EP1589141B1 - Device for the continuous heat treatment of a textile fabric, particularly for fixing of dyestuffs - Google Patents
Device for the continuous heat treatment of a textile fabric, particularly for fixing of dyestuffs Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1589141B1 EP1589141B1 EP05011446A EP05011446A EP1589141B1 EP 1589141 B1 EP1589141 B1 EP 1589141B1 EP 05011446 A EP05011446 A EP 05011446A EP 05011446 A EP05011446 A EP 05011446A EP 1589141 B1 EP1589141 B1 EP 1589141B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- roller
- web
- treatment
- fabric web
- fixing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D06—TREATMENT OF TEXTILES OR THE LIKE; LAUNDERING; FLEXIBLE MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- D06B—TREATING TEXTILE MATERIALS USING LIQUIDS, GASES OR VAPOURS
- D06B23/00—Component parts, details, or accessories of apparatus or machines, specially adapted for the treating of textile materials, not restricted to a particular kind of apparatus, provided for in groups D06B1/00 - D06B21/00
- D06B23/04—Carriers or supports for textile materials to be treated
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D06—TREATMENT OF TEXTILES OR THE LIKE; LAUNDERING; FLEXIBLE MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- D06B—TREATING TEXTILE MATERIALS USING LIQUIDS, GASES OR VAPOURS
- D06B19/00—Treatment of textile materials by liquids, gases or vapours, not provided for in groups D06B1/00 - D06B17/00
- D06B19/0005—Fixing of chemicals, e.g. dyestuffs, on textile materials
- D06B19/0029—Fixing of chemicals, e.g. dyestuffs, on textile materials by steam
- D06B19/0035—Fixing of chemicals, e.g. dyestuffs, on textile materials by steam the textile material passing through a chamber
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D06—TREATMENT OF TEXTILES OR THE LIKE; LAUNDERING; FLEXIBLE MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- D06B—TREATING TEXTILE MATERIALS USING LIQUIDS, GASES OR VAPOURS
- D06B23/00—Component parts, details, or accessories of apparatus or machines, specially adapted for the treating of textile materials, not restricted to a particular kind of apparatus, provided for in groups D06B1/00 - D06B21/00
- D06B23/14—Containers, e.g. vats
- D06B23/16—Containers, e.g. vats with means for introducing or removing textile materials without modifying container pressure
Definitions
- the invention relates to a device for the continuous heat treatment of a textile web, in particular for ink fixing, according to the preamble of claim 1.
- the fixation can be carried out by lingering the acted upon with dye liquor web at room temperature or the wet or dried web at higher temperatures.
- the fixing treatment is dependent on the material of the web and the applied dye.
- From the DE-A 16 35 140 is a method for the continuous dye fixation of man-made fibers in webs by a high-temperature treatment with convective heat transfer, for example on nozzle-ventilated Fixierspannrahmen known.
- a rapid heating and then a dwell treatment are carried out first.
- the web is guided in tensioning chains and during the dwell treatment over normal guide rollers.
- auxiliaries such as urea, which are added to the dye liquor needed. The aids keep the dye on drying in solution and evaporate during fixing.
- the treatment gas used is heated air.
- the use of aggressive auxiliaries, such as urea can at a Treatment of the acted upon with dye liquor web with a vapor-air mixture can be reduced or avoided.
- this fixing method requires a goods content in the dwelling unit, here a hotflue, of at least 80 m. It is therefore not economical to use for smaller amounts to be dyed (smaller amounts).
- the high vapor content of the treatment gas accelerates the heating time due to the condensability of the superheated steam, which leads to a further reduction of the required residence time.
- the treatment process leads to good fixation results, i. to a good color yield and a good color quality, which correspond to the results of the prior art.
- the drying of the moist web during the treatment with superheated steam has proven to be essential for a complete fixation with low fixing times. This is achieved by an acceleration of the fixing process, for example the reaction of the Reactive dye with native fibers, such as cotton and cellulose, explained by drying.
- the input moisture content of the web treated with dye liquor is 40 to 80% when dyeing native fibers with reactive dyestuff.
- urea For most reactive dyes, the use of urea can be dispensed with.
- the temperature of the superheated steam may preferably be 160 to 230 ° C.
- the residence time of the web in the device may be 5 to 60 seconds, preferably 10 to 30 seconds. This time is sufficient for complete fixation with good color yield and allows a device of small size.
- These methods could include a guide of the web through a hot steam filled chamber in the form of hanging loops and a meandering guidance of the web to two rows of guiding and conveying rollers, as far as it is suitable for transporting a moist, colored and unfixed web.
- the web can be brought in accordance with claim 5 with convection guided hot steam over the web directed nozzles in contact. This is at the o.g. Process without gradients possible, since due to the high steam content and possibly the high steam temperature, a rapid drying of the web and thus the dye takes place.
- Hotflue Devices with a meandering guidance of the web about two rows of rolls and directed onto the web nozzles are known to the applicant as Hotflue.
- the known devices have, like the WO 97/148 39 , a very high content and are, for example because of leaks, not suitable for operation with superheated steam.
- a further improvement of the heat transfer can be achieved if the web 6 is transported substantially flat through the treatment chamber and is brought into contact with hot steam via above and possibly below the web arranged nozzle boxes.
- nozzle-ventilated Fixierspannrahmen are for quick heating when dye fixing of man-made fibers, ie during thermosoling, from the DE-A 16 35 140 known.
- Devices of this type which are suitable for use as treatment gas superheated, are in the DE 35 11 950 namely a float dryer and a tenter dryer.
- Another device namely a usable for hot steam treatment tenter frame, is from the DE 195 46 344 known.
- Inlet slot and outlet slot of this dryer are mounted in the bottom of its housing. The web is flat except for the inlet area and the outlet area, and although horizontally, passed through the dryer.
- a generic device for continuous or semi-continuous heat treatment of a web is in the US-A-3,234,662 described.
- This device has a housing with a treatment chamber through which the web is guided. It is a recirculation device with a circulating fan and arranged above and below the web arranged nozzle boxes.
- a transporting device with rollers comprises three roller arrangements, wherein a first arrangement with a draw roller in front of the housing, a second arrangement with a dancer roller after the housing and a third arrangement with a draw roller behind it are arranged.
- the drives of the first and third arrangements are set so that the speed of the third arrangement is greater than that of the first Arrangement Due to the speed difference creates a certain longitudinal tension of the web.
- This device is not very suitable in the EP-B-1 063 337 to carry out the described method, in which a wet web charged with dye liquor is treated with superheated steam.
- the tension roller in front of the housing would affect the application of paint on the moist web and lead to quality losses.
- a continuous dryer for a tire cord fabric web with a transport device which also has three roller assemblies is from the FR-A-1 536 604 known.
- the first before the dryer and the third arranged behind the dryer roller assemblies each comprise a pair of rollers through which the web is driven.
- the second, interposed roller assembly is provided with a dancer roller.
- the object of the invention is to develop a device for the continuous heat treatment of a textile web, in particular for color fixing, according to the preamble of claim 1, which allows a treatment of the web with superheated steam in smaller amounts.
- the wet fabric web applied with the dye liquor should be fixed and dried.
- the web should be smoothed by a longitudinal tension to ensure a uniform fixing and thus a uniform color yield.
- a device for the continuous heat treatment of a textile web, in particular for ink fixing, comprising a housing, with at least one treatment chamber with a circulating air device, i. a device for guiding hot steam in the recirculation method, with a circulating air fan and arranged above and below the web nozzle boxes in each treatment chamber, with a transport device with rollers for substantially planar guidance of the web under a longitudinal tension through the treatment chamber of the housing has a vapor-tight housing.
- a circulating air device i. a device for guiding hot steam in the recirculation method, with a circulating air fan and arranged above and below the web nozzle boxes in each treatment chamber, with a transport device with rollers for substantially planar guidance of the web under a longitudinal tension through the treatment chamber of the housing has a vapor-tight housing.
- the distance to the front wall is at least 20%, preferably at least 30%, of the length of the horizontal transport path of the web through the treatment chambers.
- a roller gear may have two mutually offset rollers, one being adjustable relative to the other, for generating a longitudinal tension.
- a roller conveyor can also have two, the web in their transport plane leading rods or rollers and arranged between the two rods or rollers above or below the transport plane, perpendicular to the transport plane adjustable draw roller.
- the web is guided in the form of a loop around the tension roller and held by deflection of the tension roller perpendicular to the transport plane under longitudinal tension.
- the web is transported by the spaced apart from a front wall of the housing roller duct under a longitudinal stress, in particular from 10 to 100 N / m, through the treatment chambers.
- the distance to the front wall is at least 20%, preferably at least 30%, of the length of the horizontal transport path of the web through the treatment chambers.
- the web is only through the roller gear led, if they and thus the dye is already dried. During the drying and also during the entire fixing process, the web is pulled smoothly by the longitudinal tension, which ensures a uniform fixing and thus a uniform color yield.
- a guide of the web through a roller gear is also a simple transport method, which allows, for example, compared to a tension chain guide, easier inputs and outputs in the treatment chamber.
- the roller passage according to claim 2 is arranged in each case in the region in which the two treatment chambers abut one another, d. H. the distance to the front wall is about 50% of the length of the horizontal transport path of the web through the treatment chambers.
- the treatment chambers are also called fields and the areas between the treatment chambers field shocks.
- the roller gear on two guide rollers and a vertically adjustable draw roller wherein the guide rollers are arranged one behind the other and the tension roller in the middle below the guide rollers.
- a draw roller which is simultaneously formed as an alignment roller according to claim 4, saves additional means for aligning the web.
- the device according to the invention in front of and behind the housing each have a lock.
- the locks extend from the floor to the transport plane of the web and have near the bottom and at the level of the transport plane guide rollers.
- the locks are divided into a lower, downwardly open prechamber and another main chamber arranged above.
- Intake channels or suction boxes can be connected to the antechambers.
- Compared to those from the DE-A 195 46 344 known inlet and outlet slots with suction boxes is prevented by the separate locks with pre-chamber and suction devices the penetration of air and thus condensation of steam to water safer.
- One from the DE 198 58 839 Known lock in which steam is blown onto the web in front of the inlet slot of the housing is less suitable for fixing dye because of the risk of color gradients.
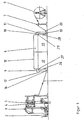
- FIG. 1 shows a system for dyeing with a device according to the invention for fixing inks.
- FIG. 2 shows an inlet lock, a first treatment chamber and a roller passage of the device.
- a plant for dyeing a textile web 1, for example made of cotton or cellulose with reactive dye has a goods storage 2, a feed device 3, a dyeing device 4, an aisle 5, a device for ink fixation 6, another supply device 7 and a arranged one behind the other in the transport direction another goods storage 8.
- the front goods storage 2 as a container
- the dyeing device 4 as a padder
- the rear goods storage 8 as a winding roller
- the feeders 3, 7 as a gallows.
- the device for color fixing 6 has an entrance lock 9, a vapor-tight, heat-insulated housing 10 and an exit lock 11.
- the housing 10 comprises at least one, preferably two to five, here two, modular-like lined-up treatment chambers 12, 13. By the treatment chambers 12, 13, the interior of the housing 10 is divided into two successively arranged fields.
- the housing 10 is not divided and includes all treatment chambers 12, 13th
- each of the treatment chambers 12, 13 is a recirculation device, i. a device for guiding superheated steam in a circuit, also called recirculation method, arranged with a circulating air fan 14, a heater not shown in Figure 2 and with nozzle boxes 15 with targeting the web 1 nozzle openings.
- a recirculation device i. a device for guiding superheated steam in a circuit, also called recirculation method, arranged with a circulating air fan 14, a heater not shown in Figure 2 and with nozzle boxes 15 with targeting the web 1 nozzle openings.
- a treatment chamber 12, 13 several, e.g. two each above and below the web 1 to be arranged across the web 1 extending nozzle boxes 15.
- the nozzle openings are preferably formed as slots.
- a transport device has, in addition to guide rollers 16, 17 in the entrance lock 9 and guide rollers 18, 19, 20 in and behind the exit lock 11 in the region in which the two treatment chambers 12, 13 abut, a roller conveyor with two guide rollers 21, 22 and a tension roller 23rd on.
- the roller gear is thus arranged on the half of the transport path of the web 1 from the inlet slot 27 in the front wall 26 to the outlet slot 29 in the rear wall 28.
- the two guide rollers 21, 22 are the same size and arranged one behind the other at a height.
- the arrangement of the guide rollers 21, 22, the last guide roller 17 of the entrance lock 9 and the first guide roller 18 of the exit lock 11 is such that the transport plane of the web 1 in the treatment chambers 12, 13 is flat and horizontal.
- the tension roller 23 is arranged vertically adjustable in the middle, below the guide rollers 21, 22. It is also used as an alignment roller, i. adjustable in a plane passing through its axis parallel to the transport plane, formed.
- the height adjustability of the draw roller 23 is indicated by the arrows 24 and the alignability by the arrows 25.
- the draw roller 23 is also connected to a drive, not shown.
- the housing 10 has an inlet slot 27 on a front wall 26 of the first treatment chamber 12 and an outlet slot 29 on a rear wall 28 of the last treatment chamber 13, through which the material web 1 is guided into or out of the housing 10.
- the entrance lock 9 has a parallel to the front wall 26 extending, in the vicinity of a lower edge 30 to above the inlet slot 27 extending front plate 31, a ceiling plate 32 and two side plates, not shown.
- the sheets 31, 32 of the entrance lock 9 are vapor-tight with each other and connected to the front wall 26.
- the entrance lock 9 is subdivided into an upper main chamber 36 and a lower prechamber 37 by intermediate plates 33, 34 which extend from the front plate 31 and from the front wall 26 into the interior of the entrance lock 9 and leave therebetween a gap 35 for the web 1.
- the pre-chamber 37 is open at the bottom.
- a suction device in this example connected to a fan, not shown suction channel 38 is connected.
- suction boxes 39 to which the suction channel 38 is connected, are located in the prechamber 37.
- the first guide roller 16 of the transport device is located below the prechamber 37 and the second, i.e. the first guide roller 16 of the transport device.
- the exit lock 11 is constructed analogously to the entrance lock 9.
- the first and second guide rollers 18, 19 are arranged analogously to those of the entrance lock 9 and the third guide roller 20 behind the second one behind the exit lock 11.
- the web 1 is scavenged from the goods storage 2 via the feed device 3 designed as a gallows and fed through the dyeing device 4 designed as a padder and the aisle 5 of the device 6 for fixing the dye.
- the web 1 is to the guide roller 16 of the transport device from below into the prechamber 37 of the entrance lock 9 through the prechamber 37 and through the gap 35 into the main chamber 36 and the guide roller 17 through the inlet slot 27 into the first treatment chamber 12 of the device. 6 transported.
- the transport of the web 1 through the treatment chambers 12, 13 takes place through the roller gear arranged between the first and second treatment chambers 12, 13 in a horizontal plane and under a longitudinal tension of 10 to 100 N / m.
- the web 1 is meander-shaped, one behind the other and around the guide roller 21, the driven tension roller 23 and the guide roller 22 around.
- the desired longitudinal tension is achieved by adjusting the height of the Pull roller 23 is set.
- Optionally occurring shifts of the web 1 are compensated by adjusting the tension roller 23, by an angular displacement of the axis of the tension roller 23 parallel to the transport plane.
- the web 1 leaves the device 6, through the exit slot 29 and the exit lock 11. It is fed via a designed as gallows supply device 7 designed as a winding roll goods storage 8.
- the web speed is for example 40 m / min.
- the web 1 is charged with dye liquor.
- the aisle 5 is a homogenization of the dye liquor on the web 1 instead.
- the moist web 1 is, while it is transported to the roller course just by the treatment chamber 12, 13 of the device 6, applied via the above and below the web 1 arranged nozzle boxes 15 directed toward the web 1 nozzle openings with superheated steam.
- the nozzle pressure is 200 to 1000 PA and the heat transfer capacity about 240 W / m 2 .
- the temperature of the superheated steam is 160 to 230 ° C and the residence time of the web 1 in the treatment chambers 12, 13 5 to 60 seconds, preferably 10 to 30 seconds.
- the residual moisture of the web 1 when leaving the housing 10 is about or less than the equilibrium moisture content under normal conditions, ie less than or equal to about 10%.
- the steam content preferably between 95 and 100% by volume, is maintained by varying the amount of extracted treatment gas via the suction channels 38 of the antechambers 37 of the inlet and outlet locks 9, 11. A regulation of a certain residual moisture of the web is not necessary.
- a fabric web 1 of cotton (BG) with a fabric weight of 80 g / m 2 applied with dye liquor of a reactive dye without urea is transported through the device 6 at a web speed of 40 m / min.
- the temperature of the pure hot steam is 180 ° C.
- the nozzle pressure at the nozzle openings of the nozzle boxes 15 is 700 PA.
- Even after a residence time of 5 seconds the majority of the dye has reacted with the fibers of the web 1 and is fixed. After another 5 seconds, the web 1 is completely dried and the remaining part of the dye is fixed.
- the input moisture of about 80% is reduced in the device 6 to a value less than 10%.
- the total residence time of the web 1 in the device 6 is 10 seconds.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Treatment Of Fiber Materials (AREA)
- Coloring (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Die Erfindung betrifft eine Vorrichtung zur kontinuierlichen Wärmebehandlung einer textilen Warenbahn, insbesondere zum Farbfixieren, gemäß dem Oberbegriff des Anspruchs 1.The invention relates to a device for the continuous heat treatment of a textile web, in particular for ink fixing, according to the preamble of
Beim Färben ist es notwendig, den auf die textile Warenbahn aufgebrachten Farbstoff zu fixieren. Die Fixierung kann durch Verweilen der mit Farbflotte beaufschlagten Warenbahn bei Raumtemperatur oder der feuchten oder getrockneten Warenbahn bei höheren Temperaturen erfolgen. Die Fixierbehandlung ist vom Material der Warenbahn und dem aufgebrachten Farbstoff abhängig.When dyeing, it is necessary to fix the applied to the textile web dye. The fixation can be carried out by lingering the acted upon with dye liquor web at room temperature or the wet or dried web at higher temperatures. The fixing treatment is dependent on the material of the web and the applied dye.
Beim Färben von Chemiefasern mit Dispersionsfarbstoffen ist es z.B. bekannt, die mit Farbflotte beaufschlagte Warenbahn zunächst zu trocknen und anschließend den Farbstoff bei höherer Temperatur auf der Warenbahn zu fixieren.When dyeing manmade fibers with disperse dyes, it is e.g. it is known to first dry the fabric web applied with the dye liquor and then to fix the dyestuff at a higher temperature on the fabric web.
Aus der
Beim Färben von Baumwolle oder Zellulose mit Reaktivfarbstoffen ist es z.B. bekannt, die mit Farbflotte beaufschlagte Warenbahn zunächst zu trocknen und anschließend den Farbstoff bei höherer Temperatur mit den Fasern der Warenbahn reagieren zu lassen. Dazu werden Hilfsmittel wie Harnstoff, die der Farbflotte beigemischt werden, benötigt. Die Hilfsmittel halten den Farbstoff beim Trocknen in Lösung und verdunsten beim Fixieren. Als Behandlungsgas wird erwärmte Luft eingesetzt. Der Einsatz aggressiver Hilfsmittel, wie Harnstoff, kann bei einer Behandlung der mit Farbflotte beaufschlagten Warenbahn mit einem Dampf-Luftgemisch reduziert oder vermieden werden.When dyeing cotton or cellulose with reactive dyes, it is known, for example, to first dry the fabric web applied with dye liquor and then to allow the dyestuff to react with the fibers of the fabric web at a higher temperature. For this purpose, auxiliaries such as urea, which are added to the dye liquor needed. The aids keep the dye on drying in solution and evaporate during fixing. The treatment gas used is heated air. The use of aggressive auxiliaries, such as urea, can at a Treatment of the acted upon with dye liquor web with a vapor-air mixture can be reduced or avoided.
Aus der
Aus der
Bei einem under
Bei einem höheren Dampfgehalt sind höhere Temperaturen der Warenbahn bei der Wärmebehandlung erreichbar; insbesondere steigt bei reinem Heißdampf die Warenbahntemperatur bis auf etwa 100° C. Die höhere Warenbahntemperatur beschleunigt die Reaktion des Farbstoffes mit den Fasern beim Fixieren von Reaktivfarbstoff auf Baumwolle oder Zellulose. Dies führt zu geringeren Fixierzeiten, entsprechend geringeren Verweilzeiten in einer Behandlungsvorrichtung und ermöglicht damit kleinere Vorrichtungen.At a higher steam content higher temperatures of the web during the heat treatment can be achieved; In particular, with pure superheated steam, the web temperature rises to about 100 ° C. The higher web temperature accelerates the reaction of the dye with the fibers when fixing reactive dye to cotton or cellulose. This leads to lower fixing times, correspondingly shorter residence times in a treatment device and thus enables smaller devices.
Der hohe Dampfgehalt des Behandlungsgases beschleunigt aufgrund der Kondensationsfähigkeit des Heißdampfes die Aufheizzeit, was zu einer weiteren Reduzierung der benötigten Verweilzeit führt.The high vapor content of the treatment gas accelerates the heating time due to the condensability of the superheated steam, which leads to a further reduction of the required residence time.
Überraschenderweise führt das Behandlungsverfahren trotz des hohen Dampfgehaltes und der hohen Warentemperatur, und damit der verstärkten Trocknung, zu guten Fixierergebnissen, d.h. zu einer guten Farbausbeute und einer guten Farbqualität, die den Ergebnissen des Standes der Technik entsprechen.Surprisingly, despite the high steam content and the high product temperature, and thus the increased drying, the treatment process leads to good fixation results, i. to a good color yield and a good color quality, which correspond to the results of the prior art.
Die Trocknung der feuchten Warenbahn während der Behandlung mit Heißdampf hat sich als wesentlich für eine vollständige Fixierung bei geringen Fixierzeiten herausgestellt. Dies wird durch eine Beschleunigung des Fixiervorgangs, zum Beispiel der Reaktion des Reaktivfarbstoffes mit nativen Fasern, wie Baumwolle und Zellulose, durch die Trocknung erklärt.The drying of the moist web during the treatment with superheated steam has proven to be essential for a complete fixation with low fixing times. This is achieved by an acceleration of the fixing process, for example the reaction of the Reactive dye with native fibers, such as cotton and cellulose, explained by drying.
Die Eingangsfeuchte der mit Farbflotte beaufschlagten Warenbahn beträgt beim Färben von nativen Fasern mit Reaktivfarbstoff 40 bis 80%.The input moisture content of the web treated with dye liquor is 40 to 80% when dyeing native fibers with reactive dyestuff.
Für die meisten Reativfarbstoffe kann auf den Einsatz von Harnstoff verzichtet werden.For most reactive dyes, the use of urea can be dispensed with.
Die Temperatur des Heißdampfes kann vorzugsweise 160 bis 230° C betragen. Je höher die Temperatur des Behandlungsgases und damit je höher die Temperaturdifferenz zwischen Behandlungsgas und Warenbahn, desto größer ist der Wärmeübergang und desto schneller die Aufheizzeit der Warenbahn und die Trocknung der Warenbahn.The temperature of the superheated steam may preferably be 160 to 230 ° C. The higher the temperature of the treatment gas and thus the higher the temperature difference between the treatment gas and the web, the greater the heat transfer and the faster the heating of the web and the drying of the web.
Die Verweilzeit der Warenbahn in der Vorrichtung kann 5 bis 60 Sekunden, vorzugsweise 10 bis 30 Sekunden, betragen. Diese Zeit reicht zur vollständigen Fixierung mit guter Farbausbeute aus und ermöglicht eine Vorrichtung kleiner Baugröße.The residence time of the web in the device may be 5 to 60 seconds, preferably 10 to 30 seconds. This time is sufficient for complete fixation with good color yield and allows a device of small size.
Überraschenderweise wurde festgestellt, daß bei dem Verfahren optimale Fixierergebnisse auch mit einer Restfeuchte der Warenbahn kleiner oder gleich der Gleichgewichtsfeuchte unter Normalbedingungen, d.h. bei etwa 10% Feuchte bezogen auf das Gewicht der Warenbahn bei Zellulose und etwa 8 % Feuchte bei Baumwolle, erzielt werden. Dies wird durch die schon erwähnte beschleunigende Wirkung der Trocknung für das Farbfixieren erklärt. Eine Regelung der Restfeuchte der Warenbahn in der Vorrichtung ist nicht notwendig.Surprisingly, it has been found that in the method optimum fixing results even with a residual moisture of the web less than or equal to the equilibrium moisture content under normal conditions, i. at about 10% moisture based on the weight of the web in cellulose and about 8% moisture in cotton, can be achieved. This is explained by the already mentioned accelerating effect of drying for dye fixing. A regulation of the residual moisture of the web in the device is not necessary.
Prinzipiell sind alle Verfahren, bei denen die Warenbahn mit Heißdampf in Kontakt gebracht wird, zum Einsatz für ein o.g. Verfahren geeignet.In principle, all processes in which the web is brought into contact with superheated steam are suitable for use in an abovementioned process.
Zu diesen Verfahren könnte eine Führung der Warenbahn durch eine mit Heißdampf gefüllte Kammer in Form von Hängeschleifen und eine mäanderförmige Führung der Warenbahn um zwei Reihen von Leit- und Förderwalzen gehören, soweit sie zum Transport einer feuchten, gefärbten und unfixierten Warenbahn geeignet ist.These methods could include a guide of the web through a hot steam filled chamber in the form of hanging loops and a meandering guidance of the web to two rows of guiding and conveying rollers, as far as it is suitable for transporting a moist, colored and unfixed web.
Zur Verbesserung des Wärmeüberganges vom Heißdampf auf die Warenbahn und damit der Reduzierung der Verweilzeit kann die Warenbahn gemäß Anspruch 5 mit im Umluftverfahren geführtem Heißdampf über auf die Warenbahn gerichtete Düsen in Kontakt gebracht werden. Dies ist bei dem o.g. Verfahren ohne Farbverläufe möglich, da aufgrund des hohen Dampfgehaltes und ggf. der hohen Dampftemperatur ein schnelles Antrocknen der Warenbahn und damit des Farbstoffes erfolgt.To improve the heat transfer from the superheated steam to the web and thus the reduction of the residence time, the web can be brought in accordance with
Vorrichtungen mit einer mäanderförmigen Führung der Warenbahn um zwei Reihen von Walzen und auf die Warenbahn gerichteten Düsen sind der Anmelderin als Hotflue bekannt. Die bekannten Vorrichtungen haben jedoch, wie die der
Eine weitere Verbesserung des Wärmeüberganges kann erreicht werden, wenn die Warenbahn 6 im wesentlichen eben durch die Behandlungskammer transportiert wird und über oberhalb und ggf. unterhalb der Warenbahn angeordneten Düsenkästen mit Heißdampf in Kontakt gebracht wird.A further improvement of the heat transfer can be achieved if the
Vorrichtungen, in denen die Warenbahn eben hindurchtransportiert und über Düsenkästen mit Behandlungsgas in Kontakt gebracht wird, nämlich düsenbelüftete Fixierspannrahmen, sind zur Schnellaufheizung beim Farbfixieren von Chemiefasern, d.h. beim Thermosolieren, aus der
Vorrichtungen dieser Art, die geeignet sind als Behandlungsgas Heißdampf einzusetzen, sind in der
Bei einer schwebenden Führung der Warenbahn in einem Schwebetrockner ist die Gefahr der Entstehung welliger Abschnitte der Warenbahn, die beim Fixieren zu Farbverläufen führen können, groß. Spannketten haben beim Farbfixieren den Nachteil, dass sie Randmarkierungen verursachen.In a floating guidance of the web in a floating dryer, the risk of the formation of wavy portions of the web, which can lead to color gradients during fixing, large. Tension chains have the drawback in dye fixing that they cause edge markings.
Eine weitere, Vorrichtung, nämlich ein zur Heißdampfbehandlung einsetzbarer Spannrahmentrockner, ist aus der
Eine gattungsgemäße Vorrichtung zur kontinuierlichen oder halbkontinuierlichen Wärmebehandlung einer Warenbahn ist in der
Diese Vorrichtung ist wenig geeignet, ein in der
Ein Durchlauftrockner für eine Reifenkordgewebebahn mit einer Transportvorrichtung, die ebenfalls drei Walzenanordnungen aufweist, ist aus der
Eine weiteres Verfahren und eine Vorrichtung zum Farbfixieren einer Warenbahn aus der
Aus der
Aufgabe der Erfindung ist es, eine Vorrichtung zur kontinuierlichen Wärmebehandlung einer textilen Warenbahn, insbesondere zum Farbfixieren, gemäß dem Oberbegriff des Anspruchs 1 zu entwickeln, die eine Behandlung der Warenbahn mit Heißdampf in kleineren Metragen ermöglicht. Bei der Behandlung soll die mit Farbflotte beaufschlagte, feuchte Warenbahn fixiert und getrocknet werden. Während der Behandlung soll die Warenbahn durch eine Längsspannung glatt gezogen werden, um ein gleichmäßiges Fixieren und damit eine gleichmäßige Farbausbeute zu gewährleisten.The object of the invention is to develop a device for the continuous heat treatment of a textile web, in particular for color fixing, according to the preamble of
Diese Aufgabe ist durch die kennzeichnenden Merkmale des Anspruchs 1 gelöst.This object is solved by the characterizing features of
Eine erfindungsgemäße Vorrichtung zur kontinuierlichen Wärmebehandlung einer textilen Warenbahn insbesondere zum Farbfixieren, mit einem Gehäuse, mit mindestens einer Behandlungskammer mit einer Umluftvorrichtung, d.h. einer Vorrichtung zum Führen von Heißdampf im Umluftverfahren, mit einem Umluftventilator und oberhalb und unterhalb der Warenbahn angeordneten Düsenkästen in jeder Behandlungskammer, mit einer Transportvorrichtung mit Walzen zur im wesentlichen ebenen Führung der Warenbahn unter einer Längsspannung durch die Behandlungskammer des Gehäuses weist ein dampfdichtes Gehäuse auf.A device according to the invention for the continuous heat treatment of a textile web, in particular for ink fixing, comprising a housing, with at least one treatment chamber with a circulating air device, i. a device for guiding hot steam in the recirculation method, with a circulating air fan and arranged above and below the web nozzle boxes in each treatment chamber, with a transport device with rollers for substantially planar guidance of the web under a longitudinal tension through the treatment chamber of the housing has a vapor-tight housing.
Sie weist als wesentlichen Teil der Transportvorrichtung mindestens einen zur vorherigen Trocknung der Warenbahn mit Abstand zu einer Vorderwand des Gehäuses angeordneten Walzengang auf. Der Abstand zur Vorderwand beträgt mindestens 20%, vorzugsweise mindestens 30 %, der Länge des horizontalen Transportweges der Warenbahn durch die Behandlungskammern.It has as an essential part of the transport device at least one for the previous drying of the web at a distance from a front wall of the housing arranged on the roller gear. The distance to the front wall is at least 20%, preferably at least 30%, of the length of the horizontal transport path of the web through the treatment chambers.
Ein Walzengang kann zwei zueinander versetzte Walzen aufweisen, wobei eine relativ zur anderen, zur Erzeugung einer Längsspannung verstellbar ist.A roller gear may have two mutually offset rollers, one being adjustable relative to the other, for generating a longitudinal tension.
Ein Walzengang kann auch zwei, die Warenbahn in ihrer Transportierebene führende Stangen oder Walzen und eine zwischen den beiden Stangen bzw. Walzen oberhalb oder unterhalb der Transportierebene angeordnete, senkrecht zur Transportierebene verstellbare Zugwalze aufweisen. In diesem Fall wird die Warenbahn in Form einer Schleife um die Zugwalze herumgeführt und durch Auslenkung der Zugwalze senkrecht zur Transportierebene unter Längsspannung gehalten.A roller conveyor can also have two, the web in their transport plane leading rods or rollers and arranged between the two rods or rollers above or below the transport plane, perpendicular to the transport plane adjustable draw roller. In this case, the web is guided in the form of a loop around the tension roller and held by deflection of the tension roller perpendicular to the transport plane under longitudinal tension.
Die Warenbahn wird mittels des mit Abstand zu einer Vorderwand des Gehäuses angeordneten Walzengangs unter einer Längsspannung, insbesondere von 10 bis 100 N /m, durch die Behandlungskammern transportiert. Der Abstand zur Vorderwand beträgt mindestens 20%, vorzugsweise mindestens 30%, der Länge des horizontalen Transportweges der Warenbahn durch die Behandlungskammern. Dabei wird die Warenbahn erst durch den Walzengang geführt, wenn sie und damit der Farbstoff bereits angetrocknet ist. Während des Antrocknens und auch während des gesamten Fixiervorganges wird die Warenbahn durch die Längsspannung glatt gezogen, was ein gleichmäßiges Fixieren und damit eine gleichmäßige Farbausbeute gewährleistet. Eine Führung der Warenbahn durch einen Walzengang ist darüber hinaus ein einfaches Transportierverfahren, das z.B. verglichen mit einer Spannkettenführung, einfachere Ein- und Ausgänge in die Behandlungskammer ermöglicht.The web is transported by the spaced apart from a front wall of the housing roller duct under a longitudinal stress, in particular from 10 to 100 N / m, through the treatment chambers. The distance to the front wall is at least 20%, preferably at least 30%, of the length of the horizontal transport path of the web through the treatment chambers. The web is only through the roller gear led, if they and thus the dye is already dried. During the drying and also during the entire fixing process, the web is pulled smoothly by the longitudinal tension, which ensures a uniform fixing and thus a uniform color yield. A guide of the web through a roller gear is also a simple transport method, which allows, for example, compared to a tension chain guide, easier inputs and outputs in the treatment chamber.
Bei einer erfindungsgemäßen Vorrichtung mit mindestens zwei hintereinander angeordneten Behandlungskammern ist der Walzengang gemäß Anspruch 2 jeweils im Bereich, in dem die beiden Behandlungskammern aneinander stoßen, angeordnet, d. h. der Abstand zur Vorderwand beträgt etwa 50% der Länge des horizontalen Transportweges der Warenbahn durch die Behandlungskammern. Die Behandlungskammern werden auch Felder und die Bereiche zwischen den Behandlungskammern Feldstöße genannt.In a device according to the invention with at least two treatment chambers arranged one behind the other, the roller passage according to
Gemäß Anspruch 3 weist der Walzengang zwei Leitwalzen und eine vertikal verstellbare Zugwalze auf, wobei die Leitwalzen dicht hintereinander und die Zugwalze in der Mitte unterhalb der Leitwalzen angeordnet sind. Diese Anordnung der Leitwalzen und Zugwalzen ermöglicht einen schmalen Stoßbereich der Behandlungskammer, d.h. der Bereich oder die Bereiche, in denen keine Düsenkästen angeordnet sind, können klein gehalten werden.According to
Eine Zugwalze, die gemäß Anspruch 4 gleichzeitig als Ausrichtwalze ausgebildet ist, erspart zusätzliche Mittel zum Ausrichten der Warenbahn.A draw roller, which is simultaneously formed as an alignment roller according to
Gemäß Anspruch 5 weist die erfindungsgemäße Vorrichtung vor und hinter dem Gehäuse jeweils eine Schleuse auf. Die Schleusen erstrecken sich vom Boden bis über die Transportebene der Warenbahn und weisen in Bodennähe und auf Höhe der Transportebene Umlenkwalzen auf. Die Schleusen sind in eine untere, nach unten offene Vorkammer und eine weitere darüber angeordnete Hauptkammer unterteilt. An die Vorkammern können Saugkanäle oder Saugkästen angeschlossen sein. Im Vergleich zu den aus der
Die Erfindung wird anhand eines in der Zeichnung schematisch dargestellten Beispiels weiter erläutert. Figur 1 zeigt eine Anlage zum Färben mit einer erfindungsgemäßen Vorrichtung zum Farbfixieren. In Figur 2 ist eine Eingangsschleuse, eine erste Behandlungskammer und ein Walzengang der Vorrichtung dargestellt.The invention will be further explained with reference to an example schematically illustrated in the drawing. FIG. 1 shows a system for dyeing with a device according to the invention for fixing inks. FIG. 2 shows an inlet lock, a first treatment chamber and a roller passage of the device.
Eine Anlage zum Färben einer textilen Warenbahn 1, z.B. aus Baumwolle oder Zellulose mit Reaktivfarbstoff, weist in Transportrichtung hintereinander angeordnet einen Warenspeicher 2, eine Zufuhrvorrichtung 3, eine Färbevorrichtung 4, einen Luftgang 5, eine Vorrichtung zum Farbfixieren 6, eine weitere Zufuhrvorrichtung 7 und einen weiteren Warenspeicher 8 auf. In diesem Beispiel sind der vordere Warenspeicher 2 als Behälter, die Färbevorrichtung 4 als Foulard, der hintere Warenspeicher 8 als Wickelwalze und die Zufuhrvorrichtungen 3, 7 als Galgen ausgebildet. Die Vorrichtung zum Farbfixieren 6 weist eine Eingangsschleuse 9, ein dampfdichtes, wärmeisoliertes Gehäuse 10 und eine Ausgangsschleuse 11 auf. Das Gehäuse 10 umfaßt mindestens eine, vorzugsweise zwei bis fünf, hier zwei, baukastenartige aneinandergereihte Behandlungskammern 12, 13. Durch die Behandlungskammern 12, 13 ist das Innere des Gehäuses 10 in zwei, hintereinander angeordnete Felder unterteilt. Das Gehäuse 10 ist nicht unterteilt und umfaßt alle Behandlungskammern 12, 13.A plant for dyeing a
In jeder der Behandlungskammern 12, 13 ist eine Umluftvorrichtung, d.h. eine Vorrichtung zum Führen von Heißdampf in einem Kreislauf, auch Umluftverfahren genannt, mit einem Umluftventilator 14, einer in Figur 2 nicht dargestellten Heizeinrichtung und mit Düsenkästen 15 mit auf die Warenbahn 1 zielenden Düsenöffnungen angeordnet. In einer Behandlungskammer 12, 13 können mehrere, z.B. jeweils zwei oberhalb und unterhalb der Warenbahn 1 sich quer über die Warenbahn 1 erstreckende Düsenkästen 15 angeordnet sein. Die Düsenöffnungen sind bevorzugt als Schlitze ausgebildet.In each of the
Eine Transportvorrichtung weist neben Führungswalzen 16, 17 in der Eingangsschleuse 9 und Führungswalzen 18, 19, 20 in und hinter der Ausgangsschleuse 11 im Bereich, in dem die beiden Behandlungskammern 12, 13 aneinanderstoßen, einen Walzengang mit zwei Leitwalzen 21, 22 und einer Zugwalze 23 auf. Der Walzengang ist damit auf der Hälfte des Transportweges der Warenbahn 1 von Einlaufschlitz 27 in der Vorderwand 26 zum Auslaufschlitz 29 in der Hinterwand 28 angeordnet. Dabei sind die beiden Leitwalzen 21, 22 gleich groß und dicht hintereinander auf einer Höhe angeordnet. Die Anordnung der Leitwalzen 21, 22, der letzten Führungswalze 17 der Eingangsschleuse 9 und der ersten Führungswalze 18 der Ausgangsschleuse 11 ist so, daß die Transportebene der Warenbahn 1 in den Behandlungskammern 12, 13 eben und horizontal ist.A transport device has, in addition to guide
Die Zugwalze 23 ist in der Mitte, unterhalb der Leitwalzen 21, 22 höhenverstellbar angeordnet. Sie ist gleichzeitig als Ausrichtwalze, d.h. in einer durch ihre Achse gehenden Ebene parallel zur Transportebene verstellbar, ausgebildet. Die Höhenverstellbarkeit der Zugwalze 23 ist durch die Pfeile 24 und die Ausrichtbarkeit durch die Pfeile 25 angedeutet. Die Zugwalze 23 ist außerdem mit einem nicht dargestellten Antrieb verbunden.The
Das Gehäuse 10 weist an einer Vorderwand 26 der ersten Behandlungskammer 12 einen Einlaufschlitz 27 und an einer Hinterwand 28 der letzten Behandlungskammer 13 einen Auslaufschlitz 29 auf, durch die die Warenbahn 1 in das Gehäuse 10 bzw. aus ihm herausgeführt ist.The
Die Eingangsschleuse 9 weist ein parallel zur Vorderwand 26 verlaufendes, sich in der Nähe einer unteren Kante 30 bis oberhalb des Einlaufschlitzes 27 erstreckendes Vorderblech 31, ein Deckenblech 32 und zwei nicht dargestellte Seitenbleche auf. Die Bleche 31, 32 der Eingangsschleuse 9 sind dampfdicht miteinander und mit der Vorderwand 26 verbunden. Die Eingangsschleuse 9 ist durch Zwischenbleche 33, 34, die sich vom Vorderblech 31 und von der Vorderwand 26 ins Innere der Eingangsschleuse 9 erstrecken und zwischen sich einen Spalt 35 für die Warenbahn 1 freilassen, in eine obere Hauptkammer 36 und eine untere Vorkammer 37 unterteilt. Die Vorkammer 37 ist nach unten offen. An die Vorkammer 37 ist eine Absaugeinrichtung, in diesem Beispiel ein mit einem nicht dargestellten Ventilator verbundenem Absaugkanal 38 angeschlossen. Gegebenenfalls befinden sich, wie in diesem Beispiel, Saugkästen 39, an die der Saugkanal 38 angeschlossen ist, in der Vorkammer 37. Die erste Führungswalze 16 der Transportvorrichtung befindet sich unterhalb der Vorkammer 37 und die zweite, d.h. letzte Führungswalze 17 vor dem Einlaufschlitz 27.The
Die Ausgangsschleuse 11 ist analog zur Eingangsschleuse 9 aufgebaut. Die erste und zweite Führungswalze 18,19 sind analog zu denen der Eingangsschleuse 9 und die dritte Führungswalze 20 hinter der zweiten hinter der Ausgangsschleuse 11 angeordnet.The
Zum Färben wird die Warenbahn 1 aus dem Warenspeicher 2 über die als Galgen ausgebildete Zufuhrvorrichtung 3 abgetafelt und durch die als Foulard ausgebildete Färbevorrichtung 4 und den Luftgang 5 der Vorrichtung 6 zum Farbfixieren zugeführt.For dyeing, the
Die Warenbahn 1 wird dazu um die Führungswalze 16 der Transportvorrichtung von unten in die Vorkammer 37 der Eingangsschleuse 9 durch die Vorkammer 37 und durch den Spalt 35 in die Hauptkammer 36 und um die Führungswalze 17 durch den Einlaufschlitz 27 in die erste Behandlungskammer 12 der Vorrichtung 6 transportiert. Der Transport der Warenbahn 1 durch die Behandlungskammern 12, 13 erfolgt durch den zwischen der ersten und zweiten Behandlungskammer 12, 13 angeordneten Walzengang in einer horizontalen Ebene und unter einer Längsspannung von 10 bis 100 N/m. Im Walzengang wird die Warenbahn 1 mäanderförmig, hintereinander und um die Leitwalze 21, die angetriebene Zugwalze 23 und die Leitwalze 22 herumgeführt. Die gewünschte Längsspannung wird durch Höhenverstellung der Zugwalze 23 eingestellt. Gegebenenfalls auftretende Verschiebungen der Warenbahn 1 werden durch Verstellen der Zugwalze 23, und zwar durch eine Winkelverstellung der Achse der Zugwalze 23 parallel zur Transportebene, ausgeglichen.
Die Warenbahn 1 verläßt die Vorrichtung 6, durch den Ausgangsschlitz 29 und die Ausgangsschleuse 11. Sie wird über eine als Galgen ausgebildete Zufuhrvorrichtung 7 dem als Wickelwalze ausgebildeten Warenspeicher 8 zugeführt. Die Warenbahngeschwindigkeit beträgt z.B. 40 m/min.The
The
In der Färbevorrichtung 4 wird die Warenbahn 1 mit Farbflotte beaufschlagt. Im Luftgang 5 findet eine Vergleichmäßigung der Farbflotte auf der Warenbahn 1 statt.In the
Die feuchte Warenbahn 1 wird, während sie bis auf den Walzengang eben durch die Behandlungskammer 12, 13 der Vorrichtung 6 transportiert wird, über die oberhalb und unterhalb der Warenbahn 1 angeordneten Düsenkästen 15 mit auf die Warenbahn 1 gerichteten Düsenöffnungen mit Heißdampf beaufschlagt. Der Düsendruck beträgt 200 bis 1000 PA und die Wärmeübergangsleistung etwa 240 W/m2.The
Die Temperatur des Heißdampfes beträgt 160 bis 230° C und die Verweilzeit der Warenbahn 1 in den Behandlungskammern 12, 13 5 bis 60 Sekunden, bevorzugt 10 bis 30 Sekunden. Die Restfeuchte der Warenbahn 1 beim Verlassen des Gehäuses 10 beträgt etwa oder weniger als die Gleichgewichtsfeuchte unter Normalbedingungen, d.h. kleiner oder etwa gleich 10 %. In den Behandlungskammern 12, 13 und in den Hauptkammern 36 der Eingangs- und Ausgangsschleuse 9, 11 wird ein leichter Überdruck aufrechterhalten. Der Dampfgehalt, bevorzugt zwischen 95 und 100 Vol.-%, wird durch Verändern der Menge abgesaugtem Behandlungsgases über die Absaugkanäle 38 der Vorkammern 37 der Eingangs- und Ausgangsschleusen 9, 11 aufrecht erhalten. Eine Regelung einer bestimmten Restfeuchte der Warenbahn ist nicht notwendig.The temperature of the superheated steam is 160 to 230 ° C and the residence time of the
Eine mit Farbflotte eines Reaktivfarbstoffes ohne Harnstoff beaufschlagte Warenbahn 1 aus Baumwolle (BG) mit einem Warengewicht von 80 g/m2 wird mit einer Warenbahngeschwindigkeit von 40 m/min durch die Vorrichtung 6 transportiert. Die Temperatur des reinen Heißdampfes beträgt 180° C. Der Düsendruck an den Düsenöffnungen der Düsenkästen 15 beträgt 700 PA. Schon nach einer Verweilzeit von 5 Sekunden hat der überwiegende Teil des Farbstoffes mit den Fasern der Warenbahn 1 reagiert und ist fixiert. Nach weiteren 5 Sekunden ist die Warenbahn 1 vollständig getrocknet und der restliche Teil des Farbstoffs fixiert. Die Eingangsfeuchte von etwa 80% reduziert sich in der Vorrichtung 6 auf einen Wert kleiner als 10 %. Die gesamte Verweilzeit der Warenbahn 1 in der Vorrichtung 6 beträgt 10 Sekunden.A
- 11
- Warenbahnweb
- 22
- Warenspeichergoods storage
- 33
- Zufuhrvorrichtungfeeding apparatus
- 44
- Färbevorrichtungdyeing apparatus
- 55
- Luftgangskying
- 66
- Vorrichtungcontraption
- 77
- Zufuhrvorrichtungfeeding apparatus
- 88th
- Warenspeichergoods storage
- 99
- Eingangsschleuseentry lock
- 1010
- Gehäusecasing
- 1111
- Ausgangsschleuseexit lock
- 1212
- Behandlungskammertreatment chamber
- 1313
- Behandlungskammertreatment chamber
- 1414
- Umluftventilatorcirculation fan
- 1515
- Düsenkastennozzle box
- 1616
- Führungswalzeguide roller
- 1717
- Führungswalzeguide roller
- 1818
- Führungswalzeguide roller
- 1919
- Führungswalzeguide roller
- 2020
- Führungswalzeguide roller
- 2121
- Leitwalzeguide roll
- 2222
- Leitwalzeguide roll
- 2323
- Zugwalzepulling roller
- 2424
- Pfeilearrows
- 2525
- Pfeilearrows
- 2626
- Vorderwandfront wall
- 2727
- Einlaufschlitzinlet slot
- 2828
- Hinterwandbehind wall
- 2929
- Auslaufschlitzoutlet slot
- 3030
- untere Gehäusekantelower case edge
- 3131
- Vorderblechfront plate
- 3232
- Deckenblechdecking
- 3333
- Zwischenblechintermediate plate
- 3434
- Zwischenblechintermediate plate
- 3535
- Spaltgap
- 3636
- Hauptkammermain chamber
- 3737
- Vorkammerantechamber
- 3838
- Absaugkanalsuction
- 3939
- Saugkästensuction boxes
Claims (6)
- A device for the continuous heat treatment of a textile fabric web (1), particularly for fixing of dyestuffs, with a casing (10) with at least one treatment chamber (12, 13) with at least one air circulation installation with at least one air circulation ventilator (14) and nozzle boxes (15) arranged above and below the fabric web, with a transport device with rollers (21, 22, 23) for substantially even guiding and for transporting of the fabric web (1) under longitudinal tensioning through the treatment chambers (12, 13) of the casing (10), characterised in that the casing (10) is vapour-proof, in that the transport device has at least one roller course, whereby the roller course has two rollers which are offset in respect of one another and of which one is able to be displaced relative to the other to produce longitudinal tensioning, or whereby the roller course has two bars or guide rollers (21, 22), which guide the fabric web (1) in its transporting level, and a draw roller (23) arranged therebetween above or below the transporting level, whereby the draw roller (23) for producing longitudinal tensioning is able to be displaced perpendicular to the transporting level and whereby the roller course, seen in the direction of transport of the fabric web, is arranged behind the front wall (26) of the casing (10) at a distance from a front wall (26) of the casing (10).
- The device according to Claim 1, with at least two treatment chambers, characterised in that the roller course is arranged in the area in which the treatment chambers (12, 13) abut one another.
- The device according to claim 1 or 2, characterised in that the two guide rollers (21, 22) of the roller course are arranged closely behind one another and the drawing roller (23) is arranged in the middle below the guide rollers (21, 22) and the drawing roller (23) is able to be vertically adjusted.
- The device according to one of claims 1 to 3, characterised in that the draw roller (23) is simultaneously configured as an alignment roller.
- The device according to one of claims 1 to 4, characterised in that an inlet sluice (9) and an outlet sluice (11) are arranged in front of and behind the casing (10), the inlet and outlet sluices (9, 11) extend from ground level to over a transport level of the fabric web (1) and have prechambers (37) that are connected to suction mechanisms and open downwardly at ground level.
- A facility for dying a textile fabric web, characterised by a device for fixing dyestuffs in accordance with one of claims 1 to 5.
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19924433 | 1999-05-28 | ||
| DE19924433 | 1999-05-28 | ||
| EP00110489A EP1063337B1 (en) | 1999-05-28 | 2000-05-17 | Method for the continuous heat treatment of a textile fabric, particularly for fixing of dyestuffs |
Related Parent Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP00110489.2 Division | 2000-05-17 | ||
| EP00110489A Division EP1063337B1 (en) | 1999-05-28 | 2000-05-17 | Method for the continuous heat treatment of a textile fabric, particularly for fixing of dyestuffs |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1589141A1 EP1589141A1 (en) | 2005-10-26 |
| EP1589141B1 true EP1589141B1 (en) | 2008-01-02 |
Family
ID=7909435
Family Applications (4)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP05011446A Expired - Lifetime EP1589141B1 (en) | 1999-05-28 | 2000-05-17 | Device for the continuous heat treatment of a textile fabric, particularly for fixing of dyestuffs |
| EP00110496A Expired - Lifetime EP1055763B1 (en) | 1999-05-28 | 2000-05-17 | Method for the continuous steam treatment of a textile fabric to fix reactive dyestuffs on natural fibres |
| EP00110489A Expired - Lifetime EP1063337B1 (en) | 1999-05-28 | 2000-05-17 | Method for the continuous heat treatment of a textile fabric, particularly for fixing of dyestuffs |
| EP06020559A Withdrawn EP1746191A3 (en) | 1999-05-28 | 2000-05-17 | Method and device for the continuous steam treatment of a textile fabric to fix reactive dyestuffs on natural fibres |
Family Applications After (3)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP00110496A Expired - Lifetime EP1055763B1 (en) | 1999-05-28 | 2000-05-17 | Method for the continuous steam treatment of a textile fabric to fix reactive dyestuffs on natural fibres |
| EP00110489A Expired - Lifetime EP1063337B1 (en) | 1999-05-28 | 2000-05-17 | Method for the continuous heat treatment of a textile fabric, particularly for fixing of dyestuffs |
| EP06020559A Withdrawn EP1746191A3 (en) | 1999-05-28 | 2000-05-17 | Method and device for the continuous steam treatment of a textile fabric to fix reactive dyestuffs on natural fibres |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (4) | US6471729B1 (en) |
| EP (4) | EP1589141B1 (en) |
| AT (3) | ATE343010T1 (en) |
| DE (5) | DE10023721A1 (en) |
| DK (2) | DK1055763T3 (en) |
| ES (1) | ES2247977T3 (en) |
Families Citing this family (26)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ES2247977T3 (en) * | 1999-05-28 | 2006-03-16 | Moenus Textilmaschinen Gmbh | PROCEDURE FOR CONTINUOUS THERMAL TREATMENT OF A TEXTILE GENDER BAND, ESPECIALLY FOR COLOR FIXATION. |
| DE10393509D2 (en) * | 2002-07-31 | 2005-06-23 | Monforts Textilmaschinen Gmbh | Process for denim finishing |
| US7931700B2 (en) * | 2002-12-27 | 2011-04-26 | Hbi Branded Apparel Enterprises, Llc | Composition for dyeing of cellulosic fabric |
| US7931699B2 (en) * | 2002-12-27 | 2011-04-26 | Hbi Branded Apparel Enterprises, Llc | Compositions for spray dyeing cellulosic fabrics |
| US7033403B2 (en) * | 2002-12-27 | 2006-04-25 | Sara Lee Corporation | Spray dyeing of garments |
| US8814953B1 (en) | 2003-06-23 | 2014-08-26 | Hbi Branded Apparel Enterprises, Llc | System and method for spray dyeing fabrics |
| US20060265816A1 (en) * | 2003-06-23 | 2006-11-30 | Michael Abbott | Formers for spray dyeing garments |
| US7799097B2 (en) * | 2003-06-23 | 2010-09-21 | Hbi Branded Apparel Enterprises, Llc | Processes for spray dyeing fabrics |
| KR20050017655A (en) * | 2003-08-08 | 2005-02-22 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Drum washing machine and control method thereof |
| US7809441B2 (en) * | 2006-05-17 | 2010-10-05 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Implantable medical device with chemical sensor and related methods |
| DE102006043600A1 (en) * | 2006-09-16 | 2008-03-27 | Mageba-Textilmaschinen Gmbh & Co. Ohg | Steam cabinet and method for steaming textile tape goods |
| DE102009010231A1 (en) * | 2009-02-24 | 2010-08-26 | Power-Heat-Set Gmbh | Vapor barrier for a yarn refining plant |
| CN101892568B (en) * | 2010-07-05 | 2011-09-14 | 江阴金田机械有限公司 | Progressive slow piling steaming box |
| CN102392340B (en) * | 2011-09-02 | 2013-07-31 | 杭州印象数码科技有限公司 | Cloth-load mechanism used for reticular conduction band rapid steamer |
| CN102634949A (en) * | 2012-05-14 | 2012-08-15 | 威海拓展纤维有限公司 | Steam shaping device for fiber |
| US9610444B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2017-04-04 | Pacesetter, Inc. | Erythropoeitin production by electrical stimulation |
| JP6409869B2 (en) * | 2014-05-08 | 2018-10-24 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | Inkjet recording method and inkjet recording apparatus |
| DE102014011696A1 (en) | 2014-08-07 | 2016-02-11 | Saurer Germany Gmbh & Co. Kg | Apparatus for the thermal treatment of yarns |
| CN107532360B (en) * | 2015-02-23 | 2020-04-21 | 麦斯印刷解决方案有限公司 | Device for steam treating printed fibrous sheet material, in particular for fixing printing ink, and process for fixing ink on said printed fibrous sheet material |
| CN105350196B (en) * | 2015-11-06 | 2018-01-12 | 德清县龙奇丝绸炼染有限公司 | Weaving face fabric section dyeing machine |
| CN105588413A (en) * | 2015-12-21 | 2016-05-18 | 无锡科莱欣机电制造有限公司 | Energy saving circulating drying box for dyed cloth |
| CN107628448A (en) * | 2017-09-18 | 2018-01-26 | 芜湖立新清洁用品有限公司 | A kind of workshop raw material transporter |
| CN108118435A (en) * | 2018-02-07 | 2018-06-05 | 海宁市美元达经编有限公司 | A kind of processing method of health knitted fabric |
| CN108642756A (en) * | 2018-07-03 | 2018-10-12 | 陶守江 | A kind of section of dye dye fixing cluster tool |
| CN109267278A (en) * | 2018-08-28 | 2019-01-25 | 浙江麦克斯科技有限公司 | A kind of cloth dyeing after-treatment device |
| KR102604692B1 (en) * | 2018-09-20 | 2023-11-20 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Conveying device and Fabric treating apparatus having the same |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE424721C (en) * | 1923-08-28 | 1926-01-29 | Robert Mohr | Device for desizing, bleaching and steaming of continuously wide webs of fabric guided through the treatment fluids |
| DE2908345A1 (en) * | 1979-03-03 | 1980-09-04 | Kleinewefers Gmbh | Fabric steamer roller - has fluted surface through structured axial grooves to prevent fabric damage |
| DE3801138A1 (en) * | 1987-02-25 | 1988-09-08 | Sperotto Rimar Spa | Machine for continuous width treatment of textiles |
Family Cites Families (59)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3124429A (en) * | 1964-03-10 | Web and strand treating apparatus | ||
| US2833136A (en) * | 1958-05-06 | Ager for processing printed fabrics | ||
| US2008230A (en) * | 1933-06-06 | 1935-07-16 | Spooner William Wycliffe | Steaming of webs of material |
| US2487197A (en) * | 1944-03-11 | 1949-11-08 | Du Pont | Process for dyeing textile fibers with vat dyes |
| US2621504A (en) * | 1946-09-04 | 1952-12-16 | Spooner William Wycliffe | Apparatus for steaming webs |
| US2590850A (en) * | 1949-10-10 | 1952-04-01 | Dungler Julien | Method of treating sheet material coated with gelatine |
| BE499403A (en) | 1949-11-30 | |||
| GB718415A (en) * | 1951-01-03 | 1954-11-17 | Sucker Gmbh Geb | Improved process and installation for physical and/or chemical treatment of yarns, warps and textile fabrics or similar goods |
| FR1090013A (en) * | 1953-08-06 | 1955-03-25 | Improvements to heat treatments intended for the development and fixing of coloring matters on fabric, paper and other supports | |
| US3234662A (en) * | 1958-02-21 | 1966-02-15 | Ind Ovens Inc | Web and strand treating apparatus |
| DE1410907A1 (en) | 1960-07-28 | 1968-10-24 | C A Litzler Company Inc | Device for the heat treatment of fabrics |
| DE1635140A1 (en) | 1964-01-09 | 1971-04-29 | Artos Meier Windhorst Kg | Process for the heat treatment of man-made fibers or blends of man-made fibers and cellulose fibers in webs for color fixing on man-made fibers |
| DE1460672C3 (en) | 1964-04-16 | 1976-01-02 | Famatex Gmbh, 7000 Stuttgart | Device for fixing a woven or knitted textile material web |
| GB1090005A (en) * | 1964-10-29 | 1967-11-08 | Ici Ltd | Coloration process |
| GB1090003A (en) * | 1964-10-29 | 1967-11-08 | Ici Ltd | Process for steaming fabrics |
| DE1594634B2 (en) | 1965-04-20 | 1973-12-06 | Technochemie Gmbh -Verfahrenstechnik, 6901 Dossenheim | lubricant |
| DE1460525A1 (en) * | 1965-12-11 | 1969-04-24 | Patentdienst Anstalt F | Device for treating textile goods |
| CH508765A (en) * | 1966-07-22 | 1971-06-15 | Vepa Ag | Apparatus for vapour treatment of |
| DE1953779A1 (en) | 1969-10-25 | 1971-05-06 | Vepa Ag | Apparatus for vapour treatment of - textiles |
| CH453274A (en) * | 1966-08-12 | 1968-06-14 | Asahi Chemical Ind | Device for the continuous treatment of fiber material |
| FR1536604A (en) * | 1967-09-05 | 1968-08-16 | Continental Gummi Werke Ag | Device for the treatment of a material in the form of a strip, and in particular strips for the covering of tires |
| BE738018A (en) * | 1968-08-28 | 1970-02-27 | Vepa Ag | PROCESS AND INSTALLATION FOR THE CONTINUOUS COMPLETION OF HOSPITALITY AND MESH FABRICS |
| US3686902A (en) * | 1969-03-24 | 1972-08-29 | Vepa Ag | Apparatus for the heat-treatment of textile material |
| US3728076A (en) * | 1970-02-06 | 1973-04-17 | Vepa Ag | Process for the heat-setting of padded and printed endless synthetic filament groups and top slivers |
| US3770374A (en) * | 1970-02-21 | 1973-11-06 | Vepa Ag | Process for the continuous steam treatment of staple fiber |
| DE2060941A1 (en) * | 1970-12-11 | 1972-08-10 | Bayer Ag | Synthetic fibres treatment - during continuous conveyance |
| US3835671A (en) * | 1972-03-27 | 1974-09-17 | Vepa Ag | Apparatus for the continuous treatment, particularly dyeing, of fibrous material |
| DE2310195C2 (en) * | 1973-02-02 | 1983-01-20 | Vepa AG, 4125 Riehen, Basel | Damper with at least partially horizontal goods guidance |
| IT1002677B (en) * | 1973-02-02 | 1976-05-20 | Vepa Ag | DEVICE FOR CONTINUOUS STEAM TREATMENT OF TEXTILE OR SYNTHETIC FIBERS |
| US4070877A (en) * | 1973-02-02 | 1978-01-31 | Vepa Aktiengesellschaft | Apparatus for the continuous steaming of textile material of man-made fiber material |
| US3896559A (en) * | 1973-03-28 | 1975-07-29 | Martin Jean Marie Michel | Machine for drying by contact veneers obtained by peeling or slicing wood |
| US4271688A (en) * | 1974-01-11 | 1981-06-09 | Tillotson Corporation | Apparatus for treating plaited yarns |
| DE2517972A1 (en) | 1975-04-23 | 1976-11-04 | Kleinewefers Ind Co Gmbh | DEVICE FOR CONTINUOUS TREATMENT OF A TEXTILE ROLL WITH HOT AIR OR STEAM |
| DE2658863C2 (en) * | 1976-12-24 | 1983-12-08 | Hoechst Ag, 6230 Frankfurt | Process for the continuous dyeing of textile materials in web form |
| GB1573094A (en) | 1977-05-31 | 1980-08-13 | Sando Iron Works Co | Continuous processing of thick textiles |
| DE2911179A1 (en) * | 1979-03-22 | 1980-10-02 | Schraud Alfred Dipl Ing Dr Ing | Continuous dyeing of textiles - includes steaming process between padding and drying to activate migration inhibitors |
| EP0021055B1 (en) * | 1979-06-01 | 1983-12-21 | Hoechst Aktiengesellschaft | Process for the local "white discharging" or "coloured discharging" of dyes on textile materials |
| FR2478150A1 (en) * | 1980-03-12 | 1981-09-18 | Superba Sa | Steam treatment chamber for yarns - has homogeneous ambient atmosphere |
| DE3039873C2 (en) * | 1980-10-22 | 1986-02-06 | Siteg Siebtechnik GmbH, 4422 Ahaus | Method for producing a screen belt provided with filling material |
| DE3206895A1 (en) * | 1982-02-26 | 1983-09-15 | Hoechst Ag, 6230 Frankfurt | METHOD FOR CONTINUOUSLY DYING TEXTILE TRACKS |
| DE3325958A1 (en) * | 1983-07-19 | 1985-02-07 | Hoechst Ag, 6230 Frankfurt | Method for the continuous fixing of reactive dyes |
| DE3418942A1 (en) * | 1984-05-22 | 1985-11-28 | Bayer Ag, 5090 Leverkusen | METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDITIONING SYNTHESIS FIBER MATERIAL |
| DE3511950C3 (en) | 1985-04-02 | 2000-04-06 | Babcock Textilmasch | Device for drying continuous fabric and knitted webs or the like |
| US4717391A (en) * | 1986-11-28 | 1988-01-05 | Burlington Industries, Inc. | Method for spraying of dyes from high-boiling solvent dispersions onto open width fabric with heat setting |
| CH673855A5 (en) * | 1987-06-19 | 1990-04-12 | Benninger Ag Maschf | |
| DE3835549C2 (en) | 1988-10-19 | 1996-05-02 | Fleissner Maschf Gmbh Co | Device for fixing dyes applied to web-shaped textile material by means of steam |
| US5105558A (en) * | 1991-03-28 | 1992-04-21 | Curry Donald P | Apparatus and process for drying cellulosic and textile substances with superheated steam |
| DE4136878C2 (en) | 1991-11-09 | 1995-07-20 | Kurt Dipl Ing Roth | Process and apparatus for the continuous fixation of vat dyes in direct and etching printing on cellulose fibers and their blends with synthetic fibers |
| IT1256253B (en) * | 1992-12-28 | 1995-11-29 | Mario Beretta | DEVICE TO REDUCE THE USE OF UREA AND / OR HYGROSCOPIC CHEMICALS, IN PRINTING PASTES OF COTTON FABRICS, VISCOUS AND SIMILAR, AND RELATED PROCEDURE |
| JPH07133595A (en) * | 1993-11-08 | 1995-05-23 | Sando Iron Works Co Ltd | Method for continuously dyeing fabric under high temperature and pressure and apparatus therefor |
| DE4338620A1 (en) * | 1993-11-11 | 1995-05-18 | Monforts Textilmaschinen Gmbh | A gas injection appts. rapidly drying and finishing moving strip cloth |
| AT406782B (en) * | 1995-03-16 | 2000-09-25 | Gawomi Textil Gesmbh | METHOD FOR PRINTING TEXTILE TRACKS |
| JP3346968B2 (en) * | 1995-10-06 | 2002-11-18 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Method of manufacturing stator for AC rotating electric machine |
| DE59603066D1 (en) * | 1995-10-16 | 1999-10-21 | Monforts Textilmaschinen Gmbh | DEVICE FOR FIXING COLORS IN REACTIVE DYEING |
| DE19546344A1 (en) * | 1995-12-12 | 1997-06-19 | Babcock Textilmasch | Device for the heat treatment of continuous material webs |
| DE19633101A1 (en) | 1996-08-16 | 1998-02-26 | Huxoll Dieter | Continuous wet on wet dyeing and transfer printing of fabric at relatively low temperature without intermediate drying |
| DE19709899A1 (en) * | 1997-03-11 | 1998-09-17 | Dystar Textilfarben Gmbh & Co | Process and device for the continuous dyeing of cellulosic circular knitted and circular knitted fabrics and their mixtures with synthetic fibers |
| DE19858839B4 (en) * | 1998-12-19 | 2005-02-10 | Babcock Textilmaschinen Gmbh | Method and apparatus for heat treating a continuous web by blowing steam |
| ES2247977T3 (en) * | 1999-05-28 | 2006-03-16 | Moenus Textilmaschinen Gmbh | PROCEDURE FOR CONTINUOUS THERMAL TREATMENT OF A TEXTILE GENDER BAND, ESPECIALLY FOR COLOR FIXATION. |
-
2000
- 2000-05-17 ES ES00110489T patent/ES2247977T3/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-05-17 EP EP05011446A patent/EP1589141B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-05-17 DK DK00110496T patent/DK1055763T3/en active
- 2000-05-17 DE DE10023721A patent/DE10023721A1/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2000-05-17 DE DE50013624T patent/DE50013624D1/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2000-05-17 DE DE50014901T patent/DE50014901D1/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2000-05-17 EP EP00110496A patent/EP1055763B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-05-17 DK DK00110489T patent/DK1063337T3/en active
- 2000-05-17 AT AT00110496T patent/ATE343010T1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2000-05-17 AT AT00110489T patent/ATE302868T1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2000-05-17 EP EP00110489A patent/EP1063337B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-05-17 EP EP06020559A patent/EP1746191A3/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2000-05-17 DE DE50011009T patent/DE50011009D1/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2000-05-17 AT AT05011446T patent/ATE382729T1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2000-05-17 DE DE10023722A patent/DE10023722A1/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2000-05-26 US US09/580,261 patent/US6471729B1/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2000-05-26 US US09/580,263 patent/US6485526B1/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2002
- 2002-05-07 US US10/140,671 patent/US7089767B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2002-05-13 US US10/144,367 patent/US6591639B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE424721C (en) * | 1923-08-28 | 1926-01-29 | Robert Mohr | Device for desizing, bleaching and steaming of continuously wide webs of fabric guided through the treatment fluids |
| DE2908345A1 (en) * | 1979-03-03 | 1980-09-04 | Kleinewefers Gmbh | Fabric steamer roller - has fluted surface through structured axial grooves to prevent fabric damage |
| DE3801138A1 (en) * | 1987-02-25 | 1988-09-08 | Sperotto Rimar Spa | Machine for continuous width treatment of textiles |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US6485526B1 (en) | 2002-11-26 |
| ATE382729T1 (en) | 2008-01-15 |
| DE10023722A1 (en) | 2000-11-30 |
| DK1063337T3 (en) | 2006-01-09 |
| EP1063337A2 (en) | 2000-12-27 |
| US20020124327A1 (en) | 2002-09-12 |
| DK1055763T3 (en) | 2007-02-19 |
| US20020170118A1 (en) | 2002-11-21 |
| EP1589141A1 (en) | 2005-10-26 |
| EP1746191A3 (en) | 2007-02-21 |
| EP1063337A3 (en) | 2002-01-30 |
| EP1746191A2 (en) | 2007-01-24 |
| DE50013624D1 (en) | 2006-11-30 |
| US6591639B2 (en) | 2003-07-15 |
| DE50014901D1 (en) | 2008-02-14 |
| US6471729B1 (en) | 2002-10-29 |
| EP1055763A2 (en) | 2000-11-29 |
| US7089767B2 (en) | 2006-08-15 |
| EP1055763A3 (en) | 2002-01-30 |
| ATE302868T1 (en) | 2005-09-15 |
| EP1055763B1 (en) | 2006-10-18 |
| ES2247977T3 (en) | 2006-03-16 |
| DE10023721A1 (en) | 2001-02-08 |
| ATE343010T1 (en) | 2006-11-15 |
| DE50011009D1 (en) | 2005-09-29 |
| EP1063337B1 (en) | 2005-08-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1589141B1 (en) | Device for the continuous heat treatment of a textile fabric, particularly for fixing of dyestuffs | |
| CH496134A (en) | Device for treating web-shaped textile or non-textile fabrics | |
| EP0797698B1 (en) | Device for fixing dye in reactive dyeing | |
| EP2519796B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for heat treatment from continuously conveyed webs | |
| EP0458089B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for sizing filament yarn | |
| DE1816483A1 (en) | Process and device for continuous finishing treatment in liquids, in particular for a variety of chemical treatments such as pretreatment, dyeing, finishing of webs such as textile webs, films and the like. | |
| DE2044217A1 (en) | Perforated drum dryer | |
| DE3221776A1 (en) | Process and device for the continuous pretreatment of open-width fabric webs | |
| DE3118971C2 (en) | Method and device for steaming a textile web | |
| DE1460375B1 (en) | Device for the wet treatment of textile goods | |
| DE4028907B4 (en) | Oven for continuous drying of at least one textile thread | |
| DE2249950C3 (en) | Method and device for rinsing or washing and drying textile material | |
| DE19516127A1 (en) | Chamber for continuous heat treatment of yarn, used for fixing yarn before dyeing | |
| DE7717141U1 (en) | DEVICE FOR HEAT TREATMENT, IN PARTICULAR DRYING AND / OR SETTING, OF CONTINUOUSLY TRANSPORTED TEXTILE TRACKS | |
| DE4201430A1 (en) | Mercerisation of textile material e.g. cotton cloth - utilises aerosol impregnation to spray the lye under steam pressure, satn. and stabilisation, to reduce time and space | |
| CH434955A (en) | Device for drying a continuously moving web of film material | |
| DE2013773A1 (en) | Continuous process for the heat treatment of textile materials | |
| DE1635102A1 (en) | Method and device for thermosetting of blocks and prints on endless synthetic sheets of threads and slivers | |
| DE1635139B2 (en) | METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONTINUOUS PAINT AND HEAT TREATMENT OF TEXTILE SHEETS | |
| DE1785689A1 (en) | DEVICE FOR HEAT TREATMENT OF PREFERRED TEXTILE GOODS | |
| DE2043561A1 (en) | Method and device for treating web materials | |
| EP0504617B1 (en) | Steamer for fabrics in suspended loops | |
| DE1952285A1 (en) | Fabric tower drying chamber | |
| DE1635334A1 (en) | Method and device for treating goods in the form of a web, in particular textile goods | |
| DE6604413U (en) | PROCESS AND DEVICE FOR TREATMENT OF RAIL-SHAPED GOODS, IN PARTICULAR TEXTILE GOODS. |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AC | Divisional application: reference to earlier application |
Ref document number: 1063337 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20060426 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| RTI1 | Title (correction) |
Free format text: DEVICE FOR THE CONTINUOUS HEAT TREATMENT OF A TEXTILE FABRIC, PARTICULARLY FOR FIXING OF DYESTUFFS |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AC | Divisional application: reference to earlier application |
Ref document number: 1063337 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 50014901 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20080214 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: BOVARD AG PATENTANWAELTE Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PFA Owner name: TEXMAG-ABWICKLUNGSGESELLSCHAFT MBH Free format text: MOENUS TEXTILMASCHINEN GMBH#HEINRICH-HERTZ-STRASSE 28#07552 GERA (DE) -TRANSFER TO- TEXMAG-ABWICKLUNGSGESELLSCHAFT MBH#HEINRICH-HERTZ-STRASSE 28#07552 GERA (DE) |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080102 |
|
| NLV1 | Nl: lapsed or annulled due to failure to fulfill the requirements of art. 29p and 29m of the patents act | ||
| GBV | Gb: ep patent (uk) treated as always having been void in accordance with gb section 77(7)/1977 [no translation filed] | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080102 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080413 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20080506 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20080403 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080602 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20080523 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FD4D |
|
| EN | Fr: translation not filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080402 Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080102 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080102 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: MOENUS TEXTILMASCHINEN G.M.B.H. Effective date: 20080531 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20081003 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20080531 Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080102 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20080531 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20081024 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PUE Owner name: INTERSPARE GMBH Free format text: TEXMAG-ABWICKLUNGSGESELLSCHAFT MBH#HEINRICH-HERTZ-STRASSE 28#07552 GERA (DE) -TRANSFER TO- INTERSPARE GMBH#ROENTGENSTRASSE 8#21465 REINBEK (DE) |
|
| PLAA | Information modified related to event that no opposition was filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009299DELT |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| R26N | No opposition filed (corrected) |
Effective date: 20081003 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080102 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20090615 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090531 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090531 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090517 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20080517 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080403 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090517 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20101201 |