EP2831900B1 - Relais électromagnétique polarisé et son procédé de fabrication - Google Patents
Relais électromagnétique polarisé et son procédé de fabrication Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2831900B1 EP2831900B1 EP13713418.5A EP13713418A EP2831900B1 EP 2831900 B1 EP2831900 B1 EP 2831900B1 EP 13713418 A EP13713418 A EP 13713418A EP 2831900 B1 EP2831900 B1 EP 2831900B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- pole
- relay
- magnetic flux
- permanent magnet
- armature
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 6
- 230000005291 magnetic effect Effects 0.000 claims description 59
- 230000004907 flux Effects 0.000 claims description 46
- 239000002243 precursor Substances 0.000 claims description 14
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000004308 accommodation Effects 0.000 claims 13
- 230000005415 magnetization Effects 0.000 description 8
- 230000005294 ferromagnetic effect Effects 0.000 description 7
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical compound [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000004804 winding Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004026 adhesive bonding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000712 assembly Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000429 assembly Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005266 casting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000000428 dust Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004382 potting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H51/00—Electromagnetic relays
- H01H51/22—Polarised relays
- H01H51/2236—Polarised relays comprising pivotable armature, pivoting at extremity or bending point of armature
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H50/00—Details of electromagnetic relays
- H01H50/02—Bases; Casings; Covers
- H01H50/04—Mounting complete relay or separate parts of relay on a base or inside a case
- H01H50/041—Details concerning assembly of relays
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H49/00—Apparatus or processes specially adapted to the manufacture of relays or parts thereof
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H51/00—Electromagnetic relays
- H01H51/22—Polarised relays
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01F—MAGNETS; INDUCTANCES; TRANSFORMERS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
- H01F7/00—Magnets
- H01F7/06—Electromagnets; Actuators including electromagnets
- H01F7/08—Electromagnets; Actuators including electromagnets with armatures
- H01F7/121—Guiding or setting position of armatures, e.g. retaining armatures in their end position
- H01F7/122—Guiding or setting position of armatures, e.g. retaining armatures in their end position by permanent magnets
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T29/00—Metal working
- Y10T29/49—Method of mechanical manufacture
- Y10T29/49002—Electrical device making
- Y10T29/4902—Electromagnet, transformer or inductor
- Y10T29/49073—Electromagnet, transformer or inductor by assembling coil and core
Definitions
- the invention relates to a method for producing a polarized electromagnetic relay with an electromagnet, permanent magnet, armature and actuatable switch and to a polarized electromagnetic relay produced in this way.
- Poled, electromagnetic relays are available with a three-pole permanent magnet ( WO 93/23866 ) and with two-pole permanent magnet ( U.S. 4,912,438 , U.S. 5,153,543 , US 6,670,871 B1 ).
- the electromagnet has a coil with a core and pole pieces in a yoke-shaped structure.
- this permanent magnet is arranged between the two yoke legs above the coil and parallel to the coil axis.
- This permanent magnet can be separated from a magnetized band and inserted into the coil body between the two yoke legs.
- this is magnetically connected at right angles to the coil axis with a pole in about the middle of the old core ( U.S. 4,912,438 , U.S. 5,153,543 ).
- U.S. 4,975,666 a polarized, electromagnetic relay which has a base housing open at the top, in which an electromagnetic block with coil, core and pole legs and, between the pole legs, a permanent magnet, and on the pole legs, a valve block with armature and switch elements are mounted.
- the design does not allow the permanent magnet located between the pole legs to be generated from an unmagnetized ferromagnetic precursor by magnetization, because the coil would be damaged by excessive, induced currents.
- a relay with a two-pole permanent magnet is also known ( US 6,670 871 B1 ), which extends parallel to the coil axis.
- the plate-shaped permanent magnet with poles on the top and bottom is held in an anchor plate.
- the electromagnet is housed in a two-part housing which has a trough-shaped lower part and a box-shaped upper part on which the fixed contacts of the switches and the rotating supports for the armature are located.
- the movable contact springs are embedded in the insulating anchor plate.
- a recess in the anchor plate is used to accommodate the two-pole permanent magnet. Whether the permanent magnet is embedded in the armature plate is magnetized is not disclosed in the document.
- the DE 38 02 688 A1 shows a polarized relay with an insulating base body in the form of a flat trough which has a central, elongated recess for receiving the coil of the polarized relay.
- the coil forms a structural unit with the core and pole pieces, which is built into the recess of the tub in order to work together with counter-contact elements, connection elements for armature contact springs and with coil connection elements. As a result of these elements, there is no lateral accessibility to the recess, which is therefore not designed in the manner of a drawer.
- a polarized electromagnetic relay which comprises a base body with a partition which isolates an overhead coil from a base arranged below.
- the coil with core and pole pieces as well as with winding connection elements is installed from above into the cavity of the base body, the winding connection elements reaching through recesses in the partition wall and being connected to the base of the device, which is housed in the space below the partition wall.
- a drawer-like receiving space which would have to be accessible from the side of the base body, is not provided.
- the invention is based on the object of magnetizing the permanent magnet of a polarized relay without endangering other relay parts.
- the components of the relay are designed separately in connection with special manufacturing steps, so that the permanent magnet can be magnetized without the risk of damaging the coil of the electromagnet.
- a coil assembly with coil, core and pole pieces is provided as a component of the relay, and also a carrier component in which magnetic flux parts of the magnetic system of the relay are included, including the pole pieces of the electromagnet and a bearing piece of the armature.
- These magnetic flux parts are made of soft iron and are not damaged by high magnetic field strengths.
- a one-piece or two-piece permanent magnet precursor made of non-magnetized, ferromagnetic alloy is built into the carrier component, which results in the permanent magnet by magnetization.
- the carrier component also has a receiving space into which the separately produced coil assembly, which represents the sensitive part of the electromagnet, is inserted and mounted after the permanent magnet has been magnetized. Then the remaining relay components to complete the relay are installed, including the switches operated by the relay.
- the invention also relates to a polarized electromagnetic relay which comprises an electromagnet, a pole assembly with magnetic flux parts and with a permanent magnet, a carrier component and an armature.
- the electromagnet comprises a coil assembly, which is designed as a unit with coil, core and pole pieces.
- the support component is preferably tiered and comprises an upper-side cavity as a receiving space for the pole assembly with the magnetic flux parts and the magnetized permanent magnet as well as a central slot as a receiving space for the coil assembly.
- the armature of the relay is arranged pivotably relative to the electromagnet on the carrier component and is connected to the movable switch elements.
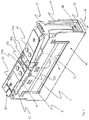
- the electromagnetic relay is made up of a magnet system and a switch system, which are held together and protected by housing components.
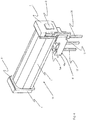
- the magnet system comprises an electromagnet, which consists of a coil assembly 10 ( Fig. 4 ) and pole pieces ( Fig. 2 ) consists.
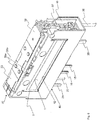
- the coil assembly 10 comprises a coil 1 wound on a coil body 5, a ferromagnetic core 2 and ferromagnetic pole pieces 3 and 4, which form a structural unit.
- the core 2 is integrally connected to one of the two pole pieces 3, 4 or to both pole pieces. Still belong to the magnet system Magnetic flux parts 7, 8, 9, a permanent magnet 11 and an armature 12.
- the magnetic flux parts 7 and 8 form the pole pieces of the electromagnet.
- the magnetic flux part 9 forms a bearing piece for the armature 12, which is designed here as a rocking armature.
- the permanent magnet 11 of the first embodiment has two poles and is arranged between the pole piece 7 and the magnetic flux part 9, while there is a magnetic flux interruption between the parts 8 and 9. It is also possible to swap the arrangement of the permanent magnet and the magnetic flux gap. The alignment of the poles of the permanent magnet with respect to the pole piece 7 or 8 and the magnetic flux part 9 is important.
- the magnetic flux parts 7, 8, 9 and the permanent magnet 11 form a pole assembly.
- connection block 6 is connected to the coil assembly 10, which is not necessary in the context of the invention.
- the connection block 6 comprises switching signal connection pins 15, 16 with bending legs 15a, 16a for direct connection to the winding ends of the coil 1.
- a test contact connection pin 25 is cranked and can thus be clamped between connection block 6 and pole piece 3.
- FIG. 4 The component shown is designed to be placed in a drawer-like receiving space 42 of a storey-like support component 40 ( Fig. 3 ) to be pushed in and assembled.
- the drawer 42 has two cavity expansions 43 and 44 in order to receive and position the connection block 6 in addition to the coil assembly 10.
- the tiered support component 40 is also responsible for receiving the pole assembly, that is to say the magnetic flux parts 7, 8, 9 and the permanent magnet 11.
- an anchor-side receiving space 41 divided into niches is provided.
- the parts 7, 8, 9 and 11 are fastened in the carrier component 40 by embedding.
- Various embedding methods come into consideration, for example overmolding, gluing, pressing in.
- a fixed contact 21 is also provided, which is in electrical connection with a connection pin 26, which is also fastened in the carrier component 40 by embedding.
- the switch system contains a diagnostic switch 20 and at least one load switch 30.
- the diagnostic switch 20 comprises the fixed contact 21 and a movable contact 22 which is attached as a double contact to the fork-shaped end of a contact spring 23.
- the contact spring 23 is attached to the leg 12a of the armature 12 and is actuated by the latter.
- the movable contact 22 establishes the electrical connection with the connecting pin 25.
- test contact connection pin 25 is embedded in the support component 40 parallel to the test contact connection pin 26 (not shown) and two separate fixed contacts are provided on the top of the support component 40.
- end of the contact spring 23 is used as a bridge contact for closing the switch 20.
- the load switch 30 comprises a fixed contact 31 and a movable contact 32 which is seated on a contact spring 33 which is fastened to the carrier component 40 via a busbar 34 and is also in electrical connection with a load connection pin 35.
- the fixed contact 31 is in conductive connection with a further load connection pin 36.
- the contact spring 33 is actuated via an electrically insulating coupling member 37, the upper end of which is mechanically connected to the second leg 12b of the armature 12.
- the mechanical connection can take place via an overtravel spring 38, as shown, or by direct connection of the ends of the rocker armature 12 and the coupling member 37.
- the armature 12 In addition to its two legs 12a and 12b, the armature 12 also has a curved bearing part 12c with which the armature rests on the magnetic flux part 9, which is built as a bearing piece.
- the legs 12a, 12b of the armature 12 are of different lengths and are held by spring forces with different pole gap widths. Such spring forces are generated by the contact spring 23, the overtravel spring 38 (if present) and the contact spring 33.
- the contact spring 23 is riveted to the arm 12a of the armature and has spring extensions 23a and 23b as well as a fastening tab 23c which is welded to the bearing piece 9 in a certain angular position between armature 12 and pole surface 7.
- the overtravel spring 38 is similarly riveted firmly to the leg 12b and also has spring extensions 38a, 38b and a fastening tab 38c which is welded to the bearing piece 9. In addition to the force of the contact spring 33, it is primarily the torsional forces of the spring legs 23b and 38b, which are responsible for the overall spring behavior of the relay.
- the magnetic force of attraction on the armature 12 also plays a role, whether a monostable or a bistable relay is obtained.
- the strength of the permanent magnet 11 and the sizes of the pole faces of the pole pieces 7, 8 play a role in the forces of attraction on the legs 12a, 12b of the armature. If the magnetic attraction force in one end position of the armature is greater than the spring force effective in the lifting direction and in the other end position the magnetic attraction force is smaller than the lifting force of the springs, then there is a monostable relay. If, on the other hand, the magnetic attraction force in both end positions of the armature is greater than the spring force effective in the lifting direction, a bistable relay is present.
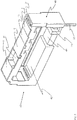
- the carrier component 40 represents the main element of the housing, there is also a housing base 50 and a housing cover 60. As in FIG Fig. 1 As shown, the carrier component 40 has a guide 46 on its front side visible there for guiding the insulating coupling member 37. This guide and the top of the relay is through the housing cover 60 according to Fig. 1 mounted relay covered. A flat cavity 45 extends along the underside of the support component 40 ( Fig. 2 ), which serves to accommodate the load contact spring 33 and its freedom of movement and which is delimited from the housing base 50 at the bottom.
- the load contact connecting pin 36 is inserted into the base part 50 and riveted to the base part by means of the fixed contact 31.
- a switch can be located on the top of the housing cover 60 in order to change the position of the armature 12 by hand.
- a second embodiment of the invention is shown. Similar components to the first embodiment are given the same reference numerals.
- the basic structure of the relay according to the second embodiment follows the first embodiment, which is why corresponding parts of the description are not repeated and only the differences are discussed.
- the permanent magnet 11 is made from two parts 11a and 11b and with a magnetic flux part 9 made of soft iron and forms a three-pole permanent magnet.
- the section 11a has the stronger coercive force compared to the section 11b.
- the two parts 11a and 11b have the same polarity towards the magnetic flux part 9, so either both are formed there as a south pole or as a north pole, while the three-pole permanent magnet 11 then shows north poles or south poles towards the outer ends of the relay.
- the magnetic flux part 9 conveys the adjacent polarity, for example the south pole when the permanent magnet faces the north pole and the north pole when the permanent magnet faces the south pole.
- the mounting of the armature 12 compared to the first embodiment is modified by a cross spring 39, the mounting of the armature 12 on the Magnet flux part 9 takes over.
- the cross spring 39 has tabs 39a, with which it is connected to the magnetic flux part 9 by welding, also a torsion bar 39b and transversely thereto a support tab 39c for supporting the armature 12.
- Another tab 39d can be attached to the cross spring 39, which serves to dampen the impact of the armature 12 on the magnetic flux part 8 and is tensioned at the same time, which is useful when the armature 12 is switched over later, since the armature then detaches more easily from the magnetic flux part 8.
- the cross spring 39 acts as a torsion spring, ie there is no bearing friction and the hysteresis losses of the spring 39 are very small.
- the second embodiment has a one-piece design of contact spring 23 and overtravel spring 38.
- the contact spring 23 is electrically conductive and connected to the electrically conductive armature 12, which in turn is connected via the electrically conductive cross spring 39 to the electrically conductive magnetic flux part 9, which in turn is in electrically conductive connection to the test contact connection pin 25.
- An intermediate piece 8a made of sheet metal or plastic is also provided in order to adapt the adhesive force of the armature 12 at the leg 12b to the magnetic flux part 8. Because of the different lengths of the legs 12a, 12b of the armature 12, the lifting forces exerted there are different, which is somewhat compensated for by the intermediate position of the part 8a.
- the polarized electromagnetic relay is manufactured and assembled in a new way.
- the individual parts shown are partially assembled into assemblies, including those in Fig. 4
- This coil assembly comprises at least the coil 1, the core 2 and the pole shoes 3 and 4.
- the individual parts shown also include a carrier component 40, which according to the invention is functionally adapted to the manufacturing method of the relay.
- the carrier component 40 namely contains an armature-side receiving space 41 for the magnetic flux parts 7, 8, 9 and the permanent magnet 11 as well as a drawer-like receiving space 42 for the coil assembly 10.
- the magnetic flux parts 7, 8 and 9 and the permanent magnet 11 can be referred to as a pole assembly, since they present the armature 12 with two outer poles and a center pole.
- the pole assembly is mounted in the receiving space 41 of the carrier component 40 and fastened, for example, by casting around it.
- the type of permanent magnet to be generated must be taken into account. If a one-piece two-pole permanent magnet is to be produced, which corresponds to the first embodiment of the relay, the procedure described is sufficient. If, on the other hand, a three-pole permanent magnet is to be generated by magnetization, the procedure is modified.
- Two precursor magnet sections 11a, 11b are used on both sides of the central magnetic flux part 9 and in contact with the adjacent magnetic flux parts 7 and 8.
- One of these precursor magnet sections, here section 11a consists of a more magnetizable alloy opposite the other section 11b. The more strongly magnetizable section 11a can also be made smaller than the less magnetizable section 11b.
- magnetization is carried out in a certain direction, as it corresponds to the stronger partial permanent magnet 11a. Then a direction opposite to the original magnetic direction, but weaker Magnetic field applied to the pole assembly, this weaker magnetic field not being sufficient to re-magnetize the permanent magnet 11a, but sufficient to re-magnetize the weaker permanent magnet 11b.
- This has the consequence that poles of the same name are opposite one another on the central magnetic flux part 9. In this way, an overall permanent magnet 11 is obtained with two poles of the same name on the outside, ie to the magnetic flux parts 7 and 8 acting as pole pieces, and an opposite pole on the central magnetic flux part 9.
- This structure forms a three-pole permanent magnet.
- the coil assembly 10 can be safely mounted in the drawer-like receiving space 42.
- the relays can be made very small, since permanent magnets with a large coercive force can be generated.
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Electromagnets (AREA)
- Manufacture Of Switches (AREA)
Claims (12)
- Procédé de fabrication d'un relais électromagnétique polarisé avec un électro-aimant, un aimant permanent (11), une armature (12) et un commutateur actionnable (20, 30), comprenant les étapes suivantes :a) mise à disposition d'un sous-ensemble de bobine (10), qui comprend une bobine (1) avec un noyau (2) et des pièces polaires (3, 4) sous la forme d'une unité modulaire ;b) mise à disposition d'un composant porteur (40) avec un espace de logement côté armature (41) pour un sous-ensemble polaire (7, 8, 9, 11) et un espace de logement en forme de tiroir (42) pour le sous-ensemble de bobine (10) ;c) montage du sous-ensemble polaire (7, 8, 9, 11) avec des parties de flux magnétique (7, 8, 9) et avec un aimant permanent précurseur non magnétisé dans l'espace de logement côté armature (41) ;d) magnétisation de l'aimant permanent précurseur à l'intérieur du sous-ensemble polaire lorsque le tiroir (42) est vide afin d'obtenir l'aimant permanent (11) ;e) montage du sous-ensemble de bobine (10) dans l'espace de logement en forme de tiroir (42) ;f) montage des composants restants du relais afin de compléter le relais.
- Procédé selon la revendication 1, pour la mise à disposition d'un aimant permanent tripolaire (11)
dans lequel l'étape c) comprend le montage de deux parties d'aimant précurseur (11a, 11b) pouvant être magnétisées avec des forces différentes entre trois parties de flux magnétique (7, 8, 9) du sous-ensemble polaire (7, 8, 9, 11) et
dans lequel l'étape d) comprend les sous-étapes suivantes :d1) magnétisation des deux parties d'aimant précurseur (11a, 11b) ;d2) démagnétisation de la partie d'aimant précurseur (11b) la plus faible de façon à ce que les pôles de même signe des parties magnétisées (11a, 11b) soient en face l'un de l'autre au niveau de la partie de flux magnétique (9) qui les sépare. - Relais électromagnétique polarisé fabriqué selon un procédé selon l'une des revendications 1 et 2, comprenant :- un composant porteur (40), qui comprend, sous forme d'étages, un espace de logement côté armature (41), un espace de logement en forme de tiroir (42) et un espace de logement côté contact de charge (45) ;- un sous-ensemble polaire (7, 8, 9, 11) avec des parties de flux magnétique (7, 8, 9), qui forment une partie de flux magnétique centrale (9) et des pièces polaires (7, 8) des deux côtés, et avec un aimant permanent (11) entre au moins une des pièces polaires et la partie de flux magnétique centrale (9), où le sous-ensemble polaire (7, 8, 9, 11) est logé dans l'espace de logement côté armature (41) du composant porteur (40) ;- un sous-ensemble de bobine (10), qui comprend une bobine (1) avec un noyau (2) et des pièces polaires (3, 4), sous la forme d'une unité modulaire, et qui forme des parties d'un électro-aimant et qui est logé dans l'espace de logement en forme de tiroir (42) ;- une armature (42), qui est disposée sur le sous-ensemble polaire (7, 8, 9, 11) et qui est pivotante par rapport à celui-ci et qui est reliée avec des éléments de commutateur mobiles (23, 33).
- Relais selon la revendication 3,
dans lequel l'espace de logement côté contact de charge (45) du composant porteur (40) loge un commutateur de charge (30) et est fermé par un fond de boîtier (50). - Relais selon la revendication 4, dans lequel le fond de boîtier (50) supporte au moins un contact fixe (31) du commutateur de charge (30) et, conjointement avec le composant porteur (40), des broches de connexion (15, 16, 25, 26, 35, 36).
- Relais selon l'une des revendications 3 à 5,- dans lequel l'électro-aimant comprend une culasse en forme de U (2, 3, 4) avec des parties de flux magnétique (7, 8) adjacentes formant des pièces polaires,- dans lequel l'armature (12) est conçue comme une armature basculante avec une première et une deuxième branches (12a, 12b), qui s'appuie sur une partie de flux magnétique centrale (9) et forme, avec respectivement une de ses branches (12a, 12b), conjointement avec la partie de flux magnétique centrale (9) et respectivement une des parties de flux magnétique (7, 8) servant de pièces polaires, un trajet de flux magnétique fermé à faible entrefer magnétique et- dans lequel chacune des branches (12a, 12b) actionne un contact mobile (22, 32) de chaque commutateur (20, 30).
- Relais selon la revendication 6,
dans lequel un premier commutateur, utilisé comme commutateur de diagnostic (20), est constitué d'un contact fixe (21) sur le composant porteur (40) et d'un contact mobile (22) sur un premier ressort de contact (23), qui est fixé à la première branche (12a) de l'armature basculante (12), et dans lequel un deuxième commutateur, utilisé comme commutateur de charge (30), est constitué d'un contact fixe (31) sur le fond de boîtier (50) et d'un contact mobile (32) sur un deuxième ressort de contact (33), qui est en liaison mécanique, par l'intermédiaire d'un élément de couplage électriquement isolant (37), avec la deuxième branche (12b) de l'armature basculante (12). - Relais selon la revendication 7,
dans lequel le composant porteur (40) comprend un guidage (46) pour l'élément de couplage électriquement isolant (37), et dans lequel un capot de boîtier (60) entoure le composant porteur (40) en venant en prise sur le fond de boîtier (50). - Relais selon l'une des revendications 3 à 8,
dans lequel l'aimant permanent (11) est constitué d'une seule pièce et est adjacent à un pôle sur la partie de flux magnétique centrale (9) et à l'autre pôle sur une des parties de flux magnétique (7, 8) servant de pôle magnétique. - Relais selon l'une des revendications 3 à 8,
dans lequel l'aimant permanent (11) comprend deux parties (11a, 11b) qui se font face avec des pôles de même signe au niveau de la partie de flux magnétique centrale (9), afin de former dans l'ensemble un aimant permanent tripolaire (11). - Relais selon la revendication 10,
dans lequel une des parties (11a) présente une force coercitive plus forte par rapport à l'autre partie (11b). - Relais selon la revendication 11,
dans lequel la partie (11a) avec la force coercitive la plus grande occupe un volume plus petit que la partie (11b) avec la force coercitive la plus faible.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102012006436.5A DE102012006436B4 (de) | 2012-03-30 | 2012-03-30 | Gepoltes elektromagnetisches Relais und Verfahren zu seiner Herstellung |
| PCT/EP2013/056547 WO2013144218A2 (fr) | 2012-03-30 | 2013-03-27 | Relais électromagnétique polarisé et son procédé de fabrication |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2831900A2 EP2831900A2 (fr) | 2015-02-04 |
| EP2831900B1 true EP2831900B1 (fr) | 2021-04-28 |
Family
ID=48044776
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP13713418.5A Active EP2831900B1 (fr) | 2012-03-30 | 2013-03-27 | Relais électromagnétique polarisé et son procédé de fabrication |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9368304B2 (fr) |
| EP (1) | EP2831900B1 (fr) |
| JP (1) | JP5989225B2 (fr) |
| CN (1) | CN104170047B (fr) |
| DE (1) | DE102012006436B4 (fr) |
| WO (1) | WO2013144218A2 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD770387S1 (en) * | 2014-03-19 | 2016-11-01 | Phoenix Contact Gmbh & Co. Kg | Electrical connector |
| JP6422249B2 (ja) * | 2014-07-03 | 2018-11-14 | 富士通コンポーネント株式会社 | 電磁継電器 |
| JP6258138B2 (ja) * | 2014-07-03 | 2018-01-10 | 富士通コンポーネント株式会社 | 電磁継電器 |
| WO2016013485A1 (fr) * | 2014-07-23 | 2016-01-28 | 富士通コンポーネント株式会社 | Relais électromagnétique |
| JP6433706B2 (ja) * | 2014-07-28 | 2018-12-05 | 富士通コンポーネント株式会社 | 電磁継電器及びコイル端子 |
| DE102016101501B4 (de) | 2016-01-28 | 2018-12-27 | Phoenix Contact Gmbh & Co. Kg | Elektromechanisches Relais und Vorrichtung zum Erkennen des Schaltzustandes eines elektromechanischen Relais |
| DE102016112663B4 (de) | 2016-07-11 | 2018-04-12 | Phoenix Contact Gmbh & Co. Kg | Elektromechanisches Relais, Reihenklemme und elektromechanische Relaisbaugruppe |
| DE102016125382A1 (de) * | 2016-12-22 | 2018-06-28 | Phoenix Contact Gmbh & Co. Kg | Modulare Schaltschützanordnung |
| BE1025465B1 (de) * | 2017-08-11 | 2019-03-11 | Phoenix Contact Gmbh & Co. Kg | Verfahren zum Magnetisieren von mindestens zwei Magneten unterschiedlicher magnetischer Koerzitivfeldstärken |
| JP7135567B2 (ja) * | 2018-08-10 | 2022-09-13 | オムロン株式会社 | リレー |
| CN110335788A (zh) * | 2019-07-09 | 2019-10-15 | 厦门宏发电声股份有限公司 | 一种小型化大功率磁保持继电器 |
Family Cites Families (21)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BE560797A (fr) * | 1956-09-14 | |||
| DE1614713B1 (de) * | 1967-11-08 | 1971-03-04 | Schaltbau Gmbh | Haftrelais |
| DD120156A1 (fr) | 1975-06-23 | 1976-06-05 | ||
| DE2614942A1 (de) * | 1976-04-07 | 1977-10-20 | Ernst Duerr | Elektromagnetisches kleinschaltrelais |
| US4286244A (en) * | 1980-02-29 | 1981-08-25 | Leach Corporation | Electromagnetic actuator for a latch relay |
| JPS5760633A (en) | 1980-09-26 | 1982-04-12 | Fujitsu Ltd | Solenoid relay |
| US4912438A (en) | 1987-10-22 | 1990-03-27 | Nec Corporation | Electromagnetic relay |
| DE3802688C2 (de) * | 1988-01-29 | 1997-04-10 | Siemens Ag | Polarisiertes Relais |
| EP0334336B1 (fr) * | 1988-03-25 | 1993-09-29 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Relais électromagnétique polarisé à contacts multiples |
| US4975666A (en) * | 1989-03-28 | 1990-12-04 | Matsushita Electric Works, Ltd. | Polarized electromagnetic relay |
| JPH04149924A (ja) | 1990-10-15 | 1992-05-22 | Nec Corp | 電磁継電器 |
| CZ281297B6 (cs) | 1992-05-15 | 1996-08-14 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Polarizované výkonové relé |
| JP3319814B2 (ja) * | 1993-05-26 | 2002-09-03 | 松下電工株式会社 | 高周波リレー |
| DE19520220C1 (de) * | 1995-06-01 | 1996-11-21 | Siemens Ag | Polarisiertes elektromagnetisches Relais |
| US5805039A (en) * | 1995-08-07 | 1998-09-08 | Siemens Electromechanical Components, Inc. | Polarized electromagnetic relay |
| DE19719355C1 (de) * | 1997-05-07 | 1998-11-05 | Siemens Ag | Polarisiertes elektromagnetisches Relais |
| WO2000007199A2 (fr) * | 1998-07-30 | 2000-02-10 | Siemens Electromechanical Components Gmbh & Co. Kg | Relais electromagnetique et son procede de production |
| WO2000007200A2 (fr) * | 1998-07-30 | 2000-02-10 | Siemens Electromechanical Components Gmbh & Co. Kg | Relais electromagnetique |
| DE10084279B3 (de) | 1999-12-24 | 2013-04-25 | Takamisawa Electric Co. Ltd. | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Wechselrelais |
| CN2829067Y (zh) * | 2005-06-09 | 2006-10-18 | 厦门宏发电声有限公司 | 一种具有高灵敏度的双工作气隙的极化继电器 |
| CN201655689U (zh) * | 2010-06-04 | 2010-11-24 | 北京松下控制装置有限公司 | 用于极化电磁继电器的轭铁和极化电磁继电器 |
-
2012
- 2012-03-30 DE DE102012006436.5A patent/DE102012006436B4/de active Active
-
2013
- 2013-03-27 JP JP2015502328A patent/JP5989225B2/ja active Active
- 2013-03-27 WO PCT/EP2013/056547 patent/WO2013144218A2/fr active Application Filing
- 2013-03-27 US US14/388,104 patent/US9368304B2/en active Active
- 2013-03-27 CN CN201380015376.3A patent/CN104170047B/zh active Active
- 2013-03-27 EP EP13713418.5A patent/EP2831900B1/fr active Active
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| None * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN104170047A (zh) | 2014-11-26 |
| JP5989225B2 (ja) | 2016-09-07 |
| DE102012006436A1 (de) | 2013-10-02 |
| US9368304B2 (en) | 2016-06-14 |
| DE102012006436B4 (de) | 2020-01-30 |
| WO2013144218A3 (fr) | 2013-12-12 |
| WO2013144218A2 (fr) | 2013-10-03 |
| US20150048909A1 (en) | 2015-02-19 |
| CN104170047B (zh) | 2017-04-05 |
| JP2015515097A (ja) | 2015-05-21 |
| EP2831900A2 (fr) | 2015-02-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2831900B1 (fr) | Relais électromagnétique polarisé et son procédé de fabrication | |
| EP2831901B1 (fr) | Relais comportant deux commutateurs agissant de façon opposée l'un par rapport à l'autre | |
| EP1032941B1 (fr) | Relais miniaturise a bobine plate | |
| DE19820821C1 (de) | Elektromagnetisches Relais | |
| DE3885508T2 (de) | Elektromagnetisches Relais. | |
| DE3303665A1 (de) | Polarisiertes elektromagnetisches relais | |
| DE69114865T2 (de) | Elektromagnetisches Relais. | |
| DE3586200T2 (de) | Elektromagnetisches relais. | |
| DE4243607A1 (en) | Polarised electromechanical relay - has pivot mounted armature block mounted on main coil block with leaf spring contact carriers attached | |
| EP2645386B1 (fr) | Relais doté de propriétés d'isolation améliorées | |
| DE69019866T2 (de) | Polarisiertes elektromagnetisches Relais. | |
| DE2749468A1 (de) | Elektromagnetisches umschlagrelais | |
| EP0072976B1 (fr) | Relais électromagnétique polarisé | |
| DE102012106330B4 (de) | Spulenkern für elektromagnetischen Antrieb und selbiger sowie Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung | |
| DE3222336C2 (fr) | ||
| DE3124412C1 (de) | Polarisiertes elektromagnetisches Kleinrelais | |
| DE69709786T2 (de) | Polarisiertes relais mit festhaltevorrichtung für den permanentmagneten | |
| DE3802688C2 (de) | Polarisiertes Relais | |
| EP2645398B1 (fr) | Relais doté de propriétés d'isolation améliorées | |
| DE2905686A1 (de) | Miniatur-relais fuer kurze umschaltzeiten | |
| EP0373109B1 (fr) | Relais polarisé pour plaquette de circuit imprimé | |
| DE3408504C2 (fr) | ||
| DE102016107410A1 (de) | Bistabiler Aktuator für ein polarisiertes elektromagnetisches Relais | |
| EP0630516B1 (fr) | Relais electromagnetique polarise | |
| EP1135786B1 (fr) | Petit relais electromagnetique |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20141030 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20151124 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: EXAMINATION IS IN PROGRESS |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20171030 |
|
| GRAJ | Information related to disapproval of communication of intention to grant by the applicant or resumption of examination proceedings by the epo deleted |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSDIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: EXAMINATION IS IN PROGRESS |
|
| INTC | Intention to grant announced (deleted) | ||
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20201202 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502013015679 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 1388035 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20210515 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG9D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210728 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210828 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210729 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210830 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210728 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MP Effective date: 20210428 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502013015679 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20220131 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210828 Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20220331 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20220327 Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20220327 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20220331 |
|
| P01 | Opt-out of the competence of the unified patent court (upc) registered |
Effective date: 20230424 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20130327 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20240319 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20240319 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20240321 Year of fee payment: 12 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20240326 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20240529 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20240401 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 |