trench gate structure is formed by forming the gate insulating film and the gate electrode in the gate trench.
前記JFET部は、前記トレンチゲート構造に対して交差する方向を長手方向として、複数本が延設されている請求項11に記載の半導体装置。 The trench gate structure is formed in a stripe shape by a plurality of extending in one direction as a longitudinal direction,
The semiconductor device according to claim 11 , wherein a plurality of the JFET portions are extended with a direction intersecting the trench gate structure as a longitudinal direction.
前記基板の上に、前記基板よりも低不純物濃度の第1導電型の半導体からなるドリフト層(2)を形成することと、
前記ドリフト層の上に、第2導電型の半導体からなるディープ層(3)を形成することと、
前記ディープ層の一部を除去してトレンチ(3a)を形成したのち、該トレンチを半導体からなる空乏層調整層(20、30)および第1導電型の半導体からなるJFET部(2a)によって埋め込むことで、前記ディープ層の側面に前記空乏層調整層を形成しつつ、前記ディープ層に挟まれる前記JFET部を形成することと、
前記ディープ層と前記空乏層調整層および前記JFET部の上に、前記JFET部よりも幅が広く前記JFET部に連結される第1導電型の半導体からなる電流分散層(4)を形成すると共に、前記ディープ層の上に、該ディープ層に連結される第2導電型の半導体からなる連結層(5)を形成することと、
前記電流分散層および前記連結層の上に、前記連結層に連結される第2導電型の半導体からなるベース領域(6)を形成することと、
前記ベース領域の上に、前記ドリフト層よりも高濃度の第1導電型の半導体からなるソース領域(7)を形成することと、
前記ベース領域の一部をチャネル領域として、該チャネル領域上にゲート絶縁膜(10)を形成することと、
前記ゲート絶縁膜上にゲート電極(11)を形成することと、
前記ゲート電極および前記ゲート絶縁膜を覆うと共にコンタクトホールが形成された層間絶縁膜(12)を形成することと、
前記コンタクトホールを通じて、前記ソース領域に電気的に接続されたソース電極(13)を形成することと、
前記基板の裏面側にドレイン電極(14)を形成することとを含む、反転型の半導体素子を備えた半導体装置の製造方法。 Preparing a substrate (1) of the first or second conductivity type composed of a semiconductor;
Forming on the substrate a drift layer (2) made of a semiconductor of the first conductivity type having an impurity concentration lower than that of the substrate;
Forming a deep layer (3) made of a second conductivity type semiconductor on the drift layer;
A part of the deep layer is removed to form a trench (3a), and then the trench is filled with a depletion layer adjusting layer (20, 30) made of a semiconductor and a JFET part (2a) made of a semiconductor of the first conductivity type. Thus, while forming the depletion layer adjusting layer on the side surface of the deep layer, the JFET portion sandwiched between the deep layers is formed,
On the deep layer, the depletion layer adjusting layer, and the JFET portion, a current spreading layer (4) having a width wider than that of the JFET portion and connected to the JFET portion and made of a semiconductor of the first conductivity type is formed. Forming a connection layer (5) on the deep layer, the connection layer (5) being formed of a second conductivity type semiconductor and connected to the deep layer;
Forming a base region (6) on the current spreading layer and the connection layer, the base region (6) being connected to the connection layer and made of a second conductivity type semiconductor;
Forming on the base region a source region (7) made of a semiconductor of the first conductivity type having a higher concentration than the drift layer;
Forming a gate insulating film (10) on the channel region by using a part of the base region as a channel region;
Forming a gate electrode (11) on the gate insulating film;
Forming an interlayer insulating film (12) covering the gate electrode and the gate insulating film and having a contact hole formed therein;
Forming a source electrode (13) electrically connected to the source region through the contact hole;
Forming a drain electrode (14) on the back surface side of the substrate, a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device having an inversion type semiconductor element.
前記ディープ層の上に前記空乏層調整層を形成するための半導体層(60)を形成することと、
前記半導体層と共に前記ディープ層に前記トレンチを形成することと、
アニール処理によって前記半導体層を流動させて前記トレンチ内における少なくとも前記ディープ層の側面に前記空乏層調整層を形成することと、
前記空乏層調整層と共に前記JFET部によって前記トレンチ内を埋め込むことと、を含んでいる請求項14に記載の半導体装置の製造方法。 Forming the depletion layer adjusting layer and the JFET portion includes:
Forming a semiconductor layer (60) on the deep layer to form the depletion layer adjusting layer;
Forming the trench in the deep layer with the semiconductor layer,
Forming a depletion layer adjustment layer on at least a side surface of the deep layer in the trench by flowing the semiconductor layer by an annealing treatment;
15. The method of manufacturing a semiconductor device according to claim 14 , further comprising: filling the inside of the trench with the JFET portion together with the depletion layer adjustment layer.
前記平坦化を行ったのちに、前記電流分散層および前記連結層を形成する請求項14または15に記載の半導体装置の製造方法。 Including forming the depletion layer adjustment layer and the JFET portion, and thereafter planarizing the surfaces of the deep layer, the depletion layer adjustment layer and the JFET portion,
The method of manufacturing a semiconductor device according to claim 14 , wherein the current spreading layer and the coupling layer are formed after the planarization is performed.
前記電流分散層をエピタキシャル成長によって形成することと、
前記電流分散層のうち前記JFET部および前記空乏層調整層から離れた位置に、第2導電型不純物をイオン注入することで前記連結層を形成することと、を含んでいる請求項14ないし16のいずれか1つに記載の半導体装置の製造方法。 Forming the current spreading layer and the connecting layer comprises:
Forming the current spreading layer by epitaxial growth,
Wherein a position away from the JFET portion and the depletion adjusting layer of the current spreading layer, a second conductivity type impurity to claims 14 and includes a forming, the said connecting layer by ion implantation 16 A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device according to any one of 1.
前記基板の上に、前記基板よりも低不純物濃度の第1導電型の半導体からなるドリフト層(2)を形成することと、
前記ドリフト層の上に、第2導電型の半導体からなるディープ層(3)を形成することと、
前記ディープ層の一部を除去して第1トレンチ(3a)を形成したのち、該第1トレンチを半導体からなる空乏層調整層(20、30)および第1導電型の半導体からなるJFET部(2a)によって埋め込むことで、前記ディープ層の側面に前記空乏層調整層を形成しつつ、前記ディープ層に挟まれる前記JFET部を形成することと、
前記ディープ層と前記空乏層調整層および前記JFET部の上に、前記JFET部に連結される第1導電型の半導体からなる電流分散層(4)を形成することと、
前記電流分散層の上に、第2導電型の半導体からなるベース領域(6)を形成することと、
前記ベース領域の上に、前記ドリフト層よりも高濃度の第1導電型の半導体からなるソース領域(7)を形成することと、
前記ソース領域と前記ベース領域および前記電流分散層を貫通して前記ディープ層に達する第2トレンチ(70)を形成することと、
前記第2トレンチ内に、前記ディープ層と連結された第2導電型層(71)を形成することと、
前記ベース領域の一部をチャネル領域として、該チャネル領域上にゲート絶縁膜(10)を形成することと、
前記ゲート絶縁膜上にゲート電極(11)を形成することと、
前記ゲート電極および前記ゲート絶縁膜を覆うと共にコンタクトホールが形成された層間絶縁膜(12)を形成することと、
前記コンタクトホールを通じて、前記ソース領域および前記第2導電型層に電気的に接続されたソース電極(13)を形成することと、
前記基板の裏面側にドレイン電極(14)を形成することとを含む、反転型の半導体素子を備えた半導体装置の製造方法。 Preparing a substrate (1) of the first or second conductivity type composed of a semiconductor;
Forming on the substrate a drift layer (2) made of a semiconductor of the first conductivity type having an impurity concentration lower than that of the substrate;
Forming a deep layer (3) made of a second conductivity type semiconductor on the drift layer;
After removing a part of the deep layer to form a first trench (3a), the depletion layer adjusting layer (20, 30) made of a semiconductor and the JFET part (made of a semiconductor of the first conductivity type are formed in the first trench (3a). 2a) to form the JFET portion sandwiched between the deep layers while forming the depletion layer adjustment layer on the side surface of the deep layer,
Forming on the deep layer, the depletion layer adjusting layer and the JFET portion a current spreading layer (4) made of a semiconductor of a first conductivity type connected to the JFET portion;
Forming a base region (6) made of a second conductivity type semiconductor on the current spreading layer;
Forming on the base region a source region (7) made of a semiconductor of the first conductivity type having a higher concentration than the drift layer;
Forming a second trench (70) penetrating the source region, the base region and the current spreading layer to reach the deep layer;
Forming a second conductivity type layer (71) connected to the deep layer in the second trench;
Forming a gate insulating film (10) on the channel region by using a part of the base region as a channel region;
Forming a gate electrode (11) on the gate insulating film;
Forming an interlayer insulating film (12) covering the gate electrode and the gate insulating film and having a contact hole formed therein;
Forming a source electrode (13) electrically connected to the source region and the second conductive type layer through the contact hole;
Forming a drain electrode (14) on the back surface side of the substrate, a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device having an inversion type semiconductor element.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016184257A JP6683083B2 (en) | 2016-09-21 | 2016-09-21 | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
| PCT/JP2017/034101 WO2018056357A1 (en) | 2016-09-21 | 2017-09-21 | Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016184257A JP6683083B2 (en) | 2016-09-21 | 2016-09-21 | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2018049928A JP2018049928A (en) | 2018-03-29 |
| JP2018049928A5 JP2018049928A5 (en) | 2019-02-14 |
| JP6683083B2 true JP6683083B2 (en) | 2020-04-15 |
Family
ID=61689519
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016184257A Active JP6683083B2 (en) | 2016-09-21 | 2016-09-21 | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6683083B2 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2018056357A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7327905B2 (en) | 2017-07-07 | 2023-08-16 | 株式会社デンソー | Semiconductor device and its manufacturing method |
| JP6870547B2 (en) | 2017-09-18 | 2021-05-12 | 株式会社デンソー | Semiconductor devices and their manufacturing methods |
| JP7167717B2 (en) * | 2019-01-07 | 2022-11-09 | 株式会社デンソー | semiconductor equipment |
| JP7180402B2 (en) * | 2019-01-21 | 2022-11-30 | 株式会社デンソー | semiconductor equipment |
| JP6969586B2 (en) * | 2019-04-23 | 2021-11-24 | 株式会社デンソー | Semiconductor devices and their manufacturing methods |
| CN110190128B (en) * | 2019-05-29 | 2024-03-19 | 西安电子科技大学芜湖研究院 | MOSFET device with silicon carbide double-side deep L-shaped base region structure and preparation method thereof |
| JP7319501B2 (en) | 2019-10-09 | 2023-08-02 | 株式会社東芝 | Substrate manufacturing method, semiconductor device manufacturing method, substrate and semiconductor device |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4879545B2 (en) * | 2005-09-29 | 2012-02-22 | 株式会社デンソー | Manufacturing method of semiconductor substrate |
| JP5736683B2 (en) * | 2010-07-30 | 2015-06-17 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Power semiconductor device |
| JP5597217B2 (en) * | 2012-02-29 | 2014-10-01 | 株式会社東芝 | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP5812029B2 (en) * | 2012-06-13 | 2015-11-11 | 株式会社デンソー | Silicon carbide semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP6214680B2 (en) * | 2014-01-10 | 2017-10-18 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Silicon carbide semiconductor device |
| JP6169985B2 (en) * | 2014-01-27 | 2017-07-26 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Semiconductor device |
| JP6589263B2 (en) * | 2014-09-11 | 2019-10-16 | 富士電機株式会社 | Semiconductor device |
-
2016
- 2016-09-21 JP JP2016184257A patent/JP6683083B2/en active Active
-
2017
- 2017-09-21 WO PCT/JP2017/034101 patent/WO2018056357A1/en active Application Filing
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2018056357A1 (en) | 2018-03-29 |
| JP2018049928A (en) | 2018-03-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6683083B2 (en) | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP7327905B2 (en) | Semiconductor device and its manufacturing method | |
| US11476360B2 (en) | Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same | |
| JP5728992B2 (en) | Silicon carbide semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP6367760B2 (en) | Insulated gate type switching device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP5776610B2 (en) | Silicon carbide semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| CN111133588B (en) | Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same | |
| JP2012169385A (en) | Silicon carbide semiconductor device | |
| JP5790573B2 (en) | Silicon carbide semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2012169384A (en) | Silicon carbide semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same | |
| WO2019009091A1 (en) | Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing same | |
| JP6207627B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP2020109808A (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP7206919B2 (en) | semiconductor equipment | |
| JP7095342B2 (en) | Silicon carbide semiconductor device and its manufacturing method | |
| JP7127315B2 (en) | Silicon carbide semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| WO2019181962A1 (en) | Semiconductor device, and production method for same | |
| JP2019165164A (en) | Silicon carbide semiconductor device and manufacturing method of the same | |
| JP7167717B2 (en) | semiconductor equipment | |
| WO2013051343A1 (en) | Silicon carbide semiconductor device and method for producing same | |
| JP2023070568A (en) | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2022184484A (en) | Semiconductor device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20190107 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20190107 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20200225 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20200309 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6683083 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |