JP5475339B2 - 単結晶半導体ナノワイヤの形成 - Google Patents
単結晶半導体ナノワイヤの形成 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5475339B2 JP5475339B2 JP2009149550A JP2009149550A JP5475339B2 JP 5475339 B2 JP5475339 B2 JP 5475339B2 JP 2009149550 A JP2009149550 A JP 2009149550A JP 2009149550 A JP2009149550 A JP 2009149550A JP 5475339 B2 JP5475339 B2 JP 5475339B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- amorphous material
- pattern
- metal
- opening
- single crystal
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 title claims description 67
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims description 22
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 title claims description 5
- 239000002070 nanowire Substances 0.000 title description 19
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 180
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 96
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 94
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 94
- 239000002086 nanomaterial Substances 0.000 claims description 77
- 239000002019 doping agent Substances 0.000 claims description 68
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 63
- 238000002425 crystallisation Methods 0.000 claims description 28
- 230000008025 crystallization Effects 0.000 claims description 28
- 238000004070 electrodeposition Methods 0.000 claims description 26
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 claims description 24
- 238000000137 annealing Methods 0.000 claims description 20
- 150000002736 metal compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims description 19
- 230000001404 mediated effect Effects 0.000 claims description 16
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 16
- 238000011049 filling Methods 0.000 claims description 15
- 229910052732 germanium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 15
- 229910021417 amorphous silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 12
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 claims description 12
- 238000005229 chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 claims description 11
- 238000005240 physical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 229910017817 a-Ge Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 7
- WPYVAWXEWQSOGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N indium antimonide Chemical compound [Sb]#[In] WPYVAWXEWQSOGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 229910021536 Zeolite Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- HNPSIPDUKPIQMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N dioxosilane;oxo(oxoalumanyloxy)alumane Chemical compound O=[Si]=O.O=[Al]O[Al]=O HNPSIPDUKPIQMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000001459 lithography Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000010457 zeolite Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910003481 amorphous carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxo(oxoalumanyloxy)alumane Chemical compound O=[Al]O[Al]=O TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 description 11
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 11
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- 229910052733 gallium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- 229910052785 arsenic Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 229910052796 boron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 229910001092 metal group alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 229910052698 phosphorus Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 229910052787 antimony Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 229910052738 indium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 5
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000002041 carbon nanotube Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229910021393 carbon nanotube Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 238000003717 electrochemical co-deposition Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000011148 porous material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229910004298 SiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000006117 anti-reflective coating Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052797 bismuth Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000003054 catalyst Substances 0.000 description 3
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N citric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC(O)(C(O)=O)CC(O)=O KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000002178 crystalline material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000001312 dry etching Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000010348 incorporation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000002105 nanoparticle Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 238000004151 rapid thermal annealing Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000231 atomic layer deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229940126214 compound 3 Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005137 deposition process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000003792 electrolyte Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000004615 ingredient Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000206 photolithography Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001020 plasma etching Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005204 segregation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052723 transition metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 150000003624 transition metals Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 238000007740 vapor deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- RZBCCAZHJQZKLL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-methoxy-12-methyl-11h-indolo[2,3-a]carbazole-6-carbonitrile Chemical compound N1C2=C3N(C)C4=CC=C[CH]C4=C3C(OC)=C(C#N)C2=C2[C]1C=CC=C2 RZBCCAZHJQZKLL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910021617 Indium monochloride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- -1 SiO 2 Chemical compound 0.000 description 1
- 229910021607 Silver chloride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000003989 dielectric material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- GNPVGFCGXDBREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N germanium atom Chemical compound [Ge] GNPVGFCGXDBREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011261 inert gas Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910021645 metal ion Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002923 metal particle Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000005300 metallic glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001465 metallisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004377 microelectronic Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002073 nanorod Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002071 nanotube Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000623 plasma-assisted chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920003229 poly(methyl methacrylate) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004926 polymethyl methacrylate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003672 processing method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000011218 segmentation Effects 0.000 description 1
- HKZLPVFGJNLROG-UHFFFAOYSA-M silver monochloride Chemical compound [Cl-].[Ag+] HKZLPVFGJNLROG-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000001509 sodium citrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011343 solid material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002194 synthesizing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001771 vacuum deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001039 wet etching Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C30—CRYSTAL GROWTH
- C30B—SINGLE-CRYSTAL GROWTH; UNIDIRECTIONAL SOLIDIFICATION OF EUTECTIC MATERIAL OR UNIDIRECTIONAL DEMIXING OF EUTECTOID MATERIAL; REFINING BY ZONE-MELTING OF MATERIAL; PRODUCTION OF A HOMOGENEOUS POLYCRYSTALLINE MATERIAL WITH DEFINED STRUCTURE; SINGLE CRYSTALS OR HOMOGENEOUS POLYCRYSTALLINE MATERIAL WITH DEFINED STRUCTURE; AFTER-TREATMENT OF SINGLE CRYSTALS OR A HOMOGENEOUS POLYCRYSTALLINE MATERIAL WITH DEFINED STRUCTURE; APPARATUS THEREFOR
- C30B29/00—Single crystals or homogeneous polycrystalline material with defined structure characterised by the material or by their shape
- C30B29/60—Single crystals or homogeneous polycrystalline material with defined structure characterised by the material or by their shape characterised by shape
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B82—NANOTECHNOLOGY
- B82Y—SPECIFIC USES OR APPLICATIONS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MEASUREMENT OR ANALYSIS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MANUFACTURE OR TREATMENT OF NANOSTRUCTURES
- B82Y10/00—Nanotechnology for information processing, storage or transmission, e.g. quantum computing or single electron logic
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B82—NANOTECHNOLOGY
- B82Y—SPECIFIC USES OR APPLICATIONS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MEASUREMENT OR ANALYSIS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MANUFACTURE OR TREATMENT OF NANOSTRUCTURES
- B82Y30/00—Nanotechnology for materials or surface science, e.g. nanocomposites
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C30—CRYSTAL GROWTH
- C30B—SINGLE-CRYSTAL GROWTH; UNIDIRECTIONAL SOLIDIFICATION OF EUTECTIC MATERIAL OR UNIDIRECTIONAL DEMIXING OF EUTECTOID MATERIAL; REFINING BY ZONE-MELTING OF MATERIAL; PRODUCTION OF A HOMOGENEOUS POLYCRYSTALLINE MATERIAL WITH DEFINED STRUCTURE; SINGLE CRYSTALS OR HOMOGENEOUS POLYCRYSTALLINE MATERIAL WITH DEFINED STRUCTURE; AFTER-TREATMENT OF SINGLE CRYSTALS OR A HOMOGENEOUS POLYCRYSTALLINE MATERIAL WITH DEFINED STRUCTURE; APPARATUS THEREFOR
- C30B1/00—Single-crystal growth directly from the solid state
- C30B1/02—Single-crystal growth directly from the solid state by thermal treatment, e.g. strain annealing
- C30B1/023—Single-crystal growth directly from the solid state by thermal treatment, e.g. strain annealing from solids with amorphous structure
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C30—CRYSTAL GROWTH
- C30B—SINGLE-CRYSTAL GROWTH; UNIDIRECTIONAL SOLIDIFICATION OF EUTECTIC MATERIAL OR UNIDIRECTIONAL DEMIXING OF EUTECTOID MATERIAL; REFINING BY ZONE-MELTING OF MATERIAL; PRODUCTION OF A HOMOGENEOUS POLYCRYSTALLINE MATERIAL WITH DEFINED STRUCTURE; SINGLE CRYSTALS OR HOMOGENEOUS POLYCRYSTALLINE MATERIAL WITH DEFINED STRUCTURE; AFTER-TREATMENT OF SINGLE CRYSTALS OR A HOMOGENEOUS POLYCRYSTALLINE MATERIAL WITH DEFINED STRUCTURE; APPARATUS THEREFOR
- C30B29/00—Single crystals or homogeneous polycrystalline material with defined structure characterised by the material or by their shape
- C30B29/60—Single crystals or homogeneous polycrystalline material with defined structure characterised by the material or by their shape characterised by shape
- C30B29/605—Products containing multiple oriented crystallites, e.g. columnar crystallites
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10D—INORGANIC ELECTRIC SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
- H10D62/00—Semiconductor bodies, or regions thereof, of devices having potential barriers
- H10D62/10—Shapes, relative sizes or dispositions of the regions of the semiconductor bodies; Shapes of the semiconductor bodies
- H10D62/117—Shapes of semiconductor bodies
- H10D62/118—Nanostructure semiconductor bodies
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10D—INORGANIC ELECTRIC SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
- H10D62/00—Semiconductor bodies, or regions thereof, of devices having potential barriers
- H10D62/10—Shapes, relative sizes or dispositions of the regions of the semiconductor bodies; Shapes of the semiconductor bodies
- H10D62/117—Shapes of semiconductor bodies
- H10D62/118—Nanostructure semiconductor bodies
- H10D62/119—Nanowire, nanosheet or nanotube semiconductor bodies
- H10D62/121—Nanowire, nanosheet or nanotube semiconductor bodies oriented parallel to substrates
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10D—INORGANIC ELECTRIC SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
- H10D62/00—Semiconductor bodies, or regions thereof, of devices having potential barriers
- H10D62/10—Shapes, relative sizes or dispositions of the regions of the semiconductor bodies; Shapes of the semiconductor bodies
- H10D62/117—Shapes of semiconductor bodies
- H10D62/118—Nanostructure semiconductor bodies
- H10D62/119—Nanowire, nanosheet or nanotube semiconductor bodies
- H10D62/122—Nanowire, nanosheet or nanotube semiconductor bodies oriented at angles to substrates, e.g. perpendicular to substrates
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10S—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10S977/00—Nanotechnology
- Y10S977/70—Nanostructure
- Y10S977/762—Nanowire or quantum wire, i.e. axially elongated structure having two dimensions of 100 nm or less
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10S—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10S977/00—Nanotechnology
- Y10S977/70—Nanostructure
- Y10S977/813—Of specified inorganic semiconductor composition, e.g. periodic table group IV-VI compositions
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Nanotechnology (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Metallurgy (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Composite Materials (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Crystals, And After-Treatments Of Crystals (AREA)
- Silicon Compounds (AREA)
- Other Surface Treatments For Metallic Materials (AREA)
Description
本発明の目的は、単結晶ナノワイヤを形成するための代わりの方法を提供することである。
この方法は、少なくとも以下の工程:
基板の主表面上に最初にパターンを形成する工程であって、パターンは少なくとも1つの開口部を有し、開口部はパターンの表面から基板の主表面まで延びる工程と、
パターンの少なくとも1つの開口部中の、露出した主表面の上に、金属を供給する工程と、
少なくとも1つの開口部を、アモルファス材料で少なくとも部分的に埋める工程と、
アモルファス材料と金属とを、300℃と1000℃の間の温度でアニールし、金属媒介結晶化により、アモルファス材料を単結晶材料に変えて、単結晶ナノ構造を形成する工程と、
任意的に、金属化合物および/またはパターンを除去する工程と、を含む。
基板の主表面上に層を堆積する工程と、
リソグラフィパターニングと反応性イオンエッチングを用いて、堆積層中にパターンを形成する工程と、を含む。
基板の主表面上に最初にパターンを形成する工程であって、パターンは少なくとも1つの開口部を有し、開口部はパターンの表面から基板の主表面まで延びる工程と、
パターンの少なくとも1つの開口部中の、露出した主表面の上に、金属を供給する工程と、
少なくとも1つの開口部を、第1のアモルファス材料で少なくとも部分的に埋める工程と、
少なくとも1つの開口部の、第1のアモルファス材料の上に残った部分を、第2のアモルファス材料で少なくとも部分的に埋める工程と、
第1および第2のアモルファス材料と金属化合物とを、300℃と1000℃の間の温度でアニールし、金属媒介結晶化により、第1および第2のアモルファス材料をそれぞれ第1および第2の単結晶材料に変えて、セグメント化された単結晶ナノ構造を形成する工程と、
任意的に、金属化合物および/またはパターンを除去する工程と、を含む。
基板の主表面上に最初にパターンを形成する工程であって、パターンは少なくとも1つの開口部を有し、開口部はパターンの表面から基板の主表面まで延びる工程と、
パターンの少なくとも1つの開口部中に、金属を供給する工程と、
少なくとも1つの開口部を、第1のアモルファス材料で部分的に埋める工程と、
第1のアモルファス材料と金属化合物とを、300℃と1000℃の間の温度でアニールし、金属媒介結晶化により、第1のアモルファス材料を第1の単結晶材料に変える工程と、
少なくとも1つの開口部の、第1の単結晶材料の上に残った部分を、第2のアモルファス材料で少なくとも部分的に埋める工程と、
第2のアモルファス材料と金属化合物とを、300℃と1000℃の間の温度でアニールし、金属媒介結晶化により、第2のアモルファス材料を第2の単結晶材料に変えて、セグメント化された単結晶ナノ構造を形成する工程と、
任意的に、金属化合物および/またはパターンを除去する工程と、を含む。
基板の主表面上に最初にパターンを形成する工程であって、パターンは少なくとも1つの開口部を有し、開口部はパターンの表面から基板の主表面まで延びる工程と、
パターンの少なくとも1つの開口部中に金属を供給する工程と、
少なくとも1つの開口部を、アモルファス材料で少なくとも部分的に埋める工程と、
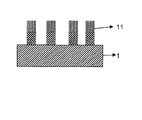
300℃と1000℃の間の温度で基板をアニールし、金属媒介結晶化により、アモルファス材料を単結晶材料に変えて、単結晶ナノ構造を形成する工程と、
任意的に、金属化合物および/またはパターンを除去する工程と、を含む。
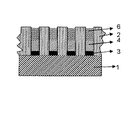
2 パターン
3 金属
4、6 アモルファス材料
5 結晶材料
7、8 単結晶構造
10、11 単結晶ナノ構造
Claims (18)
- 結晶ナノ構造を基板の上に成長させる方法であって、
基板(1)の主表面上に最初にパターン(2)を形成する工程であって、パターン(2)は少なくとも1つの開口部を有し、開口部はパターンの表面から基板(1)の主表面まで延びる工程と、
パターン(2)の開口部中の、露出した主表面の上に、金属(3)を供給する工程と、
開口部をアモルファス材料(4)で、少なくとも部分的に埋める工程と、
アモルファス材料(4)と金属化合物(3)とを、300℃と1000℃の間の温度でアニールし、金属媒介結晶化により、アモルファス材料(4)の一部を単結晶材料(5)に少なくとも変えて、結晶ナノ構造を形成する工程と、を含む方法。 - 基板(1)が伝導性または半伝導性材料であり、金属(3)を提供する工程は、電解手段により電気化学堆積(ECD)を行う工程を含む請求項1に記載の方法。
- 基板が伝導性、または半伝導性、または絶縁性であり、金属(3)を提供する工程は、無電解手段により電気化学堆積(ECD)を行う工程、または化学気相堆積(CVD)技術を行う工程、または物理気相堆積(PVD)技術を行う工程を含む請求項1に記載の方法。
- パターンが、多孔性パターンであり、開口部は2nm〜100nmの範囲の直径を有する請求項1〜3のいずれかに記載の方法。
- パターンを形成する工程が、
基板の主表面の上に層を堆積する工程と、
続いて、少なくともリソグラフィパターニングを用いて堆積された層にパターンを形成する工程であって、開口部が2nm〜100nmの範囲の直径を有する工程と、を含む請求項1〜3のいずれかに記載の方法。 - パターンは犠牲パターンであり、更に、単結晶ナノ構造の形成後にパターンを除去する工程を含む請求項1〜5のいずれかに記載の方法。
- 単結晶ナノ構造がドープされ、金属は、更に、アニール工程中にアモルファス材料中に溶けるように選択されたドーパント元素を含み、これによりドープされた単結晶ナノ構造を得る請求項1〜6のいずれかに記載の方法。
- 開口部をアモルファス材料で少なくとも部分的に埋める工程は、電気化学堆積(ECD)を用いて行われ、基板が伝導性(金属)または半伝導性(Si、Ge、III−V半導体)材料からなる請求項1〜7のいずれかに記載の方法。
- アモルファス材料が、アモルファスSi(a−Si)、アモルファスGe(a−Ge)、アモルファスInSb(a−InSb)、またはアモルファスカーボン(a−C)である請求項1〜8のいずれかに記載の方法。
- 単結晶ナノ構造がドープされ、開口部をアモルファス材料で少なくとも部分的に埋める工程は、ドーパント元素とアモルファス材料との同時堆積により行われ、これによりドープされたアモルファス材料を形成する請求項1〜9のいずれかに記載の方法。
- 単結晶ナノ構造がドーパント濃度のばらつきを有し、ドープされたアモルファス材料で開口部を少なくとも部分的に埋める工程は、所定の膜厚を有するドープされたアモルファス材料を最初に堆積する工程と、所定の膜厚を有するアンドープのアモルファス材料を堆積する工程とを含む請求項10に記載の方法。
- 単結晶構造は、それぞれ一のアモルファス材料と他のアモルファス材料から形成された第1および第2のセグメントを含み、更に、開口部をアモルファス材料で部分的に埋めた後に、開口部の残りの部分を他のアモルファス材料で、少なくとも部分的に埋める工程を含む請求項1〜11のいずれかに記載の方法。
- アモルファス材料と他のアモルファス材料が、同じアニール工程中にアニールされ、それぞれ第1および第2のセグメントを形成する請求項12に記載の方法。
- 開口部の残りの部分を他のアモルファス材料で部分的に埋める工程の前に、アモルファス材料(4)がアニールされて第1のセグメントを形成する請求項12に記載の方法。
- 第1のセグメントを形成した後に、他の金属化合物が第1のセグメントの上に供給される請求項14に記載の方法。
- 半導体デバイスの作製における、請求項1〜15のいずれかに記載の方法の使用。
- 基板(1)が、金属、Si、Ge、またはIII−V半導体からなることを特徴とする請求項2に記載の方法。
- 多孔性パターンが、陽極酸化アルミニウム酸化物(AAO)または配向ゼオライトからなることを特徴とする請求項4に記載の方法。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US7514108P | 2008-06-24 | 2008-06-24 | |
| US61/075,141 | 2008-06-24 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010064951A JP2010064951A (ja) | 2010-03-25 |
| JP2010064951A5 JP2010064951A5 (ja) | 2012-08-09 |
| JP5475339B2 true JP5475339B2 (ja) | 2014-04-16 |
Family
ID=41009806
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009149550A Active JP5475339B2 (ja) | 2008-06-24 | 2009-06-24 | 単結晶半導体ナノワイヤの形成 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US7897494B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP2138609B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5475339B2 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011023610A (ja) * | 2009-07-16 | 2011-02-03 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| US8518826B2 (en) * | 2010-07-13 | 2013-08-27 | Lam Research Corporation | Metallization processes, mixtures, and electronic devices |
| TWI585032B (zh) | 2012-06-28 | 2017-06-01 | 無限科技全球公司 | 用於製造奈米結構的方法 |
| FR3073321B1 (fr) * | 2017-11-07 | 2019-12-20 | Commissariat A L'energie Atomique Et Aux Energies Alternatives | Procede de cristallisation d'une couche utile |
| US10790145B2 (en) * | 2018-09-05 | 2020-09-29 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Methods of forming crystallized materials from amorphous materials |
| US10707298B2 (en) | 2018-09-05 | 2020-07-07 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Methods of forming semiconductor structures |
| US11018229B2 (en) | 2018-09-05 | 2021-05-25 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Methods of forming semiconductor structures |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4701161B2 (ja) * | 2003-04-04 | 2011-06-15 | キューナノ エービー | 正確に位置決めされたナノウィスカおよびナノウィスカアレイ、およびそれらを作成する方法 |
| DE602005020051D1 (de) | 2004-10-27 | 2010-04-29 | Koninkl Philips Electronics Nv | Halbleiterbauelement mit abstimmbarem abstand zwischen energiebändern |
| KR101138865B1 (ko) | 2005-03-09 | 2012-05-14 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 나노 와이어 및 그 제조 방법 |
| JP2007137762A (ja) * | 2005-11-10 | 2007-06-07 | Samsung Electronics Co Ltd | 多孔性テンプレートを利用するナノワイヤの製造方法、ならびにナノワイヤを用いたマルチプローブ、電界放出チップおよび素子 |
| JP5137095B2 (ja) * | 2006-02-20 | 2013-02-06 | 国立大学法人 筑波大学 | シリコンナノ結晶材料の製造方法及び該製造方法で製造されたシリコンナノ結晶材料 |
| US7425491B2 (en) * | 2006-04-04 | 2008-09-16 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Nanowire transistor with surrounding gate |
| EP2002470B1 (en) * | 2006-04-04 | 2016-03-09 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Method fo growing nanofin transistors |
| KR100791790B1 (ko) * | 2006-05-30 | 2008-01-03 | 고려대학교 산학협력단 | 육각형의 나노 판상 다이아몬드 형성방법 |
-
2009
- 2009-06-23 US US12/490,189 patent/US7897494B2/en active Active
- 2009-06-24 JP JP2009149550A patent/JP5475339B2/ja active Active
- 2009-06-24 EP EP09075275A patent/EP2138609B1/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2138609A1 (en) | 2009-12-30 |
| US20100075486A1 (en) | 2010-03-25 |
| US7897494B2 (en) | 2011-03-01 |
| JP2010064951A (ja) | 2010-03-25 |
| EP2138609B1 (en) | 2012-08-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5231105B2 (ja) | 偏長ナノ構造を成長させるための触媒ナノ粒子の形成方法 | |
| JP5475339B2 (ja) | 単結晶半導体ナノワイヤの形成 | |
| JP2009255025A6 (ja) | 偏長ナノ構造を成長させるための触媒ナノ粒子の形成方法 | |
| JP5329800B2 (ja) | 触媒ナノ粒子の制御および選択的な形成 | |
| US7741197B1 (en) | Systems and methods for harvesting and reducing contamination in nanowires | |
| KR100666187B1 (ko) | 나노선을 이용한 수직형 반도체 소자 및 이의 제조 방법 | |
| KR101093364B1 (ko) | 다원계 나노선 제조방법 | |
| KR100834896B1 (ko) | 반도체 나노 구조체 및 이의 제조방법과, 이를 포함하는반도체 소자 | |
| US10037896B2 (en) | Electro-assisted transfer and fabrication of wire arrays | |
| KR101636907B1 (ko) | 다공성 나노 구조체 및 그 제조 방법 | |
| EP2102900B1 (en) | Self-constrained anisotropic germanium nanostructure from electroplating | |
| US10147789B2 (en) | Process for fabricating vertically-aligned gallium arsenide semiconductor nanowire array of large area | |
| US9691849B2 (en) | Ultra-long silicon nanostructures, and methods of forming and transferring the same | |
| CN110499489A (zh) | 一种半导体/金属异质结纳米线阵列材料的制备工艺 | |
| KR100810983B1 (ko) | 위치 선택적 수직형 나노선 성장 방법, 수직형 나노선을포함하는 반도체 나노 소자 및 이의 제조 방법 | |
| JP2012011374A (ja) | カーボンナノチューブの成長に適した触媒の形成方法 | |
| Leonardi et al. | Silicon Nanowires Synthesis by Metal-Assisted Chemical Etching: A Review. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 383 | |
| Chen et al. | Fabrication of ultrahigh-density nanowires by electrochemical nanolithography | |
| TWI323516B (en) | The fabricating method of single electron transistor (set) by employing nano-lithographical technology in the semiconductor process | |
| Das et al. | Novel nonlithographic quantum wire array fabrication | |
| KR20110003216A (ko) | 탄소나노튜브의 제조 방법 | |
| Arutyunov | Fabrication of quasi-one-dimensional superconducting micro-and nanostructures | |
| Kim et al. | The organization of carbon nanotube and silicon nanowires using lateral-type porous anodic alumina |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120621 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20120621 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20130709 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130716 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20131016 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20140107 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20140206 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5475339 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |