JP4233767B2 - Game machine - Google Patents
Game machine Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4233767B2 JP4233767B2 JP2001035252A JP2001035252A JP4233767B2 JP 4233767 B2 JP4233767 B2 JP 4233767B2 JP 2001035252 A JP2001035252 A JP 2001035252A JP 2001035252 A JP2001035252 A JP 2001035252A JP 4233767 B2 JP4233767 B2 JP 4233767B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- display
- memory
- start winning
- winning
- upper limit
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Pinball Game Machines (AREA)
- Display Devices Of Pinball Game Machines (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、特定入賞口への入賞記憶数を報知することのできる遊技機に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
従来、例えば変動表示装置を備え、遊技領域に設けられている始動入賞口(特定入賞口)への入賞で変動表示装置が変動表示され、停止時の表示が所定の態様と一致したときに大当り状態(特別遊技状態)を発生するいわゆる『第1種』のパチンコ遊技機では、変動表示装置が作動中、或いは特別遊技の発生中等において始動入賞口への入賞が発生した場合に、この始動入賞が所定個数(例えば4個)まで記憶可能であった。
【0003】
この種のパチンコ遊技機では、変動表示装置の停止態様によっては特別遊技の終了後に遊技者に有利となり得る特定遊技状態(例えば、確率変動状態)となり、この特定遊技状態の間は特図(特別図柄)が高確率で特別遊技となる特別停止態様を導出し易くなったり、また、この期間中には特図の回転数を向上させたり持ち球を減らさないようにする補助遊技(例えば、普図変動による普電開放制御)が実行され、始動入賞口への入賞が通常遊技状態と比べて容易となり、前記始動入賞記憶はほとんど記憶が存在している状態(満杯状態を含む)となる。
【0004】
ところで、前記始動入賞記憶は現在の規定では最大4個であり、それ以上入賞しても始動入賞記憶はされないようになっていた。即ち、実際には、前述の特定遊技状態期間中等では始動入賞記憶が4個存在していても、さらなる始動入賞が頻繁に発生しているのであるが、折角球が入っても上記のように予め低い上限値が決められているので、そのオーバーフローする始動入賞に関わる記憶を行うことはできなかった。そこで、さらに多くの入賞記憶(例えば最大8個等)を可能にした遊技機も考案されている。
【0005】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかしながら、上述のように入賞記憶の上限を上げた場合に以下のような問題点が生じる。
【0006】
例えば、入賞記憶の上限が上がったとしても、通常遊技状態中には始動入賞口に入賞する数(割合)は今までと同等(例えば、1分当り入賞6個等)であって、多くなった記憶上限を満たすほどの入賞は中々望めない(但し、例えば長いリーチが続くなどして、その間も発射行為を続けた場合等の時には記憶上限に達することもあり得る。)。
【0007】
このように入賞数は実質的に増加しないような遊技機で、記憶表示可能なエリアに上限が変化した分を単に追加した表示を行うようにした場合には、遊技者からすれば、記憶される入賞は相変わらず4個未満であることが多い状態で、残りの記憶可能な数の空きばかりが目に付く状態となり、かえって始動入賞口ヘの入賞率が低いような印象を与えかねない。そのため、遊技機に対する印象が悪くなって遊技に早めに見切りをつけてしまったり、また遊技店が入賞させないような釘調整を行っているような悪いイメージを抱いてしまう虞れもある。
【0008】
本発明は上述のような問題点に鑑みなされたもので、遊技者に嫌悪感を与えることなく始動入賞記憶可能な上限を増加させることのできる始動入賞記憶表示態様を備えた遊技機を提供することを目的とする。
【0009】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上記目的を達成するため本発明は、発射された遊技球が誘導される遊技盤に設けられた特定入賞口(103)への入賞に基づく始動入賞記憶を上限数(例えば、「8」)まで記憶可能な始動入賞記憶手段と、該始動入賞記憶手段の始動入賞記憶の数を表示可能な始動入賞記憶表示手段(始動入賞記憶表示領域A)と、前記始動入賞記憶手段に始動入賞記憶がある場合に複数の図柄を変動表示させる変動表示ゲームを実行する変動表示装置と、を有し、前記変動表示ゲームの実行で前記始動入賞記憶を消化し、前記変動表示ゲームの実行の結果、前記変動表示装置に予め設定された図柄が停止表示されると遊技者に有利となる特別遊技状態を発生する遊技機において、
前記始動入賞記憶表示手段は、所定数(例えば「5」)より一つ少ない数(例えば4つ)の彩色領域で構成される始動記憶詳細表示領域(A1a)と、一つの彩色領域で構成され始動入賞記憶の上限数を曖昧な状態で表示する始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示領域(A1b)と、からなり、前記始動入賞記憶表示手段に記憶された始動入賞記憶の数が、一つから前記所定数より一つ少ない数までの場合に、前記始動記憶詳細表示領域にて一つの始動入賞記憶に対して一つの彩色領域を彩色状態とし、前記始動入賞記憶の数が、前記所定数から前記上限数までの場合に、全ての前記始動記憶詳細表示領域及び始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示領域の彩色領域を彩色状態とするように構成して、始動入賞記憶の数を曖昧な状態で表示するようにした。
【0010】
これにより、始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示手段によって、記憶可能な上限数が曖昧となるように報知されるので、多くの始動入賞記憶が可能な遊技機において少ない始動入賞記憶の可能性しかない場合(例えば通常遊技状態)であっても、始動入賞口(特定入賞口)への入賞があまり無いようなイメージを抱かせ難くすることが可能である。よって、始動入賞記憶可能な上限数を増やした場合においても遊技機や遊技店のイメージを低下させないようにすることができる。
【0016】
また、前記特定入賞口への入賞が通常遊技状態に比べて容易となる特定遊技状態を発生可能に構成され、前記始動入賞記憶表示手段は、前記始動入賞記憶手段に記憶可能な始動入賞記憶の上限数を明瞭にした状態で表示可能な始動入賞記憶上限数明瞭表示手段を備え、前記特定遊技状態において前記始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示手段に代えて前記始動入賞記憶上限数明瞭表示手段を作動するように構成してもよい。これにより、通常遊技状態では上限数を曖昧な表示にして、遊技者に始動入賞口(特定入賞口)への入賞が余り無いようなイメージを抱かせ難くし、特定遊技状態では上限数の曖昧な表示に代えて上限数を明瞭な表示を行うことで、記憶の頻度が高まる記憶の上限数近くの始動入賞記憶部分を正確に表示することができる。
【0017】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明の好適な実施の形態を図面に基づいて説明する。
【0018】
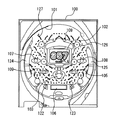
図1は、本発明を適用して好適な遊技機の一例としてのパチンコ機の遊技盤の構成例を示すものである。
【0019】
図1において、符号100で示されているのは遊技盤であり、この遊技盤100の前面に、下方より発射された遊技球を遊技盤上部に誘導する円弧状のガイドレール101、変動表示ゲームや特別遊技(大当たり遊技)における演出表示を行なう特別図柄表示器(変動表示装置)102(特図始動入賞口への入賞に基づく始動入賞情報を所定数まで記憶可能な始動入賞記憶手段の記憶に関わる情報を表示可能な始動入賞記憶表示手段としての始動入賞記憶表示領域Aを備える)、普通電動役物からなり上記変動表示ゲームの起動条件を与える特図始動入賞口(特定入賞口)103、上記普通電動役物の始動条件を与える普図始動ゲート104,105、アタッカーと呼ばれる変動入賞装置106、一般入賞口107,108,109、変動表示を利用した補助遊技を行なう普通図柄表示器122、普図始動ゲートへの遊技球の通過数を所定数(例えば最大4個)まで記憶する普図始動記憶表示器123、遊技の演出効果を高める装飾ランプ124,125、打球の流れにランダム性を与える風車と呼ばれる打球方向変換部材126と多数の障害釘127が設けられている。
【0020】
特に限定されるわけでないが、この実施例では、遊技盤100に設けられた全ての入賞口103〜109のそれぞれに対応してそこへ入賞した球を検出するためにマイクロスイッチや非接触型のセンサからなる入賞センサが設けられている。すなわち、特図始動入賞口103の内部には特図始動センサSS1が配置され、変動入賞装置106の内部にはカウントセンサSS4と継続入賞センサSS5、一般入賞口107〜109の内部には入賞センサSS4〜SS10がそれぞれ配置されている。そして、遊技球がこれらの入賞口に入賞すると、入賞口センサSS4〜SS10から入賞球検出信号が後述の遊技制御装置200へ送られ、遊技制御装置200から排出制御装置300へ賞球数データが送信されるようになっている。
【0021】
ここで、上記普図始動ゲート104,105への通過球が検出されると普通図柄表示器122が所定時間変動表示動作されるとともに、その間にさらに普図始動ゲート104,105への通過球が発生するとその球数が記憶され、その記憶数に応じて普図始動入賞記憶表示器123が点灯される。そして、普通図柄表示器122の変動表示が停止したときにその表示内容が所定の態様になると上記普通電動役物からなる特図始動入賞口103が開成される。
【0022】
この開成された特図始動入賞口103あるいは閉成状態の特図始動入賞口103に遊技球が入賞すると特別図柄表示器102が所定時間変動表示動作されるとともに、その間にさらに特図始動入賞口103への入賞球が発生するとその球数が記憶されその記憶数に応じて始動入賞記憶表示領域Aによる記憶数表示が行われる。
【0023】
ここで、特図始動入賞口103への始動入賞記憶可能な数は最大8個までであるが、記憶可能な数(上限数)をそのまま始動入賞記憶表示領域Aに表示してしまうと、始動入賞記憶している数が少ない場合には入賞部分の表示が目立ってしまい、特図始動入賞口103への入賞率が低いようなイメージを抱かせる虞があるため、本発明の特徴である始動入賞記憶手段に記憶可能な始動入賞記憶の上限数をあえて不明瞭にした曖昧な状態で表示可能な始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示手段を備えて記憶表示を行っている。この曖昧表示に係る表示態様の詳細については後述する。
【0024】
次いで、特図始動入賞口103への入賞に関連して抽出された乱数値の判定を行なった後に、当該判定結果に対応した停止図柄を導出すべく、特別図柄表示器102における変動表示を開始し所定時間経た後に前記停止図柄にて停止すべく変動表示を終了する。
【0025】
そして、上記変動表示の終了を契機に、当該変動表示に係わった前記判定結果が当たりの場合は、上記変動入賞装置106が所定時間又は所定入賞球数に達するまで開成される。
【0026】
さらに、上記変動入賞装置106内には一般入賞領域と継続入賞領域とが設けられており、継続入賞領域に遊技球が入賞したことを条件として上記変動入賞装置106の開成動作が所定回数まで繰り返される。
【0027】
遊技盤100における上記のような遊技の進行の制御および遊技制御において使用される乱数の生成は、上記遊技制御装置200が一連のプログラムを実行することによって行なわれる。また、上記特別図柄表示器102における変動表示制御は遊技制御装置200とは別個に設けられた表示制御装置400によって、遊技制御装置200の指令に従って行われる。
【0028】
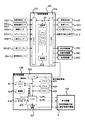
次に、図2に基づいて、遊技制御装置200と表示制御装置400の構成を説明する。図2は、遊技制御装置200と表示制御装置400の概略構成を示すブロック図である。
【0029】
図2に示されているように、遊技制御装置200は遊技に必要な役物制御を行う半導体集積回路化されたワンチップマイコン(広義のCPU)からなる遊技用マイクロコンピュータ211と、水晶発振子の発振信号を分周して所定の周波数のクロック信号を得るクロック生成回路(発振器)212と、各種センサからの信号を受け入れる入力インターフェース213と、ソレノイドなどの駆動手段に対する駆動信号や他の制御装置に対する制御信号を出力したりする出力インターフェース214とを含んで構成される。
【0030】
上記遊技用マイクロコンピュータ211は、演算制御手段としての中央処理ユニット(CPU)と、記憶手段としてROM(リードオンリメモリ)およびRAM(始動入賞記憶手段:ランダムアクセスメモリ)、割込み制御回路(図示省略)などを内蔵しており、いわゆるアミューズチップ用のICとして製造されている。CPUが行なう遊技進行制御に必要なプログラムや賞球数データはROMに格納されている。
【0031】
遊技制御装置200には、入力インターフェース213を介して、賞球排出流路内の賞球検出センサ304からの信号、前記特図始動入賞口103内の特図始動センサSS1、普図始動ゲート104,105内の普図始動センサSS2,SS3、変動入賞装置106内の継続入賞領域に対応したV入賞センサSS4と一般入賞領域に対応したカウントセンサSS5、一般入賞口107〜111内の入賞センサSS6〜SS10からの検出信号などが入力される。
【0032】
一方、遊技制御装置200からは出力インターフェース214を介して、前記普通図柄表示器122等に対する表示駆動信号、普通電動役物を開閉駆動する普電ソレノイド315の駆動信号、表示制御装置400に対するデータ信号、変動入賞装置106の大入賞口を開閉駆動するアタッカーソレノイド(大入賞口ソレノイド)314の駆動信号、排出制御装置300、装飾制御装置500、音制御装置600に対するデータ信号、図示しない遊技店の管理装置に対して大当り発生などのデータを送信する盤用外部端子(データ出力端子)312への信号などが出力される。
【0033】
表示制御装置400は、制御用マイクロコンピュータ(CPU)421、遊技制御装置200とのインタフェース回路422、制御用プログラムや固定データを記憶するリード・オンリ・メモリ(ROM)423、制御用CPU421の作業領域を提供したり遊技制御装置200から送られて来たデータや表示データを記憶するランダム・アクセス・メモリ(RAM)424、表示装置(特別図柄表示器)102を表示駆動する画像表示コントローラ(VDC)425、表示される画像データを格納したフォントROM426、表示補正を行うγ補正回路427、RAM424から画像表示コントローラ425へデータをDMA(ダイレクト・メモリ・アクセス)転送するDMAコントローラ(DMAC)428、水晶発振子の発振信号を分周して所定の周波数のクロック信号を得るクロック生成回路(発振器)429などで構成される。
【0034】
表示制御装置400の制御用CPU421には、インターフェース422を介して、前記遊技制御装置200から表示変動時間データや停止図柄データ、停止コマンドなどの表示制御情報が入力される。前記遊技制御装置200から表示制御情報が入力されるとインターフェース422から制御用CPU421に対して受信割込みがかかり、これに応じて制御用CPU421は受信データ(表示制御情報)をRAM424のバッファ領域に格納する。そして、制御用CPU421は受信データを解析し、例えば変動時間データに基づいて変動表示すべき演出パターン(連続した表示図柄データの集まり)を決定して、表示する図柄を示すコードや表示位置、スクロールなどのコマンドを生成してRAM424に格納する。そして、上記演出パターンは、変動時間データと対応させたテーブルの形でROM423に予め記憶されている。
【0035】
画像表示コントローラ425は、DMAコントローラ428によってRAM424から転送されて来る上記演出パターンに対応したデータ群を内部のRAMに読み込み展開する。具体的には、図柄を示すコードに応じてフォントROM426内に格納されているキャラクタフォントデータを読み出すとともに表示位置データやコマンドに従って、表示すべき画像データを表示画面と対応させて内部RAMの表示画像格納領域に格納する。このとき、数字などの特図遊技のための変動図柄とは別に演出効果を高めるための背景図柄も生成され表示画像格納領域に格納される。変動図柄と背景図柄は、合成してから格納しても良いが、別々に格納して読み出す際に合成することも可能である。
【0036】
その後、画像表示コントローラ425は、内蔵RAMの表示画像格納領域から表示画像データを読み出して順次γ補正回路427へ送り、特別図柄表示器102の表示駆動信号を形成させる。このとき、変動表示のためのスクロールは、コマンドとスクロール速度などのパラメータに従って、画像表示コントローラ425がアドレス演算によって表示すべき画像データの開始位置を変化させることによって行われる。また、画像表示コントローラ425は、表示装置102に対して垂直同期信号V-SYNCと水平同期信号H-SYNCを送る。γ補正回路427は、表示装置の信号電圧に対する照度の非線形特性を補正して、表示装置102の表示照度を調整する。これによって、表示装置102の画面上に所定の表示が行われる。
【0037】
また、始動入賞記憶表示領域Aにおける表示制御も遊技制御装置200から送られてくる表示制御情報に基づいて表示制御装置400によって行われる。
【0038】
次に、図3〜図8を参照して、表示装置(特別図柄表示器)102の画面上における始動入賞記憶表示領域A(始動入賞記憶表示手段)の表示態様について説明する。
【0039】
まず、図3と図4に基づいて第1の実施態様に係る始動入賞記憶表示領域A1について説明する。
【0040】
この実施態様においては図3に示すように、始動入賞記憶表示領域A1は、表示装置102の下方に設けられている。この始動入賞記憶表示領域A1は、記憶可能な8個の入賞のうち、記憶頻度が比較的高い1〜4個までを表示する始動入賞記憶詳細表示領域A1a(始動入賞記憶詳細表示手段)と、記憶頻度が比較的低い5〜8個までの記憶可能な数を曖昧にして表示する始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示領域A1b(始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示手段)とから構成されている。ここで、記憶頻度とは、始動入賞記憶が発生している割合を示しており、始動入賞記憶が1→8になるにつれて、記憶頻度が高→低となる。
【0041】
図4の(a)〜(e)には、始動入賞記憶表示領域A1における表示経過の例を示す。
【0042】
まず、図4(a)は、特図始動入賞口103への入賞記憶が無い時の表示例であり、始動入賞記憶詳細表示領域A1aと始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示領域A1bは彩色される領域がともに無彩色の状態とされて、彩色される領域を示す外形のみが表示されている。
【0043】
図4(b)は、特図始動入賞口103への入賞記憶が「1」の場合の表示例であり、始動入賞記憶詳細表示領域A1aの彩色領域のうち[1]のみが彩色され、他の[2]〜[4]および始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示領域A1bの彩色領域は無彩色の状態とされる。
【0044】
図4(c)は、特図始動入賞口103への入賞記憶が「4」となった場合の表示例であり、始動入賞記憶詳細表示領域A1aの彩色領域[1]〜[4]が彩色され、始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示領域A1bの彩色領域のみが無彩色の状態とされる。
【0045】
図4(d)は、特図始動入賞口103への入賞記憶が「5」〜「8」となった場合の表示例であり、始動入賞記憶詳細表示領域A1aの彩色領域の[1]〜[4]および始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示領域A1bの彩色領域の全てが彩色状態とされる。
【0046】
図4(e)は、図4(d)の状態から、変動表示ゲームの実行によって記憶が消化されて入賞記憶が「4」に減った場合の表示例であり、始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示領域A1bの彩色領域は無彩色の状態に戻り、始動入賞記憶詳細表示領域A1aの彩色領域[1]〜[4]のみが彩色状態とされる。
【0047】
これにより、記憶される頻度が比較的低い「5」〜「8」の入賞記憶については始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示領域A1bにより記憶可能な上限数がいくつであるかを敢えて不明瞭にする曖昧な表示態様とすることができ、特図始動入賞口103への入賞が通常の割合となる例えば通常遊技状態での遊技であっても遊技者が特図始動入賞口103への入賞率が低いようなイメージを抱くことを回避することができる。一方、記憶される頻度が比較的高い「1」〜「4」の入賞記憶については、始動入賞記憶詳細表示領域A1aにより幾つの記憶があるかを明確に表示して、遊技者が遊技の方針を立て易いようにすることができる。ここで、始動入賞記憶詳細表示領域は、一つの始動入賞記憶に対して一つの彩色領域にて始動入賞記憶数を表示しているが、これに限らず、始動入賞記憶数が詳細に判ればどのような表示態様でも良く、例えば、複数の始動入賞記憶に対して一つの彩色領域を用いるような表示でもよい。
【0048】
次に、図5を参照して第2の実施態様に係る始動入賞記憶表示領域A2について説明する。
【0049】
この実施態様においては始動入賞記憶表示領域A2は、通常は記憶可能な8個の入賞のうち記憶頻度が比較的高い1〜4個までを表示する表示領域A2aと、記憶頻度が比較的低い5〜8個までの記憶可能な数を曖昧にして表示する始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示領域A2bとから構成される第1の表示態様(図5(a)、(b))と、始動入賞記憶されている数を一括して表示する表示領域A2cと、記憶可能な上限数を明瞭にするとともに入賞記憶数も詳細に表示する始動入賞記憶上限数明瞭表示領域A2d(始動入賞記憶上限数明瞭表示手段)とから構成される第2の表示態様(図5(c))とを備え、始動入賞記憶が5〜8個になっている場合に、第1の表示態様から第2の表示態様へと表示態様が変化する。
【0050】
図5(a)に示すように、特図始動入賞口103への入賞記憶が例えば「1」の場合には表示領域A2aの彩色領域[1]のみが彩色され、図5(b)に示すように、入賞記憶が例えば「4」の場合には表示領域A2aの彩色領域[1] 〜[4] の全てが彩色される。
【0051】
そして、入賞記憶が例えば「6」の場合には図5(c)に示すように、表示領域A2aおよび始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示領域A2bの第1の表示態様から表示領域A2c及び始動入賞記憶上限数明瞭表示領域A2dとの第2の表示態様に変化して、表示領域A2bの[5],[6]のみを彩色する。
【0052】
これにより、記憶頻度が比較的低い5〜8個の記憶を示す始動入賞記憶上限数明瞭表示領域A2dは、入賞記憶が1〜4個までの間は表示されないので、記憶可能数の最大値(8個)を遊技者に余り意識させることがなく、記憶数が「1」〜「4」の間で推移することが多くても遊技者が特図始動入賞口103への入賞率が低いようなイメージを抱くことを回避することができる。ここで、第1の表示態様から第2の表示態様へと変化する場合、一気に画面切換を行うようにしても良いが、スライドさせるように画面を徐々に変換させるようにしても良い。
【0053】
次に、図6を参照して第3の実施態様に係る始動入賞記憶表示領域A3について説明する。
【0054】
この実施態様における始動入賞記憶表示領域A3は、通常(始動入賞記憶が無い状態)は消灯状態にある例えば8個のドット表示(例えば、丸型のLEDを現したようなドット表示)で構成され、遊技者には記憶可能な上限の数(例えば8個)が分かり難いようになっている。
【0055】
そして、図6(a)に示すように、特図始動入賞口103への入賞記憶が例えば「1」の場合には表示領域A3の略中央に1つのドットを点灯表示させ、図6(b)に示すように、特図始動入賞口103への入賞記憶が例えば「2」の場合には表示領域A3の略中央に2つのドットを並べて点灯表示させる。また、図6(c)に示すように、特図始動入賞口103への入賞記憶が例えば「8」になった場合には表示領域A3に8つのドットを点灯表示させる。
【0056】
このように、入賞記憶が増減する過程において、遊技者は始動入賞記憶可能な上限の数が幾つであるか分かり難いため、記憶数が例えば「1」〜「4」の間で推移することが多くても遊技者が特図始動入賞口103への入賞率が低いようなイメージを抱くことを回避することができる。
【0057】
次に、図7を参照して第4の実施態様に係る始動入賞記憶表示領域A4について説明する。
【0058】
この実施態様における始動入賞記憶表示領域A4は、通常(入賞記憶が無い状態)は図7(a)に示すように、無表示状態にある表示領域Sで構成されている。
【0059】
そして、図7(b)に示すように、表示領域Sの全体を彩色して特図始動入賞口103への入賞記憶が「1」であることを表示する。また、図7(c)に示すように、表示領域SをS2a〜S2cに3分割して各領域S2a〜S2cを彩色して特図始動入賞口103への入賞記憶が「3」であることを表示する。
【0060】
さらに、図7(d)に示すように、表示領域SをS3a〜S3hに8分割して各領域S3a〜S3hを彩色して特図始動入賞口103への入賞記憶が「8」であることを表示する。
【0061】
このように、図7の例では、入賞記憶が増減する過程においても表示の幅は全て同じであるため、遊技者は最大の記憶数が幾つであるか分かり難くなるので、記憶数が例えば「1」〜「4」の間で推移することが多くても遊技者が特図始動入賞口103への入賞率が低いようなイメージを抱くことを回避することができる。
【0062】
次に、図8を参照して始動入賞記憶表示領域A5について説明する。
【0063】
この実施態様において始動入賞記憶表示領域A5は、上述の始動入賞記憶表示領域A1とA2の変形例であって、始動入賞記憶可能な上限数(例えば8個)が遊技者に分かる始動入賞記憶上限数明瞭表示領域を備えている。具体的には、記憶可能な8個の入賞のうち記憶頻度が比較的高い1〜4個までを表示する表示領域A5aと、記憶頻度が比較的低い5〜8個までの記憶可能な上限数を明瞭にするとともに入賞記憶数も詳細に表示する始動入賞記憶上限数明瞭表示領域A5bとから構成されている。これにより、遊技者は、「1」〜「8」までの入賞記憶の増減を彩色領域[1] 〜[8]の彩色または無彩色により把握することができる。
【0064】
但し、この実施態様は、図8に示されている始動入賞記憶表示領域A5の表示を例えば変動表示領域102で実行される変動表示遊技の結果により、特図の大当り確率が上がり、且つ、特図始動入賞口103への入賞確率が高くなるような特定遊技状態となった場合などに、前述の実施態様における始動入賞記憶表示領域A1における始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示領域A1b、または、始動入賞記憶表示領域A1における始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示領域A2dから切り換えて表示させるようにしている。即ち、通常の遊技状態における始動入賞記憶表示は、前述の始動入賞記憶表示領域A1、またはA2のような表示態様で行い、入賞確率が高まった特定遊技状態において始動入賞記憶表示領域A5の表示のように始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示領域A1b、A2dから始動入賞記憶上限数明瞭表示領域A5bに切り換える。これにより、通常遊技状態においては始動入賞記憶数が例えば「1」〜「4」の間で推移することが多くても遊技者が特図始動入賞口103への入賞率が低いようなイメージを抱くことを回避させることができ、入賞記憶数が例えば「1」〜「8」の間で推移する可能性が高い状態においては幾つの始動入賞記憶があるかの詳細を遊技者に表示して遊技の方針が立て易いようにすることができる。
【0065】
また、上述の始動入賞記憶表示領域A5は、その他の条件により表示するようにしても良い。例えば、特別遊技が発生した場合には、この特別遊技が終了するまでは変動表示ゲームは行われない。しかしながら、この間も特図始動入賞口103への入賞が発生し、特別遊技が終了するときには大抵始動入賞記憶は上限まで記憶された状態となる。よって、特別遊技状態が終了した後、例えば始動入賞記憶が満タン状態から所定数(記憶4以下)に減少するまで、或いは、終了した後の1分間等の所定期間、始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示領域での表示に代えて始動入賞記憶上限数明瞭表示領域にて記憶数を表示するようにしても良い。
【0066】
また、始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示領域にて始動入賞記憶の上限数を曖昧にした表示状態であっても、始動入賞記憶した数が上限に達した場合には報知するようにしても良い。上限数に達したことが判ればどのような報知の態様でも良く、例えば、始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示領域A1bのみを点灯状態から点滅状態にしたり、また、その他の彩色領域の色を通常の彩色から異なる彩色に変化させたり、また、この上限に達したことを音、文字情報等により報知するようにしても良い。
【0068】
また、始動入賞記憶がされている場合に、遊技者が任意に操作可能な始動入賞記憶実行操作ボタン等を設けて、始動入賞記憶を一度に消化できるようにしても良い。この場合、始動入賞記憶が一気に消化されるのでスピーディな変動表示ゲームを実行可能である。
【0069】
以上本発明者によってなされた発明を実施形態に基づき具体的に説明したが、本明細書で開示された実施の形態はすべての点で例示であって開示された技術に限定されるものではないと考えるべきである。すなわち、本発明の技術的な範囲は、上記の実施形態における説明に基づいて制限的に解釈されるものでなく、あくまでも特許請求の範囲の記載に従って解釈すべきであり、特許請求の範囲の記載技術と均等な技術および特許請求の範囲内でのすべての変更が含まれる。
【0070】
例えば、本実施形態では、特図始動入賞口103への始動入賞記憶の表示を表示装置102上の画面に設けた始動入賞記憶表示領域A1〜A5で行う場合について述べたが、これに限定されるものではなく、例えばLEDや液晶パネル等の表示装置を別途設け、その表示装置で始動入賞記憶を表示させるようにしてもよい。
【0071】
【発明の効果】
本願請求項1の発明によれば、多くの始動入賞記憶が可能な遊技機において始動入賞口への入賞が少ない場合(例えば通常遊技状態)であっても、始動入賞口(特定入賞口)への入賞が余り無いようなイメージを抱かせ難くすることができ、記憶の上限を増やした場合においても遊技機や遊技店のイメージを低下させないようにすることができるという効果がある。
また、請求項2の発明は、特定遊技状態において前記始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示手段に代えて前記始動入賞記憶上限数明瞭表示手段を作動させるので、通常遊技状態では上限数を曖昧な表示にして、遊技者に始動入賞口(特定入賞口)への入賞が余り無いようなイメージを抱かせ難くし、特定遊技状態では上限数の曖昧な表示に代えて上限数を明瞭な表示を行うことで、記憶の頻度が高まる記憶の上限数近くの始動入賞記憶部分を正確に表示することができ、遊技者に発射調整等(無駄球の発射等)の遊技の方針を立てる目安を与えることが可能となるという効果がある。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明を適用して好適な遊技機の一例としてのパチンコ機の遊技盤の構成例および始動入賞記憶表示の第1の実施形態を示す正面図である。
【図2】上記遊技盤の裏面を含むパチンコ機の裏側に設けられる制御系全体の構成例を示すブロック図である。
【図3】始動入賞記憶表示領域A1の表示例を示す説明図である。
【図4】始動入賞記憶表示領域A1の表示の過程を示す説明図である。
【図5】始動入賞記憶表示領域A2の表示の過程を示す説明図である。
【図6】始動入賞記憶表示領域A3の表示の過程を示す説明図である。
【図7】始動入賞記憶表示領域A4の表示の過程を示す説明図である。
【図8】始動入賞記憶表示領域A5の表示例を示す説明図である。
【符号の説明】
100 遊技盤
101 ガイドレール
102 特別図柄表示器(変動表示装置)
A(A1〜A5) 始動入賞記憶表示領域(始動入賞記憶表示手段)
A1b 始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示領域(始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示手段)
103 特図始動入賞口
104,105 普図始動ゲート
106 変動入賞装置
107,108,109,110,111 一般入賞口
122 普通図柄表示器
123 普図始動入賞記憶表示器
124,125 装飾ランプ
126 打球方向変換部材
200 遊技制御装置
211 遊技用マイクロコンピュータ
212 クロック生成回路(発振器)
213 入力インターフェース
214 出力インターフェース
300 排出制御装置
500 装飾制御装置
600 音制御装置
304 賞球検出センサ
314 大入賞口ソレノイド
315 普通電動役物駆動ソレノイド
400 表示制御装置
421 表示制御用マイクロコンピュータ
422 インタフェース回路
423 リード・オンリ・メモリ
424 ランダム・アクセス・メモリ
425 画像表示コントローラ
426 フォントROM
427 γ補正回路
428 DMAコントローラ
429 クロック生成回路(発振器)[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a gaming machine capable of notifying the number of winning prizes stored in a specific winning opening.
[0002]
[Prior art]
Conventionally, for example, a variable display device has been provided, and the variable display device is variably displayed by winning at a start winning port (specific winning port) provided in the game area, and a big hit is obtained when the display at the stop matches a predetermined mode. In a so-called “first type” pachinko gaming machine that generates a state (special game state), this start prize is awarded when a winning entry to the start prize opening occurs while the variable display device is operating or a special game is occurring. Can be stored up to a predetermined number (for example, four).
[0003]
In this type of pachinko gaming machine, depending on the stop mode of the variable display device, a special game state (for example, a probability fluctuation state) that can be advantageous to the player after the special game is ended, and a special figure (special) is used during the specific game state. It is easy to derive a special stop mode in which the symbol is a special game with a high probability, and during this period, an auxiliary game (for example, a general game that does not increase the number of rotations of the special diagram or reduce the holding ball) (Opening control based on figure fluctuation) is executed, and winning at the start winning opening becomes easier as compared with the normal gaming state, and the start winning memory is almost in a state (including a full state).
[0004]
By the way, the number of the start winning memories is four at the maximum in the current regulations, and the starting winning memories are not stored even if winning more than that. That is, in fact, even during the above-mentioned specific gaming state period, even if there are four start winning memories, even more start winnings occur frequently, Since a low upper limit value was determined in advance, it was not possible to store the start winning prize that overflowed. In view of this, a gaming machine has been devised that enables more winning memories (for example, a maximum of 8).
[0005]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, the following problems occur when the upper limit of the winning memory is raised as described above.
[0006]
For example, even if the upper limit of the winning memory is increased, the number (ratio) of winning in the starting winning opening during the normal gaming state is the same as before (for example, 6 winnings per minute, etc.) and increases. It is difficult to expect a prize that satisfies the upper limit of memory (however, the upper limit of memory may be reached when, for example, a long reach is continued and the launch action is continued during that time).
[0007]
In this way, in a gaming machine in which the number of winnings does not increase substantially, if the display is made by simply adding the amount of change in the upper limit to the memory displayable area, it will be stored for the player. In many cases, the number of winnings is still less than four, and the remaining memorable number of vacancies is noticeable, which may give the impression that the winning rate at the starting winning opening is rather low. For this reason, there is a possibility that the impression of the gaming machine will be worsened and the game will be given up early, or that the game store may have a bad image such as making nail adjustments that will not win the game.
[0008]
The present invention has been made in view of the above-described problems, and provides a gaming machine having a start winning memory display mode capable of increasing the upper limit for starting winning memorization without giving disgust to the player. For the purpose.
[0009]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In order to achieve the above-mentioned object, the present invention has a maximum number of start winning memories (for example, “8”) based on winning in a specific winning opening (103) provided in a game board on which a launched game ball is guided. A start winning memory means that can be stored, a start winning memory display means (start winning memory display area A) capable of displaying the number of start winning memories of the start winning memory means, and a start winning memory in the start winning memory means. A variable display device that executes a variable display game that displays a plurality of symbols in a case, and the start winning memory is digested by executing the variable display game, and the change display game results in the change In a gaming machine that generates a special gaming state that is advantageous to the player when a preset symbol on the display device is stopped and displayed,
The start winning memory display means is composed of a start memory detail display area (A1a) constituted by a number (for example, four) of coloring areas which is one less than a predetermined number (for example, “5”), and one coloring area.Display the maximum number of starting winning memories in an ambiguous stateStarting prize storage upper limit number ambiguous display area (A1b), and when the number of start winning memories stored in the starting prize storage display means is from one to one less than the predetermined number, In the start memory detail display area, all the start memories are set when one coloring area is set in a colored state with respect to one start prize memory, and the number of start prize memories is from the predetermined number to the upper limit number. Configure the coloring area of the detailed display area and the starting prize storage upper limit number ambiguous display area to be in a colored state, and start winning prizeNumber of memoriesWas displayed in an ambiguous state.
[0010]
As a result, the start prize storage upper limit number ambiguous display means informs that the storable upper limit number is ambiguous, so there is only a small possibility of start prize memory in a gaming machine capable of many start prize memories. Even in a normal game state, for example, it is possible to make it difficult to hold an image in which there is not much winning at the start winning opening (specific winning opening). Therefore, even when the maximum number of start winnings that can be stored is increased, the image of the gaming machine or the amusement store can be prevented from being lowered..
[0016]
Also,It is configured to be able to generate a specific gaming state in which winning to the specific winning opening is easier than in a normal gaming state, and the starting winning memory display means has an upper limit number of starting winning memories that can be stored in the starting winning memory means The starting prize memory upper limit number clear display means that can be displayed in a clear state, and the starting prize memory upper limit number clear display means operates in place of the starting prize memory upper limit ambiguous display means in the specific game state. Configured toMay be. ThisIn the normal gaming state, the upper limit number is ambiguously displayed, making it difficult for the player to have an image that there is not much winning in the starting prize opening (specific winning opening), and in the specific gaming state, the upper limit number is ambiguously displayed. Instead, by clearly displaying the upper limit number, it is possible to accurately display the start winning memorized portion near the upper limit number of memories whose memory frequency increases.
[0017]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
DESCRIPTION OF EXEMPLARY EMBODIMENTS Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
[0018]
FIG. 1 shows a configuration example of a game board of a pachinko machine as an example of a suitable game machine to which the present invention is applied.
[0019]
In FIG. 1,
[0020]
Although not limited in particular, in this embodiment, a micro switch or a non-contact type is used to detect a ball that has won a prize corresponding to each of the winning
[0021]
Here, when the passing ball to the normal
[0022]
When a game ball is won in the opened special figure
[0023]
Here, the maximum number of start prizes that can be stored in the special drawing
[0024]
Next, after the random number value extracted in relation to the winning in the special figure
[0025]
Then, when the determination result related to the variation display is a win when the variation display ends, the
[0026]
Further, the
[0027]
Control of the progress of the game as described above in the
[0028]
Next, the configuration of the
[0029]
As shown in FIG. 2, the
[0030]
The
[0031]
In the
[0032]
On the other hand, from the
[0033]
The
[0034]
Display control information such as display variation time data, stop symbol data, and a stop command is input to the control CPU 421 of the
[0035]
The
[0036]
Thereafter, the
[0037]
Further, the display control in the start winning storage display area A is also performed by the
[0038]
Next, with reference to FIGS. 3 to 8, a display mode of the start winning memory display area A (start winning memory display means) on the screen of the display device (special symbol display) 102 will be described.
[0039]
First, the start winning memory display area A1 according to the first embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS.
[0040]
In this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 3, the start winning memory display area A <b> 1 is provided below the
[0041]
4A to 4E show examples of display progress in the start winning memory display area A1.
[0042]
First, FIG. 4A is a display example when there is no winning memory in the special drawing start winning
[0043]
FIG. 4B is a display example in the case where the winning memory at the special drawing
[0044]
FIG. 4C is a display example when the winning memory at the special drawing start winning
[0045]
FIG. 4D is a display example in the case where the winning memory at the special drawing start winning
[0046]
FIG. 4E shows the state of FIG.Memory is digested by running a variable display gameThis is a display example when the winning memory is reduced to “4”, the coloring area of the starting winning memory upper limit number ambiguous display area A1b returns to the achromatic state, and the coloring area [1] to the starting winning memory detail display area A1a Only [4] is colored.
[0047]
As a result, for the winning memories of “5” to “8” that are stored at a relatively low frequency, the starting winning memory upper limit number ambiguous display area A1b ambiguously obscures how many upper limit numbers can be stored. The special display
[0048]
Next, the start winning memory display area A2 according to the second embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
[0049]
In this embodiment, the start winning memory display area A2 is a display area A2a for displaying 1 to 4 memory frequencies that are normally relatively high among 8 storable prizes, and a memory frequency 5 that is relatively low. A first display mode (FIGS. 5A and 5B) including a start winning storage upper limit number ambiguous display area A2b that displays vaguely the storable number of up to 8 and a start winning memory Display area A2c that collectively displays the number of the winning prizes, and a clear display area A2d that clearly displays the upper limit number that can be stored and also displays the number of winning prizes stored in detail. And the second display mode (FIG. 5C), and when the start winning memory is 5 to 8, the first display mode is changed to the second display mode. The display mode changes.
[0050]
As shown in FIG. 5A, when the winning memory at the special drawing
[0051]
When the winning memory is “6”, for example, as shown in FIG. 5C, the display area A2c and the starting winning memory are displayed from the first display mode of the display area A2a and the starting winning memory upper limit number ambiguous display area A2b. The display mode changes to the second display mode with the upper limit number clear display area A2d, and only [5] and [6] of the display area A2b are colored.
[0052]
As a result, the clear display area A2d of the start-winning memory upper limit number indicating 5 to 8 memories having a relatively low memory frequency is not displayed until 1 to 4 winning memories are stored. 8) is less noticeable to the player, and even if the number of memories frequently changes between “1” to “4”, the player seems to have a low winning rate to the special drawing
[0053]
Next, the start winning memory display area A3 according to the third embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
[0054]
The start winning memory display area A3 in this embodiment is configured by, for example, eight dot displays (for example, dot display that shows a round LED) that are normally off (in a state where there is no start winning memory). It is difficult for the player to know the upper limit (for example, 8) that can be stored.
[0055]
Then, as shown in FIG. 6A, when the winning memory at the special drawing start winning
[0056]
Thus, in the process of increasing / decreasing the winning memory, it is difficult for the player to know the maximum number of start winning memories that can be stored, so the number of memories may change between “1” to “4”, for example. At most, it can be avoided that the player has an image that the winning rate to the special drawing start winning
[0057]
Next, the start winning memory display area A4 according to the fourth embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
[0058]
The start winning storage display area A4 in this embodiment is normally configured with a display area S in a non-display state, as shown in FIG.
[0059]
Then, as shown in FIG. 7B, the entire display area S is colored to display that the winning memory in the special drawing start winning
[0060]
Further, as shown in FIG. 7 (d), the display area S is divided into eight parts S3a to S3h, and each of the areas S3a to S3h is colored and the winning memory at the special drawing
[0061]
In this way, in the example of FIG. 7, since the display widths are all the same even in the process of increasing or decreasing the winning memory, it becomes difficult for the player to know how many maximum memories are stored. It is possible to prevent the player from having an image that the winning rate to the special figure
[0062]
Next, the start winning storage display area A5 will be described with reference to FIG.
[0063]
In this embodiment, the start prize memory display area A5 is a modification of the above-mentioned start prize memory display areas A1 and A2, and the start prize memory upper limit that allows the player to know the upper limit number (for example, eight) that can be memorized for the start prize. A number display area is provided. Specifically, the display area A5a that displays from 1 to 4 having a relatively high storage frequency among the 8 winning storable prizes, and the upper limit number that can be stored to 5 to 8 having a relatively low storage frequency And the start winning memory upper limit clear display area A5b for displaying the number of winning memories in detail. Thereby, the player can grasp the increase or decrease of the winning memory from “1” to “8” by the coloring or achromatic coloring of the chromatic areas [1] to [8].
[0064]
However, in this embodiment, the jackpot probability of the special figure increases due to the result of the variable display game executed in the
[0065]
Further, the start winning memory display area A5 described above may be displayed under other conditions. For example, when a special game occurs, the variable display game is not played until the special game ends. However, during this time, the winning at the special drawing
[0066]
Further, even in a display state where the upper limit number of start winning memories is ambiguous in the start winning memory upper limit number ambiguous display area, a notification may be made when the number of stored start winning memories reaches the upper limit. As long as it is known that the upper limit has been reached, any notification mode may be used. For example, only the start winning memory upper limit number ambiguity display area A1b is switched from a lighting state to a blinking state, and the colors of other coloring areas are set to normal. It is also possible to change from coloring to different coloring or to notify that the upper limit has been reached by sound, character information, or the like.
[0068]
In addition, when the start winning memory is stored, a start winning memory execution operation button or the like that can be arbitrarily operated by the player may be provided so that the start winning memory can be digested at a time. In this case, since the start winning memory is exhausted at once, a speedy variation display game can be executed.
[0069]
Although the invention made by the present inventor has been specifically described based on the embodiments, the embodiments disclosed in the present specification are examples in all respects and are not limited to the disclosed technology. Should be considered. That is, the technical scope of the present invention should not be construed restrictively based on the description in the above embodiment, but should be construed according to the description of the claims to the last. All modifications within the scope of the claims and the equivalent technology are included.
[0070]
For example, in the present embodiment, the case where the start winning memory display on the special drawing start winning
[0071]
【The invention's effect】
BookIn the invention of claim 1According to the gaming machine capable of storing a lot of start prizes, even if there are few prizes at the start prize opening (for example, in the normal gaming state), there is not much prize at the start prize opening (specific prize opening). The image can be made difficult to hold, and even when the upper limit of the memory is increased, there is an effect that the image of the gaming machine or the game shop can be prevented from being lowered.
Further, in the invention of
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a front view showing a configuration example of a game board of a pachinko machine as an example of a suitable gaming machine to which the present invention is applied and a first embodiment of a start winning memory display.
FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing a configuration example of the entire control system provided on the back side of the pachinko machine including the back side of the game board.
FIG. 3 is an explanatory diagram showing a display example of a start winning storage display area A1.
FIG. 4 is an explanatory diagram showing a display process of a start winning memory display area A1.
FIG. 5 is an explanatory diagram showing a process of displaying a start winning memory display area A2.
FIG. 6 is an explanatory diagram showing a process of displaying a start winning memory display area A3.
FIG. 7 is an explanatory diagram showing a display process of a start winning memory display area A4.
FIG. 8 is an explanatory diagram showing a display example of a start winning storage display area A5.
[Explanation of symbols]
100 game board
101 guide rail
102 Special symbol display (variable display device)
A (A1 to A5) Start winning memory display area (start winning memory display means)
A1b Start winning memory upper limit number ambiguous display area (start winning memory upper limit number ambiguous display means)
103 Special drawing start winning entrance
104,105 Universal map start gate
106 Variable prize-winning device
107,108,109,110,111 General prize opening
122 Normal symbol display
123 Normal start winning memory indicator
124,125 Decorative lamp
126 Hitting direction changing member
200 Game control device
211 Microcomputer for game
212 Clock generation circuit (oscillator)
213 Input interface
214 Output interface
300 Emission control device
500 Decoration control device
600 sound control device
304 prize ball detection sensor
314 Grand Prize Solenoid
315 Ordinary electric accessory drive solenoid
400 Display control device
421 Display control microcomputer
422 interface circuit
423 Read-only memory
424 Random access memory
425 Image display controller
426 Font ROM
427 γ correction circuit
428 DMA controller
429 Clock generation circuit (oscillator)
Claims (2)
該始動入賞記憶手段の始動入賞記憶の数を表示可能な始動入賞記憶表示手段と、
前記始動入賞記憶手段に始動入賞記憶がある場合に複数の図柄を変動表示させる変動表示ゲームを実行する変動表示装置と、
を有し、前記変動表示ゲームの実行で前記始動入賞記憶を消化し、前記変動表示ゲームの実行の結果、前記変動表示装置に予め設定された図柄が停止表示されると遊技者に有利となる特別遊技状態を発生する遊技機において、
前記始動入賞記憶表示手段は、所定数より一つ少ない数の彩色領域で構成される始動記憶詳細表示領域と、一つの彩色領域で構成され始動入賞記憶の上限数を曖昧な状態で表示する始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示領域と、からなり、
前記始動入賞記憶表示手段に記憶された始動入賞記憶の数が、一つから前記所定数より一つ少ない数までの場合に、前記始動記憶詳細表示領域にて一つの始動入賞記憶に対して一つの彩色領域を彩色状態とし、
前記始動入賞記憶の数が、前記所定数から前記上限数までの場合に、全ての前記始動記憶詳細表示領域及び始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示領域の彩色領域を彩色状態とするように構成して、始動入賞記憶の数を曖昧な状態で表示することを特徴とする遊技機。A start winning memory means capable of storing up to a maximum number of start winning memories based on winning in a specific winning opening provided on a game board to which a launched game ball is guided;
Start prize memory display means capable of displaying the number of start prize memories stored in the start prize memory means;
A variable display device for executing a variable display game for variably displaying a plurality of symbols when the start winning memory means has a start winning memory;
When the variation display game is executed, the start winning memory is digested. As a result of the execution of the variation display game, a symbol preset in the variation display device is stopped and displayed, which is advantageous to the player. In a gaming machine that generates a special gaming state,
The start winning storage display means that displays at ambiguous state the maximum number of the predetermined number starting with storage detail display area composed of one fewer color space than is composed of a single color region starting winning storage The starting prize memory upper limit number vague display area,
When the number of start prize memories stored in the start prize memory display means is from one to one less than the predetermined number, one start prize memory is stored in the start memory detail display area. Set two chromatic areas as chromatic states,
When the number of start winning memories is from the predetermined number to the upper limit number, the starting storage detail display area and the starting winning memory upper limit number ambiguous display area are configured to be in a colored state. A game machine characterized by displaying the number of start winning memories in an ambiguous state.
前記始動入賞記憶表示手段は、前記始動入賞記憶手段に記憶可能な始動入賞記憶の上限数を明瞭にした状態で表示可能な始動入賞記憶上限数明瞭表示手段を備え、前記特定遊技状態において前記始動入賞記憶上限数曖昧表示手段に代えて前記始動入賞記憶上限数明瞭表示手段を作動することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の遊技機。It is configured to be able to generate a specific gaming state in which winning to the specific winning opening is easier than in a normal gaming state,
The start winning memory display means includes a start winning memory upper limit clear display means that can be displayed in a state where the upper limit of the start winning memory that can be stored in the start winning memory means is clarified. 2. A gaming machine according to claim 1, wherein said starting winning memory upper limit number clear display means is operated in place of the winning memory upper limit number ambiguous display means.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001035252A JP4233767B2 (en) | 2001-02-13 | 2001-02-13 | Game machine |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001035252A JP4233767B2 (en) | 2001-02-13 | 2001-02-13 | Game machine |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2002233617A JP2002233617A (en) | 2002-08-20 |
| JP2002233617A5 JP2002233617A5 (en) | 2005-06-02 |
| JP4233767B2 true JP4233767B2 (en) | 2009-03-04 |
Family
ID=18898725
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001035252A Expired - Fee Related JP4233767B2 (en) | 2001-02-13 | 2001-02-13 | Game machine |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4233767B2 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019010163A (en) * | 2017-06-29 | 2019-01-24 | 株式会社三洋物産 | Game machine |
| JP2019010165A (en) * | 2017-06-29 | 2019-01-24 | 株式会社三洋物産 | Game machine |
| JP2019010223A (en) * | 2017-06-29 | 2019-01-24 | 株式会社三洋物産 | Game machine |
Families Citing this family (24)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4292309B2 (en) * | 2002-03-28 | 2009-07-08 | 株式会社大一商会 | Game machine |
| JP3926201B2 (en) * | 2002-05-13 | 2007-06-06 | マルホン工業株式会社 | Pachinko machine |
| JP2004089695A (en) * | 2002-07-10 | 2004-03-25 | Heiwa Corp | Game machine |
| JP4318947B2 (en) * | 2003-04-10 | 2009-08-26 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Pachinko machine |
| JP2005087449A (en) * | 2003-09-17 | 2005-04-07 | Heiwa Corp | Game machine |
| JP4902242B2 (en) * | 2006-03-29 | 2012-03-21 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP4902241B2 (en) * | 2006-03-29 | 2012-03-21 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP5126953B2 (en) * | 2007-07-20 | 2013-01-23 | 株式会社大一商会 | Pachinko machine |
| JP5126954B2 (en) * | 2007-07-26 | 2013-01-23 | 株式会社大一商会 | Game machine |
| JP5178382B2 (en) * | 2008-07-31 | 2013-04-10 | 株式会社大一商会 | Pachinko machine |
| JP5178381B2 (en) * | 2008-07-31 | 2013-04-10 | 株式会社大一商会 | Pachinko machine |
| JP2013031575A (en) * | 2011-08-02 | 2013-02-14 | Daito Giken:Kk | Game machine |
| JP5344440B2 (en) * | 2011-08-31 | 2013-11-20 | 株式会社大都技研 | Amusement stand |
| JP5806724B2 (en) * | 2013-12-11 | 2015-11-10 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Game machine |
| JP6303216B2 (en) * | 2014-05-12 | 2018-04-04 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP5997820B2 (en) * | 2015-09-04 | 2016-09-28 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Game machine |
| JP6313370B2 (en) * | 2016-06-22 | 2018-04-18 | 株式会社大都技研 | Amusement stand |
| JP2018033915A (en) * | 2016-08-30 | 2018-03-08 | 株式会社三洋物産 | Game machine |
| JP6642388B2 (en) * | 2016-08-30 | 2020-02-05 | 株式会社三洋物産 | Gaming machine |
| JP6500879B2 (en) * | 2016-08-30 | 2019-04-17 | 株式会社三洋物産 | Gaming machine |
| JP6642389B2 (en) * | 2016-08-30 | 2020-02-05 | 株式会社三洋物産 | Gaming machine |
| JP6642387B2 (en) * | 2016-08-30 | 2020-02-05 | 株式会社三洋物産 | Gaming machine |
| JP6939952B2 (en) * | 2017-08-15 | 2021-09-22 | 株式会社三洋物産 | Pachinko machine |
| JP6950359B2 (en) * | 2017-08-25 | 2021-10-13 | 株式会社三洋物産 | Pachinko machine |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000079201A (en) * | 1998-09-03 | 2000-03-21 | Kyoraku Sangyo Kk | Pachinko machine |
| JP2000135332A (en) * | 1998-10-31 | 2000-05-16 | Sophia Co Ltd | Game machine |
| JP2002210144A (en) * | 2001-01-17 | 2002-07-30 | Kyoraku Sangyo | Pachinko game machine |
| JP2002224321A (en) * | 2001-02-02 | 2002-08-13 | Takeya Co Ltd | Game machine |
-
2001
- 2001-02-13 JP JP2001035252A patent/JP4233767B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019010163A (en) * | 2017-06-29 | 2019-01-24 | 株式会社三洋物産 | Game machine |
| JP2019010165A (en) * | 2017-06-29 | 2019-01-24 | 株式会社三洋物産 | Game machine |
| JP2019010223A (en) * | 2017-06-29 | 2019-01-24 | 株式会社三洋物産 | Game machine |
| JP6996131B2 (en) | 2017-06-29 | 2022-01-17 | 株式会社三洋物産 | Pachinko machine |
| JP7052232B2 (en) | 2017-06-29 | 2022-04-12 | 株式会社三洋物産 | Pachinko machine |
| JP7056019B2 (en) | 2017-06-29 | 2022-04-19 | 株式会社三洋物産 | Pachinko machine |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2002233617A (en) | 2002-08-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4233767B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4116753B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4236829B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2009195475A (en) | Pachinko game machine | |
| JP4475939B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4318947B2 (en) | Pachinko machine | |
| JP2001300056A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2008284060A (en) | Game table | |
| JP2003245426A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2009254531A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2000325597A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2012161644A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2005007091A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4034444B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2008284062A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP3976264B2 (en) | Pachinko machine | |
| JP4756754B2 (en) | Pachinko machine | |
| JP4107464B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2000126424A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2001149571A (en) | Pinball game machine | |
| JP4717030B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4732412B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2004000731A (en) | Pachinko game machine | |
| JP4679564B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2003117113A (en) | Game machine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20040811 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20040811 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20080331 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20080424 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20080623 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20081009 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20081106 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20081204 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20081210 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (prs date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20111219 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent (=grant) or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (prs date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20111219 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (prs date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20111219 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (prs date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121219 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (prs date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121219 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (prs date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121219 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (prs date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121219 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (prs date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131219 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |