EP3305412A1 - Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung - Google Patents
Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP3305412A1 EP3305412A1 EP17194704.7A EP17194704A EP3305412A1 EP 3305412 A1 EP3305412 A1 EP 3305412A1 EP 17194704 A EP17194704 A EP 17194704A EP 3305412 A1 EP3305412 A1 EP 3305412A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- fluid outlet
- fluid
- jet
- opening
- generating device
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 239000007921 spray Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 13
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 187
- 229920001971 elastomer Polymers 0.000 claims description 22
- 239000000806 elastomer Substances 0.000 claims description 14
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 claims 1
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 13
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 11
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 11
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 235000008733 Citrus aurantifolia Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 235000011941 Tilia x europaea Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000004571 lime Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920001296 polysiloxane Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 208000004434 Calcinosis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000001154 acute effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000013013 elastic material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003993 interaction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007493 shaping process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000006228 supernatant Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B05—SPRAYING OR ATOMISING IN GENERAL; APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05B—SPRAYING APPARATUS; ATOMISING APPARATUS; NOZZLES
- B05B15/00—Details of spraying plant or spraying apparatus not otherwise provided for; Accessories
- B05B15/50—Arrangements for cleaning; Arrangements for preventing deposits, drying-out or blockage; Arrangements for detecting improper discharge caused by the presence of foreign matter
- B05B15/52—Arrangements for cleaning; Arrangements for preventing deposits, drying-out or blockage; Arrangements for detecting improper discharge caused by the presence of foreign matter for removal of clogging particles
- B05B15/528—Arrangements for cleaning; Arrangements for preventing deposits, drying-out or blockage; Arrangements for detecting improper discharge caused by the presence of foreign matter for removal of clogging particles by resilient deformation of the nozzle
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B05—SPRAYING OR ATOMISING IN GENERAL; APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05B—SPRAYING APPARATUS; ATOMISING APPARATUS; NOZZLES
- B05B1/00—Nozzles, spray heads or other outlets, with or without auxiliary devices such as valves, heating means
- B05B1/14—Nozzles, spray heads or other outlets, with or without auxiliary devices such as valves, heating means with multiple outlet openings; with strainers in or outside the outlet opening
- B05B1/18—Roses; Shower heads
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B05—SPRAYING OR ATOMISING IN GENERAL; APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05B—SPRAYING APPARATUS; ATOMISING APPARATUS; NOZZLES
- B05B1/00—Nozzles, spray heads or other outlets, with or without auxiliary devices such as valves, heating means
- B05B1/14—Nozzles, spray heads or other outlets, with or without auxiliary devices such as valves, heating means with multiple outlet openings; with strainers in or outside the outlet opening
- B05B1/18—Roses; Shower heads
- B05B1/185—Roses; Shower heads characterised by their outlet element; Mounting arrangements therefor
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B05—SPRAYING OR ATOMISING IN GENERAL; APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05B—SPRAYING APPARATUS; ATOMISING APPARATUS; NOZZLES
- B05B1/00—Nozzles, spray heads or other outlets, with or without auxiliary devices such as valves, heating means
- B05B1/02—Nozzles, spray heads or other outlets, with or without auxiliary devices such as valves, heating means designed to produce a jet, spray, or other discharge of particular shape or nature, e.g. in single drops, or having an outlet of particular shape
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B05—SPRAYING OR ATOMISING IN GENERAL; APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05B—SPRAYING APPARATUS; ATOMISING APPARATUS; NOZZLES
- B05B1/00—Nozzles, spray heads or other outlets, with or without auxiliary devices such as valves, heating means
- B05B1/30—Nozzles, spray heads or other outlets, with or without auxiliary devices such as valves, heating means designed to control volume of flow, e.g. with adjustable passages
- B05B1/3006—Nozzles, spray heads or other outlets, with or without auxiliary devices such as valves, heating means designed to control volume of flow, e.g. with adjustable passages the controlling element being actuated by the pressure of the fluid to be sprayed
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B05—SPRAYING OR ATOMISING IN GENERAL; APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05B—SPRAYING APPARATUS; ATOMISING APPARATUS; NOZZLES
- B05B1/00—Nozzles, spray heads or other outlets, with or without auxiliary devices such as valves, heating means
- B05B1/30—Nozzles, spray heads or other outlets, with or without auxiliary devices such as valves, heating means designed to control volume of flow, e.g. with adjustable passages
- B05B1/32—Nozzles, spray heads or other outlets, with or without auxiliary devices such as valves, heating means designed to control volume of flow, e.g. with adjustable passages in which a valve member forms part of the outlet opening
- B05B1/323—Nozzles, spray heads or other outlets, with or without auxiliary devices such as valves, heating means designed to control volume of flow, e.g. with adjustable passages in which a valve member forms part of the outlet opening the valve member being actuated by the pressure of the fluid to be sprayed
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E03—WATER SUPPLY; SEWERAGE
- E03C—DOMESTIC PLUMBING INSTALLATIONS FOR FRESH WATER OR WASTE WATER; SINKS
- E03C1/00—Domestic plumbing installations for fresh water or waste water; Sinks
- E03C1/02—Plumbing installations for fresh water
- E03C1/08—Jet regulators or jet guides, e.g. anti-splash devices
Definitions
- the invention relates to an effervescent jet generating device having a effervescent jet disc which has at least one jet disc opening and a fluid chamber on the outlet side, and a fluid outlet element arranged on the at least one jet disc opening and movable in an axial main direction component which has a movable valve body with a fluid outlet opening opening out of the fluid chamber is released depending on a fluid pressure in the fluid chamber in a release position of the fluid outlet element and shut off in a shut-off position of the fluid outlet element.
- axial main direction component of the movement of the fluid outlet element is to be understood that the component of this movement in an axial direction is greater than perpendicular to it.
- the axial direction of the movable fluid outlet element may in particular be parallel to a longitudinal axis of the fluid outlet opening and / or to a jet direction of a fluid emerging from its fluid outlet opening and / or an axial direction of the effervescent jet disc.
- the effervescent jet generating device can be used, in particular, for a sanitary shower head to which a fluid, for example water, can be supplied via a supply line, which then passes into the fluid chamber and from there into the one or more fluid outlet openings and exits from it or the same with the formation of an effervescent jet ,
- a fluid for example water
- Such devices for generating a shower jet are used in particular in sanitary shower heads, such as hand showers, overhead showers and body sprays of shower facilities.
- EP 1 700 636 A2 discloses a shower head with a effervescent spray generating device of the type mentioned, in which each jet disc opening is associated with a valve element in the form of a curved, at least one incision membrane portion which is axially movable and bendable by a pending water pressure, whereby a closed in the non-pressurized state water outlet is provided ,
- the invention is based on the technical problem of providing an effervescent jet generating device of the type mentioned above, which reliably prevents unwanted dripping, is relatively easy to manufacture and functionally reliable, and an outlet cross-section which is largely uninfluenced by the fluid pressure in the fluid chamber having for the fluid outlet opening.
- the movable valve body cooperates with an immovable valve seat, which releases the fluid outlet opening in the release position of the fluid outlet element and blocks it in a shut-off position of the fluid outlet element.
- the effervescent jet generating device according to the invention can reliably prevent unwanted dripping and is relatively easy to manufacture and functionally reliable. Furthermore, the outlet cross section of the fluid outlet opening is largely uninfluenced by the fluid pressure in the fluid chamber.
- the jet disk can be made in one piece or composed of several components, which can consist of different materials, in particular an elastic material and / or a plastic and / or a metal.
- the jet disc may comprise a rubber plate or rubber mat and a metal and / or hard plastic disc having corresponding jet disc openings, wherein the rubber plate or rubber mat from the inside of the Fluid chamber is applied to the metal or hard plastic disk, so that the corresponding jet disk openings of the rubber plate or rubber mat and the metal and / or hard plastic disc are aligned with each other.
- the possible material combinations of rubber plate or rubber mat and the metal and / or hard plastic disc are advantageous in terms of increased freedom of design, in particular in the design of the spray jet generating device.
- the jet disk opening can be designed, for example, as a counterbore. The geometry of the countersinking of the counterbore can help to receive and / or support and / or to encompass the fluid exit element arranged in the jet disk opening.
- the blocking of the fluid outlet opening can be accomplished by the immovable valve seat in particular by the fact that the movable valve body rests in the shut-off position with its fluid outlet opening against him. In the release position of the valve body, however, the fluid outlet opening can be spaced from the immovable valve seat and thereby released.
- the fluid outlet element or its valve body is designed to assume the releasing position as soon as the fluid pressure in the fluid chamber is greater than a previously defined limit pressure.
- the previously defined limit pressure may, for example, be between 0.2 bar and 0.35 bar, in particular between 0.24 bar and 0.26 bar. As long as the limit pressure is not reached, the fluid outlet opening remains shut off.
- the fluid outlet element or the movable valve body is elastically elastic, e.g. is biased by appropriate shaping in the direction of the shut-off and is pushed out of this by the fluid pressure in the fluid chamber in the release position. If the fluid pressure in the fluid chamber drops, e.g. under the mentioned limit pressure, the fluid outlet element or the movable valve body automatically returns to the shut-off position.
- the fluid chamber is limited on one of the jet disk opposite side by an immovable valve seat having intermediate plate or housing plate.
- an immovable valve seat having intermediate plate or housing plate.
- the immovable valve seat as a separate component on the intermediate plate or the housing plate attached.
- the intermediate plate or the housing plate can fulfill additional functions if required, it can serve as a mounting plate for a single or multi-part jet disk, for example.
- the movable valve body is in the release position against a valve contact surface of the jet disk.
- the valve contact surface of the jet disc allows limiting the movement of the movable valve body. So it is e.g. possible that the release position of the fluid outlet element is predetermined by the valve contact surface.
- the fluid outlet element extends with its fluid outlet opening in the releasing and / or shut-off position through the jet disk opening.
- the fluid outlet opening and / or the movable valve body are made of an elastomer, in particular of a silicone having a Shore hardness between fifty and seventy. If limescale constricts the fluid outlet opening or even clogs, they can be removed in a conventional manner that the user by rubbing or the like. A force exerted on the fluid outlet opening force exerts on selbige, whereby the lime deposits are brought to flake.
- the valve seat has a valve seat projection, which protrudes into the fluid outlet opening when the fluid outlet opening is shut off.
- valve seat projection By projecting into the fluid outlet opening valve seat projection, for example, the formation of calcium deposits can be counteracted by any limescale deposits are replaced by the protruding valve seat projection when moving the fluid outlet element between the closed position and the released position.
- the protruding valve seat projection for the interaction of the movable valve body with the immovable valve seat may be advantageous, in particular for the tight shut-off of the fluid outlet opening. This is preferably supported by a corresponding negative shape of the valve seat projection or the immovable valve seat with respect to the shape of the fluid outlet opening or the movable valve body.
- the fluid outlet opening has a fluid-pressure-independent dimensionally stable and / or circular-cylindrical and / or conical geometry.
- a dimensionally stable i.
- a geometry of the fluid outlet opening which is largely independent of the fluid pressures occurring during operation ensures that the characteristic of a spray jet produced to a very high degree is independent of the fluid pressure in the fluid chamber when the spray jet generating device is used as intended. Because the fluid outlet opening then always has a substantially constant passage cross-sectional area and cross-sectional shape.
- the fluid outlet opening is formed by an outlet nozzle with a nozzle longitudinal axis, which is parallel to a local surface normal of an outer side of the jet disk.
- the nozzle longitudinal axis can in the case of rotationally symmetrical fluid outlet openings, for. be the axis of rotation of the fluid outlet opening.
- the fluid outlet element on an elastomeric ring membrane, which surrounds the movable valve body and carries.
- the elastomeric ring membrane is e.g. on the jet disk, so that the fluid outlet element is arranged in the associated jet disk opening.
- the elastomeric ring membrane may facilitate or facilitate the placement of the fluid exit element in the jet disk opening.
- the fluid outlet element is made in one piece. This allows simplification and cost reduction e.g. in the production of the fluid outlet element and / or the assembly of the spray jet generating device.
- the jet disk has a plurality of jet disk openings and associated fluid outlet elements. Furthermore, the jet disc has a one-piece elastomer plate on which the plurality of fluid outlet elements is formed. For example, any number between ten and two hundred jet disk openings can be provided. If the fluid outlet elements have elastomer ring diaphragms, it is advantageous to mold the fluid outlet elements with the elastomer ring diaphragm on the elastomer plate.
- the one-piece design of elastomer plate and fluid outlet elements can both in the production be advantageous as well for the assembly, since a component reduction and a simplified handling can be achieved.
- the jet disk may comprise a single or a plurality of one-piece elastomer plates, on each of which a plurality of fluid outlet elements is formed. These one-piece elastomer plates may differ, for example, in the geometric shape of their arranged fluid outlet openings, whereby the effervescent jet generating device has areas that can produce different effervescent jets.
- the effervescent jet generating device shown is integrated into a sanitary shower head in order to produce a water spray jet whose jet shape is largely independent of the pressure of the supplied water.
- the shower head supplied water is introduced into a fluid chamber 3, which is the exit side of a here exemplary multi-part jet disk 1 of the effervescent jet generating device limited.
- the jet disk 1 has a plurality of preferably between ten and two hundred, for example thirty, jet disk openings 2, through which the water can be conducted from the fluid chamber 3 to the outside.
- the multi-part jet disk 1 comprises an elastomer plate 13, e.g. of a silicone material having a Shore hardness of preferably between fifty and seventy, e.g. sixty, and a metal plate 14, wherein the elastomeric plate 13 fluid chamber side abuts against the metal plate 14. Furthermore, a housing plate 8 of the shower head of the jet disk 1 opposite and the fluid chamber 3 is arranged delimiting. In this case, the elastomer plate 13 is held with its outer edge region between the housing plate 8 and the metal plate 14, the fluid chamber 3 sealingly.
- a plurality of elastomeric annular membranes 12 is formed, each surrounded and carry a movable fluid outlet element 4.
- the fluid outlet element 4 is connected via the elastomeric annular membrane 12 with the elastomer plate 13 and held on this.
- the in Fig. 1 to 4 shown elastomer plate 13 integrally with the fluid outlet element 4 and the elastomeric ring membrane 12 executed.
- the elastomer plate 13 is applied to the metal plate 14 such that a movable fluid outlet element 4 is arranged at each jet disk opening 2.
- the respective fluid outlet element 4 has a fluid outlet opening 5, which opens out of the fluid chamber 3 and is designed in the manner of an outlet nozzle.
- the fluid outlet opening 5 or the outlet nozzle has a conical geometry coming from the fluid chamber 3 on the inlet side, followed by a circular-cylindrical geometry as the end section, in which the fluid outlet opening 5 tapers to an outlet diameter which is typically in the range of 0, for example. 6 mm to 1.2 mm, in particular from 0.85 mm to 0.95 mm.
- the fluid outlet opening 5 or outlet nozzle has a geometry which is fluid-pressure-independent and dimensionally stable when the spray-jet generating device is used as intended.
- the axis of symmetry of the fluid outlet opening 5 is a nozzle longitudinal axis 11, the at the same time is an axial main direction component of the movement of the movable fluid outlet element 4.
- the nozzle longitudinal axis 11 also corresponds to a local surface normal of an outside of the jet disk 1 at the relevant point.
- the fluid outlet element 4 has a movable valve body 6, on which the fluid outlet opening 5 is arranged, wherein the movable valve body 6 is a rotationally symmetrical element in the manner of a disc spring.
- the movable valve body 6 is responsible for the movement of the fluid outlet element 4 and thus also for the movement of the fluid outlet opening 5.
- the fluid outlet element 4 is switched between a fluid outlet opening 5 releasing or shut-off position, wherein the movable valve body 6 cooperates with a stationary valve seat 7.
- the cause of this movement is a fluid pressure prevailing in the fluid chamber 3, which is generated by the supplied water.
- the fluid pressure acts on the movable valve body 6, and as soon as a predetermined limit pressure between 0.2 bar to 0.35 bar, in particular between 0.24 bar to 0.26 bar, is exceeded in the fluid chamber, the valve body 6 and thus the Fluid outlet element 4 with axial main direction component moves by the pressure from a shut-off position to a release position in which the valve body 6, the fluid outlet opening 5 releases. If the fluid pressure falls below the predetermined limit pressure, the valve body 6 automatically moves back into its original, the fluid outlet opening 5 shut-off position.
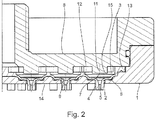
- Fig. 1 the shut-off position of the movable valve body 6 is shown.
- the valve body 6 cooperates with the immovable valve seat 7 to the effect that the valve body 6 abuts against the valve seat 7 or presses, whereby the valve seat 7, the fluid outlet opening 5 shuts fluid-tight. Due to the tight fit of the movable valve body 6 against the immovable valve seat 7 no water can leave the fluid chamber 3 through the fluid outlet opening 5, the shower head is thus secured against dripping.
- the in Fig. 1 to 4 shown immovable valve seat 7 is integral with the housing plate 8 of the shower head and has a flat seat surface against which the movable valve body 6 abuts.
- the immovable valve seat 7 is formed by a plateau-like projection 15 of the housing plate 8.
- the distance between the jet disk 1 and the housing plate 8 without consideration of the plateaus 15 preferably at least 2 mm. This distance may be referred to as the height of the fluid chamber 3.
- the fluid outlet opening 5 extends in shut-off position of the movable valve body 6 through the jet disk opening 2 and on the outlet side has a projection with respect to the metal plate 14.
- This projection of the fluid outlet opening 5 may be, for example, in the range of 1 mm to 3 mm, for example about 2 mm.
- the supernatant is preferably between 3 mm and 7 mm, for example about 5 mm.
- the respective fluid outlet element 4 or its valve body 6 has a monostable design, ie a shape such that the fluid outlet element 4 or its valve body 6 has exactly one stable position, which in the present case corresponds to the shut-off position Fig. 1 given is. From this, the fluid outlet element 4 and its valve body 6 at pending in the fluid chamber fluid pressure by the stroke length in the release position according to Fig. 2 advances if and as soon as the fluid pressure exceeds an associated limit pressure value of eg 0.25 bar to 0.35 bar. In the release position, the valve body 6 is no longer against the immovable valve seat 7, and the water can leave through the respective fluid outlet opening 5 through the fluid chamber 3 to form the desired shower spray.
- a monostable design ie a shape such that the fluid outlet element 4 or its valve body 6 has exactly one stable position, which in the present case corresponds to the shut-off position Fig. 1 given is.
- the fluid outlet element 4 or its valve body 6 automatically returns to the shut-off position by elastic restoring force, so that water dripping off of the fluid outlet opening 5 is reliably prevented becomes.
- the jet disk opening 2, on which the fluid outlet element 4 shown is arranged as a counterbore in the metal plate 14th executed, wherein the countersinking a geometry, in particular a valve bearing surface 9, which supports the movable valve body 6 in the releasing position and limited in its movement.
- the counterbore counterbore is preferably shaped so as not to have acute angles.
- Fig. 5 to 8 is a variant of the effervescent jet generating device of Fig. 1 to 4 are shown, for better understanding of identical and functionally equivalent elements, the same reference numerals are used and to that extent also to the above comments on the embodiment of Fig. 1 to 4 can be referenced so that below essentially only addresses the existing differences, which are here specifically in the design of the immovable valve seat 7.
- the immovable valve seat 7 has a valve seat projection 10 which protrudes into the fluid outlet opening 5 when the fluid outlet opening 5 is shut off and does not protrude into the fluid outlet opening 5 when the fluid outlet opening 5 is released.
- lime deposits on the fluid outlet opening 5 can be counteracted by being detached from the fluid outlet opening 5 by the valve seat projection 10 when the fluid outlet element 4 moves between the releasing position and the blocking position.
- the immovable valve seat 7 in the variant of Fig. 5 to 8 a shape conformed to that of the movable valve body 6.
- the immovable valve seat 7 has an annular recess or recess in the form of a negative shape of the voltage applied in the shut-off movable valve body 6. This increases the contact area between the movable valve body 6 and the immovable valve seat 7 in the Absperrposition compared with the flat seat in the Variant of Fig. 1 to 4 and contributes to a centering of the pressing against the valve seat 7 in the shut-off position of the valve body 6 at. This enlarged contact surface and the centered position of the valve body 6 advantageously assist the secure sealing of the fluid outlet opening 5.
- the immovable valve seat 7 is in the form of a preferably frustoconical Plugged, which closes the fluid outlet opening 5 in the shut-off position.
- the plug-shaped immovable valve seat 7 protrudes into the fluid outlet opening 5.
- an intermediate plate instead of the housing plate 8 shown on the immovable valve seat.
- This intermediate plate is preferably integrated in a shower head and acts as a boundary of the fluid chamber on the side opposite the jet disc.
- the invention provides a effervescent jet generating device that reliably prevents the unwanted dripping, is relatively easy to produce and reliable. Furthermore, the outlet cross section of the fluid outlet opening is largely uninfluenced by the fluid pressure in the fluid chamber. The invention is particularly useful in sanitary engineering, but also in other applications where there is a need to produce a shower jet functionally reliable and without dripping.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Hydrology & Water Resources (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Water Supply & Treatment (AREA)
- Nozzles (AREA)
- Bathtubs, Showers, And Their Attachments (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- Die Erfindung betrifft eine Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung mit einer Brausestrahlscheibe, die mindestens eine Strahlscheibenöffnung aufweist und eine Fluidkammer austrittsseitig begrenzt, und einem an der mindestens einen Strahlscheibenöffnung angeordneten und in einer axialen Hauptrichtungskomponente beweglichen Fluidaustrittselement, das einen beweglichen Ventilkörper mit einer aus der Fluidkammer ausmündenden Fluidaustrittsöffnung aufweist, die abhängig von einem Fluiddruck in der Fluidkammer in einer Freigabeposition des Fluidaustrittselements freigegeben und in einer Absperrposition des Fluidaustrittselements abgesperrt ist.
- Unter axialer Hauptrichtungskomponente der Bewegung des Fluidaustrittselements ist hierbei zu verstehen, dass die Komponente dieser Bewegung in einer axialen Richtung größer ist als senkrecht dazu. Die Axialrichtung des beweglichen Fluidaustrittselements kann insbesondere parallel zu einer Längsachse der Fluidaustrittsöffnung und/oder zu einer Strahlrichtung eines aus seiner Fluidaustrittsöffnung austretenden Fluid und/oder einer Axialrichtung der Brausestrahlscheibe sein. Der bei bestimmungsgemäßem Gebrauch der Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung in der Fluidkammer herrschende Fluiddruck sorgt dafür, dass der bewegliche Ventilkörper seine Freigabeposition einnimmt und die Fluidaustrittsöffnung freigegeben ist, während der Ventilkörper im drucklosen Zustand der Fluidkammer seine Absperrposition einnimmt und die Fluidaustrittsöffnung abgesperrt ist. Mit einer solchen Anordnung kann einem unerwünschten Nachtropfen einer entsprechend ausgerüsteten Brause nach Absperren der Wasserzufuhr begegnet werden.
- Die Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung ist insbesondere für einen sanitären Brausekopf verwendbar, dem über eine Zuleitung ein Fluid, z.B. Wasser, zugeführt werden kann, das dann in die Fluidkammer und von dort in die eine oder mehreren Fluidaustrittsöffnungen gelangt und unter Bildung eines Brausestrahls aus dieser bzw. diesen austritt. Derartige Vorrichtungen zur Erzeugung eines Brausestrahls werden insbesondere in sanitären Brauseköpfen eingesetzt, wie z.B. Handbrausen, Kopfbrausen und Seitenbrausen von Duscheinrichtungen.
- Die Offenlegungsschrift
EP 1 700 636 A2 offenbart einen Brausekopf mit einer Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung der eingangs genannten Art, bei der jeder Strahlscheibenöffnung ein Ventilelement in Form eines gewölbten, mindestens einen Einschnitt aufweisenden Membranabschnittes zugeordnet ist, der durch einen anstehenden Wasserdruck axial bewegbar und aufbiegbar ist, wodurch eine im drucklosen Zustand geschlossene Wasseraustrittsöffnung bereitgestellt ist. - Der Erfindung liegt das technische Problem zugrunde, eine Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung der eingangs genannten Art bereitzustellen, die gegenüber dem oben erläuterten Stand der Technik verbessert ist und insbesondere unerwünschtes Nachtropfen zuverlässig verhindert, relativ einfach herstellbar und funktionssicher ist und dabei einen vom Fluiddruck in der Fluidkammer weitestgehend unbeeinflussten Austrittsquerschnitt für die Fluidaustrittsöffnung aufweist.
- Die Erfindung löst dieses Problem durch die Bereitstellung einer Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung mit den Merkmalen des Anspruchs 1. Vorteilhafte sowie bevorzugte Ausgestaltungen der Erfindung sind Gegenstand der weiteren Ansprüche, deren Wortlaut hiermit durch Verweis vollumfänglich in die Beschreibung aufgenommen wird.
- Bei der erfindungsgemäßen Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung, die insbesondere für einen sanitären Brausekopf einsetzbar ist, wirkt der bewegliche Ventilkörper mit einem unbeweglichen Ventilsitz zusammen, der die Fluidaustrittsöffnung in der Freigabeposition des Fluidaustrittselements freigibt und in einer Absperrposition des Fluidaustrittselements absperrt. Die erfindungsgemäße Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung kann unerwünschtes Nachtropfen zuverlässig verhindern und sie ist relativ einfach herstellbar und funktionssicher. Des Weiteren ist der Austrittsquerschnitt der Fluidaustrittsöffnung vom Fluiddruck in der Fluidkammer weitestgehend unbeeinflusst.
- Die Strahlscheibe kann einteilig ausgeführt oder aus mehreren Bauteilen zusammengesetzt sein, die aus unterschiedlichen Materialien, insbesondere einem elastischem Material und/oder einem Kunststoff und/oder einem Metall, bestehen können. So kann zum Beispiel die Strahlscheibe eine Gummiplatte bzw. Gummimatte und eine Metall- und/oder Hartkunststoffscheibe aufweisen, die über korrespondierende Strahlscheibenöffnungen verfügen, wobei die Gummiplatte bzw. Gummimatte von der Innenseite der Fluidkammer an die Metall- oder Hartkunststoffscheibe angelegt ist, so dass die korrespondierenden Strahlscheibenöffnungen der Gummiplatte bzw. Gummimatte und der Metall- und/oder Hartkunststoffscheibe zueinander ausgerichtet sind. Die möglichen Materialkombinationen von Gummiplatte bzw. Gummimatte und der Metall- und/oder Hartkunststoffscheibe sind bezüglich einer erhöhten Gestaltungsfreiheit, insbesondere im Design der Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung vorteilhaft. Die Strahlscheibenöffnung kann z.B. als Senkbohrung ausgeführt sein. Die Geometrie der Senkung der Senkbohrung kann dazu beitragen, das in der Strahlscheibenöffnung angeordnete Fluidaustrittselement aufzunehmen und/oder abzustützen und/oder zu umfassen.
- Das Absperren der Fluidaustrittsöffnung, die vorzugsweise als eine umfangseitig geschlossene Öffnung ausgebildet ist, kann von dem unbeweglichen Ventilsitz insbesondere dadurch bewerkstelligt werden, dass der bewegliche Ventilkörper in der Absperrposition mit seiner Fluidaustrittsöffnung gegen ihn anliegt. In der Freigabeposition des Ventilkörpers kann die Fluidaustrittsöffnung hingegen vom unbeweglichen Ventilsitz beabstandet und dadurch freigegeben sein. In entsprechenden Realisierungen der Erfindung ist das Fluidaustrittselement bzw. sein Ventilkörper dazu ausgebildet, die freigebende Stellung einzunehmen, sobald der Fluiddruck in der Fluidkammer größer als ein zuvor festgelegter Grenzdruck ist. Der zuvor festgelegte Grenzdruck kann beispielsweise zwischen 0,2 bar bis 0,35 bar liegen, insbesondere zwischen 0,24 bar bis 0,26 bar. Solange der Grenzdruck nicht erreicht ist, bleibt die Fluidaustrittsöffnung abgesperrt.
- Vorteilhaft kann vorgesehen sein, dass das Fluidaustrittselement bzw. der bewegliche Ventilkörper elastisch z.B. durch entsprechende Formgebung in Richtung der Absperrposition vorgespannt ist und aus dieser durch den Fluiddruck in der Fluidkammer in die Freigabeposition gedrückt wird. Fällt der Fluiddruck in der Fluidkammer ab, z.B. unter den erwähnten Grenzdruck, kehrt das Fluidaustrittselement bzw. der bewegliche Ventilkörper selbsttätig in die Absperrposition zurück.
- In einer Ausgestaltung der Erfindung ist die Fluidkammer auf einer der Strahlscheibe gegenüberliegenden Seite durch eine den unbeweglichen Ventilsitz aufweisende Zwischenplatte oder Gehäuseplatte begrenzt. Dadurch kann eine Bauteilreduktion erreicht werden. Alternativ kann der unbewegliche Ventilsitz als eigenes Bauteil an der Zwischenplatte oder der Gehäuseplatte befestigt sein. Die Zwischenplatte oder die Gehäuseplatte kann bei Bedarf zusätzliche Funktionen erfüllt, so kann sie z.B. als Montageplatte für eine ein- oder mehrteilige Strahlscheibe dienen.
- In einer Ausgestaltung der Erfindung liegt der bewegliche Ventilkörper in der Freigabeposition gegen eine Ventilanlagefläche der Strahlscheibe an. Die Ventilanlagefläche der Strahlscheibe ermöglicht eine Begrenzung der Bewegung des beweglichen Ventilkörpers. So ist es z.B. möglich, dass die Freigabeposition des Fluidaustrittselements durch die Ventilanlagefläche vorgegeben wird.
- In einer Ausgestaltung der Erfindung erstreckt sich das Fluidaustrittselement mit seiner Fluidaustrittsöffnung in der freigebenden und/oder absperrenden Stellung durch die Strahlscheibenöffnung hindurch. Dadurch kann z.B. die Entfernung von Kalkablagerungen erleichtert werden. Vorzugsweise sind die Fluidaustrittsöffnung und/oder der bewegliche Ventilkörper aus einem Elastomer, insbesondere aus einem Silikon mit einer Shore-Härte zwischen fünfzig und siebzig. Falls Kalkablagerungen die Fluidaustrittsöffnung verengen oder gar verstopfen, können diese in an sich bekannter Weise dadurch entfernt werden, dass der Benutzer durch Rubbeln oder dgl. eine die Fluidaustrittsöffnung deformierende Kraft auf selbige ausübt, wodurch die Kalkablagerungen zum Abplatzen gebracht werden.
- In einer Ausgestaltung der Erfindung weist der Ventilsitz einen Ventilsitzvorsprung auf, der bei abgesperrter Fluidaustrittsöffnung in die Fluidaustrittsöffnung hineinragt. Durch den in die Fluidaustrittsöffnung hineinragenden Ventilsitzvorsprung kann beispielsweise der Entstehung von Kalkablagerungen entgegengewirkt werden, indem eventuelle Kalkablagerungen durch den hineinragenden Ventilsitzvorsprung beim Bewegen des Fluidaustrittselements zwischen der abgesperrten Stellung und der freigegebenen Stellung abgelöst werden. Des Weiteren kann der hineinragende Ventilsitzvorsprung für das Zusammenwirken des beweglichen Ventilkörpers mit dem unbeweglichen Ventilsitz vorteilhaft sein, insbesondere für die dichte Absperrung der Fluidaustrittsöffnung. Dies wird vorzugsweise durch eine korrespondierende negative Form des Ventilsitzvorsprungs bzw. des unbeweglichen Ventilsitzes in Bezug auf die Form der Fluidaustrittsöffnung bzw. des beweglichen Ventilkörpers unterstützt.
- In einer Ausgestaltung der Erfindung weist die Fluidaustrittsöffnung eine fluiddruckunabhängig formstabile und/oder kreiszylindrische und/oder konische Geometrie auf. Eine formstabile, d.h. eine von den im Betrieb auftretenden Fluiddrücken weitgehend unabhängige Geometrie der Fluidaustrittsöffnung sorgt beispielsweise dafür, dass beim bestimmungsgemäßen Gebrauch der Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung die Charakteristik eines erzeugten Brausestrahls in sehr hohem Maß unabhängig vom Fluiddruck in der Fluidkammer ist. Denn die Fluidaustrittsöffnung hat dann stets eine im Wesentlichen konstant bleibende Durchtrittsquerschnittsfläche und Querschnittsform.
- In einer Ausgestaltung der Erfindung ist die Fluidaustrittsöffnung von einer Austrittsdüse mit einer Düsenlängsachse gebildet, die parallel zu einer lokalen Flächennormale einer Außenseite der Strahlscheibe ist. Die Düsenlängsachse kann im Falle von rotationssymmetrischen Fluidaustrittsöffnungen z.B. die Rotationsachse der Fluidaustrittsöffnung sein.
- In einer Ausgestaltung der Erfindung weist das Fluidaustrittselement eine Elastomer-ringmembran auf, welche den beweglichen Ventilkörper umgibt und trägt. Die Elastomerringmembran liegt z.B. an der Strahlscheibe an, so dass das Fluidaustrittselement in der zugehörigen Strahlscheibenöffnung angeordnet ist. Die Elastomerringmembran kann die Platzierung des Fluidaustrittselements in der Strahlscheibenöffnung vereinfachen bzw. erleichtern.
- In einer Ausgestaltung der Erfindung ist das Fluidaustrittselement einteilig ausgeführt. Dies ermöglicht eine Vereinfachung und Kostenreduktion z.B. in der Herstellung des Fluidaustrittselements und/oder der Montage der Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung.
- In einer Ausgestaltung der Erfindung hat die Strahlscheibe eine Mehrzahl von Strahlscheibenöffnungen und zugeordneten Fluidaustrittselementen. Des Weiteren weist die Strahlscheibe eine einteilige Elastomerplatte auf, an der die Mehrzahl von Fluidaustrittselementen ausgebildet ist. Es können z.B. eine beliebige Anzahl zwischen zehn und zweihundert Strahlscheibenöffnungen vorgesehen sein. Verfügen die Fluidaustrittselemente über Elastomerringmembranen, so ist es vorteilhaft, die Fluidaustrittselemente mit der Elastomerringmembran an der Elastomerplatte anzuformen. Die einteilige Ausführung von Elastomerplatte und Fluidaustrittselementen kann sowohl in der Herstellung als auch für die Montage vorteilhaft sein, da eine Bauteilreduktion und eine vereinfachte Handhabung erreicht werden. Die Strahlscheibe kann eine einzige oder eine Mehrzahl von einteiligen Elastomerplatten aufweisen, an denen jeweils eine Mehrzahl von Fluidaustrittselementen ausgebildet ist. Diese einteiligen Elastomerplatten können sich z.B. in der geometrischen Form ihrer angeordneten Fluidaustrittsöffnungen unterscheiden, wodurch die Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung Bereiche aufweist, die unterschiedliche Brausestrahlen erzeugen können.
- Vorteilhafte Ausführungsformen der Erfindung sind in den Zeichnungen dargestellt und werden im Folgenden näher erläutert. Hierbei zeigen:
- Fig. 1
- eine ausschnittweise Schnittansicht einer Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung mit mehreren Fluidaustrittselementen in Absperrposition und ebenen Ventilsitzen,
- Fig. 2
- die Schnittansicht von
Fig. 1 mit den Fluidaustrittselementen in Freigabeposition, - Fig. 3
- eine Detailansicht eines einzelnen Fluidaustrittselements von
Fig. 1 , - Fig. 4
- eine Detailansicht eines einzelnen Fluidaustrittselements von
Fig. 2 , - Fig. 5
- eine Schnittansicht entsprechend
Fig. 1 für eine Variante mit profilierten Ventilsitzen, - Fig. 6
- eine Schnittansicht entsprechend
Fig. 2 für die Variante vonFig. 5 , - Fig. 7
- eine Detailschnittansicht eines einzelnen Fluidaustrittselements von
Fig. 5 und - Fig. 8
- eine Detailansicht eines einzelnen Fluidaustrittselements von
Fig. 6 . - Die in
Fig. 1 bis 4 gezeigte Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung ist in einen sanitären Brausekopf integriert, um einen Wasser-Brausestrahl zu erzeugen, dessen Strahlform weitestgehend unabhängig vom Druck des zugeführten Wassers ist. Das dem Brausekopf zugeführte Wasser wird in eine Fluidkammer 3 eingeleitet, die austrittsseitig von einer hier beispielhaft mehrteiligen Strahlscheibe 1 der Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung begrenzt ist. Die Strahlscheibe 1 verfügt über eine Mehrzahl von vorzugsweise zwischen zehn und zweihundert, z.B. dreißig, Strahlscheibenöffnungen 2, durch die hindurch das Wasser von der Fluidkammer 3 nach außen geleitet werden kann. - Die mehrteilige Strahlscheibe 1 umfasst eine Elastomerplatte 13, die z.B. aus einem Silikonmaterial mit einer Shore-Härte von vorzugsweise zwischen fünfzig und siebzig, z.B. sechzig, bestehen kann, und eine Metallplatte 14, wobei die Elastomerplatte 13 fluidkammerseitig an der Metallplatte 14 anliegt. Des Weiteren ist eine Gehäuseplatte 8 des Brausekopfs der Strahlscheibe 1 gegenüberliegend und die Fluidkammer 3 begrenzend angeordnet. Dabei ist die Elastomerplatte 13 mit ihrem äußeren Randbereich zwischen der Gehäuseplatte 8 und der Metallplatte 14 die Fluidkammer 3 abdichtend gehalten.
- An der einteiligen Elastomerplatte 13 ist eine Mehrzahl von Elastomer-Ringmembranen 12 ausgebildet, die je ein bewegliches Fluidaustrittselement 4 umgeben und tragen. Somit ist das Fluidaustrittselement 4 über die Elastomer-Ringmembran 12 mit der Elastomerplatte 13 verbunden bzw. an dieser gehalten. Des Weiteren ist die in
Fig. 1 bis 4 gezeigte Elastomerplatte 13 einteilig mit dem Fluidaustrittselement 4 und der Elastomer-Ringmembran 12 ausgeführt. Ferner ist die Elastomerplatte 13 derart an die Metallplatte 14 angelegt, dass an jeder Strahlscheibenöffnung 2 ein bewegliches Fluidaustrittselement 4 angeordnet ist. - Das jeweilige Fluidaustrittselement 4 weist eine Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 auf, die aus der Fluidkammer 3 ausmündet und nach Art einer Austrittsdüse ausgebildet ist. Die Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 bzw. die Austrittsdüse hat eine von der Fluidkammer 3 aus kommend eintrittsseitig kegelstumpfförmig konische Geometrie, an die sich austrittsseitig eine kreiszylindrische Geometrie als Endabschnitt anschließt, in welchem die Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 auf einen Austrittsdurchmesser verjüngt ist, der z.B. typisch im Bereich von 0,6 mm bis 1,2 mm, insbesondere von 0,85 mm bis 0,95 mm, liegt. Die Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 bzw. Austrittsdüse weist eine bei bestimmungsgemäßem Gebrauch der Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung fluiddruckunabhängige und formstabile Geometrie auf. Die Symmetrieachse der Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 ist eine Düsenlängsachse 11, die gleichzeitig eine axiale Hauptrichtungskomponente der Bewegung des beweglichen Fluidaustrittselements 4 ist. Die Düsenlängsachse 11 entspricht zudem einer lokalen Flächennormale einer Außenseite der Strahlscheibe 1 an der betreffenden Stelle.
- Des Weiteren weist das Fluidaustrittselement 4 einen beweglichen Ventilkörper 6 auf, an dem die Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 angeordnet ist, wobei der bewegliche Ventilkörper 6 ein rotationssymmetrisches Element in der Art einer Tellerfeder ist. Der bewegliche Ventilkörper 6 ist für die Bewegung des Fluidaustrittselements 4 und somit auch für die Bewegung der Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 verantwortlich. Infolge der Bewegung des Ventilkörpers 6 wird das Fluidaustrittselement 4 zwischen einer die Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 freigebenden oder absperrenden Position geschaltet, wobei der bewegliche Ventilkörper 6 mit einem unbeweglichen Ventilsitz 7 zusammenwirkt. Ursächlich für diese Bewegung ist ein in der Fluidkammer 3 herrschender Fluiddruck, der vom zugeleiteten Wasser erzeugt wird. Der Fluiddruck wirkt auf den beweglichen Ventilkörper 6, und sobald ein vorgegebener Grenzdruck zwischen 0,2 bar bis 0,35 bar, insbesondere zwischen 0,24 bar bis 0,26 bar, in der Fluidkammer überschritten ist, wird der Ventilkörper 6 und damit das Fluidaustrittselement 4 mit axialer Hauptrichtungskomponente durch den Druck aus einer Absperrposition in eine Freigabeposition bewegt, in welcher der Ventilkörper 6 die Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 freigibt. Fällt der Fluiddruck unter den vorgegebenen Grenzdruck, bewegt sich der Ventilkörper 6 selbsttätig in seine ursprüngliche, die Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 absperrende Position zurück.
- In
Fig. 1 ist die absperrende Position des beweglichen Ventilkörpers 6 gezeigt. In dieser Position wirkt der Ventilkörper 6 mit dem unbeweglichen Ventilsitz 7 dahingehend zusammen, dass der Ventilkörper 6 gegen den Ventilsitz 7 anliegt bzw. andrückt, wodurch der Ventilsitz 7 die Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 fluiddicht absperrt. Aufgrund des dichten Anliegens des beweglichen Ventilkörpers 6 gegen den unbeweglichen Ventilsitz 7 kann kein Wasser die Fluidkammer 3 durch die Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 verlassen, der Brausekopf ist damit gegen Nachtropfen gesichert. - Der in
Fig. 1 bis 4 gezeigte unbewegliche Ventilsitz 7 ist einteilig mit der Gehäuseplatte 8 des Brausekopfs ausgeführt und weist eine ebene Sitzfläche auf, gegen die der bewegliche Ventilkörper 6 anliegt. Dazu ist der unbewegliche Ventilsitz 7 von einem plateauartigen Vorsprung 15 der Gehäuseplatte 8 gebildet. Dabei beträgt der Abstand zwischen der Strahlscheibe 1 und der Gehäuseplatte 8 ohne Berücksichtigung der Plateaus 15 vorzugsweise mindestens 2 mm. Dieser Abstand kann als Höhe der Fluidkammer 3 bezeichnet werden. - Des Weiteren ist in
Fig. 1 ersichtlich, dass sich die Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 in absperrender Position des beweglichen Ventilkörpers 6 durch die Strahlscheibenöffnung 2 hindurch erstreckt und austrittsseitig einen Überstand in Bezug auf die Metallplatte 14 aufweist. Dieser Überstand der Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 kann z.B. im Bereich von 1 mm bis 3 mm liegen, z.B. ca. 2 mm sein. In der freigebenden Position des beweglichen Ventilkörpers 6, die inFig. 2 dargestellt ist, beträgt der Überstand vorzugsweise zwischen 3 mm und 7 mm, z.B. ca. 5 mm. Durch die vom Fluiddruck in der Fluidkammer 3 gesteuerte Bewegung des Ventilkörper 6 führt die Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 somit eine Hubbewegung mit einer axialen Hublänge von vorzugsweise 2 mm bis 5 mm, z.B. ca. 3 mm, aus. - Im gezeigten Beispiel weist das jeweilige Fluidaustrittselement 4 bzw. sein Ventilkörper 6 eine monostabile Formgebung auf, d.h. eine Formgebung derart, dass das Fluidaustrittselement 4 bzw. sein Ventilkörper 6 genau eine stabile Position aufweist, die vorliegend durch die Absperrposition entsprechend
Fig. 1 gegeben ist. Aus dieser wird das Fluidaustrittselement 4 bzw. sein Ventilkörper 6 bei in der Fluidkammer anstehendem Fluiddruck um die Hublänge in die Freigabeposition gemäßFig. 2 vorbewegt, wenn und sobald der Fluiddruck einen zugehörigen Grenzdruckwert von z.B. 0,25 bar bis 0,35 bar überschreitet. In der Freigabestellung liegt der Ventilkörper 6 nicht mehr gegen den unbeweglichen Ventilsitz 7 an, und das Wasser kann durch die jeweilige Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 hindurch die Fluidkammer 3 verlassen, um den gewünschten Brausestrahl zu bilden. Wenn der Fluiddruck z.B. durch Abstellen der Wasserzufuhr wieder unter den Grenzwert fällt bzw. bis auf null abnimmt, kehrt das Fluidaustrittselement 4 bzw. sein Ventilkörper 6 selbsttätig durch elastische Rückstellkraft in die Absperrposition zurück, so dass ein Nachtropfen von Wasser aus der Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 zuverlässig vermieden wird. - In den
Fig. 3 und 4 sind eines der Fluidaustrittselemente 4 und seine Umgebung in absperrender Position bzw. in freigebender Position vergrößert dargestellt. Wie daraus genauer zu erkennen, ist in diesem Beispiel die Strahlscheibenöffnung 2, an der das gezeigte Fluidaustrittselement 4 angeordnet ist, als Senkbohrung in der Metallplatte 14 ausgeführt, wobei die Senkung eine Geometrie, insbesondere eine Ventilanlagefläche 9, aufweist, die den beweglichen Ventilkörper 6 in der freigebender Position abstützt und in seiner Bewegung begrenzt. Um den beweglichen Ventilkörper 6 nicht zu beschädigen, ist die Senkung der Senkbohrung vorzugsweise derart geformt, dass sie keine spitzen Winkel aufweist. - In den
Fig. 5 bis 8 ist eine Variante der Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung derFig. 1 bis 4 gezeigt, wobei zum besseren Verständnis für identische und funktionell äquivalente Elemente gleiche Bezugszeichen verwendet sind und insoweit auch auf die obigen Ausführungen zum Ausführungsbeispiel derFig. 1 bis 4 verwiesen werden kann, so dass nachstehend im Wesentlichen nur auf die bestehenden Unterschiede eingegangen wird, die hier speziell in der Gestaltung des unbeweglichen Ventilsitzes 7 liegen. - Bei der Variante der
Fig. 5 bis 8 weist der unbewegliche Ventilsitz 7 einen Ventilsitzvorsprung 10 auf, der bei abgesperrter Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 in die Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 hinein ragt und bei freigegebener Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 nicht in die Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 hinein ragt. Dadurch kann Kalkablagerungen an der Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 entgegengewirkt werden, indem diese durch den Ventilsitzvorsprung 10 von der Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 abgelöst werden, wenn sich das Fluidaustrittselement 4 zwischen der freigebenden Position und der absperrenden Position bewegt. - Außerdem weist der unbewegliche Ventilsitz 7 bei der Variante der
Fig. 5 bis 8 eine Gestalt auf, die an diejenige des beweglichen Ventilkörpers 6 formangepasst ist. Dazu besitzt der unbewegliche Ventilsitz 7 eine ringförmige Vertiefung bzw. Ausnehmung in Form einer negativen Gestalt des in der Absperrposition anliegenden beweglichen Ventilkörpers 6. Dies vergrößert die Kontaktfläche zwischen dem beweglichen Ventilkörper 6 und dem unbeweglichen Ventilsitz 7 in der Absperrposition verglichen mit der ebenen Sitzfläche bei der Variante derFig. 1 bis 4 und trägt zu einer Zentrierung der gegen den Ventilsitz 7 in der Absperrposition andrückenden Lage des Ventilkörpers 6 bei. Diese vergrößerte Kontaktfläche und die zentrierte Lage des Ventilkörpers 6 unterstützen vorteilhaft das sichere Abdichten der Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5. - In einer nicht dargestellten erfindungsgemäßen Variante der Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung ist der unbewegliche Ventilsitz 7 in Form eines vorzugsweise kegelstumpfförmigen Stopfens ausgeführt, welcher in Absperrposition die Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 verschließt. Der stopfenförmige unbewegliche Ventilsitz 7 ragt dabei in die Fluidaustrittsöffnung 5 hinein.
- In einer nicht dargestellten erfindungsgemäßen Variante der Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung weist eine Zwischenplatte statt der gezeigten Gehäuseplatte 8 den unbeweglichen Ventilsitz auf. Diese Zwischenplatte ist vorzugsweise in einen Brausekopf integriert und wirkt als Begrenzung der Fluidkammer auf deren der Strahlscheibe gegenüberliegenden Seite.
- Wie die gezeigten und oben erläuterten Ausführungsbeispiele deutlich machen, stellt die Erfindung eine Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung bereit, die das unerwünschte Nachtropfen zuverlässig verhindert, relativ einfach herstellbar und funktionssicher ist. Des Weiteren ist der Austrittsquerschnitt der Fluidaustrittsöffnung weitestgehend vom Fluiddruck in der Fluidkammer unbeeinflusst. Die Erfindung ist insbesondere in der Sanitärtechnik einsetzbar, aber auch in anderen Anwendungen, in denen der Bedarf besteht, einen Brausestrahl funktionssicher und ohne Nachtropfen erzeugen zu können.
Claims (10)
- Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung für einen sanitären Brausekopf, mit- einer Strahlscheibe (1), die mindestens eine Strahlscheibenöffnung (2) aufweist und eine Fluidkammer (3) austrittsseitig begrenzt, und- einem an der mindestens einen Strahlscheibenöffnung angeordneten und in einer axialen Hauptrichtungskomponente beweglichen Fluidaustrittselement (4), das einen beweglichen Ventilkörper (6) mit einer aus der Fluidkammer ausmündenden Fluidaustrittsöffnung (5) aufweist, die abhängig von einem Fluiddruck in der Fluidkammer in einer Freigabeposition des Fluidaustrittselements freigegeben und in einer Absperrposition des Fluidaustrittselements abgesperrt ist,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass- der bewegliche Ventilkörper (6) mit einem unbeweglichen Ventilsitz (7) zusammenwirkt, der die Fluidaustrittsöffnung (5) in der Freigabeposition des Fluidaustrittselements freigibt und in einer Absperrposition des Fluidaustrittselements absperrt. - Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Fluidkammer durch eine den unbeweglichen Ventilsitz aufweisende Zwischenplatte oder Gehäuseplatte (8) begrenzt ist, wobei die Zwischenplatte oder Gehäuseplatte der Strahlscheibe gegenüberliegend angeordnet ist.
- Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung nach einem der vorherigen Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass der bewegliche Ventilkörper in der Freigabeposition des Fluidaustrittselements gegen eine Ventilanlagefläche (9) der Strahlscheibe anliegt.
- Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung nach einem der vorherigen Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass sich das Fluidaustrittselement mit seiner Fluidaustrittsöffnung in seiner Freigabeposition und/oder in seiner Absperrposition durch die Strahlscheibenöffnung hindurch erstreckt.
- Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung nach einem der vorherigen Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass der Ventilsitz einen Ventilsitzvorsprung (10) aufweist, der bei abgesperrter Fluidaustrittsöffnung in die Fluidaustrittsöffnung hinein ragt.
- Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung nach einem der vorherigen Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Fluidaustrittsöffnung eine fluiddruckunabhängig formstabile und/oder kreiszylindrische und/oder konische Geometrie aufweist.
- Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung nach einem der vorherigen Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Fluidaustrittsöffnung von einer Austrittsdüse mit einer Düsenlängsachse (11) gebildet ist, die parallel zu einer lokalen Flächennormale einer Außenseite der Strahlscheibe ist.
- Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung nach einem der vorherigen Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das Fluidaustrittselement eine Elastomer-Ringmembran (12) aufweist, welche den beweglichen Ventilkörper umgibt und trägt.
- Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung nach einem der vorherigen Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das Fluidaustrittselement einteilig ausgeführt ist.
- Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung nach einem der vorherigen Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass eine Mehrzahl von Strahlscheibenöffnungen und zugeordneten Fluidaustrittselementen vorgesehen ist und die Strahlscheibe eine einteilige Elastomerplatte (13) aufweist, an der die Mehrzahl von Fluidaustrittselementen ausgebildet ist.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102016219551.4A DE102016219551B4 (de) | 2016-10-07 | 2016-10-07 | Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP3305412A1 true EP3305412A1 (de) | 2018-04-11 |
| EP3305412B1 EP3305412B1 (de) | 2020-11-18 |
Family
ID=60019791
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP17194704.7A Active EP3305412B1 (de) | 2016-10-07 | 2017-10-04 | Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10821453B2 (de) |
| EP (1) | EP3305412B1 (de) |
| CN (1) | CN107913807B (de) |
| DE (1) | DE102016219551B4 (de) |
| RU (1) | RU2668252C1 (de) |
| ZA (1) | ZA201706662B (de) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3586974A1 (de) * | 2018-06-25 | 2020-01-01 | Hansgrohe SE | Sanitärer brausekopf |
| WO2023180466A1 (de) * | 2022-03-23 | 2023-09-28 | Grohe Ag | Sanitäre brause |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL249680B (en) * | 2016-12-21 | 2018-05-31 | Zabari Lidor | Self-sealing and disinfecting shower head |
| DE102016225987A1 (de) | 2016-12-22 | 2018-06-28 | Hansgrohe Se | Brausestrahlaustrittsvorrichtung und damit ausgerüstete Brause |
| SG11201909600XA (en) * | 2017-04-19 | 2019-11-28 | Baxter Int | Non-clogging dispensing device |
| DE102018201183B3 (de) | 2018-01-25 | 2019-01-31 | Hansgrohe Se | Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung mit Überdruckventil |
| DE102019105974A1 (de) * | 2019-03-08 | 2020-09-10 | Grohe Ag | Sanitärbrause aufweisend einen Strahlbildner mit mindestens einem Entenschnabelventil |
| CN113492079A (zh) * | 2020-04-03 | 2021-10-12 | 路达(厦门)工业有限公司 | 自清洁装置及花洒、喷枪、龙头 |
| DE102021205915A1 (de) * | 2021-06-10 | 2022-12-15 | Hansgrohe Se | Topfförmige Brausestrahlaustrittsdüse und Brause |
| DE102021132866A1 (de) * | 2021-12-13 | 2023-06-15 | Grohe Ag | Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung mit Tropfschutz |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6382531B1 (en) * | 2001-02-21 | 2002-05-07 | Martin Tracy | Shower head |
| EP1700636A2 (de) * | 2005-03-11 | 2006-09-13 | Hansa Metallwerke Ag | Duschkopf |
| CN203108678U (zh) * | 2012-12-28 | 2013-08-07 | 厦门水大卫浴洁具有限公司 | 一种出水嘴自清洁含氧顶喷 |
| WO2014029636A2 (de) * | 2012-08-22 | 2014-02-27 | Ideal Standard International Bvba | Duschkopf mit einer federnden wasserleitmatte |
Family Cites Families (21)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US1236617A (en) * | 1915-09-17 | 1917-08-14 | Speakman Supply & Pipe Company | Self-cleaning shower-head. |
| US2402741A (en) | 1944-10-03 | 1946-06-25 | Adolphe O Draviner | Spray head |
| US3734410A (en) * | 1971-09-30 | 1973-05-22 | Stanadyne Inc | Pulsating spray head |
| BE795888A (fr) | 1972-03-29 | 1973-06-18 | Grohe Kg Hans | Pomme de douche |
| WO1991012894A1 (de) | 1990-02-22 | 1991-09-05 | Masco Gmbh | Brausekopf |
| JPH0499243U (de) | 1991-01-17 | 1992-08-27 | ||
| WO1995022407A1 (de) | 1994-02-17 | 1995-08-24 | Ideal-Standard Gmbh | Bodenteil für einen brausekopf sowie brausekopf |
| DE19733291A1 (de) | 1997-08-01 | 1999-02-04 | Grohe Kg Hans | Brauseeinrichtung |
| US6378790B1 (en) * | 2000-01-26 | 2002-04-30 | Speakman Company | Shower head having a rubber/plastic face plate and a diverter valve using rubber sleeve back pressure activation |
| US6935581B2 (en) | 2001-07-24 | 2005-08-30 | Visentin Usa | Shower head with nozzles having self cleaning tips |
| GB0121377D0 (en) * | 2001-09-04 | 2001-10-24 | Aqualisa Products Ltd | Shower handset |
| US7040554B2 (en) * | 2002-12-20 | 2006-05-09 | Asept International Ab | Spray head |
| DE102006032017B3 (de) | 2006-07-10 | 2008-01-17 | Grohe Ag | Kopfbrause |
| AU2009238194B2 (en) | 2008-04-17 | 2017-05-18 | Exell Technology Pty Limited | A showerhead |
| FR2946546B1 (fr) | 2009-06-15 | 2012-06-08 | Air Liquide | Procede de regulation de la purete d'oxygene produit par une unite d'adsorption par controle du debit |
| US8985483B2 (en) * | 2012-01-24 | 2015-03-24 | John E. Petrovic | Adjustable trajectory spray nozzles |
| DE102012212300A1 (de) | 2012-07-13 | 2014-01-16 | Hansgrohe Se | Brause |
| US9839923B2 (en) * | 2012-08-02 | 2017-12-12 | Fabrimar S/A Industria E Comercio | Showerhead |
| US9661850B2 (en) | 2012-08-24 | 2017-05-30 | Syngenta Participations Ag | Methods of soil pest control |
| DE102014200741A1 (de) | 2014-01-16 | 2015-07-16 | Hansgrohe Se | Brause mit mehrkanaligen Strahlaustrittseinheiten |
| DE102016225987A1 (de) | 2016-12-22 | 2018-06-28 | Hansgrohe Se | Brausestrahlaustrittsvorrichtung und damit ausgerüstete Brause |
-
2016
- 2016-10-07 DE DE102016219551.4A patent/DE102016219551B4/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2017
- 2017-09-30 CN CN201710913672.5A patent/CN107913807B/zh active Active
- 2017-10-02 US US15/722,411 patent/US10821453B2/en active Active
- 2017-10-04 RU RU2017134870A patent/RU2668252C1/ru active
- 2017-10-04 EP EP17194704.7A patent/EP3305412B1/de active Active
- 2017-10-04 ZA ZA2017/06662A patent/ZA201706662B/en unknown
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6382531B1 (en) * | 2001-02-21 | 2002-05-07 | Martin Tracy | Shower head |
| EP1700636A2 (de) * | 2005-03-11 | 2006-09-13 | Hansa Metallwerke Ag | Duschkopf |
| WO2014029636A2 (de) * | 2012-08-22 | 2014-02-27 | Ideal Standard International Bvba | Duschkopf mit einer federnden wasserleitmatte |
| CN203108678U (zh) * | 2012-12-28 | 2013-08-07 | 厦门水大卫浴洁具有限公司 | 一种出水嘴自清洁含氧顶喷 |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3586974A1 (de) * | 2018-06-25 | 2020-01-01 | Hansgrohe SE | Sanitärer brausekopf |
| WO2023180466A1 (de) * | 2022-03-23 | 2023-09-28 | Grohe Ag | Sanitäre brause |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3305412B1 (de) | 2020-11-18 |
| CN107913807A (zh) | 2018-04-17 |
| DE102016219551A1 (de) | 2018-04-12 |
| US20180099295A1 (en) | 2018-04-12 |
| RU2668252C1 (ru) | 2018-09-27 |
| ZA201706662B (en) | 2019-05-29 |
| DE102016219551B4 (de) | 2022-01-05 |
| US10821453B2 (en) | 2020-11-03 |
| CN107913807B (zh) | 2020-08-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE102016219551B4 (de) | Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung | |
| EP2664719B1 (de) | Sanitäres Einbauelement | |
| DE102005012706B4 (de) | Duschkopf | |
| EP3517212B1 (de) | Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung mit überdruckventil | |
| EP3276231B1 (de) | Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung | |
| DE102007054673B4 (de) | Bandschmiereinrichtung und/oder Reinigungs-Desinfektionsanlage | |
| EP3338898A1 (de) | Brausestrahlaustrittsvorrichtung und damit ausgerüstete brause | |
| EP3175923B1 (de) | Brausekopf | |
| DE212014000056U1 (de) | Druckschaltventil | |
| DE1152583B (de) | Membranventil | |
| DE20307538U1 (de) | Wasserzuflußsteuervorrichtung | |
| EP3517211B1 (de) | Brausekopf mit überdruckventil | |
| EP3325864B1 (de) | Eigenmediumgesteuertes regelventil | |
| DE9317654U1 (de) | Perlator für Armaturen | |
| DE112019004251T5 (de) | Wasserauslassdüse und Wasserstrahleinrichtung mit derselben | |
| DE102013014942B4 (de) | Brausekopf für eine Sanitärbrause | |
| EP1619315A1 (de) | Wasserstrahlbildner | |
| EP3702541B1 (de) | Brause für eine sanitärarmatur mit einer rückstellfeder | |
| DE711583C (de) | Brause | |
| EP3586974B1 (de) | Sanitärer brausekopf | |
| DE1299962B (de) | Kombiniertes Membranabsperr- und -rueckschlagventil | |
| WO2023110370A1 (de) | Brausestrahlerzeugungsvorrichtung mit tropfschutz | |
| DE102017103133B4 (de) | Verschluss für einen Behälter zur Aufnahme und Abgabe von Flüssigkeiten | |
| WO2023180466A1 (de) | Sanitäre brause | |
| DE2111829C3 (de) | Selbstreinigender Sprühkopf |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION HAS BEEN PUBLISHED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| RIN1 | Information on inventor provided before grant (corrected) |
Inventor name: DIETERLE, JOACHIM Inventor name: STEIERT, SEBASTIAN Inventor name: ARMBRUSTER, JOCHEN |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: REQUEST FOR EXAMINATION WAS MADE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20181008 |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20200602 |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: B05B 15/528 20180101ALI20200518BHEP Ipc: B05B 1/18 20060101AFI20200518BHEP Ipc: B05B 1/30 20060101ALI20200518BHEP Ipc: B05B 1/32 20060101ALI20200518BHEP |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502017008238 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 1335155 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20201215 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MP Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210218 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210318 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210219 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210218 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210318 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG9D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502017008238 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20210819 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210318 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20211031 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20211004 Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20211031 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20211031 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20211031 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20211004 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20171004 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 1335155 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20221004 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20231024 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20221004 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20231026 Year of fee payment: 7 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20231027 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20201118 |