JP4130226B2 - 内視鏡の正確な位置決定 - Google Patents
内視鏡の正確な位置決定 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4130226B2 JP4130226B2 JP52916597A JP52916597A JP4130226B2 JP 4130226 B2 JP4130226 B2 JP 4130226B2 JP 52916597 A JP52916597 A JP 52916597A JP 52916597 A JP52916597 A JP 52916597A JP 4130226 B2 JP4130226 B2 JP 4130226B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- endoscope
- sheath
- sensor
- insertion tube
- sensors
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 claims description 80
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 claims description 80
- 230000005291 magnetic effect Effects 0.000 claims description 37
- 239000003302 ferromagnetic material Substances 0.000 claims description 10
- 230000002452 interceptive effect Effects 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 229920000915 polyvinyl chloride Polymers 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000004800 polyvinyl chloride Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000000414 obstructive effect Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- -1 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 30
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 26
- 238000001574 biopsy Methods 0.000 description 14
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 12
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 11
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 5
- 210000000056 organ Anatomy 0.000 description 5
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000000007 visual effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 4
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 210000004204 blood vessel Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 239000007769 metal material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 210000001519 tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000005520 electrodynamics Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 2
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241001653121 Glenoides Species 0.000 description 1
- 229920000271 Kevlar® Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000003570 air Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000004556 brain Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000000621 bronchi Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000000747 cardiac effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000001072 colon Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000012141 concentrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012790 confirmation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007797 corrosion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005260 corrosion Methods 0.000 description 1
- KAATUXNTWXVJKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N cypermethrin Chemical compound CC1(C)C(C=C(Cl)Cl)C1C(=O)OC(C#N)C1=CC=CC(OC=2C=CC=CC=2)=C1 KAATUXNTWXVJKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 210000003238 esophagus Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005286 illumination Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007943 implant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001802 infusion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000000936 intestine Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000002427 irreversible effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004761 kevlar Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000005036 nerve Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000012811 non-conductive material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000003200 peritoneal cavity Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 229920003023 plastic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002787 reinforcement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000005245 right atrium Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000005241 right ventricle Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000000523 sample Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001954 sterilising effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000002784 stomach Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000008400 supply water Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001356 surgical procedure Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001225 therapeutic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000003462 vein Anatomy 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/06—Devices, other than using radiation, for detecting or locating foreign bodies ; determining position of probes within or on the body of the patient
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/00131—Accessories for endoscopes
- A61B1/00135—Oversleeves mounted on the endoscope prior to insertion
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/31—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor for the rectum, e.g. proctoscopes, sigmoidoscopes, colonoscopes
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods, e.g. tourniquets
- A61B17/22—Implements for squeezing-off ulcers or the like on the inside of inner organs of the body; Implements for scraping-out cavities of body organs, e.g. bones; Calculus removers; Calculus smashing apparatus; Apparatus for removing obstructions in blood vessels, not otherwise provided for
- A61B17/22004—Implements for squeezing-off ulcers or the like on the inside of inner organs of the body; Implements for scraping-out cavities of body organs, e.g. bones; Calculus removers; Calculus smashing apparatus; Apparatus for removing obstructions in blood vessels, not otherwise provided for using mechanical vibrations, e.g. ultrasonic shock waves
- A61B17/22012—Implements for squeezing-off ulcers or the like on the inside of inner organs of the body; Implements for scraping-out cavities of body organs, e.g. bones; Calculus removers; Calculus smashing apparatus; Apparatus for removing obstructions in blood vessels, not otherwise provided for using mechanical vibrations, e.g. ultrasonic shock waves in direct contact with, or very close to, the obstruction or concrement
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods, e.g. tourniquets
- A61B17/34—Trocars; Puncturing needles
- A61B17/3403—Needle locating or guiding means
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/06—Devices, other than using radiation, for detecting or locating foreign bodies ; determining position of probes within or on the body of the patient
- A61B5/065—Determining position of the probe employing exclusively positioning means located on or in the probe, e.g. using position sensors arranged on the probe
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B8/00—Diagnosis using ultrasonic, sonic or infrasonic waves
- A61B8/08—Detecting organic movements or changes, e.g. tumours, cysts, swellings
- A61B8/0833—Detecting organic movements or changes, e.g. tumours, cysts, swellings involving detecting or locating foreign bodies or organic structures
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B8/00—Diagnosis using ultrasonic, sonic or infrasonic waves
- A61B8/08—Detecting organic movements or changes, e.g. tumours, cysts, swellings
- A61B8/0833—Detecting organic movements or changes, e.g. tumours, cysts, swellings involving detecting or locating foreign bodies or organic structures
- A61B8/0841—Detecting organic movements or changes, e.g. tumours, cysts, swellings involving detecting or locating foreign bodies or organic structures for locating instruments
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B90/00—Instruments, implements or accessories specially adapted for surgery or diagnosis and not covered by any of the groups A61B1/00 - A61B50/00, e.g. for luxation treatment or for protecting wound edges
- A61B90/36—Image-producing devices or illumination devices not otherwise provided for
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B90/00—Instruments, implements or accessories specially adapted for surgery or diagnosis and not covered by any of the groups A61B1/00 - A61B50/00, e.g. for luxation treatment or for protecting wound edges
- A61B90/36—Image-producing devices or illumination devices not otherwise provided for
- A61B90/37—Surgical systems with images on a monitor during operation
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61M—DEVICES FOR INTRODUCING MEDIA INTO, OR ONTO, THE BODY; DEVICES FOR TRANSDUCING BODY MEDIA OR FOR TAKING MEDIA FROM THE BODY; DEVICES FOR PRODUCING OR ENDING SLEEP OR STUPOR
- A61M25/00—Catheters; Hollow probes
- A61M25/01—Introducing, guiding, advancing, emplacing or holding catheters
- A61M25/0105—Steering means as part of the catheter or advancing means; Markers for positioning
- A61M25/0127—Magnetic means; Magnetic markers
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61M—DEVICES FOR INTRODUCING MEDIA INTO, OR ONTO, THE BODY; DEVICES FOR TRANSDUCING BODY MEDIA OR FOR TAKING MEDIA FROM THE BODY; DEVICES FOR PRODUCING OR ENDING SLEEP OR STUPOR
- A61M25/00—Catheters; Hollow probes
- A61M25/10—Balloon catheters
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B10/00—Other methods or instruments for diagnosis, e.g. instruments for taking a cell sample, for biopsy, for vaccination diagnosis; Sex determination; Ovulation-period determination; Throat striking implements
- A61B10/02—Instruments for taking cell samples or for biopsy
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods, e.g. tourniquets
- A61B17/34—Trocars; Puncturing needles
- A61B17/3415—Trocars; Puncturing needles for introducing tubes or catheters, e.g. gastrostomy tubes, drain catheters
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods, e.g. tourniquets
- A61B2017/00477—Coupling
- A61B2017/00482—Coupling with a code
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods, e.g. tourniquets
- A61B2017/00681—Aspects not otherwise provided for
- A61B2017/00725—Calibration or performance testing
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods, e.g. tourniquets
- A61B17/22—Implements for squeezing-off ulcers or the like on the inside of inner organs of the body; Implements for scraping-out cavities of body organs, e.g. bones; Calculus removers; Calculus smashing apparatus; Apparatus for removing obstructions in blood vessels, not otherwise provided for
- A61B17/22004—Implements for squeezing-off ulcers or the like on the inside of inner organs of the body; Implements for scraping-out cavities of body organs, e.g. bones; Calculus removers; Calculus smashing apparatus; Apparatus for removing obstructions in blood vessels, not otherwise provided for using mechanical vibrations, e.g. ultrasonic shock waves
- A61B2017/22005—Effects, e.g. on tissue
- A61B2017/22007—Cavitation or pseudocavitation, i.e. creation of gas bubbles generating a secondary shock wave when collapsing
- A61B2017/22008—Cavitation or pseudocavitation, i.e. creation of gas bubbles generating a secondary shock wave when collapsing used or promoted
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/20—Surgical navigation systems; Devices for tracking or guiding surgical instruments, e.g. for frameless stereotaxis
- A61B2034/2046—Tracking techniques
- A61B2034/2051—Electromagnetic tracking systems
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/20—Surgical navigation systems; Devices for tracking or guiding surgical instruments, e.g. for frameless stereotaxis
- A61B2034/2046—Tracking techniques
- A61B2034/2063—Acoustic tracking systems, e.g. using ultrasound
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B90/00—Instruments, implements or accessories specially adapted for surgery or diagnosis and not covered by any of the groups A61B1/00 - A61B50/00, e.g. for luxation treatment or for protecting wound edges
- A61B90/36—Image-producing devices or illumination devices not otherwise provided for
- A61B2090/363—Use of fiducial points
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B90/00—Instruments, implements or accessories specially adapted for surgery or diagnosis and not covered by any of the groups A61B1/00 - A61B50/00, e.g. for luxation treatment or for protecting wound edges
- A61B90/39—Markers, e.g. radio-opaque or breast lesions markers
- A61B2090/3925—Markers, e.g. radio-opaque or breast lesions markers ultrasonic
- A61B2090/3929—Active markers
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B90/00—Instruments, implements or accessories specially adapted for surgery or diagnosis and not covered by any of the groups A61B1/00 - A61B50/00, e.g. for luxation treatment or for protecting wound edges
- A61B90/39—Markers, e.g. radio-opaque or breast lesions markers
- A61B2090/3954—Markers, e.g. radio-opaque or breast lesions markers magnetic, e.g. NMR or MRI
- A61B2090/3958—Markers, e.g. radio-opaque or breast lesions markers magnetic, e.g. NMR or MRI emitting a signal
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B2560/00—Constructional details of operational features of apparatus; Accessories for medical measuring apparatus
- A61B2560/02—Operational features
- A61B2560/0266—Operational features for monitoring or limiting apparatus function
- A61B2560/0276—Determining malfunction
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/20—Surgical navigation systems; Devices for tracking or guiding surgical instruments, e.g. for frameless stereotaxis
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B90/00—Instruments, implements or accessories specially adapted for surgery or diagnosis and not covered by any of the groups A61B1/00 - A61B50/00, e.g. for luxation treatment or for protecting wound edges
- A61B90/36—Image-producing devices or illumination devices not otherwise provided for
- A61B90/361—Image-producing devices, e.g. surgical cameras
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B90/00—Instruments, implements or accessories specially adapted for surgery or diagnosis and not covered by any of the groups A61B1/00 - A61B50/00, e.g. for luxation treatment or for protecting wound edges
- A61B90/39—Markers, e.g. radio-opaque or breast lesions markers
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61M—DEVICES FOR INTRODUCING MEDIA INTO, OR ONTO, THE BODY; DEVICES FOR TRANSDUCING BODY MEDIA OR FOR TAKING MEDIA FROM THE BODY; DEVICES FOR PRODUCING OR ENDING SLEEP OR STUPOR
- A61M25/00—Catheters; Hollow probes
- A61M25/0021—Catheters; Hollow probes characterised by the form of the tubing
- A61M25/0023—Catheters; Hollow probes characterised by the form of the tubing by the form of the lumen, e.g. cross-section, variable diameter
- A61M2025/0025—Catheters; Hollow probes characterised by the form of the tubing by the form of the lumen, e.g. cross-section, variable diameter having a collapsible lumen
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61M—DEVICES FOR INTRODUCING MEDIA INTO, OR ONTO, THE BODY; DEVICES FOR TRANSDUCING BODY MEDIA OR FOR TAKING MEDIA FROM THE BODY; DEVICES FOR PRODUCING OR ENDING SLEEP OR STUPOR
- A61M25/00—Catheters; Hollow probes
- A61M25/01—Introducing, guiding, advancing, emplacing or holding catheters
- A61M25/0105—Steering means as part of the catheter or advancing means; Markers for positioning
- A61M2025/0166—Sensors, electrodes or the like for guiding the catheter to a target zone, e.g. image guided or magnetically guided
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61M—DEVICES FOR INTRODUCING MEDIA INTO, OR ONTO, THE BODY; DEVICES FOR TRANSDUCING BODY MEDIA OR FOR TAKING MEDIA FROM THE BODY; DEVICES FOR PRODUCING OR ENDING SLEEP OR STUPOR
- A61M25/00—Catheters; Hollow probes
- A61M25/10—Balloon catheters
- A61M2025/1043—Balloon catheters with special features or adapted for special applications
- A61M2025/1052—Balloon catheters with special features or adapted for special applications for temporarily occluding a vessel for isolating a sector
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61M—DEVICES FOR INTRODUCING MEDIA INTO, OR ONTO, THE BODY; DEVICES FOR TRANSDUCING BODY MEDIA OR FOR TAKING MEDIA FROM THE BODY; DEVICES FOR PRODUCING OR ENDING SLEEP OR STUPOR
- A61M25/00—Catheters; Hollow probes
- A61M25/0021—Catheters; Hollow probes characterised by the form of the tubing
- A61M25/0023—Catheters; Hollow probes characterised by the form of the tubing by the form of the lumen, e.g. cross-section, variable diameter
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (AREA)
- Pulmonology (AREA)
- Anesthesiology (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Gynecology & Obstetrics (AREA)
- Child & Adolescent Psychology (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Orthopedic Medicine & Surgery (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Endoscopes (AREA)
Description
この出願は、1996年2月15日に出願された「ポインティング装置パッケージ」の名称の米国仮出願第60/011,743号、および1996年2月26日に出願された「開放内腔受動位置センサー」の名称の同第60/012,242号に関連する。なおこれらの開示を参考文献として本明細書に含める。この出願はまた、出願人Biosense Inc.により本願と同日に出願された以下のPCT出願にも関連する。それらの出願はイスラエル受領庁に出願された「位置確認可能なバイオプシー針」の名称のPCT出願、共に米国受領庁に出願された「内腔を有するカテーテル」の名称のPCT出願と「フィールドトランスジューサーを備えた医療プローブ」の名称のPCT出願であり、それらの開示を本明細書に参考文献として含める。この出願は「心臓の電気力学」の名称で、1997年1月8日に出願人Biosense LTD.によりイスラエル受領庁に出願された国際特許出願第PCT/IL97/00010号のCIP出願であり、その開示を本明細書に参考文献として含める。
発明の分野
本発明は一般に内視鏡の分野、より詳細には位置センサーを備えた内視鏡アンブリーに関する。
発明の背景
診断と治療の指標のために内視鏡を使用することが急速に広まっている。今や、上部食道、胃および十二指腸用内視鏡、血管用血管鏡、気管支用気管支鏡、関節窩用関節鏡、結腸用結腸鏡、腹膜腔用腹腔鏡のような多くのタイプの特殊内視鏡がある。本発明は全てのタイプの内視鏡に適応する。
内視鏡は15mm〜25mmの範囲内の直径を有する長い柔軟性がある挿入チューブを有するのが代表的である。この挿入チューブは内視鏡手技(手順)時に選択された通路に沿って患者の体内に挿入される。多くの操作導管が挿入チューブ内の内視鏡の長さに沿って通常延在している。その操作導管は例えば体内へのエアー吸入と給水が可能である。さらに操作導管によって患者の体内へのバイオプシー装具の挿入とその引き出しが可能である。内視鏡に組み込まれる他の機構としては、目視映像装置、照明装置、偏向機構がある。内視鏡の基端部に内視鏡を制御するハンドル(取っ手)があるのが普通である。通常、内視鏡は導電性の金属材料から製造される。米国特許第4,869,238号は、金属コイルとワイヤーメッシュを備えた標準的な内視鏡の3層壁を記載している。なおこの特許の開示を参考文献として本明細書に含める。
内視鏡を洗浄し滅菌することは高価で時間がかかる手順である。内視鏡は洗浄時に損傷させる可能性のある高価で繊細な装置を組み込んでいる。また、挿入チューブの長くて細い操作導管は洗浄しにくい。
内視鏡を洗浄し滅菌する必要性を避けるために使い捨てシースが開発されている。これらのシースは内視鏡を患者から十分に離して内視鏡が汚染されないようにする。これらのシースの幾つかはその内部に操作導管を通した厚い壁があり(肉厚であり)、それにより断面の一部のみが内視鏡の挿入チューブを収納する腔を通すことができる。操作導管の壁と操作導管同士の間の領域は外壁と同じ材料からなっているのが普通である。
肉厚のシースは、例えばPCT公報第WO 94/28782号に記載されており、その開示を参考文献として本明細書に含める。その公報第WO 94/28782号は操作導管を備える使い捨てシースを開示している。このシースは、内視鏡の制御装置(コントロール)と他の繊細な装置を備えた円筒挿入チューブを取り外し可能に収納する。他の使い捨てシースは米国特許第5,483,951号に記載され、その開示を参考文献として本明細書に含める。この使い捨てシースは薄い外壁、内側操作導管および「D」字形断面の内腔から構成されている。この内腔は内視鏡の非使い捨て挿入チューブを収納し十分離すように適合されており、それにより「D」字形となっている。
内視鏡手技の多くは、内視鏡の挿入チューブの先端部での組織サンプルの採取や切除のような元に戻せない動作を含む。これらの動作を不正確な位置で行なうと、重要な血管と神経を損傷したり、腸を刺したり、あるいは患者に重大な損傷を引き起こすことがある。従って、内視鏡の先端部の位置および/又は方向を決定する方法を有することは有効である。
目視映像装置によってユーザーは内視鏡の先端部から送られた画像を観察することができる。これらの画像からそして内視鏡が辿った通路の知識からユーザーは内視鏡の位置を通常決定(判断)することができる。しかしながら、画像と通路の知識が内視鏡の位置を十分正確に決定するには十分でない人間の体の臓器がある。脳のような臓器は外観が一様で、映像装置からの画像だけに基づいて特定の場所を見つけることが困難もしくは不可能である。さらに、画像から内視鏡の位置を判断することは非常に時間がかかることもある。内視鏡的バイパス手術のような多数の内視鏡的手技では、患者がその内視鏡的手技に耐えられる時間が制限される。
幾つかの手技では、内視鏡が臓器の一部分をマップ化(マッピング)するために使用される。そのマップは、内視鏡の先端部を臓器内の複数の場所(地点)に系統的に接触させ、そしてその場所の位置を記録する(位置合わせ)ことによって作られる。その臓器の全体断面がマップ化されたことを確認するために、十分な密度で場所を断面内で記録しなければならない。十分な密度で場所を記録するために、場所ごとに独自の位置確認を行なう必要がある。
例えば結腸鏡手技で発生する他の問題は結腸鏡の長くて細いチューブが環(ループ)を作ることである。そのような環は挿入チューブが障害物に当たった時か、細い通路にはまり込んだ時にできる。前進する代わりにそのチューブは患者体内で環を作る。結腸鏡を挿入しようとする試みでは、過剰な力をかけ、そのため患者の体の繊細な組織を傷つける。ユーザーは問題があることを十分理解しないで内視鏡の挿入を続ける場合がある。患者の体内での内視鏡挿入チューブの形状を見る機能があれば、環の存在を早期に発見しその環を簡単に真っ直ぐにすることができる。
内視鏡挿入チューブの形状を判断するために当技術で使用される方法の一つがX線映像法である。使用される他の方法は、患者と担当者にX線を暴露しない磁界位置決定法である。開示を参考文献として本明細書に含める国際特許出願第PCT/GB93/01736号は、低周波数磁界を使用して結腸鏡チューブ内に埋め込まれたミニセンサーの位置を決定する磁界位置決定法を記載する。時間毎のセンサーの逐次位置に基づいて結腸鏡チューブの形状の画像が作られる。
国際特許出願第PCT/GB93/01736号に記載された試験では、結腸鏡の金属構造のため画像に幾分ゆがみがあることが分かった。結腸鏡の金属構造は検出用の磁界に反応してしまう。電流が磁界によって結腸鏡内に誘導されるのである。渦電流と呼ばれるこれらの電流は、検出用磁界と重なった攪乱磁界を発生させる。従って、この位置決定装置(システム)が用いる磁界の振幅および/又は相が、金属物質の近傍で変化する。渦電流の大きさと効果は金属材料(物質)のサイズと形状に依存する。例えば大きな金属環は大体その近傍で磁界を変える。反対に、内部で渦電流が略形成されない小さな金属物体と比較的高抵抗の物体は実質的に磁界に影響を与えない。
磁界位置決定装置は磁界の振幅および/又は磁界の相により複数の位置を決定するのが普通である。渦電流による振幅および/又は相の変化により決定された位置が不正確となり、正確な位置決定を妨げる。その妨害は、磁界をその近傍に集中させる内視鏡の強磁性材料から生じることもある。従って、強磁性材料は磁界にゆがみを引き起こし、それによって測定場所で磁界の振幅と相を変える。
妨害は、磁界を発生させるドライブ信号の周波数に依存している。高いドライブ信号周波数はセンサー感度を上げるのに好ましいが、位置決定装置に対する妨害を強くしないように制限しなければならない。従って、国際特許出願第PCT/GB93/01736号の装置は使用周波数の選択において妥協する。その妨害を最小にする異なった方法を使用すれば、高ドライブ信号周波数の利点を生かすことが可能であろう。
現存するカテーテルはその内部に金属コイル(構造目的のため)を有している。その金属コイルは、カテーテルの先端部の小さな部分を除いてカテーテルの全長に沿って延在する。磁界位置決定装置と連結したセンサーはカテーテルの先端部内に埋め込まれている。
発明の概要
本発明の目的は磁界位置決定装置を使用して内視鏡の正確な位置決定法を提供することである。
本発明の他の目的は、内視鏡シースが内視鏡の挿入チューブを収納する場合にその挿入チューブ内で複数の場所の正確な位置決定を可能にする内視鏡シースを提供することである。
本発明の幾つかの態様の他の目的は、内視鏡の挿入チューブに沿った場所に埋め込まれた1個以上の位置センサーを、内視鏡内部の位置決定を妨害する材料、構造および信号源(ソース)から遠ざけることである。そのような材料、構造および信号源を本明細書では「妨害起因構造体」と呼ぶ。
本発明の好ましい幾つかの実施形態では、位置決定装置は磁界を使用して位置を決定する。これらの実施形態では、妨害起因構造体は、通常、導電性および/又は強磁性の材料からなっている。制御ワイヤー、金属コイル、内視鏡壁補強材、電線などのような内視鏡の様々な構成部品が妨害起因構造体となりうる。妨害は妨害起因構造体のサイズと形状、およびセンサーと妨害起因構造体物質との間の距離に依存する。さらに詳細には、妨害はセンサーと妨害起因構造体との間の距離の三乗に略反比例する。振幅ベースの位置決定装置を使用する場合、その位置決定装置で使用される磁界の1%未満まで妨害を減らすには1mm〜3mm間の距離で普通十分である。
本発明の好ましい実施形態によれば、内視鏡シースは非妨害起因構造体だけから構成されることが好ましい。内視鏡シースの壁はその内部に操作導管を備えており、そのため肉厚であるのが好ましい。内視鏡シースは内視鏡の挿入チューブを収納する内腔を備えていることが好ましい。1個以上のセンサーがシース内部、好ましくは内腔から最も離れた領域に埋め込まれる。従って、挿入チューブを内腔に配置すると、センサーは妨害起因構造体から離れる。挿入チューブがシース内に好ましく丁度良く正確に配置され、それによって挿入チューブ内の様々な地点の位置がセンサーに対して容易に決定される。
本発明の他の実施形態では、内視鏡シース先端部が挿入チューブを越えて延在し患者の体から挿入チューブの先端を離している。本発明の幾つかのシースでは、その先端部には、内視鏡の先端部をはっきり見ることができる透明な窓がある。そのシースの先端部には妨害起因構造体が実質的にないことが好ましい。センサーは、挿入チューブ内にある妨害起因構造体から離れたシースの先端部内に埋め込まれている。センサーが透明な窓を通した視野を覆わないことが好ましい。従って、挿入チューブをシース内に挿入する場合、センサーをその近傍に妨害起因構造体が実質的にない内視鏡の先端に置く。これは挿入チューブの先端が妨害起因構造体から構成されている場合にも当てはまる。
幾つかの先行技術による内視鏡シースではシース内に幾つかの金属構成部品を有することが分かる。本発明の好ましい実施形態によれば、これらのシースでは、挿入チューブがシース内にある時妨害が最小になる場所に、センサーが好適に埋め込まれている。これらの場所を見つけるため設計段階中に試験を行なうことが好ましい。挿入チューブがシース内にある時に行なうこれらの試験では、妨害起因構造体によって誘発された妨害が計測され、その結果としてセンサーの位置が選択される。この実施形態ではセンサーに対する妨害が試験の時と同じになるように、シース内での挿入チューブの好ましい方向を確認することが重要である。
1996年9月17日にBiosense Ltd.によって出願されたイスラエル特許出願第119,262号は使い捨てバイオプシー針に適合した埋め込み位置センサーを有するシースを記載している。なおこの出願は本発明の譲受人に譲渡され参考文献として本明細書に含める。本発明の好ましい実施形態によれば、バイオプシー針は炭素のような非妨害起因構造体から製造され、それによってバイオプシー針の構造は位置決定装置の操作を妨害しない。また、シースにセンサーをバイオプシー針から離すのに十分な厚みを持たせてもよい。1996年2月15日にBiosense Ltd.によって出願された「内腔を備えたカテーテル」の名称のイスラエル特許出願第117,148号は、大きな内腔を有するカテーテルと、その内腔をその操作時に閉塞しない位置センサーを記載している。なおこの出願の開示を参考文献として本明細書に含める。
本発明の他の好ましい実施形態では、1個以上の位置センサーが侵入装具を覆うシース内に埋め込まれる。本発明の具体的な実施形態では、侵入装具はペースメーカー電極であり、その電極はガイドにより静脈を通して右心房に、そして次に右心室に通常挿入され、その部位ではねじ、クリップあるいは他のタイプの縫合糸を使うことによって先端に電極が固定される。電極の正確な取り付け場所を知ることは、様々な理由、特に1997年1月8日にイスラエル受領庁に出願され、発明者、Shiomo Ben-HaimおよびMaier Fensterの「心臓の電気力学」の名称のPCT出願に記載された理由により望ましい。なおその出願の開示を参考文献として本明細書に含める。このPCT出願は心臓の活性プロフィールを決定し、そしてそのプロフィールおよび/又は心臓の電気活性マップおよび/又は機械的活性マップに基づいて、そのようなペースメーカー電極の最適な場所を決定する様々な方法を記載している。目的の一つがその電極を疾患組織(ペースメーカー電源を消耗したり患者に傷を与える)に取り付けないことである。他の目的はペースメーカー電極を使用して心臓の特定の活性プロフィールを得ることである。位置センサーはペースメーカー電極を患者の心臓の所定の位置へ挿入するのをガイドする際に役立てられる。ペースメーカーをその所定位置に取り付けた後、シースをペースメーカー電極から外し、センサーと共に患者の体から取り出す。本発明の好ましい実施形態では、当技術で知られているように、電極を曲げ、同時に血管や心臓を介して所定の場所に向けてナビゲートするステアリング機構を備えている。ペースメーカー電極が、通常、患者の心臓内にあり、各心臓の鼓動で収縮するため、その電極をいくつかの外部材料が壊す可能性が大であり、患者に損傷を与える可能性があることを認識する必要がある。ペースメーカー電極は腐食やこの種の定歪みによる破損に耐えるように特殊加工されることが普通であるが、コストを考えたり技術的制約を考えると同じ加工原理を位置センサーに適用することは望ましくない。本発明のこの実施形態は、患者の体内に長期間留置される注入チューブのような他の侵入装具で特に有効である。
本発明の幾つかの好ましい実施形態では、センサーをシース内に埋め込まない。センサーはむしろ内視鏡に固定される取り付け具内に埋め込まれる。これらの取り付け具は位置決定装置の操作に妨害を実質的に与えない材料からなり、内視鏡内でセンサーと妨害起因構造体との間を効果的に分離するだけ十分に厚いことが好ましい。この取り付け具は接着剤を使用してあるいは他の接合法によって内視鏡に取り付けることができる。本発明の幾つかの実施形態では、シースは内視鏡とその上の取り付け具の両方を覆うために使用される。そのシースは内視鏡を周囲の物から隔離し、また取り付け具とセンサーを内視鏡に固定する。好ましい実施形態では、一つの長い取り付け具が内視鏡の全長に渡り、その取り付け具内に1個以上のセンサーがある。
本発明の他の好ましい実施形態では、センサーと妨害起因構造体との分離が別個の使い捨て部品を使わないで達成される。それよりも挿入チューブそれ自体が分割され、位置決定装置の操作を妨害する材料がない領域を形成する。これらの領域内では、1個以上のセンサーが埋め込まれ、妨害起因構造体から離される。従って、センサーと妨害起因構造体が分離されることになり、位置決定装置の操作を実質的に妨害しなくなる。
本発明の幾つかの好ましい実施形態では、横方向分離が使用される。横方向分離では妨害起因構造体が無い領域を挿入チューブの所定断面領域に配置する。本発明の一つの好ましい実施形態では、その分離は、妨害起因構造体が軸方向に中心配置であり、周縁に隣接する領域には妨害起因構造体が無いようになっている。従って、シースの直径が十分大きければこれらの領域の殆どの部分では妨害が実質的に発生しない。本発明の他の好ましい実施形態では、妨害起因構造体は、通常は円形である内視鏡の断面のうちの「D」字形領域に制約される。従って、残りの断面は妨害起因構造体が無く、そのため断面の殆どの部分で略妨害が無くなる。
本発明の一つの好ましい実施形態では、長手方向の分離に基づき、挿入チューブの長さに沿った1個以上の部分で妨害起因構造体が実質的にない。本発明の他の好ましい実施形態では、妨害起因構造体が挿入チューブの全長に及ぶ。しかしながら、挿入チューブの長さに沿って妨害起因構造体が断面の一部に制約される1個以上の部分(セグメント)がある。従って、これらの部分の断面の一部領域には妨害起因構造体が無い。その結果、位置決定装置のセンサーが、実質的に妨害が生じない場所のこれらの領域内に埋め込まれる。
これらの場所は妨害が最小の挿入チューブの場所であることが好ましい。これらの場所は本発明の前述の実施形態に関して述べた上記試験によって選択されることが好ましい。また、センサーは、挿入チューブ内で全ての妨害起因構造体から実質的に最も遠い場所に埋め込まれる。
従って、本発明の好ましい実施形態によれば、内視鏡の位置を決定するために内視鏡に接続可能な位置決定可能な内視鏡取り付け具と、1個以上のセンサーであってそれらセンサーの位置を決定するために使用される取り付け具に対して固定配置されるセンサーが提供される。
その取り付け具を内視鏡に固定取り付けした時に、1個以上のセンサーが、そのセンサーの位置決定を妨害する内視鏡の要素から離されることが好ましい。
1個以上のセンサーが取り付け具内に埋め込まれることが好ましい。
その取り付け具は1個以上のセンサーの位置決定を実質的に妨害する要素を備えていないことが好ましい。
本発明の好ましい実施形態では1個以上のセンサーの位置決定が磁界を送りそして受けることによって行なわれる。
取り付け具の外側に1個以上のセンサーの位置を示す表示(マーキング)があることが好ましい。
本発明の好ましい実施形態では取り付け具がチューブを備えている。
本発明の好ましい実施形態によれば上記のように1個以上の取り付け具を有する内視鏡位置決めおよび感知キット、および内視鏡と1個以上の取り付け具を覆う薄いシースがさらに提供される。
本発明の好ましい実施形態では、取り付け具が内腔と周縁を有するシースを備え、その内腔が「D」字形断面を有し、1個以上のセンサーが位置決定を妨害する材料から、その材料の妨害効果を実質的に回避するのに十分な距離だけ離されることが好ましい。
また別に、あるいはさらに、内腔がシース内で軸方向に中心に位置し、1個以上のセンサーがシースの周縁に隣接して配置される。
シースが内腔を越えて延在する先端部を有し、1個以上のセンサーの内の少なくとも1個がその先端部に埋め込まれることが好ましい。
本発明の好ましい実施形態によれば、断面、周縁および先端を備えた細長い本体を有する挿入チューブを有する位置決定可能な内視鏡と、その細長い本体の固定位置に配置された1個以上のセンサーがさらに提供される。1個以上のセンサーはそのセンサーの位置決定のために使用され、先端から離れ1個以上のセンサーに隣接する細長い本体の断面部分が1個以上のセンサーの位置決定を実質的に妨害する材料を含まないことが好ましい。
1個以上のセンサーの位置決定を妨害する挿入チューブの要素が最小の効果を有する細長い本体の断面の場所にその1個以上のセンサーが配置されることが好ましい。
1個以上のセンサーが挿入チューブ内に埋め込まれることが好ましい。
1個以上のセンサーの位置決定が磁界を送りそして受けることによって行なわれることが好ましい。
1個以上のセンサーが、挿入チューブ内の、導電性の強磁性材料から実質的に最も遠い場所に配置されることが好ましい。
1個以上のセンサーの位置決定を妨害する材料が細長い本体の「D」字形断面に制約され、そして1個以上のセンサーが、位置決定を妨害する材料から、その材料の妨害効果を実質的に回避するのに十分な距離だけ離されることが好ましい。
また、1個以上のセンサーの位置決定を妨害する材料が細長い本体の丸い、軸方向に中心配置の断面に制約され、そして1個以上のセンサーが挿入チューブの周縁に隣接して配置される。
本発明は、図面と共に考慮した本発明の好ましい実施形態の以下の詳細な説明からさらに十分理解されるであろう。
【図面の簡単な説明】
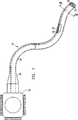
図1は本発明の好ましい実施形態による結腸鏡に取り付けられた内視鏡シースの斜視図である。
図2は内視鏡シースの先端部の図1のラインII−IIに沿った拡大断面図であり、結腸鏡の挿入チューブを示していない。
図3は本発明の他の好ましい実施形態の側面断面図である。
図4は本発明の他の好ましい実施形態の断面図である。
図5は本発明の好ましい実施形態によるセンサー取り付け具を備えた内視鏡の斜視図である。
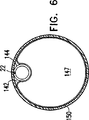
図6は本発明のさらに他の好ましい実施形態の断面図である。
図7は本発明の他の好ましい実施形態による内視鏡の側面断面図である。
好ましい実施形態の詳細な説明
結腸鏡の内視鏡挿入チューブ14に取り付けられた柔軟な内視鏡シース20を示す図1を参照する。結腸鏡10は制御ユニット12と、先端部15を有する挿入チューブ14とを具備している。結腸鏡10は、挿入チューブ14を丁度良く収納するように適合された柔軟な内視鏡シース20内に配置されている。挿入チューブ14とシース20は、チューブ14が患者の体から隔離されるように共に患者の体内に挿入される。1個以上のセンサー22は以下説明するようにシース20に沿って埋め込まれている。位置決定装置(図示せず)は、好ましくはセンサー22との間で送受信される磁界によりセンサー22のスペースでの位置を決定する。
挿入チューブ14は耐久性のある壁を備えた長くて細い柔軟なチューブであり、好適に「D」字形断面を有する。偏向機構、目視映像装置および他の装置がチューブ14内に配置される。結腸鏡内の装置に使用されるワイヤーが挿入チューブ14に沿ってその先端部15から制御ユニット12まで通っている。チューブ14は、通常、導電性材料から構成される非使い捨ての細長いチューブである。
柔軟な内視鏡チューブ20は、位置決定装置の操作を妨害しない材料から一般に構成される細長い使い捨てチューブである。妨害材料としては導電性材料と強磁性材料がある。シース20がポリエチレンあるいはポリ塩化ビニル(「PVC」)からなるのが好ましいが、その他耐久性のある滑らかな材料でも構成される。幾つかの先行技術の説明ではシース20が金属ばねあるいは他の導電性部品からできているということが分かる。そのようなシースを使う本発明では、設計段階で測定を好適に行ない、その導電性部品で誘発される妨害を決定する。シースの導電性部品の影響は、その部品が誘発する妨害が結腸鏡内の材料によって誘発された妨害に対して小さければ無視してもよい。また、本発明によれば、導電性部品を非導電性材料からなる機能的に同等の部品に代えた同様のシースを使用することができる。
図1の内視鏡シース20の断面図であり結腸鏡の挿入チューブを示していない図2で最もよく分かるように、シース20は好適に円形外断面を有する。シース20内には挿入チューブ14を丁度良く収納する形状とサイズの内腔17がある。シース20の残りの断面には、シース20の長手方向の軸(縦軸)に略平行に通っている数本の操作導管25,26,27がある。操作導管25,26,27は、エアー、水のような材料とバイオプシー採取具などの材料や装具を患者の体内と体外へ通すために使用される。具体的な実施形態では、導管25はエアー導管であり、導管26は水導管であり、導管27は患者の体内にバイオプシー採取具を通すために使用され、バイオプシー導管と呼ばれている。妨害を誘発する導電性装具がバイオプシー導管27に通されることもあることが分かる。装具のサイズが小さく、装具とセンサー22との間に距離があるために、そのような装具では、通常、位置決定装置の操作に対する妨害が略発生しない。しかしながら、センサー22に近い操作導管には妨害材料を通さない作業が割り当てられる。その結果、センサー22がバイオプシー導管27から最も遠くに埋め込まれる。言い換えればセンサー22から最も遠い導管がバイオプシー装具に使用される。
上記のように、シース20に沿って位置決定装置と共に使用される1個以上のセンサー22がある。本発明の好ましい実施形態では、センサー22はその近傍で磁界の振幅および/又は相を感知する。位置決定装置はその振幅および/又は相を使用して内視鏡内の位置を決定する。センサー22の各々は少なくとも3つの座標で測定する。各センサー22は位置と方向の6つの座標の決定を可能にすることが好ましい。また、数センサーを互いに固定配置する場合は、2つの座標だけを測定する幾つかのセンサーを使用してもよい。センサーは例えば国威特許出願第PCT/GB93/01736号,米国特許第5,391,199号,PCT公報第WO 95/04938号,PCT公報第WO 96/05768号,あるいは1996年2月15日に出願され本願の譲渡人に譲渡された米国仮特許出願第60/011,724号に記載されたようなミニコイルであることが好ましい。なお上記全ての特許、公報および出願を参考文献として本明細書に含める。センサー22は、位置決定装置の操作に対する妨害を回避するのに十分な距離だけ妨害材料から離して、シース20の内側であってその周縁近傍に配置される。本発明の好ましい実施形態ではセンサー22は内腔17と正反対の側にある。図1で最もよく分かるように、シース20に沿って走るワイヤー24はセンサー22を位置決定装置(図示せず)に接続する。ワイヤー24はシース20の内部の最小スペースをとるように、また位置決定装置の操作を妨害しないように十分に細い。また、その代わりセンサー22はワイヤーが無くてもよい。本発明の好ましい実施形態では、少なくとも1個のセンサーを集積回路の送信機と連結する。
チューブ14を患者に挿入する前に、チューブ14をシース20内に丁度良く配置し、正確に方向付ける。さらに、チューブ14の先端部15をシース20内の再配置可能な深さまで導入することが好ましい。これによりセンサー22と挿入チューブ14の精確な位置調整を行うことができる。
シース20を内視鏡に丁度良く取り付ける方法の一つが化学的方法あるいは加熱法を使用して内視鏡周囲にシースを収縮させることである。そのようなシースは、使用後にシースの取り外しを容易にするために、シースの内側に沿って走るKevlar(商標)のような「リップコード(rip cord)」を含むことが好ましい。内視鏡に垂直なそのようなリップコードを引いてシースを裂き、それによってシースを内視鏡から容易に外すことができる。取り付け具を備えている等の理由で内視鏡の断面が一定でない場合、そのようなコードは特に重要である。
シースに対して、従って挿入チューブ14に対してセンサー22を正確に固定し、それにより位置決定装置がシース20と挿入チューブ14に沿ったどの場所の位置をも決定できる。さらに、センサー22をシース20内に好適に埋め込み、センサー22を周囲から保護する。
本発明の幾つかの好ましい実施形態では、位置決定装置がDC電流を使用する。これらの実施形態では導電材料は位置決定装置の操作を妨害しない。従って、センサー22を強磁性材料からだけ離す。これらの装置では、どこにセンサーを配置するかが挿入チューブ内の強磁性材料の配置により決定される。
ここで本発明の好ましい実施形態による内視鏡シースを示す図3を参照する。本発明の幾つかの実施形態では、シース20は、チューブ14の先端部15を越えて延在する先端部28を有している。先端部28は患者の体から先端部15を好適に隔離する。シース20はその先端部28に透明な窓30を好適に備え、チューブ14内の映像装置の視野を遮らない。窓30は、例えば米国特許第5,402,768号に記載したように、きれいな透明な光学グレードプラスチックから好適に構成される。なおこの特許を参考文献として本明細書に含める。本発明によれば、先端部28は位置決定装置の操作に妨害を引き起こす材料(物質)が実質的にない。従って、先端部28に埋め込まれたセンサー22には妨害が誘発されない。先端部28は、少なくとも1個のセンサー22を納める厚さを有し、かつ窓30を通して見えることが好ましい。本発明の好ましい実施形態では、位置決定装置に対する妨害を先端部28内の異なった場所で計測し、妨害が最も少ない場所にセンサー22を埋め込む。
本発明の他の実施形態によるシース120の断面を示す図4を参照する。シース120は円筒形内腔117を備え、この内腔はシース120内で軸方向に好適に中心配置となっている。内腔117は内視鏡挿入チューブを丁度良く収納する形状である。幾つかの操作導管が内腔117に平行に、シース120内で内腔117を放射状に包囲して走っている。例えばエアー125用、水126用およびバイオプシー装具127用の3つの導管があるのが好ましい。1個以上のセンサー22をシース120に沿って、好ましくは内腔117からできるだけ遠く、シース120の外周縁に埋め込む。センサー22をエアー導管125と水導管126の近傍に埋め込み、それによりバイオプシー導管127を通る金属装具からセンサー22を離すことが好ましい。
挿入チューブには、腔内の挿入チューブの正確な方向を指示するマーキングがあるのが好ましい。本発明の好ましい実施形態では、挿入チューブがキーを有し、腔がそれに対応するスロットを有する。従って、挿入チューブを正確な方向でだけ腔内に挿入することができる。さらに、挿入チューブの先端部が腔の先端部内面に接触する。従って、位置決定装置は、センサー22の位置により挿入チューブの位置と方向を正確に位置合わせすることができる。
本発明の幾つかの好ましい実施形態では、センサーを内視鏡への取り付け具内に埋め込む。本発明の好ましい実施形態によるセンサーを備えた内視鏡を示す図5を参照する。図5に示したように、内視鏡90は、センサー22を組み込んだ1個以上の取り付け具94を有している。内視鏡90の少なくとも一部に長さ方向の溝(グルーブ)96を有することが好ましい。取り付け具94は溝96内に好適に配置され、溝から突出せずに溝96に滑らかに好適にフィットする形状になっている。取り付け具は94は、実質的に非妨害起因材料からなり、内視鏡内でセンサー22と妨害起因構造体とを実質的に分離するように十分厚いのが好ましい。取り付け具94を内視鏡90に接着剤で接合するのが好ましい。また別に、あるいはさらに、当技術で既知の接合法を使用して取り付け具94を内視鏡90に接合する。センサー22を取り付け具94内の内視鏡90から最も離れた取り付け具94の一部に埋め込むことが好ましい。従って各取り付け具94の殆どがその関連センサー22を内視鏡90内の妨害起因構造体から分離する。
本発明の好ましい実施形態では、薄いシース92で内視鏡90と取り付け具94を覆い、それにより内視鏡90を患者の体から隔離し、また取り付け具94を内視鏡94の固定位置で保持する。内視鏡90を患者に挿入する前に、内視鏡90を外部基準目盛り地点まで導入することが好ましく、その後、位置決定装置が内視鏡90に対してセンサーの位置を位置合わせする。
本発明の好ましい実施形態では、内視鏡に沿って配置される1個の長い取り付け具内に1個以上のセンサーの位置を定める。ここで本発明の他の実施形態による内視鏡アセンブリーの断面を示す図6を参照する。図6に示したように、使い捨てシース150が内視鏡147を患者の体から隔離する。溝142が内視鏡147の長さに沿って走っている。シース150が内視鏡147とチューブ144を覆うように、使い捨てチューブ144を内視鏡147に沿って溝142内に取り付ける。内視鏡147とチューブ144は例えば米国特許第4,646,722号に記載されたようにすることが可能である。なおこの特許の開示を参考文献として本明細書に含める。本発明によれば、1個以上のセンサー22を使い捨てチューブ144に沿って固定し、そしてその壁内に好適に埋め込む。センサー22をチューブ144の長手方向軸に平行な直線に略沿って埋め込む。チューブ144の外側ではこの直線をマークしてセンサー22をどこに埋め込んだかを確認できることが好ましい。このマークは、センサー22がシース150に隣接し、従って、内視鏡147内の妨害起因構造体から遠ざけられるように、ユーザーがチューブ144を溝142に配置する一助となる。同様にして内視鏡147に対するセンサーの位置を正確に決定することができる。
上記実施形態ではシースが内視鏡の挿入チューブとは別個になっているが、シースを挿入チューブの一体部分から構成することができることが分かる。そのような実施形態では、分離できるシースはなく、むしろ2つの部分を備えた1本の内視鏡挿入チューブがある。一部分は挿入チューブと操作導管の周縁を有し、妨害起因構造体が実質的に無く、そして他の部分は妨害起因構造体を有する挿入チューブのコアである。本発明の好ましい実施形態によれば、センサーを妨害起因構造体が無い部分に埋め込む。
ここで本発明の好ましい実施形態による長さ方向の仕切りと幅方向の仕切りを組み合わせた内視鏡挿入チューブ160を示す図7を参照する。図7に示したように、挿入チューブ160は、軸方向金属コア162と、挿入チューブ160の様々な装具を入れる部分164を有している。部分164の装具は偏向装置の部品あるいは目視映像装置のような他の装置であり、妨害起因構造体を含む。妨害起因構造体を含まない他の部分168はその内部に1個以上のセンサー22を埋め込んである。軸方向コア162は細い方が好ましく、挿入チューブ160内の装具を挿入チューブ160の基端部につなぐワイヤーを有する。同様にセンサー22を内視鏡の外側の位置決定装置につなぐワイヤー170が軸方向コア162に内を走っている。
本発明は磁界位置決定装置と関連させて説明したが、音響位置決定装置のような他の位置決定装置に対しても本発明を使用することができることも分かる。音響位置決定装置を使用する場合、挿入チューブ内の硬い材料が音波を反射し、従って、操作決定位置を妨害する。従って、本発明によれば、通常トランスジューサーであるセンサーを挿入チューブ内で硬い材料から離間する。磁界センサーを導電性の強磁性材料から離間する上記方法と同様の方法でその離間を行なう。
本発明は内視鏡に関連して説明したが、位置決定が望まれる他の医療器具でも本発明を使用することもできることも分かる。特に、本発明はカテーテルや供給チューブのような侵入器具を用いて使用することができる。
上記好ましい実施形態はあくまでも例示であり、本発明の全範囲は請求の範囲によってのみ限定されることが理解されよう。
〔実施の態様〕
1.位置決定可能な内視鏡取り付け具であって、
前記内視鏡の位置を決定するために内視鏡の挿入チューブ部分に連結可能な取り付け具と、
1個以上のセンサーの位置を決定するために使用され、前記取り付け具に対して固定配置された1個以上のセンサーとを具備する取り付け具。
2.前記取り付け具を前記内視鏡に固定取り付けする場合、前記1個以上のセンサーが、そのセンサー位置の決定を妨害する内視鏡の要素から離間される実施態様1に記載の取り付け具。
3.前記1個以上のセンサーが前記取り付け具内に埋め込まれる実施態様1に記載の取り付け具。
4.前記取り付け具が、前記1個以上のセンサーの位置の決定を実質的に妨害する要素を含まない実施態様1に記載の取り付け具。
5.前記1個以上のセンサーの位置決定が、磁界を送り、そして受けることによって行なわれる実施態様1に記載の取り付け具。
6.前記1個以上のセンサーの位置を示すマーキングを、前記取り付け具の外側に有する実施態様1から実施態様5のいずれかに記載の取り付け具。
7.前記取り付け具がチューブからなる実施態様1から実施態様5のいずれかに記載の取り付け具。
8.実施態様1−5のいずれかに記載の少なくとも1個の位置決定可能な取り付け具と、
前記内視鏡および前記1個以上の取り付け具を覆う薄いシースとを具備する内視鏡位置決めおよび感知キット。
9.前記取り付け具が内腔と周縁を有するシースを具備する実施態様1から実施態様5のいずれかに記載の取り付け具。
10.前記センサーが、位置の決定を妨害するシースの材料から、前記材料の妨害効果を実質的に回避するのに十分な距離だけ離すように配置される実施態様9に記載の取り付け具。
11.内腔がシース内で軸方向に中心に配置され、前記1個以上のセンサーが前記シースの周縁に隣接して配置される実施態様9に記載の取り付け具。
12.前記シースが内腔を越えて延在する先端部を有し、前記1個以上のセンサーの少なくとも1個が前記先端部に埋め込まれる実施態様9に記載の取り付け具。
13.位置決定可能な内視鏡であって、
周縁を有する断面を有する細長い本体と、先端とを具備する挿入チューブと、
前記本体の固定場所に配置された1個以上の位置センサーとを具備し、
前記先端から離れ前記1個以上のセンサーに隣接した前記細長い本体の断面の複数部分が、前記1個以上のセンサーの位置の決定を実質的に妨害する材料を含まない位置決定可能な内視鏡。
14.前記1個以上のセンサーの位置の決定を妨害する前記挿入チューブの要素が最小の効果を有する前記細長い本体の断面の複数の場所に、前記1個以上のセンサーが配置される実施態様13に記載の内視鏡。
15.前記1個以上のセンサーが前記挿入チューブ内に埋め込まれる実施態様13に記載の内視鏡。
16.前記1個以上のセンサーの位置の決定が磁界を送り、そして受けることによって行なわれる実施態様13に記載の内視鏡。
17.前記1個以上のセンサーが、導電性の強磁性材料から実質的に最も遠い前記挿入チューブ内の場所に配置される実施態様16に記載の内視鏡。
18.前記1個以上のセンサーの位置の決定を妨害する材料が前記細長い本体の「D」字形断面に制約され、前記1個以上のセンサーが位置の決定を妨害する材料から、前記材料の妨害効果を実質的に回避するのに十分な距離だけ離間されている実施態様13から実施態様17のいずれかに記載の内視鏡。
19.前記1個以上のセンサーの位置の決定を妨害する材料が、前記細長い本体の丸く、軸方向に中心配置の断面に制約され、前記1個以上のセンサーが前記挿入チューブの周縁に隣接して配置される実施態様13から実施態様17のいずれかに記載の内視鏡。
20.外側に取り付けた位置感知装置を有する医療器具を体内の所定の位置までガイドする方法であって、
前記位置感知装置の場所を決定する工程と、
前記決定された場所に応じて前記医療器具を前進させる工程と、
前記医療器具を所定の場所に配置した後、前記位置感知装置を前記医療器具から外すと同時に、前記医療器具を所定の場所に留置させる工程を有する方法。
21.前記位置センサーの取り外しが、前記位置センサーを包囲するシースを前記医療器具から剥離する工程を有する実施態様20に記載の方法。
22.位置決定可能な侵入医療器具であって、
本体と、
取り外し可能なシースとを具備し、
前記器具が経皮的に体内に配置されている間に前記シースが取り外し可能である器具。
23.前記本体がペースメーカー電極を具備する実施態様22に記載の器具。
24.前記シースが偏向機構を構える実施態様22あるいは実施態様23のいずれかに記載の器具。
Claims (12)
- 磁界を妨害する妨害要素を有する内視鏡のための位置決め装置において、内視鏡の適所に連結可能な取り付け具と、
前記内視鏡の妨害要素から1〜3mm離間して前記取り付け具内に設けられており、磁界を発するか、または磁界を受けるための少なくとも1個のセンサーと、
前記取り付け具の外面に設けられており、前記少なくとも1個のセンサーの位置を示す、複数のマーキングと、
前記取り付け具を覆うシースと、
を具備する、装置。 - 請求項1に記載の装置において、
内視鏡、をさらに備えている、装置。 - 請求項1または2に記載の装置において、
前記取り付け具は、チューブを具備する、装置。 - 磁界を妨害する妨害要素を有する内視鏡のための位置決め装置において、
前記内視鏡の挿入チューブの部分を挿入可能な内腔、および1つ以上の操作導管が設けられた周縁部、を備えたシースと、
少なくとも1つのセンサーであって、前記内視鏡の妨害要素から離間して前記シースの周縁部内に設けられており、かつ、磁界を発するか、または磁界を受ける、センサーと、
を具備する、装置。 - 請求項4に記載の装置において、
前記シースは、磁界を妨害する妨害要素を含んでおり、
前記1個以上のセンサーは、前記シースの妨害要素から離間している、
装置。 - 請求項4または5に記載の装置において、
前記内腔は、軸が前記シース内において中心に合わされている、装置。 - 請求項4または5に記載の装置において、
前記内腔が、D字形断面を有する、装置。 - 請求項4ないし7のいずれか1項に記載の装置において、
前記1つ以上の操作導管のうちの少なくとも1つは、磁界を妨害する妨害要素を通過させるために使用され、
前記センサーは、前記内視鏡の妨害要素、および前記操作導管を通過する妨害要素から1〜3mm離間している、
装置。 - 請求項4ないし8のいずれか1項に記載の装置において、
前記妨害要素は、導電性で強磁性の材料からなる、装置。 - 請求項4ないし9のいずれか1項に記載の装置において、
前記シースは、ポリエチレンまたはポリ塩化ビニルからなる、装置。 - 位置決定可能な内視鏡アセンブリーにおいて、
磁界を妨害する妨害要素を含み、挿入チューブを備える、内視鏡と、
請求項4ないし10のいずれか1項に記載の装置と、
を具備する、アセンブリー。 - 請求項11に記載のアセンブリーにおいて、
前記シースは、前記挿入チューブを越えて延びる先端部を有し、
前記センサーの少なくとも1つが、前記先端部に埋め込まれている、
アセンブリー。
Applications Claiming Priority (11)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US1174396P | 1996-02-15 | 1996-02-15 | |
| IL11714896A IL117148A (en) | 1996-02-15 | 1996-02-15 | Catheter with lumen |
| US1224296P | 1996-02-26 | 1996-02-26 | |
| IL11926296A IL119262A0 (en) | 1996-02-15 | 1996-09-17 | Locatable biopsy needle |
| WO117148 | 1997-01-08 | ||
| WO60/012,242 | 1997-01-08 | ||
| WO60/011,743 | 1997-01-08 | ||
| PCT/IL1997/000010 WO1997024981A2 (en) | 1996-01-08 | 1997-01-08 | Cardiac electro-mechanics |
| WO97/00010 | 1997-01-08 | ||
| WO119262 | 1997-01-08 | ||
| PCT/IL1997/000061 WO1997029679A2 (en) | 1996-02-15 | 1997-02-14 | Precise position determination of endoscopes |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2002514947A JP2002514947A (ja) | 2002-05-21 |
| JP2002514947A5 JP2002514947A5 (ja) | 2004-11-18 |
| JP4130226B2 true JP4130226B2 (ja) | 2008-08-06 |
Family
ID=27517640
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP52916597A Expired - Lifetime JP4130226B2 (ja) | 1996-02-15 | 1997-02-14 | 内視鏡の正確な位置決定 |
Country Status (9)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6203493B1 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP0883375B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP4130226B2 (ja) |
| AU (1) | AU711668B2 (ja) |
| CA (1) | CA2246341C (ja) |
| DE (1) | DE69733249T8 (ja) |
| ES (1) | ES2241037T3 (ja) |
| IL (1) | IL125781A (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO1997029679A2 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (254)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9289618B1 (en) | 1996-01-08 | 2016-03-22 | Impulse Dynamics Nv | Electrical muscle controller |
| IL121450A0 (en) * | 1997-08-01 | 1998-02-08 | Smollett Neil | Ophthalmic surgical equipment |
| US6147480A (en) * | 1997-10-23 | 2000-11-14 | Biosense, Inc. | Detection of metal disturbance |
| DE19800471A1 (de) * | 1998-01-09 | 1999-07-15 | Philips Patentverwaltung | MR-Verfahren mit im Untersuchungsbereich befindlichen Mikrospulen |
| US6373240B1 (en) | 1998-10-15 | 2002-04-16 | Biosense, Inc. | Metal immune system for tracking spatial coordinates of an object in the presence of a perturbed energy field |
| CA2356322A1 (en) | 1998-12-23 | 2000-06-29 | Peter D. Jakab | Magnetic resonance scanner with electromagnetic position and orientation tracking device |
| WO2006073671A1 (en) | 2004-12-09 | 2006-07-13 | Impulse Dynamics Nv | Protein activity modification |
| US9101765B2 (en) | 1999-03-05 | 2015-08-11 | Metacure Limited | Non-immediate effects of therapy |
| JP4612196B2 (ja) * | 1999-03-17 | 2011-01-12 | アーオー テクノロジー アクチエンゲゼルシャフト | 靭帯移植片配置のため造影し、計画する装置 |
| WO2001054567A1 (en) * | 2000-01-27 | 2001-08-02 | Vision Sciences, Inc. | Endoscopic assembly with non-visual locating device |
| US6984203B2 (en) * | 2000-04-03 | 2006-01-10 | Neoguide Systems, Inc. | Endoscope with adjacently positioned guiding apparatus |
| US6468203B2 (en) * | 2000-04-03 | 2002-10-22 | Neoguide Systems, Inc. | Steerable endoscope and improved method of insertion |
| US8517923B2 (en) | 2000-04-03 | 2013-08-27 | Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc. | Apparatus and methods for facilitating treatment of tissue via improved delivery of energy based and non-energy based modalities |
| US8888688B2 (en) | 2000-04-03 | 2014-11-18 | Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc. | Connector device for a controllable instrument |
| US6610007B2 (en) * | 2000-04-03 | 2003-08-26 | Neoguide Systems, Inc. | Steerable segmented endoscope and method of insertion |
| US6858005B2 (en) | 2000-04-03 | 2005-02-22 | Neo Guide Systems, Inc. | Tendon-driven endoscope and methods of insertion |
| US20050171508A1 (en) * | 2000-04-21 | 2005-08-04 | Pinhas Gilboa | System and method for intravascular catheter navigation |
| US6484118B1 (en) | 2000-07-20 | 2002-11-19 | Biosense, Inc. | Electromagnetic position single axis system |
| EP1311226A4 (en) | 2000-08-23 | 2008-12-17 | Micronix Pty Ltd | CATHETERING DEVICE AND USER METHOD |
| US6846286B2 (en) * | 2001-05-22 | 2005-01-25 | Pentax Corporation | Endoscope system |
| US6992477B2 (en) * | 2001-06-15 | 2006-01-31 | Biosense, Inc. | Medical device with position sensor having core with high permeability material for determining location coordinates of a portion of the medical device |
| US7286868B2 (en) * | 2001-06-15 | 2007-10-23 | Biosense Inc. | Medical device with position sensor having accuracy at high temperatures |
| US20030040670A1 (en) * | 2001-06-15 | 2003-02-27 | Assaf Govari | Method for measuring temperature and of adjusting for temperature sensitivity with a medical device having a position sensor |
| US6745065B2 (en) * | 2001-08-02 | 2004-06-01 | Olympus Corporation | Endoscope apparatus |
| DE10151398B4 (de) * | 2001-10-18 | 2005-03-17 | Schaerer Mayfield USA, Inc., Cincinnati | Vorrichtung zur Adaption chirurgischer Instrumente als Zeigereinrichtung |
| US7081097B2 (en) * | 2002-01-04 | 2006-07-25 | Vision Sciences, Inc. | Endoscope sheath assemblies having an attached biopsy sampling device |
| AU2002359847A1 (en) | 2002-01-09 | 2003-07-30 | Neoguide Systems, Inc | Apparatus and method for endoscopic colectomy |
| US6790206B2 (en) * | 2002-01-31 | 2004-09-14 | Scimed Life Systems, Inc. | Compensation for power variation along patient cables |
| GB0204549D0 (en) * | 2002-02-27 | 2002-04-10 | Depuy Int Ltd | A surgical instrument system |
| JP4551051B2 (ja) * | 2002-04-17 | 2010-09-22 | オリンパス株式会社 | 超音波診断装置 |
| US7998062B2 (en) | 2004-03-29 | 2011-08-16 | Superdimension, Ltd. | Endoscope structures and techniques for navigating to a target in branched structure |
| AU2003269450A1 (en) * | 2002-10-03 | 2004-04-23 | Etview Ltd. | Tube for inspecting internal organs of a body |
| US8862204B2 (en) | 2002-11-18 | 2014-10-14 | Mediguide Ltd. | Reducing mechanical stress on conductors and connection points in a position determinable interventional medical device |
| US7881769B2 (en) * | 2002-11-18 | 2011-02-01 | Mediguide Ltd. | Method and system for mounting an MPS sensor on a catheter |
| US7599730B2 (en) | 2002-11-19 | 2009-10-06 | Medtronic Navigation, Inc. | Navigation system for cardiac therapies |
| US7697972B2 (en) | 2002-11-19 | 2010-04-13 | Medtronic Navigation, Inc. | Navigation system for cardiac therapies |
| US7945309B2 (en) | 2002-11-22 | 2011-05-17 | Biosense, Inc. | Dynamic metal immunity |
| US7201749B2 (en) * | 2003-02-19 | 2007-04-10 | Biosense, Inc. | Externally-applied high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) for pulmonary vein isolation |
| US20040176683A1 (en) * | 2003-03-07 | 2004-09-09 | Katherine Whitin | Method and apparatus for tracking insertion depth |
| US8882657B2 (en) | 2003-03-07 | 2014-11-11 | Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc. | Instrument having radio frequency identification systems and methods for use |
| US20040199052A1 (en) | 2003-04-01 | 2004-10-07 | Scimed Life Systems, Inc. | Endoscopic imaging system |
| US20050245789A1 (en) | 2003-04-01 | 2005-11-03 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Fluid manifold for endoscope system |
| US7578786B2 (en) | 2003-04-01 | 2009-08-25 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Video endoscope |
| US7591783B2 (en) | 2003-04-01 | 2009-09-22 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Articulation joint for video endoscope |
| US8118732B2 (en) | 2003-04-01 | 2012-02-21 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Force feedback control system for video endoscope |
| US20040204645A1 (en) * | 2003-04-10 | 2004-10-14 | Vahid Saadat | Scope position and orientation feedback device |
| US20040218792A1 (en) * | 2003-04-29 | 2004-11-04 | Eastman Kodak Company | Probe position measurement to facilitate image registration and image manipulation in a medical application |
| US6939293B2 (en) | 2003-08-07 | 2005-09-06 | Chris N. Conteas | Gastrointestinal lavage system |
| US7021164B2 (en) * | 2003-08-12 | 2006-04-04 | The Goodyear Tire & Rubber Company | Tire sensor insertion tool and method |
| JP2007519425A (ja) | 2003-09-15 | 2007-07-19 | スーパー ディメンション リミテッド | 気管支鏡用アクセサリー・システム |
| EP2316328B1 (en) | 2003-09-15 | 2012-05-09 | Super Dimension Ltd. | Wrap-around holding device for use with bronchoscopes |
| US20050165275A1 (en) * | 2004-01-22 | 2005-07-28 | Kenneth Von Felten | Inspection device insertion tube |
| US8764725B2 (en) | 2004-02-09 | 2014-07-01 | Covidien Lp | Directional anchoring mechanism, method and applications thereof |
| EP1715788B1 (en) | 2004-02-17 | 2011-09-07 | Philips Electronics LTD | Method and apparatus for registration, verification, and referencing of internal organs |
| JP3931177B2 (ja) * | 2004-03-08 | 2007-06-13 | オリンパス株式会社 | 内視鏡装置と内視鏡の挿入部形状検出装置 |
| JP3981364B2 (ja) * | 2004-03-19 | 2007-09-26 | オリンパス株式会社 | ダブルバルーン式内視鏡システム |
| US7922654B2 (en) | 2004-08-09 | 2011-04-12 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Fiber optic imaging catheter |
| US11819192B2 (en) | 2004-03-23 | 2023-11-21 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | In-vivo visualization system |
| WO2005094665A2 (en) | 2004-03-23 | 2005-10-13 | Boston Scientific Limited | In-vivo visualization system |
| JP4505345B2 (ja) * | 2004-03-31 | 2010-07-21 | オリンパス株式会社 | 内視鏡挿入補助用プローブ及びこれを適用する内視鏡装置 |
| US20060009679A1 (en) * | 2004-07-08 | 2006-01-12 | Pentax Corporation | Electronic endoscope system capable of detecting inserted length |
| US20060036137A1 (en) * | 2004-08-13 | 2006-02-16 | John Lewicke | Patient monitoring apparatus |
| US9033870B2 (en) * | 2004-09-24 | 2015-05-19 | Vivid Medical, Inc. | Pluggable vision module and portable display for endoscopy |
| US8858425B2 (en) * | 2004-09-24 | 2014-10-14 | Vivid Medical, Inc. | Disposable endoscope and portable display |
| US8878924B2 (en) * | 2004-09-24 | 2014-11-04 | Vivid Medical, Inc. | Disposable microscope and portable display |
| US8827899B2 (en) * | 2004-09-24 | 2014-09-09 | Vivid Medical, Inc. | Disposable endoscopic access device and portable display |
| US7241263B2 (en) | 2004-09-30 | 2007-07-10 | Scimed Life Systems, Inc. | Selectively rotatable shaft coupler |
| US8353860B2 (en) | 2004-09-30 | 2013-01-15 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Device for obstruction removal with specific tip structure |
| EP1799094A2 (en) | 2004-09-30 | 2007-06-27 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Multi-functional endoscopic system for use in electrosurgical applications |
| US8083671B2 (en) | 2004-09-30 | 2011-12-27 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Fluid delivery system for use with an endoscope |
| US7479106B2 (en) | 2004-09-30 | 2009-01-20 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Automated control of irrigation and aspiration in a single-use endoscope |
| US8199187B2 (en) | 2004-09-30 | 2012-06-12 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Adapter for use with digital imaging medical device |
| EP1827243B1 (en) * | 2004-11-05 | 2010-01-20 | THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, as represented by THE SECRETARY, DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES | Access system |
| US7805269B2 (en) * | 2004-11-12 | 2010-09-28 | Philips Electronics Ltd | Device and method for ensuring the accuracy of a tracking device in a volume |
| US7751868B2 (en) * | 2004-11-12 | 2010-07-06 | Philips Electronics Ltd | Integrated skin-mounted multifunction device for use in image-guided surgery |
| US8182422B2 (en) | 2005-12-13 | 2012-05-22 | Avantis Medical Systems, Inc. | Endoscope having detachable imaging device and method of using |
| US8235887B2 (en) | 2006-01-23 | 2012-08-07 | Avantis Medical Systems, Inc. | Endoscope assembly with retroscope |
| US7976518B2 (en) | 2005-01-13 | 2011-07-12 | Corpak Medsystems, Inc. | Tubing assembly and signal generator placement control device and method for use with catheter guidance systems |
| US8611983B2 (en) * | 2005-01-18 | 2013-12-17 | Philips Electronics Ltd | Method and apparatus for guiding an instrument to a target in the lung |
| US7840254B2 (en) * | 2005-01-18 | 2010-11-23 | Philips Electronics Ltd | Electromagnetically tracked K-wire device |
| US9821158B2 (en) | 2005-02-17 | 2017-11-21 | Metacure Limited | Non-immediate effects of therapy |
| US20060235458A1 (en) * | 2005-04-15 | 2006-10-19 | Amir Belson | Instruments having an external working channel |
| US7846107B2 (en) | 2005-05-13 | 2010-12-07 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Endoscopic apparatus with integrated multiple biopsy device |
| US8097003B2 (en) * | 2005-05-13 | 2012-01-17 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Endoscopic apparatus with integrated variceal ligation device |
| WO2008045016A2 (en) * | 2005-06-21 | 2008-04-17 | Traxtal Inc. | Device and method for a trackable ultrasound |
| US8632461B2 (en) * | 2005-06-21 | 2014-01-21 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | System, method and apparatus for navigated therapy and diagnosis |
| EP1924197B1 (en) * | 2005-08-24 | 2017-10-11 | Philips Electronics LTD | System for navigated flexible endoscopy |
| US8052597B2 (en) | 2005-08-30 | 2011-11-08 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Method for forming an endoscope articulation joint |
| WO2007033379A2 (en) * | 2005-09-14 | 2007-03-22 | Neoguide Systems, Inc. | Methods and apparatus for performing transluminal and other procedures |
| DE102005050344A1 (de) * | 2005-10-20 | 2007-05-03 | Siemens Ag | Kryokatheter zur Einführung in ein Körpergefäß sowie medizinische Untersuchungs- und Behandlungsvorrichtung |
| JP2007130174A (ja) * | 2005-11-09 | 2007-05-31 | Pentax Corp | 内視鏡挿入部形状把握システム |
| JP4827495B2 (ja) * | 2005-11-09 | 2011-11-30 | Hoya株式会社 | 内視鏡挿入部形状把握システム |
| EP3788944B1 (en) | 2005-11-22 | 2024-02-28 | Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc. | System for determining the shape of a bendable instrument |
| WO2007062066A2 (en) * | 2005-11-23 | 2007-05-31 | Neoguide Systems, Inc. | Non-metallic, multi-strand control cable for steerable instruments |
| JP4714570B2 (ja) * | 2005-11-24 | 2011-06-29 | Hoya株式会社 | 内視鏡形状検出プローブ |
| US8190238B2 (en) * | 2005-12-09 | 2012-05-29 | Hansen Medical, Inc. | Robotic catheter system and methods |
| US8862200B2 (en) * | 2005-12-30 | 2014-10-14 | DePuy Synthes Products, LLC | Method for determining a position of a magnetic source |
| US7525309B2 (en) | 2005-12-30 | 2009-04-28 | Depuy Products, Inc. | Magnetic sensor array |
| US20070161888A1 (en) * | 2005-12-30 | 2007-07-12 | Sherman Jason T | System and method for registering a bone of a patient with a computer assisted orthopaedic surgery system |
| US20070167741A1 (en) * | 2005-12-30 | 2007-07-19 | Sherman Jason T | Apparatus and method for registering a bone of a patient with a computer assisted orthopaedic surgery system |
| US7967759B2 (en) | 2006-01-19 | 2011-06-28 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Endoscopic system with integrated patient respiratory status indicator |
| US8016749B2 (en) | 2006-03-21 | 2011-09-13 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Vision catheter having electromechanical navigation |
| US8888684B2 (en) | 2006-03-27 | 2014-11-18 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Medical devices with local drug delivery capabilities |
| US7471202B2 (en) | 2006-03-29 | 2008-12-30 | General Electric Co. | Conformal coil array for a medical tracking system |
| US7532997B2 (en) | 2006-04-17 | 2009-05-12 | General Electric Company | Electromagnetic tracking using a discretized numerical field model |
| US7955255B2 (en) | 2006-04-20 | 2011-06-07 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Imaging assembly with transparent distal cap |
| US8202265B2 (en) | 2006-04-20 | 2012-06-19 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Multiple lumen assembly for use in endoscopes or other medical devices |
| US8568299B2 (en) | 2006-05-19 | 2013-10-29 | Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc. | Methods and apparatus for displaying three-dimensional orientation of a steerable distal tip of an endoscope |
| JP4153963B2 (ja) * | 2006-06-12 | 2008-09-24 | オリンパスメディカルシステムズ株式会社 | 内視鏡挿入形状検出装置 |
| US8197494B2 (en) * | 2006-09-08 | 2012-06-12 | Corpak Medsystems, Inc. | Medical device position guidance system with wireless connectivity between a noninvasive device and an invasive device |
| WO2008125910A2 (en) | 2006-11-10 | 2008-10-23 | Superdimension, Ltd. | Adaptive navigation technique for navigating a catheter through a body channel or cavity |
| US8068648B2 (en) * | 2006-12-21 | 2011-11-29 | Depuy Products, Inc. | Method and system for registering a bone of a patient with a computer assisted orthopaedic surgery system |
| US20080167639A1 (en) * | 2007-01-08 | 2008-07-10 | Superdimension Ltd. | Methods for localized intra-body treatment of tissue |
| IL188262A (en) | 2007-01-10 | 2011-10-31 | Mediguide Ltd | System and method for superimposing a representation of the tip of a catheter on an image acquired by a moving imager |
| US8146874B2 (en) | 2007-02-02 | 2012-04-03 | Hansen Medical, Inc. | Mounting support assembly for suspending a medical instrument driver above an operating table |
| US8064666B2 (en) | 2007-04-10 | 2011-11-22 | Avantis Medical Systems, Inc. | Method and device for examining or imaging an interior surface of a cavity |
| DE102007019333A1 (de) | 2007-04-24 | 2008-11-06 | Siemens Ag | Medizinisches Instrument zur Durchführung eines medizinischen Eingriffs |
| EP2192855B1 (en) | 2007-07-09 | 2020-03-25 | Covidien LP | Patent breathing modeling |
| US8166967B2 (en) * | 2007-08-15 | 2012-05-01 | Chunyuan Qiu | Systems and methods for intubation |
| US8905920B2 (en) | 2007-09-27 | 2014-12-09 | Covidien Lp | Bronchoscope adapter and method |
| US8357152B2 (en) | 2007-10-08 | 2013-01-22 | Biosense Webster (Israel), Ltd. | Catheter with pressure sensing |
| US8535308B2 (en) * | 2007-10-08 | 2013-09-17 | Biosense Webster (Israel), Ltd. | High-sensitivity pressure-sensing probe |
| US9220398B2 (en) | 2007-10-11 | 2015-12-29 | Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc. | System for managing Bowden cables in articulating instruments |
| US8391952B2 (en) | 2007-10-11 | 2013-03-05 | General Electric Company | Coil arrangement for an electromagnetic tracking system |
| JP5244815B2 (ja) * | 2007-10-31 | 2013-07-24 | オリンパス株式会社 | 薬液投与システム |
| WO2009100368A1 (en) | 2008-02-06 | 2009-08-13 | Neoguide Systems Inc. | A segmented instrument having braking capabilities |
| US8182418B2 (en) | 2008-02-25 | 2012-05-22 | Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc. | Systems and methods for articulating an elongate body |
| US9575140B2 (en) | 2008-04-03 | 2017-02-21 | Covidien Lp | Magnetic interference detection system and method |
| US8218846B2 (en) | 2008-05-15 | 2012-07-10 | Superdimension, Ltd. | Automatic pathway and waypoint generation and navigation method |
| WO2009147671A1 (en) | 2008-06-03 | 2009-12-10 | Superdimension Ltd. | Feature-based registration method |
| US8218847B2 (en) | 2008-06-06 | 2012-07-10 | Superdimension, Ltd. | Hybrid registration method |
| US8437832B2 (en) | 2008-06-06 | 2013-05-07 | Biosense Webster, Inc. | Catheter with bendable tip |
| US8932207B2 (en) | 2008-07-10 | 2015-01-13 | Covidien Lp | Integrated multi-functional endoscopic tool |
| US9101734B2 (en) * | 2008-09-09 | 2015-08-11 | Biosense Webster, Inc. | Force-sensing catheter with bonded center strut |
| US8442620B2 (en) * | 2008-10-01 | 2013-05-14 | Pacesetter, Inc. | Implantable lead/electrode delivery measurement and feedback system |
| EP2351509A4 (en) * | 2008-10-28 | 2018-01-17 | Olympus Corporation | Medical device |
| US8175681B2 (en) | 2008-12-16 | 2012-05-08 | Medtronic Navigation Inc. | Combination of electromagnetic and electropotential localization |
| US9326700B2 (en) | 2008-12-23 | 2016-05-03 | Biosense Webster (Israel) Ltd. | Catheter display showing tip angle and pressure |
| US8600472B2 (en) * | 2008-12-30 | 2013-12-03 | Biosense Webster (Israel), Ltd. | Dual-purpose lasso catheter with irrigation using circumferentially arranged ring bump electrodes |
| US8475450B2 (en) * | 2008-12-30 | 2013-07-02 | Biosense Webster, Inc. | Dual-purpose lasso catheter with irrigation |
| US8632468B2 (en) * | 2009-02-25 | 2014-01-21 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Method, system and devices for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) procedures |
| US8611984B2 (en) | 2009-04-08 | 2013-12-17 | Covidien Lp | Locatable catheter |
| EP2429438A1 (en) * | 2009-04-24 | 2012-03-21 | Medtronic, Inc. | Electromagnetic navigation of medical instruments for cardiothoracic surgery |
| US9254123B2 (en) | 2009-04-29 | 2016-02-09 | Hansen Medical, Inc. | Flexible and steerable elongate instruments with shape control and support elements |
| US8494614B2 (en) | 2009-08-31 | 2013-07-23 | Regents Of The University Of Minnesota | Combination localization system |
| US8494613B2 (en) | 2009-08-31 | 2013-07-23 | Medtronic, Inc. | Combination localization system |
| US10688278B2 (en) | 2009-11-30 | 2020-06-23 | Biosense Webster (Israel), Ltd. | Catheter with pressure measuring tip |
| US8920415B2 (en) * | 2009-12-16 | 2014-12-30 | Biosense Webster (Israel) Ltd. | Catheter with helical electrode |
| US8521462B2 (en) | 2009-12-23 | 2013-08-27 | Biosense Webster (Israel), Ltd. | Calibration system for a pressure-sensitive catheter |
| US8529476B2 (en) | 2009-12-28 | 2013-09-10 | Biosense Webster (Israel), Ltd. | Catheter with strain gauge sensor |
| US8608735B2 (en) * | 2009-12-30 | 2013-12-17 | Biosense Webster (Israel) Ltd. | Catheter with arcuate end section |
| US8374670B2 (en) * | 2010-01-22 | 2013-02-12 | Biosense Webster, Inc. | Catheter having a force sensing distal tip |
| US8428328B2 (en) | 2010-02-01 | 2013-04-23 | Superdimension, Ltd | Region-growing algorithm |
| WO2011092710A2 (en) | 2010-02-01 | 2011-08-04 | Metacure Limited | Gastrointestinal electrical therapy |
| US8894569B2 (en) | 2010-04-21 | 2014-11-25 | Chunyuan Qiu | Intubation systems and methods based on airway pattern identification |
| US9795753B2 (en) | 2012-03-07 | 2017-10-24 | Chunyuan Qiu | Intubation delivery systems and methods |
| US20110301414A1 (en) * | 2010-06-04 | 2011-12-08 | Robert Hotto | Intelligent endoscopy systems and methods |
| US8798952B2 (en) | 2010-06-10 | 2014-08-05 | Biosense Webster (Israel) Ltd. | Weight-based calibration system for a pressure sensitive catheter |
| WO2011159834A1 (en) | 2010-06-15 | 2011-12-22 | Superdimension, Ltd. | Locatable expandable working channel and method |
| US8672837B2 (en) | 2010-06-24 | 2014-03-18 | Hansen Medical, Inc. | Methods and devices for controlling a shapeable medical device |
| US8226580B2 (en) | 2010-06-30 | 2012-07-24 | Biosense Webster (Israel), Ltd. | Pressure sensing for a multi-arm catheter |
| US10390889B2 (en) | 2010-07-26 | 2019-08-27 | St Jude Medical International Holding S.Á R.L. | Removable navigation system and method for a medical device |
| US8380276B2 (en) | 2010-08-16 | 2013-02-19 | Biosense Webster, Inc. | Catheter with thin film pressure sensing distal tip |
| US8731859B2 (en) | 2010-10-07 | 2014-05-20 | Biosense Webster (Israel) Ltd. | Calibration system for a force-sensing catheter |
| US8979772B2 (en) | 2010-11-03 | 2015-03-17 | Biosense Webster (Israel), Ltd. | Zero-drift detection and correction in contact force measurements |
| DE102010061133A1 (de) * | 2010-12-09 | 2012-06-14 | G & H Medical Gmbh & Co. Kg | Schutzüberzug für ein Laparoskop |
| US20120191086A1 (en) | 2011-01-20 | 2012-07-26 | Hansen Medical, Inc. | System and method for endoluminal and translumenal therapy |
| US8333103B2 (en) * | 2011-03-30 | 2012-12-18 | Biosense Webster (Israel), Ltd. | Calibration of a force measuring system for large bend angles of a catheter |
| US8880147B2 (en) | 2011-05-02 | 2014-11-04 | St. Jude Medical, Atrial Fibrillation Division, Inc. | Sensor assembly tethered within catheter wall |
| JP6180405B2 (ja) * | 2011-05-03 | 2017-08-16 | エンドーシー コーポレイションEndosee Corporation | ヒステロスコピー及び子宮内膜生検用の方法及び装置 |
| US9220433B2 (en) | 2011-06-30 | 2015-12-29 | Biosense Webster (Israel), Ltd. | Catheter with variable arcuate distal section |
| DK2611356T3 (en) | 2011-07-11 | 2015-03-23 | Etview Ltd | ENDOBRONCIAL HOSE |
| US9138166B2 (en) | 2011-07-29 | 2015-09-22 | Hansen Medical, Inc. | Apparatus and methods for fiber integration and registration |
| US9662169B2 (en) | 2011-07-30 | 2017-05-30 | Biosense Webster (Israel) Ltd. | Catheter with flow balancing valve |
| US9028441B2 (en) | 2011-09-08 | 2015-05-12 | Corpak Medsystems, Inc. | Apparatus and method used with guidance system for feeding and suctioning |
| US20130303944A1 (en) | 2012-05-14 | 2013-11-14 | Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc. | Off-axis electromagnetic sensor |
| US9452276B2 (en) | 2011-10-14 | 2016-09-27 | Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc. | Catheter with removable vision probe |
| US9387048B2 (en) | 2011-10-14 | 2016-07-12 | Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc. | Catheter sensor systems |
| US10238837B2 (en) | 2011-10-14 | 2019-03-26 | Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc. | Catheters with control modes for interchangeable probes |
| WO2013065473A1 (ja) * | 2011-10-31 | 2013-05-10 | オリンパスメディカルシステムズ株式会社 | 医療機器 |
| US9687289B2 (en) | 2012-01-04 | 2017-06-27 | Biosense Webster (Israel) Ltd. | Contact assessment based on phase measurement |
| WO2013116140A1 (en) | 2012-02-03 | 2013-08-08 | Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc. | Steerable flexible needle with embedded shape sensing |
| US20130345514A1 (en) * | 2012-06-22 | 2013-12-26 | Empire Technology Development Llc | Proprioceptive endoscope and virtual dynamic tomography |
| US9622646B2 (en) | 2012-06-25 | 2017-04-18 | Coopersurgical, Inc. | Low-cost instrument for endoscopically guided operative procedures |
| US20140148673A1 (en) | 2012-11-28 | 2014-05-29 | Hansen Medical, Inc. | Method of anchoring pullwire directly articulatable region in catheter |
| US9717422B2 (en) * | 2012-12-12 | 2017-08-01 | Volcano Corporation | Sheath with optically interrogatable sensors |
| EP2754384B1 (en) | 2013-01-10 | 2018-07-11 | Ambu A/S | Endobronchial tube with integrated image sensor and cleaning nozzle arrangement |
| US9057600B2 (en) | 2013-03-13 | 2015-06-16 | Hansen Medical, Inc. | Reducing incremental measurement sensor error |
| US20140277334A1 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2014-09-18 | Hansen Medical, Inc. | Active drives for robotic catheter manipulators |
| US9326822B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2016-05-03 | Hansen Medical, Inc. | Active drives for robotic catheter manipulators |
| US9408669B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2016-08-09 | Hansen Medical, Inc. | Active drive mechanism with finite range of motion |
| US9014851B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2015-04-21 | Hansen Medical, Inc. | Systems and methods for tracking robotically controlled medical instruments |
| US9271663B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2016-03-01 | Hansen Medical, Inc. | Flexible instrument localization from both remote and elongation sensors |
| US20140276936A1 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-09-18 | Hansen Medical, Inc. | Active drive mechanism for simultaneous rotation and translation |
| US9629595B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2017-04-25 | Hansen Medical, Inc. | Systems and methods for localizing, tracking and/or controlling medical instruments |
| US11020016B2 (en) | 2013-05-30 | 2021-06-01 | Auris Health, Inc. | System and method for displaying anatomy and devices on a movable display |
| WO2015119573A1 (en) * | 2014-02-05 | 2015-08-13 | National University Of Singapore | Systems and methods for tracking and displaying endoscope shape and distal end orientation |
| JP6431678B2 (ja) * | 2014-03-20 | 2018-11-28 | オリンパス株式会社 | 挿入形状検出装置 |
| US10046140B2 (en) | 2014-04-21 | 2018-08-14 | Hansen Medical, Inc. | Devices, systems, and methods for controlling active drive systems |
| US10952593B2 (en) | 2014-06-10 | 2021-03-23 | Covidien Lp | Bronchoscope adapter |
| US10426555B2 (en) | 2015-06-03 | 2019-10-01 | Covidien Lp | Medical instrument with sensor for use in a system and method for electromagnetic navigation |
| KR101764327B1 (ko) | 2015-07-08 | 2017-08-02 | 울산과학기술원 | 삽관 튜브용 내비게이션 센서 및 그의 제조방법 |
| CN108778113B (zh) | 2015-09-18 | 2022-04-15 | 奥瑞斯健康公司 | 管状网络的导航 |
| US10143526B2 (en) | 2015-11-30 | 2018-12-04 | Auris Health, Inc. | Robot-assisted driving systems and methods |
| US10702305B2 (en) | 2016-03-23 | 2020-07-07 | Coopersurgical, Inc. | Operative cannulas and related methods |
| US10478254B2 (en) | 2016-05-16 | 2019-11-19 | Covidien Lp | System and method to access lung tissue |
| US10463439B2 (en) | 2016-08-26 | 2019-11-05 | Auris Health, Inc. | Steerable catheter with shaft load distributions |
| US11241559B2 (en) | 2016-08-29 | 2022-02-08 | Auris Health, Inc. | Active drive for guidewire manipulation |
| US10517505B2 (en) | 2016-10-28 | 2019-12-31 | Covidien Lp | Systems, methods, and computer-readable media for optimizing an electromagnetic navigation system |
| US10638952B2 (en) | 2016-10-28 | 2020-05-05 | Covidien Lp | Methods, systems, and computer-readable media for calibrating an electromagnetic navigation system |
| US10792106B2 (en) | 2016-10-28 | 2020-10-06 | Covidien Lp | System for calibrating an electromagnetic navigation system |
| US10722311B2 (en) | 2016-10-28 | 2020-07-28 | Covidien Lp | System and method for identifying a location and/or an orientation of an electromagnetic sensor based on a map |
| US10446931B2 (en) | 2016-10-28 | 2019-10-15 | Covidien Lp | Electromagnetic navigation antenna assembly and electromagnetic navigation system including the same |
| US10418705B2 (en) | 2016-10-28 | 2019-09-17 | Covidien Lp | Electromagnetic navigation antenna assembly and electromagnetic navigation system including the same |
| US10751126B2 (en) | 2016-10-28 | 2020-08-25 | Covidien Lp | System and method for generating a map for electromagnetic navigation |
| US10615500B2 (en) | 2016-10-28 | 2020-04-07 | Covidien Lp | System and method for designing electromagnetic navigation antenna assemblies |
| US10244926B2 (en) | 2016-12-28 | 2019-04-02 | Auris Health, Inc. | Detecting endolumenal buckling of flexible instruments |
| CN108990412B (zh) | 2017-03-31 | 2022-03-22 | 奥瑞斯健康公司 | 补偿生理噪声的用于腔网络导航的机器人系统 |
| US11571262B2 (en) * | 2017-04-18 | 2023-02-07 | Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc. | Graphical user interface for planning a procedure |
| US20180338673A1 (en) * | 2017-05-26 | 2018-11-29 | Covidien Lp | Surgical sheath and surgical apparatus including the same |
| US10022192B1 (en) | 2017-06-23 | 2018-07-17 | Auris Health, Inc. | Automatically-initialized robotic systems for navigation of luminal networks |
| EP3644885B1 (en) | 2017-06-28 | 2023-10-11 | Auris Health, Inc. | Electromagnetic field generator alignment |
| AU2018292281B2 (en) | 2017-06-28 | 2023-03-30 | Auris Health, Inc. | Electromagnetic distortion detection |
| US11185215B2 (en) * | 2017-08-07 | 2021-11-30 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Medical systems, devices, and related methods |
| US11058493B2 (en) | 2017-10-13 | 2021-07-13 | Auris Health, Inc. | Robotic system configured for navigation path tracing |
| US10555778B2 (en) | 2017-10-13 | 2020-02-11 | Auris Health, Inc. | Image-based branch detection and mapping for navigation |
| US11219489B2 (en) | 2017-10-31 | 2022-01-11 | Covidien Lp | Devices and systems for providing sensors in parallel with medical tools |
| US11510736B2 (en) | 2017-12-14 | 2022-11-29 | Auris Health, Inc. | System and method for estimating instrument location |
| EP3684283A4 (en) | 2017-12-18 | 2021-07-14 | Auris Health, Inc. | METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR MONITORING AND NAVIGATION OF INSTRUMENTS IN LUMINAL NETWORKS |
| US11547481B2 (en) * | 2018-01-11 | 2023-01-10 | Covidien Lp | Systems and methods for laparoscopic planning and navigation |
| JP7214747B2 (ja) * | 2018-03-28 | 2023-01-30 | オーリス ヘルス インコーポレイテッド | 位置センサの位置合わせのためのシステム及び方法 |
| JP7225259B2 (ja) | 2018-03-28 | 2023-02-20 | オーリス ヘルス インコーポレイテッド | 器具の推定位置を示すためのシステム及び方法 |
| CN108837283A (zh) * | 2018-04-12 | 2018-11-20 | 上海市东方医院 | 支气管干细胞精准定位缓释系统 |
| EP3773301B1 (en) | 2018-04-13 | 2024-03-06 | Karl Storz SE & Co. KG | Guidance system and associated computer program |
| CN114601559B (zh) | 2018-05-30 | 2024-05-14 | 奥瑞斯健康公司 | 用于基于定位传感器的分支预测的系统和介质 |
| KR102455671B1 (ko) | 2018-05-31 | 2022-10-20 | 아우리스 헬스, 인코포레이티드 | 이미지-기반 기도 분석 및 매핑 |
| EP3801189B1 (en) | 2018-05-31 | 2024-09-11 | Auris Health, Inc. | Path-based navigation of tubular networks |
| CN112236083B (zh) | 2018-05-31 | 2024-08-13 | 奥瑞斯健康公司 | 用于导航检测生理噪声的管腔网络的机器人系统和方法 |
| WO2019232296A1 (en) * | 2018-05-31 | 2019-12-05 | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology | Retrieval systems and related methods |
| US20190374129A1 (en) * | 2018-06-07 | 2019-12-12 | Acclarent, Inc. | Endoscope with integral navigation sensor |
| JP7536752B2 (ja) | 2018-09-28 | 2024-08-20 | オーリス ヘルス インコーポレイテッド | 内視鏡支援経皮的医療処置のためのシステム及び方法 |
| US20200205781A1 (en) * | 2018-12-27 | 2020-07-02 | Avent, Inc. | Miniscule Transducer for a Medical Article |
| WO2020236691A1 (en) * | 2019-05-20 | 2020-11-26 | Innoblative Designs, Inc. | Minimally invasive assembly for lung ablation |
| WO2020264084A1 (en) * | 2019-06-27 | 2020-12-30 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Detection of an endoscope to a fluid management system |
| CN114025822B (zh) * | 2019-06-28 | 2023-12-15 | 南微医学科技股份有限公司 | 鞘管装置及内窥镜组件 |
| US12089902B2 (en) | 2019-07-30 | 2024-09-17 | Coviden Lp | Cone beam and 3D fluoroscope lung navigation |
| WO2021038495A1 (en) | 2019-08-30 | 2021-03-04 | Auris Health, Inc. | Instrument image reliability systems and methods |
| JP2022546421A (ja) | 2019-08-30 | 2022-11-04 | オーリス ヘルス インコーポレイテッド | 位置センサの重みベースの位置合わせのためのシステム及び方法 |
| WO2021044297A1 (en) | 2019-09-03 | 2021-03-11 | Auris Health, Inc. | Electromagnetic distortion detection and compensation |
| EP4084721A4 (en) | 2019-12-31 | 2024-01-03 | Auris Health, Inc. | IDENTIFICATION OF AN ANATOMIC FEATURE AND AIMING |
| WO2021137108A1 (en) | 2019-12-31 | 2021-07-08 | Auris Health, Inc. | Alignment interfaces for percutaneous access |
| EP4084720A4 (en) | 2019-12-31 | 2024-01-17 | Auris Health, Inc. | ALIGNMENT TECHNIQUES FOR PERCUTANE ACCESS |
| US20220257093A1 (en) * | 2021-02-18 | 2022-08-18 | Acclarent, Inc. | Flexible sensor assembly for ent instrument |
| FR3145471A1 (fr) * | 2023-02-06 | 2024-08-09 | Axess Vision Technology | Endoscope médical avec gaine |
Family Cites Families (105)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3644825A (en) | 1969-12-31 | 1972-02-22 | Texas Instruments Inc | Magnetic detection system for detecting movement of an object utilizing signals derived from two orthogonal pickup coils |
| JPS506192A (ja) * | 1973-05-18 | 1975-01-22 | ||
| US3868565A (en) | 1973-07-30 | 1975-02-25 | Jack Kuipers | Object tracking and orientation determination means, system and process |
| US4017858A (en) | 1973-07-30 | 1977-04-12 | Polhemus Navigation Sciences, Inc. | Apparatus for generating a nutating electromagnetic field |
| US4054881A (en) | 1976-04-26 | 1977-10-18 | The Austin Company | Remote object position locater |
| US4710708A (en) | 1981-04-27 | 1987-12-01 | Develco | Method and apparatus employing received independent magnetic field components of a transmitted alternating magnetic field for determining location |
| JPS59672A (ja) | 1982-06-27 | 1984-01-05 | Tsutomu Jinno | 測距センサ |
| US4613866A (en) | 1983-05-13 | 1986-09-23 | Mcdonnell Douglas Corporation | Three dimensional digitizer with electromagnetic coupling |
| US4642786A (en) | 1984-05-25 | 1987-02-10 | Position Orientation Systems, Ltd. | Method and apparatus for position and orientation measurement using a magnetic field and retransmission |
| US4570354A (en) | 1984-08-03 | 1986-02-18 | Humphrey Inc. | Radius of curvature transducer |
| US4592356A (en) | 1984-09-28 | 1986-06-03 | Pedro Gutierrez | Localizing device |
| US4646722A (en) | 1984-12-10 | 1987-03-03 | Opielab, Inc. | Protective endoscope sheath and method of installing same |
| US4651436A (en) * | 1985-06-05 | 1987-03-24 | Gaal Peter S | Probe for measuring deviations from linearity |
| US4917095A (en) | 1985-11-18 | 1990-04-17 | Indianapolis Center For Advanced Research, Inc. | Ultrasound location and therapy method and apparatus for calculi in the body |
| EP0242522B1 (de) | 1986-02-27 | 1991-05-29 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Vorrichtung zur Messung des Ortes, der Lage und/oder der Orts- bzw. Lageänderung eines starren Körpers im Raum |
| US4945305A (en) | 1986-10-09 | 1990-07-31 | Ascension Technology Corporation | Device for quantitatively measuring the relative position and orientation of two bodies in the presence of metals utilizing direct current magnetic fields |
| US4849692A (en) | 1986-10-09 | 1989-07-18 | Ascension Technology Corporation | Device for quantitatively measuring the relative position and orientation of two bodies in the presence of metals utilizing direct current magnetic fields |
| US4931059A (en) | 1986-11-24 | 1990-06-05 | Markham Charles W | Needle/stylet combination |
| US5588432A (en) | 1988-03-21 | 1996-12-31 | Boston Scientific Corporation | Catheters for imaging, sensing electrical potentials, and ablating tissue |
| US4869238A (en) | 1988-04-22 | 1989-09-26 | Opielab, Inc. | Endoscope for use with a disposable sheath |
| US5078144A (en) | 1988-08-19 | 1992-01-07 | Olympus Optical Co. Ltd. | System for applying ultrasonic waves and a treatment instrument to a body part |
| DE68909355T2 (de) | 1988-09-02 | 1994-03-31 | British Gas Plc | Einrichtung zum Steuern der Lage eines selbstgetriebenen Bohrwerkzeuges. |
| US4905698A (en) | 1988-09-13 | 1990-03-06 | Pharmacia Deltec Inc. | Method and apparatus for catheter location determination |
| US4921482A (en) | 1989-01-09 | 1990-05-01 | Hammerslag Julius G | Steerable angioplasty device |
| US5301682A (en) | 1989-02-03 | 1994-04-12 | Elie Debbas | Method for locating a breast mass |
| GB2230191B (en) | 1989-04-15 | 1992-04-22 | Robert Graham Urie | Lesion location device |
| DE3914619A1 (de) | 1989-05-03 | 1990-11-08 | Kontron Elektronik | Vorrichtung zur transoesophagealen echokardiographie |
| CN1049287A (zh) | 1989-05-24 | 1991-02-20 | 住友电气工业株式会社 | 治疗导管 |
| US5234426A (en) | 1989-06-15 | 1993-08-10 | Research Corporation Technologies, Inc. | Helical-tipped lesion localization needle device and method of using the same |
| US5197482A (en) | 1989-06-15 | 1993-03-30 | Research Corporation Technologies, Inc. | Helical-tipped lesion localization needle device and method of using the same |
| EP0419729A1 (de) | 1989-09-29 | 1991-04-03 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Ortung eines Katheters mittels nichtionisierender Felder |
| US5158084A (en) | 1989-11-22 | 1992-10-27 | Board Of Regents, The University Of Texas System | Modified localization wire for excisional biopsy |
| US5195968A (en) | 1990-02-02 | 1993-03-23 | Ingemar Lundquist | Catheter steering mechanism |
| US5267960A (en) | 1990-03-19 | 1993-12-07 | Omnitron International Inc. | Tissue engaging catheter for a radioactive source wire |
| US5253647A (en) | 1990-04-13 | 1993-10-19 | Olympus Optical Co., Ltd. | Insertion position and orientation state pickup for endoscope |
| JP2750201B2 (ja) | 1990-04-13 | 1998-05-13 | オリンパス光学工業株式会社 | 内視鏡の挿入状態検出装置 |
| US5215680A (en) | 1990-07-10 | 1993-06-01 | Cavitation-Control Technology, Inc. | Method for the production of medical-grade lipid-coated microbubbles, paramagnetic labeling of such microbubbles and therapeutic uses of microbubbles |
| FR2665530B1 (fr) | 1990-08-03 | 1994-04-08 | Sextant Avionique | Radiateur et capteur magnetiques pour la determination de la position et de l'orientation d'un mobile. |
| GB9018660D0 (en) | 1990-08-24 | 1990-10-10 | Imperial College | Probe system |
| US5125924A (en) | 1990-09-24 | 1992-06-30 | Laser Engineering, Inc. | Heart-synchronized vacuum-assisted pulsed laser system and method |
| US5125926A (en) | 1990-09-24 | 1992-06-30 | Laser Engineering, Inc. | Heart-synchronized pulsed laser system |
| JPH04146716A (ja) * | 1990-10-08 | 1992-05-20 | Toshiba Corp | 内視鏡装置 |
| EP0553246B1 (en) | 1990-10-19 | 2000-09-13 | St. Louis University | Surgical probe locating system for head use |
| US5383923A (en) | 1990-10-20 | 1995-01-24 | Webster Laboratories, Inc. | Steerable catheter having puller wire with shape memory |
| US5389096A (en) | 1990-12-18 | 1995-02-14 | Advanced Cardiovascular Systems | System and method for percutaneous myocardial revascularization |
| US5380316A (en) | 1990-12-18 | 1995-01-10 | Advanced Cardiovascular Systems, Inc. | Method for intra-operative myocardial device revascularization |
| US5465717A (en) | 1991-02-15 | 1995-11-14 | Cardiac Pathways Corporation | Apparatus and Method for ventricular mapping and ablation |
| US5217484A (en) | 1991-06-07 | 1993-06-08 | Marks Michael P | Retractable-wire catheter device and method |
| US5195540A (en) | 1991-08-12 | 1993-03-23 | Samuel Shiber | Lesion marking process |
| US5211165A (en) | 1991-09-03 | 1993-05-18 | General Electric Company | Tracking system to follow the position and orientation of a device with radiofrequency field gradients |
| US5265610A (en) | 1991-09-03 | 1993-11-30 | General Electric Company | Multi-planar X-ray fluoroscopy system using radiofrequency fields |
| US5255680A (en) | 1991-09-03 | 1993-10-26 | General Electric Company | Automatic gantry positioning for imaging systems |
| US5251635A (en) | 1991-09-03 | 1993-10-12 | General Electric Company | Stereoscopic X-ray fluoroscopy system using radiofrequency fields |
| EP0531081A1 (en) | 1991-09-03 | 1993-03-10 | General Electric Company | Tracking system to follow the position and orientation of a device with radiofrequency fields |
| US5425367A (en) | 1991-09-04 | 1995-06-20 | Navion Biomedical Corporation | Catheter depth, position and orientation location system |
| US5383874A (en) | 1991-11-08 | 1995-01-24 | Ep Technologies, Inc. | Systems for identifying catheters and monitoring their use |
| US5437277A (en) | 1991-11-18 | 1995-08-01 | General Electric Company | Inductively coupled RF tracking system for use in invasive imaging of a living body |
| WO1995005773A1 (en) | 1992-02-11 | 1995-03-02 | Cardiac Pathways Corporation | Endocardial electrical mapping catheter |
| US5555883A (en) | 1992-02-24 | 1996-09-17 | Avitall; Boaz | Loop electrode array mapping and ablation catheter for cardiac chambers |
| WO1993020886A1 (en) | 1992-04-13 | 1993-10-28 | Ep Technologies, Inc. | Articulated systems for cardiac ablation |
| US5423807A (en) | 1992-04-16 | 1995-06-13 | Implemed, Inc. | Cryogenic mapping and ablation catheter |
| US5295484A (en) | 1992-05-19 | 1994-03-22 | Arizona Board Of Regents For And On Behalf Of The University Of Arizona | Apparatus and method for intra-cardiac ablation of arrhythmias |
| US5341807A (en) | 1992-06-30 | 1994-08-30 | American Cardiac Ablation Co., Inc. | Ablation catheter positioning system |
| US5325873A (en) | 1992-07-23 | 1994-07-05 | Abbott Laboratories | Tube placement verifier system |
| EP0655138B1 (en) | 1992-08-14 | 1998-04-29 | BRITISH TELECOMMUNICATIONS public limited company | Position location system |
| AU675077B2 (en) | 1992-08-14 | 1997-01-23 | British Telecommunications Public Limited Company | Position location system |
| US5402768A (en) | 1992-09-01 | 1995-04-04 | Adair; Edwin L. | Endoscope with reusable core and disposable sheath with passageways |
| DE69315354T2 (de) | 1992-09-23 | 1998-03-19 | Endocardial Solutions Inc | Endokard-mapping system |
| US5471982A (en) | 1992-09-29 | 1995-12-05 | Ep Technologies, Inc. | Cardiac mapping and ablation systems |
| US5375596A (en) | 1992-09-29 | 1994-12-27 | Hdc Corporation | Method and apparatus for determining the position of catheters, tubes, placement guidewires and implantable ports within biological tissue |
| US5275166A (en) | 1992-11-16 | 1994-01-04 | Ethicon, Inc. | Method and apparatus for performing ultrasonic assisted surgical procedures |
| US5309913A (en) | 1992-11-30 | 1994-05-10 | The Cleveland Clinic Foundation | Frameless stereotaxy system |
| US5368564A (en) | 1992-12-23 | 1994-11-29 | Angeion Corporation | Steerable catheter |
| US5385146A (en) | 1993-01-08 | 1995-01-31 | Goldreyer; Bruce N. | Orthogonal sensing for use in clinical electrophysiology |
| WO1994015533A2 (en) | 1993-01-18 | 1994-07-21 | John Crowe | Endoscope forceps |
| US5373849A (en) | 1993-01-19 | 1994-12-20 | Cardiovascular Imaging Systems, Inc. | Forward viewing imaging catheter |
| US5423321A (en) | 1993-02-11 | 1995-06-13 | Fontenot; Mark G. | Detection of anatomic passages using infrared emitting catheter |
| US5433198A (en) | 1993-03-11 | 1995-07-18 | Desai; Jawahar M. | Apparatus and method for cardiac ablation |
| ZA942812B (en) | 1993-04-22 | 1995-11-22 | Pixsys Inc | System for locating the relative positions of objects in three dimensional space |
| US5403356A (en) | 1993-04-28 | 1995-04-04 | Medtronic, Inc. | Method and apparatus for prevention of atrial tachy arrhythmias |
| BR9405324A (pt) | 1993-06-03 | 1999-08-31 | Xomed Treace Inc | Capa descartável para endoscópio |
| US5409004A (en) | 1993-06-11 | 1995-04-25 | Cook Incorporated | Localization device with radiopaque markings |
| US5391199A (en) | 1993-07-20 | 1995-02-21 | Biosense, Inc. | Apparatus and method for treating cardiac arrhythmias |
| US5385148A (en) | 1993-07-30 | 1995-01-31 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Cardiac imaging and ablation catheter |
| FR2708746B1 (fr) | 1993-08-06 | 1995-09-01 | Thomson Csf | Procédé d'évaluation de la charge restante dans une batterie d'accumulateurs. |
| US5431168A (en) | 1993-08-23 | 1995-07-11 | Cordis-Webster, Inc. | Steerable open-lumen catheter |
| US5425382A (en) | 1993-09-14 | 1995-06-20 | University Of Washington | Apparatus and method for locating a medical tube in the body of a patient |
| US5409000A (en) | 1993-09-14 | 1995-04-25 | Cardiac Pathways Corporation | Endocardial mapping and ablation system utilizing separately controlled steerable ablation catheter with ultrasonic imaging capabilities and method |
| US5558091A (en) | 1993-10-06 | 1996-09-24 | Biosense, Inc. | Magnetic determination of position and orientation |
| WO1995010226A1 (en) | 1993-10-14 | 1995-04-20 | Ep Technologies, Inc. | Locating and ablating pathways in the heart |
| JP3212775B2 (ja) * | 1993-10-18 | 2001-09-25 | オリンパス光学工業株式会社 | 内視鏡挿入状態検出装置 |
| JP3260930B2 (ja) * | 1993-10-18 | 2002-02-25 | オリンパス光学工業株式会社 | 内視鏡挿入状態検出装置 |
| JP3506770B2 (ja) * | 1994-04-21 | 2004-03-15 | オリンパス株式会社 | 内視鏡位置検出装置 |
| US5471988A (en) | 1993-12-24 | 1995-12-05 | Olympus Optical Co., Ltd. | Ultrasonic diagnosis and therapy system in which focusing point of therapeutic ultrasonic wave is locked at predetermined position within observation ultrasonic scanning range |
| US5404297A (en) | 1994-01-21 | 1995-04-04 | Puritan-Bennett Corporation | Aircraft reading light |
| US5487391A (en) | 1994-01-28 | 1996-01-30 | Ep Technologies, Inc. | Systems and methods for deriving and displaying the propagation velocities of electrical events in the heart |
| US5483951A (en) | 1994-02-25 | 1996-01-16 | Vision-Sciences, Inc. | Working channels for a disposable sheath for an endoscope |
| CA2607769C (en) | 1994-08-19 | 2012-04-24 | Biosense, Inc. | Medical diagnosis, treatment and imaging systems |
| US5728044A (en) * | 1995-03-10 | 1998-03-17 | Shan; Yansong | Sensor device for spacial imaging of endoscopes |
| US5577502A (en) | 1995-04-03 | 1996-11-26 | General Electric Company | Imaging of interventional devices during medical procedures |
| US5617857A (en) | 1995-06-06 | 1997-04-08 | Image Guided Technologies, Inc. | Imaging system having interactive medical instruments and methods |
| US5558092A (en) | 1995-06-06 | 1996-09-24 | Imarx Pharmaceutical Corp. | Methods and apparatus for performing diagnostic and therapeutic ultrasound simultaneously |
| US5729129A (en) | 1995-06-07 | 1998-03-17 | Biosense, Inc. | Magnetic location system with feedback adjustment of magnetic field generator |
| US5715822A (en) | 1995-09-28 | 1998-02-10 | General Electric Company | Magnetic resonance devices suitable for both tracking and imaging |
| DE69738813D1 (de) * | 1996-01-08 | 2008-08-14 | Biosense Webster Inc | Mappingkatheter |
-
1997
- 1997-02-14 WO PCT/IL1997/000061 patent/WO1997029679A2/en active IP Right Grant
- 1997-02-14 US US09/117,792 patent/US6203493B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1997-02-14 CA CA002246341A patent/CA2246341C/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1997-02-14 IL IL12578197A patent/IL125781A/xx not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1997-02-14 ES ES97904556T patent/ES2241037T3/es not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1997-02-14 AU AU17315/97A patent/AU711668B2/en not_active Expired
- 1997-02-14 JP JP52916597A patent/JP4130226B2/ja not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1997-02-14 DE DE69733249T patent/DE69733249T8/de active Active
- 1997-02-14 EP EP97904556A patent/EP0883375B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0883375B1 (en) | 2005-05-11 |
| IL125781A0 (en) | 1999-04-11 |
| CA2246341C (en) | 2007-05-01 |
| DE69733249T2 (de) | 2006-01-12 |
| WO1997029679A3 (en) | 1997-10-23 |
| WO1997029679A2 (en) | 1997-08-21 |
| DE69733249D1 (de) | 2005-06-16 |
| EP0883375A4 (en) | 1999-04-07 |
| AU1731597A (en) | 1997-09-02 |
| ES2241037T3 (es) | 2005-10-16 |
| US6203493B1 (en) | 2001-03-20 |
| IL125781A (en) | 2003-06-24 |
| EP0883375A2 (en) | 1998-12-16 |
| JP2002514947A (ja) | 2002-05-21 |
| DE69733249T8 (de) | 2006-04-27 |
| CA2246341A1 (en) | 1997-08-21 |
| AU711668B2 (en) | 1999-10-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4130226B2 (ja) | 内視鏡の正確な位置決定 | |
| JP4166277B2 (ja) | 体内プローブを用いた医療方法および装置 | |
| JP5452500B2 (ja) | カテーテルの血管内留置のための統合システム | |
| JP4581036B2 (ja) | 超音波内視鏡システム、超音波プローブ及び超音波内視鏡 | |
| US8235908B2 (en) | Blood vessel sensing catheter having working lumen for medical appliances | |
| EP3294181B1 (en) | Adjustable length medical instrument assembly with localization elements for tracking medical instrument extension | |
| US6102867A (en) | Sheath and methods of ultrasonic guidance of biopsy and catheter insertion | |
| WO1997029682A1 (en) | Locatable biopsy needle | |
| JP7367976B2 (ja) | 手術器具の自動検出のための検出システムおよび方法 | |
| WO2006031765A2 (en) | Fluoroscopy-free guidewire systems and methods | |
| US11986411B2 (en) | Devices and methods for treatment of body lumens | |
| KR20220004073A (ko) | 센서 캐리어 | |
| EP3539500B1 (en) | Navigation sleeve for medical instrument | |
| WO1999002098A1 (fr) | Detecteur de site presentant une lesion afin d'effectuer une intervention chirurgicale par laparotomie ou laparoscopie | |
| WO2001054567A1 (en) | Endoscopic assembly with non-visual locating device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20040213 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20040213 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20061010 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20070110 |
|
| A602 | Written permission of extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A602 Effective date: 20070226 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070410 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20070911 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20071203 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20071128 |
|
| A602 | Written permission of extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A602 Effective date: 20080121 |
|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A712 Effective date: 20080207 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20080310 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20080422 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20080521 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110530 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110530 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120530 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130530 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130530 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| EXPY | Cancellation because of completion of term |