EP3136629A1 - Rundfunkweiterleitungsunterstützungsvorrichtung, steuerungsverfahren für rundfunkweiterleitungsunterstützungsvorrichtung und steuerungsprogramm - Google Patents
Rundfunkweiterleitungsunterstützungsvorrichtung, steuerungsverfahren für rundfunkweiterleitungsunterstützungsvorrichtung und steuerungsprogramm Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP3136629A1 EP3136629A1 EP14889887.7A EP14889887A EP3136629A1 EP 3136629 A1 EP3136629 A1 EP 3136629A1 EP 14889887 A EP14889887 A EP 14889887A EP 3136629 A1 EP3136629 A1 EP 3136629A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- broadcast
- broadcast audio
- anomaly
- audio signals
- assistance device
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 11
- 230000005236 sound signal Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 78
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 44
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000001012 protector Effects 0.000 description 17
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 13
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 8
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000002547 anomalous effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006378 damage Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009499 grossing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001629 suppression Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B17/00—Monitoring; Testing
- H04B17/40—Monitoring; Testing of relay systems
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04H—BROADCAST COMMUNICATION
- H04H20/00—Arrangements for broadcast or for distribution combined with broadcast
- H04H20/02—Arrangements for relaying broadcast information
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04H—BROADCAST COMMUNICATION
- H04H20/00—Arrangements for broadcast or for distribution combined with broadcast
- H04H20/12—Arrangements for observation, testing or troubleshooting
Definitions
- Embodiments of the present invention relate to a broadcast relay assistance device, and a control method and a control program for a broadcast relay assistance device.
- broadcast audio signals (radio program) are produced in a studio with studio equipment and transmitted to a transmitting station with a transmitter via a relay device.
- AM waves are generated with the transmitter and sent to a certain broadcast service area.
- transmitters adopt control technique for blocking AM wave outputs for a short period of time in case of occurrence of anomaly such as stroke of lightning and release thunder energy to the ground (grounding), for example.
- AM wave outputs are blocked for a short period of time for the purpose of blocking continuation of a load short circuit state (follow current) generated by the thunder energy.
- Patent Literatures propose a technique to monitor a standing wave ratio (SWR) or discharge light and to block AM wave outputs for a short period of time.
- SWR standing wave ratio
- conventional transmitters include a mechanism to block AM wave outputs for a short period of time upon occurrence of anomaly such as a stroke of lightning to protect the transmitters.
- short-time blocking of AM wave outputs may cause silent time in broadcast audio signals received by a receiver and thus interruption of sound for example, which may result in auditorily undesirable broadcasting.
- the present invention has been devised in consideration to the above.
- An object thereof is to provide a broadcast relay assistance device, and a control method and a control program for a broadcast relay assistance device which can mitigate the influence of a silent state on a listener even when the silent state occurs (short-time blocking of AM wave outputs) upon occurrence of anomaly.
- a memory of a broadcast relay assistance device of an embodiment stores broadcast audio data corresponding to input broadcast audio signals in a chronological order.
- an output unit performs processing including reading, from the memory, based on an anomaly detection signal received from outside, the broadcast audio data corresponding to the broadcast audio signals that would have been broadcast during an anomaly detected period, and outputting the corresponding broadcast audio signals after an anomaly is resolved.
- FIG. 1 is a schematic explanatory diagram of the configuration of a medium wave radio broadcast system of an embodiment.
- a medium wave radio broadcast system 10 includes a broadcast audio signal generation device 21 to generate a broadcast audio signal Sba that is audio signals for broadcasting, a relay device 22 to relay the broadcast audio signal Sba generated by the broadcast audio signal generation device 21, a transmitter 23 to modulate the amplitude of the broadcast audio signal Sba relayed by the relay device 22 and to output it as transmission signal, an antenna matcher 24 to match impedance between an output terminal of the transmitter 23 and an antenna 25, and the antenna 25 to emit the transmission signal being high frequency signal into a space as radio wave.
- FIG. 2 is a schematic block diagram of the configuration of a transmitter.
- the transmitter 23 functions as a broadcast relay assistance device.
- the transmitter 23 includes an audio unit 32 which receives the broadcast audio signal Sba generated by the broadcast audio signal generation device 21 via the relay device 22 and an audio signal input terminal 31 and adds a time code representing a reproduction order to the broadcast audio signal Sba to store it as broadcast audio data Dba and output the broadcast audio signal in association with the time code, and an AM wave generator 33 having n power amplifiers (PAs) (not illustrated), to generate AM waves by AM modulation of carrier waves based on the broadcast audio signal output by the audio unit 32 and to output the AM waves.
- PAs power amplifiers
- the transmitter 23 includes a pickup 35 to output the AM waves output from the AM wave generator 33 without change to the antenna matcher 24 via an AM wave output terminal 34 and to pick up AM waves for detection of anomaly such as a stroke of lightning when continuance of broadcasting may cause the transmitter 23 to fail due to such anomaly, an anomaly detector 36 to detect an anomaly based on the AM waves picked up by the pickup 35 and to output an anomaly detection signal upon detection of the anomaly, and an instantaneous halting unit 37 to, upon receipt of the anomaly detection signal, control the AM wave generator 33 to halt the output, and to notify the audio unit 32 of output halting start upon the receipt of the anomaly detection signal and to notify the audio unit 32 of output halting cancellation upon no receipt of the anomaly detection signal.
- a pickup 35 to output the AM waves output from the AM wave generator 33 without change to the antenna matcher 24 via an AM wave output terminal 34 and to pick up AM waves for detection of anomaly such as a stroke of lightning when continuance of broadcasting may cause the transmitter 23 to fail due to
- the pickup 35 picks up an AM wave output from the AM wave generator 33 and measures a voltage value and a current value.
- the pickup 35 outputs the measured voltage value and current value to the anomaly detector 36 as pick-up signals Sp.
- the anomaly detector 36 is configured as an analog circuit including an analog IC such as an operational amplifier which receives the voltage value and the current value (measured values) measured by the pickup 35 as the pick-up signals Sp.
- the anomaly detector 36 performs addition, subtraction, division, smoothing, or correction on the measured voltage value and current value and outputs them to the instantaneous halting unit 37 as an anomaly discrimination value Vm.
- the anomaly detector 36 can calculate the anomaly discrimination value Vm from the voltage value and a voltage value different in phase by n/2 from the voltage value.
- the instantaneous halting unit 37 In order to block the AM wave generator 33 from outputting AM waves for a certain period of time by controlling a power amplifier (not illustrated) of the AM wave generator 33 to be into an off state from an on-controlled state based on the anomaly discrimination value Vm, the instantaneous halting unit 37 outputs the anomaly detection signal Se to the audio unit 32.
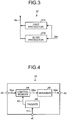
- FIG. 3 is a functional block diagram of the configuration of the instantaneous halting unit.
- the instantaneous halting unit 37 includes a fast protector 37A.
- This fast protector 37A is configured of an analog circuit for example as illustrated in FIG. 3 .
- the fast protector 37A controls all of the power amplifiers (not illustrated) of the AM wave generator 33 to be placed into an off state from an on-controlled state based on the anomaly discrimination value Vm and outputs as the anomaly detection signal Se a first control signal PC11 which places the AM wave generator 33 in a halting state.
- the instantaneous halting unit 37 further includes a slow protector 37B.
- This slow protector 37B is configured as a composite circuit of an analog circuit and a digital circuit as illustrated in FIG. 3 .
- the slow protector 37B outputs as the anomaly detection signal Se a second control signal PC12 which controls all of the power amplifiers (not illustrated) of the AM wave generator 33 to be placed in the off state from the on-controlled state based on the anomaly discrimination value Vm to place the AM wave generator 33 in the halting state.
- the fast protector 37A of the instantaneous halting unit 37 is configured of an analog circuit including an analog IC such as an operational amplifier or a comparator to output to the audio unit 32 the first control signal PC11 as the anomaly detection signal Se that controls all of the on-controlled power amplifiers of the AM wave generator to be placed in the off state when the anomaly discrimination value Vm output by the anomaly detector 36 is more than or equal to a first reference value which is a preset threshold value.
- the slow protector 37B of the instantaneous halting unit 37 is configured as a composite circuit of an analog circuit including an analog IC such as an operational amplifier or an A/D converter and a digital circuit such as a CPU, a CPLD, and an FPGA.
- the slow protector 37B outputs the second control signal PC12 as the anomaly detection signal Se to the audio unit 32.
- a pulse width of the first control signal PC11 output by the fast protector 37A is set to be longer than an operation delay time in the slow protector 37B configured as a composite circuit of an analog circuit and a digital circuit. This is to prevent the protection by the fast protector 37A from being cancelled before the protection by the slow protector 37B starts, that is, before the second control signal PC12 is output.
- the slow protector 37B restarts all of the power amplifiers (not illustrated) to place them in the on state again for a short period of time and recalculates the anomaly discrimination value Vm.
- the anomaly discrimination value Vm falls to or below the first reference value, the output of the anomaly detection signal Se is canceled.
- the slow protector 37B further has a function to increase or decrease the anomaly discrimination value Vm when the value vm output by the anomaly detector 36 is less than or equal to the first reference value and more than or equal to the second reference value which are preset threshold values.
- the AM wave output is not blocked during the increase or decrease operation and the anomaly detection signal Se is thus not output basically.
- the anomaly detection signal Se can be output to implement broadcast relay assistance processing.
- the broadcast relay assistance processing will be described later. In this case, for example a dynamic range controlling process may be added to add a sound quality improving method.
- the anomaly discrimination values Vm of the fast protector 37A and the slow protector 37B may differ, however, they can be deemed equivalent for the operation since the difference is attributable to different calculation results from the same source.
- FIG. 4 is a schematic block diagram of the configuration of the audio unit.
- the audio unit 32 generally includes a trigger 42, a control memory 44, and a shrinker 46.
- the trigger 42 receives the anomaly detection signal Se via an anomaly information input terminal 41 and outputs a control signal for the output control of the broadcast audio signal Sba based on the anomaly detection signal Se.
- the control memory 44 receives the broadcast audio signal Sba via an audio signal input terminal 43, encodes the broadcast audio signal Sba, and stores it as the broadcast audio data added with a time code representing a reproduction order.
- the control memory 44 further sequentially outputs the broadcast audio data during normalcy, calculates silent time upon occurrence of anomaly based on the control signal output by the trigger 42, and outputs silent time data corresponding to the silent time and the broadcast audio data Dba corresponding to the silent time data.
- the shrinker 46 adjusts actual reproduction time of the broadcast audio signal Sba corresponding to the broadcast audio data Dba based on the decoded broadcast audio data Dba and the silent time data for output from an audio signal output terminal 45.
- the broadcast audio signal generation device 21 of the medium wave radio broadcast system 10 generates broadcast audio signals Sba as audio signals for broadcasting and outputs them to the relay device 22.
- the relay device 22 relays the broadcast audio signals Sba generated by the broadcast audio signal generation device 21 to the audio signal input terminal 31 of the transmitter 23.
- the audio unit 32 of the transmitter 23 receives the broadcast audio signals Sba from the relay device 22 via the audio signal input terminal 31, adds a time code representing a reproduction order to the signals and stores them as broadcast audio data. In parallel with this, the audio unit 32 outputs, to the AM wave generator 33, the broadcast audio signals Sba in association with the time code.
- the AM wave generator 33 performs AM modulation of carrier waves based on the broadcast audio signals Sba output by the audio unit 32 to generate AM waves and outputs them to the pickup 35.
- the pickup 35 outputs the AM waves output by the AM wave generator 33 to the antenna matcher 24 via the AM wave output terminal 34. In parallel with this, the pickup 35 picks up AM waves for anomaly detection.
- the anomaly detector 36 calculates the anomaly discrimination value Vm based on the AM waves picked up by the pickup 35 and outputs the value to the instantaneous halting unit 37.
- the instantaneous halting unit 37 does not output the anomaly detection signal Se.
- the AM wave generator 33 thus continues to output AM waves and the antenna matcher 24 matches impedance between the output terminal of the transmitter 23 and the antenna 25.
- the antenna 25 emits high-frequency transmission signals to a space as radio waves for broadcasting.
- the broadcast audio signal generation device 21 of the medium wave radio broadcast system 10 generates the broadcast audio signals Sba as audio signals for broadcasting and outputs them to the relay device 22.
- the relay device 22 relays the broadcast audio signals Sba generated by the broadcast audio signal generation device 21 to the audio signal input terminal 31 of the transmitter 23.
- the audio unit 32 of the transmitter 23 receives the broadcast audio signals Sba from the relay device 22 via the audio signal input terminal 31, adds to the signals Sba a time code representing a reproduction order, and stores them as broadcast audio data. In parallel with this, the audio unit 32 outputs, to the AM wave generator 33, the broadcast audio signals Sba in association with the time code.
- the AM wave generator 33 performs AM modulation of carrier waves based on the broadcast audio signals Sba output by the audio unit 32 and thereby generates and outputs AM waves to the pickup 35.
- the pickup 35 outputs the AM waves output by the AM wave generator 33 to the antenna matcher 24 via the AM wave output terminal 34. In parallel with this, the pickup 35 picks up AM waves for anomaly detection.
- the anomaly detector 36 calculates the anomaly discrimination value Vm based on the AM waves picked up by the pickup 35 and outputs the anomaly detection signal Se to the instantaneous halting unit 37 based on the anomaly discrimination value Vm.
- the instantaneous halting unit 37 upon receipt of the anomaly detection signal Se, the instantaneous halting unit 37 outputs the anomaly detection signal Se to the audio unit 32 and controls the AM wave generator 33 to interrupt AM wave outputs for a certain period of time.
- the AM wave generator 33 stops outputting the AM waves and thus the transmission antenna 25 halts emitting the high-frequency transmission signals to a space as radio waves, thereby interrupting broadcasting.
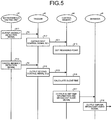
- FIG. 5 is a process sequence chart of the audio unit upon detection of anomaly.
- the trigger 42 of the audio unit 32 controls the output of the broadcast audio signals Sba based on the anomaly detection signal Se. More specifically, the trigger 42 of the audio unit 32 outputs, to the control memory 44 (step S12), the first control signal SC1 for setting a reproduction start point (rewinding point).
- the control memory 44 sets the reproduction start point (reproduction start time: rewinding point) (step S13).
- the trigger 42 of the audio unit 32 outputs, to the control memory 44, the second control signal SC2 for processing a silent part due to anomaly detection, in response to the cancellation of the anomaly detection signal Se (step S15).
- the control memory 44 then outputs, to the shrinker 46, broadcast audio data which, with no interruption of broadcasting, would otherwise have been broadcast during the calculated silent time and until the silent time elapses from the reproduction start point (reproduction start time) (step S17).
- the shrinker 46 outputs, to the AM wave generator 33, the broadcast audio signals Sba corresponding to the broadcast audio data based on the decoded broadcast audio data from the control memory 44 and the silent time data (step S18).
- FIG. 6 is an explanatory diagram of specific operations.
- FIG. 6(a) schematically presents reproduction states of the broadcast audio signals Sba at a transmitting end and a receiving end when no anomaly is detected, and occurrence of the same audio waveform.
- FIG. 6(b) schematically presents conventional reproduction states of broadcast audio signals Sba on a transmitting end and a receiving end upon detection of anomaly. It is seen from the drawing that the reproduced broadcast audio signals Sba is interrupted at the receiving end from occurrence of the anomaly to recovery from the anomaly at the transmitting end. Conventionally, sound is thus interrupted at the receiving end and transmitted contents are also interrupted.
- the broadcast audio signals Sba from output start time to output cancellation time of the anomaly detection signal Se are transmitted.
- the shrinker 46 can be configured to adjust the actual reproduction time of the broadcast audio signals Sba for output to the AM wave generator 33.
- FIG. 6(d) is an explanatory diagram of adjustment of the actual reproduction time of the broadcast audio signals Sba.
- the shrinker 46 here shortens only the reproduction time by so-called time stretching without changing the pitch of the broadcast sound, and reproduces the signals for a length of time obtained by subtracting the silent time from the original reproduction time.
- FIG. 7 is an explanatory diagram of the relation between a program broadcasting period and a commercial broadcasting period.
- a commercial broadcasting period TB2 continues with a program broadcasting period TB1 .
- broadcast program sound NS1 is broadcast sound which is originally scheduled to be broadcast in the silent period NS while broadcast program sound SS1 is broadcast sound which is originally scheduled to be broadcast in the broadcasting period TB1 after the silent period NS.
- the broadcast program sound NS1 and the broadcast program sound SS1 are together subjected to time stretching and thereby controlled to be completely broadcast within a broadcasting period SS.
- An actual program period thus falls within the original program period as illustrated in FIG. 7(c) , and is prevented from cutting into the commercial period.
- the broadcast program sound NS1 and the broadcast program sound SS1 are both subjected to time stretching in the above description; however, with a short silent period NS, the broadcast program sound NS1 and a part of the broadcast program sound SS1 can be subjected to time stretching.
- the part of the broadcast program sound SS1 can be a continuous part or discrete parts.
- a head of the broadcast program sound SS1 may be subjected to time stretching integrally with the broadcast program sound NS1.
- ends of the program broadcast sound NS1 and the broadcast program sound SS1 may be integrally subjected to time stretching.
- the respective multiple parts of the broadcast program sound NS1 and the broadcast program sound SS1 may be integrally subjected to time stretching.
- a part of the broadcast program sound NS1 can be deleted (usually a head part) and the remaining part of the broadcast program sound NS1 and the broadcast program sound SS1 can be subjected to the processing (time stretching) in the program period in the same manner.
- the reproduction start point coincides with anomaly detection timing, and hence does not always fall at a phonetically appropriate point. Specifically, it may come at the middle of a word (for example a reproduction start time of the "r" sound of the word “broadcast”) or during reproduction of one sound (for example during reproduction of the "e” sound of the word “speech"). In such a case, it is possible to extract the head of a word or the head of a sound by sound recognition, for example and transmit the broadcast audio data from time corresponding to a phonetically appropriate separating point prior to the reproduction start point.
- a word for example a reproduction start time of the "r" sound of the word "broadcast”
- reproduction of one sound for example during reproduction of the "e” sound of the word "speech”
- control memory 44 of the audio unit 32 outputs, to the AM wave generator 33, the broadcast audio signals Sba output within a period from the anomaly detection to the end of the anomaly detection.
- the AM wave generator 33 This allows the AM wave generator 33 to generate AM waves again by the AM modulation of carrier waves based on the broadcast audio signals Sba output by the audio unit 32, and to output them to the pickup 35.
- the pickup 35 outputs the AM waves output by the AM wave generator 33 to the antenna matcher 24 via the AM wave output terminal 34.
- the antenna matcher 24 matches impedance between the output terminal of the transmitter 23 and the antenna 25.
- the antenna 25 emits high-frequency transmission signals to a space as radio waves and continues to broadcast again.
- the suppression of missing information can inhibit a listener from being affected by the silent state, for example.
- the trigger 4 outputs the first control signal SC1 and the second control signal SC2 to the control memory 44 based on the anomaly detection signal Se from the instantaneous halting unit 37; however, the trigger 42 can be omitted and the control memory 44 can be configured to output and cancel the output of the anomaly detection signal Se, the first control signal SC1, and the second control signal SC2 in the same manner.
- the audio unit 32 of the transmitter 23 functions as the broadcast relay assistance device; however, the broadcast audio signal generation device 21 or the relay device 22 can be configured to have the same or like functions (functions of the trigger 42, the control memory 44, and the shrinker 46).
- the instantaneous halting unit 37 of the transmitter 23 is required to feed back the signals to the broadcast audio signal generation device 21 or the relay device 22.
- a pilot signal may be superimposed on the broadcast audio signal Sba.
- the pilot signal of a single tone may be used and added to a frequency other than audible frequencies (e.g. 7.5 kHz or more).
- the above descriptions have exemplified a configuration that a commercial broadcasting period is not subjected to anomaly handling.
- the above processing may not be performed, for example, to a broadcast period where the processing of broadcast sound may induce a copyright issue (e.g. music broadcasting period) or a broadcast period where processing to content is prohibited by law and content is required to be broadcast as it is (e.g. election broadcasting period).
- the broadcast relay assistance device of the present embodiment includes a control device such as a CPU and a memory device such as a read only memory (ROM) or a RAM and thus can have a hardware configuration using a general computer.
- a control device such as a CPU
- a memory device such as a read only memory (ROM) or a RAM
- a control program executed in the broadcast relay assistance device of the present embodiment can be stored and provided in an installable or executable file format on a computer-readable recording medium such as a CD-ROM, a flexible disc (FD), a CD-R, and a digital versatile disk (DVD).
- a computer-readable recording medium such as a CD-ROM, a flexible disc (FD), a CD-R, and a digital versatile disk (DVD).
- control program executed in the broadcast relay assistance device of the present embodiment may be stored in a computer connected to a network such as the Internet and provided by download via the network. Moreover, the control program executed in the broadcast relay assistance device of the present embodiment may be provided or distributed via a network such as the Internet.
- control program of the broadcast relay assistance device of the present embodiment may be incorporated into a ROM or the like in advance.
- the control program executed in the broadcast relay assistance device of the present embodiment has a module configuration including the aforementioned respective units or elements (memory, output unit, ).
- a CPU processor
- the memory, the output unit, ... are thus generated on the main memory device.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Radio Relay Systems (AREA)
- Transmitters (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014089566A JP5937134B2 (ja) | 2014-04-23 | 2014-04-23 | 放送継続支援装置、放送継続支援装置の制御方法及び制御プログラム |
| PCT/JP2014/084634 WO2015162831A1 (ja) | 2014-04-23 | 2014-12-26 | 放送継続支援装置、放送継続支援装置の制御方法及び制御プログラム |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP3136629A1 true EP3136629A1 (de) | 2017-03-01 |
| EP3136629A4 EP3136629A4 (de) | 2017-09-27 |
| EP3136629B1 EP3136629B1 (de) | 2020-01-22 |
Family
ID=54332015
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP14889887.7A Active EP3136629B1 (de) | 2014-04-23 | 2014-12-26 | Rundfunkweiterleitungsunterstützungsvorrichtung, steuerungsverfahren für rundfunkweiterleitungsunterstützungsvorrichtung und steuerungsprogramm |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10250344B2 (de) |
| EP (1) | EP3136629B1 (de) |
| JP (1) | JP5937134B2 (de) |
| CN (1) | CN106233645B (de) |
| WO (1) | WO2015162831A1 (de) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP4084366A1 (de) * | 2021-04-26 | 2022-11-02 | Aptiv Technologies Limited | Verfahren zum testen einer rundfunkempfängervorrichtung in einem fahrzeug |
Family Cites Families (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH09162759A (ja) | 1995-12-11 | 1997-06-20 | Nec Eng Ltd | 中波放送装置の保護回路 |
| US6961513B2 (en) * | 1999-12-16 | 2005-11-01 | Sony Corporation | Audio signal processing method, audio signal processing apparatus, Hi-Fi video apparatus, digital video apparatus and 8 mm video apparatus |
| JP2001177803A (ja) * | 1999-12-16 | 2001-06-29 | Sony Corp | オーディオ信号処理方法、オーディオ信号再生装置、ハイファイビデオ装置、ディジタルビデオ装置、8mmビデオ装置 |
| JP2004040604A (ja) * | 2002-07-05 | 2004-02-05 | Nippon Hoso Kyokai <Nhk> | 放送通信コンテンツ送出方法、放送通信コンテンツ送出装置、放送通信コンテンツ送出プログラムおよび放送通信コンテンツ受信方法、放送通信コンテンツ受信装置、放送通信コンテンツ受信プログラム |
| KR20050121067A (ko) | 2004-06-21 | 2005-12-26 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 무선 채널에 의한 무선 통신 시스템 및 그의 무선 통신 방법 |
| US7511467B2 (en) * | 2005-10-14 | 2009-03-31 | Nokia Corporation | Detection of lightning |
| JP2007243906A (ja) * | 2006-02-07 | 2007-09-20 | Toshiba Corp | 閉空間用放送装置 |
| JP5130734B2 (ja) | 2007-02-15 | 2013-01-30 | ソニー株式会社 | 情報処理装置、および情報処理方法、並びにコンピュータ・プログラム |
| KR101337116B1 (ko) | 2010-09-08 | 2013-12-05 | 가부시끼가이샤 도시바 | 책자의 페이지 넘김 장치 |
| JP5631672B2 (ja) | 2010-09-08 | 2014-11-26 | 株式会社東芝 | 冊子の頁捲り装置 |
| JP5342033B2 (ja) * | 2012-03-13 | 2013-11-13 | 株式会社東芝 | デジタル振幅変調装置及びデジタル振幅変調装置の制御方法 |
| US8935581B2 (en) * | 2012-04-19 | 2015-01-13 | Netflix, Inc. | Upstream fault detection |
| KR20130123713A (ko) * | 2012-05-03 | 2013-11-13 | 현대모비스 주식회사 | 팝 노이즈 제거 방법 |
| JP5575189B2 (ja) * | 2012-07-04 | 2014-08-20 | 株式会社東芝 | デジタル振幅変調装置及びデジタル振幅変調装置の制御方法 |
| JP6180780B2 (ja) * | 2013-04-22 | 2017-08-16 | 三菱電機ビルテクノサービス株式会社 | 映像データ送信装置及び映像データ管理システム |
| CN103986833A (zh) * | 2014-05-22 | 2014-08-13 | 小米科技有限责任公司 | 异常状态监控方法及装置 |
-
2014
- 2014-04-23 JP JP2014089566A patent/JP5937134B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2014-12-26 US US15/305,508 patent/US10250344B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2014-12-26 EP EP14889887.7A patent/EP3136629B1/de active Active
- 2014-12-26 CN CN201480078113.1A patent/CN106233645B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2014-12-26 WO PCT/JP2014/084634 patent/WO2015162831A1/ja not_active Ceased
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2015162831A1 (ja) | 2015-10-29 |
| EP3136629B1 (de) | 2020-01-22 |
| JP2015210288A (ja) | 2015-11-24 |
| JP5937134B2 (ja) | 2016-06-22 |
| US10250344B2 (en) | 2019-04-02 |
| US20170041089A1 (en) | 2017-02-09 |
| CN106233645B (zh) | 2020-01-31 |
| CN106233645A (zh) | 2016-12-14 |
| EP3136629A4 (de) | 2017-09-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| AU2016402256A1 (en) | Voice input exception determining method, apparatus, terminal, and storage medium | |
| KR20060093722A (ko) | 적응성 사운드 재생 | |
| US10250344B2 (en) | Broadcast of audio data based on input broadcast signals stored during a detected anomaly period by lightning energy | |
| CN103168479A (zh) | 振鸣抑制装置、助听器、振鸣抑制方法和集成电路 | |
| US8949116B2 (en) | Signal processing method and apparatus for amplifying speech signals | |
| US20090029665A1 (en) | Receiver system and method that detects and attenuates noise in a predetermined frequency range | |
| US8879583B1 (en) | Radio frequency conditioning unit | |
| US20190296782A1 (en) | Receiver and non-transitory computer readable medium storing program | |
| JP5575189B2 (ja) | デジタル振幅変調装置及びデジタル振幅変調装置の制御方法 | |
| JP2015133546A (ja) | ディジタル振幅変調装置及びディジタル振幅変調制御方法 | |
| JP2007325225A (ja) | ノイズ検出装置及びam放送受信装置 | |
| US9461604B2 (en) | Sound output device and method of adjusting sound volume | |
| JP2010087591A (ja) | スピーカ装置 | |
| KR102078839B1 (ko) | 터널용 비상방송 무선전송장치 및 그 방법 | |
| JP2009159020A (ja) | 信号処理装置、信号処理方法、プログラム | |
| KR101067489B1 (ko) | Opt에 class-d 샘플링주파수를 공급하여 경량화된 전관방송증폭기 | |
| JP4613138B2 (ja) | 中継装置 | |
| JP4869874B2 (ja) | 高周波増幅器 | |
| JP2009267615A (ja) | オーディオ用増幅装置 | |
| JP7090801B2 (ja) | 送信装置、受信装置、およびワイヤレスマイクロホンシステム | |
| US10298181B2 (en) | Low-noise amplification device, method, and attenuation adjustment program | |
| JP2014179695A (ja) | Ofdm送信装置及びofdm信号送信方法 | |
| JP7150536B2 (ja) | インピーダンス調整方法、および、インピーダンス調整プログラム | |
| JP4606864B2 (ja) | Agc回路および制御方法 | |
| JP2017212540A (ja) | ディジタル振幅変調装置及び方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE INTERNATIONAL PUBLICATION HAS BEEN MADE |
|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: REQUEST FOR EXAMINATION WAS MADE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20161018 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| A4 | Supplementary search report drawn up and despatched |
Effective date: 20170828 |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: G10L 21/057 20130101ALI20170822BHEP Ipc: H04H 20/12 20080101AFI20170822BHEP Ipc: G10L 19/005 20130101ALI20170822BHEP |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: EXAMINATION IS IN PROGRESS |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20180924 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20190913 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 602014060514 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: HOFFMANN - EITLE PATENT- UND RECHTSANWAELTE PA, DE |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 1227619 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20200215 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 602014060514 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MP Effective date: 20200122 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200422 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200614 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200522 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200423 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200422 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 602014060514 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MK05 Ref document number: 1227619 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20200122 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20201023 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20201217 Year of fee payment: 7 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20201216 Year of fee payment: 7 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20201112 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20201231 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20201226 Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20201226 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20201231 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20201231 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200122 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 602014060514 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20201231 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20211226 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20211226 Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20220701 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20211231 |