JP5213861B2 - イメージング装置及び方法 - Google Patents
イメージング装置及び方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5213861B2 JP5213861B2 JP2009527885A JP2009527885A JP5213861B2 JP 5213861 B2 JP5213861 B2 JP 5213861B2 JP 2009527885 A JP2009527885 A JP 2009527885A JP 2009527885 A JP2009527885 A JP 2009527885A JP 5213861 B2 JP5213861 B2 JP 5213861B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- acousto
- optic
- aod
- deflector
- acoustic wave
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 56
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 title description 20
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 claims description 110
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 claims description 103
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 claims description 57
- 230000005670 electromagnetic radiation Effects 0.000 claims description 54
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 claims description 37
- 230000001902 propagating effect Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- 230000004075 alteration Effects 0.000 description 116
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 description 47
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 28
- 230000010287 polarization Effects 0.000 description 24
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 23
- 230000005284 excitation Effects 0.000 description 15
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 14
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 14
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 description 14
- 230000003595 spectral effect Effects 0.000 description 13
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 11
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 8
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000001228 spectrum Methods 0.000 description 7
- 210000002569 neuron Anatomy 0.000 description 6
- 238000006303 photolysis reaction Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000015843 photosynthesis, light reaction Effects 0.000 description 6
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000005331 crown glasses (windows) Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000005308 flint glass Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000000946 synaptic effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 3
- 210000004027 cell Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 238000010226 confocal imaging Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000033001 locomotion Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000000644 propagated effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000002123 temporal effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000003491 array Methods 0.000 description 2
- 210000005013 brain tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 238000002425 crystallisation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008025 crystallization Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000005357 flat glass Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003269 fluorescent indicator Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000010354 integration Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000001537 neural effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000002858 neurotransmitter agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005457 optimization Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000035790 physiological processes and functions Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000010936 titanium Substances 0.000 description 2
- OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Calcium Chemical compound [Ca] OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium Chemical compound [Ti] RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000002441 X-ray diffraction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000036982 action potential Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 201000009310 astigmatism Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004071 biological effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012620 biological material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000031018 biological processes and functions Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013480 data collection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013500 data storage Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001627 detrimental effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009977 dual effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005684 electric field Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007850 fluorescent dye Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000338 in vitro Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001727 in vivo Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000010365 information processing Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003993 interaction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003834 intracellular effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000037041 intracellular level Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012886 linear function Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000386 microscopy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000340 multi-photon laser scanning microscopy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000035515 penetration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008832 photodamage Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052594 sapphire Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010980 sapphire Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004904 shortening Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008054 signal transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010186 staining Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000000225 synapse Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- LAJZODKXOMJMPK-UHFFFAOYSA-N tellurium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Te]=O LAJZODKXOMJMPK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000001131 transforming effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002604 ultrasonography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012800 visualization Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N21/00—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of optical means, i.e. using sub-millimetre waves, infrared, visible or ultraviolet light
- G01N21/62—Systems in which the material investigated is excited whereby it emits light or causes a change in wavelength of the incident light
- G01N21/63—Systems in which the material investigated is excited whereby it emits light or causes a change in wavelength of the incident light optically excited
- G01N21/64—Fluorescence; Phosphorescence
- G01N21/645—Specially adapted constructive features of fluorimeters
- G01N21/6456—Spatial resolved fluorescence measurements; Imaging
- G01N21/6458—Fluorescence microscopy
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B21/00—Microscopes
- G02B21/0004—Microscopes specially adapted for specific applications
- G02B21/002—Scanning microscopes
- G02B21/0024—Confocal scanning microscopes (CSOMs) or confocal "macroscopes"; Accessories which are not restricted to use with CSOMs, e.g. sample holders
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B21/00—Microscopes
- G02B21/0004—Microscopes specially adapted for specific applications
- G02B21/002—Scanning microscopes
- G02B21/0024—Confocal scanning microscopes (CSOMs) or confocal "macroscopes"; Accessories which are not restricted to use with CSOMs, e.g. sample holders
- G02B21/0036—Scanning details, e.g. scanning stages
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/0009—Materials therefor
- G02F1/0072—Mechanical, acoustic, electro-elastic, magneto-elastic properties
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/29—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the position or the direction of light beams, i.e. deflection
- G02F1/33—Acousto-optical deflection devices
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/29—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the position or the direction of light beams, i.e. deflection
- G02F1/33—Acousto-optical deflection devices
- G02F1/332—Acousto-optical deflection devices comprising a plurality of transducers on the same crystal surface, e.g. multi-channel Bragg cell
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F2201/00—Constructional arrangements not provided for in groups G02F1/00 - G02F7/00
- G02F2201/16—Constructional arrangements not provided for in groups G02F1/00 - G02F7/00 series; tandem
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F2203/00—Function characteristic
- G02F2203/28—Function characteristic focussing or defocussing
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Nonlinear Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Acoustics & Sound (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Optical Modulation, Optical Deflection, Nonlinear Optics, Optical Demodulation, Optical Logic Elements (AREA)
- Microscoopes, Condenser (AREA)
- Mechanical Optical Scanning Systems (AREA)
- Investigating, Analyzing Materials By Fluorescence Or Luminescence (AREA)
- Lenses (AREA)
Description
本発明を完全に理解するために本発明に関連する技術的効果を説明することは有用である。図1は音響光学偏向器の中でのブラッグ回折の原理を示す。
fac(t)=fac(0)+at (2)
を付与することによってその周波数が時間と共に直線的に増加又は減少するように「チャープ」され得る。
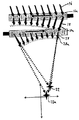
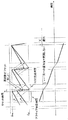
図10は本発明による2光子顕微鏡システムを示す。
図12は、図10の第1イメージフィールドXi1、Yi1、Zi1内の点に関する(図9で説明したような)色収差の影響を示す。
f1=レンズ110の焦点距離
f2=レンズ150の焦点距離
λ=動作波長
である。
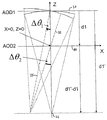
上記の図6と図8とを比較すると、図8の第1 AOD内で生じている回折の任意の0次成分は、第2 AODを通って透過されイメージフィールドと干渉する恐れがあることが分かる。この理由は、図8が、図6とは異なり、回折されていないビームが回折されたビームと極めて類似の方向に通過するように平行配置に取り付けられたAODを有するからである。この問題は、回折の0次成分の透過を妨げるための偏光子及びオプションの2分の1波長板の使用を含む本発明の第2の態様によって緩和される。
通常、AODを製造するために使用される異方性音響光学結晶は、レーザ光に対して値付けされた受光角を有する。結晶自体はこの受光角に関して最大の透過効率になるように最適化されている。一定の受光角でレーザ光を受光するシステム内の第1及び第3 AODにとっては、こうした結晶は極めて適している。しかし、こうした結晶が第2及び第4 AODに使用されるときには問題が生じ、それは、第1及び第3 AOD内でそれぞれなされ得る偏向角度範囲によって規定される範囲にわたって受光角度が変化するからである。これらの知れられたデバイスは、3Wの音響パワーを有する800nmのレーザを±20mradにわたって偏向できる(17.43mrad=1°)。透過効率は80%を超える。
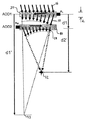
本発明の本態様は二つの結晶変換器を有するAODを提供する。これは図33に示される。第1結晶変換器12aは光の伝播方向に狭い幅を有するように構成され、第2結晶変換器12bは光の伝播方向に広い幅を有するように構成される。本実施形態において、変換器12aは0.25mmの幅を有し変換器12bは3mmの幅を有する。変換器に電力を供給するために励起源300が設けられ、スイッチ310により、オペレータは次に第1又は第2変換器を励起させるかどうかを選択できる。
本発明の本態様を図34に示す。一つのAOD結晶には二つ以上の結晶変換器を設けることができる。各結晶変換器は音響波の伝播を助けるために選択的に使用できる。図34の例では、三つの結晶変換器12a、12b及び12cが示される。好ましくは、変換器の幅は例えばそれぞれの度に2倍だけ幾何級数的に増加する。好適には、結晶変換器は、それぞれ後続の変換器が先行する変換器の幅より2倍広いという特性を有する。例えば、変換器12aは0.25mm幅であってよく、変換器12bは0.5mm幅及び変換器12cは1mm幅であってよい。スイッチ310a、310b又は310cの適切な選択により0.25mmと1.75mmの範囲内の実効的変換器幅が得られる。これにより、AODは使用される用途に最も適した方法で利用できる。したがって、これは、多様に異なる実験に使用できる汎用目的装置の実現を助ける。必要であればより多くの変換器を設けることができる。
普通、AOD結晶はX軸の周りに約6°及びY軸の周りに0°だけ回転される。これによって、偏向角範囲を最大化し回折されたビームからのパワーの縮退再回折(degenerate re-diffraction)を避けるために、中心周波数を増加できる。音波伝播は高度に異方性であるので、6°の結晶回転が、Y軸に対して約50°の角度の音波パワー伝播をもたらす。
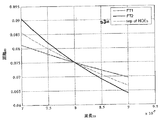
図35a及び図35bは、図27に示した4 AODシステムに関する典型的な実際の構成を示す。これから分かるように、AOD 30、50、40、60のそれぞれは、テレセントリックリレー400により後続のAODに結合されている。通常、このようなテレセントリックリレーは、レーザ光路ビームに沿って400mm以上の長さを有する。図35bから分かるように、各テレセントリックリレーは4fの全長を有し、但しfは一つのリレーレンズの焦点距離である。典型的にはf=100mmである。したがって、AODを共に結合させるために少なくとも三つのテレセントリックリレーを使用するという要件は、システムの全ビーム長に1.2mを付け加える。上記で説明したように、光の様々な波長が異なる大きさだけ回折される。そのため、レーザ波長が変化すると、AOD及びテレセントリックリレーは再度位置決めされなければならない。図35bは、二つの変位H1及びH2を示す。これらは、入力ビーム中心線と比較した出力ビーム中心線の変位である。この変位は光の波長と共に変化する。波長λ=700nmではこの変位は約32mmである。波長λ=900nmではこの変位は約40mmである。したがって、レーザ波長を700nmから900nmまで変化させると、光学的構成要素は8mmだけ再アライメントされなければならない。こうした再アライメントはテレセントリックリレーを使用することの必然的結果である。したがって、レーザ波長を頻繁に変えることが意図されたシステムでは、テレセントリックリレーは理想的ではない。それゆえ、本発明の本態様はテレセントリックリレーを不要にするための手段を提供し、これによって、よりコンパクトで構成可能なシステムが提供できる。
ここで、
V=AOD内の音速(m/s)
a1=第1 AOD駆動のランプ率(Hz/s)
λ=光の波長(m)
である。
ターゲットの3次元画像を構築するためには、ターゲットを通る所定の経路に沿って焦点でラスター走査を行うことができることが有用である。一つの可能なラスター走査は、Y値及びZ値を一定に維持しながら焦点をX方向に移動させ、次いである小量だけY位置を増加させ、新たな走査をX方向で行い、走査の2次元グリッドが達成されるまでこれを続けることである。その後でZ方向を増加させ、3次元体積が構築されるまで新たな2次元グリッドが走査される。これは、3次元画像が形成できるようになされた本発明のシステムで極めて迅速に行うことができる。
第1 AOD 30と第3 AOD 50との間の実効的離隔距離は
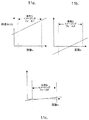
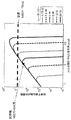
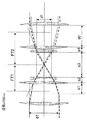
上記の図20〜図23は、Z平面での色収差を完全に補正する(図23)か、Z及びY平面での色収差を完全に補正する(図22)か、又は、色収差は全ての面で補正されるが最大限度までは補正されないある中間的補正を達成する(図20)かのいずれかのために、補償係数Cを変化させることの可能性を示している。この補償係数Cを変化させるためには、テレセントリックリレーに使用されるレンズの屈折強度を変化させる必要がある。例えば、図17のレンズ110及び150は、補償係数Cを変えるためにより強い又はより弱い分散性レンズに取り替えることができる。システムの任意の実際の実施形態では、レンズを物理的に交換せずに補償係数Cを変化させる方法をシステムの設計に盛り込むことが有益である。
Claims (20)
- 電磁放射のビームを操作するためのシステムであって、
第1音響光学偏向器と、
前記第1音響光学偏向器の下流に直列に配置され、前記第1音響光学偏向器から実効的光学離隔距離だけ離隔された第2音響光学偏向器と、
前記第1及び第2音響光学偏向器内に音響波を供給するためのドライバーであって、前記音響波は、前記第1及び第2音響光学偏向器の間の前記実効的光学離隔距離を考慮するために異なるランプ率でチャープされるドライバーと、
を備えるシステム。 - 第3音響光学偏向器と、
前記第3音響光学偏向器の下流に配置され、前記第3音響光学偏向器から実効的光学離隔距離だけ離隔された第4音響光学偏向器と
をさらに備え、
前記ドライバーは音響波を前記第3及び第4音響光学偏向器内に供給するように構成され、前記音響波は前記第3及び前記第4音響光学偏向器間の前記実効的光学離隔距離を考慮するために異なるランプ率でチャープされる請求項1に記載のシステム。 - 前記ドライバーは、電磁放射のビームを空間内の定常点(焦点)に集束させる音響波を供給するように構成された請求項2に記載のシステム。
- 前記ドライバーは、ランプ率a1を有する音響波を前記第1音響光学偏向器に供給し、ランプ率a2を有する音響波を前記第2音響光学偏向器に供給し、前記ランプ率は、
前記ドライバーは、ランプ率a3を有する音響波を前記第3音響光学偏向器に供給し、ランプ率a4を有する音響波を前記第4音響光学偏向器に供給し、前記ランプ率は、
- 前記音響光学偏向器は、前記レーザビームの光路内で、
第1音響光学偏向器、
第3音響光学偏向器、
第2音響光学偏向器、
第4音響光学偏向器、
の順序で配置される、請求項2、3又は4に記載のシステム。 - 前記ドライバーは、ターゲットをX及び/又はY方向に走査するように前記音響波の周波数を選択するように構成された請求項2ないし6のいずれか一項に記載のシステム。
- 前記ドライバーは、ターゲットを前記X及び/又はY方向に走査するように音響波を供給し、前記走査は、各ミニ走査の各アクティブ期間の間に非アクティブ期間を有する一連の前記ミニ走査から構成され、
選択的に、前記非アクティブ期間は、焦点位置を移動させることなく前記音響光学偏向器に供給される前記周波数の絶対値を調節するためのものであり、
選択的に、前記ドライバーは、2次元又は3次元でターゲット上の点を、各ミニ走査の各アクティブ期間の間に非アクティブ期間を有する一連のミニ走査をするように4つの音響波を供給し、
選択的に、前記非アクティブ期間は、前記焦点位置を移動させることなく前記第1、第2、第3及び第4音響光学偏向器に供給される前記周波数の前記絶対値を調整するためのものであり、
選択的に、前記第1及び第2音響光学偏向器に供給される前記周波数の絶対値は、
選択的に、前記第3及び第4音響光学偏向器に供給される前記周波数の前記絶対値は、
- 電磁放射を第1音響光学偏向器に通過させ、次に、当該第1音響光学偏向器の下流側の第2音響光学偏向器に通過させるステップを含み、
前記第1及び第2音響光学偏向器は、第1及び第2音響波をそれぞれ含んでおり、
前記第1及び第2音響波は、前記第1及び第2音響光学偏向器の間の実効的光学離隔距離を考慮するために、異なるランプ率でチャープされる、電磁放射のビームを操作する方法。 - さらに、第3音響光学偏向器、及び当該第3音響光学偏向器の下流の第4音響光学偏向器に、前記電磁放射を通過せるステップを含み、
前記第3及び第4音響光学偏向器は、第3及び第4音響波をそれぞれ含んでおり、
前記第3及び第4音響波は、前記第3及び第4音響光学偏向器の間の実効的光学離隔距離を考慮するために、異なるランプ率でチャープされる、請求項9に記載の方法。 - 前記電磁放射のビームは、空間定留点に焦点が合わせられている、請求項10に記載の方法。
- 前記第1音響波はランプ率a1を有し、前記第2音響波はランプ率a2を有し、前記ランプ率は、
前記ドライバーは、ランプ率a3を有する音響波を前記第3音響光学偏向器に供給し、ランプ率a4を有する音響波を前記第4音響光学偏向器に供給し、前記ランプ率は、
- 前記電磁放射のビームは、前記音響光学偏向器を、
第1音響光学偏向器、
第3音響光学偏向器、
第2音響光学偏向器、
第4音響光学偏向器
の順序で通過する、請求項10ないし12のいずれか一項に記載の方法。 - 前記電磁放射のビームはターゲットをX及び/又はY方向に走査する請求項10ないし13のいずれか一項に記載の方法。
- 前記電磁放射のビームはターゲットをX及び/又はY方向に走査し、前記走査は、各ミニ走査の間に非アクティブ期間を有する一連のミニ走査から構成され、
選択的に、前記非アクティブ期間は、前記焦点位置を移動させることなく前記音響光学偏向器に供給される周波数の絶対値を調節するためのものであり、
選択的に、前記非アクティブ期間は周波数リセット時間及びAOD充填時間を含み、
選択的に、前記第1及び第2音響波の周波数の前記絶対値は、
- 前記電磁放射のビームは、1つの点が2又は3方向に走査されるように四つの音響波を通過し、
前記走査は、各ミニ走査の各アクティブ期間の間の非アクティブ期間を有する一連のミニ走査から構成された請求項10ないし16のいずれか一項に記載の方法。 - 前記ビームの入力方向は、負のZ軸によって定義され、
前記第2音響光学偏向器の前記結晶構造は、X軸の周りに2°以下だけ回転されている、請求項1ないし8のいずれか一項に記載のシステム。 - 前記第2音響光学偏向器の前記結晶構造は、Y軸の周りに約3°だけ回転されている、請求項18に記載のシステム。
- 前記第2音響光学偏向器は、伝播する音響波がその波動ベクトルとポインティングベクトルとの間に約20°の角度を有するように方位されている、請求項18又は19に記載のシステム。
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| GB0617945.1 | 2006-09-12 | ||
| GBGB0617945.1A GB0617945D0 (en) | 2006-09-12 | 2006-09-12 | Imaging apparatus and methods |
| PCT/GB2007/003455 WO2008032061A2 (en) | 2006-09-12 | 2007-09-12 | Imaging apparatus and methods |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013036172A Division JP2013152471A (ja) | 2006-09-12 | 2013-02-26 | ビーム偏向装置及び方法 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010503001A JP2010503001A (ja) | 2010-01-28 |
| JP2010503001A5 JP2010503001A5 (ja) | 2010-10-28 |
| JP5213861B2 true JP5213861B2 (ja) | 2013-06-19 |
Family
ID=37232800
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009527885A Expired - Fee Related JP5213861B2 (ja) | 2006-09-12 | 2007-09-12 | イメージング装置及び方法 |
| JP2013036172A Pending JP2013152471A (ja) | 2006-09-12 | 2013-02-26 | ビーム偏向装置及び方法 |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013036172A Pending JP2013152471A (ja) | 2006-09-12 | 2013-02-26 | ビーム偏向装置及び方法 |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (4) | US8294977B2 (ja) |
| EP (4) | EP2634622A1 (ja) |
| JP (2) | JP5213861B2 (ja) |
| GB (1) | GB0617945D0 (ja) |
| HU (1) | HUE029308T2 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2008032061A2 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (41)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB0617945D0 (en) | 2006-09-12 | 2006-10-18 | Ucl Business Plc | Imaging apparatus and methods |
| HU0800781D0 (en) * | 2008-12-31 | 2009-03-02 | Femtonics Kft | Focusing system comprising acousto-optic deflectors for focusing an electromagnetic beam |
| TWI594828B (zh) * | 2009-05-28 | 2017-08-11 | 伊雷克托科學工業股份有限公司 | 應用於雷射處理工件中的特徵的聲光偏轉器及相關雷射處理方法 |
| US8786757B2 (en) * | 2010-02-23 | 2014-07-22 | Primesense Ltd. | Wideband ambient light rejection |
| GB201006679D0 (en) | 2010-04-21 | 2010-06-09 | Ucl Business Plc | Methods and apparatus to control acousto-optic deflectors |
| EP3358387A1 (en) | 2010-08-27 | 2018-08-08 | The Board of Trustees of The Leland Stanford Junior University | Microscopy imaging device with advanced imaging properties |
| US8891157B2 (en) * | 2010-08-30 | 2014-11-18 | Micronic Ab | Acousto-optic deflectors over one octave |
| GB201106787D0 (en) | 2011-04-20 | 2011-06-01 | Ucl Business Plc | Methods and apparatus to control acousto-optic deflectors |
| US8939006B2 (en) * | 2011-05-04 | 2015-01-27 | Honeywell International Inc. | Photoacoustic detector with long term drift compensation |
| WO2013098568A1 (en) * | 2011-12-28 | 2013-07-04 | Femtonics Kft. | Compensator system and method for compensating angular dispersion |
| ES2732423T3 (es) * | 2012-01-05 | 2019-11-22 | Femtonics Kft | Método para escanear a lo largo de una trayectoria de escaneo continuo con un sistema de escáner |
| EP2802861A4 (en) * | 2012-01-11 | 2015-08-19 | Hughes Howard Med Inst | MULTIDIMENSIONAL IMAGING USING MULTI-ROOM MICROSCOPY |
| ES2727498T3 (es) | 2012-09-30 | 2019-10-16 | Optica Amuka A A Ltd | Lentes con potencia y alineación eléctricamente ajustable |
| US11126040B2 (en) | 2012-09-30 | 2021-09-21 | Optica Amuka (A.A.) Ltd. | Electrically-tunable lenses and lens systems |
| US9395340B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2016-07-19 | Kla-Tencor Corporation | Interleaved acousto-optical device scanning for suppression of optical crosstalk |
| JP6296730B2 (ja) * | 2013-09-06 | 2018-03-20 | 株式会社Screenホールディングス | 光変調器および露光ヘッド |
| EP3066512A1 (en) * | 2013-11-08 | 2016-09-14 | Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale | Adjustable speed fast laser scanning system and two-photon microscope associated |
| WO2015186010A1 (en) | 2014-06-05 | 2015-12-10 | Optica Amuka (A.A.) Ltd. | Control of dynamic lenses |
| WO2015164886A2 (en) | 2014-08-05 | 2015-10-29 | Waag Robert C | Device, system, and method for hemispheric breast imaging |
| IL234766A (en) * | 2014-09-21 | 2015-09-24 | Visionsense Ltd | Fluorescent Imaging System |
| HUP1500264A2 (en) * | 2015-06-01 | 2018-05-02 | Femtonics Kft | Layered structured acousto-optical deflector and method for optical beam deflection with deflectior |
| CN108369211B (zh) * | 2015-12-03 | 2021-12-07 | 浜松光子学株式会社 | 检查装置及检查方法 |
| EP3958048A1 (en) | 2016-04-17 | 2022-02-23 | Optica Amuka (A.A.) Ltd. | Liquid crystal lens with enhanced electrical drive |
| US11360330B2 (en) | 2016-06-16 | 2022-06-14 | Optica Amuka (A.A.) Ltd. | Tunable lenses for spectacles |
| DE102017107915A1 (de) * | 2016-07-18 | 2018-01-18 | Carl Zeiss Meditec Ag | System zur Augentherapie mittels Gewebebearbeitung durch nichtlineare Wechselwirkung |
| US10401704B2 (en) * | 2016-11-11 | 2019-09-03 | Asml Netherlands B.V. | Compensating for a physical effect in an optical system |
| JP6931705B2 (ja) * | 2017-02-10 | 2021-09-08 | ノバダック テクノロジーズ ユーエルシー | オープンフィールドハンドヘルド蛍光イメージングシステムおよび方法 |
| US9939381B1 (en) * | 2017-04-07 | 2018-04-10 | Vidrio Technologies, Llc | Automated scanning path planner with path calibration for high frame rate multi photon laser scanning microscope with wide field of view |
| EP3649508B1 (en) | 2017-07-03 | 2023-04-05 | Electro Scientific Industries, Inc. | Optically contacted acousto-optic device and method of making the same |
| US11953764B2 (en) | 2017-07-10 | 2024-04-09 | Optica Amuka (A.A.) Ltd. | Tunable lenses with enhanced performance features |
| US11747619B2 (en) | 2017-07-10 | 2023-09-05 | Optica Amuka (A.A.) Ltd. | Virtual reality and augmented reality systems with dynamic vision correction |
| EP3698212A4 (en) | 2017-10-16 | 2021-07-14 | Optica Amuka (A.A.) Ltd. | GLASSES WITH ELECTRICALLY ADJUSTABLE LENSES CONTROLLED BY AN EXTERNAL SYSTEM |
| WO2019143729A1 (en) | 2018-01-16 | 2019-07-25 | Pacific Light & Hologram, Inc. | Three-dimensional displays using electromagnetic field computations |
| CN109343320B (zh) * | 2018-10-31 | 2020-12-18 | 华中科技大学 | 一种光控制装置 |
| DE102018132327B4 (de) | 2018-12-14 | 2021-02-25 | Leica Microsystems Cms Gmbh | Verfahren und Signalgenerator zum Ansteuern eines akustooptischen Elements sowie Anordnung und Mikroskop mit einem Signalgenerator |
| GB201913703D0 (en) * | 2019-09-23 | 2019-11-06 | Imperial College Innovations Ltd | Improved oblique plane microscopy |
| EP3933499A1 (en) * | 2020-07-03 | 2022-01-05 | Mycronic Ab | Device and method for controlling focus of a laser beam |
| US11360430B2 (en) | 2020-09-17 | 2022-06-14 | Pacific Light & Hologram, Inc. | Reconstructing objects with display zero order light suppression |
| WO2022060733A1 (en) * | 2020-09-17 | 2022-03-24 | Pacific Light & Hologram, Inc. | Displaying three-dimensional objects |
| US11813697B1 (en) * | 2023-04-07 | 2023-11-14 | Intraaction Corp | Laser methods of fabrication of clothing |
| US11900842B1 (en) | 2023-05-12 | 2024-02-13 | Pacific Light & Hologram, Inc. | Irregular devices |
Family Cites Families (73)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3944948A (en) | 1974-10-22 | 1976-03-16 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Secretary Of The Army | Cascaded data modulation system |
| US4217036A (en) | 1978-04-17 | 1980-08-12 | Itek Corporation | Acoustic-optic coherent modulator and detection system |
| HU180848B (en) | 1979-04-18 | 1983-04-29 | Mta Szamitastech Autom Kutato | Multiple acoustooptical,multiray intensity modulator and ray deflector |
| US4344675A (en) * | 1980-05-29 | 1982-08-17 | Rockwell International Corporation | Optical signal processing device |
| US4443066A (en) * | 1981-06-17 | 1984-04-17 | Hazeltine Corporation | Acousto-optical apparatus for shifting a beam of light |
| US4588296A (en) | 1981-10-07 | 1986-05-13 | Mcdonnell Douglas Corporation | Compact optical gyro |
| GB2119109B (en) | 1982-04-22 | 1985-08-07 | Standard Telephones Cables Ltd | Optical scanning system |
| US4435041A (en) | 1982-05-28 | 1984-03-06 | Sperry Corporation | Chromatic aberration correction in a multiwavelength light beam deflection system |
| US4514056A (en) | 1982-11-05 | 1985-04-30 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Secretary Of The Air Force | Acoustically tuned optical filter system |
| JPS63194236A (ja) * | 1987-02-09 | 1988-08-11 | Anritsu Corp | 光偏向装置 |
| JPH01310327A (ja) * | 1988-06-08 | 1989-12-14 | Fuji Photo Film Co Ltd | 光偏向装置 |
| USH884H (en) | 1988-08-06 | 1991-02-05 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Secretary Of The Air Force | Method and apparatus for increasing the angular aperture of an acousto-optic device |
| FR2642883B1 (ja) | 1989-02-09 | 1995-06-02 | Asahi Optical Co Ltd | |
| US5491587A (en) | 1989-02-28 | 1996-02-13 | Asahi Kogaku Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Collimating lens for optical system using semiconductor laser |
| JPH034216A (ja) | 1989-05-31 | 1991-01-10 | Dainippon Screen Mfg Co Ltd | 光ビーム制御装置 |
| US5034613A (en) | 1989-11-14 | 1991-07-23 | Cornell Research Foundation, Inc. | Two-photon laser microscopy |
| GB2249845A (en) | 1990-11-09 | 1992-05-20 | Marconi Gec Ltd | Acousto-optic device |
| JPH0534735A (ja) | 1991-07-31 | 1993-02-12 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | 音響光学偏向素子を用いたビーム偏向器 |
| US5191466A (en) * | 1991-08-26 | 1993-03-02 | Optrotech Ltd. | High resolution two-directional optical scanner |
| JP3082346B2 (ja) * | 1991-09-12 | 2000-08-28 | 株式会社ニコン | 蛍光コンフォーカル顕微鏡 |
| US5365239A (en) * | 1991-11-06 | 1994-11-15 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Secretary Of The Navy | Fiber optic feed and phased array antenna |
| US5197074A (en) | 1991-12-26 | 1993-03-23 | Electro Scientific Industries, Inc. | Multi-function intra-resonator loss modulator and method of operating same |
| US5267188A (en) * | 1992-04-21 | 1993-11-30 | Photonic Systems, Inc. | Multi-channel acousto-optic spectrum analyzer |
| JP3323548B2 (ja) | 1992-09-07 | 2002-09-09 | レーザーテック株式会社 | ビーム偏向装置 |
| JP3343276B2 (ja) | 1993-04-15 | 2002-11-11 | 興和株式会社 | レーザー走査型光学顕微鏡 |
| FR2708355A1 (fr) | 1993-07-01 | 1995-02-03 | Aa Sa | Déflecteur acousto-optique multi-cellules. |
| JP2807965B2 (ja) * | 1994-04-11 | 1998-10-08 | 登 中谷 | ヘテロダイン干渉計用微小角交差ビーム型直交2周波数光源 |
| JPH07335526A (ja) * | 1994-06-08 | 1995-12-22 | Nikon Corp | 位置検出装置及び該装置に使用される音響光学変調素子 |
| US5680252A (en) | 1995-03-23 | 1997-10-21 | Martin Marietta Energy Systems, Inc. | Miniature hybrid optical imaging lens |
| JPH08328050A (ja) * | 1995-05-29 | 1996-12-13 | Fuji Xerox Co Ltd | 光走査素子、光走査方法及びそれを用いた画像形成装置 |
| US5801389A (en) * | 1995-05-30 | 1998-09-01 | Nikon Corporation | Acousto-optic modulator, position detector using it, and projection exposure apparatus |
| NZ318277A (en) | 1995-09-19 | 1999-02-25 | Cornell Res Foundation Inc | Multi-photon laser microscopy |
| US5646411A (en) * | 1996-02-01 | 1997-07-08 | Molecular Dynamics, Inc. | Fluorescence imaging system compatible with macro and micro scanning objectives |
| JP3696349B2 (ja) * | 1996-09-06 | 2005-09-14 | 富士写真フイルム株式会社 | 光偏向器及び光ビーム走査装置 |
| KR100195136B1 (ko) | 1996-10-24 | 1999-06-15 | 윤종용 | 물체 표면 높이 측정장치 |
| KR19980029976A (ko) | 1996-10-28 | 1998-07-25 | 김광호 | 음향광 변조장치 |
| JPH1172763A (ja) | 1997-08-29 | 1999-03-16 | Ando Electric Co Ltd | 音響光学変調器 |
| JPH11237503A (ja) | 1997-12-03 | 1999-08-31 | Canon Inc | 回折光学素子及びそれを有する光学系 |
| US6137612A (en) * | 1998-01-02 | 2000-10-24 | Motorola, Inc. | Method and system for channelization and down conversion of wideband subscriber information signals |
| JPH11218682A (ja) * | 1998-01-30 | 1999-08-10 | Fujitsu Ltd | レーザ走査顕微鏡 |
| US5946141A (en) | 1998-06-26 | 1999-08-31 | Eastman Kodak Company | Apochromatic lens system for relaying laser beam waists |
| JP2000105335A (ja) | 1998-09-29 | 2000-04-11 | Minolta Co Ltd | カラー画像読み取り用レンズ |
| JP2000131603A (ja) | 1998-10-22 | 2000-05-12 | Sony Corp | 光学ヘッド及び記録再生装置 |
| JP3965504B2 (ja) | 1999-06-11 | 2007-08-29 | 株式会社オーク製作所 | マルチビーム光学系 |
| US6906824B1 (en) | 1999-09-02 | 2005-06-14 | Pentax Corporation | Tandem type printer scanning optical system having diffraction lens structure |
| DE10029167B8 (de) | 2000-06-19 | 2015-07-02 | Leica Microsystems Cms Gmbh | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Temperaturstabilisierung optischer Bauteile |
| JP4076047B2 (ja) | 2000-08-11 | 2008-04-16 | フジノン株式会社 | 光記録媒体用対物レンズおよびこれを用いた光ピックアップ装置 |
| KR100765736B1 (ko) | 2000-09-21 | 2007-10-15 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 색수차 보정렌즈를 구비한 광픽업장치 |
| IL140309A0 (en) | 2000-12-14 | 2002-02-10 | Yeda Res & Dev | Acousto-optic scanner with fast non-linear scan |
| AU2002245119A1 (en) | 2000-12-15 | 2002-07-30 | Sloan-Kettering Institute For Cancer Research | Beam-steering of multi-chromatic light using acousto-optical deflectors and dispersion-compensatory optics |
| US6885807B2 (en) * | 2001-03-14 | 2005-04-26 | Nuonics, Inc. | High speed fiber-optic attenuation modules |
| US6563654B2 (en) | 2001-04-12 | 2003-05-13 | Raytheon Company | External pupil lens system |
| US6775051B2 (en) * | 2001-05-03 | 2004-08-10 | Kla-Tencor Technologies | Systems and methods for scanning a beam of light across a specimen |
| AU2002357016A1 (en) | 2001-11-28 | 2003-06-10 | James W. Overbeck | Scanning microscopy, fluorescence detection, and laser beam positioning |
| CN1761906A (zh) * | 2003-03-21 | 2006-04-19 | 皇家飞利浦电子股份有限公司 | 后物镜扫描装置 |
| GB0308072D0 (en) | 2003-04-08 | 2003-05-14 | Visitech Internat Ltd | Fast multi-line laser confocal scanning microscope |
| JP2005070124A (ja) | 2003-08-27 | 2005-03-17 | Canon Inc | 光走査装置及びそれを用いた画像形成装置 |
| US7483196B2 (en) * | 2003-09-23 | 2009-01-27 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Apparatus for multiple beam deflection and intensity stabilization |
| JP2005164840A (ja) | 2003-12-01 | 2005-06-23 | Canon Inc | 光学系及びその設計方法 |
| US7196831B2 (en) * | 2003-12-31 | 2007-03-27 | Reliant Technologies, Inc. | Two-dimensional optical scan system using a counter-rotating disk scanner |
| US7197208B2 (en) | 2004-04-13 | 2007-03-27 | Agilent Technologies | Wavelength tunable light sources and methods of operating the same |
| DE602005015157D1 (de) | 2004-05-11 | 2009-08-13 | St Microelectronics Sa | Verzweigungsschutz in einem Programm |
| JP4729269B2 (ja) | 2004-06-01 | 2011-07-20 | オリンパス株式会社 | レーザ走査型顕微鏡 |
| GB2428399B (en) * | 2004-06-07 | 2010-05-05 | Electro Scient Ind Inc | AOM modulation techniques for improving laser system performance |
| US7027199B2 (en) * | 2004-06-07 | 2006-04-11 | Electro Scientific Industries, Inc. | AOM modulation techniques for facilitating pulse-to-pulse energy stability in laser systems |
| TWI245108B (en) | 2004-08-27 | 2005-12-11 | Asia Optical Co Inc | Laser sight |
| US7227127B2 (en) | 2004-10-06 | 2007-06-05 | Peter Saggau | High speed microscope with three-dimensional laser beam scanning including acousto-optic deflector for controlling the lateral position and collimation of the light beam |
| KR100576874B1 (ko) | 2004-10-25 | 2006-05-10 | 삼성전기주식회사 | 회절광학소자를 이용한 광학계 |
| DE602007002008D1 (de) | 2006-05-29 | 2009-10-01 | Olympus Corp | Laserscan-Mikroskop und mikroskopisches Überwachungsverfahren |
| US7838818B2 (en) | 2006-06-22 | 2010-11-23 | Olympus Corporation | Light-stimulus illumination apparatus which scans light-stimulus laser light in a direction intersecting an optical axis |
| GB0617945D0 (en) | 2006-09-12 | 2006-10-18 | Ucl Business Plc | Imaging apparatus and methods |
| US7580182B2 (en) | 2007-01-30 | 2009-08-25 | Crystal Technology, Inc. | Frequency synthesis for acousto-optic devices |
| HU0800781D0 (en) | 2008-12-31 | 2009-03-02 | Femtonics Kft | Focusing system comprising acousto-optic deflectors for focusing an electromagnetic beam |
-
2006
- 2006-09-12 GB GBGB0617945.1A patent/GB0617945D0/en not_active Ceased
-
2007
- 2007-09-12 WO PCT/GB2007/003455 patent/WO2008032061A2/en active Application Filing
- 2007-09-12 EP EP13170151.8A patent/EP2634622A1/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2007-09-12 US US12/440,809 patent/US8294977B2/en active Active
- 2007-09-12 HU HUE07804249A patent/HUE029308T2/en unknown
- 2007-09-12 EP EP07804249.6A patent/EP2064583B1/en active Active
- 2007-09-12 JP JP2009527885A patent/JP5213861B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2007-09-12 EP EP13170153.4A patent/EP2634615A3/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2007-09-12 EP EP13170156.7A patent/EP2634623A3/en not_active Withdrawn
-
2012
- 2012-09-14 US US13/616,680 patent/US8687268B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2013
- 2013-02-26 JP JP2013036172A patent/JP2013152471A/ja active Pending
-
2014
- 2014-02-10 US US14/176,729 patent/US9104087B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2015
- 2015-07-10 US US14/796,669 patent/US20160187761A1/en not_active Abandoned
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2008032061A3 (en) | 2008-10-30 |
| WO2008032061A2 (en) | 2008-03-20 |
| US20130057946A1 (en) | 2013-03-07 |
| EP2634615A3 (en) | 2013-12-11 |
| JP2013152471A (ja) | 2013-08-08 |
| US8687268B2 (en) | 2014-04-01 |
| US20100328759A1 (en) | 2010-12-30 |
| US20160187761A1 (en) | 2016-06-30 |
| EP2634622A1 (en) | 2013-09-04 |
| US8294977B2 (en) | 2012-10-23 |
| GB0617945D0 (en) | 2006-10-18 |
| JP2010503001A (ja) | 2010-01-28 |
| US9104087B2 (en) | 2015-08-11 |
| HUE029308T2 (en) | 2017-02-28 |
| EP2634615A2 (en) | 2013-09-04 |
| EP2634623A2 (en) | 2013-09-04 |
| EP2064583B1 (en) | 2016-05-11 |
| US20140153081A1 (en) | 2014-06-05 |
| EP2634623A3 (en) | 2013-12-04 |
| EP2064583A2 (en) | 2009-06-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5213861B2 (ja) | イメージング装置及び方法 | |
| US7332705B2 (en) | Method for high speed microscopy with three-dimensional laser beam scanning | |
| Reddy et al. | Fast three-dimensional laser scanning scheme using acousto-optic deflectors | |
| WO2009087392A1 (en) | Optical beam deflection apparatus and methods | |
| EP3207418B1 (en) | Method for analyzing a sample with a non-linear microscopy technique and non-linear microscope associated | |
| JP5890536B2 (ja) | 角度分散を補償する装置及び方法 | |
| DE10042840A1 (de) | Vorrichtung und Verfahren zur Anregung von Fluoreszenzmikroskopmarkern bei der Mehrphotonen-Rastermikroskopie | |
| US9705275B2 (en) | Laser assembly | |
| EP2976670B1 (en) | Random access stimulated emission depletion (sted) microscopy | |
| US9341919B2 (en) | Methods and apparatus for controling drive frequencies of acousto-optic deflectors | |
| EP2800995B1 (en) | Method for scanning along a continuous scanning trajectory with a scanner system | |
| CN111630432B (zh) | 声光的装置和方法 | |
| JP2016530570A (ja) | 照明光の焦点の形状を変える部材を有する顕微鏡 | |
| EP3837580B1 (en) | Method of scanning an optical beam using an acousto-optic deflector driven by chirped acoustic signals | |
| Zeng et al. | Femtosecond pulse laser scanning using Acousto-Optic Deflector | |
| Reddy et al. | Fast three-dimensional random access multi-photon microscopy for functional recording of neuronal activity | |
| Reddy et al. | Fast three-dimensional laser scanning using acousto-optic deflectors | |
| Iyer et al. | Compensation of temporal and spatial dispersion for multi-photon acousto-optic laser-scanning microscopy |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100910 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20100910 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20120523 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120605 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20120830 |
|
| A602 | Written permission of extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A602 Effective date: 20120906 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20121204 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130129 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130226 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5213861 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20160308 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |