JP2017531418A - バックsmpsにおける出力電流の測定 - Google Patents
バックsmpsにおける出力電流の測定 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2017531418A JP2017531418A JP2017519887A JP2017519887A JP2017531418A JP 2017531418 A JP2017531418 A JP 2017531418A JP 2017519887 A JP2017519887 A JP 2017519887A JP 2017519887 A JP2017519887 A JP 2017519887A JP 2017531418 A JP2017531418 A JP 2017531418A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- voltage
- timing capacitor
- current
- constant current
- power inductor
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 title claims description 19
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 132
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 33
- 238000005070 sampling Methods 0.000 claims description 25
- 238000007600 charging Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000007599 discharging Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000005669 field effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000000737 periodic effect Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 150000004706 metal oxides Chemical group 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000012935 Averaging Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 12
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 8
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000010277 constant-current charging Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000593 degrading effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002699 waste material Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01R—MEASURING ELECTRIC VARIABLES; MEASURING MAGNETIC VARIABLES
- G01R19/00—Arrangements for measuring currents or voltages or for indicating presence or sign thereof
- G01R19/0046—Arrangements for measuring currents or voltages or for indicating presence or sign thereof characterised by a specific application or detail not covered by any other subgroup of G01R19/00
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M1/00—Details of apparatus for conversion
- H02M1/0003—Details of control, feedback or regulation circuits
- H02M1/0009—Devices or circuits for detecting current in a converter
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M3/00—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output
- H02M3/02—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac
- H02M3/04—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters
- H02M3/10—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode
- H02M3/145—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal
- H02M3/155—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only
- H02M3/156—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M3/00—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output
- H02M3/02—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac
- H02M3/04—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters
- H02M3/10—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode
- H02M3/145—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal
- H02M3/155—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only
- H02M3/156—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators
- H02M3/158—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators including plural semiconductor devices as final control devices for a single load
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M3/00—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output
- H02M3/02—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac
- H02M3/04—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters
- H02M3/10—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode
- H02M3/145—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal
- H02M3/155—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only
- H02M3/156—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators
- H02M3/158—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators including plural semiconductor devices as final control devices for a single load
- H02M3/1588—Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only with automatic control of output voltage or current, e.g. switching regulators including plural semiconductor devices as final control devices for a single load comprising at least one synchronous rectifier element
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02B—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO BUILDINGS, e.g. HOUSING, HOUSE APPLIANCES OR RELATED END-USER APPLICATIONS
- Y02B70/00—Technologies for an efficient end-user side electric power management and consumption
- Y02B70/10—Technologies improving the efficiency by using switched-mode power supplies [SMPS], i.e. efficient power electronics conversion e.g. power factor correction or reduction of losses in power supplies or efficient standby modes
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Dc-Dc Converters (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本願は、2014年10月17日に出願された共有の米国仮特許出願第62/065,152号に対する優先権を主張し、この出願は、あらゆる目的のために、参照により、本明細書に援用される。
本開示は、スイッチモード電源(SMPS)に関し、より具体的には、バックSMPSにおける出力電流の正確な測定に関する。
スイッチモード電源(SMPS)は、SMPSの回路要素が極めて効率的でありかつ電力を殆ど消散しないため、大量の電力を殆ど無駄にすることなく送達する。SMPS(特に、負荷点(POL)コンバータ)では、最大動作効率のために高正確度(全負荷において1%〜3%)で出力電流のリアルタイム測定を提供することが不可欠である。この電流測定は、正確でなければならないだけではなく、SMPS POLコンバータの効率または動的性能に影響を及ぼしてはならない。そのような高正確度(1%〜3%)まで電流を感知および測定することは、SMPS設計において長年にわたって存在してきた問題である。POLコンバータの効率に悪影響を及ぼさないというこの要件を満たす公知の解決策は、今日まで存在していない。
したがって、SMPSの効率および/または動的性能を低下させることのないSMPS出力電流のより正確な測定の必要性がある。
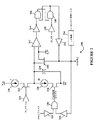
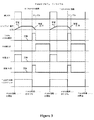
本開示の種々の実施形態によると、サンプルホールド回路が、パルス幅変調(PWM)周期のローサイド部分の実質的に中間(ローサイドスイッチON中の50パーセント点)において、バックスイッチモード電源(SMPS)のインダクタを通って流れる電流のサンプルを取得する。ローサイドONの50%点中にSMPSインダクタを通る電流のこのサンプルは、SMPSの「平均」電流または「DC出力」電流とみなされ得る。また、好ましくは、SMPSインダクタ電流がサンプリングされる度に、全く同一のローサイドONの50%点において取得されるはずである。
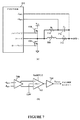
L/RL=RS×CSであり、式中、
Lは、出力インダクタ708のインダクタンス値であり、
RLは、出力インダクタ708の直列抵抗712であり、
RSは、電流感知フィルタ抵抗器770であり、
CSは、電流感知フィルタコンデンサ772である。
Claims (20)
- 供給電圧と供給コモンとの間に直列に結合されるハイサイドスイッチおよびローサイドスイッチと、前記ハイサイドスイッチおよび前記ローサイドスイッチの接合部と負荷との間に結合される電力インダクタとを有するスイッチモード電源(SMPS)において電流測定を実施するための方法であって、前記方法は、
前記ハイサイドスイッチがオンであるとき、第1の一定電流を用いてタイミングコンデンサを充電するステップと、
パルス幅変調(PWM)周期が50%に到達しかつ前記ハイサイドスイッチがオンであるとき、前記第1の一定電流を用いて前記タイミングコンデンサを放電するステップと、
前記PWM周期が50%に到達しかつ前記ハイサイドスイッチがオフであるとき、第2の一定電流を用いて前記タイミングコンデンサを放電するステップであって、前記第2の一定電流は、前記第1の一定電流の2倍である、ステップと、
前記タイミングコンデンサ上の電圧が所定の基準電圧に到達すると、電力インダクタ電流をサンプリングするステップと、
を含む、方法。 - 前記ハイサイドスイッチがオフでありかつ前記PWM周期が50%を下回るとき、前記タイミングコンデンサは、充電または放電されていない、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 前記電力インダクタ電流がサンプリングされると、前記コンデンサを前記基準電圧まで事前充電するステップをさらに含む、請求項1に記載の方法。
- アナログ/デジタルコンバータ(ADC)を用いて前記電力インダクタ電流サンプルを前記電力インダクタ電流サンプルのデジタル表現に変換するステップをさらに含む、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 複数の前記電力インダクタ電流サンプルを平均化するステップと、
アナログ/デジタルコンバータ(ADC)を用いて前記複数の電力インダクタ電流サンプルの平均を前記複数の電力インダクタ電流サンプルの平均のデジタル表現に変換するステップと
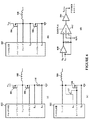
をさらに含む、請求項1に記載の方法。 - 前記電力インダクタ電流をサンプリングするステップは、
前記ローサイドスイッチと前記供給コモンとの間に電流測定抵抗器を提供するステップと、
前記タイミングコンデンサ上の電圧が前記所定の基準電圧に到達すると、前記電流測定抵抗器を横断して生じた電圧をサンプリングするステップと
を含む、請求項1に記載の方法。 - 前記ハイサイドスイッチおよび前記ローサイドスイッチは、電力トランジスタである、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 前記電力トランジスタは、金属酸化物半導体電界効果トランジスタ(MOSFET)である、請求項7に記載の方法。
- 前記電力インダクタ電流をサンプリングするステップは、前記タイミングコンデンサ上の電圧が前記所定の基準電圧に到達すると、ローサイドMOSFETを横断して生じた電圧をサンプリングするステップを含む、請求項8に記載の方法。
- 前記電力インダクタ電流をサンプリングするステップは、
前記ローサイドMOSFETに関連付けられるパイロット電界効果トランジスタ(FET)を提供するステップであって、前記パイロットFETは、前記電力インダクタを通って流れる前記電力インダクタ電流のごく一部を有する、ステップと、
前記タイミングコンデンサ上の電圧が前記所定の基準電圧に到達すると、前記パイロットFETおよび前記ローサイドMOSFETを横断して生じた電圧をサンプリングするステップと、
を含む、請求項8に記載の方法。 - 前記電力インダクタ電流をサンプリングするステップは、
前記電力インダクタと直列に電流測定抵抗器を提供するステップと、
前記タイミングコンデンサ上の電圧が前記所定の基準電圧に到達すると、前記電流測定抵抗器を横断して生じた電圧をサンプリングするステップと、
を含む、請求項1に記載の方法。 - 前記電力インダクタ電流をサンプリングするステップは、前記タイミングコンデンサ上の電圧が前記所定の基準電圧に到達すると、前記電力インダクタを横断する電圧をサンプリングするステップを含む、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 所定の閾値電圧は、約ゼロ(0)ボルトである、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 前記タイミングコンデンサ上の電圧が前記所定の基準電圧に到達すると、サンプル信号を生成するステップをさらに含む、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 前記タイミングコンデンサ上の電圧が前記所定の基準電圧に到達するn回目毎に、アナログ/デジタルコンバータ(ADC)を用いて電力インダクタ電流サンプルを前記電力インダクタ電流サンプルのデジタル表現に変換するステップをさらに含む、請求項1に記載の方法。
- バックスイッチモード電源(SMPS)において電力インダクタ電流サンプル点を決定するための装置であって、前記装置は、
第1のノードおよび第2のノードを有する一定電流源であって、前記一定電流源の第1のノードは、電圧源に結合される、一定電流源と、
第1のノードおよび第2のノードを有する一定電流シンクであって、前記一定電流シンクは、前記一定電流源の電流値の2倍である、一定電流シンクと、
前記一定電流源の第2のノードと前記一定電流シンクの第1のノードとの間に結合される電流源スイッチと、
前記一定電流シンクの第2のノードと電圧源コモンとの間に結合される電流シンクスイッチと、
前記一定電流シンクの第1のノードと前記電圧源コモンとの間に結合されるタイミングコンデンサと、
所定の基準電圧に結合される第1の入力と、前記タイミングコンデンサに結合される第2の入力と、出力とを有する電圧比較器であって、前記電圧比較器の前記出力は、前記タイミングコンデンサ上の電圧が前記所定の基準電圧を上回るとき、第1の論理レベルにあり、前記タイミングコンデンサ上の電圧が前記所定の基準電圧に等しいかまたは前記所定の基準電圧を下回るとき、第2の論理レベルにある、電圧比較器と、
を備え、
前記SMPSからのハイサイドスイッチ信号が第1の論理レベルになると、前記電流源スイッチは、オンになり、かつ、前記一定電流源を前記タイミングコンデンサに結合し、それによって、前記タイミングコンデンサ上の電圧は増加し、
前記SMPSからのハイサイドスイッチ信号が第2の論理レベルになると、前記電流源スイッチは、オフになり、かつ、前記一定電流源を前記タイミングコンデンサから分離し、それによって、前記タイミングコンデンサ上の電圧は同一のままであり、
前記SMPSからの50%パルス幅変調(PWM)周期信号が受信されると、前記電流シンクスイッチは、オンになり、かつ、前記一定電流シンクを前記タイミングコンデンサに結合し、それによって、前記タイミングコンデンサ上の電圧は、前記ハイサイドスイッチ信号が前記第2の論理レベルにあるとき、前記タイミングコンデンサ上の電圧が増加したときよりも2倍早く減少し、前記ハイサイドスイッチ信号が前記第1の論理レベルにあるとき、前記タイミングコンデンサ上の電圧は、前記タイミングコンデンサ上の電圧が増加したときと同一の速度で減少する、装置。 - 前記電圧比較器の前記出力が前記第2の論理レベルにあるとき、サンプル信号が生成される、請求項16に記載の装置。
- 前記タイミングコンデンサと前記所定の基準電圧との間に結合される電圧等化スイッチをさらに備え、前記サンプル信号が生成されると、前記電圧等化スイッチは、オンになり、かつ、前記タイミングコンデンサ上の電圧が前記所定の基準電圧と実質的に同一になるように強制する、請求項17に記載の装置。
- 電力インダクタ電流のサンプルは、前記サンプル信号が生成されたときに取得される、請求項18に記載の装置。
- 請求項16に記載の装置を備える、マイクロコントローラ。
Applications Claiming Priority (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201462065152P | 2014-10-17 | 2014-10-17 | |
| US62/065,152 | 2014-10-17 | ||
| US14/883,381 US9778289B2 (en) | 2014-10-17 | 2015-10-14 | Measuring output current in a buck SMPS |
| US14/883,381 | 2015-10-14 | ||
| PCT/US2015/055859 WO2016061426A1 (en) | 2014-10-17 | 2015-10-16 | Measuring output current in a buck smps |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2017531418A true JP2017531418A (ja) | 2017-10-19 |
| JP2017531418A5 JP2017531418A5 (ja) | 2018-11-08 |
Family
ID=54364753
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017519887A Ceased JP2017531418A (ja) | 2014-10-17 | 2015-10-16 | バックsmpsにおける出力電流の測定 |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US9778289B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP3207627B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP2017531418A (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR20170071473A (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN106664018B (ja) |
| TW (2) | TW201625967A (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2016061426A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9778289B2 (en) * | 2014-10-17 | 2017-10-03 | Microchip Technology Incorporated | Measuring output current in a buck SMPS |
| CN106130319B (zh) * | 2016-08-22 | 2019-04-16 | 昂宝电子(上海)有限公司 | 一种驱动功率晶体管的系统和方法 |
| US10199929B2 (en) * | 2016-10-03 | 2019-02-05 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Transient event detector circuit and method |
| US9853548B1 (en) * | 2017-02-06 | 2017-12-26 | Alpha And Omega Semiconductor Incorporated | Accurate high-side current emulation with auto-conversion for smart power stage applications |
| US10063146B1 (en) * | 2017-03-31 | 2018-08-28 | Alpha And Omega Semiconductor (Cayman) Ltd. | Full-time inductor current monitoring method by sensing low side switch |
| CN107132404B (zh) * | 2017-05-15 | 2019-11-05 | 矽力杰半导体技术(杭州)有限公司 | 检测方法、检测电路、控制器及开关电源 |
| KR102281654B1 (ko) | 2017-06-08 | 2021-07-29 | 현대자동차주식회사 | 하이브리드 자동차 및 그를 위한 제어방법 |
| US10361684B2 (en) * | 2017-07-19 | 2019-07-23 | Invecas, Inc. | Duty cycle detection |
| CN107493099B (zh) * | 2017-08-22 | 2021-11-26 | 钰泰半导体股份有限公司 | 一种芯片工作模式的设置方法 |
| US10056819B1 (en) * | 2017-10-24 | 2018-08-21 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Predicting the timing of current phases of a DC-DC converter |
| TWI650922B (zh) * | 2018-02-07 | 2019-02-11 | 新唐科技股份有限公司 | 具保護電路之半橋電路驅動晶片及其保護方法 |
| JP2019149614A (ja) * | 2018-02-26 | 2019-09-05 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 電流検出回路、半導体装置、及び、半導体システム |
| CN109450016B (zh) * | 2018-10-29 | 2020-11-03 | Oppo广东移动通信有限公司 | 放电方法、移动电源及计算机存储介质 |
| US10830799B1 (en) | 2019-07-12 | 2020-11-10 | Alpha And Omega Semiconductor (Cayman) Ltd. | Temperature and VGS compensation for current sensing using Rdson in MOSFETS |
| DE112020003785T5 (de) * | 2019-08-08 | 2022-07-07 | Casco Products Corporation | Verfahren zum Vorladen von großen Kondensatoren und Schaltung |
| CN110768510B (zh) | 2019-09-30 | 2022-09-20 | 上海矽力杰微电子技术有限公司 | 控制电路和方法以及功率变换器 |
| TWI728588B (zh) * | 2019-12-11 | 2021-05-21 | 茂達電子股份有限公司 | 固定導通時間電源轉換器的電流偵測電路及方法 |
| US11469669B2 (en) * | 2020-01-31 | 2022-10-11 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Methods and circuitry to detect PFM mode entry in wide duty range DC converter |
| KR102624192B1 (ko) * | 2021-11-30 | 2024-01-11 | 한국과학기술원 | 프리차지 방법 및 이를 이용하는 프리차지 회로 |
| US12055565B2 (en) | 2022-11-22 | 2024-08-06 | Alpha And Omega Semiconductor International Lp | Linear discrete Rdson temperature VGS compensation |
Family Cites Families (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5835361A (en) * | 1997-04-16 | 1998-11-10 | Thomson Consumer Electronics, Inc. | Switch-mode power supply with over-current protection |
| US7026797B2 (en) * | 2003-03-21 | 2006-04-11 | Tropian, Inc. | Extremely high-speed switchmode DC-DC converters |
| EP1668770A1 (en) * | 2003-09-25 | 2006-06-14 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. | A switch mode power converter |
| US7362191B2 (en) * | 2004-04-29 | 2008-04-22 | Linear Technology Corporation | Methods and circuits for frequency modulation that reduce the spectral noise of switching regulators |
| US7274183B1 (en) | 2005-11-02 | 2007-09-25 | National Semiconductor Corporation | Versatile system for high-power switching controller in low-power semiconductor technology |
| GB0615029D0 (en) * | 2005-12-22 | 2006-09-06 | Cambridge Semiconductor Ltd | Switch mode power supply controllers |
| US7460441B2 (en) | 2007-01-12 | 2008-12-02 | Microchip Technology Incorporated | Measuring a long time period |
| US7764213B2 (en) | 2008-07-01 | 2010-07-27 | Microchip Technology Incorporated | Current-time digital-to-analog converter |
| US8525498B2 (en) | 2008-07-31 | 2013-09-03 | Monolithic Power Systems, Inc. | Average input current limit method and apparatus thereof |
| JP2010103707A (ja) * | 2008-10-22 | 2010-05-06 | Canon Inc | チャージポンプ回路、及びクロック生成器 |
| CN103427647B (zh) * | 2012-05-22 | 2016-02-17 | 通嘉科技股份有限公司 | 电源供应器以及电源控制器 |
| AT512780B1 (de) * | 2012-06-13 | 2013-11-15 | Fronius Int Gmbh | Schaltnetzteil sowie Wechselrichter und Strangüberwachung mit einem solchen Schaltnetzteil |
| US9285399B2 (en) | 2012-06-29 | 2016-03-15 | Infineon Technologies Austria Ag | Switching regulator cycle-by-cycle current estimation |
| CN102891611B (zh) * | 2012-06-30 | 2014-10-08 | 华为技术有限公司 | 五电平功率变换器及其控制方法、控制装置 |
| CN102820781B (zh) * | 2012-08-30 | 2014-08-06 | 东南大学 | 一种基于纹波控制的单电感双输出开关电源 |
| US9564810B2 (en) * | 2013-03-28 | 2017-02-07 | Infineon Technologies Austria Ag | Switched mode power supply |
| TWM472362U (zh) * | 2013-08-07 | 2014-02-11 | Richtek Technology Corp | 降壓型切換式電源供應器 |
| CN103532555A (zh) * | 2013-10-23 | 2014-01-22 | 电子科技大学 | 基于压控振荡器的电压比较器 |
| US9778289B2 (en) * | 2014-10-17 | 2017-10-03 | Microchip Technology Incorporated | Measuring output current in a buck SMPS |
-
2015
- 2015-10-14 US US14/883,381 patent/US9778289B2/en active Active
- 2015-10-16 JP JP2017519887A patent/JP2017531418A/ja not_active Ceased
- 2015-10-16 CN CN201580045951.3A patent/CN106664018B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2015-10-16 EP EP15787391.0A patent/EP3207627B1/en not_active Not-in-force
- 2015-10-16 TW TW104134090A patent/TW201625967A/zh unknown
- 2015-10-16 TW TW108119510A patent/TWI688775B/zh not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2015-10-16 WO PCT/US2015/055859 patent/WO2016061426A1/en active Application Filing
- 2015-10-16 KR KR1020177006189A patent/KR20170071473A/ko unknown
-
2017
- 2017-10-02 US US15/723,115 patent/US10114046B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3207627B1 (en) | 2019-10-16 |
| US9778289B2 (en) | 2017-10-03 |
| TW201625967A (zh) | 2016-07-16 |
| TWI688775B (zh) | 2020-03-21 |
| US20160109488A1 (en) | 2016-04-21 |
| KR20170071473A (ko) | 2017-06-23 |
| CN106664018A (zh) | 2017-05-10 |
| TW201937178A (zh) | 2019-09-16 |
| WO2016061426A1 (en) | 2016-04-21 |
| EP3207627A1 (en) | 2017-08-23 |
| US10114046B2 (en) | 2018-10-30 |
| US20180024171A1 (en) | 2018-01-25 |
| CN106664018B (zh) | 2019-09-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10114046B2 (en) | Measuring output current in a buck SMPS | |
| JP2017531418A5 (ja) | ||
| TWI519044B (zh) | A system and method for adjusting the output current of a power conversion system | |
| US9344002B2 (en) | Adaptive sampling circuit for detecting the demagnetized voltage of the transformer | |
| US9559592B2 (en) | Synchronous rectifier timer for discontinuous mode DC/DC converter | |
| JP5418899B2 (ja) | 電力コンバータでの使用のための制御回路および電力コンバータにおける変圧器の飽和を防止する方法 | |
| CN110022051B (zh) | 用于驱动功率级的装置和方法 | |
| US9450487B2 (en) | DC to DC converter | |
| US8587275B2 (en) | Instantaneous average current measurement method | |
| US11323110B2 (en) | Duty timing detector detecting duty timing of toggle signal, device including duty timing detector, and operating method of device receiving toggle signal | |
| CN105978317A (zh) | 开关电源装置的控制电路和开关电源装置 | |
| JP7177340B2 (ja) | スイッチング電源用半導体装置およびac-dcコンバータ | |
| US9857395B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for measuring average inductor current delivered to a load | |
| US10468981B2 (en) | Switching power supply device | |
| US10340796B2 (en) | Constant on time boost converter control | |
| JP2009254061A (ja) | 半導体集積回路及びそのテスト方法 | |
| US9077294B2 (en) | Measurement of the output current of an amplifier circuit | |
| JP6853684B2 (ja) | Dc/dcコンバータおよびその制御回路、制御方法および車載電装機器 | |
| US10177644B1 (en) | Input current extraction from inductor current in a voltage converter | |
| WO2020129414A1 (ja) | 集積回路、電源回路 | |
| US9541989B2 (en) | Power transfer estimation | |
| JP7107314B2 (ja) | Dc-dcコンバータ、スイッチ素子による電圧降下を測定する方法、スイッチ素子の故障を検知する方法、3相インバータ | |
| TWI697186B (zh) | 轉換裝置及其方法 | |
| TWM445301U (zh) | 電壓轉換裝置及次諧波偵測器 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20180928 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20180928 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20190719 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20190717 |
|
| A045 | Written measure of dismissal of application [lapsed due to lack of payment] |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A045 Effective date: 20191121 |