EP1978833B1 - Dispositif de déviation pour un cordon filtrant continu, procédé pour le transport et la déviation d'un cordon filtrant, et appareil pour la fabrication de filtres de cigarette - Google Patents
Dispositif de déviation pour un cordon filtrant continu, procédé pour le transport et la déviation d'un cordon filtrant, et appareil pour la fabrication de filtres de cigarette Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1978833B1 EP1978833B1 EP06818621A EP06818621A EP1978833B1 EP 1978833 B1 EP1978833 B1 EP 1978833B1 EP 06818621 A EP06818621 A EP 06818621A EP 06818621 A EP06818621 A EP 06818621A EP 1978833 B1 EP1978833 B1 EP 1978833B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- machine
- funnel
- tubular body
- filtering material
- deflection
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 5
- 235000019504 cigarettes Nutrition 0.000 title claims description 4
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title description 4
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 58
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000001914 filtration Methods 0.000 claims 11
- 239000007921 spray Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 9
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 9
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- URAYPUMNDPQOKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N triacetin Chemical compound CC(=O)OCC(OC(C)=O)COC(C)=O URAYPUMNDPQOKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000010349 pulsation Effects 0.000 description 5
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000003750 conditioning effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 235000013773 glyceryl triacetate Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 239000001087 glyceryl triacetate Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229960002622 triacetin Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 230000000712 assembly Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000000429 assembly Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000013016 damping Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000004014 plasticizer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001154 acute effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007792 addition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000003608 fece Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000000796 flavoring agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019634 flavors Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000005243 fluidization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007062 hydrolysis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006460 hydrolysis reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008092 positive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005507 spraying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000017260 vegetative to reproductive phase transition of meristem Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A24—TOBACCO; CIGARS; CIGARETTES; SIMULATED SMOKING DEVICES; SMOKERS' REQUISITES
- A24D—CIGARS; CIGARETTES; TOBACCO SMOKE FILTERS; MOUTHPIECES FOR CIGARS OR CIGARETTES; MANUFACTURE OF TOBACCO SMOKE FILTERS OR MOUTHPIECES
- A24D3/00—Tobacco smoke filters, e.g. filter-tips, filtering inserts; Filters specially adapted for simulated smoking devices; Mouthpieces for cigars or cigarettes
- A24D3/02—Manufacture of tobacco smoke filters
- A24D3/0204—Preliminary operations before the filter rod forming process, e.g. crimping, blooming
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A24—TOBACCO; CIGARS; CIGARETTES; SIMULATED SMOKING DEVICES; SMOKERS' REQUISITES
- A24D—CIGARS; CIGARETTES; TOBACCO SMOKE FILTERS; MOUTHPIECES FOR CIGARS OR CIGARETTES; MANUFACTURE OF TOBACCO SMOKE FILTERS OR MOUTHPIECES
- A24D3/00—Tobacco smoke filters, e.g. filter-tips, filtering inserts; Filters specially adapted for simulated smoking devices; Mouthpieces for cigars or cigarettes
- A24D3/02—Manufacture of tobacco smoke filters
- A24D3/0204—Preliminary operations before the filter rod forming process, e.g. crimping, blooming
- A24D3/0212—Applying additives to filter materials
- A24D3/022—Applying additives to filter materials with liquid additives, e.g. application of plasticisers
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A24—TOBACCO; CIGARS; CIGARETTES; SIMULATED SMOKING DEVICES; SMOKERS' REQUISITES
- A24D—CIGARS; CIGARETTES; TOBACCO SMOKE FILTERS; MOUTHPIECES FOR CIGARS OR CIGARETTES; MANUFACTURE OF TOBACCO SMOKE FILTERS OR MOUTHPIECES
- A24D3/00—Tobacco smoke filters, e.g. filter-tips, filtering inserts; Filters specially adapted for simulated smoking devices; Mouthpieces for cigars or cigarettes
- A24D3/02—Manufacture of tobacco smoke filters
- A24D3/027—Multiple line manufacturing devices
Definitions
- the invention relates to a deflection device for conveying and deflecting at least one filter tow strand.
- This device can be coupled with a format part, in particular with an intake system of a machine for the production of filter rods.
- the invention relates to a machine comprising such a deflection device and a method for conveying and deflecting at least one filter tow.
- a deflection device of the type mentioned is, for example, from the WO 2005/058 079 A1 known.
- This deflection device is used in double-strand machines, which comprise two format sections for forming continuous filter rods and a filter material supply line for each format section.
- the supply lines receive the filter material from a conveyor line which extends between an inlet region of the supply lines and a storage area of two filter material bales.
- a blower which is provided in the inlet area to pull the two Lunten transversely in two strips of filter material.
- the two strips are blown along respective feeds by a pressing device, then by an expander, in the air in the strips to increase their volume, and finally conveyed by a conditioning device where chemical substances are added to the strip to give the filter material flavor and formability.
- Each feeder is connected to the format section by a diverter which serves to convert and stabilize the strips into strands of filter material.
- the diverter receives a strip from the feeder and conveys this, in the shape of a uniform strand, on a strip of previously rubberized paper in the format section.
- the diverter unit typically includes a hopper for each feeder into which the strip is inserted and compacted, thereby forming the filter material strand.
- air can be blown into the hopper, such as in the US 4,522,616 A1 described.
- the paper strip is wound in the format section transversally around the strand, whereby a continuous filter rod is formed.
- a control unit controls the density of the filter rods.
- a cutting head cuts the bars into individual filter sections.
- the reduction of the distance between the two strands in the deflection unit of the machine according to WO 2005/058 079 A1 is effected by two pulleys, which have a V-shaped cross-section.
- the two deflection rollers interact with the curvature arcs of the two inlet funnels and receive the filter tow strand from two transport rollers.
- the filter material strand is therefore fed mechanically into the two inlet funnel.
- Filter rods made on known filter rod machines with a deflection unit described above have insufficient homogeneity.
- the invention has for its object to further develop the aforementioned deflection such that filter rods can be produced with improved homogeneity. Moreover, the device with comparatively be easy to implement at a low cost. Another object of the invention is to provide a machine with such a deflection device and a method for conveying and deflecting at least one filter tow.
- the above-mentioned object is achieved by a machine for producing cigarette filters according to independent claim 1.
- An essential aspect of the invention is the provision of a transport device for pneumatically conveying the at least one filter strand and a deflection device which cooperates with the transport device for pneumatically driven deflection of the filter tow strand.
- the combination of pneumatic transport with strand deflection results in increased fluidization of the material, resulting in a very homogeneous filter material.
- the draw resistance and draw resistance spread of a filter rod are significantly improved, which is obtainable by a filter rod machine with the inventive deflection device.
- the deflection device according to the invention can be realized cost-effectively, so that the total cost of the filter rod machine can be reduced.
- the inventive deflection device can be used in a simple manner in known filter rod machines, wherein only the existing deflection unit of such a machine is replaced by the deflection device according to the invention.
- the known deflection device according to WO 2005/058 079 A1 designed to feed the filter tow line mechanically into the format section of the machine.
- the known deflection device couples to a mechanical conveyor with a deflection.
- This filter rod machine is therefore unable to produce a filter material which is comparable in terms of homogeneity, draw resistance and draw resistance scattering to a filter material obtainable by a filter rod machine comprising a deflection device according to the invention.
- the deflection device also works on a mechanical basis using a pulley.
- the strand coming from the pulley is introduced into a hopper by a forward flow of air from a nozzle located immediately in front of the hopper. This means that the nozzle is used exclusively to insert the strand into the hopper, whereby no distraction or deflection of the strand takes place.
- the deflection device is adapted such that the deflection of the at least one filter tow strand has at least one horizontal component. It has been found that due to the horizontal component of the deflection, the draw resistance and draw resistance scattering can be further improved. In contrast, the deflection device according to US 4,522,616 only a vertical deflection of the strand before.
- the transport device may have at least one pneumatically operated transport nozzle, whereby a particularly simple technical implementation the transport device is achieved since conventional transport nozzles can be used.
- the transport device has two transport nozzles, which are arranged in the region of the inlet side and the outlet side of the device.
- the two nozzles can be operated at different pressures to influence the properties of the filter tow.
- the deflection device comprises at least one curvature arc which determines the conveying path of the filter tow strand at least in sections.
- the use of a curvature arc in connection with the deflection device has the advantage that a continuous deflection of the filter tow strand is achieved.
- any component having a continuously curved configuration that causes a deflection of an airflow such as a baffle, is suitable for implementing the baffle.
- the curvature arc can be connected to the transport nozzle provided on the outlet side and / or with the transport nozzle provided on the inlet side, in particular detachably connected. In this way, the curvature arc and the transport nozzle act together directly, which ensures that the deflection is driven pneumatically or pneumatically. Due to the detachable connection between the curvature arc and the transport nozzle, in each case one of the two transport nozzles can be equipped with a curvature arc or both transport nozzles each with a curvature arc.
- curvature arc or the plurality of curvature arcs are arranged rotatably or pivotally.
- the lower limit of the curvature angle of the curvature arc may be at least 10 °, with preferred ranges between 10 ° - 80 °, 20 ° - 60 ° and 30 ° - 50 °.
- a uniform transfer of the filter tow strand from a curve of curvature to the associated further curve of curvature can be achieved by the fact that the ends of the curved bends remote from the respective transport nozzle are aligned.
- curvature arches are connected by a pipe section, in particular a rectilinear pipe section.
- a pipe section in particular a rectilinear pipe section.
- the tube section is an effective means of increasing the length of the diverter, resulting in the positive effect of dampening pulsations, which become critical particularly at high processing speeds.
- Increased pulsations are related to the higher pressures applied to the inlet nozzle, which are necessary to ensure proper feeding of the strand into the finger. Due to the short guide channels in conventional deflection systems such pulsations are transmitted almost undamped on the format part of the machine. This leads to an increased scattering of the draw resistance, especially at high processing speeds.
- the increased length of the system according to this embodiment of the invention enhances the blooming effect.
- the pipe section may be perforated at least in sections, whereby the escape of compressed air from the pipe section is made possible.
- the pipe section is provided with a feed device for feeding in additives, such as activated carbon, plasticizer and / or for feeding water.
- additives such as activated carbon, plasticizer and / or for feeding water. Due to the increased length of the system, the feed of additives and / or water in the pipe section leads to a homogeneous distribution of the additives and / or the water in the filter tow line. Moreover, the feeding of water in the pipe section of the deflector ensures a safe separation of the water supply from the triacetin, which must be anhydrous to prevent hydrolysis of the triacetin.
- a clearance is formed between the arcs of curvature, thereby enabling the release of chemical substances from the filter tow strand that have been added to the strand before it is introduced into the diverter.
- the deflecting device is adapted for a horizontal offset of the at least one filter tow strand of at least 5 cm, in particular from 5 to 50 cm, in particular from 10 to 40 cm, in particular from 15 to 30 cm.
- a suitable length of the device in order to achieve a good turbulence of the filter rod material is achieved if the total longitudinal length of the device is at least 200 mm, in particular 200-1000 mm, in particular 500-900 mm, in particular 600-800 mm.
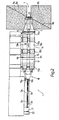
- Reference numeral 1 in FIG Fig. 1 overall designates a double-strand machine for the production of cigarette filters.
- the machine 1 comprises a format part with two format sections 2a, 2b in each case for forming continuous filter rods 3a, 3b and, for each format section 2a, 2b, in each case one filter material feed 4a, 4b.
- the feeds 4a, 4b receive filter material from the conveyor line 5, which forms part of the machine 1 and extends between an inlet station 6 of the feeders 4a, 4b and a storage area 7 comprising two bales 8a, 8b of filter material.
- respective slivers 9a, 9b are unwound from the bales 8a, 8b and conveyed along the conveying path 5 by a guide roller arrangement 10a, which is arranged at the inlet station 6.
- the conveyor line 5 comprises a double guide device 11, which is arranged above the bales 8a, 8b for guiding the lunts 9a, 9b.
- the conveyor line 5 further comprises a suction device 12, which is arranged directly in the conveying direction in front of the guide assembly 10a at the inlet station 6 to the Lunten 9a, 9b in the transverse direction in respective Partially flat strips 13a, 13b to pull apart, which are supplied to the guide device 10a.
- a pressing device 15 which comprises a guide roller or brake roller arrangement 10a and two drive roller arrangements 10b, 10c.
- the two strips 13a, 13b are then conveyed along the respective feeds 4a, 4b in the direction 14 through an expansion device 16 which injects air into the strips 13a, 13b in order to increase their volume. Thereafter, the strips 13a, 13b are transported through a conditioning device 17, where chemical substances, in particular triacetin, are added to the strips 13a, 13b so as to impart moldability and / or aroma to the filter material. Finally, the two strips 13a, 13b are conveyed along the respective feeds 4a, 4b in the direction 14 by a drive roller assembly 10d, which is constructed similarly to the arrangements 10b, 10c and defines a discharge region of the feeds 4a, 4b or feed paths 4a, 4b.
- a drive roller assembly 10d which is constructed similarly to the arrangements 10b, 10c and defines a discharge region of the feeds 4a, 4b or feed paths 4a, 4b.
- the feeds 4a, 4b are connected to the format sections 2a, 2b of the format part by a deflection unit or deflecting device 18, which is immediately downstream of the roller arrangement 10d.
- the deflection unit 18 receives the strips 13a, 13b from the feeds 4a, 4b, collects the strips 13a, 13b uniformly to form two strands of filter material and conveys the filter material strands to the format sections 2a, 2b.
- each filter material strand is conveyed onto a paper strip 19a, 19b which has been previously gummed in a gumming station 20 and then wound transversely around the filter material strand to form a continuous filter rod 3a, 3b.
- the Deflection unit 18 which is fixed to the frame of the machine 1 and inside two laterally juxtaposed deflection lines 24a, 24b holds, which converge to reduce the distance between the two filter material strands.
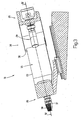
- Each deflection line 24 comprises an inlet funnel 25, into which the strip 13 is conveyed out of the feed 4, and a downstream outlet funnel 26, through which the filter tow line is conveyed to the format line 2.
- the inlet funnel 25 and the outlet funnel 26 each have a nozzle, by means of which a drive gas flow, in particular air flow, is generated to convey the strand.
- the funnels 25, 26 therefore each function as a transport nozzle.
- Each hopper 25 has a straight central axis of symmetry 27, which runs parallel to the conveying direction, or lies in the conveying plane of the strip 13 in the region of the feed 4.
- Each outlet funnel 26 likewise has a rectilinear central axis of symmetry 28, which runs inclined with respect to the conveying direction of the filter material strand out of the inlet funnel 25 and with respect to the conveying direction of the filter material line along the format line 2.
- a tubular deflection part is arranged, in particular a curvature arc 29, which has a curved section for deflecting the conveying direction of the filter material strand from the inlet funnel 25.
- Each arc of curvature 29 is preferably connected directly to the outlet of the inlet funnel 25.
- each hopper 25, 26 comprises a tubular body 30 having a narrowly tapered entrance area (ie, with a gradually decreasing flow channel diameter) and a cylindrical intermediate section (ie with a constant flow channel diameter).
- Each hopper 25, 26 further includes a slightly flared further tubular body 31 (ie, having a gradually increasing flow channel diameter) downstream of the tubular body 30.
- the tubular body 30 is screwed into the further tubular body 31, whereby between an outer surface of the tubular body 30 and an inner surface of the further tubular body 31, a tubular air flow channel 32 is limited, in which a plurality of injection ports 33 open, which are the inner surface of the tubular Break body 30 in the cylindrical intermediate section.
- Supply channels 34 are formed in the further tubular body 31, through which, in operation, compressed air is introduced into the tubular channel 32 and from there through the injection openings 33 into the flow channel of the tubular body 30.
- the injection openings 33 in the inlet funnel 25 are oriented with respect to the central axis of symmetry 27 in such a way that the air flow has an axial component, i. a component parallel to the central axis of symmetry 27, imprinted.
- the injection ports 33 in the feed hopper 25 are oriented with respect to the central axis of symmetry 27 such that both an axial component and a radial component (i.e., perpendicular to the central axis of symmetry 27) are impressed on the airflow.
- the axial air flow component prevails, which serves to press the filter material through the inlet funnel 25, whereas the radial air flow component serves to swirl the air flow.
- the injection openings 33 in the discharge funnel 26 are oriented with respect to the central axis of symmetry 28 such that primarily an axial component (ie parallel to the central axis of symmetry 28) of the air flow is impressed, whereby the feed acting on the filter material is maximized.
- each tubular channel 32 can be adjusted by screwing the tubular body 13 into and out of the further tubular body 31, thereby adjusting the air velocity and flow through the injection openings 33.
- the filter rod material is conveyed between each inlet hopper 25 and outlet hopper 26 through the clearance 35, the filter rod material being exposed, i.e., free, to flow. moved without guide part.
- each hopper 25 may be connected to the corresponding hopper 26 through a perforated tubular expansion member.
- the clearance 35 through which the filter rod material is moved freely, allows expansion of the injected through the injection ports 33 of each inlet funnel 25 compressed air, whereby unwanted backpressure phenomena are avoided. Furthermore, it is thereby made possible for the filter rod material to release excess chemical substances which have been added in the treatment device 17.
- the housing 23 In order to collect and remove the released from the filter rod material chemical substances, the housing 23 is arranged inclined downwards and has at the lowest point a collecting channel, which leads to a catch basin. In order to prevent the chemical substances released from the filter rod material from escaping from the housing 23 and contaminating the rest of the machine 1, the housing 23 is substantially sealed and has only outlet openings arranged in a central region of the housing 23 and against direct spraying are shielded.
- each discharge hopper 26 is provided with a slightly conical perforated tubular body 37 having a plurality of openings 38 and the Outlet funnel 26 is located immediately downstream.
- the passage openings 38 in each perforated tubular body 37 are preferably arranged only on the upper side of the perforated tubular body 37 in order to avoid a downwardly directed air flow, ie an air flow directed onto the format section 2.
- each deflection section 24 of the deflection unit 18 comprises one, two or even more intermediate funnels, which are arranged between the inlet funnel 25 and the outlet funnel 26 and are constructed identically to the funnels 25, 26.
- the machine 1 described above is designed as a single-strand machine and therefore comprises a format part with a format section 2 to form a continuous filter rod 3 and a filter material supply 4.
- the deflection unit or deflection device 18 comprises a deflection path 24 with above
- the machine 1 described above may be formed as a triple or quadruple strand machine and thus a format part with three or four format plug 2 to form three or four continuous filter rods 3 and three or four filter material feeds. 4 include.
- the deflection unit or deflection device 18 has three or four deflection paths 24, which are each equipped with the inlet and outlet funnels 25, 26 described above.
- the filter material obtainable with the deflector 18 described above has excellent homogeneity and, at least in terms of homogeneity, is superior to filter materials made with the deflector currently available on the market.
- the drive roller assemblies 10b, 10c, 10d are different along the feeds 4a, 4b in size and arrangement, but are functionally identical. The following description therefore refers only to one of the drive roller assemblies 10b, 10c, 10d, which is designated by the reference numeral 10 for the sake of simplicity.
- Each drive roller assembly 10 includes, for each feed 4, a drive roller rotated by a motor independent of the motors of the other rollers and a free rotating roller which abuts and engages the drive roller.
- the two motors of the two drive rollers of each drive roller assembly 10 may be located on the same side of the feeders 4 in the machine frame. Alternatively, in each drive roller assembly 10, the motor of a drive roller in the frame of the machine 1 and the motor of the other drive roller may be arranged adjacent to the drive roller.
- the deflection device which is also referred to as a deflection unit 18, described in detail.
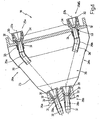
- the deflection device essentially comprises a deflection device 50 and a transport device 40, which cooperate with each other such that the deflection of the filter tow rope 13, which is moved by the deflection device, takes place pneumatically.
- Fig. 4 illustrated to use a curvature arc 29 which is connected to the pneumatically driven transport nozzles 25, 26.
- Fig. 3 Fig. 4
- the transport nozzles 25a, 25b on the inlet side of the deflecting device 18 are each provided with a curvature arc 29a, 29b.
- curvature arc 29 in the conveying direction above and / or below the respective nozzle, wherein the alternative of arranging the curvature in the conveying direction below the nozzle and thus to pneumatically press the strand through the curvature, leads to better results in terms of Draw resistance and draw resistance spread of the filter material.
- the deflector 50 is adapted to effect a deflection of the filter tow string in a direction comprising at least one horizontal component.
- the deflection is carried out with both a horizontal and a vertical component, since the entire deflection device is arranged inclined with respect to a horizontal plane.
- Diversion generally means that the conveying direction is changed at least once.
- the curvature bends 29 can be replaced by other means, for example by components with an open structure, in particular by a curved baffle plate, which is associated with the pneumatic transport device 40.
- the curved baffle plate can be used to achieve the desired offset of the filter tow string 13 while continuously redirecting the filter tow string.
- the deflection device 50 comprises a deflection part, which is arranged between an inlet funnel or an inlet-transport nozzle and a discharge funnel or a discharge transport nozzle.
- the deflection part may be tubular and comprises a curved section for deflecting the conveying direction of the filter material strand or the sliver coming from the inlet funnel or the inlet transport nozzle.
- the deflection device is to be used in a double-strand machine, it is advantageous to change the conveying direction such that the two strands are fed to one another, ie converge ( Fig. 4 ).
- the strands can then be fed to the infeed system of a format part of the machine.
- the device is designed to be even more flexible when the bends 29 are detachably connected to the respective transport nozzle 25, 26, since the device can then be adapted to different process conditions.
- the curvature bends 29 can be arranged to be pivotable, whereby the direction under which the strands leave the respective curvature arc 29 can be changed.
- the curvature arc 29 on the inlet side and the curvature arc 29 on the outlet side of the device can be easily aligned by the respective curvature arcs 29 are pivoted accordingly.
- each curvature arc 29a, 29b oriented on the inlet side of the device such that the central axis of symmetry of the free end of the arc of curvature 29a, 29b, the central axis of symmetry of the remote transport nozzle 26a, 26b on the outlet side of the device in the inlet plane intersects.
- This alignment of the arc of curvature 29a, 29b with respect to the delivery nozzles 26a, 26b on the outlet side of the device provides for uniform transfer of the strand 13 from the respective arc of curvature 29a, 29b to the transport nozzles 26a, 26b.
- the embodiment according to the Figures 3 . 4 relates to a deflection device having a clearance 35 between the curvature arches 29a, 29b and the outlet transport nozzles 26a, 26b.
- a pipe section 51 in particular a straight pipe section 51, which connects a curvature arc 29 on the inlet side of the device and a curvature arc 29 'on the outlet side of the device.
- the two curvature arcs 29, 29 ' are curved in opposite directions, with the central axis of symmetry of the arcs 29, 29' coaxial with the central axis of symmetry of the respective transport nozzle 25, 26 being parallel.
- the ends of the respective curvature arcs 29, 29 ' which are located away from the respective associated transport nozzle 25, 26, are aligned, so that the pipe section 51 can be fitted between the two curvature arcs 29, 29'.
- the pipe section 51 is an extremely effective means for increasing the length of the pipe system. This enhances the turbulence of the filter material that can be achieved with the system and the blooming effect.
- the pipe section 51 does not necessarily have to extend straight. It is also possible to use a pipe section which, at least in sections, has bends or is generally curved.
- a supply device is associated with the pipe section, which allows the feeding of additives, such as activated carbon, plasticizer or other substances into the filter tow line.
- the feeder can be used to feed water into the strand, thereby affecting the cure time.
- a particular advantage of the pipe section 51 is that the length of the system is increased. This makes it possible that the injected additives and / or the injected water is distributed homogeneously over the length of the pipe section in the filter tow line. The quality of the filter rods, which are produced with a machine comprising such a deflection device, can thus be significantly improved.
- the horizontal offset of the deflection device 50 is at least 5 cm.
- a preferred range is 5 - 50 cm, in particular 10 - 40 cm, in particular 15 - 30 cm.
- the total longitudinal length of the device should be at least 200 mm. This means that the axial distance between the inlet side and the outlet side of the device is at least 200 mm.
- Preferred ranges are from 200 to 1000 mm, in particular 500 to 900 mm, in particular 600 to 800 mm.
- the device according to the invention improves the draw resistance as well as the draw resistance spread due to the combined deflection and pneumatic conveying, which leads to an improvement of the turbulence in the system and thus to an increased homogeneity of the filter material.
- the deflection devices described above allow damping of the pulsations that occur at higher processing speeds.
- the damping of the pulsations is due to the increased length of the conveying path, in particular in connection with the use of a pipe section between two associated curves on the inlet and outlet side of the device. In this way, the flowering effect can be improved.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Cigarettes, Filters, And Manufacturing Of Filters (AREA)
Abstract
Claims (19)
- Machine (1) pour la fabrication de filtres de cigarettes, comprenant :une pluralité d'alimentations (4) pour des bandes (13) continues respectives en matériau filtrant ;une pluralité de parties de mise au format (2), pour former des barres de filtre (3) continues respectives ; etun dispositif de déviation (18), disposé entre les alimentations (4) et les parties de mise au format (2), recevant les bandes (13) provenant des alimentations (4), collectant les bandes (3) régulièrement pour former deux cordons en matériau filtrant, et transportant les cordons en matériau filtrant aux parties de mise au format ;le dispositif de déviation (18) comprenant une pluralité de parcours de déviation (24), comprenant chacun un entonnoir d'entrée (25), dans lequel la bande (13) provenant des alimentations (4) est insérée ;caractérisée en ce que chaque parcours de déviation (24) du dispositif de déviation (18) comprend un entonnoir de sortie (26), installé en aval et séparé de l'entonnoir d'entrée (25), au moyen duquel un cordon de matériau filtrant est amené à la partie de mise au format (2).
- Machine (1) selon la revendication 1, dans laquelle les parcours de déviation (24) du dispositif de déviation (18) sont disposés côte à côte, et convergent pour diminuer l'espacement entre les cordons de matériau filtrant.
- Machine (1) selon la revendication 1 ou 2, dans laquelle chaque entonnoir d'entrée (25) présente un axe de symétrie central (27), s'étendant en ligne droite et parallèlement à la direction de transport, ou étant situé dans le plan de transport de la bande (13) hors du parcours de transport (4).
- Machine (1) selon l'une des revendications 1 à 3, dans laquelle, entre chaque entonnoir d'entrée (25) et entonnoir de sortie (26), est disposée une partie de déviation (29) à configuration tubulaire, et un tronçon incurvé pour dévier la direction de transport du cordon de matériau filtrant sortant de l'entonnoir d'entrée (25).
- Machine (1) selon la revendication 4, dans laquelle chaque partie de déviation (29) est directement reliée à la sortie de l'entonnoir d'entrée (25).
- Machine (1) selon l'une des revendications 1 à 5, dans laquelle chaque entonnoir de sortie (26) présente un axe de symétrie central (28), s'étendant en ligne droite et de manière légèrement inclinée par rapport à la direction de transport du matériau de cordon filtrant sortant de l'entonnoir d'entrée (25) et par rapport à la direction de transport du cordon de matériau filtrant le long de la partie de mise au format (2).
- Machine (1) selon l'une des revendications 1 à 6, dans laquelle de l'air est soufflé dans chaque entonnoir (25, 26), au moyen d'ouvertures d'insufflation (33) débouchant dans l'entonnoir (25, 26).
- Machine (1) selon la revendication 7, dans laquelle chaque entonnoir (25, 26) comprend un premier corps tubulaire (30) et un deuxième corps tubulaire (31), disposé en aval du premier corps tubulaire (30) en observant dans la direction de transport, le premier corps tubulaire (30) étant vissé dans le deuxième corps tubulaire (31), faisant que, entre une face extérieure du premier corps tubulaire (30) et une face intérieure du deuxième corps tubulaire (31), est défini un canal d'écoulement d'air (32) tubulaire, débouchant dans l'ouverture d'insufflation (33).
- Machine (1) selon la revendication 8, dans laquelle le premier corps tubulaire (30) comprend un tronçon initial, allant en s'effilant de manière étroite, et un tronçon intermédiaire cylindrique, et le deuxième corps tubulaire (31) s'évase légèrement.
- Machine (1) selon la revendication 8 ou 9, dans laquelle les ouvertures d'insufflation (33) de chaque entonnoir d'entrée (25) sont inclinées par rapport à l'axe de symétrie central (27), de manière qu'à l'écoulement d'air soient imprimées tant une composante axiale qu'également une composant radiale.
- Machine (1) selon la revendication 8 ou 9, dans laquelle les ouvertures d'insufflation (33) de chaque entonnoir d'entrée (25) sont inclinées par rapport à l'axe de symétrie central (27), de manière qu'à l'écoulement d'air ne soit imprimée qu'une composante axiale.
- Machine (1) selon l'une des revendications 8 à 11, dans laquelle les ouvertures d'insufflation (33) de chaque entonnoir de sortie (26) sont inclinées par rapport à l'axe de symétrie central (28), de manière qu'à l'écoulement d'air ne soit imprimée qu'une composante axiale.
- Machine (1) selon l'une des revendications 8 à 12, dans laquelle le cordon de matériau filtrant est transporté entre chaque entonnoir d'entrée (25) et entonnoir de sortie (26), à travers un espace libre (35), dans lequel le cordon de matériau filtrant se déplace librement sans parties de guidage.
- Machine (1) selon la revendication 13, dans laquelle le dispositif de déviation (18) comprend un boîtier ou un caisson (23), contenant intérieurement les parcours de déviation (24).
- Machine (1) selon la revendication 14, dans laquelle le caisson (23), pour la collecte et l'évacuation de substances chimiques dégagées du cordon de matériau filtrant, est incliné vers le bas et présente au point le plus bas un canal de captage, menant à un réservoir de captage.
- Machine (1) selon la revendication 14 ou 15, dans laquelle le caisson (23) est pratiquement isolé de manière étanche et présente, pour l'échappement de l'air comprimé, des ouvertures (36) protégées contre toute aspersion directe.
- Machine (1) selon l'une des revendications 1 à 16, dans laquelle chaque entonnoir de sortie (26) est équipé d'un corps tubulaire (37) perforé, présentant une pluralité d'ouvertures de passage (38) et disposé immédiatement en aval de l'entonnoir de sortie (26), en observant la direction de transport.
- Machine (1) selon la revendication 17, dans laquelle les ouvertures de passage (38), dans chaque corps tubulaire (37) perforé, ne sont réalisées que sur la face supérieure du corps tubulaire (37) perforé, pour éviter que l'écoulement d'air soit dirigé sur la partie de mise au format (2).
- Machine (1) selon l'une des revendications 1 à 18, dans laquelle chaque parcours de déviation (24) du dispositif de déviation (18) comprend au moins un entonnoir intermédiaire, disposé entre l'entonnoir d'entrée (25) et l'entonnoir de sortie (26).
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE200610001643 DE102006001643A1 (de) | 2006-01-12 | 2006-01-12 | Umlenkvorrichtung, Maschine umfassend eine derartige Umlenkvorrichtung und Verfahren zum Fördern und Umlenken wenigstens eines Filtertowstranges |
| PCT/EP2006/011042 WO2007087848A2 (fr) | 2006-01-12 | 2006-11-15 | Dispositif de déviation, machine comportant un tel dispositif de déviation et procédé de transport et de déviation d'au moins un écheveau de mèche pour filtre |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1978833A2 EP1978833A2 (fr) | 2008-10-15 |
| EP1978833B1 true EP1978833B1 (fr) | 2011-01-19 |
Family
ID=37461573
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP06818621A Active EP1978833B1 (fr) | 2006-01-12 | 2006-11-15 | Dispositif de déviation pour un cordon filtrant continu, procédé pour le transport et la déviation d'un cordon filtrant, et appareil pour la fabrication de filtres de cigarette |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP1978833B1 (fr) |
| JP (1) | JP2009523015A (fr) |
| CN (1) | CN101394760B (fr) |
| DE (2) | DE102006001643A1 (fr) |
| WO (1) | WO2007087848A2 (fr) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3231298B1 (fr) | 2009-04-21 | 2020-05-20 | Hauni Maschinenbau GmbH | Réglage de la position de capsule dans des filtres de l'industrie de traitement du tabac |
Families Citing this family (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102007057396A1 (de) | 2007-11-27 | 2009-05-28 | Hauni Maschinenbau Ag | Vorrichtung zur Bearbeitung von mindestens zwei Filtertowsträngen |
| DE102008003368A1 (de) * | 2008-01-08 | 2009-07-09 | Hauni Maschinenbau Aktiengesellschaft | Vorrichtung zum Transport eines Filtertows |
| DE102008016827A1 (de) * | 2008-04-01 | 2009-10-08 | Hauni Maschinenbau Ag | Vorrichtung zum Transport eines Filtertows |
| DE102008024553A1 (de) | 2008-05-21 | 2009-12-03 | Hauni Maschinenbau Aktiengesellschaft | Vorrichtung zum Einbringen von Additiven in einen zur Herstellung eines Rauchartikels vorgesehenen und bereits rundgeformten Strang |
| DE102008057457A1 (de) * | 2008-11-14 | 2010-05-20 | Hauni Maschinenbau Aktiengesellschaft | Vorrichtung zum Transport eines Filtertowstreifens |
| DE102009022790A1 (de) | 2009-05-27 | 2010-12-02 | Hauni Maschinenbau Aktiengesellschaft | Vorrichtung zur Bearbeitung mindestens eines Filtertowstranges |
| IT1395043B1 (it) * | 2009-08-18 | 2012-09-05 | Gd Spa | Metodo e macchina per la produzione contemporanea di almeno due bachi di filtro per sigarette. |
| IT1408375B1 (it) * | 2010-10-20 | 2014-06-20 | Gd Spa | Unita' e metodo di alimentazione di elementi additivi a del materiale fibroso in una macchina per la produzione di articoli da fumo |
| ITBO20100637A1 (it) * | 2010-10-22 | 2012-04-23 | Gd Spa | Macchina per la produzione di filtri per sigarette. |
| ITBO20110206A1 (it) | 2011-04-18 | 2012-10-19 | Gd Spa | Gruppo compattatore per una macchina per la produzione di filtri per sigarette. |
| ITBO20130314A1 (it) | 2013-06-21 | 2014-12-22 | Gd Spa | Macchina per la produzione di filtri per sigarette |
Family Cites Families (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB2089190B (en) * | 1980-12-16 | 1985-05-30 | Molins Ltd | Quality control in continuous rod manufacture |
| US4511420A (en) * | 1980-12-16 | 1985-04-16 | Molins, Ltd. | Continuous rod manufacture |
| US4522616A (en) * | 1982-03-10 | 1985-06-11 | Celanese Corporation | Method and apparatus for forming cigarette filter rods |
| US4541825A (en) * | 1982-12-27 | 1985-09-17 | Celanese Corporation | Low air pressure method and apparatus for forming filter rods |
| IT1185472B (it) | 1984-11-10 | 1987-11-12 | Hauni Werke Koerber & Co Kg | Procedimento e dispositivo per produrre bastoncini-filtro |
| DE3640883A1 (de) | 1986-11-29 | 1988-06-09 | Rhodia Ag | Verfahren und vorrichtungen zum herstellen von tabakrauchfilterstaeben |
| JP2965184B2 (ja) * | 1991-12-09 | 1999-10-18 | 三菱レイヨン株式会社 | エアージェット |
| DE4300841A1 (fr) * | 1992-01-16 | 1993-07-22 | Molins Plc | |
| US5331976A (en) * | 1992-10-21 | 1994-07-26 | Hoechst Celanese Corporation | Transport jet adapter |
| DE10200320A1 (de) * | 2002-01-07 | 2003-07-17 | Hauni Maschinenbau Ag | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung eines Faserstranges der tabakverarbeitenden Industrie |
| CN2642061Y (zh) * | 2003-04-16 | 2004-09-22 | 云南烟草科学研究院 | 醋酸纤维丝束中施加液体物料、线性物料的装置 |
| KR100714525B1 (ko) * | 2003-07-25 | 2007-05-07 | 미츠비시 레이온 가부시키가이샤 | 담배 필터의 플러그 제조 장치와 그 필터 제조 방법 |
| DE10354924B4 (de) * | 2003-11-25 | 2024-01-18 | Körber Technologies Gmbh | Vorrichtung zum Aufbereiten von Filtertowmaterial sowie Vorrichtung zur Herstellung von Filtern |
-
2006
- 2006-01-12 DE DE200610001643 patent/DE102006001643A1/de not_active Ceased
- 2006-11-15 JP JP2008549773A patent/JP2009523015A/ja active Pending
- 2006-11-15 CN CN200680053609.9A patent/CN101394760B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2006-11-15 EP EP06818621A patent/EP1978833B1/fr active Active
- 2006-11-15 DE DE502006008784T patent/DE502006008784D1/de active Active
- 2006-11-15 WO PCT/EP2006/011042 patent/WO2007087848A2/fr active Application Filing
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3231298B1 (fr) | 2009-04-21 | 2020-05-20 | Hauni Maschinenbau GmbH | Réglage de la position de capsule dans des filtres de l'industrie de traitement du tabac |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101394760A (zh) | 2009-03-25 |
| WO2007087848A3 (fr) | 2007-10-25 |
| DE102006001643A1 (de) | 2007-07-26 |
| WO2007087848A2 (fr) | 2007-08-09 |
| CN101394760B (zh) | 2011-09-28 |
| EP1978833A2 (fr) | 2008-10-15 |
| JP2009523015A (ja) | 2009-06-18 |
| DE502006008784D1 (de) | 2011-03-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1978833B1 (fr) | Dispositif de déviation pour un cordon filtrant continu, procédé pour le transport et la déviation d'un cordon filtrant, et appareil pour la fabrication de filtres de cigarette | |
| EP2292107B1 (fr) | Dispositif de préparation d'une mèche de filtre et dispositif de fabrication de filtres | |
| EP1847186B1 (fr) | Unité de préparation destinée à la préparation d'au moins une bande de cordon filtrant pour la fabrication de filtre pour les articles à fumer en forme de tige | |
| EP0919144B2 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif pour le traitement d'une bande de cordons filtrant | |
| EP1847187B1 (fr) | Unité de préparation destinée à la préparation d'au moins une bande de filtre tout comme un dispositif doté d'au moins deux telles unités de préparation | |
| DE102007006674A1 (de) | Luftspinnvorrichtung | |
| WO2013117493A1 (fr) | Machine à filer à jet d'air pourvue de filières et de buses de commencement de filage séparées | |
| EP3165635A1 (fr) | Dispositif d'étirage | |
| EP2123180A1 (fr) | Dispositif d'introduction d'additifs dans un faisceau déjà formé rond et prévu pour la fabrication de particules à fumer | |
| DE202012003924U1 (de) | Kompaktier- oder Verdichtergruppe für eine Maschine zur Produktion von Zigarettenfiltern | |
| DE102012204443A1 (de) | Faseraufbereitungsvorrichtung der Tabak verarbeitenden Industrie und Verfahren zur Aufbereitung von endlichen Fasern zum Herstellen eines Faserstrangs der Tabak verarbeitenden Industrie | |
| EP1692957A1 (fr) | Traitement d'une bande de matière filtrante pour l'industrie du tabac | |
| EP1490539B1 (fr) | Dispositif de serrage pneumatique pour un assemblage de fibres et procede de serrage pneumatique d'un assemblage de fibres | |
| EP3165636A1 (fr) | Dispositif d'étirage | |
| EP2982253A1 (fr) | Buse de transport pour un dispositif de fabrication de tiges de filtre pour l'industrie de transformation du tabac et dispositif de fabrication de tiges de filtre pour l'industrie de transformation du tabac | |
| DE1710017A1 (de) | Verfahren und Einrichtung zum Spinnen von Garn | |
| DE10321283A1 (de) | Vliesmaschine | |
| DE102006006504A1 (de) | Streckverfahren und Streckwerk zur Verfeinerung von Fasermaterial | |
| DE102009022790A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Bearbeitung mindestens eines Filtertowstranges | |
| EP1654407B1 (fr) | Dispositif de guidage de non-tisse pour machine textile et machine textile | |
| DE102006006505B4 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Kompaktierung von bandförmigen Fasermaterial | |
| WO2007025535A2 (fr) | Banc d'etirage destine au traitement de materiaux fibreux | |
| DE202014010449U1 (de) | Zigarettenfilterherstellungsmaschine | |
| DE102009021808B4 (de) | Umlenkeinrichtung für Filtertow | |
| DE10352152A1 (de) | Filter sowie Verfahren und Einrichtung zur Herstellung von Filtern der tabakverarbeitenden Industrie |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20080731 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): CH DE GB LI NL |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): CH DE GB LI NL |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| TPAC | Observations filed by third parties |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNTIPA |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): CH DE GB LI NL |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: HEPP WENGER RYFFEL AG |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 502006008784 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20110303 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502006008784 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20110303 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: T3 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20111020 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502006008784 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20111020 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: V1 Effective date: 20120601 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20111130 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120601 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20111130 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20121126 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20131115 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20131115 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20231129 Year of fee payment: 18 |