JP2015507363A - スペーサおよびスペーサ保護用途のための共形アモルファスカーボン - Google Patents
スペーサおよびスペーサ保護用途のための共形アモルファスカーボン Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2015507363A JP2015507363A JP2014553383A JP2014553383A JP2015507363A JP 2015507363 A JP2015507363 A JP 2015507363A JP 2014553383 A JP2014553383 A JP 2014553383A JP 2014553383 A JP2014553383 A JP 2014553383A JP 2015507363 A JP2015507363 A JP 2015507363A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- nitrogen
- substrate
- amorphous carbon
- layer
- patterned
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 229910003481 amorphous carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 title claims abstract description 54
- 125000006850 spacer group Chemical group 0.000 title claims abstract description 53
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 85
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 70
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 21
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 20
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 37
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 33
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 33
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 claims description 33
- 229930195733 hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 claims description 32
- 239000004215 Carbon black (E152) Substances 0.000 claims description 30
- -1 nitrogen-containing hydrocarbon Chemical class 0.000 claims description 27
- JFDZBHWFFUWGJE-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzonitrile Chemical compound N#CC1=CC=CC=C1 JFDZBHWFFUWGJE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 24
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 claims description 23
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 18
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 15
- GETQZCLCWQTVFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N trimethylamine Chemical compound CN(C)C GETQZCLCWQTVFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 claims description 10
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 10
- 229920005591 polysilicon Polymers 0.000 claims description 10
- ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethylamine Chemical compound CCN(CC)CC ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 9
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 8
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- QJGQUHMNIGDVPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N nitrogen group Chemical group [N] QJGQUHMNIGDVPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 7
- PAYRUJLWNCNPSJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Aniline Chemical compound NC1=CC=CC=C1 PAYRUJLWNCNPSJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- ROSDSFDQCJNGOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethylamine Chemical compound CNC ROSDSFDQCJNGOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- BAVYZALUXZFZLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methylamine Chemical compound NC BAVYZALUXZFZLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyridine Chemical compound C1=CC=NC=C1 JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- SMWDFEZZVXVKRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Quinoline Chemical compound N1=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C21 SMWDFEZZVXVKRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000002194 amorphous carbon material Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- KAKZBPTYRLMSJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Butadiene Chemical compound C=CC=C KAKZBPTYRLMSJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- UEXCJVNBTNXOEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethynylbenzene Chemical group C#CC1=CC=CC=C1 UEXCJVNBTNXOEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- ATUOYWHBWRKTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propane Chemical compound CCC ATUOYWHBWRKTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- NLHHRLWOUZZQLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acrylonitrile Chemical compound C=CC#N NLHHRLWOUZZQLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyridine Natural products COC1=CC=CN=C1 UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- OTMSDBZUPAUEDD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethane Chemical compound CC OTMSDBZUPAUEDD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- VGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethene Chemical compound C=C VGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000005977 Ethylene Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- HSFWRNGVRCDJHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N alpha-acetylene Natural products C#C HSFWRNGVRCDJHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000001273 butane Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000002534 ethynyl group Chemical group [H]C#C* 0.000 claims description 2
- IJDNQMDRQITEOD-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-butane Chemical compound CCCC IJDNQMDRQITEOD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- OFBQJSOFQDEBGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-pentane Natural products CCCCC OFBQJSOFQDEBGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000001294 propane Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- QQONPFPTGQHPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N propylene Natural products CC=C QQONPFPTGQHPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000004805 propylene group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([*:1])C([H])([H])[*:2] 0.000 claims description 2
- MWWATHDPGQKSAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N propyne Chemical compound CC#C MWWATHDPGQKSAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000000383 tetramethylene group Chemical group [H]C([H])([*:1])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[*:2] 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 99
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 46
- 238000000059 patterning Methods 0.000 description 25
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- 238000000623 plasma-assisted chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 12
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 12
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 12
- 238000000206 photolithography Methods 0.000 description 11
- 239000011241 protective layer Substances 0.000 description 10
- XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Argon Chemical compound [Ar] XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 239000006117 anti-reflective coating Substances 0.000 description 7
- 229910052734 helium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 150000004767 nitrides Chemical class 0.000 description 7
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 7
- UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Benzene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1 UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 229910052786 argon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 239000003575 carbonaceous material Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000005137 deposition process Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000001307 helium Substances 0.000 description 5
- SWQJXJOGLNCZEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N helium atom Chemical compound [He] SWQJXJOGLNCZEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 5
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonia Chemical compound N QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229910017840 NH 3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229910021417 amorphous silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 238000000231 atomic layer deposition Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000003085 diluting agent Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000009977 dual effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 4
- 235000012239 silicon dioxide Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- YCKRFDGAMUMZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorine atom Chemical compound [F] YCKRFDGAMUMZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Toluene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1 YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000004380 ashing Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000011737 fluorine Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000001020 plasma etching Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000002210 silicon-based material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 235000012431 wafers Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- KWOLFJPFCHCOCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetophenone Chemical compound CC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 KWOLFJPFCHCOCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102100022717 Atypical chemokine receptor 1 Human genes 0.000 description 2
- YNQLUTRBYVCPMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylbenzene Chemical compound CCC1=CC=CC=C1 YNQLUTRBYVCPMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Furan Chemical compound C=1C=COC=1 YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 101000678879 Homo sapiens Atypical chemokine receptor 1 Proteins 0.000 description 2
- RRHGJUQNOFWUDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isoprene Chemical compound CC(=C)C=C RRHGJUQNOFWUDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phenol Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=C1 ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Styrene Chemical compound C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NRTOMJZYCJJWKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium nitride Chemical compound [Ti]#N NRTOMJZYCJJWKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910021529 ammonia Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- KDKYADYSIPSCCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N but-1-yne Chemical compound CCC#C KDKYADYSIPSCCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000012159 carrier gas Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000003989 dielectric material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910001873 dinitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- ZQBFAOFFOQMSGJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexafluorobenzene Chemical compound FC1=C(F)C(F)=C(F)C(F)=C1F ZQBFAOFFOQMSGJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011261 inert gas Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000012212 insulator Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 238000001459 lithography Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 2
- QPJVMBTYPHYUOC-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl benzoate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 QPJVMBTYPHYUOC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000011946 reduction process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005549 size reduction Methods 0.000 description 2
- YHQGMYUVUMAZJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N α-terpinene Chemical compound CC(C)C1=CC=C(C)CC1 YHQGMYUVUMAZJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- PMJHHCWVYXUKFD-SNAWJCMRSA-N (E)-1,3-pentadiene Chemical compound C\C=C\C=C PMJHHCWVYXUKFD-SNAWJCMRSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GOYDNIKZWGIXJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-difluorobenzene Chemical compound FC1=CC=CC=C1F GOYDNIKZWGIXJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IOYUAOCHSFBWGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-butyl-2,3,4,5-tetramethylbenzene Chemical compound CCCCC1=CC(C)=C(C)C(C)=C1C IOYUAOCHSFBWGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UROUUEDWXIQAAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxymethyl]furan Chemical compound CC(C)(C)OCC1=CC=CO1 UROUUEDWXIQAAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QTWJRLJHJPIABL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylphenol;3-methylphenol;4-methylphenol Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1.CC1=CC=CC(O)=C1.CC1=CC=CC=C1O QTWJRLJHJPIABL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PKXHXOTZMFCXSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3,3-dimethylbut-1-ene Chemical group CC(C)(C)C=C PKXHXOTZMFCXSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JBRZTFJDHDCESZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N AsGa Chemical compound [As]#[Ga] JBRZTFJDHDCESZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Boron Chemical compound [B] ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910001218 Gallium arsenide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- WSTYNZDAOAEEKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Mayol Natural products CC1=C(O)C(=O)C=C2C(CCC3(C4CC(C(CC4(CCC33C)C)=O)C)C)(C)C3=CC=C21 WSTYNZDAOAEEKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VVQNEPGJFQJSBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methyl methacrylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C(C)=C VVQNEPGJFQJSBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N O-Xylene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1C CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004952 Polyamide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910000577 Silicon-germanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- LEVVHYCKPQWKOP-UHFFFAOYSA-N [Si].[Ge] Chemical compound [Si].[Ge] LEVVHYCKPQWKOP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IPBVNPXQWQGGJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N acetic acid phenyl ester Natural products CC(=O)OC1=CC=CC=C1 IPBVNPXQWQGGJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052796 boron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- WFYPICNXBKQZGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N butenyne Chemical group C=CC#C WFYPICNXBKQZGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229930003836 cresol Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 229940013361 cresol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229910021419 crystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229930007927 cymene Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- AQEFLFZSWDEAIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N di-tert-butyl ether Chemical compound CC(C)(C)OC(C)(C)C AQEFLFZSWDEAIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000010790 dilution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012895 dilution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000004907 flux Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052732 germanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- GNPVGFCGXDBREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N germanium atom Chemical compound [Ge] GNPVGFCGXDBREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- AHAREKHAZNPPMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexa-1,3-diene Chemical compound CCC=CC=C AHAREKHAZNPPMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000002431 hydrogen Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000002887 hydroxy group Chemical group [H]O* 0.000 description 1
- 230000000977 initiatory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000031700 light absorption Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007791 liquid phase Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012705 liquid precursor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940095102 methyl benzoate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011368 organic material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- HFPZCAJZSCWRBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N p-cymene Chemical compound CC(C)C1=CC=C(C)C=C1 HFPZCAJZSCWRBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YWAKXRMUMFPDSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N pentene Chemical compound CCCC=C YWAKXRMUMFPDSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960003742 phenol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940049953 phenylacetate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- WLJVXDMOQOGPHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N phenylacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC1=CC=CC=C1 WLJVXDMOQOGPHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920002492 poly(sulfone) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002647 polyamide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052594 sapphire Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010980 sapphire Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009966 trimming Methods 0.000 description 1
- WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N tungsten Chemical compound [W] WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052721 tungsten Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010937 tungsten Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012808 vapor phase Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008096 xylene Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/027—Making masks on semiconductor bodies for further photolithographic processing not provided for in group H01L21/18 or H01L21/34
- H01L21/0271—Making masks on semiconductor bodies for further photolithographic processing not provided for in group H01L21/18 or H01L21/34 comprising organic layers
- H01L21/0273—Making masks on semiconductor bodies for further photolithographic processing not provided for in group H01L21/18 or H01L21/34 comprising organic layers characterised by the treatment of photoresist layers
- H01L21/0274—Photolithographic processes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/027—Making masks on semiconductor bodies for further photolithographic processing not provided for in group H01L21/18 or H01L21/34
- H01L21/033—Making masks on semiconductor bodies for further photolithographic processing not provided for in group H01L21/18 or H01L21/34 comprising inorganic layers
- H01L21/0334—Making masks on semiconductor bodies for further photolithographic processing not provided for in group H01L21/18 or H01L21/34 comprising inorganic layers characterised by their size, orientation, disposition, behaviour, shape, in horizontal or vertical plane
- H01L21/0337—Making masks on semiconductor bodies for further photolithographic processing not provided for in group H01L21/18 or H01L21/34 comprising inorganic layers characterised by their size, orientation, disposition, behaviour, shape, in horizontal or vertical plane characterised by the process involved to create the mask, e.g. lift-off masks, sidewalls, or to modify the mask, e.g. pre-treatment, post-treatment
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02107—Forming insulating materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02109—Forming insulating materials on a substrate characterised by the type of layer, e.g. type of material, porous/non-porous, pre-cursors, mixtures or laminates
- H01L21/02112—Forming insulating materials on a substrate characterised by the type of layer, e.g. type of material, porous/non-porous, pre-cursors, mixtures or laminates characterised by the material of the layer
- H01L21/02115—Forming insulating materials on a substrate characterised by the type of layer, e.g. type of material, porous/non-porous, pre-cursors, mixtures or laminates characterised by the material of the layer the material being carbon, e.g. alpha-C, diamond or hydrogen doped carbon
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02107—Forming insulating materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02225—Forming insulating materials on a substrate characterised by the process for the formation of the insulating layer
- H01L21/0226—Forming insulating materials on a substrate characterised by the process for the formation of the insulating layer formation by a deposition process
- H01L21/02263—Forming insulating materials on a substrate characterised by the process for the formation of the insulating layer formation by a deposition process deposition from the gas or vapour phase
- H01L21/02271—Forming insulating materials on a substrate characterised by the process for the formation of the insulating layer formation by a deposition process deposition from the gas or vapour phase deposition by decomposition or reaction of gaseous or vapour phase compounds, i.e. chemical vapour deposition
- H01L21/02274—Forming insulating materials on a substrate characterised by the process for the formation of the insulating layer formation by a deposition process deposition from the gas or vapour phase deposition by decomposition or reaction of gaseous or vapour phase compounds, i.e. chemical vapour deposition in the presence of a plasma [PECVD]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/027—Making masks on semiconductor bodies for further photolithographic processing not provided for in group H01L21/18 or H01L21/34
- H01L21/033—Making masks on semiconductor bodies for further photolithographic processing not provided for in group H01L21/18 or H01L21/34 comprising inorganic layers
- H01L21/0332—Making masks on semiconductor bodies for further photolithographic processing not provided for in group H01L21/18 or H01L21/34 comprising inorganic layers characterised by their composition, e.g. multilayer masks, materials
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/027—Making masks on semiconductor bodies for further photolithographic processing not provided for in group H01L21/18 or H01L21/34
- H01L21/033—Making masks on semiconductor bodies for further photolithographic processing not provided for in group H01L21/18 or H01L21/34 comprising inorganic layers
- H01L21/0334—Making masks on semiconductor bodies for further photolithographic processing not provided for in group H01L21/18 or H01L21/34 comprising inorganic layers characterised by their size, orientation, disposition, behaviour, shape, in horizontal or vertical plane
- H01L21/0338—Process specially adapted to improve the resolution of the mask
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/30—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26
- H01L21/31—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26 to form insulating layers thereon, e.g. for masking or by using photolithographic techniques; After treatment of these layers; Selection of materials for these layers
- H01L21/3105—After-treatment
- H01L21/311—Etching the insulating layers by chemical or physical means
- H01L21/31105—Etching inorganic layers
- H01L21/31111—Etching inorganic layers by chemical means
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/30—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26
- H01L21/31—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26 to form insulating layers thereon, e.g. for masking or by using photolithographic techniques; After treatment of these layers; Selection of materials for these layers
- H01L21/3105—After-treatment
- H01L21/311—Etching the insulating layers by chemical or physical means
- H01L21/31105—Etching inorganic layers
- H01L21/31111—Etching inorganic layers by chemical means
- H01L21/31116—Etching inorganic layers by chemical means by dry-etching
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/30—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26
- H01L21/31—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26 to form insulating layers thereon, e.g. for masking or by using photolithographic techniques; After treatment of these layers; Selection of materials for these layers
- H01L21/3105—After-treatment
- H01L21/311—Etching the insulating layers by chemical or physical means
- H01L21/31144—Etching the insulating layers by chemical or physical means using masks
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/30—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26
- H01L21/31—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26 to form insulating layers thereon, e.g. for masking or by using photolithographic techniques; After treatment of these layers; Selection of materials for these layers
- H01L21/3205—Deposition of non-insulating-, e.g. conductive- or resistive-, layers on insulating layers; After-treatment of these layers
- H01L21/321—After treatment
- H01L21/3213—Physical or chemical etching of the layers, e.g. to produce a patterned layer from a pre-deposited extensive layer
- H01L21/32133—Physical or chemical etching of the layers, e.g. to produce a patterned layer from a pre-deposited extensive layer by chemical means only
- H01L21/32135—Physical or chemical etching of the layers, e.g. to produce a patterned layer from a pre-deposited extensive layer by chemical means only by vapour etching only
- H01L21/32136—Physical or chemical etching of the layers, e.g. to produce a patterned layer from a pre-deposited extensive layer by chemical means only by vapour etching only using plasmas
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/30—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26
- H01L21/31—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26 to form insulating layers thereon, e.g. for masking or by using photolithographic techniques; After treatment of these layers; Selection of materials for these layers
- H01L21/3205—Deposition of non-insulating-, e.g. conductive- or resistive-, layers on insulating layers; After-treatment of these layers
- H01L21/321—After treatment
- H01L21/3213—Physical or chemical etching of the layers, e.g. to produce a patterned layer from a pre-deposited extensive layer
- H01L21/32133—Physical or chemical etching of the layers, e.g. to produce a patterned layer from a pre-deposited extensive layer by chemical means only
- H01L21/32135—Physical or chemical etching of the layers, e.g. to produce a patterned layer from a pre-deposited extensive layer by chemical means only by vapour etching only
- H01L21/32136—Physical or chemical etching of the layers, e.g. to produce a patterned layer from a pre-deposited extensive layer by chemical means only by vapour etching only using plasmas
- H01L21/32137—Physical or chemical etching of the layers, e.g. to produce a patterned layer from a pre-deposited extensive layer by chemical means only by vapour etching only using plasmas of silicon-containing layers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/30—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26
- H01L21/31—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26 to form insulating layers thereon, e.g. for masking or by using photolithographic techniques; After treatment of these layers; Selection of materials for these layers
- H01L21/3205—Deposition of non-insulating-, e.g. conductive- or resistive-, layers on insulating layers; After-treatment of these layers
- H01L21/321—After treatment
- H01L21/3213—Physical or chemical etching of the layers, e.g. to produce a patterned layer from a pre-deposited extensive layer
- H01L21/32139—Physical or chemical etching of the layers, e.g. to produce a patterned layer from a pre-deposited extensive layer using masks
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Plasma & Fusion (AREA)
- Internal Circuitry In Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Devices (AREA)
- Drying Of Semiconductors (AREA)
- Formation Of Insulating Films (AREA)
- Electrodes Of Semiconductors (AREA)
- Exposure Of Semiconductors, Excluding Electron Or Ion Beam Exposure (AREA)
Abstract
Description
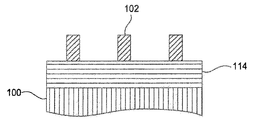
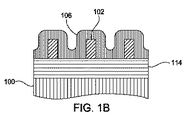
図2は、本発明の1つの実施形態による例示的な自己整合ダブルパターニングプロセスに関連するステップを示す方法流れ図である。図3A〜図3Eは、図2に記載されたステップによって形成される構造体の断面図を示す。自己整合ダブルパターニングプロセスは、例証目的のために選ばれていると考えられる。本発明の概念は、NANDフラッシュ用途、DRAM用途、またはCMOS用途などのような様々な半導体プロセスでの必要に応じて、可変ライン幅および間隔をもつ保護スペーサまたは保護犠牲層の使用を必要とすることがあるビア/孔縮小プロセス、自己整合三重パターニング(SATP)プロセス、または自己整合四重パターニング(SAQP)プロセスなどのような他のプロセス、単一または二重パターニング方式に同等に適用可能である。加えて、本明細書で説明する本発明の基本範囲を逸脱することなく1つまたは複数のステップを追加する、削除する、かつ/または再度順序を設定することができるので、図2に示したステップの数または順序は本明細書で説明する本発明の範囲に関して限定するものではない。
Claims (15)
- 処理チャンバ内で基板上にアモルファスカーボン層を形成する方法であって、
基板の上に所定の厚さの犠牲誘電体層を堆積させることと、
前記基板の上部表面を露出させるために前記犠牲誘電体層の一部分を除去することによって前記基板上にパターン化特徴部を形成することと、
前記パターン化特徴部および前記基板の前記露出された上部表面に所定の厚さのアモルファスカーボン層を共形に堆積させることと、
異方性エッチングプロセスを使用して、前記パターン化特徴部の上部表面および前記基板の前記上部表面から前記アモルファスカーボン層を選択的に除去して、前記アモルファスカーボン層から形成された側壁スペーサの内部に充填されている前記パターン化特徴部を設けることと、
前記基板から前記パターン化特徴部を除去することと
を含む、方法。 - 前記アモルファスカーボン層が、炭化水素源、窒素含有ガス、およびプラズマ開始ガスを前記処理チャンバに導入することによって形成される、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 前記炭化水素源が、アセチレン(C2H2)、エチレン(C2H4)、エタン(C2H6)、プロピレン(C3H6)、プロピン(C3H4)、プロパン(C3H8)、ブタン(C4H10)、ブチレン(C4H8)、ブタジエン(C4H6)、フェニルアセチレン(C8H6)、およびそれらの組合せからなる群から選択された1つまたは複数の炭化水素化合物を含む、請求項2に記載の方法。
- 前記アモルファスカーボン層が、窒素含有炭化水素源およびプラズマ開始ガスを前記処理チャンバに導入することによって形成される、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 前記窒素含有炭化水素が、メチルアミン、ジメチルアミン、トリメチルアミン(TMA)、トリエチルアミン、アニリン、キノリン、ピリジン、アクリロニトリル、ベンゾニトリル、およびそれらの組合せからなる群から選択された1つまたは複数の窒素含有炭化水素化合物を含む、請求項4に記載の方法。
- 前記窒素含有炭化水素化合物がベンゾニトリルである、請求項5に記載の方法。
- 前記アモルファスカーボン層が、約0.1%窒素から約4.0%窒素の間のカーボン:窒素比を有する窒素ドープアモルファスカーボンである、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 前記犠牲誘電体層が、酸化ケイ素、窒化ケイ素、ポリシリコン、またはアモルファスカーボンを含む、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 処理チャンバ内でデバイスを形成する方法であって、
基板の上部表面にパターン化特徴部を形成することと、
前記パターン化特徴部および前記基板の露出された上部表面に所定の厚さの犠牲誘電体層を共形に堆積させることと、
前記パターン化特徴部の上部表面および前記基板の前記露出された上部表面から前記犠牲誘電体層を選択的に除去して、前記犠牲誘電体層から形成された第1の側壁スペーサの内部に充填されている前記パターン化特徴部を設けることと、
前記第1の側壁スペーサに隣接する第2の側壁スペーサを形成することであり、前記第2の側壁スペーサが、約0.1%窒素から約4.0%窒素の間のカーボン:窒素比を有する窒素ドープアモルファスカーボン材料から形成される、形成することと、
前記第1の側壁スペーサの内部に充填されている前記パターン化特徴部を除去することと
を含む、方法。 - 前記パターン化特徴部がアモルファスカーボンから形成される、請求項9に記載の方法。
- 前記窒素ドープアモルファスカーボン材料が、窒素含有炭化水素源およびプラズマ開始ガスを前記処理チャンバに導入することによって形成される、請求項9に記載の方法。
- 前記窒素含有炭化水素源が、メチルアミン、ジメチルアミン、トリメチルアミン(TMA)、トリエチルアミン、アニリン、キノリン、ピリジン、アクリロニトリル、ベンゾニトリル、およびそれらの組合せからなる群から選択された1つまたは複数の窒素含有炭化水素化合物を含む、請求項11に記載の方法。
- 前記窒素含有炭化水素化合物がベンゾニトリルである、請求項12に記載の方法。
- 処理チャンバ内で基板上に窒素ドープアモルファスカーボン層を形成する方法であって、
前記基板上に形成されたパターン化特徴部に窒素ドープアモルファスカーボン層を共形に堆積させることであり、前記堆積が、窒素含有炭化水素源およびプラズマ開始ガスを前記処理チャンバに導入することによって行われ、そして前記窒素含有炭化水素源がベンゾニトリルを含む、堆積させることと、
異方性エッチングプロセスを使用して、前記パターン化特徴部の上部表面および前記基板の上部表面から前記窒素ドープアモルファスカーボン層を選択的に除去して、前記窒素ドープアモルファスカーボン層から形成された側壁スペーサの内部に充填されている前記パターン化特徴部を設けることと、
前記基板から前記パターン化特徴部を除去することと
を含む、方法。 - 前記窒素ドープアモルファスカーボン層が、約100mg/分から約1000mg/分の流量で窒素含有炭化水素源を、および0sccmから約2000sccmの流量で窒素含有ガスを前記処理チャンバに導入することによって、約30Wから約200WのRF電力(200mm基板に対して)を印加することによって、および約100ミルから約800ミルの電極間隔で、堆積される、請求項14に記載の方法。
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US13/354,129 US20130189845A1 (en) | 2012-01-19 | 2012-01-19 | Conformal amorphous carbon for spacer and spacer protection applications |
| US13/354,129 | 2012-01-19 | ||
| PCT/US2013/021769 WO2013109645A1 (en) | 2012-01-19 | 2013-01-16 | Conformal amorphous carbon for spacer and spacer protection applications |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2015507363A true JP2015507363A (ja) | 2015-03-05 |
| JP2015507363A5 JP2015507363A5 (ja) | 2016-03-03 |
Family
ID=48797563
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014553383A Pending JP2015507363A (ja) | 2012-01-19 | 2013-01-16 | スペーサおよびスペーサ保護用途のための共形アモルファスカーボン |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (4) | US20130189845A1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP2015507363A (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR20140115353A (ja) |
| TW (1) | TW201339349A (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2013109645A1 (ja) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018516463A (ja) * | 2015-06-03 | 2018-06-21 | アプライド マテリアルズ インコーポレイテッドApplied Materials,Incorporated | 先進的なパターニングプロセスにおけるスペーサ堆積および選択的除去のための装置および方法 |
| JP2020519938A (ja) * | 2017-05-01 | 2020-07-02 | アドバンスト・マイクロ・ディバイシズ・インコーポレイテッドAdvanced Micro Devices Incorporated | ダブルスペーサ液浸リソグラフィトリプルパターニングのフロー及び方法 |
| KR20210090698A (ko) | 2018-12-18 | 2021-07-20 | 도쿄엘렉트론가부시키가이샤 | 카본 하드마스크, 성막 장치 및 성막 방법 |
Families Citing this family (36)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9117764B2 (en) * | 2010-08-27 | 2015-08-25 | Tokyo Electron Limited | Etching method, substrate processing method, pattern forming method, method for manufacturing semiconductor element, and semiconductor element |
| KR20130015145A (ko) * | 2011-08-02 | 2013-02-13 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 반도체 소자의 미세 패턴 형성 방법 |
| JP2014072226A (ja) * | 2012-09-27 | 2014-04-21 | Tokyo Electron Ltd | パターン形成方法 |
| US8828839B2 (en) * | 2013-01-29 | 2014-09-09 | GlobalFoundries, Inc. | Methods for fabricating electrically-isolated finFET semiconductor devices |
| US9721784B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2017-08-01 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Ultra-conformal carbon film deposition |
| US9064813B2 (en) * | 2013-04-19 | 2015-06-23 | International Business Machines Corporation | Trench patterning with block first sidewall image transfer |
| CN104425225A (zh) * | 2013-09-04 | 2015-03-18 | 中芯国际集成电路制造(上海)有限公司 | 三重图形的形成方法 |
| US9698015B2 (en) | 2013-10-21 | 2017-07-04 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Method for patterning a semiconductor substrate |
| US9159579B2 (en) * | 2013-10-25 | 2015-10-13 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Lithography using multilayer spacer for reduced spacer footing |
| US9564312B2 (en) | 2014-11-24 | 2017-02-07 | Lam Research Corporation | Selective inhibition in atomic layer deposition of silicon-containing films |
| TWI555082B (zh) * | 2015-05-15 | 2016-10-21 | 力晶科技股份有限公司 | 圖案化方法 |
| US9659771B2 (en) | 2015-06-11 | 2017-05-23 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Conformal strippable carbon film for line-edge-roughness reduction for advanced patterning |
| US10629435B2 (en) * | 2016-07-29 | 2020-04-21 | Lam Research Corporation | Doped ALD films for semiconductor patterning applications |
| US10074543B2 (en) | 2016-08-31 | 2018-09-11 | Lam Research Corporation | High dry etch rate materials for semiconductor patterning applications |
| US10410872B2 (en) | 2016-09-13 | 2019-09-10 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Borane mediated dehydrogenation process from silane and alkylsilane species for spacer and hardmask application |
| US10832908B2 (en) | 2016-11-11 | 2020-11-10 | Lam Research Corporation | Self-aligned multi-patterning process flow with ALD gapfill spacer mask |
| US10454029B2 (en) | 2016-11-11 | 2019-10-22 | Lam Research Corporation | Method for reducing the wet etch rate of a sin film without damaging the underlying substrate |
| US10134579B2 (en) | 2016-11-14 | 2018-11-20 | Lam Research Corporation | Method for high modulus ALD SiO2 spacer |
| US9935012B1 (en) | 2016-11-28 | 2018-04-03 | Globalfoundries Inc. | Methods for forming different shapes in different regions of the same layer |
| US10276379B2 (en) * | 2017-04-07 | 2019-04-30 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Treatment approach to improve film roughness by improving nucleation/adhesion of silicon oxide |
| US20180323061A1 (en) * | 2017-05-03 | 2018-11-08 | Tokyo Electron Limited | Self-Aligned Triple Patterning Process Utilizing Organic Spacers |
| US10593543B2 (en) | 2017-06-05 | 2020-03-17 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Method of depositing doped amorphous silicon films with enhanced defect control, reduced substrate sensitivity to in-film defects and bubble-free film growth |
| US10559465B2 (en) * | 2017-07-24 | 2020-02-11 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Pre-treatment approach to improve continuity of ultra-thin amorphous silicon film on silicon oxide |
| US10269559B2 (en) | 2017-09-13 | 2019-04-23 | Lam Research Corporation | Dielectric gapfill of high aspect ratio features utilizing a sacrificial etch cap layer |
| US10096475B1 (en) * | 2017-11-17 | 2018-10-09 | Lam Research Corporation | System and method for depositing a homogenous interface for PECVD metal-doped carbon hardmasks |
| US10515815B2 (en) | 2017-11-21 | 2019-12-24 | Lam Research Corporation | Atomic layer deposition and etch in a single plasma chamber for fin field effect transistor formation |
| US10734238B2 (en) | 2017-11-21 | 2020-08-04 | Lam Research Corporation | Atomic layer deposition and etch in a single plasma chamber for critical dimension control |
| US10658174B2 (en) | 2017-11-21 | 2020-05-19 | Lam Research Corporation | Atomic layer deposition and etch for reducing roughness |
| US10446394B2 (en) * | 2018-01-26 | 2019-10-15 | Lam Research Corporation | Spacer profile control using atomic layer deposition in a multiple patterning process |
| WO2019169335A1 (en) | 2018-03-02 | 2019-09-06 | Lam Research Corporation | Selective deposition using hydrolysis |
| CN112041481A (zh) * | 2018-05-03 | 2020-12-04 | 应用材料公司 | 用于进行图案化的高品质c膜的脉冲等离子体(dc/rf)沉积 |
| KR102147149B1 (ko) * | 2018-06-11 | 2020-08-24 | 에스케이하이닉스 주식회사 | 반도체 소자의 제조 방법 |
| US11315787B2 (en) | 2019-04-17 | 2022-04-26 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Multiple spacer patterning schemes |
| US11145509B2 (en) * | 2019-05-24 | 2021-10-12 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Method for forming and patterning a layer and/or substrate |
| JP7357528B2 (ja) * | 2019-12-06 | 2023-10-06 | 東京エレクトロン株式会社 | エッチング方法及びエッチング装置 |
| CN113078105B (zh) * | 2021-03-29 | 2022-07-05 | 长鑫存储技术有限公司 | 掩膜结构的制备方法、半导体结构及其制备方法 |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07131009A (ja) * | 1993-11-04 | 1995-05-19 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| JPH07161657A (ja) * | 1993-12-08 | 1995-06-23 | Fujitsu Ltd | パターン形成方法 |
| US6500756B1 (en) * | 2002-06-28 | 2002-12-31 | Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. | Method of forming sub-lithographic spaces between polysilicon lines |
| US6596599B1 (en) * | 2001-07-16 | 2003-07-22 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company | Gate stack for high performance sub-micron CMOS devices |
| JP2009130035A (ja) * | 2007-11-21 | 2009-06-11 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| WO2010134176A1 (ja) * | 2009-05-20 | 2010-11-25 | 株式会社 東芝 | 凹凸パターン形成方法 |
| US20110021026A1 (en) * | 2009-07-27 | 2011-01-27 | Globalfoundries Inc. | Methods for fabricating finfet semiconductor devices using l-shaped spacers |
| WO2011126612A2 (en) * | 2010-03-30 | 2011-10-13 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Nitrogen doped amorphous carbon hardmask |
| JP2011215371A (ja) * | 2010-03-31 | 2011-10-27 | Toshiba Corp | マスクの製造方法 |
Family Cites Families (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3751651T2 (de) * | 1986-10-14 | 1996-10-17 | Minolta Camera Kk | Elektrophotographisches lichtempfindliches Element, das einen Überzug enthält |
| US6893967B1 (en) * | 2004-01-13 | 2005-05-17 | Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. | L-shaped spacer incorporating or patterned using amorphous carbon or CVD organic materials |
| US7390746B2 (en) * | 2005-03-15 | 2008-06-24 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Multiple deposition for integration of spacers in pitch multiplication process |
| US8852851B2 (en) * | 2006-07-10 | 2014-10-07 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Pitch reduction technology using alternating spacer depositions during the formation of a semiconductor device and systems including same |
| US7560784B2 (en) * | 2007-02-01 | 2009-07-14 | International Business Machines Corporation | Fin PIN diode |
| CN102203921A (zh) | 2007-06-15 | 2011-09-28 | 应用材料股份有限公司 | 在基板间隙中形成氧化物牺牲衬层的氧气sacvd方法 |
| KR100955265B1 (ko) * | 2007-08-31 | 2010-04-30 | 주식회사 하이닉스반도체 | 반도체 소자의 미세패턴 형성방법 |
| US20090311634A1 (en) * | 2008-06-11 | 2009-12-17 | Tokyo Electron Limited | Method of double patterning using sacrificial structure |
| US7709396B2 (en) * | 2008-09-19 | 2010-05-04 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Integral patterning of large features along with array using spacer mask patterning process flow |
| US8105465B2 (en) * | 2008-10-14 | 2012-01-31 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Method for depositing conformal amorphous carbon film by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) |
| US8084310B2 (en) | 2008-10-23 | 2011-12-27 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Self-aligned multi-patterning for advanced critical dimension contacts |
| US7935464B2 (en) | 2008-10-30 | 2011-05-03 | Applied Materials, Inc. | System and method for self-aligned dual patterning |
| US7972959B2 (en) | 2008-12-01 | 2011-07-05 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Self aligned double patterning flow with non-sacrificial features |
| US7842622B1 (en) | 2009-05-15 | 2010-11-30 | Asm Japan K.K. | Method of forming highly conformal amorphous carbon layer |
| US8242560B2 (en) * | 2010-01-15 | 2012-08-14 | International Business Machines Corporation | FinFET with thin gate dielectric layer |
| US20130109198A1 (en) * | 2011-10-26 | 2013-05-02 | American Air Liquide, Inc. | High carbon content molecules for amorphous carbon deposition |
-
2012
- 2012-01-19 US US13/354,129 patent/US20130189845A1/en not_active Abandoned
-
2013
- 2013-01-16 WO PCT/US2013/021769 patent/WO2013109645A1/en active Application Filing
- 2013-01-16 KR KR1020147022970A patent/KR20140115353A/ko not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2013-01-16 US US14/371,989 patent/US20140349490A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2013-01-16 JP JP2014553383A patent/JP2015507363A/ja active Pending
- 2013-01-18 TW TW102102025A patent/TW201339349A/zh unknown
-
2015
- 2015-06-11 US US14/736,848 patent/US9570303B2/en active Active
-
2017
- 2017-02-14 US US15/432,605 patent/US10236182B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07131009A (ja) * | 1993-11-04 | 1995-05-19 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| JPH07161657A (ja) * | 1993-12-08 | 1995-06-23 | Fujitsu Ltd | パターン形成方法 |
| US6596599B1 (en) * | 2001-07-16 | 2003-07-22 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company | Gate stack for high performance sub-micron CMOS devices |
| US6500756B1 (en) * | 2002-06-28 | 2002-12-31 | Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. | Method of forming sub-lithographic spaces between polysilicon lines |
| JP2009130035A (ja) * | 2007-11-21 | 2009-06-11 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| WO2010134176A1 (ja) * | 2009-05-20 | 2010-11-25 | 株式会社 東芝 | 凹凸パターン形成方法 |
| US20110021026A1 (en) * | 2009-07-27 | 2011-01-27 | Globalfoundries Inc. | Methods for fabricating finfet semiconductor devices using l-shaped spacers |
| WO2011126612A2 (en) * | 2010-03-30 | 2011-10-13 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Nitrogen doped amorphous carbon hardmask |
| JP2011215371A (ja) * | 2010-03-31 | 2011-10-27 | Toshiba Corp | マスクの製造方法 |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018516463A (ja) * | 2015-06-03 | 2018-06-21 | アプライド マテリアルズ インコーポレイテッドApplied Materials,Incorporated | 先進的なパターニングプロセスにおけるスペーサ堆積および選択的除去のための装置および方法 |
| JP2020519938A (ja) * | 2017-05-01 | 2020-07-02 | アドバンスト・マイクロ・ディバイシズ・インコーポレイテッドAdvanced Micro Devices Incorporated | ダブルスペーサ液浸リソグラフィトリプルパターニングのフロー及び方法 |
| JP7157081B2 (ja) | 2017-05-01 | 2022-10-19 | アドバンスト・マイクロ・ディバイシズ・インコーポレイテッド | ダブルスペーサ液浸リソグラフィトリプルパターニングのフロー及び方法 |
| KR20210090698A (ko) | 2018-12-18 | 2021-07-20 | 도쿄엘렉트론가부시키가이샤 | 카본 하드마스크, 성막 장치 및 성막 방법 |
| US11993849B2 (en) | 2018-12-18 | 2024-05-28 | Tokyo Electron Limited | Carbon hard mask, film forming apparatus, and film forming method |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20130189845A1 (en) | 2013-07-25 |
| US9570303B2 (en) | 2017-02-14 |
| WO2013109645A1 (en) | 2013-07-25 |
| US20170170015A1 (en) | 2017-06-15 |
| US20140349490A1 (en) | 2014-11-27 |
| TW201339349A (zh) | 2013-10-01 |
| KR20140115353A (ko) | 2014-09-30 |
| US20150279676A1 (en) | 2015-10-01 |
| US10236182B2 (en) | 2019-03-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10236182B2 (en) | Conformal amorphous carbon for spacer and spacer protection applications | |
| US10074534B2 (en) | Ultra-conformal carbon film deposition | |
| JP7266068B2 (ja) | 横方向ハードマスク凹部縮小のためのハイブリッドカーボンハードマスク | |
| US10014174B2 (en) | Conformal strippable carbon film for line-edge-roughness reduction for advanced patterning | |
| KR102513424B1 (ko) | 스페이서 및 하드마스크 애플리케이션을 위한 실란 및 알킬실란 종으로부터의 보란 매개 탈수소화 프로세스 | |
| US8513129B2 (en) | Planarizing etch hardmask to increase pattern density and aspect ratio | |
| TWI671795B (zh) | 利用共形碳薄膜減低臨界尺寸之方法 | |
| US10453751B2 (en) | Tone inversion method and structure for selective contact via patterning | |
| US9922972B1 (en) | Embedded silicon carbide block patterning |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20160115 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20160115 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20161026 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20161101 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20170606 |