EP1888794B1 - Verfahren zum herstellen eines metallbauteils mit aneinander angrenzenden abschnitten unterschiedlicher materialeigenschaften - Google Patents
Verfahren zum herstellen eines metallbauteils mit aneinander angrenzenden abschnitten unterschiedlicher materialeigenschaften Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1888794B1 EP1888794B1 EP06763268A EP06763268A EP1888794B1 EP 1888794 B1 EP1888794 B1 EP 1888794B1 EP 06763268 A EP06763268 A EP 06763268A EP 06763268 A EP06763268 A EP 06763268A EP 1888794 B1 EP1888794 B1 EP 1888794B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- sheet metal
- metal element
- forming
- temperature
- component
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B21—MECHANICAL METAL-WORKING WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21D—WORKING OR PROCESSING OF SHEET METAL OR METAL TUBES, RODS OR PROFILES WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21D37/00—Tools as parts of machines covered by this subclass
- B21D37/16—Heating or cooling
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B21—MECHANICAL METAL-WORKING WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21D—WORKING OR PROCESSING OF SHEET METAL OR METAL TUBES, RODS OR PROFILES WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21D22/00—Shaping without cutting, by stamping, spinning, or deep-drawing
- B21D22/02—Stamping using rigid devices or tools
- B21D22/022—Stamping using rigid devices or tools by heating the blank or stamping associated with heat treatment
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C21—METALLURGY OF IRON
- C21D—MODIFYING THE PHYSICAL STRUCTURE OF FERROUS METALS; GENERAL DEVICES FOR HEAT TREATMENT OF FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS METALS OR ALLOYS; MAKING METAL MALLEABLE, e.g. BY DECARBURISATION OR TEMPERING
- C21D1/00—General methods or devices for heat treatment, e.g. annealing, hardening, quenching or tempering
- C21D1/62—Quenching devices
- C21D1/673—Quenching devices for die quenching
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C21—METALLURGY OF IRON
- C21D—MODIFYING THE PHYSICAL STRUCTURE OF FERROUS METALS; GENERAL DEVICES FOR HEAT TREATMENT OF FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS METALS OR ALLOYS; MAKING METAL MALLEABLE, e.g. BY DECARBURISATION OR TEMPERING
- C21D2221/00—Treating localised areas of an article
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C21—METALLURGY OF IRON
- C21D—MODIFYING THE PHYSICAL STRUCTURE OF FERROUS METALS; GENERAL DEVICES FOR HEAT TREATMENT OF FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS METALS OR ALLOYS; MAKING METAL MALLEABLE, e.g. BY DECARBURISATION OR TEMPERING
- C21D9/00—Heat treatment, e.g. annealing, hardening, quenching or tempering, adapted for particular articles; Furnaces therefor
- C21D9/46—Heat treatment, e.g. annealing, hardening, quenching or tempering, adapted for particular articles; Furnaces therefor for sheet metals
Definitions
- the invention relates to a method for producing a metal component with adjoining sections of different material properties.
- methods of this type are used to produce by press hardening, for example, manganese-boron steels components that have a uniform hardness profile of up to 1,500 MPa. Due to their low ductility remaining after the hardening process, components made of such steels are usually first preformed, then heated to austenitizing temperature and then rapidly cooled in a mold under high pressure. The parts obtained in this way, in addition to their high hardness on a good dimensional stability.
- a heated to a forming temperature sheet metal element is formed in a forming tool into a final molded component, wherein the forming a tempering device for adjusting the temperature of at least one of his during forming with the sheet metal element coming into contact Sections has in the form of ceramic inserts that delay the cooling of their contacting section, in the form of recesses that reduce the cooling effect or in the form of induction elements with which the respective section can be actively heated so that in the course of Cooling in the respective areas no hardness structure sets.
- the forming itself should also be as fast as possible in this known method, so that the workpiece does not harden during the deformation.
- the sheet metal part which is rapidly formed in this way, subsequently remains in the cooled forming tool, so that it is cured only in the already completely deformed state.
- a patched composite sheet can be hot formed and defined cooled.
- a uniform cooling As essential for the provided with a brazing composite sheet is considered a uniform cooling. This uniformity is to be achieved by cooling in two stages, with forced cooling to a target temperature of 500 ° C., in order to maintain a solidification point of the brazing alloy and thus the joining of the two sheets.
- An example of the type of the above-mentioned prior art counting method for press hardening is, for example, from DE 103 41 867 A1 known.
- this method can be a hardened sheet metal profile in that first an intermediate shape is formed from a sheet metal blank, this sheet metal profile is then heated to hardening temperature and that the heated sheet metal profile is finally selectively cooled in a device similar to a deep drawing tool under the action of a predetermined pressure.
- the intermediate form produced in the first step of the method already corresponds approximately to the final shape of the component to be produced.
- the device used for carrying out the known method has channel-like cooling arrangements, which, depending on the heat to be dissipated, are flushed through by oil, water, ice-water or saline solution.
- the cooling arrangements can be controlled separately from each other to form zones with mutually different degrees of hardness on the finished component.
- the invention proposes a method for producing a metal component designed according to claim 1.
- the speed with which the deformation of the respectively processed sheet metal element is carried out in its final shape adjusted so that with the tempered area of the tool, which have a relation to the adjacent sections different temperature within an optimal time for the desired work result with time the separately treated zones of the sheet metal element come into contact and that this contact is maintained under consideration of the other general forming conditions over an equally optimal period of time.
- a sheet-metal component can be produced which has precisely determined zones with different material properties compared to its other sections.
- the sheet metal element can be heated to a forming temperature according to the invention, from which it starts with a correspondingly rapid cooling to form hardened structures.
- the tempering device is designed as a cooling device, which cools its respectively assigned section of the forming tool to such a low temperature that the zone of the sheet metal element in contact with this cooled section is quenched with a speed sufficient for the formation of the desired hardened structure.
- the invention provided tempering be designed as a heater that holds the portion of the tool that is associated with the less hard zone of the finished sheet metal component at such a high temperature that is maintained at a contact of the sheet with this section, a relatively soft structure.
- tempering devices If a plurality of tempering devices are present, then specifically cooled and heated sections of the tool can be arranged closely adjacent to one another with the aim of minimizing the spread of areas with undefined mixed structures at the transition between a zone of high hardness and its adjacent surroundings in the finished sheet metal part and thus to produce perfectly precisely defined zones with different material properties in the finished component.
- the inventively provided coupling of the forming speed of the position and propagation of the generated in the finished component zones of different material properties is in this context of particular importance.
- the forming speed can be selected according to the invention such that the zone in question comes into contact with the strongly cooled section of the tool as quickly as possible.
- the forming speed is reduced, for example, when a particular zone of the component is to cool particularly slowly in order to produce a softer microstructure there.
- all sheet metal elements made of metal materials are suitable for the application of the method according to the invention, the structure of which changes when heated or cooled.
- the method according to the invention can be used particularly advantageously for sheet metal elements which consist of steel.
- the advantages of the invention can be used particularly targeted.
- the sheet metal element used as the starting material in the method according to the invention is a flat sheet metal blank.
- the heated sheet metal element is finished, for example, finished in the form of a deep-drawing process in the forming tool.
- the targeted, locally limited cooling or heating treatment of the zones of the sheet metal element in which the special properties are to be generated takes place in the forming tool.
- a further advantage of the procedure according to the invention is that they are particularly suitable for processing sheet metal elements having regions of different thickness.
- the invention allows the formation of the desired, localized zones with certain material properties, which allow the forming speed and the respective temperature of the tool to adapt to the non-uniform thickness of the sheet metal element, that an optimal work result is obtained.
- This has a particularly advantageous effect when the sheet metal element is composed of different, materially joined together, in particular by welding, sheet metal pieces.
- Such sheet metal elements are commonly referred to as "tailored blanks". They are composed, for example, of pieces of sheet metal whose thickness or material properties, such as hardness and toughness, are adapted to the stresses to which the product produced from the tailored blank is exposed in practical use.
- the forming tool can be any type of tool which, taking into account the respective shaping of the component to be produced, is suitable for exerting the required forming and pressing forces on the respective deformed sheet metal element. Suitable for this purpose In particular, such forming tools, which have a die and an adjustable for forming in the die stamp.
- the inventive method is particularly suitable for the production of body parts that are exposed to changing loads in practical use.
- spring strut receptacles can be produced particularly well, in which, for example, high strengths are required in the region of the strut tower, while higher extensibilities are required in the region of the flanks of the receptacles.
- a purely martensitic, particularly firm structure can be specifically produced in the region of the spring strut dome by rapidly cooling this region during the forming process according to the invention and at a high cooling rate.
- Another particularly advantageous application of the method according to the invention is the production of crash-relevant vehicle components which, in the event of a collision, must have a high energy absorption capacity and at the same time optimum strength.
- the invention makes it possible by targeted heating of the forming tool in certain sections in the finished component to form zones in which particularly high residual strains are ensured.
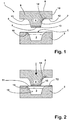
- the forming tool 1 is designed in the manner of a deep-drawing device and has a stationarily arranged die 2. In the die 2, a recess 3 is formed, which images the outer shape of the produced, forming a profile component B.
- the forming tool 1 comprises a punch 4, which determines the inner shape of the component B to be produced.
- the punch 4 can by means of an adjusting device, not shown, from a remote from the die 2 starting position ( Fig. 1 ) are moved into its end position in which it is fully retracted into the recess 3 of the die 2 ( Fig. 3 ).
- the adjusting device comprises a control device that the Speed at which the punch 4 enters the recess 3 of the die 2, controlled.
- the punch 4 has a trapezoidal in cross-section basic shape with an end face 5 and obliquely to the end face 5 tapered side surfaces 6,7.
- the stamp 4 is carried by an integrally connected thereto carrier 8, the lateral edge portions 9,10 are in the manner of a collar laterally beyond the side surfaces 6,7 of the punch 4 at the upper edge.
- the lower edge surfaces 11,12 of the edge regions 9,10 are connected in a horizontal orientation to the side surfaces 6,7 of the punch 4.
- not preformed sheet metal elements E are processed in the embodiment described here, which are in the manner of tailored blanks of two welded together, consisting of a steel material sheet metal parts T1, T2 assembled.
- the first sheet metal part 1 is thinner than the second sheet metal part T2 for weight savings.
- cooling channels 13 are introduced into the stamp.
- the cooling channels 13 are part of a further not shown as a cooling device first tempering. Depending on the respectively required degree of cooling, the cooling channels 13 are traversed by water, ice-water, a frozen salt solution, liquid nitrogen or another cooling medium which is suitable for the rapid removal of large amounts of heat.
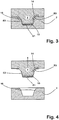
- channels 16 of a third tempering device is formed, which is also not shown here in detail further. Through the channels 16 of the tempering a cooling oil is promoted, which causes a moderate cooling of the die in this area.
- the sheet metal element E is first heated to austenitizing temperature in an oven, not shown here. Subsequently, the sheet metal element E is placed in the forming tool 1, so that it lies with its edge on the upper side of the die 2. If this is necessary for the further deformation of the sheet metal element E carried out in the forming tool 1, hold-downs, not shown, are now used, which hold down the sheet metal elements E in its edge region during the subsequent forming.
- the Nierdehaltekraft exerted by the holddown can be adjusted depending on the particular deformation rate, to allow an optimized Nachfie filed the material of the sheet metal element 4 in the recess 3.
- the punch 4 is placed on the sheet metal element 4 at a high speed, so that the strongly cooled end face 5 of the punch 4 quickly comes into intensive contact with its associated surface portion E1 of the sheet metal element E.
- the sheet metal element E is quenched in this way in its section E1 so fast that there forms a zone with a hardness which is higher than the hardness of the other, adjacent to the section E1 sections E2 and E3 of the sheet metal element E.
- the feed of the punch 4 is reduced in order not to cause cooling, in particular in the sections E2 and E3, which could lead to the formation of hardened structures.
- the feed of the punch 4 is reduced in order not to cause cooling, in particular in the sections E2 and E3, which could lead to the formation of hardened structures.
- only a reduced heat dissipation via the punch 4 takes place, so that a softer, tougher structure is retained in the regions of the sheet metal element E which comes into contact with this region of the punch 4.
- the areas which are cooled only moderately cooled side surfaces via the cooling oil flowing through the channels 16 in the deformation in the section E2 of the sheet metal element E forms a zone in which the hardened portion E1 gradually merges into a softer, more compliant zone of the finished component B.
- the punch 4 After the punch 4 has fully retracted into the receptacle 3 of the die 2 and there pressed the sheet metal element 4 so finished that it has adopted the final shape of the manufactured component B, the punch moves 4 back to its original position. Due to the fact that the sheet metal element E has contracted as a result of cooling, the finished component B is still held on the punch 4, so that it can be easily removed from the die 2 and then separated from the punch 4.
- the component B produced in this way by forming the sheet metal element E has a first zone Z1 with a hardness which is higher than the hardness of the adjacent zones Z2 and Z3 of the component B.
- the zone Z3 is followed by a zone Z4 of markedly lower hardness, however higher extensibility.
- This zone Z4 corresponds to the region of the sheet metal element E, which has been cooled during the forming in the region of the heating coils 14 only to a small extent.
- the zone Z2 corresponds to the region of the sheet metal element E, which has been cooled only moderately during the forming in the region of the side surface 15 of the die 2 and accordingly has an average hardness.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Metallurgy (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Shaping Metal By Deep-Drawing, Or The Like (AREA)
- Heat Treatment Of Articles (AREA)
- Mounting, Exchange, And Manufacturing Of Dies (AREA)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PL06763268T PL1888794T3 (pl) | 2005-05-30 | 2006-05-24 | Sposób wytwarzania metalowego elementu konstrukcyjnego z przylegającymi do siebie odcinkami o różnych właściwościach materiałowych |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102005025026A DE102005025026B3 (de) | 2005-05-30 | 2005-05-30 | Verfahren zum Herstellen eines Metallbauteils mit aneinander angrenzenden Abschnitten unterschiedlicher Materialeigenschaften |
| PCT/EP2006/062579 WO2006128821A1 (de) | 2005-05-30 | 2006-05-24 | Verfahren zum herstellen eines metallbauteils mit aneinander angrenzenden abschnitten unterschiedlicher materialeigenschaften, mittels presshärten |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1888794A1 EP1888794A1 (de) | 2008-02-20 |
| EP1888794B1 true EP1888794B1 (de) | 2012-05-16 |
Family
ID=36804209
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP06763268A Active EP1888794B1 (de) | 2005-05-30 | 2006-05-24 | Verfahren zum herstellen eines metallbauteils mit aneinander angrenzenden abschnitten unterschiedlicher materialeigenschaften |
Country Status (11)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8118954B2 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP1888794B1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP5568235B2 (enExample) |
| CN (2) | CN103382518B (enExample) |
| BR (1) | BRPI0610872B1 (enExample) |
| CA (1) | CA2610378C (enExample) |
| DE (1) | DE102005025026B3 (enExample) |
| ES (1) | ES2385579T3 (enExample) |
| PL (1) | PL1888794T3 (enExample) |
| PT (1) | PT1888794E (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2006128821A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106232255A (zh) * | 2014-07-18 | 2016-12-14 | 宝马股份公司 | 用于制造热成形构件的模具 |
| DE102023121542A1 (de) | 2023-08-11 | 2025-02-13 | Thyssenkrupp Steel Europe Ag | Maßgeschneidertes Halbzeug und äußere Seitenwandverstärkung |
Families Citing this family (78)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102006057864A1 (de) | 2006-12-08 | 2008-07-17 | GM Global Technology Operations, Inc., Detroit | Verbund aus zwei Stahlblechen |
| JP5011531B2 (ja) * | 2007-01-17 | 2012-08-29 | 国立大学法人長岡技術科学大学 | 深絞り加工装置 |
| DE102007003745B4 (de) * | 2007-01-19 | 2017-04-06 | Müller Weingarten AG | Vorrichtung zur Herstellung pressgehärteter Blechbauteile |
| KR101504370B1 (ko) | 2007-02-23 | 2015-03-19 | 타타 스틸 이즈무이덴 베.뷔. | 초고강도를 갖는 최종 제품을 열가공 정형하는 방법 및 이에 의해 제조된 제품 |
| DE102007024797A1 (de) * | 2007-05-26 | 2008-11-27 | Linde + Wiemann Gmbh Kg | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Profilbauteils, Profilbauteil und Verwendung eines Profilbauteils |
| HUE037337T2 (hu) * | 2007-07-19 | 2018-08-28 | Muhr & Bender Kg | Hosszirányban változó vastagságú acélszalag |
| CN101755063A (zh) * | 2007-07-19 | 2010-06-23 | 科鲁斯斯塔尔有限公司 | 用于对在长度方向具有不同厚度的钢带进行退火的方法 |
| EP2025771A1 (en) * | 2007-08-15 | 2009-02-18 | Corus Staal BV | Method for producing a coated steel strip for producing taylored blanks suitable for thermomechanical shaping, strip thus produced, and use of such a coated strip |
| FR2927828B1 (fr) * | 2008-02-26 | 2011-02-18 | Thyssenkrupp Sofedit | Procede de formage a partir de flan en materiau trempant avec refroidissement differentiel |
| DE102008047971B3 (de) * | 2008-09-18 | 2010-05-12 | Aisin Takaoka Co., Ltd., Toyota | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Presshärten eines metallischen Formbauteils |
| EP2175041A1 (en) * | 2008-10-09 | 2010-04-14 | C.R.F. Società Consortile per Azioni | Method of hot forming metal plates |
| WO2010076247A1 (de) * | 2008-12-19 | 2010-07-08 | Voestalpine Automotive Gmbh | Verfahren zum herstellen partiell gehärteter bauteile aus stahlblech |
| DE102008055106A1 (de) | 2008-12-22 | 2010-07-01 | Technische Universität Graz | Werkzeug für das Presshärten von Stählen sowie Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung |
| JP4861518B2 (ja) * | 2009-01-23 | 2012-01-25 | 株式会社深井製作所 | エンボスが形成された鋼板の加圧成形方法 |
| DE102009003508B4 (de) * | 2009-02-19 | 2013-01-24 | Thyssenkrupp Steel Europe Ag | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines pressgehärteten Metallbauteils |
| DE102009012348B4 (de) | 2009-03-09 | 2019-04-18 | Faurecia Emissions Control Technologies, Germany Gmbh | Verfahren und Werkzeugmaschine zum Herstellen von abgasreinigenden Vorrichtungen |
| DE102009025896A1 (de) * | 2009-06-03 | 2011-01-05 | Technische Universität Graz | Warmumformung mit Einlegematerial |
| SE533825C2 (sv) | 2009-06-15 | 2011-01-25 | Gestamp Hardtech Ab | Sätt att forma och härda ett ämne av stålplåt |
| US8506732B2 (en) * | 2009-08-07 | 2013-08-13 | Radyne Corporation | Heat treatment of helical springs or similarly shaped articles by electric resistance heating |
| JP5402404B2 (ja) * | 2009-08-28 | 2014-01-29 | 新日鐵住金株式会社 | 差厚金属板及びその製造方法 |
| DE102009052210B4 (de) * | 2009-11-06 | 2012-08-16 | Voestalpine Automotive Gmbh | Verfahren zum Herstellen von Bauteilen mit Bereichen unterschiedlicher Duktilität |
| KR100951042B1 (ko) | 2009-11-13 | 2010-04-05 | 현대하이스코 주식회사 | 냉각 효율을 향상시킨 열간 프레스 성형 장치 |
| KR101164323B1 (ko) | 2009-12-28 | 2012-07-09 | 현대하이스코 주식회사 | 국부적으로 이종 강도를 갖는 열간 프레스 성형체 제조용 금형 시스템 및 이를 이용한 성형체 제조방법 |
| KR101171450B1 (ko) | 2009-12-29 | 2012-08-06 | 주식회사 포스코 | 도금 강재의 열간 프레스 성형방법 및 이를 이용한 열간 프레스 성형품 |
| DE102010012579B3 (de) * | 2010-03-23 | 2011-07-07 | Benteler Automobiltechnik GmbH, 33102 | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung von gehärteten Formbauteilen |
| DE102010012832B4 (de) * | 2010-03-25 | 2016-01-21 | Benteler Automobiltechnik Gmbh | Kraftfahrzeugsäule |
| DE102010012830B4 (de) * | 2010-03-25 | 2017-06-08 | Benteler Automobiltechnik Gmbh | Verfahren zur Herstellung einer Kraftfahrzeugkomponente und Karosseriebauteil |
| DE102010015000A1 (de) | 2010-04-14 | 2011-10-20 | Benteler Automobiltechnik Gmbh | Karosseriestruktur für ein Kraftfahrzeug und Verhalten zur Herstellung eines Strukturbauteils für eine Karosseriestruktur |
| CN102266900B (zh) * | 2010-06-07 | 2015-11-25 | 蒂森克虏伯金属成型技术有限公司 | 用于制造锻压的钢板成型构件的方法和热成型装置 |
| DE102010027554A1 (de) | 2010-07-19 | 2012-01-19 | Thyssenkrupp Umformtechnik Gmbh | Umformwerkzeug und Verfahren zum Warmumformen und partiellen Presshärten eines Werkstückes aus Stahlblech |
| JP5695381B2 (ja) * | 2010-09-30 | 2015-04-01 | 株式会社神戸製鋼所 | プレス成形品の製造方法 |
| DE102010048209C5 (de) * | 2010-10-15 | 2016-05-25 | Benteler Automobiltechnik Gmbh | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines warmumgeformten pressgehärteten Metallbauteils |
| MX348408B (es) * | 2011-03-03 | 2017-06-12 | Nippon Steel & Sumitomo Metal Corp | Método para combar metal en lámina y producto de metal en lámina. |
| CN102199693B (zh) * | 2011-05-27 | 2012-09-05 | 张光荣 | 气动快换模具连接装置 |
| WO2013001630A1 (ja) * | 2011-06-29 | 2013-01-03 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | ホットプレス装置 |
| WO2013023906A1 (de) * | 2011-08-17 | 2013-02-21 | Kirchhoff Automotive Deutschland Gmbh | Presshärtwerkzeug |
| DE102011053698C5 (de) * | 2011-09-16 | 2017-11-16 | Benteler Automobiltechnik Gmbh | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Struktur- und Chassisbauteilen durch Warmformen und Erwärmungsstation |
| DE102011086813A1 (de) * | 2011-11-22 | 2013-05-23 | Ford Global Technologies, Llc | Einstückiges Blechbauteil für ein Fahrzeug |
| CN102513798A (zh) * | 2011-12-31 | 2012-06-27 | 钢铁研究总院 | 一种热成形零件的定制设备及其方法 |
| DE102012003154A1 (de) | 2012-02-17 | 2012-09-20 | Daimler Ag | Verfahren zum Warmumformen eines metallischen Halbzeugs |
| JP2013233548A (ja) * | 2012-05-02 | 2013-11-21 | Unipres Corp | 熱間プレス成形装置 |
| DE102012210958A1 (de) * | 2012-06-27 | 2014-04-03 | Bayerische Motoren Werke Aktiengesellschaft | Gekühltes Werkzeug zum Warmumformen und/oder Presshärten eines Blechmaterials sowie Verfahren zur Herstellung einer Kühleinrichtung für dieses Werkzeug |
| AT513467B1 (de) * | 2012-09-26 | 2014-07-15 | Trumpf Maschinen Austria Gmbh | Verfahren zum Biegen eines Werkstücks |
| DE102013002121B4 (de) * | 2013-02-08 | 2015-04-02 | Benteler Automobiltechnik Gmbh | Verfahren und Presswerkzeug zur Herstellung von Karosseriebauteilen aus Aluminium sowie Karossereibauteil |
| JP6093630B2 (ja) * | 2013-04-12 | 2017-03-08 | 東プレ株式会社 | 熱間プレス製品の製造方法 |
| JP6194526B2 (ja) * | 2013-06-05 | 2017-09-13 | 高周波熱錬株式会社 | 板状ワークの加熱方法及び加熱装置並びにホットプレス成形方法 |
| CN103357764A (zh) * | 2013-07-24 | 2013-10-23 | 陈扬 | 基于硼钢钢板的热成形模具的冷却气体直冷工艺及装置 |
| CN103433391A (zh) * | 2013-08-26 | 2013-12-11 | 北京理工大学 | 高强钢板热增量成形装置 |
| US9616482B2 (en) * | 2013-11-05 | 2017-04-11 | Martinrea Industries, Inc. | Hot forming metal die with improved cooling system |
| CN103934360A (zh) * | 2014-04-25 | 2014-07-23 | 吉林大学 | 超高强度钢热冲压、温冲裁复合成形工艺及模具 |
| CN105149428A (zh) * | 2014-06-09 | 2015-12-16 | Gnssolitech株式会社 | 毛坯成型和切边用的热冲压加工方法以及模具装置 |
| DE102014109553A1 (de) * | 2014-07-08 | 2016-01-14 | Thyssenkrupp Ag | Härtewerkzeug und Verfahren zum Herstellen gehärteter Profilformteile |
| DE102014109773A1 (de) * | 2014-07-11 | 2016-01-14 | Thyssenkrupp Ag | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines pressgehärteten Bauteils |
| DE102014112244A1 (de) * | 2014-08-26 | 2016-03-03 | Benteler Automobiltechnik Gmbh | Verfahren und Presse zur Herstellung wenigstens abschnittsweise gehärteter Blechbauteile |
| CN105436275A (zh) * | 2014-08-26 | 2016-03-30 | 刘平 | 一种低碳硼合金钢汽车加强板的热冲压成形工艺 |
| DE102014221997A1 (de) | 2014-10-29 | 2016-05-04 | Bayerische Motoren Werke Aktiengesellschaft | Formwerkzeug zur Herstellung von warmumgeformten Bauteilen |
| EP3088092B1 (de) | 2015-04-30 | 2017-06-07 | Benteler Automobiltechnik GmbH | Warmumform- und presshärtewerkzeug sowie verfahren zum betreiben des warmumform- und presshärtewerkzeuges |
| DE102015213485B4 (de) * | 2015-07-17 | 2022-04-28 | Bayerische Motoren Werke Aktiengesellschaft | Pressenwerkzeug mit einer Formschale für die Umformung von Tailored Blanks und Verfahren zur Herstellung einer Formschale |
| DE102016103539B4 (de) | 2016-02-29 | 2018-09-20 | Thyssenkrupp Ag | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines mehrdimensional gefügestrukturierten, tiefziehfähigen Metallflachprodukts und Metallflachprodukt |
| JP6633445B2 (ja) * | 2016-04-25 | 2020-01-22 | アイシン・エィ・ダブリュ工業株式会社 | 金型、金型装置およびワークの冷却方法 |
| CN106181240A (zh) * | 2016-07-20 | 2016-12-07 | 中国科学院金属研究所 | 一种C‑Mn‑B系高强钢异形空心零件热挤胀差强淬火一体化工艺 |
| EP3558892B1 (en) | 2016-12-23 | 2025-05-28 | Nu-Rock Corporation S.a.r.l. | Process for producing a shaped article |
| US10633037B2 (en) | 2017-06-16 | 2020-04-28 | Ford Global Technologies, Llc | Vehicle underbody assembly with thermally treated rear rail |
| US10556624B2 (en) | 2017-06-16 | 2020-02-11 | Ford Global Technologies, Llc | Vehicle underbody component protection assembly |
| US10399519B2 (en) | 2017-06-16 | 2019-09-03 | Ford Global Technologies, Llc | Vehicle bumper beam with varied strength zones |
| US11141769B2 (en) | 2017-06-16 | 2021-10-12 | Ford Global Technologies, Llc | Method and apparatus for forming varied strength zones of a vehicle component |
| JP7214973B2 (ja) * | 2018-03-30 | 2023-01-31 | マツダ株式会社 | 熱間プレス加工方法及び加工装置 |
| DE102018121770A1 (de) * | 2018-09-06 | 2020-03-12 | Salzgitter Flachstahl Gmbh | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung eines Bandes aus umwandlungsfähigem Stahl als Vormaterial für ein Bauteil mit Bereichen unterschiedlicher Festigkeiten |
| EP3865227B1 (en) * | 2018-10-10 | 2025-04-02 | Unipres Corporation | Method for manufacturing a press-molded article, a retainer, and a manufacturing system for a press-molded article |
| JP7155986B2 (ja) * | 2018-12-13 | 2022-10-19 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 鋼板部材及びその製造方法 |
| CN118989087A (zh) * | 2019-02-13 | 2024-11-22 | 麦格纳国际公司 | 热冲压方法和热冲压系统 |
| DE102019215053A1 (de) * | 2019-09-30 | 2021-04-01 | Thyssenkrupp Steel Europe Ag | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines zumindest teilweise vergüteten Stahlblechbauteils und zumindest teilweise vergütetes Stahlblechbauteil |
| CN111229905B (zh) * | 2020-01-09 | 2021-06-11 | 安徽工业大学 | 一种基于液压成形装置的热冲压及淬火一体化处理方法 |
| CN113770653A (zh) * | 2021-09-14 | 2021-12-10 | 广东皓耘科技有限公司 | 锰硼钢耙柱的制造方法 |
| EP4283004A1 (de) | 2022-05-24 | 2023-11-29 | ThyssenKrupp Steel Europe AG | Blechformteil mit verbesserten verarbeitungseigenschaften |
| CN115740269B (zh) * | 2022-12-01 | 2025-08-12 | 中国航空制造技术研究院 | 一种铝合金薄壁整体封头壁厚均匀性控制方法 |
| WO2025022840A1 (ja) * | 2023-07-26 | 2025-01-30 | 住友重機械工業株式会社 | 成形装置、成形システム、及び金属パイプ |
| CN118721051B (zh) * | 2024-08-29 | 2025-08-29 | 万华化学集团电子材料有限公司 | 化学机械抛光垫的抛光层的制备方法和化学机械抛光垫 |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3703093A (en) * | 1969-11-11 | 1972-11-21 | Aisin Seiki | Process and apparatus for performing a simultaneous and combined press-forming and heat-treatment of steel stock |
| SE435527B (sv) | 1973-11-06 | 1984-10-01 | Plannja Ab | Forfarande for framstellning av en detalj av herdat stal |
| JPS5714423A (en) | 1980-06-27 | 1982-01-25 | Onkyo Corp | Drawing method for vibration diaphragm |
| SE9602257L (sv) | 1996-06-07 | 1997-12-08 | Plannja Hardtech Ab | Sätt att framställa ståldetalj |
| JPH11309519A (ja) * | 1998-04-24 | 1999-11-09 | Kawasaki Steel Corp | ステンレス製多角筒ケースの高速深絞り加工方法 |
| JP2001252729A (ja) | 2000-03-10 | 2001-09-18 | Aida Eng Ltd | プレス加工装置 |
| DE10049660B4 (de) | 2000-10-07 | 2005-02-24 | Daimlerchrysler Ag | Verfahren zum Herstellen lokal verstärkter Blechumformteile |
| JP2002241835A (ja) * | 2001-02-20 | 2002-08-28 | Aisin Takaoka Ltd | ワークの部分強化方法 |
| DE10305725B3 (de) * | 2003-02-12 | 2004-04-08 | Benteler Automobiltechnik Gmbh | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Formbauteils aus Stahl mit mindestens zwei Gefügebereichen unterschiedlicher Duktilität |
| KR20060117304A (ko) | 2003-08-28 | 2006-11-16 | 유겐가이샤 리나시메타리 | 액압 성형 장치 및 액압 성형 방법 |
| DE10341867B4 (de) * | 2003-09-09 | 2012-03-08 | Volkswagen Ag | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung eines gehärteten Blechprofils |
| JP4833531B2 (ja) * | 2003-11-11 | 2011-12-07 | 新日本製鐵株式会社 | プレス成形加工装置、プレス成形加工方法、コンピュータプログラム及び記録媒体 |
-
2005
- 2005-05-30 DE DE102005025026A patent/DE102005025026B3/de not_active Withdrawn - After Issue
-
2006
- 2006-05-24 US US11/916,215 patent/US8118954B2/en active Active
- 2006-05-24 CN CN201310254884.9A patent/CN103382518B/zh active Active
- 2006-05-24 CN CNA2006800192043A patent/CN101189350A/zh active Pending
- 2006-05-24 CA CA2610378A patent/CA2610378C/en active Active
- 2006-05-24 JP JP2008514068A patent/JP5568235B2/ja active Active
- 2006-05-24 EP EP06763268A patent/EP1888794B1/de active Active
- 2006-05-24 PT PT06763268T patent/PT1888794E/pt unknown
- 2006-05-24 WO PCT/EP2006/062579 patent/WO2006128821A1/de not_active Ceased
- 2006-05-24 PL PL06763268T patent/PL1888794T3/pl unknown
- 2006-05-24 ES ES06763268T patent/ES2385579T3/es active Active
- 2006-05-24 BR BRPI0610872-5A patent/BRPI0610872B1/pt active IP Right Grant
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106232255A (zh) * | 2014-07-18 | 2016-12-14 | 宝马股份公司 | 用于制造热成形构件的模具 |
| CN106232255B (zh) * | 2014-07-18 | 2019-11-19 | 宝马股份公司 | 用于制造热成形构件的模具 |
| DE102023121542A1 (de) | 2023-08-11 | 2025-02-13 | Thyssenkrupp Steel Europe Ag | Maßgeschneidertes Halbzeug und äußere Seitenwandverstärkung |
| WO2025036741A1 (de) | 2023-08-11 | 2025-02-20 | Thyssenkrupp Steel Europe Ag | MAßGESCHNEIDERTES HALBZEUG UND ÄUßERE SEITENWANDVERSTÄRKUNG |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE102005025026B3 (de) | 2006-10-19 |
| CN101189350A (zh) | 2008-05-28 |
| CN103382518B (zh) | 2015-10-21 |
| EP1888794A1 (de) | 2008-02-20 |
| CA2610378A1 (en) | 2006-12-07 |
| PL1888794T3 (pl) | 2012-09-28 |
| JP2008542031A (ja) | 2008-11-27 |
| US20080196800A1 (en) | 2008-08-21 |
| BRPI0610872B1 (pt) | 2018-02-27 |
| CA2610378C (en) | 2013-06-18 |
| PT1888794E (pt) | 2012-07-12 |
| WO2006128821A1 (de) | 2006-12-07 |
| US8118954B2 (en) | 2012-02-21 |
| CN103382518A (zh) | 2013-11-06 |
| JP5568235B2 (ja) | 2014-08-06 |
| ES2385579T3 (es) | 2012-07-26 |
| BRPI0610872A2 (pt) | 2010-08-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1888794B1 (de) | Verfahren zum herstellen eines metallbauteils mit aneinander angrenzenden abschnitten unterschiedlicher materialeigenschaften | |
| DE102008047971B3 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Presshärten eines metallischen Formbauteils | |
| EP2496371B1 (de) | Verfahren zum herstellen von bauteilen mit bereichen unterschiedlicher duktilität | |
| EP2429733B1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung eines bestandteils einer synchronisierungseinrichtung für ein schaltgetriebe | |
| EP3037186B1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung eines warmumform- und pressgehärteten stahlbauteils mit scharf berandetem übergangsbereich | |
| EP2993241B1 (de) | Verfahren und presse zur herstellung wenigstens abschnittsweise gehärteter blechbauteile | |
| EP2366805B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von pressgehärteten Formbauteilen | |
| EP3160667B1 (de) | Verfahren und umformwerkzeug zum warmumformen sowie entsprechendes werkstück | |
| EP2059355A1 (de) | Verfahren und werkzeug zum warmumformen eines metallwerkstücks | |
| EP2851138A1 (de) | Partiell gekühltes Warmformwerkzeug | |
| DE102009012940B4 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Bauteils, insbesondere eines Blechbauteils sowie Fertigungsstraße zur Herstellung des Bauteils | |
| DE102004054795A1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Blechbauteilen sowie Karosseriebauteil | |
| DE102012012518A1 (de) | Warmumformwerkzeug zur Herstellung von Formteilen | |
| EP2548671A1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines rohrförmigen Strukturbauteils für ein Kraftfahrzeug und Strukturbauteil | |
| DE102011110597A1 (de) | Warmumformvorrichtung mit Schneideeinrichtung | |
| DE102009038896A1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines aus einem ersten und zweiten Bauteil mittels Durchsetzfügen, insbesondere mittels Clinchen gefügten Strukturbauteils | |
| DE112016001842T5 (de) | Lasergesinterte Oberfläche einer Matritze für ein Werkzeug | |
| DE102006015666B4 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines metallischen Formbauteils durch Warmumformen mit simultaner Beschneideoperation | |
| DE102005041741B4 (de) | Verfahren zum Herstellen eines pressgehärteten Bauteils | |
| DE102017201674B3 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines pressgehärteten Bauteils sowie Pressform | |
| WO2019048025A1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung eines bauteils und werkzeug dafür | |
| EP3689490B1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung eines bauteils aus metall mittels innenhochdruckumformen | |
| DE102014203767A1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Fahrzeugbauteilen | |
| DE102007002678A1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Herstellen eines warmumgeformten Blechbauteils | |
| DE102008043401B4 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung von Blechbauteilen mittels Warmumformung sowie dadurch hergestellte Blechbauteile |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20071130 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| RIN1 | Information on inventor provided before grant (corrected) |
Inventor name: BEENKEN, HEIKO Inventor name: SIKORA, SASCHA Inventor name: HELLER, THOMAS Inventor name: LENZE, FRANZ-JOSEF |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: THYSSENKRUPP STEEL EUROPE AG |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20091022 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R079 Ref document number: 502006011448 Country of ref document: DE Free format text: PREVIOUS MAIN CLASS: C21D0001673000 Ipc: B21D0022020000 |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: C21D 1/673 20060101ALI20111101BHEP Ipc: B21D 22/02 20060101AFI20111101BHEP Ipc: B21D 37/16 20060101ALI20111101BHEP |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| RTI1 | Title (correction) |
Free format text: METHOD FOR PRODUCING A METALLIC COMPONENT COMPRISING ADJACENT SECTIONS HAVING DIFFERENT MATERIAL PROPERTIES |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 557794 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20120615 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 502006011448 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: COHAUSZ & FLORACK PATENT- UND RECHTSANWAELTE P, DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: PT Ref legal event code: SC4A Free format text: AVAILABILITY OF NATIONAL TRANSLATION Effective date: 20120705 Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502006011448 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20120712 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2385579 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 Effective date: 20120726 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: T3 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: TRGR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: PL Ref legal event code: T3 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D Effective date: 20120516 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120516 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120516 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120516 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120916 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SK Ref legal event code: T3 Ref document number: E 12328 Country of ref document: SK |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120516 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120817 Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120516 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120531 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120531 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120516 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120531 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120516 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120516 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20130219 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120524 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502006011448 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20130219 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120816 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120524 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20060524 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R084 Ref document number: 502006011448 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| P01 | Opt-out of the competence of the unified patent court (upc) registered |
Effective date: 20230526 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20240521 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20240521 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20240521 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20240620 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CZ Payment date: 20240416 Year of fee payment: 19 Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20240522 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SK Payment date: 20240416 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20240521 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Payment date: 20240415 Year of fee payment: 19 Ref country code: PT Payment date: 20240423 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Payment date: 20240412 Year of fee payment: 19 Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20240521 Year of fee payment: 19 Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20240521 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20240522 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20251124 |